MFAFNet: A Multi-Feature Attention Fusion Network for Infrared Small Target Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose MFAFNet, a novel multi-feature attention fusion network designed specifically for infrared small target detection in remote sensing imagery. By integrating CNN-based local perception and transformer-inspired global reasoning within a unified architecture, MFAFNet effectively addresses the challenges of low signal-to-clutter ratio and limited spatial resolution.
- (2)
- We design a Multi-Feature Interactive Fusion Module (FIFM) that progressively combines the original input with multi-scale local-enhanced feature maps. This fusion enhances the representation of weak targets by emphasizing their saliency and suppressing background interference.
- (3)
- We introduce a Patch Attention Block (PAB) with cascaded channel-spatial attention, enabling the model to capture long-range dependencies and contextual relationships among patches at multiple scales. This improves target localization in cluttered and heterogeneous infrared scenes.
- (4)
- We enhance the Asymmetric Contextual Fusion Module to integrate low-level spatial features with high-level semantic information. By aligning hierarchical feature distributions, this module reduces semantic gaps and supports more accurate target discrimination.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Model-Driven Approaches
2.2. Data-Driven Deep Learning Approaches
2.3. Transformer-Based Methods in Vision
3. Methods
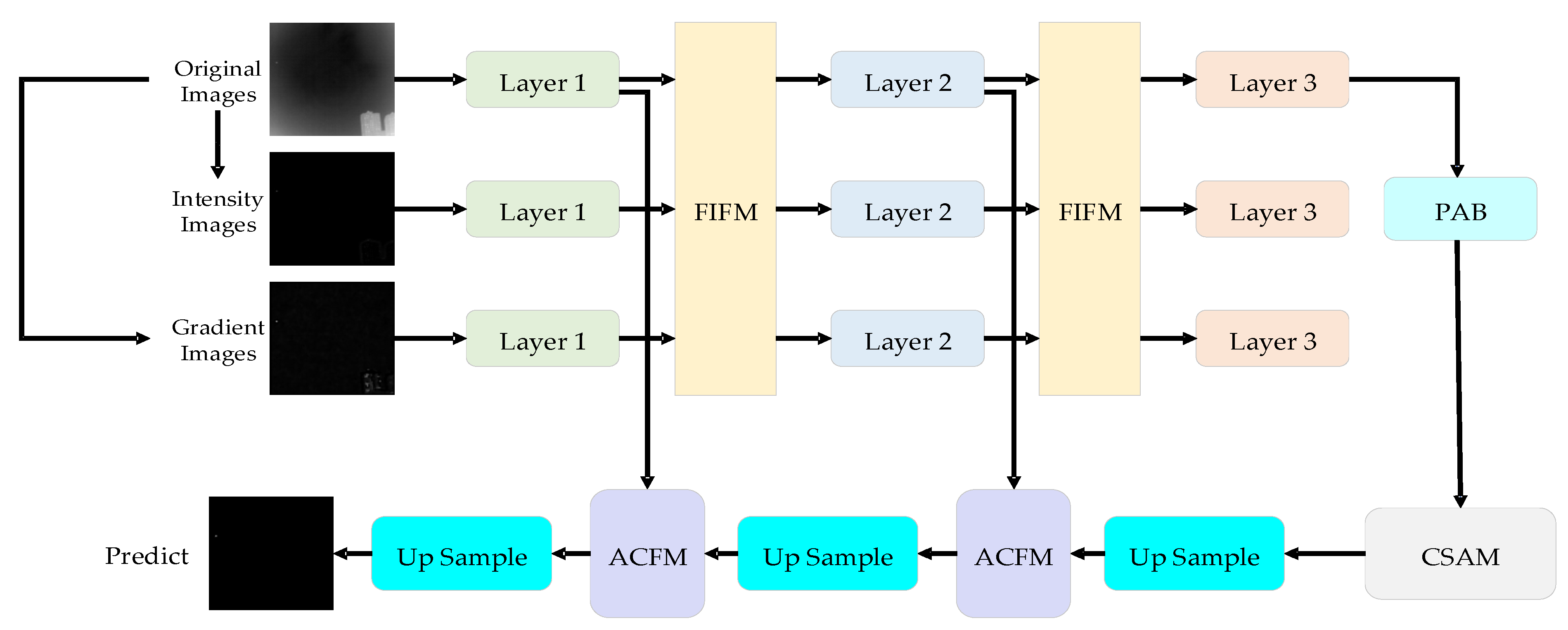
3.1. Overall Architecture
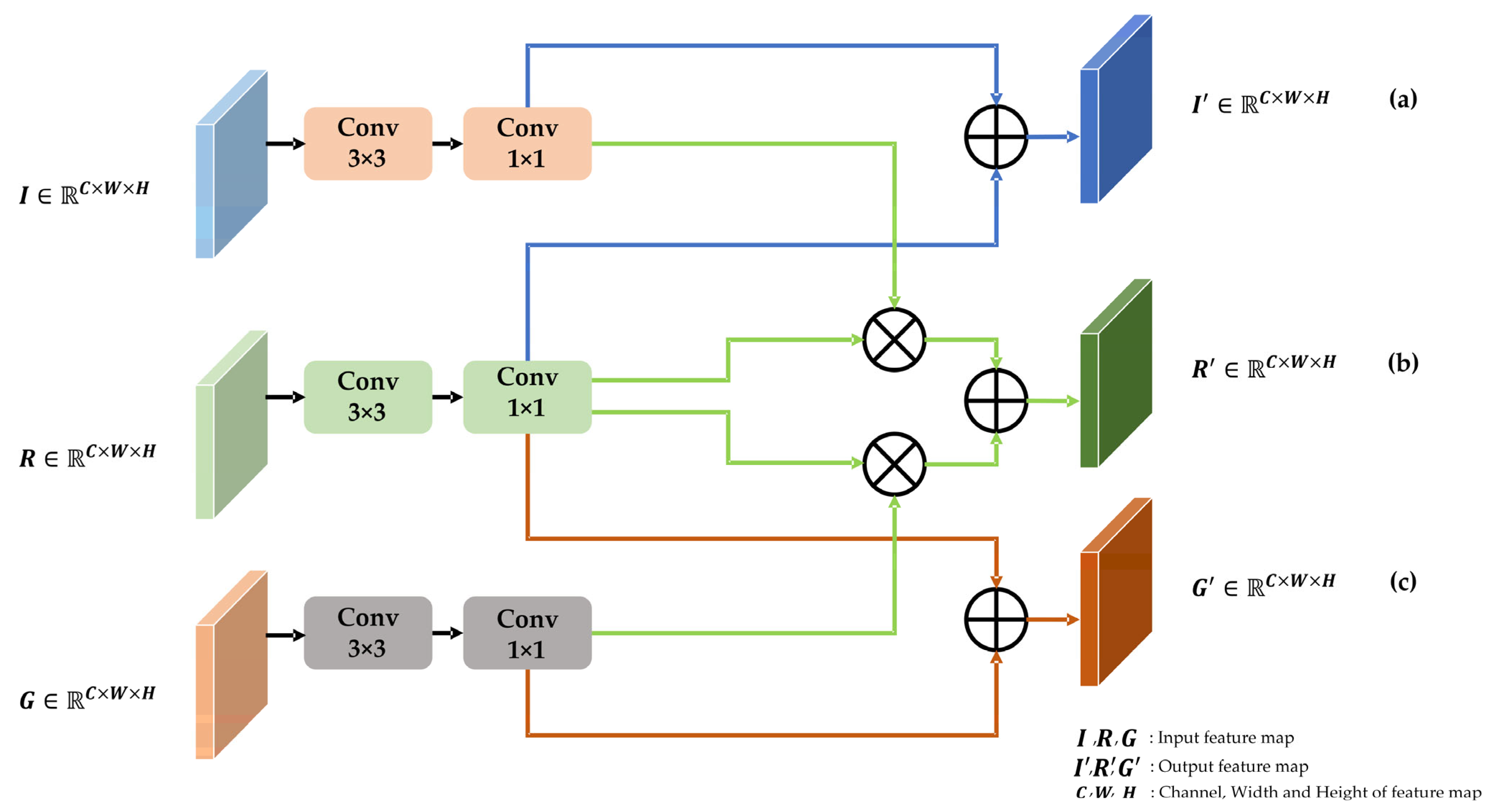
3.2. Multi-Feature Interactive Fusion Module
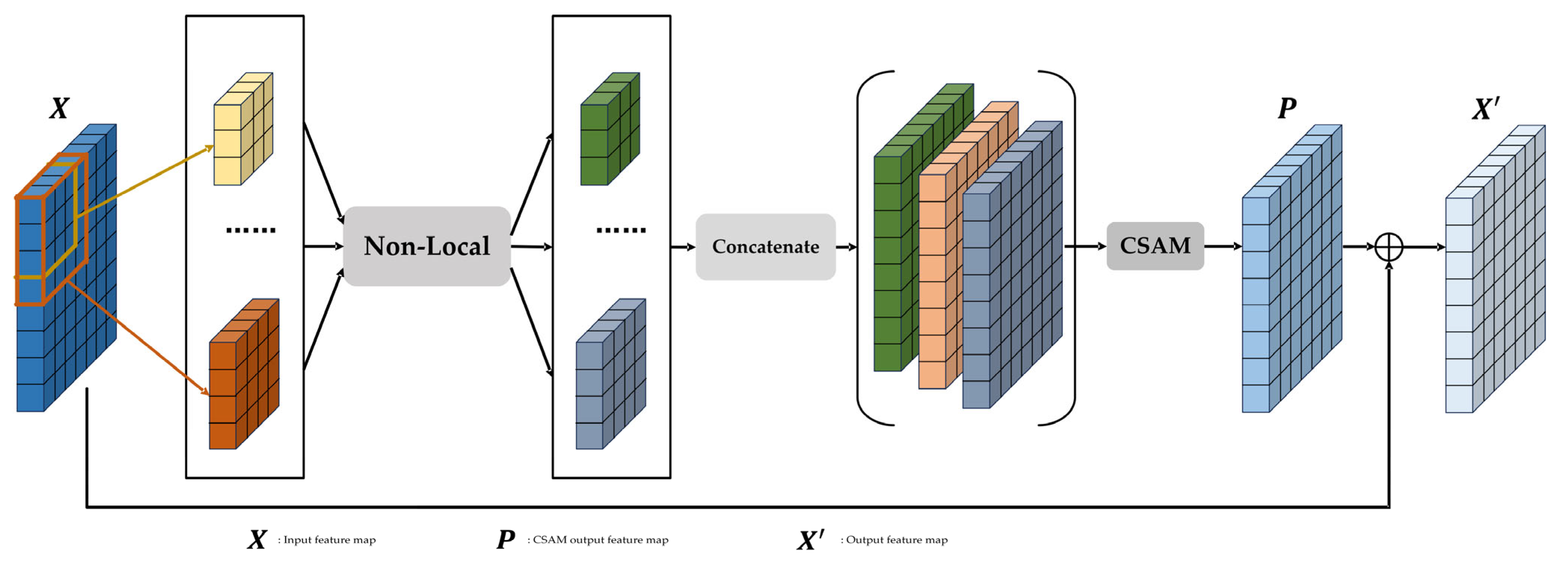
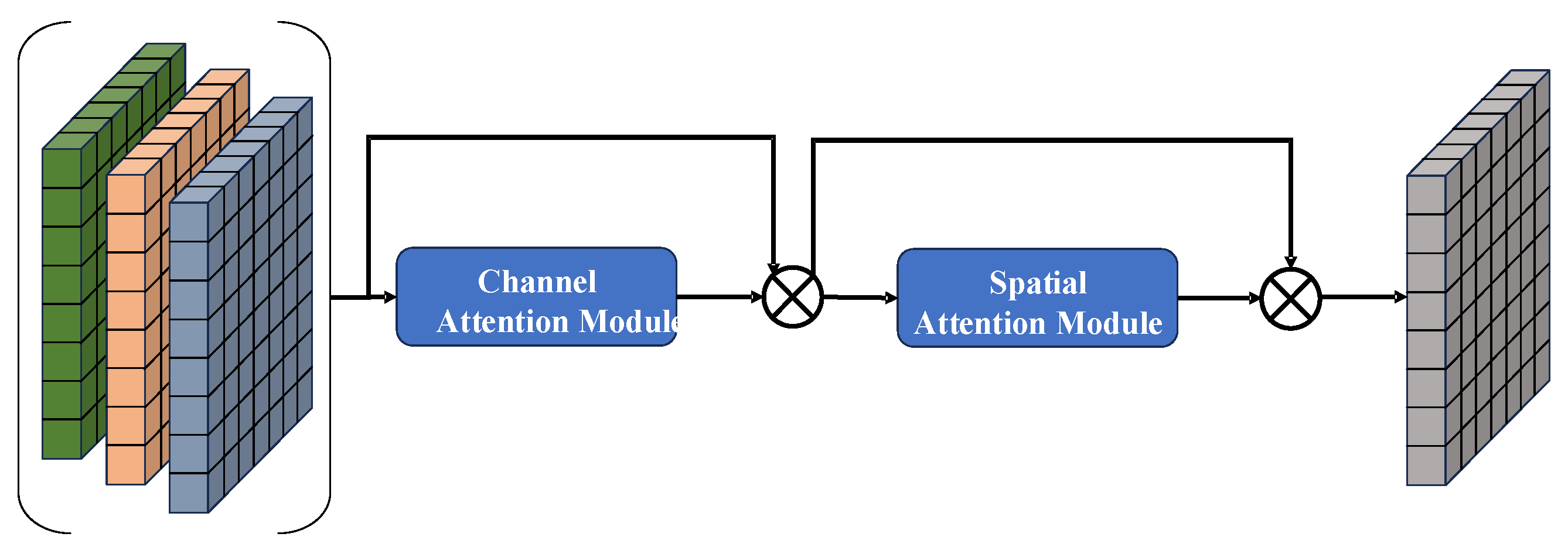
3.3. Patch Attention Block
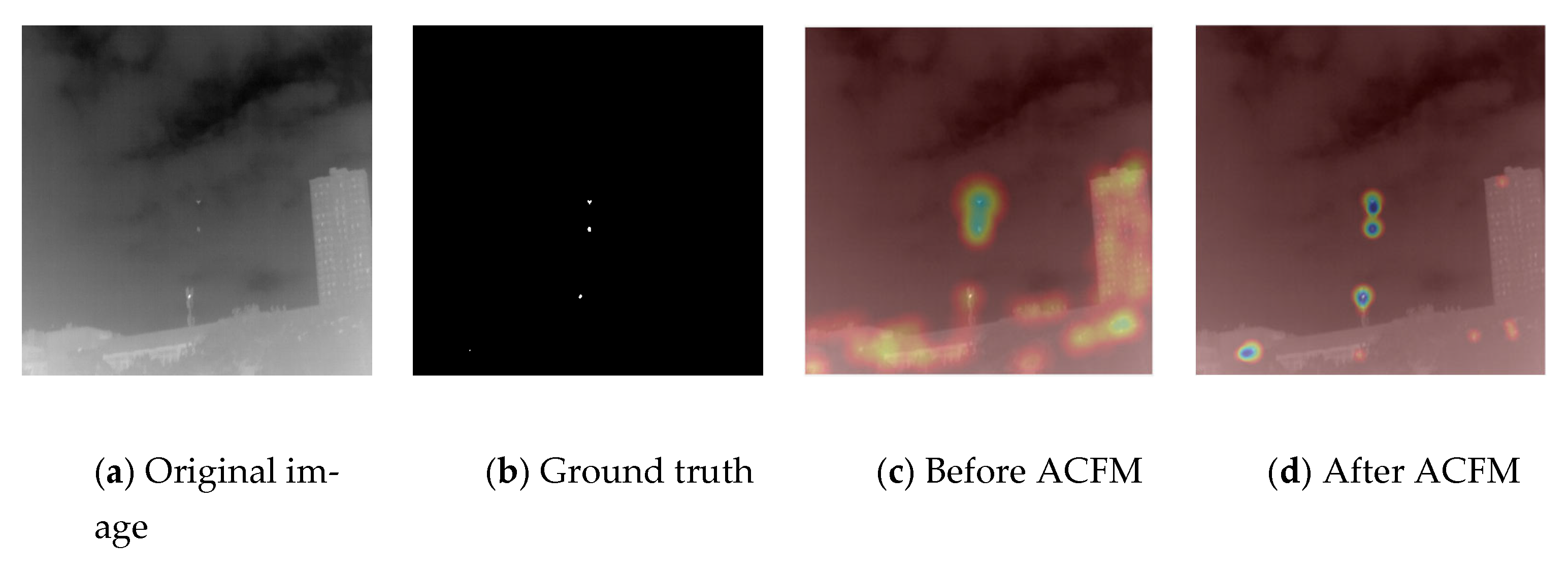
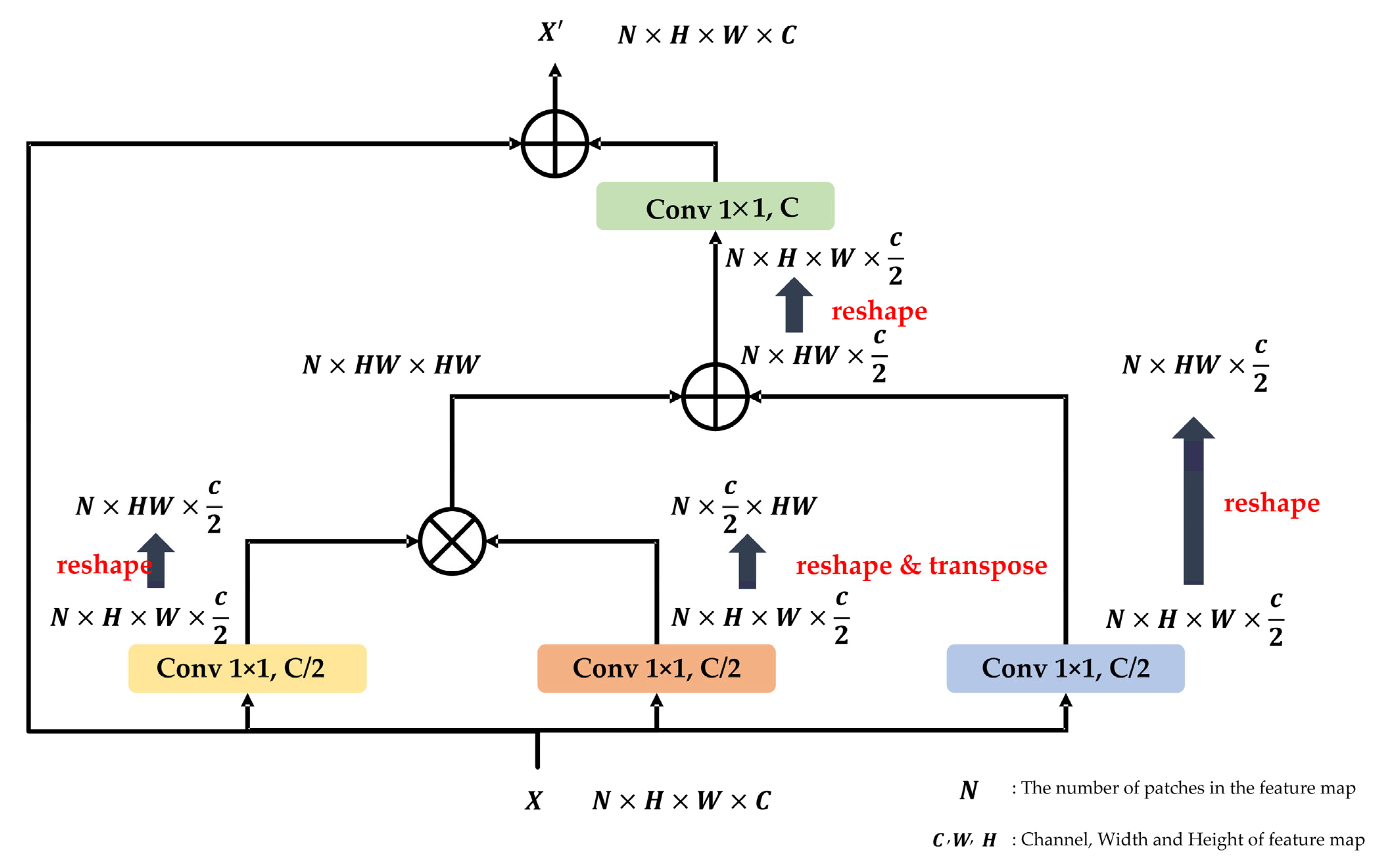
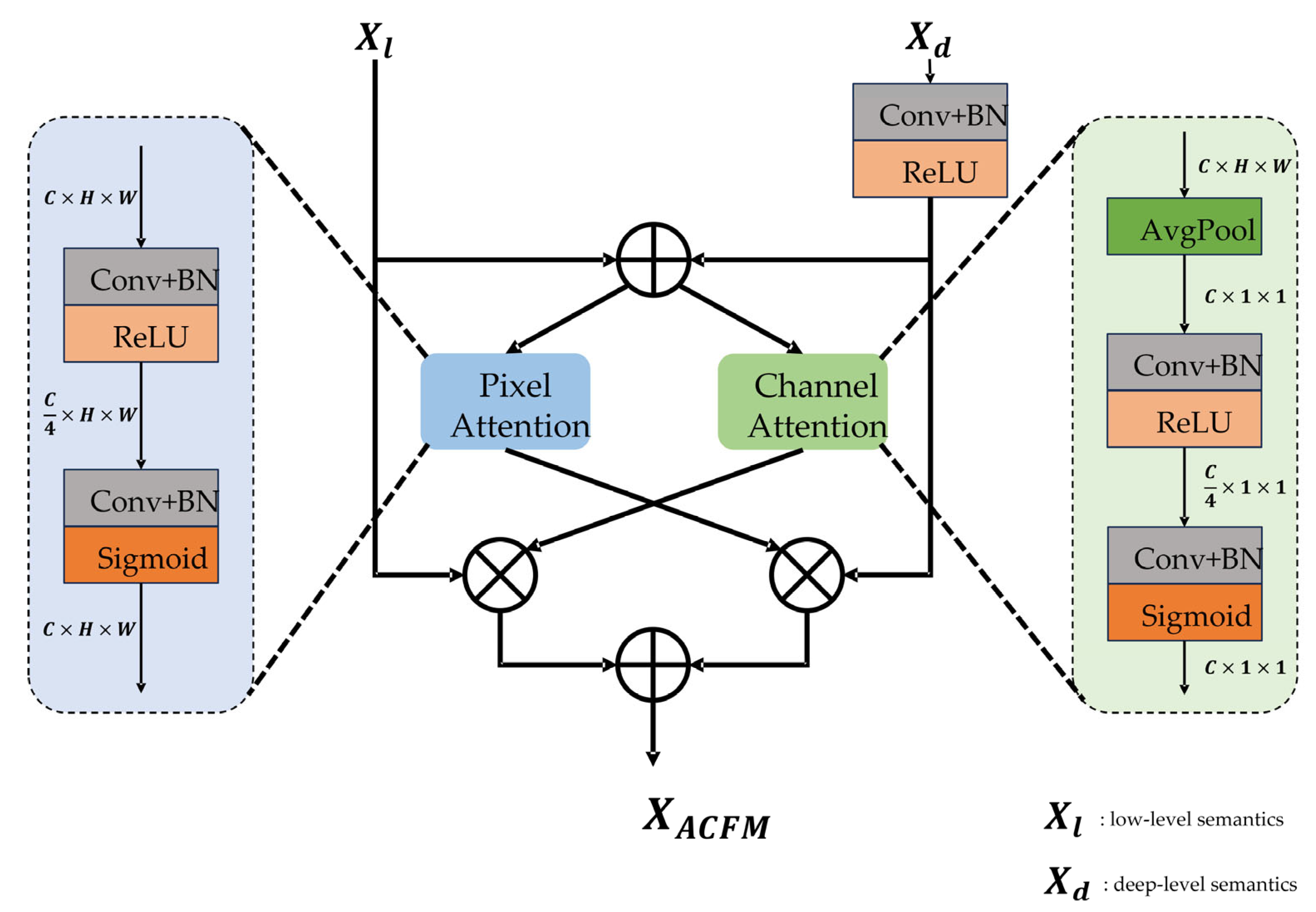
3.4. Asymmetric Contextual Fusion Module
