DATNet: Dynamic Adaptive Transformer Network for SAR Image Denoising
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose a novel Dynamic Gated Attention Module (DGAM) to address the spatial heterogeneity of noise intensity and terrain structure in SAR images. DGAM constructs multi-granularity association maps through dual-path feature embeddings. It incorporates a dynamic gating mechanism that critically screens interaction pathways, breaking away from the static weight allocation paradigm of conventional attention mechanisms. This enables robust suppression of high-noise regions while simultaneously preserving intricate edge and textural details.
- (2)
- We introduce an innovative frequency-aware feature enhancement strategy that integrates frequency-domain decomposition with dynamic expert networks. High- and low-frequency components are separated via the Fourier transform and adaptively processed by activating the top-K expert networks. This strategy specifically optimizes high-frequency components for enhanced noise suppression and detail preservation while reinforcing low-frequency components to improve structure retention, thereby achieving complementary optimization of spatial- and frequency-domain features.
- (3)
- We design a lightweight multi-scale convolutional block that captures multi-scale terrain features through parallel depthwise separable convolutions. By incorporating a channel shuffle strategy, this block significantly enhances cross-scale feature fusion. It effectively enlarges the receptive field while maintaining computational efficiency, thereby overcoming the feature degradation issue prevalent in existing methods when handling multi-scale SAR images.
- (4)
- The proposed model achieves adaptive discrimination of noise typologies and targeted suppression through its dynamically gated attention module and frequency-domain multi-expert enhancement module, thereby completing coordinated removal of multi-source noise within a unified architecture. This innovation bridges a critical research gap in understudied hybrid noise scenarios, which existing methods fail to adequately address.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Denoising Methods
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Denoising Methods
2.3. Vision Transformer
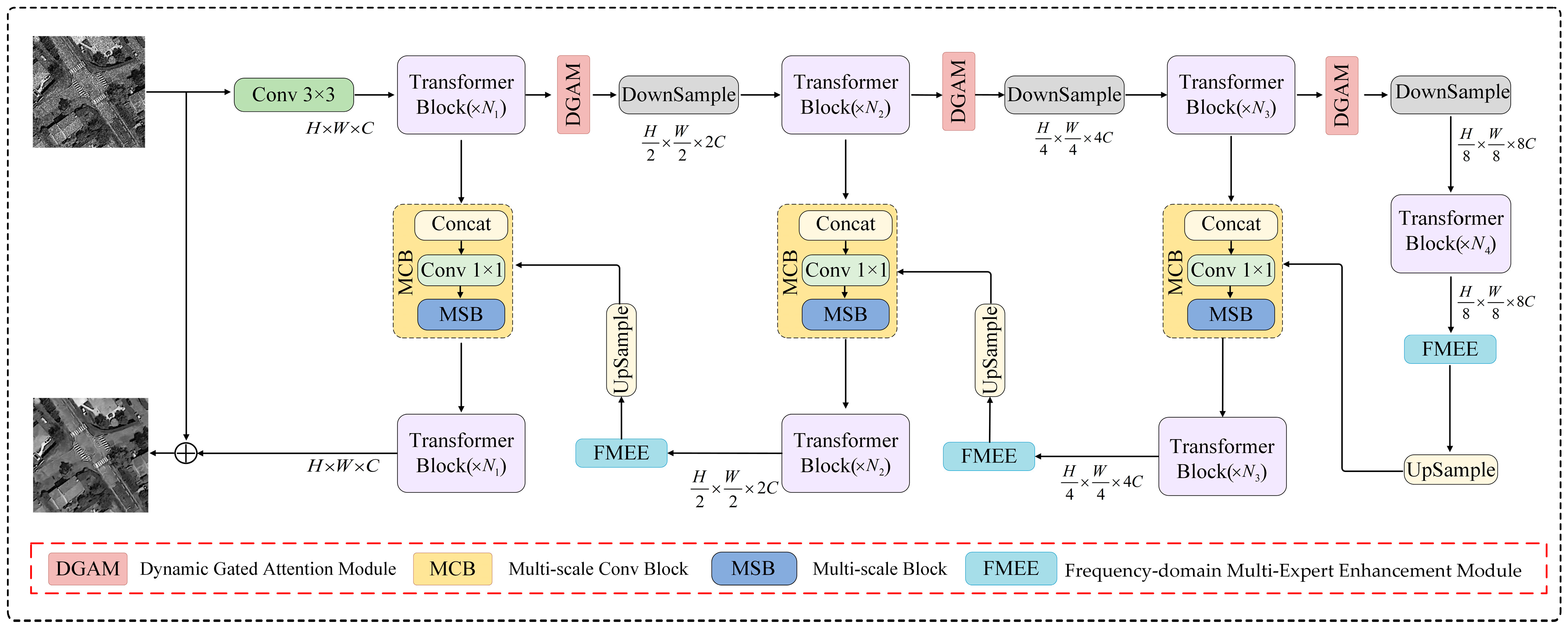
3. Methodology
3.1. Overall Network Architecture
3.2. Dynamic Gated Attention Module
3.2.1. Feature Embedding and Multi-Scale Patch Extraction
3.2.2. Patch Similarity Graph Construction
3.2.3. Adaptive Threshold Gating
3.2.4. Feature Reconstruction and Aggregation
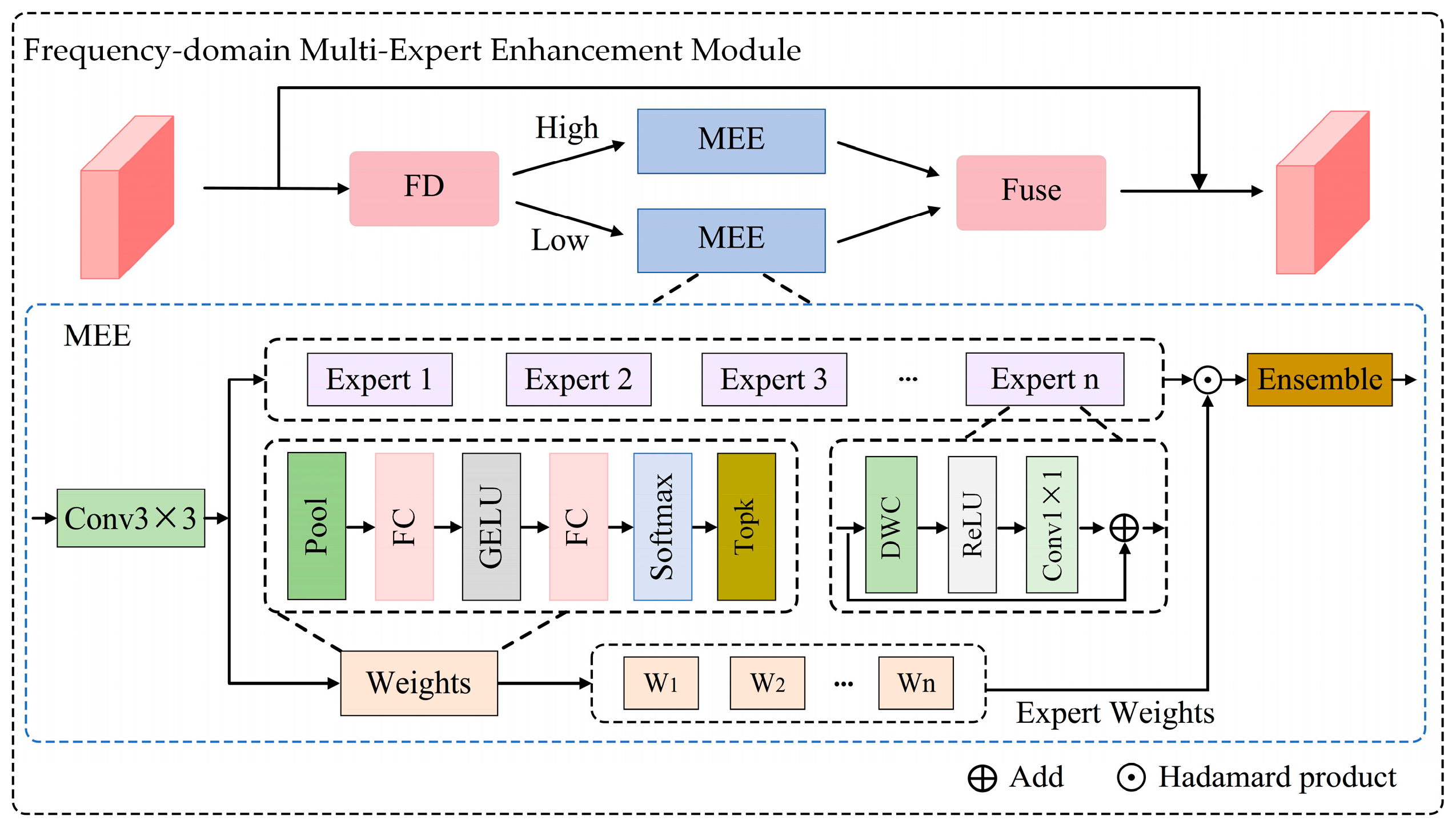
3.3. Frequency-Domain Multi-Expert Enhancement Module
- Physics-Driven Noise Suppression:
- 2.
