Evolution and Attribution Analysis of the Relationship Among Soil Erosion Negative Service, Carbon Sequestration, and Water Yield in the Yellow River Basin After the Grain for Green Program
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
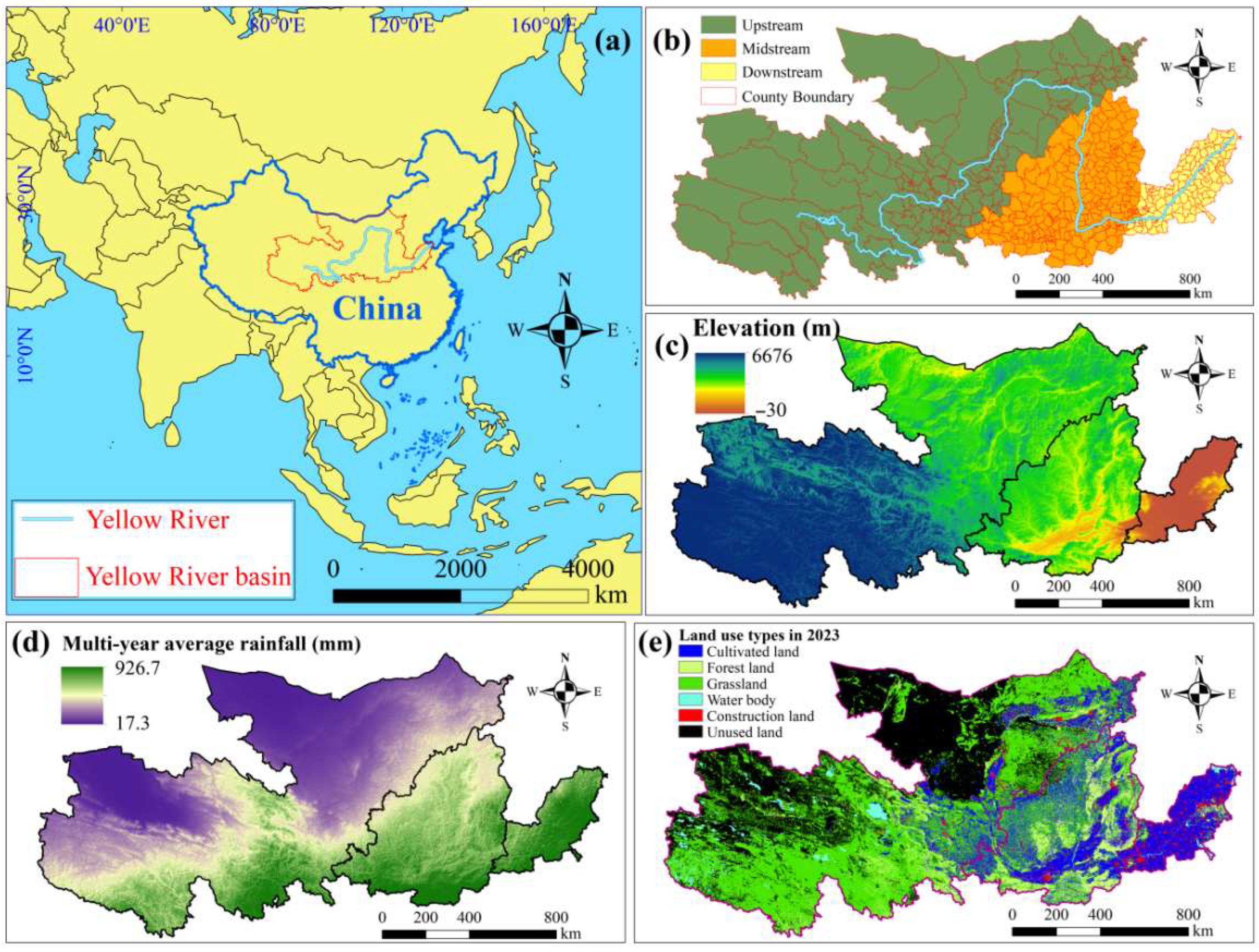
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methodological Process
2.2.1. Calculation of ESs
- (1)
- Soil erosion negative service
- (2)
- Carbon sequestration
- (3)
- Water yield
2.2.2. Identification of Tradeoff and Synergy
- (1)
- Overall interaction
- (2)
- Spatial interaction
2.2.3. Analysis of the Drivers
- (1)
- Selecting of the latent drivers
- (2)
- OPGD model
2.3. Data Preparation
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation in ESs
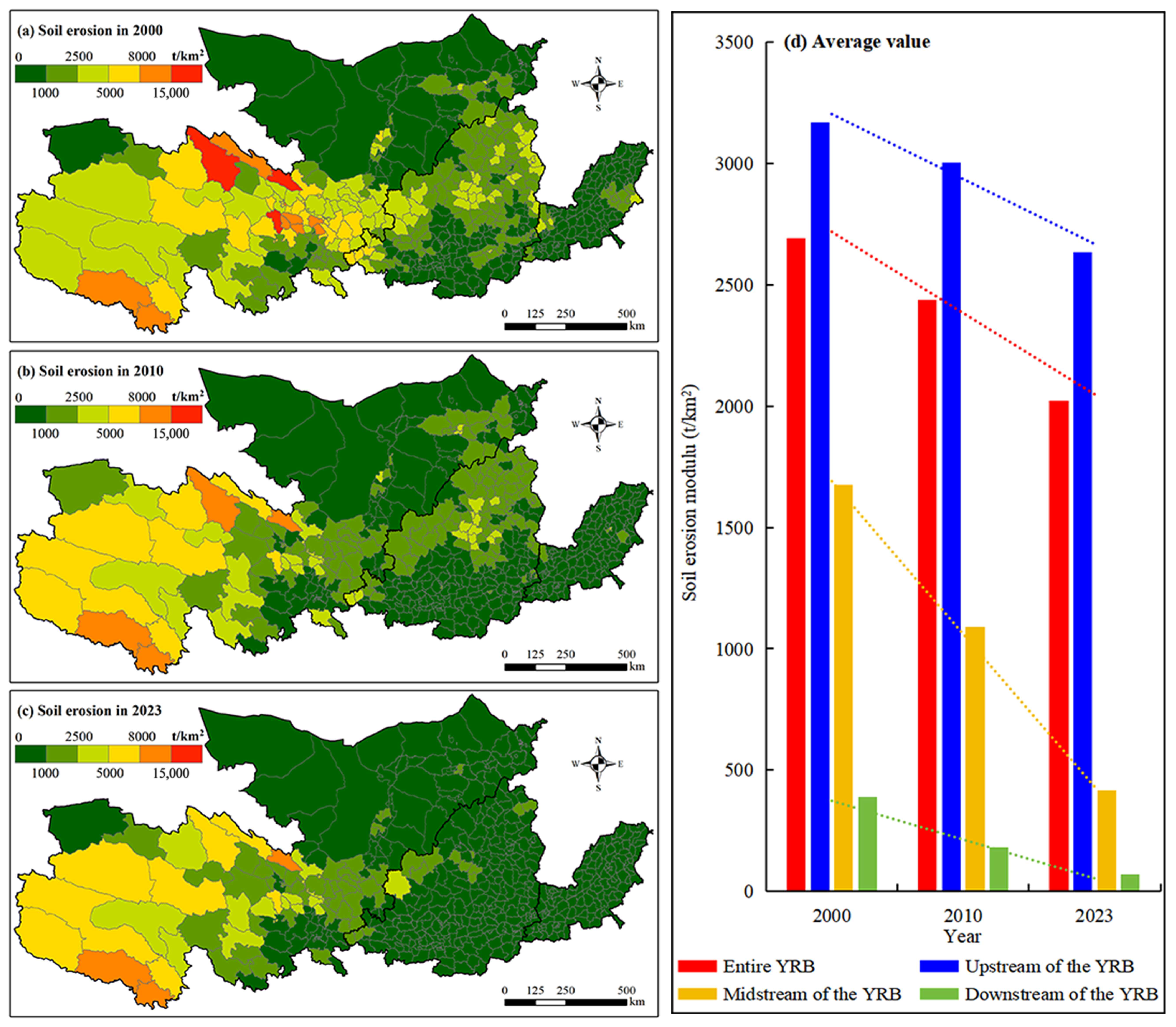
3.1.1. Soil Erosion Negative Service
3.1.2. Carbon Sequestration
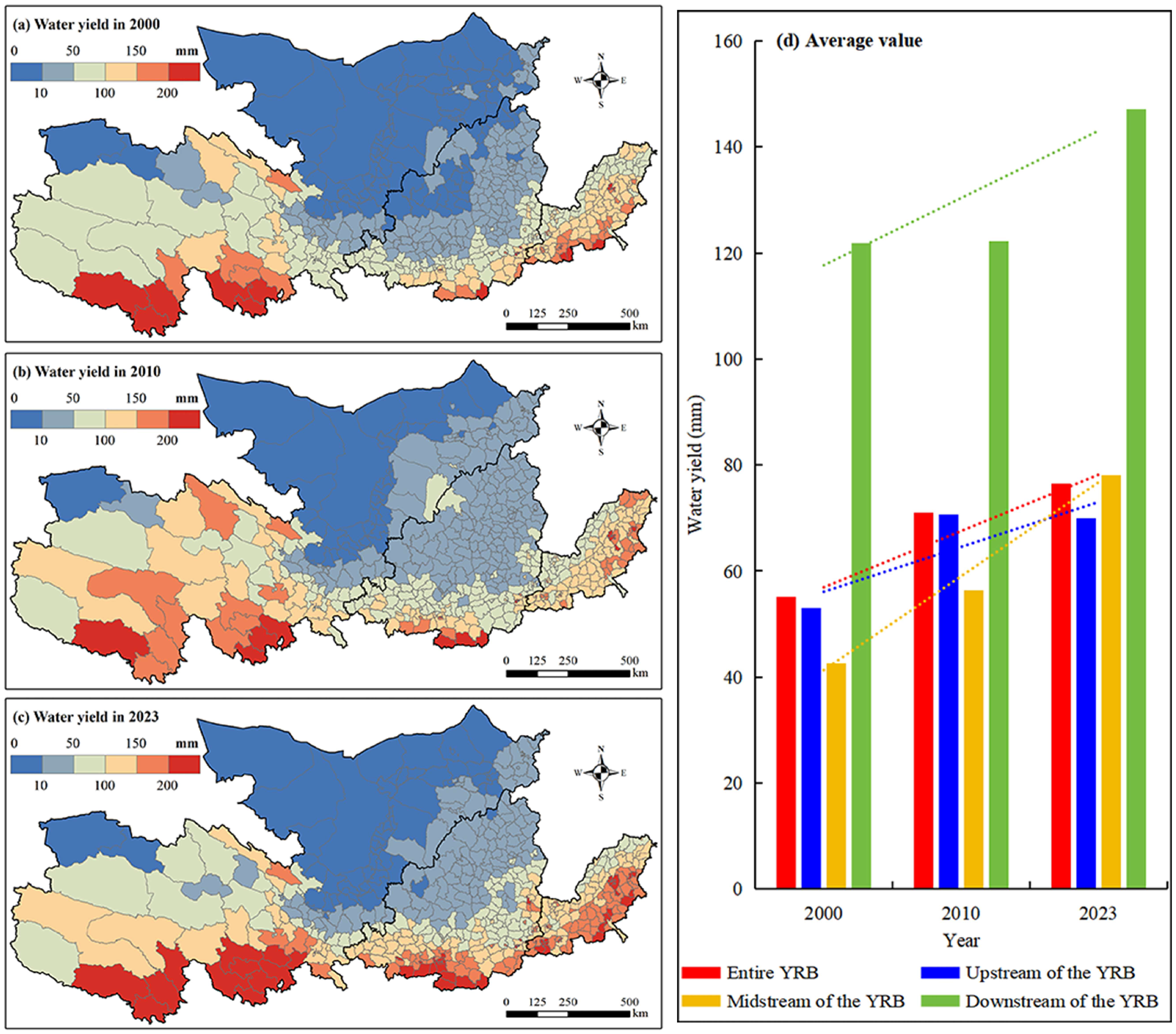
3.1.3. Water Yield
3.2. Tradeoff and Synergy Relationships Between ES Pairs
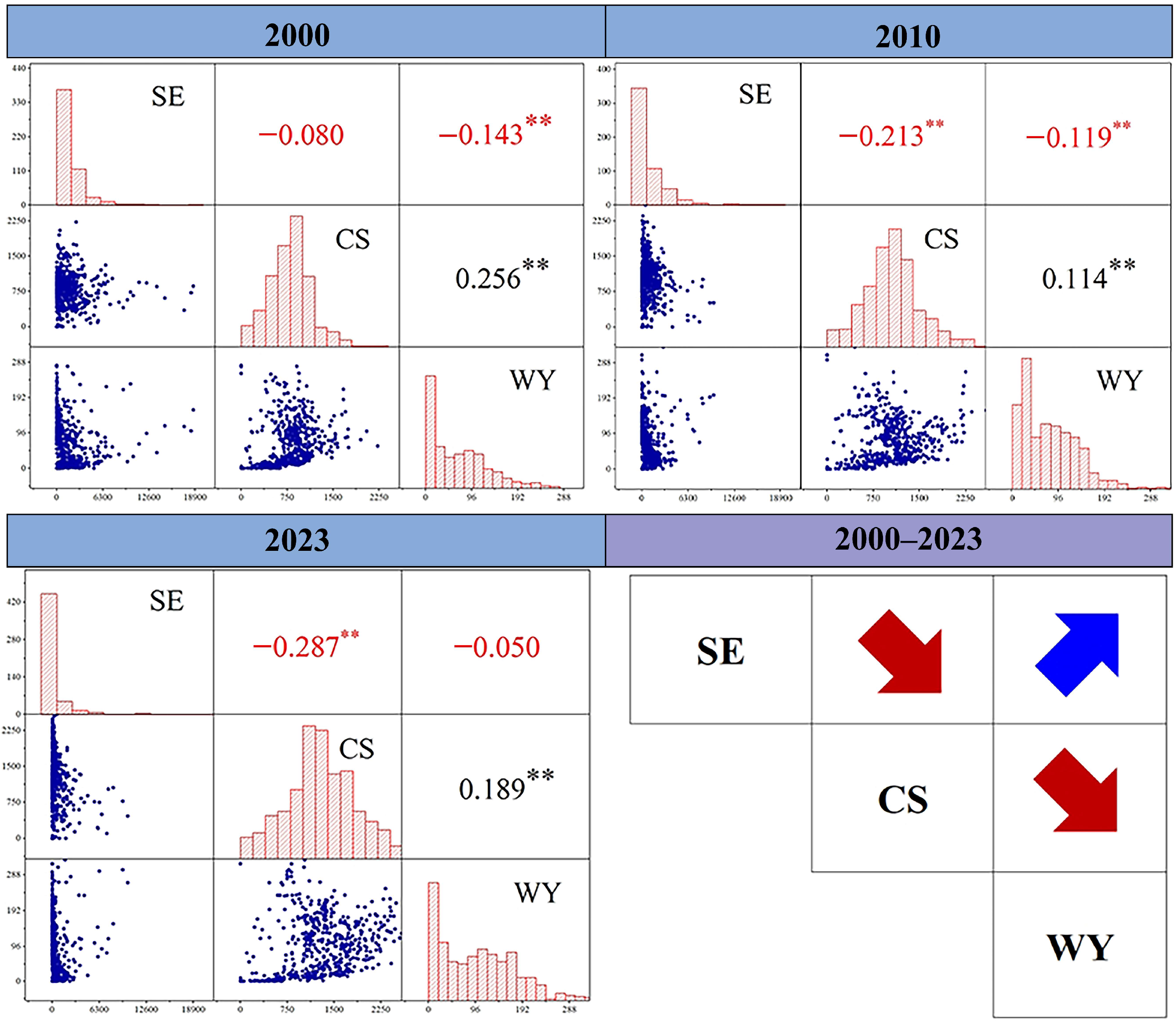
3.2.1. Overall Tradeoff/Synergy Among ESs
3.2.2. Spatial Tradeoff /Synergy Among ESs
3.3. Driving Forces of ES Tradeoff/Synergy
3.3.1. Parameter Discretization Results
3.3.2. Driving Forces Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Development of ESs After the GFGP
4.2. The Influencing Mechanism of Tradeoff/Synergy Among Pairwise ESs
4.3. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, W.V.; Mooney, H.A.; Cropper, A.; Capistrano, D. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wong, C.P.; Jiang, B.; Hughes, A.C.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q. Developing China’s ecological redline policy using ecosystem services assessments for land use planning. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, M.; Crouzat, E.; Hölting, L.; Massenberg, J.; Rode, J.; Hanisch, M.; Kabisch, N.; Palliwoda, J.; Priess, J.A.; Seppelt, R.; et al. Assumptions in ecosystem service assessments: Increasing transparency for conservation. Ambio 2021, 50, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPBES. Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. 2019. Available online: https://www.ipbes.net/system/tdf/spm_global_unedited_advance.pdf?file=1&type=node&id=35245 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Su, B.; Liu, M. How to manage the ecosystem services effectively and fairly? J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeon, M.; Wana, D. Synergies and trade-offs among key ecosystem services in Maze National Park and its environs, southwestern Ethiopia. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 57, e03398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Du, Y.; Tang, Y. Ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies and their drivers in severely affected areas of the Wenchuan earthquake, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 3881–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwantes, A.M.; Firkowski, C.R.; Gonzalez, A.; Fortin, M.J. Revealing driver-mediated indirect interactions between ecosystem services using Bayesian Belief Networks. Ecosyst. Serv. 2025, 73, 101717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Jin, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, J. Understanding trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services to support the decision-making in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Z. Variations in Ecosystem Service Value and Its Driving Factors in the Nanjing Metropolitan Area of China. Forests 2023, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.P.; Beard, T.D., Jr.; Bennett, E.M.; Cumming, G.S.; Cork, S.J.; Agard, J.; Dobson, A.P.; Peterson, G.D. Trade-offs across space, time, and ecosystem services. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P. Scale effect and spatially explicit drivers of interactions between ecosystem services—A case study from the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Eviron. 2021, 785, 147389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.D.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A. Bundling ecosystem services at a high resolution in the UK: Trade-offs and synergies in urban landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1817–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, K.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Z. Social-ecological system sustainability in China from the perspective of supply-demand balance for ecosystem services. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 497, 145039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Yuan, S.; Prishchepov, A.V. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecosystem service interactions and their social-ecological drivers: Implications for spatial planning and management. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlenwerger, C.; Spake, R.; Tambosi, L.R.; Aristizábal, N.; González-Chaves, A.; Librán-Embid, F.; Saturni, F.; Eigenbrod, F.; Metzger, J.P. Coffee pollination and pest control are affected by edge diversity at local scales but multiscalar approaches and disservices can not be ignored. Landscape Ecol. 2024, 39, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Niu, J.; Xiao, C.; Sun, Y. Spatial-Temporal Differentiation