State-Space Model Meets Linear Attention: A Hybrid Architecture for Internal Wave Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
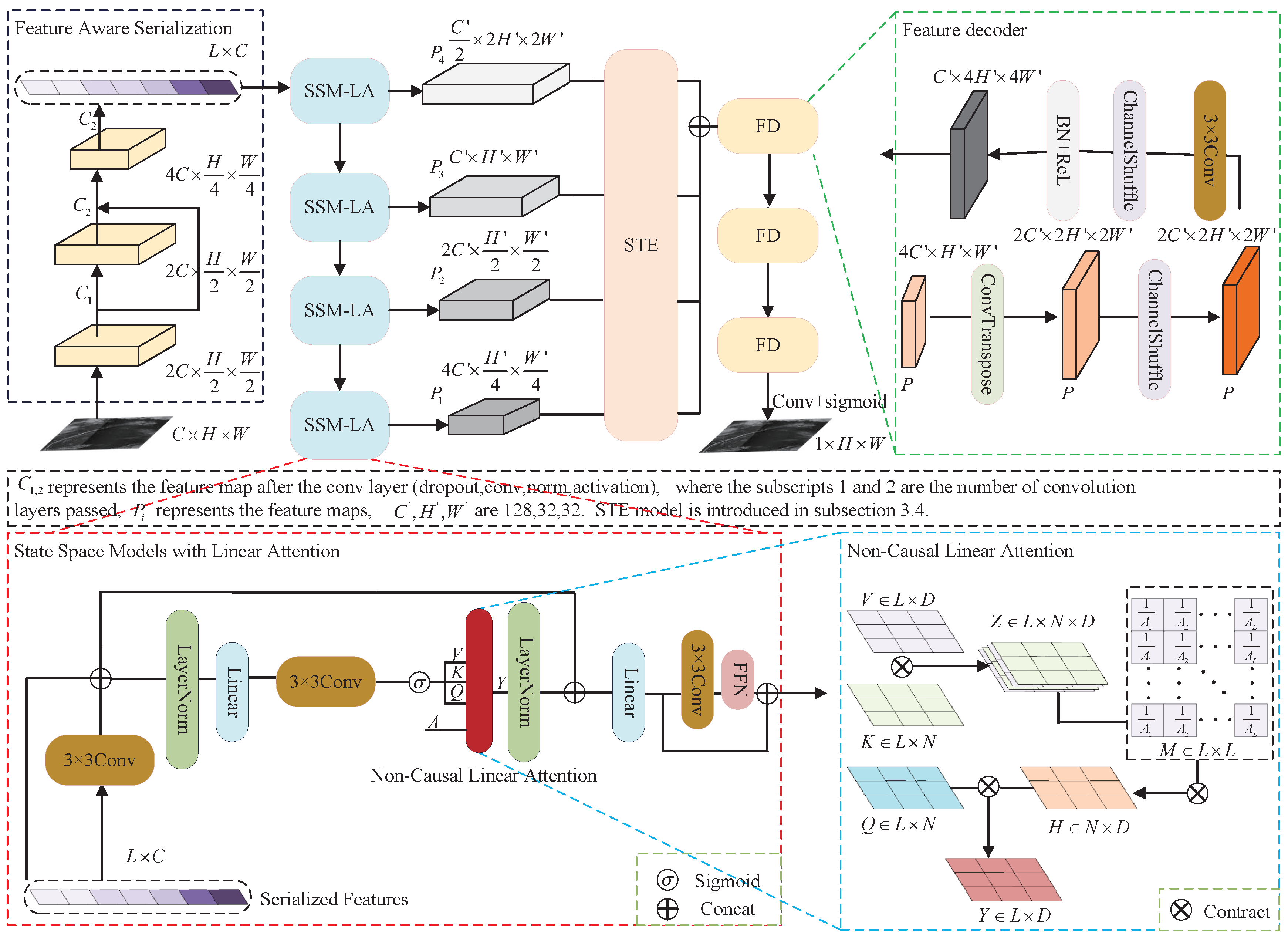
- A decoder structure driven by hierarchical fusion and upsampling is constructed, which performs channel alignment and scale unification on multi-level features to achieve high precision spatial detail recovery. This significantly improves boundary segmentation accuracy of IWs. In addition, a feature-aware serialization (FAS) block is designed to compress the spatial dimension while effectively preserving and enhancing multi-scale salient feature representations, providing high quality inputs for subsequent sequence modeling.