- Adaptive Enhancement for SAR-Specific Artifacts:
- 3.
- Cross-Domain Synergy:
- 4.
- Robustness to Complex Scattering:
3.3.1. Frequency Decomposition
3.3.2. Multi-Expert Enhancement Network
3.4. Multi-Scale Convolution Block
- 1.
- Scale-Variant Structural Complexity:
- 2.
- Multiplicative Noise and Edge Preservation:
- 3.
- Complementary Feature Abstraction:
- 1.
- Computational Efficiency via Depthwise Separable Convolutions (DSC):
- 2.
- Enhanced Cross-Scale Interaction via Channel Shuffle:
- 3.
- Balanced Representation and Gradient Flow:
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Training and Test Data
- 1.
- Additive noise: Four intensity levels with variances .
- 2.
- Multiplicative noise: Four levels parametrized by values .
- 3.
- Hybrid noise: Combined additive and multiplicative noise emulating complex real-world SAR noise distributions (; ; ; ).
- 1.
- Simulated Images Evaluation: To comprehensively evaluate denoising performance under conditions analogous to SAR image characteristics, we utilized four widely recognized benchmark natural image datasets:
- Classic5 [58]: This dataset comprises five classic grayscale test images (e.g., Lena, Barbara, Boat, House, and Peppers) known for their diverse content, including smooth regions, strong edges, periodic patterns, and fine textures. Its small size allows for efficient testing while covering fundamental image features crucial for assessing detail preservation and artifact suppression.
- Kodak24 [59]: Consisting of 24 uncompressed, high-quality true-color photographic images (each 768 × 512 pixels), this dataset offers a rich variety of natural scenes, including landscapes, portraits, and man-made objects with complex textures and color transitions. Its moderate size and visual appeal make it a standard for evaluating the perceptual quality and robustness of denoising algorithms across diverse content.
- McMaster [60]: This dataset contains 18 high-resolution color images (minimum dimension 500 pixels) featuring significant amounts of fine details, intricate textures (e.g., feathers, fabrics, and foliage), and challenging smooth regions. It is particularly valuable for assessing an algorithm’s ability to recover subtle structures and preserve high-frequency information without introducing artifacts, which is critical for SAR image interpretation.
- Set12 [61]: A commonly used benchmark comprising 12 standard grayscale test images of varying sizes and content (e.g., aerial images, faces, and textural patterns). It provides a good balance of different structural elements and is frequently used for direct comparison with state-of-the-art denoising methods, ensuring consistency in benchmarking.
- These datasets were artificially corrupted with additive, multiplicative, and hybrid noise at multiple intensity levels. To ensure unbiased evaluation, quantitative metrics were computed individually per image and subsequently averaged over each complete dataset. This protocol mitigates performance bias toward images while enabling robust evaluation under diverse noise conditions.
- 2.
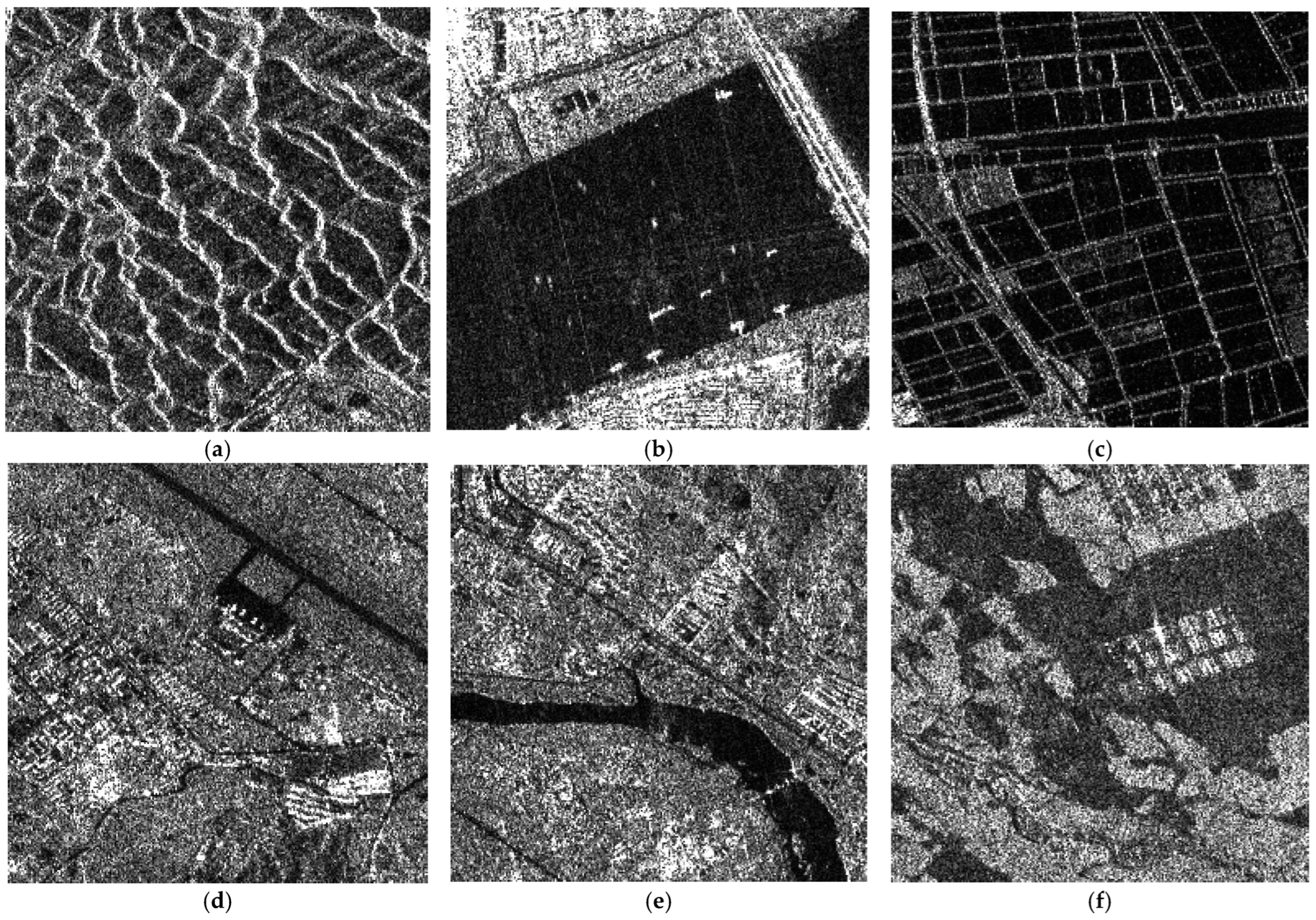
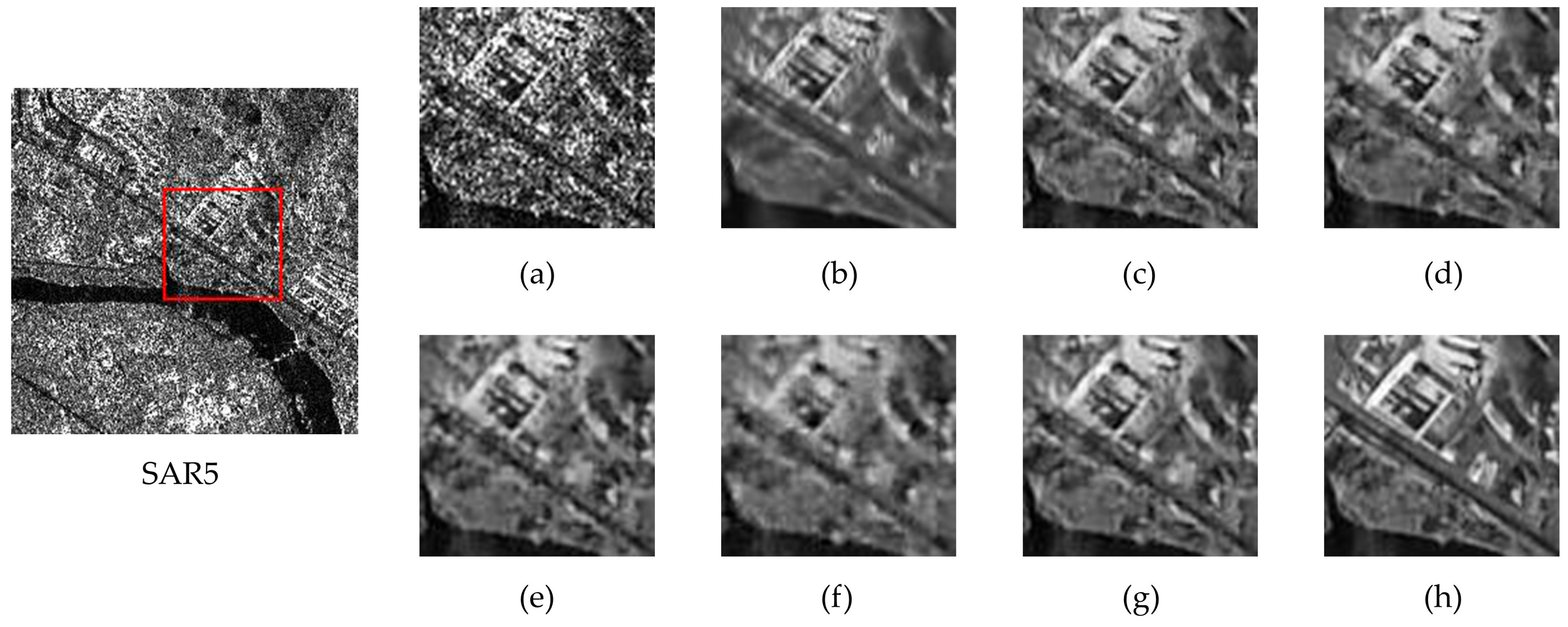
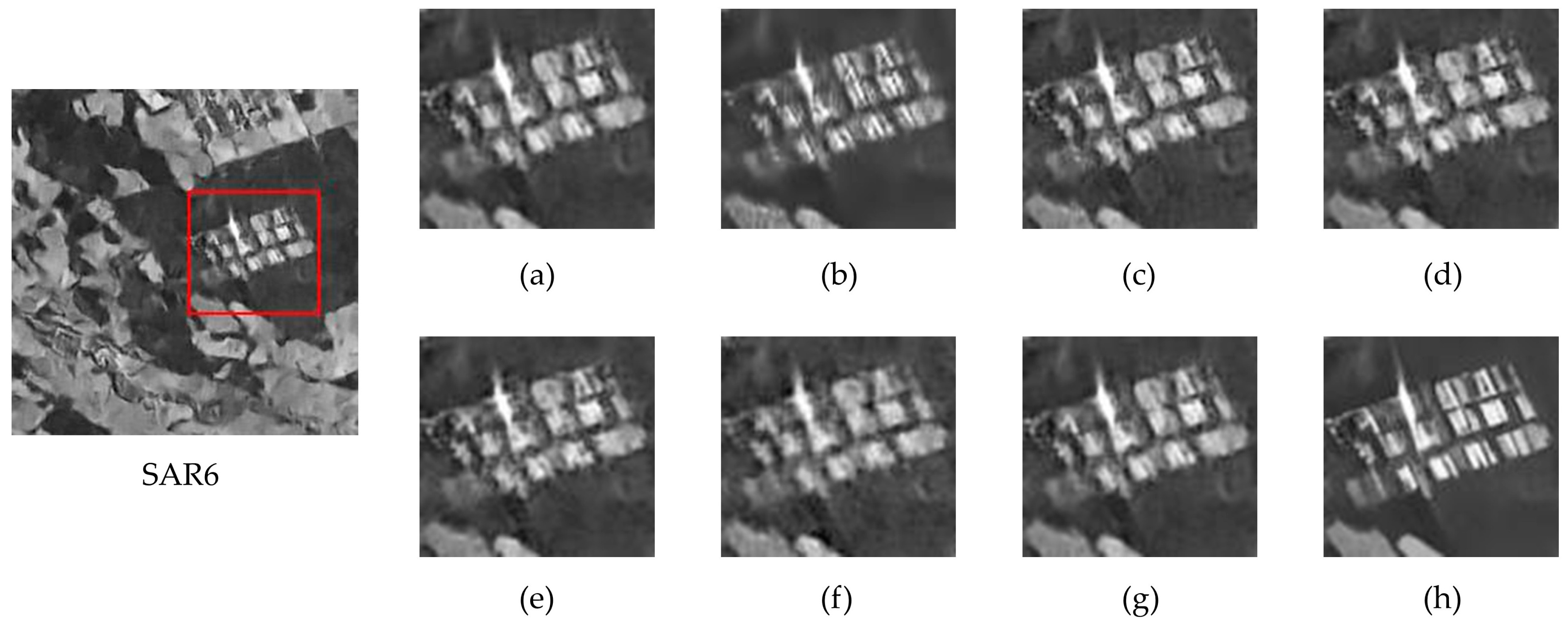
- Real SAR Image Evaluation: Real SAR images evaluation was conducted on three distinct 256 × 256 SAR scenes (designated SAR1-SAR6 in Figure 6) to validate the superiority of the proposed method. These samples were selected from the SARBuD 1.0 dataset [62], a building inventory compiled by the Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS). The dataset comprises single-polarization Gaofen-3 satellite imagery acquired in fine stripmap mode.
4.2. Experimental Setting
4.2.1. Parameter Setting and Network Training
4.2.2. Comparison Method
4.3. Evaluation Metrics and Computational Efficiency Analysis
4.3.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.3.2. Computational Efficiency Analysis
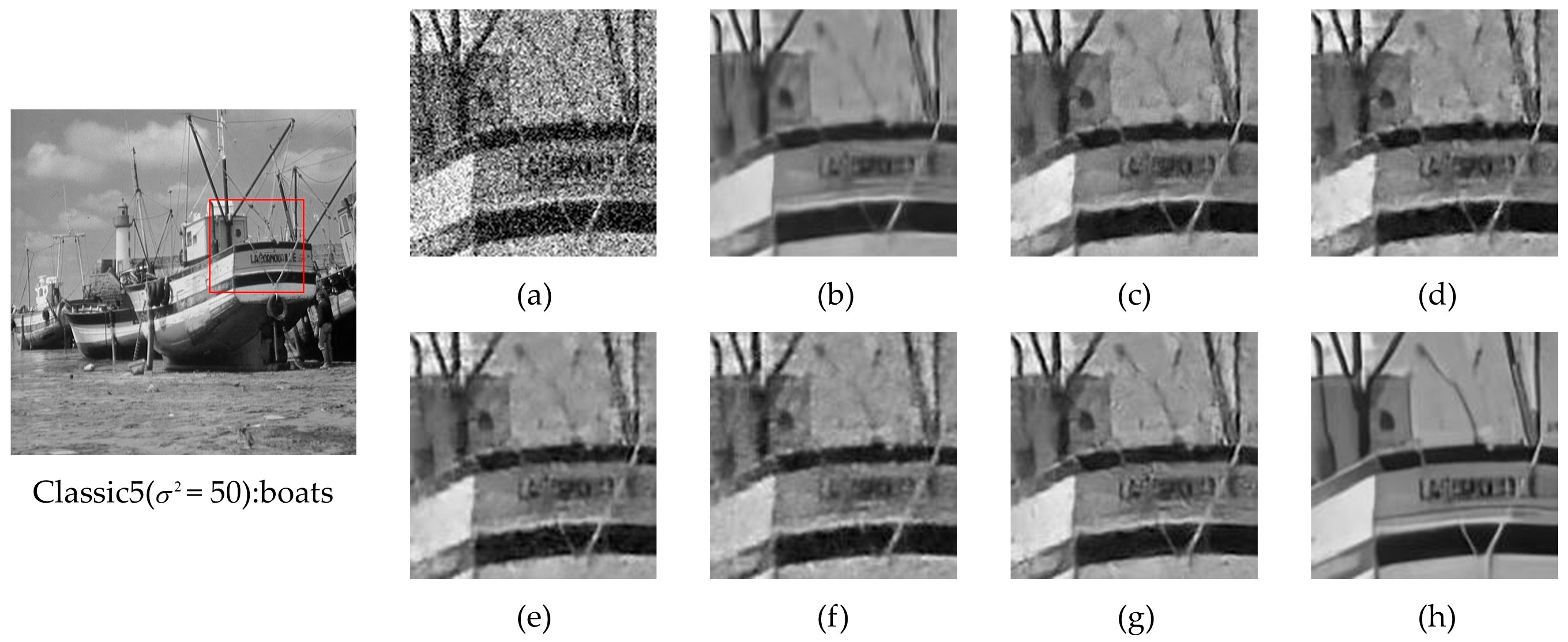
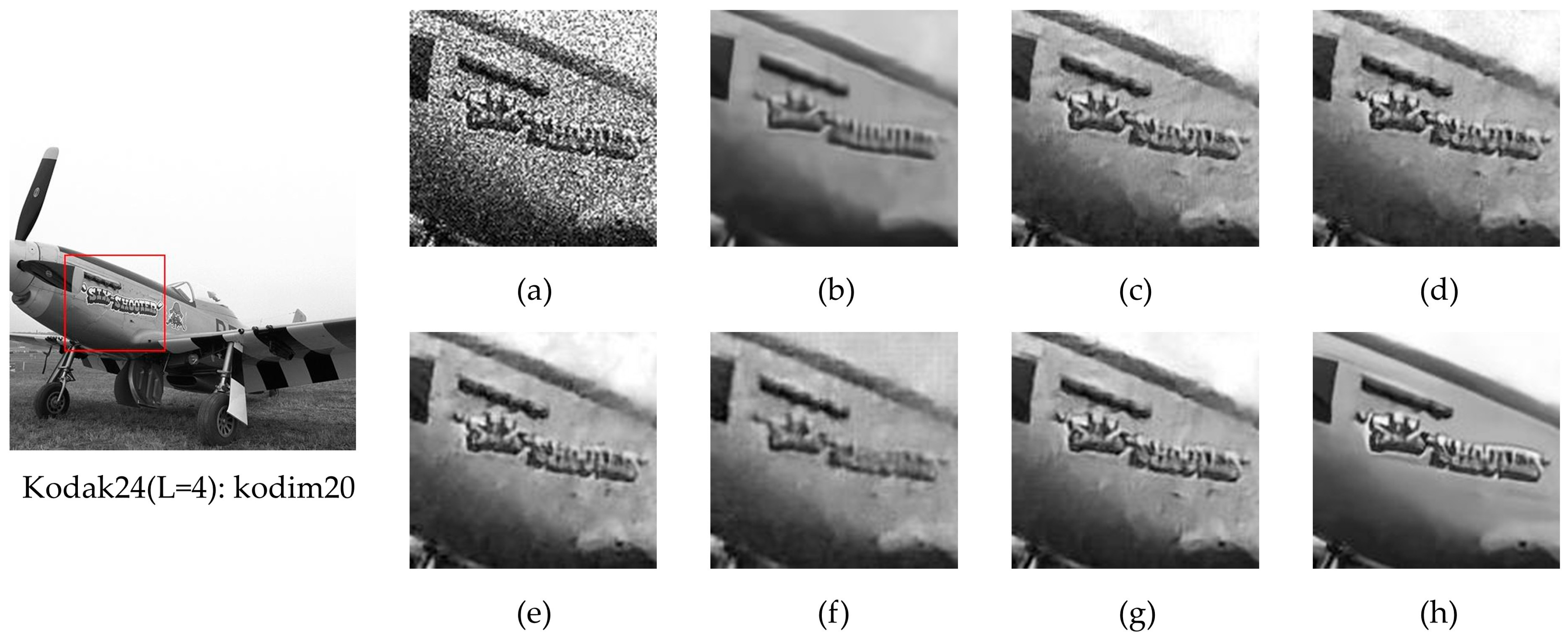