3.5. Loss Function
- (1)
- Binary Cross-Entropy (BCE) Loss
- (2)
- Soft-IoU Loss
- (3)
- Multi-Scale Feature Supervision Loss
- (4)
- Semantic Alignment Loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details and Setting
4.2. Ablation Study
4.3. Comparison to Excellent Methods
- (1)
- Quantitative evaluation: The results of different methods on two public datasets, SIRST-Aug and IRSTD-1k, are presented in Table 5. The maximum value of each column is indicated in bold black. For the model-driven method, the obtained predicts indicate the probability of detecting targets. Hence, we set an adaptive threshold to remove low-response areas:
- (2)
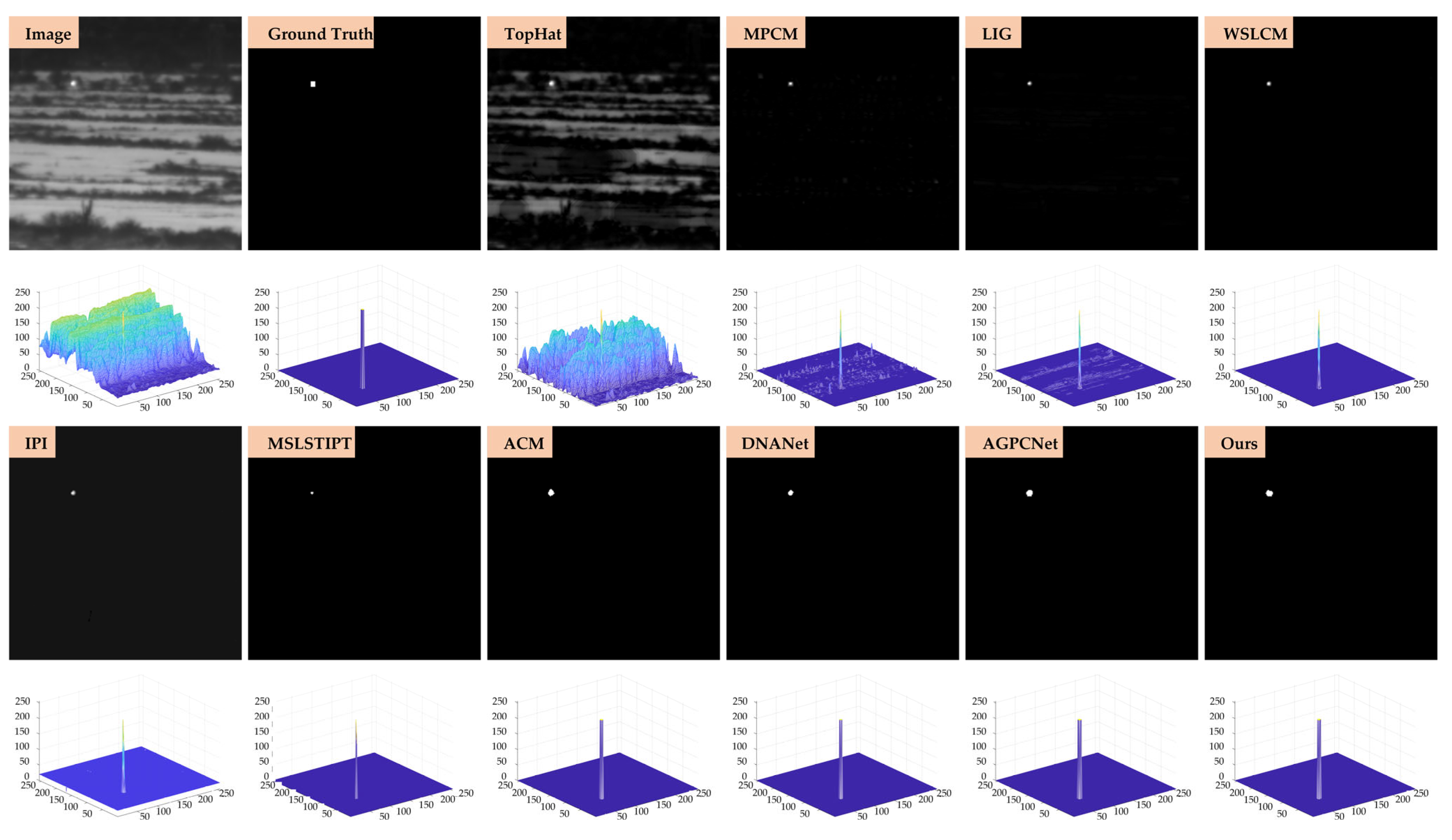
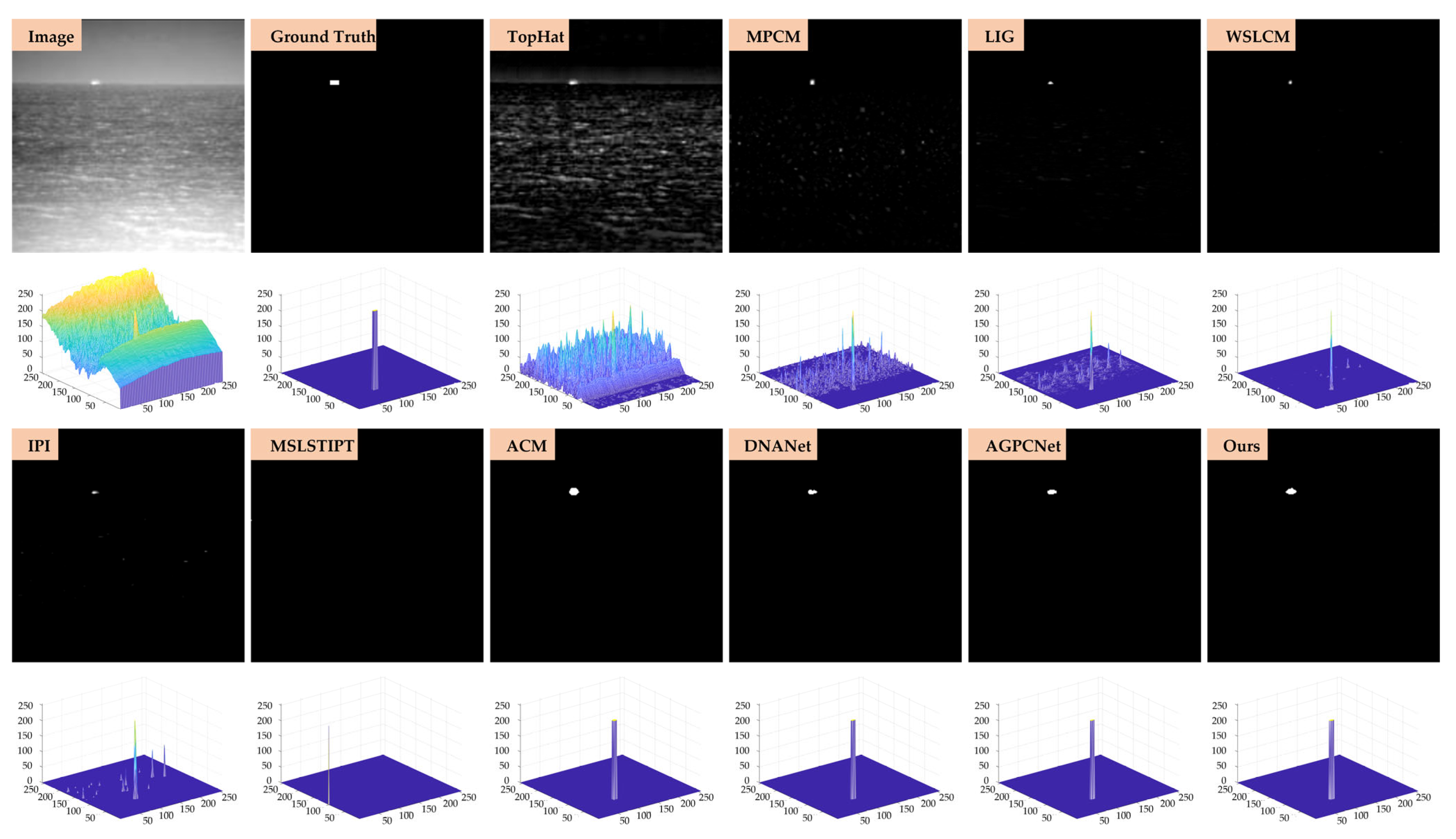
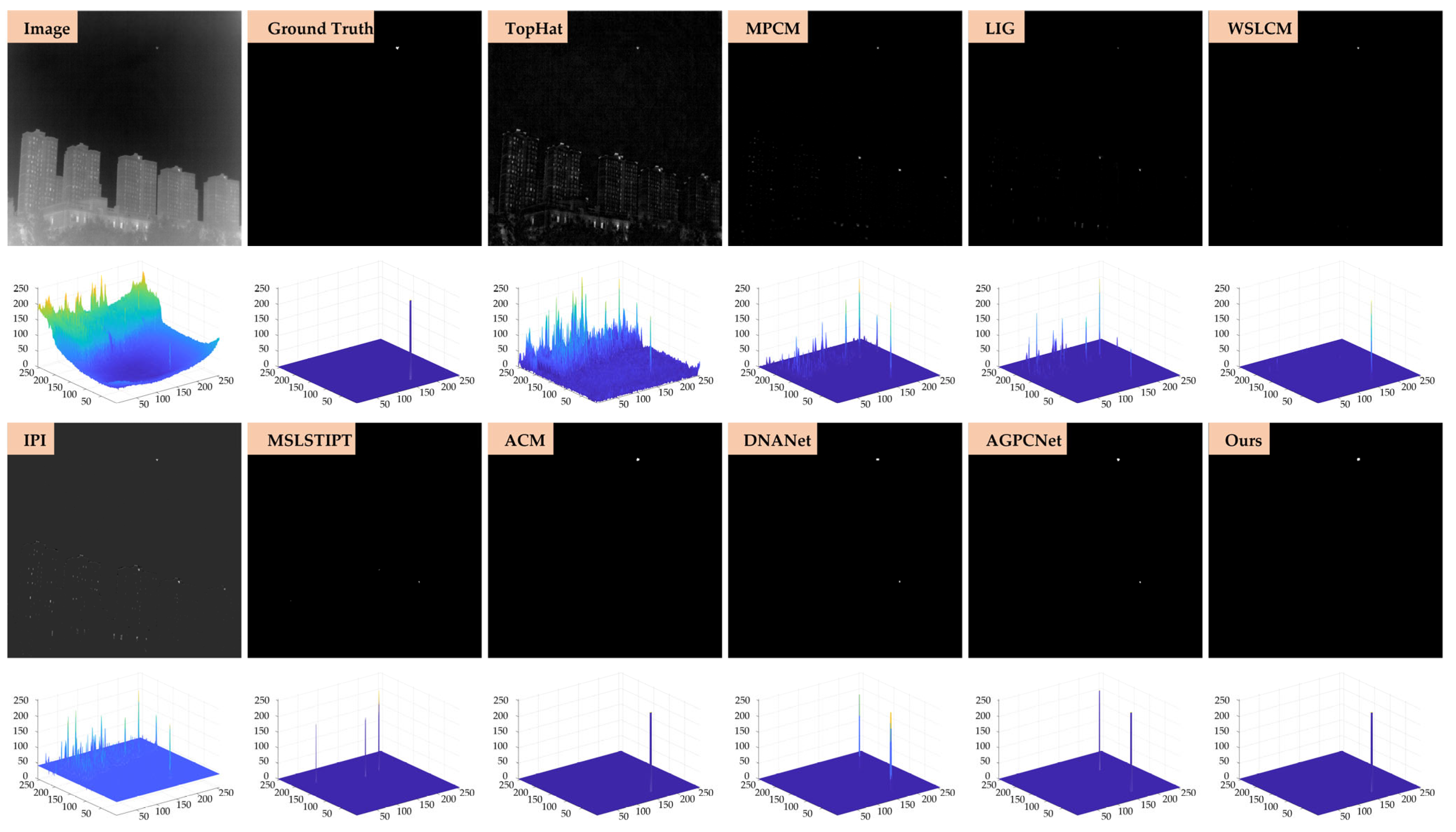
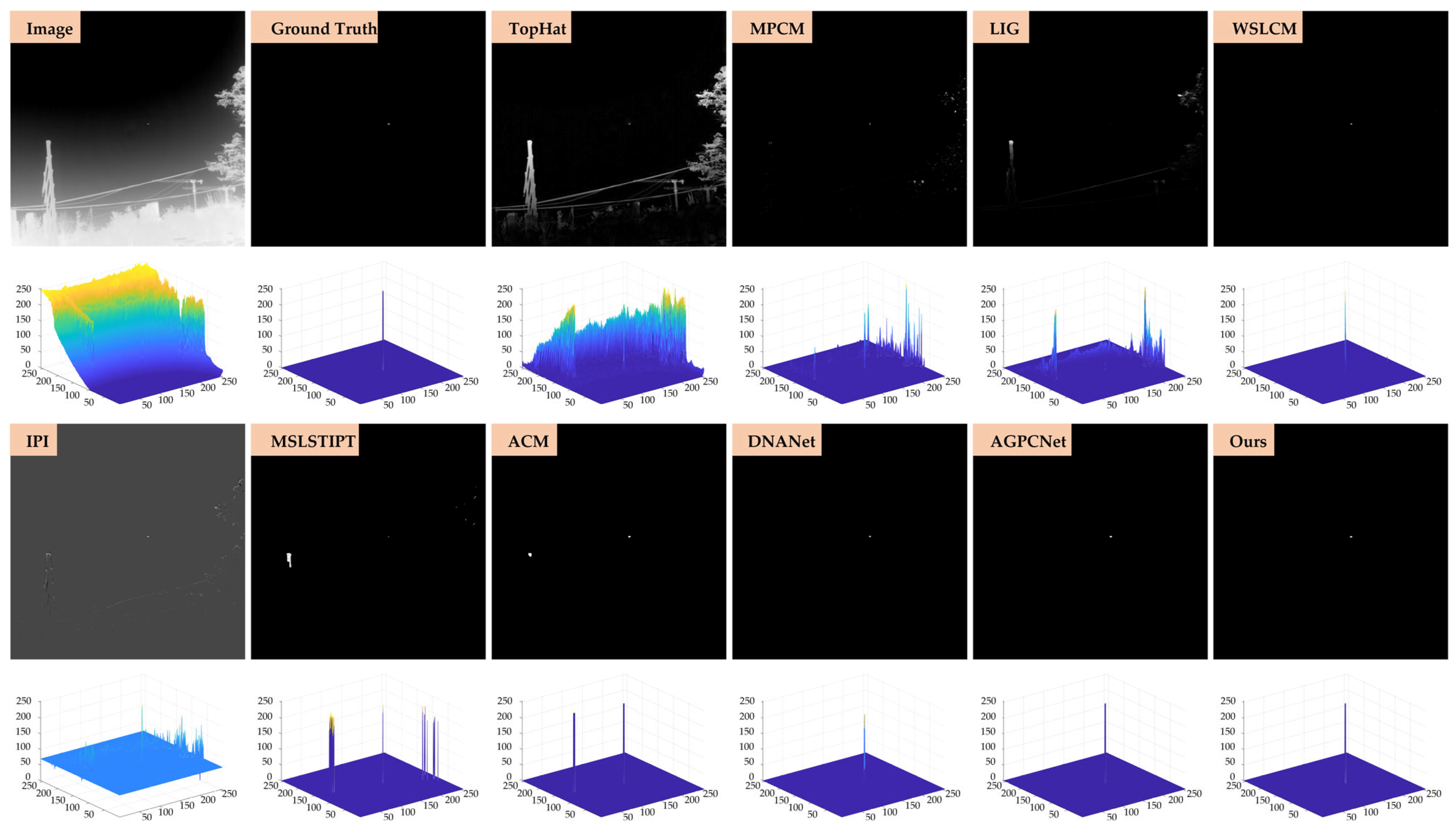
- Qualitative evaluation: To further illustrate the effectiveness of our method in complex infrared imaging scenarios, qualitative detection results are presented on two benchmark datasets, SIRST-Aug and IRSTD-1k, as shown in Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14. Four representative scenes are selected from each dataset, covering typical challenges such as low contrast, cluttered backgrounds, and small-scale targets. The output results of ten representative methods, including both model-driven and learning-based approaches, are displayed in a unified 3D visualization format for intuitive comparison. Each method’s output is marked in the upper-left corner of the corresponding subfigure to ensure clarity.
4.4. Efficiency and Deployment Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, J.; Pan, N.; Yin, D.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J. MEFA-Net: Multilevel feature extraction and fusion attention network for infrared small-target detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Duan, Q.; Li, Z. WT-HMFF: Wavelet transform convolution and hierarchical multi-scale feature fusion network for detecting infrared small targets. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, P.; Fei, C.; Wang, X. Infrared small target detection based on spatio-temporal saliency in video sequence. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing, Chengdu, China, 18–20 December 2015; pp. 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Q. Small aerial target detection for airborne infrared detection systems using LightGBM and trajectory constraints. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9959–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.D.; Er, M.H.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Chan, P. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small targets. In Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1993, Proceedings of the Optical Engineering and Photonics in Aerospace Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 20–22 July 1999; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1993; pp. 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lv, G.; Xu, L. Infrared dim target detection based on visual attention. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2012, 55, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xia, T.; Tang, Y. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; You, X.; Li, H. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 58, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, D.; Chen, H. Infrared small target detection based on local intensity and gradient properties. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 89, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, L.; Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection via non-convex rank approximation minimization joint/2,1 norm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Gao, C.; Li, B. Infrared small target detection based on facet kernel and random walker. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7104–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Chang, S.; Deng, Y.; Xue, F.; Wang, C.; Jia, X. Oriented SAR ship detection based on edge deformable convolution and point set representation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Barnard, K. Asymmetric contextual modulation for infrared small target detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual Conference, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 950–959. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Du, S.; Liu, C.; Cao, Z. Interior Attention-Aware Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 3163410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Pu, T.; Peng, Z. AGPCNet: Attention-guided pyramid context networks for infrared small target detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Sun, X.; Liu, M.; Ye, C.; Zhou, X. Small infrared target detection based on weighted local difference measure. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4204–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, B.; Fan, F.; Liang, K.; Fang, Y. A robust infrared small target detection algorithm based on human visual system. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Liang, K.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L. Infrared small target detection utilizing the multiscale relative local contrast measure. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Moradi, S.; Faramarzi, I.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, N. Infrared small target detection based on the weighted strengthened local contrast measure. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Moradi, S.; Faramarzi, I.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q. A local contrast method for infrared small-target detection utilizing a tri-layer window. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Shu, R. Infrared small target detection based on multiscale local contrast measure using local energy factor. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, L.; Hui, M.; Wang, S.X. Image small target detection based on deep learning with SNR controlled sample generation. Curr. Trends Comput. Sci. Mech. Autom. 2017, 1, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Tan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, W. RISTDnet: Robust infrared small target detection network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 7000805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ma, T.; Ku, Y.; Ma, Q.; Fu, J. DFFIR-net: Infrared dim small object detection network constrained by gray-level distribution model. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 5026215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gao, C.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, D.; Zuo, W. Local patch network with global attention for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 3979–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Gao, C.; Chen, F.; Meng, D.; Zuo, W.; Gao, X. Infrared small and dim target detection with transformer under complex backgrounds. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 5921–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, M.; An, W.; Guo, Y. Dense nested attention network for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 32, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Aidan, N.; Kziser, L. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2017, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Alexey, D.; Lucas, B.; Alexander, K.; Dirk, W.; Zhai, X.; Thomas, U.; Mostafa, D.; Matthias, M.; Georg, H.; Sylvain, G.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Cai, B.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J. Up-detr: Unsupervised pre-training for object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1601–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J. ISNet: Shape matters for infrared small target detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–23 June 2022; pp. 877–886. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; An, W. Infrared dim and small target detection via multiple subspace learning and spatial-temporal patch-tensor model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 3737–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, R.; Zheng, B. Infrared small target detection with scale and location sensitivity. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 17490–17499. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J. IRSAM: Advancing segment anything model for infrared small target detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 233–249. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qiao, B.J.; Li, S. Patch spatial attention networks for semantic token transformer in infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5003014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Ye, Z.; Tan, Z.; Gong, T.; Wu, Y.; Chu, C.; Liu, B.; Yu, N.; Ye, J. MiM-ISTD: Mamba-in-mamba for efficient infrared small-target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5007613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Datasets | Training Images | Testing Images | Image Size | Smallest Target Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIRST-Aug | 8525 | 545 | 256 × 256 | 2 × 2 |
| IRSTD-1k | 800 | 201 | 512 × 512 | 3 × 3 |
| MIFM | SIRST-Aug | IRSTD-1k | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | Fmeasure | IoU | Fmeasure | |
| Without I and G | 0.6861 | 0.8138 | 0.6217 | 0.7713 |
| With I | 0.7252 | 0.8440 | 0.6514 | 0.7885 |
| With G | 0.7101 | 0.8337 | 0.6413 | 0.7803 |
| With I and G | 0.7465 | 0.8512 | 0.6701 | 0.8025 |
| Patch Size | SIRST-Aug | IRSTD-1k | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | Fmeasure | IoU | Fmeasure | |
| [3] | 0.6986 | 0.8289 | 0.6252 | 0.7754 |