of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Synergies in the Taihang Mountains, China. Land 2025, 14, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umwali, E.D.; Chen, X.; Ma, X.; Guo, Z.; Mbigi, D.; Zhang, Z.; Umugwaneza, A.; Gasirabo, A.; Umuhoza, J. Integrated SSP-RCP Scenarios for Modeling the Impacts of Climate Change and Land Use on Ecosystem Services in East Africa. Ecol. Model. 2025, 504, 111092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.; Cui, L.; Gao, Y. Integrating ecosystem services conservation into the optimization of urban planning policies in eco-fragile areas: A scenario-based case study. Cities 2023, 134, 104200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovric, M.; Torralba, M.; Orsi, F.; Pettenella, D.; Mann, C.; Geneletti, D.; Plieninger, T.; Primmer, E.; Hernandez-Morcillo, M.; Thorsen, B.J.; et al. Mind the income gap: Income from wood production exceed income from providing diverse ecosystem services from Europe’s forests. Ecosyst. Serv. 2025, 71, 101689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhao, Y. Balancing ecosystem services supply-flow-demand for watershed ecological security: A case study of the Hai River Basin, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 13, 1587167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, S. Urban Spatial Management and Planning Based on the Interactions Between Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Fang, Q.; Chang, C.; Li, A.; Wang, H. Integrating ecosystem services trade-off, drivers and zoning into watershed water environment management in Nansihu Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, Z.; Zuo, D. Investigating on Trade-offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and their Driving Mechanisms Under Different Land Use Scenarios. Water Resour. Manag. 2025, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Jiang, S.; Li, K.; Xin, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z. Impacts of rice-crayfish co-culture on ecosystem service trade-offs/ synergies in agricultural watersheds: A case exploration in Sihu Lake Basin, China. Agr. Water Manag. 2025, 310, 109389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, M.; Fischer, J.; Law, E.A.; Schultner, J.; Abson, D.J. Drivers of ecosystem service specialization in a smallholder agricultural landscape of the Global South: A case study in Ethiopia. Ecol. Soc. 2023, 28, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Geng, H. Spatiotemporal trends in ecosystem carbon stock evolution and quantitative attribution in a karst watershed in southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; He, S.; Lan, Y.; Liu, F. Evaluation of Ecosystem Service Capacity Using the Integrated Ecosystem Services Index at Optimal Scale in Central Yunnan, China. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e71222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Gao, X.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X. Spatiotemporal exploration of ecosystem service, urbanization, and their interactive coercing relationship in the Yellow River Basin over the past 40 years. Sci. Total Eviron. 2023, 858, 159757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, C.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y. Mechanisms of Human-natural System Coupling and Optimization of the Yellow River Basin. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2021, 35, 504–509. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Wen, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Cumming, G.S.; Fu, B. Quantifying the effects of institutional shifts on water governance in the Yellow River Basin: A social-ecological system perspective. J. Hydrol. 2024, 629, 130638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lv, Y.; Hao, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, R.; Xue, K.; Fu, B. Ecosystem Change and Its Ecohydrological Effect in the Yellow River Basin. Bull. Natl. Nat. Sci. Found. China 2021, 35, 520–528. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Q.; Feng, X.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Fu, B. Cross-scale coupling of ecosystem service flows and socio-ecological interactions in the Yellow River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Estimation and influencing factors of agricultural water efficiency in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Rainfall energy and its relationship to soil loss. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1958, 39, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Jones, C.A.; Kiniry, J.R.; Spanel, D.A. The EPIC crop growth-model. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A.; Risse, L.M. Slope Gradient Effects on Soil Loss for Steep Slopes. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Ding, S.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Study of applying USLE and geographical information system IDRISI to predict soil erosion in small watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 19–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L.; Zhang, J. Analysis of spatial and temporal changes in soil erosion in Henan Province over the last ten years. J. Agr. Resour. Environ. 2021, 38, 232–240. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Guo, B.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, D.; Zhen, X.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Wei, C.; Yang, L.; et al. Spatial–temporal evolution patterns of soil erosion in the Yellow River Basin from 1990 to 2015: Impacts of natural factors and land use change. Geomat. Nat. Haz. Risk 2021, 12, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Chang, J. Analysis of soil erosion and its driving factors in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2020. J. Xi’an Univ. Technol. 2023, 39, 360–368. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y. Mapping Watershed-Level Ecosystem Service Bundles in the Pearl River Delta, China. Eco. Econ. 2018, 152, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Shrestha, U.B.; Luo, D.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J. Assessing Climate and Land Use Change Impacts on Ecosystem Services in the Upper Minjiang River Basin. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, B.; Zhang, D. Spatio-temporal variation of water yield and its response to precipitation and land use change in the Yellow River Basin based on InVEST model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 2731–2739. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mashizi, A.K.; Sharafatmandrad, M. Dry forests conservation: A comprehensive approach linking ecosystem services to ecological drivers and sustainable management. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 47, e02652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Geng, G.; Zheng, R. Variation Characteristics and Its Driving Forces of Fractional Vegetation Cover in the Shaanxi Section of the Yellow River Basin Under the Background of the Grain for Green Program. Environ. Sci. 2025. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y. Socio-ecological changes on the Loess Plateau of China after Grain to Green Program. Sci. Total Eviron. 2019, 678, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Hou, H.; Chen, W. Effects of vegetation cover and slope on soil erosion in the Eastern Chinese Loess Plateau under different rainfall regimes. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Tian, X.; Geng, R.; Zhao, G.; Yang, L.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Response of soil erosion to vegetation restoration and terracing on the Loess Plateau. CATENA 2023, 227, 107103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Lv, M.; Ma, Z. Climate, Hydrology, and Vegetation Coverage Changes in Source Region of Yellow River and Countermeasures for Challenges. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35, 61–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, M. The study of ecosystem services and the comparison of trade-off and synergy in Yangtze River Basin and Yellow River Basin. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 821–838. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Hu, H.; Sun, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, P.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Effects of national ecological restoration projects on carbon sequestration in China from 2001 to 2010. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Xiao, P.; Zhao, G. Evolution of ecosystem carbon sink and its driving factors in the Loess Plateau. Res. Soil. Water Conserv. 2025, 32, 266–274+284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Wang, L.; Wen, Q. Dynamic Responses of Sequestration of Soil Organic Carbon to Vegetation Restoration and the Values of Carbon Sink in the Loess Plateau. Res. Soil. Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 53–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, J.; Slater, L.J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, L.Q.; Zhang, Y. Global vegetation dynamics under decreased terrestrial water storage: Insights into water stress response. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2025, 368, 110549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Piao, S.; Li, L.Z.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Huang, L.; Lian, X.; Peng, S.; Zeng, Z.Z.; et al. Divergent hydrological response to large-scale afforestation and vegetation greening in China. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Su, L.; Wang, Y. Variation Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Drought in the Loess Plateau in Recent 20 Years. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 4551–4560. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Xu, M. Evaluating the inter-annual surplus/deficit dynamic of water retention service in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, P.; He, L.; Liu, B. Improvement of water yield and net primary productivity ecosystem services in the Loess Plateau of China since the “Grain for Green” project. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Spatially explicit assessment of ecosystem services in China’s Loess Plateau: Patterns, interactions, drivers, and implications. Glob. Planet Change 2018, 161, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, B.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, R.; Hao, R.; Liu, B. Assessment of trade-off/synergy relationships between ecosystem services andidentification of ecological restoration thresholds. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 7431–7444. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Spatio-temporal Variation of Ecosystem Service Trade-offs/Synergies and Ecosystem Service Bundles in Western Jilin. Environ. Sci. 2025. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Yuan, X.; Yang, R.; An, Q.; Su, Q. Effeet of the Grain for Green Program on Ecosystem Services in Northern Shaanxi, China. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 2410–2427. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Change 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.C.; Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; Cardoso, I.M.; Fernandes, E.I.; Schulte, R.P.O. Land use change drives the spatio-temporal variation of ecosystem services and their interactions along an altitudinal gradient in Brazil. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantz, C.A.; Manuel, J.J. Estimating impacts of population growth and land use policy on ecosystem services: A community-level case study in Virginia, USA. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




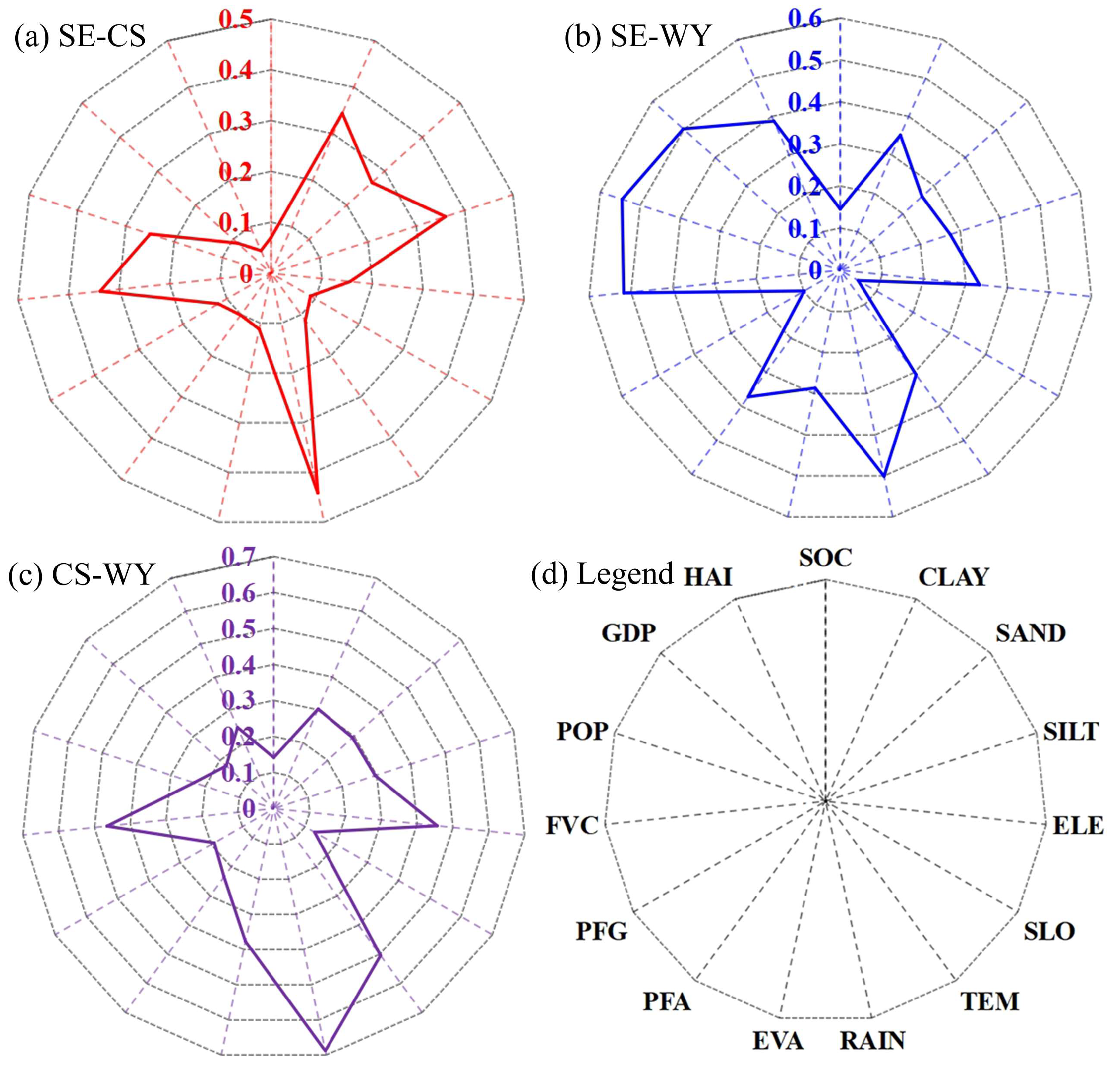
| Slope (°) | ≤5 | 5~10 | 10~15 | 15~20 | 2~25 | ≥25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p value | 0.100 | 0.221 | 0.305 | 0.575 | 0.705 | 0.800 |
| Variable | Latent Driver | Abbreviation | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil properties | Soil organic carbon content | SOC | % |
| Clay content | CLAY | % | |
| Sand content | SAND | % | |
| Silt content | SILT | % | |
| Topographic conditions | Average elevation | ELE | m |
| Average slope | SLO | ° | |
| Climatic conditions | Annual average temperature | TEM | ℃ |
| Annual average rainfall | RAIN | mm | |
| Annual average evapotranspiration | EVA | mm | |
| GFGP | Proportion of farmland | PFA | % |
| Proportion of forestland and grassland | PFG | % | |
| Fractional vegetation cover | FVC | % | |
| Socioeconomic situations | Population density | POP | people/km2 |
| GDP density | GDP | 104 CNY/km2 | |
| Human activity intensity | HAI | - |
| Data Type | Dataset | Format | Source | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial vector data | Administrative boundaries data | Vector, County | Resource and Environmental Science Data Center (RESDC, http://www.resdc.cn/) | For all analyses |
| Remote sensing data | Land use data | Raster, 1000 m | RESDC (http://www.resdc.cn/) | Soil erosion negative service calculation; water yield calculation; driver analysis |