- (2)
- A state-space model block integrated with a linear attention mechanism (SSM-LA) is introduced. This module innovatively combines the linear properties of Mamba2 with visual feature modeling, achieving a unified representation of fine-grained local details and global contextual information, balancing performance and computational efficiency.
- (3)
- The proposed architecture fully integrates the advantages of structured state-space modeling and linear attention mechanisms, effectively enhancing the representation capability for complex ripple patterns while significantly reducing the computational redundancy typically associated with conventional Transformer architectures in remote sensing image processing. The resulting lightweight and efficient segmentation framework achieves a dual optimization of accuracy and computational efficiency, demonstrating strong adaptability for practical remote sensing applications in resource-constrained environments.
2. Related Work
3. Method
3.1. Architecture Overview
3.2. Feature-Aware Serialization Block
3.3. State-Space Models with Linear Attention Block
3.4. Decoder
4. Experiment and Results
4.1. Data
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Metrics
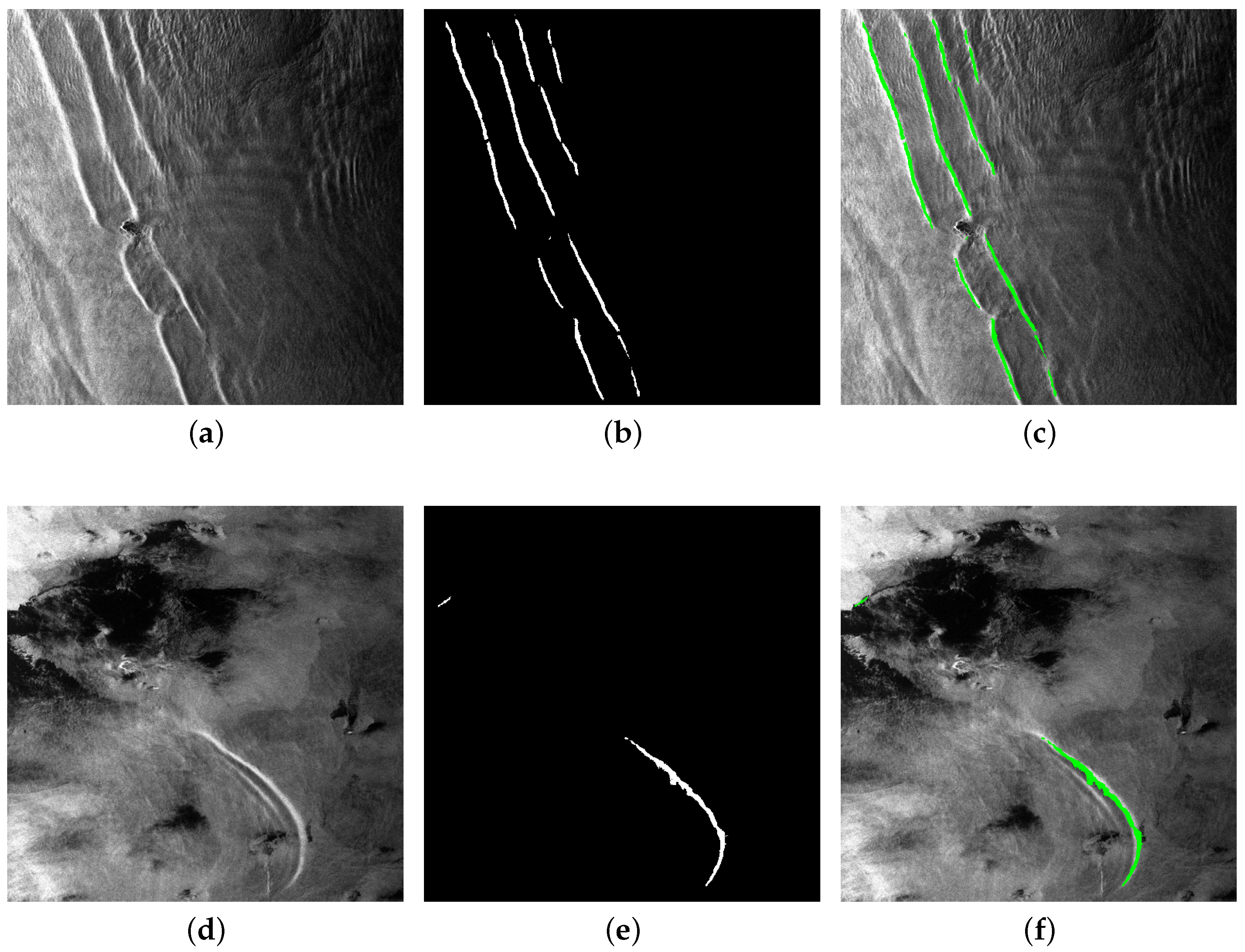
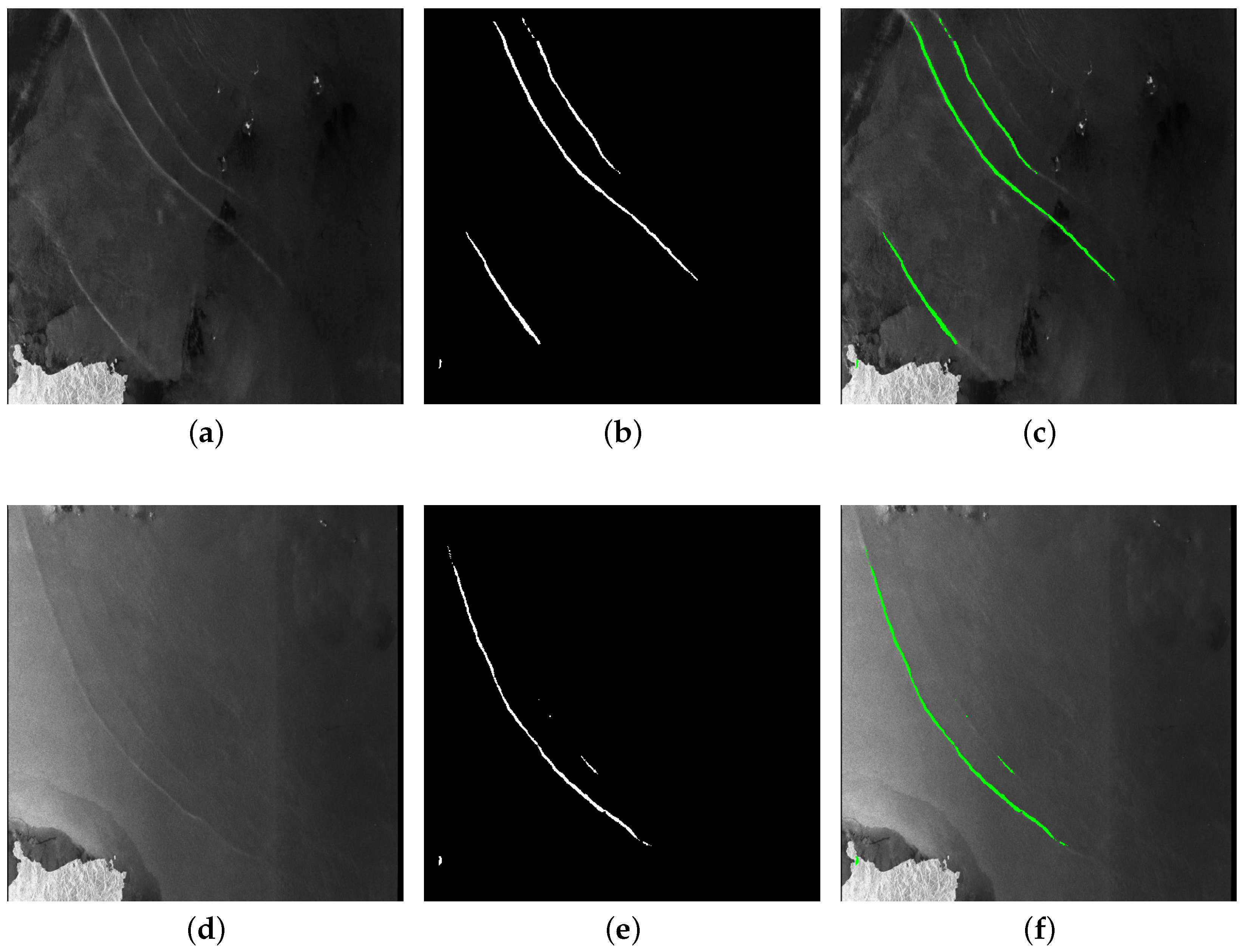
4.4. Comparative Experiments
4.5. Ablation Studies
4.6. Generalization Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ENVISAT ASAR | Environmental Satellite Advanced Synthetic-Aperture Radar |
| IWs | Internal Wave |
| SMLA | State Space Model Meets Linear Attention |
| MIoU | Mean Intersection over Union |
| FAS | Feature-Aware Serialization |
| SSM-LA | State Space Model Block with Linear Attention |
| NCLA | Non-Causal Linear Attention |
| SAR | Synthetic-Aperture Radar |
| STE | Sample to Example |
| FWIoU | Frequency-Weighted Intersection over Union |
| TP | True Positive |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| TN | True Negative |
References
- Kozlov, I.; Romanenkov, D.; Zimin, A.; Chapron, B. SAR observing large-scale nonlinear internal waves in the White Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Jay, D.A.; Orton, P.M. Analyses of internal solitary waves generated at the Columbia River plume front using SAR imagery. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H.; Peacock, T.; MacKinnon, J.A.; Nash, J.D.; Buijsman, M.C.; Centurioni, L.R.; Chao, S.Y.; Chang, M.H.; Farmer, D.M.; Fringer, O.B.; et al. The formation and fate of internal waves in the South China Sea. Nature 2015, 521, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C. Internal wave detection using the moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Susanto, R.D.; Ho, C.R.; Song, Y.T.; Xu, Q. Statistical and dynamical analyses of generation mechanisms of solitary internal waves in the northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, D.J. The State-of-the-Art in Ship Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery; Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, A.K.; Seemanth, M.; Ratheesh, R. Characterization of internal solitary waves in the Andaman Sea and Arabian Sea using EOS-04 and sentinel observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 1201–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surampudi, S.; Sasanka, S. Internal wave detection and characterization with SAR data. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Recent Advances in Geoscience and Remote Sensing: Technologies, Standards and Applications (TENGARSS), Kochi, India, 17–20 October 2019; pp. 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Meng, J.; Fang, Y.; Su, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, H. Internal solitary waves in the central Andaman sea observed by combining mooring data and satellite remote sensing. Cont. Shelf Res. 2024, 277, 105249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Ferreira, A.M.; Da Silva, J.C.; Magalhaes, J.M. SAR mode altimetry observations of internal solitary waves in the tropical ocean Part 1: Case studies. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Internal wave signature extraction from SAR and optical satellite imagery based on deep learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheya, B.; Cai, R.; Zhao, H.; Gong, M.; Li, X. MCS Filter: A Multichannel Structure-Aware Speckle Filter for SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, Q. A machine-learning model for forecasting internal wave propagation in the Andaman Sea. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3095–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheya, B.; Ren, X.; Gong, M.; Li, X. IW Extraction From SAR Images Based on Generative Networks with Small Datasets. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 16473–16487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barintag, S.; An, Z.; Jin, Q.; Chen, X.; Gong, M.; Zeng, T. MTU2-Net: Extracting Internal Solitary Waves from SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleissaee, A.A.; Kumar, A.; Anwer, R.M.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Xia, G.S.; Khan, F.S. Transformers in remote sensing: A survey. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, J.; Han, C.; Xia, J.; Yokoya, N. Changemamba: Remote sensing change detection with spatio-temporal state space model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4409720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Cai, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Fan, L.; Nguyen, A. Samba: Semantic segmentation of remotely sensed images with state space model. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.S.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.E.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L.D. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, J. Ce-net: Context encoder network for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Cheng, G.; Lang, C.; Xie, X.; Han, J. Centric Probability-Based Sample Selection for Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 3290–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Cheng, G.; Lang, C.; Yuan, X.; Xie, X.; Han, J. Hierarchical Mask Prompting and Robust Integrated Regression for Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 13071–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, L.; Wu, B.; Lin, B.; He, X.; Liu, W. Crossformer++: A versatile vision transformer hinging on cross-scale attention. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 3123–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, B.Z.; Khabsa, M.; Fang, H.; Ma, H. Linformer: Self-attention with linear complexity. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.04768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Goel, K.; Ré, C. Efficiently modeling long sequences with structured state spaces. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00396. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-Time Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wu, D.; Hu, B. Surface Vision Mamba: Leveraging Bidirectional State Space Model for Efficient Spherical Manifold Representation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.14679. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J.; Liu, Y. Vmamba: Visual state space model. NeurIPS 2024, 37, 103031–103063. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Hu, H. Audio mamba: Pretrained audio state space model for audio tagging. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.; Gu, A. Transformers are ssms: Generalized models and efficient algorithms through structured state space duality. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.21060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavi, S.; Divya, C.; Sarma, A.S. Detection of solitary ocean internal waves from SAR images by using U-Net and KDV solver technique. Glob. Transitions Proc. 2021, 2, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Ning, C.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Sangmanee, C.; Cui, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, W. An automatic internal wave recognition algorithm based on CNN applicable to an ocean data buoy system. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Gao, X.; Shi, L.; Li, N.; Zou, L. Detection of Ocean Internal Waves Based on Modified Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network and WaveNet in Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. CoRR 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chaurasia, A.; Culurciello, E. LinkNet: Exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 VCIR, St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–13 December 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, K.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Mutual Affine Network for Spatially Variant Kernel Estimation in Blind Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 4096–4105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Proceedings 4. Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J. Unified Perceptual Parsing for Scene Understanding. CoRR 2018, arXiv:1807.10221. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Dong, M.; Li, M.; Xu, C. VSSD: Vision Mamba with Non-Causal State Space Duality. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.18559. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z.; Han, Y.; Pu, Y.; Ge, C.; Song, J.; Song, S.; Zheng, B.; Huang, G. Demystify Mamba in Vision: A Linear Attention Perspective. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | Backbone | MIoU | FWIoU | Accuracy | Precision | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabV3 [41] | densennet161 | 0.664 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| dpn131 | 0.684 | 0.981 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| resnet101 | 0.668 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| resnet152 | 0.668 | 0.978 | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.993 | |
| se_resnext101_32x4d | 0.676 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| vgg19_bn | 0.649 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| FPN [42] | densenet161 | 0.674 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| dpn131 | 0.663 | 0.980 | 0.989 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| resnet101 | 0.683 | 0.981 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| resnet152 | 0.493 | 0.974 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.993 | |
| se_resnext101_32x4d | 0.672 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| vgg19_bn | 0.674 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| Linknet [43] | densenet161 | 0.682 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| dpn131 | 0.671 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| resnet101 | 0.661 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| resnet152 | 0.493 | 0.974 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.993 | |
| se_resnext101_32x4d | 0.683 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.995 | 0.993 | |
| vgg19_bn | 0.677 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| MAnet [44] | densenet161 | 0.684 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| dpn131 | 0.683 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.995 | 0.994 | |
| resnet101 | 0.680 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| resnet152 | 0.494 | 0.974 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.993 | |
| se_resnext101_32x4d | 0.673 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| vgg19_bn | 0.667 | 0.978 | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.993 | |
| PSPNet [45] | densenet161 | 0.676 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| dpn131 | 0.649 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| resnet101 | 0.654 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| resnet152 | 0.493 | 0.974 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.993 | |
| se_resnext101_32x4d | 0.656 | 0.978 | 0.987 | 0.993 | 0.993 | |
| vgg19_bn | 0.664 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| Unet [22] | densenet161 | 0.684 | 0.981 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| dpn131 | 0.676 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| resnet101 | 0.659 | 0.979 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| resnet152 | 0.493 | 0.974 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.993 | |