| [3, 5] | 0.7154 | 0.8365 | 0.6326 | 0.7791 |
| [3, 5, 6] | 0.7266 | 0.8402 | 0.6537 | 0.7965 |
| [3, 5, 6, 10] | 0.7465 | 0.8512 | 0.6701 | 0.8025 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | mIoU | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o ACFM | 0.8057 | 0.8150 | 0.7036 | 0.8102 |
| w/o ACFM + FIFM | 0.7821 | 0.8038 | 0.6802 | 0.7928 |
| w/o ACFM + PAB | 0.7946 | 0.7991 | 0.6855 | 0.7968 |
| w/o ACFM + FIFM + PAB | 0.7812 | 0.7925 | 0.6824 | 0.7868 |
| Full MFAFNet | 0.8376 | 0.8652 | 0.7465 | 0.8512 |
| Configuration | λ1 (BCE) | λ2 (IoU) | λ3 (Feature) | λ4 (Semantic) | F-Measure | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equal Weights (default) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.8512 | 0.7465 |
| Emphasis on BCE | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.8365 | 0.7281 |
| Emphasis on IoU | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0.8427 | 0.7346 |
| Emphasis on Feature Supervision | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.8442 | 0.7391 |
| Emphasis on Semantic Alignment | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.8475 | 0.7410 |
| Methods | SIRST-Aug | IRSTD-1k | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | mIoU | Fmeasure | Precision | Recall | mIoU | Fmeasure | |
| LEF | 0.6837 | 0.3929 | 0.3325 | 0.4990 | 0.0832 | 0.3248 | 0.0709 | 0.1324 |
| WSLCM | 0.9334 | 0.1038 | 0.1030 | 0.1868 | 0.5443 | 0.0952 | 0.0882 | 0.1621 |
| RIPT | 0.9484 | 0.0800 | 0.0797 | 0.1476 | 0.5765 | 0.0591 | 0.0567 | 0.1073 |
| PSTNN | 0.9421 | 0.1043 | 0.1036 | 0.1878 | 0.4838 | 0.0884 | 0.0808 | 0.1495 |
| MSLSTIPT | 0.8810 | 0.0400 | 0.0398 | 0.0766 | 0.6602 | 0.0470 | 0.0458 | 0.0877 |
| ACM | 0.6145 | 0.1061 | 0.0994 | 0.1809 | 0.8117 | 0.1169 | 0.1138 | 0.2044 |
| DNANet | 0.8420 | 0.0304 | 0.0302 | 0.0587 | 0.8324 | 0.0540 | 0.0535 | 0.1015 |
| AGPC | 0.9531 | 0.0605 | 0.0603 | 0.1138 | 0.6208 | 0.0465 | 0.0453 | 0.0866 |