4.4. Performance Comparisons on Simulated Image
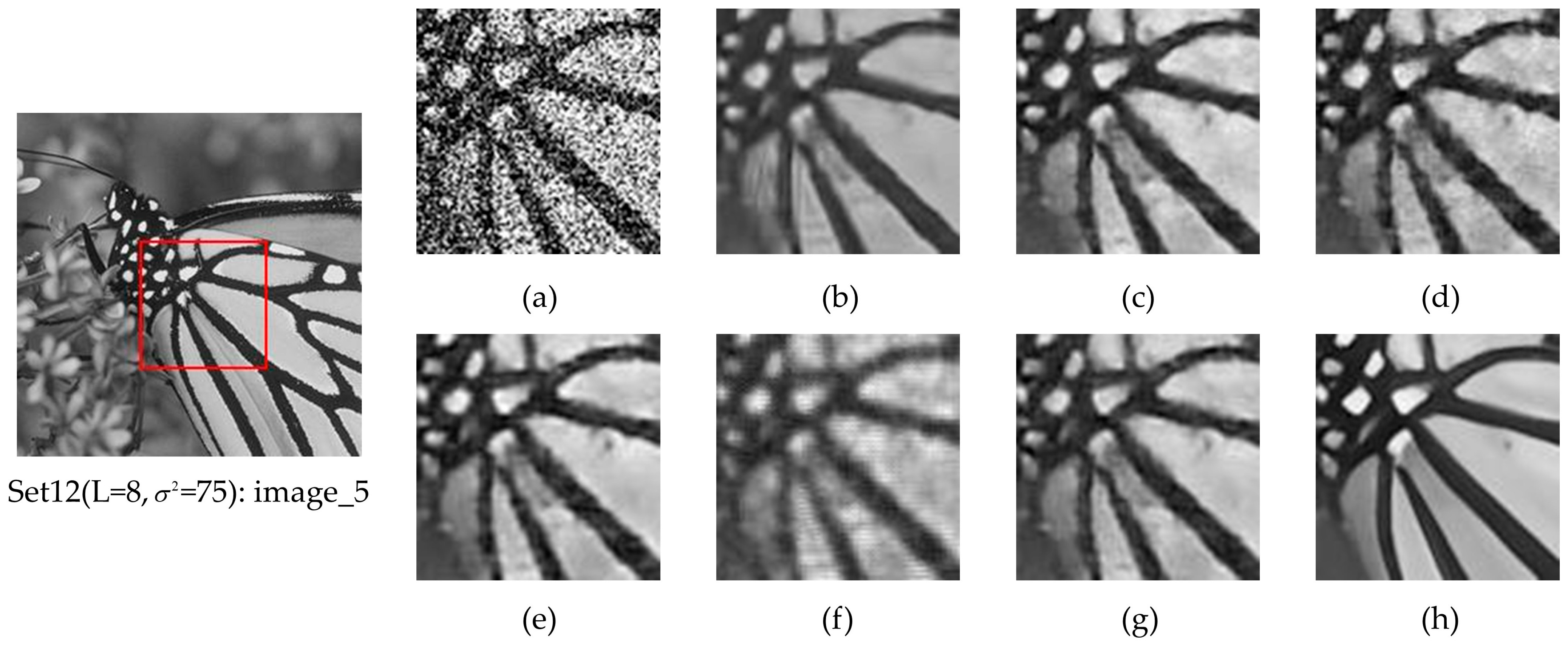
4.4.1. Qualitative Analysis
4.4.2. Quantitative Analysis
4.5. Performance Comparisons on Real SAR Images
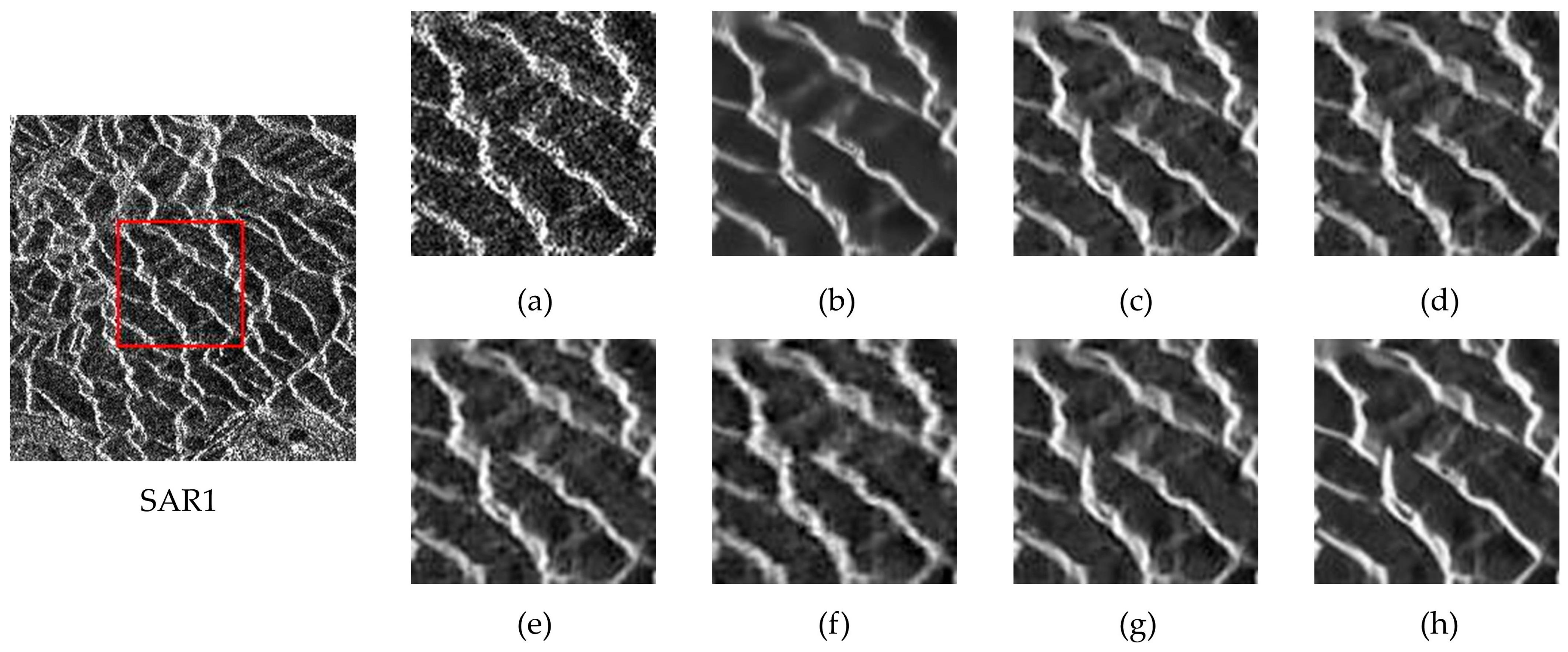
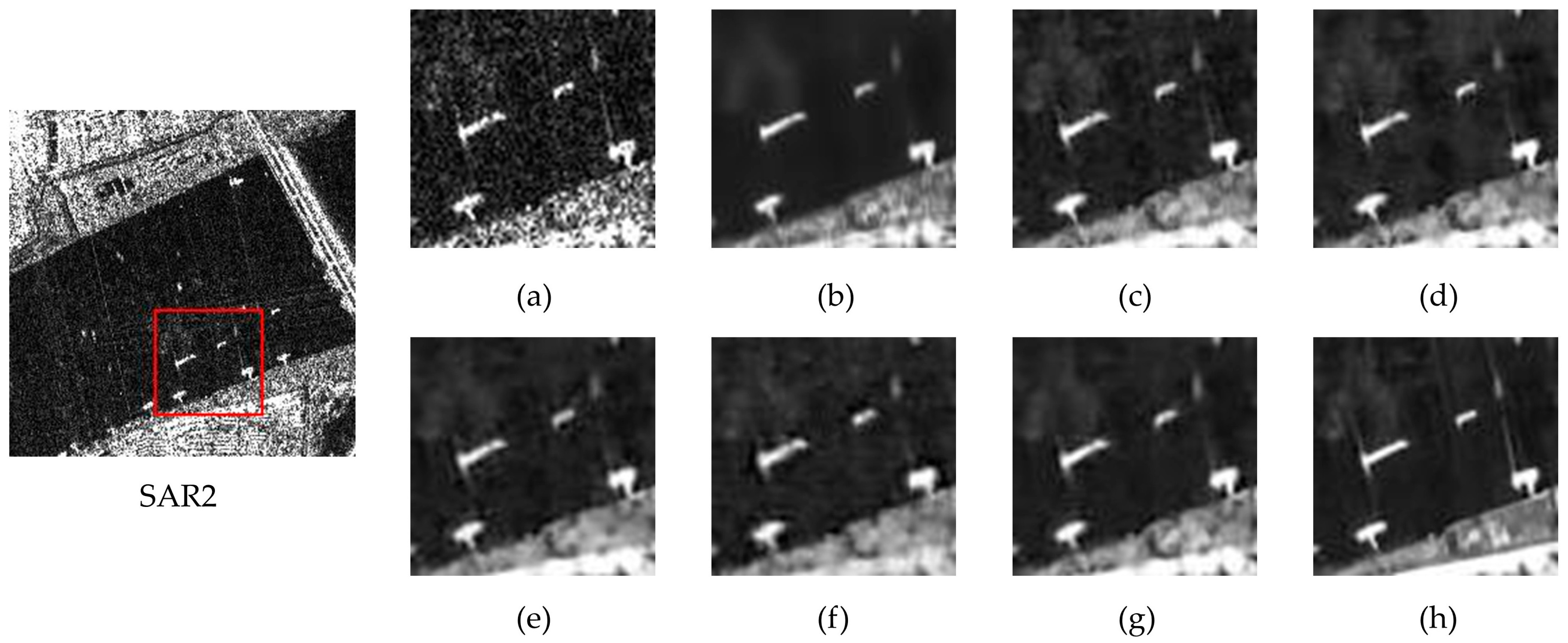
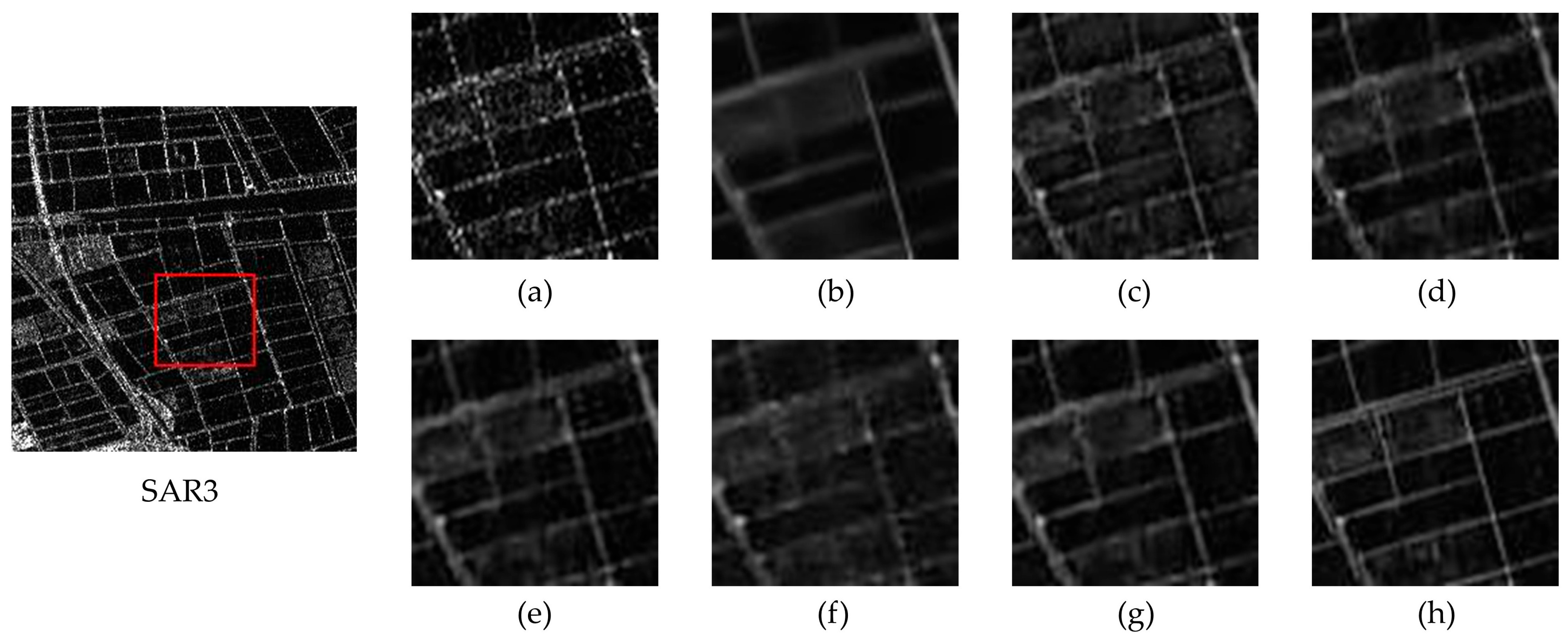
4.5.1. Qualitative Analysis
4.5.2. Quantitative Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amitrano, D.; Di Martino, G.; Di Simone, A.; Imperatore, P. Flood Detection with SAR: A Review of Techniques and Datasets. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Jianhua, W.; Mingming, X.; Hui, S.; Zhe, Z.; Shanwei, L.; Colak, A.T.; Hossain, M.S. Ship detection based on deep learning using SAR imagery: A systematic literature review. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xiao, C.; Peng, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. DiffDet4SAR: Diffusion-Based Aircraft Target Detection Network for SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4007905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, G.; He, L.; An, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Evaluating Urban Building Damage of 2023 Kahramanmaras, Turkey Earthquake Sequence Using SAR Change Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, K.; Li, X.; Bouvet, A.; Mathieu, R.; Main, R.; Naidoo, L.; Erasmus, B.; Asner, G.P. Quantifying the sensitivity of L-Band SAR to a decade of vegetation structure changes in savannas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 284, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, S.-E.; Lee, S.-J. Detection of Damaged Buildings Using Temporal SAR Data with Different Observation Modes. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Shree, R. Analysis and effects of speckle noise in SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication, & Automation (ICACCA), Bareilly, India, 30 September–1 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chong, M.; Tan, Y.; Liu, P. Blind Super-Resolution for SAR Images with Speckle Noise Based on Deep Learning Probabilistic Degradation Model and SAR Priors. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhad, S.V.; Warhade, K.K.; Shitole, S.S. Speckle noise reduction in SAR images using improved filtering and supervised classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 54615–54636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Shi, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X. ANED-Net: Adaptive Noise Estimation and Despeckling Network for SAR Image. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 4036–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Tao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Hong, W. Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation in SAR Systems via Multi-Polarization Framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5210216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, G.; Liu, X.; Li, K.; Yu, C.; Zhai, Y.; Xing, H.; Zhang, X. Intelligent Detection and Segmentation of Space-Borne SAR Radio Frequency Interference. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lang, P.; Lu, X.; Chen, S.; Xi, F.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J. Robust Block Subspace Filtering for Efficient Removal of Radio Interference in Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5206812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ran, Y.; Chen, K.; Maidan, A.; Huan, L.; Liao, H. Blind Signal Separation with Deep Residual Networks for Robust Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing in Interference Electromagnetic Environments. Electronics 2025, 14, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Diwakar, M.; Shankar, A.; Shree, R.; Kumar, M. A Review on SAR Image and its Despeckling. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 4633–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Shankar, A.; Diwakar, M. Review on nontraditional perspectives of synthetic aperture radar image despeckling. J. Electron. Imaging 2022, 32, 021609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G. Refined filtering of image noise using local statistics. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 1981, 15, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, D.T.; Sawchuk, A.A.; Strand, T.C.; Chavel, P. Adaptive noise smoothing filter for images with signal-dependent noise. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1985, 7, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, V.S.; Stiles, J.A.; Shanmugam, K.S.; Holtzman, J.C.; Smith, S.A. An adaptive filter for smoothing noisy radar images. Proc. IEEE 1981, 69, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, M.; Devi, L.S.; Shankaravadivu, M.; Santhanamari, M. Image denoising based on adaptive spatial and Wavelet Thresholding methods. In Proceedings of the IEEE-International Conference on Advances in Engineering, Science and Management (ICAESM-2012), Nagapattinam, India, 30–31 March 2012; pp. 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Deledalle, C.-A.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. Iterative Weighted Maximum Likelihood Denoising with Probabilistic Patch-Based Weights. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image Denoising by Sparse 3-D Transform-Domain Collaborative Filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painam, R.K.; Manikandan, S. A comprehensive review of SAR image filtering techniques: Systematic survey and future directions. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebur, R.S.; Zabil, M.H.B.M.; Hammood, D.A.; Cheng, L.K. A comprehensive review of image denoising in deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 58181–58199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierchia, G.; Cozzolino, D.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L. SAR image despeckling through convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5438–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M. SAR Image Despeckling Using a Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, X. Learning a Dilated Residual Network for SAR Image Despeckling. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, Y. HDRANet: Hybrid Dilated Residual Attention Network for SAR Image Despeckling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Lee, S. SAR Image Despeckling Using Continuous Attention Module. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattari, F.; Gonzalez Leon, B.; Asaro, F.; Rucci, A.; Prati, C.; Matteucci, M. Deep Learning for SAR Image Despeckling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Qiu, C.; Jiang, H.; Zou, L. A Deep Neural Network Based on Prior-Driven and Structural Preserving for SAR Image Despeckling. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 6372–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panati, C.; Wagner, S. Investigating SAR Data Denoising: A Comparative Analysis of CNN Models with Multi-Channel Signal Processing Features. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Radar Conference (RADAR), Rennes, France, 21–25 October 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleissaee, A.A.; Kumar, A.; Anwer, R.M.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Xia, G.-S.; Khan, F.S. Transformers in Remote Sensing: A Survey. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapriya, M.S.; Suresh, S. ViT-DexiNet: A Vision Transformer-Based Edge Detection Operator for Small Object Detection in SAR Images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 7057–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.V.; Bandara, W.G.C.; Valanarasu, J.M.J.; Patel, V.M. Transformer-Based SAR Image Despeckling. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2022—2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Shin, Y. SAR Image Despeckling Based on U-Shaped Transformer from a Single Noisy Image. In Proceedings of the 2022 13th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 19–21 October 2022; pp. 1738–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, W.Q. Trans-NLM Network for SAR Image Despeckling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5211912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, R.; Zhu, J.; Xu, W.; Li, X. A Practical SAR Despeckling Method Combining Swin Transformer and Residual CNN. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 21, 4001205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, Y.; Xiao, J.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yang, H.; Wang, F. Spectral Aggregation Cross-Square Transformer for Hyperspectral Image Denoising. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Kolkata, India, 1–5 December 2024; pp. 458–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imad, H.; Sara, Z.; Hajji, M.; Yassine, T.; Abdelkrim, N. Recent Advances in SAR Image Analysis Using Deep Learning Approaches: Examples of Speckle Denoising and Change Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET), Fez, Morocco, 16–17 May 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, S.; Ma, L.; Huang, M. RCA-GAN: An Improved Image Denoising Algorithm Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. Electronics 2023, 12, 4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, L. Multilevel Denoising for High-Quality SAR Object Detection in Complex Scenes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5226813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Feng, P.; Fu, Y.; Wu, Y. Segmentation-Guided Semantic-Aware Self-Supervised Denoising for SAR Image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5218416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Gong, G.; Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Ye, Y. RMSO-ConvNeXt: A Lightweight CNN Network for Robust SAR and Optical Image Matching Under Strong Noise Interference. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5208013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, C.; Min, W.; Han, Q.; Li, W.; Xiong, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M. SAR ship localization method with denoising and feature refinement. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a Gaussian Denoiser: Residual Learning of Deep CNN for Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. A Two-Component Deep Learning Network for SAR Image Denoising. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 17792–17803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Fu, X.; Lv, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Synthetic aperture radar images denoising based on multi-scale attention cascade convolutional neural network. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 085403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsasso, E.; Denis, L.; Tupin, F. SAR2SAR: A Semi-Supervised Despeckling Algorithm for SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4321–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S. Unsupervised SAR Despeckling Based on Diffusion Model. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023—2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, L.; He, M.; He, J.; Yuan, Q.; Shen, H. Sentinel-1 Dual-Polarization SAR Images Despeckling Network Based on Unsupervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Ferraioli, G.; Frery, A.C.; Pascazio, V.; Yue, D.-X.; Xu, F. SAR Despeckling Using Multiobjective Neural Network Trained with Generic Statistical Samples. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5216812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.D. LG-DBNet: Local and Global Dual-Branch Network for SAR Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5205515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhou, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, H. HCformer: Hybrid CNN-Transformer for LDCT Image Denoising. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 2290–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Restormer: Efficient Transformer for High-Resolution Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 5728–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Jin, Y.; Ma, H. Cross-Layer Feature Pyramid Transformer for Small Object Detection in Aerial Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5625714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification: Benchmark and State of the Art. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Pointwise Shape-Adaptive DCT for High-Quality Denoising and Deblocking of Grayscale and Color Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 1395–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzen, R. Kodak Lossless True Color Image Suite. 1999. Available online: https://github.com/Soniya2829/KODAK24 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Buades, A.; Li, X. Color Demosaicking by Local Directional Interpolation and Nonlocal Adaptive Thresholding. J. Electron. Imaging 2011, 20, 023016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyde, R.; Elad, M.; Protter, M. On Single Image Scale-Up Using Sparse-Representations. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference, Curves and Surfaces, Avignon, France, 24–30 June 2010; pp. 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Li, J.J.; Chen, W.R.; Zhang, B. SARBuD1.0: A SAR Building Dataset Based on GF-3 FSII Imageries for Built-up Area Extraction with Deep Learning Method. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hore, A.; Ziou, D. Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Scarpa, G.; Poggi, G. Nonlocal CNN SAR Image Despeckling. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. SAR image despeckling employing a recursive deep CNN prior. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Method | FLOPs (G) | Params (M) | Inference Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BM3D | N/A | N/A | 3580 |
| DnCNN | 72.63 | 0.56 | 3.12 |
| SAR-CNN | 72.63 | 0.56 | 3.15 |
| SAR-DRN | 31.61 | 0.24 | 1.58 |
| SAR-Transformer | 147.8 | 2.14 | 18.7 |
| SAR-CAM | 84.2 | 1.37 | 9.5 |
| DAT-Net | 310.5 | 28.7 | 42.8 |
| Datasets | Noise Variance | BM3D | DnCNN | SAR-CNN | SAR-DRN | SAR- Transformer | SAR-CAM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic5 | 25 | 29.94 | 28.73 | 28.12 | 27.95 | 25.84 | 28.08 | 30.01 |
| 50 | 26.68 | 25.26 | 24.91 | 25.06 | 24.26 | 25.43 | 27.05 | |
| 75 | 24.30 | 23.79 | 23.42 | 23.40 | 23.33 | 23.75 | 25.27 | |
| 100 | 22.32 | 22.79 | 22.73 | 22.92 | 21.84 | 22.71 | 24.11 | |
| Kodak24 | 25 | 29.41 | 28.97 | 28.36 | 28.35 | 27.04 | 28.36 | 30.06 |
| 50 | 26.13 | 25.57 | 25.22 | 25.21 | 24.65 | 25.72 | 27.20 | |
| 75 | 23.85 | 23.81 | 23.17 | 23.34 | 23.62 | 23.87 | 25.64 | |
| 100 | 21.87 | 22.31 | 22.61 | 22.76 | 21.22 | 22.59 | 24.56 | |
| McMaster | 25 | 30.37 | 29.99 | 29.35 | 29.46 | 27.82 | 29.64 | 31.16 |
| 50 | 26.61 | 25.50 | 26.07 | 26.20 | 25.64 | 26.70 | 28.04 | |
| 75 | 23.20 | 24.48 | 24.06 | 24.12 | 24.40 | 24.60 | 26.13 | |
| 100 | 20.81 | 23.07 | 23.00 | 23.42 | 21.55 | 23.24 | 24.88 | |
| Set12 | 25 | 29.80 | 29.31 | 28.62 | 28.49 | 26.05 | 28.67 | 30.10 |
| 50 | 26.31 | 25.62 | 25.26 | 25.35 | 24.25 | 25.82 | 26.97 | |
| 75 | 23.64 | 23.85 | 23.52 | 23.37 | 23.19 | 23.90 | 25.02 | |
| 100 | 21.45 | 22.76 | 22.62 | 22.78 | 21.27 | 22.66 | 23.77 |
| Datasets | Noise Variance | BM3D | DnCNN | SAR-CNN | SAR-DRN | SAR- Transformer | SAR-CAM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic5 | 25 | 0.8189 | 0.7877 | 0.7522 | 0.7639 | 0.6465 | 0.7703 | 0.8269 |
| 50 | 0.7093 | 0.6271 | 0.6024 | 0.6430 | 0.5957 | 0.6613 | 0.7294 | |
| 75 | 0.6222 | 0.5496 | 0.5006 | 0.5360 | 0.5437 | 0.5539 | 0.6609 | |
| 100 | 0.5609 | 0.5149 | 0.4815 | 0.5355 | 0.4898 | 0.4815 | 0.6061 | |
| Kodak24 | 25 | 0.8090 | 0.7916 | 0.7535 | 0.7739 | 0.7515 | 0.7776 | 0.8267 |
| 50 | 0.6971 | 0.6338 | 0.6165 | 0.6577 | 0.6916 | 0.6759 | 0.7299 | |
| 75 | 0.6226 | 0.5616 | 0.5089 | 0.5474 | 0.6388 | 0.5685 | 0.6752 | |