| FVC data | Raster, 250 m | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/) | Soil erosion negative service calculation; driver analysis | |
| Net primary production data | Raster, 1000 m | RESDC (http://www.resdc.cn/) | Carbon sequestration calculation | |
| Physical geographical data | Climate-related data | Raster, 1000 m | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn/) | Soil erosion negative service calculation; water yield calculation; driver analysis |
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data | Raster, 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn/) | Soil erosion negative service calculation; driver analysis | |
| Soil data | Raster, 1000 m | National Cryosphere Desert Data Center (http://www.ncdc.ac.cn/portal/) | Soil erosion negative service calculation; water yield calculation; driver analysis | |
| Socioeconomic data | Population | Spreadsheet, county | China Statistical Database (https://www.shujuku.org/, accessed on 12 March 2025) | Driver analysis |
| GDP | Spreadsheet, county | China Statistical Database (https://www.shujuku.org/, accessed on 12 March 2025) | Driver analysis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Wang, M.; Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Niu, H.; Liu, J. Evolution and Attribution Analysis of the Relationship Among Soil Erosion Negative Service, Carbon Sequestration, and Water Yield in the Yellow River Basin After the Grain for Green Program. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173028
Yang M, Wang M, Cao L, Zhang H, Niu H, Liu J. Evolution and Attribution Analysis of the Relationship Among Soil Erosion Negative Service, Carbon Sequestration, and Water Yield in the Yellow River Basin After the Grain for Green Program. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(17):3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173028
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Menghao, Ming Wang, Lianhai Cao, Haipeng Zhang, Huhu Niu, and Jun Liu. 2025. "Evolution and Attribution Analysis of the Relationship Among Soil Erosion Negative Service, Carbon Sequestration, and Water Yield in the Yellow River Basin After the Grain for Green Program" Remote Sensing 17, no. 17: 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173028
APA StyleYang, M., Wang, M., Cao, L., Zhang, H., Niu, H., & Liu, J. (2025). Evolution and Attribution Analysis of the Relationship Among Soil Erosion Negative Service, Carbon Sequestration, and Water Yield in the Yellow River Basin After the Grain for Green Program. Remote Sensing, 17(17), 3028. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17173028