| MSHNet | 0.9575 | 0.1325 | 0.1317 | 0.2328 | 0.2594 | 0.2072 | 0.1302 | 0.2303 |
| Trans-IRSD | 0.9670 | 0.0740 | 0.0738 | 0.1374 | 0.6020 | 0.1066 | 0.0996 | 0.1812 |
| RISTDnet | 0.6595 | 0.1229 | 0.1155 | 0.2072 | 0.4236 | 0.2352 | 0.1782 | 0.3024 |
| IRSAM | 0.8031 | 0.8493 | 0.7025 | 0.8256 | 0.7107 | 0.7998 | 0.6034 | 0.7526 |
| STPSA-Net | 0.8384 | 0.7566 | 0.6603 | 0.7954 | 0.7653 | 0.7195 | 0.5895 | 0.7417 |
| MiM-ISTD | 0.8323 | 0.8542 | 0.7288 | 0.8431 | 0.7850 | 0.7908 | 0.6500 | 0.7879 |
| MFAFNet | 0.8376 | 0.8652 | 0.7465 | 0.8512 | 0.7907 | 0.8146 | 0.6701 | 0.8025 |
| Method | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | Inference Time (ms/img) | GPU Memory (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNANet | 9.2 | 21.8 | 13.6 | 1790 |
| Trans-IRSD | 38.7 | 102.3 | 48.2 | 3110 |
| MiM-ISTD | 27.3 | 61.5 | 37.4 | 2685 |
| MFAFNet | 16.8 | 34.9 | 24.7 | 2163 |
| MFAFNet-Lite (MobileNetV2) | 6.1 | 13.7 | 11.2 | 1420 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Dong, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. MFAFNet: A Multi-Feature Attention Fusion Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173070
Zhao Z, Chen W, Dong S, Chen Y, Wang H. MFAFNet: A Multi-Feature Attention Fusion Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(17):3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173070
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zehao, Weining Chen, Seng Dong, Yaohong Chen, and Hao Wang. 2025. "MFAFNet: A Multi-Feature Attention Fusion Network for Infrared Small Target Detection" Remote Sensing 17, no. 17: 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173070
APA StyleZhao, Z., Chen, W., Dong, S., Chen, Y., & Wang, H. (2025). MFAFNet: A Multi-Feature Attention Fusion Network for Infrared Small Target Detection. Remote Sensing, 17(17), 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173070