| 100 | 0.5680 | 0.5060 | 0.4847 | 0.5477 | 0.5735 | 0.4918 | 0.6316 | |
| McMaster | 25 | 0.8409 | 0.8284 | 0.7952 | 0.8160 | 0.7358 | 0.8227 | 0.8679 |
| 50 | 0.7212 | 0.6471 | 0.6634 | 0.7026 | 0.7110 | 0.7285 | 0.7839 | |
| 75 | 0.6339 | 0.6155 | 0.5661 | 0.6044 | 0.6716 | 0.6215 | 0.7252 | |
| 100 | 0.5655 | 0.5558 | 0.5145 | 0.5980 | 0.5814 | 0.5438 | 0.6761 | |
| Set12 | 25 | 0.8476 | 0.8223 | 0.7817 | 0.8013 | 0.6793 | 0.8064 | 0.8561 |
| 50 | 0.7543 | 0.6750 | 0.6516 | 0.6938 | 0.6441 | 0.7141 | 0.7754 | |
| 75 | 0.6766 | 0.6103 | 0.5530 | 0.5840 | 0.5941 | 0.6081 | 0.7175 | |
| 100 | 0.6087 | 0.5622 | 0.5291 | 0.5819 | 0.5284 | 0.5338 | 0.6711 |
| Datasets | Looks | BM3D | DnCNN | SAR-CNN | SAR-DRN | SAR- Transformer | SAR-CAM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic5 | L = 1 | 17.96 | 21.98 | 21.93 | 22.38 | 21.21 | 21.89 | 23.72 |
| L = 4 | 24.09 | 24.34 | 24.29 | 24.44 | 23.59 | 24.78 | 26.26 | |
| L = 8 | 26.54 | 25.93 | 25.55 | 25.52 | 24.56 | 25.29 | 27.83 | |
| L = 16 | 27.65 | 27.52 | 26.98 | 27.19 | 24.99 | 26.60 | 29.29 | |
| Kodak24 | L = 1 | 18.34 | 22.03 | 21.92 | 22.19 | 20.36 | 21.89 | 24.08 |
| L = 4 | 23.49 | 24.66 | 24.58 | 24.62 | 23.54 | 25.10 | 26.63 | |
| L = 8 | 25.63 | 26.36 | 26.06 | 25.88 | 25.81 | 25.73 | 28.04 | |
| L = 16 | 26.66 | 28.11 | 27.54 | 27.75 | 26.88 | 27.19 | 29.50 | |
| McMaster | L = 1 | 19.32 | 21.56 | 22.68 | 22.96 | 21.31 | 22.74 | 25.11 |
| L = 4 | 24.83 | 24.26 | 25.80 | 25.99 | 24.66 | 26.51 | 28.13 | |
| L = 8 | 27.20 | 26.69 | 27.22 | 27.42 | 26.86 | 27.19 | 29.76 | |
| L = 16 | 28.27 | 29.56 | 28.86 | 29.37 | 27.92 | 28.81 | 31.33 | |
| Set12 | L = 1 | 17.02 | 21.81 | 21.76 | 22.07 | 20.62 | 21.74 | 23.00 |
| L = 4 | 23.29 | 24.55 | 24.48 | 24.56 | 23.40 | 25.02 | 26.05 | |
| L = 8 | 25.99 | 26.32 | 25.85 | 25.82 | 24.71 | 25.57 | 27.69 | |
| L = 16 | 27.30 | 28.00 | 27.46 | 27.69 | 25.17 | 27.08 | 29.18 |
| Datasets | Looks | BM3D | DnCNN | SAR-CNN | SAR-DRN | SAR- Transformer | SAR-CAM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic5 | L = 1 | 0.5281 | 0.4353 | 0.4377 | 0.5100 | 0.4530 | 0.4559 | 0.5909 |
| L = 4 | 0.6407 | 0.5761 | 0.5690 | 0.6121 | 0.5639 | 0.6282 | 0.6999 | |
| L = 8 | 0.7059 | 0.6670 | 0.6168 | 0.6556 | 0.5801 | 0.6225 | 0.7609 | |
| L = 16 | 0.7285 | 0.7399 | 0.7047 | 0.7389 | 0.5854 | 0.6794 | 0.8078 | |
| Kodak24 | L = 1 | 0.5485 | 0.4504 | 0.4623 | 0.5308 | 0.5446 | 0.4739 | 0.6307 |
| L = 4 | 0.6479 | 0.6124 | 0.6024 | 0.6465 | 0.6846 | 0.6671 | 0.7322 | |
| L = 8 | 0.7050 | 0.7027 | 0.6599 | 0.6919 | 0.7021 | 0.6607 | 0.7827 | |
| L = 16 | 0.7206 | 0.7745 | 0.7448 | 0.7718 | 0.7204 | 0.7160 | 0.8289 | |
| McMaster | L = 1 | 0.6139 | 0.4216 | 0.5517 | 0.6081 | 0.5610 | 0.5796 | 0.7170 |
| L = 4 | 0.7174 | 0.6354 | 0.6970 | 0.7369 | 0.7242 | 0.7570 | 0.8141 | |
| L = 8 | 0.7719 | 0.7291 | 0.6782 | 0.7737 | 0.7264 | 0.7318 | 0.8555 | |
| L = 16 | 0.7904 | 0.8337 | 0.7890 | 0.8368 | 0.7466 | 0.7955 | 0.8882 | |
| Set12 | L = 1 | 0.5680 | 0.4616 | 0.4806 | 0.5492 | 0.4871 | 0.5010 | 0.6515 |
| L = 4 | 0.6999 | 0.6241 | 0.6239 | 0.6623 | 0.6121 | 0.6853 | 0.7555 | |
| L = 8 | 0.7559 | 0.7123 | 0.6602 | 0.7045 | 0.6240 | 0.6635 | 0.8045 | |
| L = 16 | 0.7841 | 0.7761 | 0.7456 | 0.7792 | 0.6222 | 0.7211 | 0.8418 |
| Datasets | Level | BM3D | DnCNN | SAR-CNN | SAR-DRN | SAR- Transformer | SAR-CAM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic5 | = 25, L = 1 | 17.74 | 21.99 | 21.71 | 22.25 | 20.47 | 21.69 | 23.51 |
| = 50, L = 4 | 22.82 | 23.39 | 23.28 | 23.61 | 22.95 | 23.51 | 24.99 | |
| = 75, L = 8 | 23.01 | 23.17 | 22.92 | 23.42 | 22.02 | 23.44 | 24.57 | |
| = 100, L = 16 | 21.91 | 22.74 | 22.43 | 22.73 | 22.42 | 22.51 | 23.84 | |
| Kodak24 | = 25, L = 1 | 18.13 | 22.01 | 21.68 | 22.02 | 19.67 | 21.80 | 23.90 |
| = 50, L = 4 | 22.31 | 23.49 | 23.18 | 23.58 | 23.09 | 23.60 | 25.35 | |
| = 75, L = 8 | 22.39 | 23.26 | 22.86 | 23.37 | 21.96 | 23.35 | 24.88 | |
| = 100, L = 16 | 21.29 | 22.75 | 22.33 | 22.45 | 22.45 | 22.45 | 24.24 | |