| se_resnext101_32x4d | 0.668 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| vgg19_bn | 0.657 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.993 | |
| Unet++ [46] | densenet161 | 0.684 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| dpn131 | 0.674 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| resnet101 | 0.676 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.993 | |
| resnet152 | 0.493 | 0.974 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.993 | |
| se_resnext101_32x4d | 0.664 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.993 | |
| vgg19_bn | 0.666 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| UPerNet [47] | densenet161 | 0.683 | 0.981 | 0.989 | 0.994 | 0.994 |
| dpn131 | 0.680 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| resnet101 | 0.664 | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.993 | 0.994 | |
| resnet152 | 0.494 | 0.974 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.993 | |
| se_resnext101_32x4d | 0.675 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| vgg19_bn | 0.681 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.994 | |
| MTU2-Net [15] | - | 0.721 | 0.982 | 0.989 | 0.994 | 0.996 |
| Ours | - | 0.743 | 0.981 | 0.990 | 0.995 | 0.996 |
| Baseline | FAS | SSM-LA | MIoU | GFLOPs | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 65.4 | 12.67 | 26.49 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 70.2 | 13.36 | 26.59 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 71.5 | 8.08 | 32.00 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 74.3 | 8.77 | 32.10 |
| Area | Quantity | MIoU | FWIoU | Accuracy | Precision | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaman Sea | 234 | 69.6 | 98.1 | 98.7 | 99.3 | 99.3 |
| Sulu Sea | 138 | 70.1 | 98.2 | 98.7 | 99.3 | 99.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, Z.; Li, Z.; Barintag, S.; Zhao, H.; Yao, Y.; Jiao, L.; Gong, M. State-Space Model Meets Linear Attention: A Hybrid Architecture for Internal Wave Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172969
An Z, Li Z, Barintag S, Zhao H, Yao Y, Jiao L, Gong M. State-Space Model Meets Linear Attention: A Hybrid Architecture for Internal Wave Segmentation. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(17):2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172969
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Zhijie, Zhao Li, Saheya Barintag, Hongyu Zhao, Yanqing Yao, Licheng Jiao, and Maoguo Gong. 2025. "State-Space Model Meets Linear Attention: A Hybrid Architecture for Internal Wave Segmentation" Remote Sensing 17, no. 17: 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172969
APA StyleAn, Z., Li, Z., Barintag, S., Zhao, H., Yao, Y., Jiao, L., & Gong, M. (2025). State-Space Model Meets Linear Attention: A Hybrid Architecture for Internal Wave Segmentation. Remote Sensing, 17(17), 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172969