| McMaster | = 25, L = 1 | 19.07 | 22.67 | 22.37 | 22.80 | 20.26 | 22.53 | 24.79 |
| = 50, L = 4 | 22.93 | 23.99 | 24.00 | 24.49 | 23.97 | 24.48 | 26.20 | |
| = 75, L = 8 | 22.16 | 23.91 | 23.51 | 24.12 | 22.42 | 24.11 | 25.52 | |
| = 100, L = 16 | 20.46 | 23.25 | 22.58 | 22.97 | 22.97 | 23.01 | 24.59 | |
| Set12 | = 25, L = 1 | 16.76 | 21.75 | 21.44 | 21.93 | 19.71 | 21.56 | 22.77 |
| = 50, L = 4 | 21.81 | 23.42 | 23.29 | 23.58 | 22.71 | 23.56 | 24.62 | |
| = 75, L = 8 | 22.07 | 23.20 | 22.86 | 23.38 | 21.64 | 23.40 | 24.17 | |
| = 100, L = 16 | 20.88 | 22.65 | 22.27 | 22.44 | 22.02 | 22.34 | 23.39 |
| Datasets | Level | BM3D | DnCNN | SAR-CNN | SAR-DRN | SAR- Transformer | SAR-CAM | Proposed |
| Classic5 | = 25, L = 1 | 0.5145 | 0.4609 | 0.4102 | 0.5157 | 0.4750 | 0.4583 | 0.5840 |
| = 50, L = 4 | 0.6041 | 0.5263 | 0.5172 | 0.5779 | 0.5180 | 0.5529 | 0.6474 | |
| = 75, L = 8 | 0.5820 | 0.5266 | 0.4727 | 0.5725 | 0.4526 | 0.5636 | 0.6228 | |
| = 100, L = 16 | 0.5513 | 0.5038 | 0.4590 | 0.5220 | 0.4917 | 0.4942 | 0.5945 | |
| Kodak24 | = 25, L = 1 | 0.5310 | 0.4763 | 0.4320 | 0.5341 | 0.5652 | 0.4790 | 0.6224 |
| = 50, L = 4 | 0.6116 | 0.5443 | 0.5334 | 0.6005 | 0.6212 | 0.5759 | 0.6732 | |
| = 75, L = 8 | 0.5899 | 0.5408 | 0.4873 | 0.5926 | 0.5446 | 0.5825 | 0.6468 | |
| = 100, L = 16 | 0.5583 | 0.5139 | 0.4614 | 0.5317 | 0.5867 | 0.5068 | 0.6207 | |
| McMaster | = 25, L = 1 | 0.5997 | 0.5622 | 0.5239 | 0.6154 | 0.5717 | 0.5702 | 0.7010 |
| = 50, L = 4 | 0.6423 | 0.5350 | 0.5907 | 0.6626 | 0.6584 | 0.6398 | 0.7352 | |
| = 75, L = 8 | 0.6005 | 0.5921 | 0.5426 | 0.6429 | 0.5587 | 0.6330 | 0.7019 | |
| = 100, L = 16 | 0.5561 | 0.5632 | 0.4905 | 0.5773 | 0.5920 | 0.5611 | 0.6703 | |
| Set12 | = 25, L = 1 | 0.5598 | 0.4994 | 0.4487 | 0.5547 | 0.5034 | 0.5026 | 0.6438 |
| = 50, L = 4 | 0.6511 | 0.5718 | 0.5686 | 0.6276 | 0.5619 | 0.6027 | 0.7054 | |
| = 75, L = 8 | 0.6303 | 0.5821 | 0.5172 | 0.6259 | 0.4860 | 0.6173 | 0.6865 | |
| = 100, L = 16 | 0.5932 | 0.5548 | 0.5002 | 0.5606 | 0.5276 | 0.5337 | 0.6566 |
| Image | Indicators | BM3D | DnCNN | SAR-CNN | SAR-DRN | SAR- Transformer | SAR-CAM | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAR1 | Entropy | 7.0773 | 7.3267 | 7.3114 | 7.3621 | 7.4886 | 7.3649 | 7.252 |
| AG | 125.78 | 151.29 | 145.47 | 150.32 | 147.46 | 151.47 | 155.75 | |
| SAR2 | Entropy | 6.7088 | 7.0178 | 7.1687 | 6.9238 | 6.9269 | 6.8223 | 6.7678 |
| AG | 89.58 | 94.96 | 90.85 | 84.29 | 75.16 | 89.85 | 101.19 | |
| SAR3 | Entropy | 5.9628 | 6.4752 | 6.3434 | 6.3996 | 6.3220 | 6.3870 | 6.1563 |
| AG | 69.97 | 101.28 | 90.88 | 95.13 | 79.25 | 97.86 | 99.09 | |
| SAR4 | Entropy | 6.8907 | 7.1730 | 7.1415 | 7.1542 | 7.0952 | 7.1666 | 7.0917 |
| AG | 84.29 | 114.14 | 108.26 | 105.41 | 89.64 | 112.65 | 113.77 | |
| SAR5 | Entropy | 7.1418 | 7.4117 | 7.3737 | 7.3765 | 7.2880 | 7.3937 | 7.3303 |
| AG | 100.59 | 123.6 | 115.64 | 111.32 | 94.77 | 120.25 | 127.59 | |
| SAR6 | Entropy | 6.9720 | 7.0996 | 7.0860 | 7.1262 | 7.1940 | 7.1043 | 6.9711 |
| AG | 76.65 | 86.36 | 82.08 | 79.57 | 83.42 | 79.91 | 88.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhang, X. DATNet: Dynamic Adaptive Transformer Network for SAR Image Denoising. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173031
Shen Y, Chen Y, Wang Y, Ma L, Zhang X. DATNet: Dynamic Adaptive Transformer Network for SAR Image Denoising. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(17):3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173031
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yan, Yazhou Chen, Yuming Wang, Liyun Ma, and Xiaolu Zhang. 2025. "DATNet: Dynamic Adaptive Transformer Network for SAR Image Denoising" Remote Sensing 17, no. 17: 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173031
APA StyleShen, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., Ma, L., & Zhang, X. (2025). DATNet: Dynamic Adaptive Transformer Network for SAR Image Denoising. Remote Sensing, 17(17), 3031. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173031







