Texture-Adaptive Hierarchical Encryption Method for Large-Scale HR Remote Sensing Image Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Image Encryption Methods
2.2. Encryption Methods for Remote Sensing Images
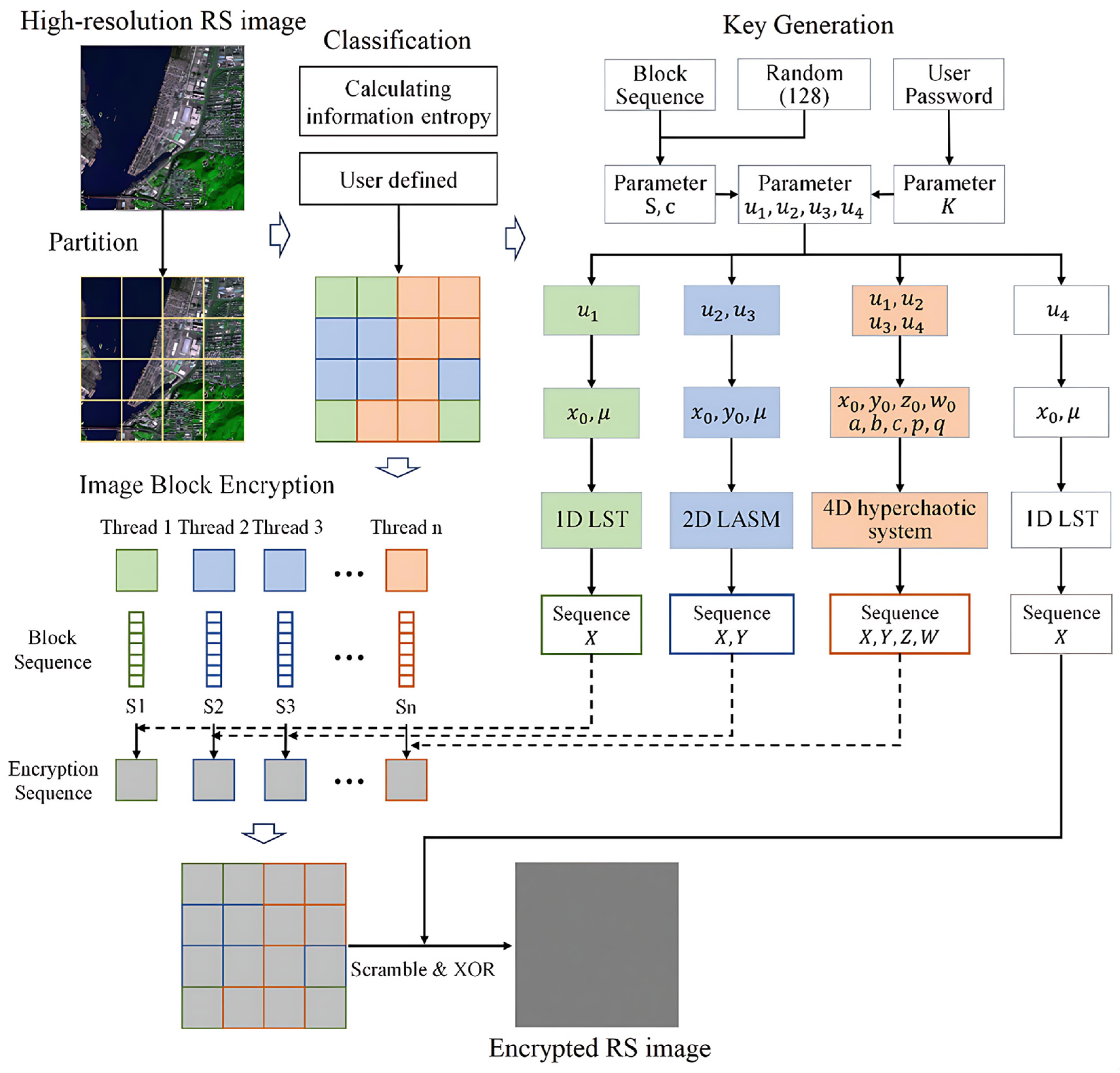
3. Methodology
3.1. Preliminaries
3.1.1. One-Dimensional Logistic-Tent Chaotic System
3.1.2. Two-Dimensional Logistic-Adjusted-Sine Map
3.1.3. Four-Dimensional Hyperchaotic System
3.2. Texture-Adaptive Hierarchical Encryption Method
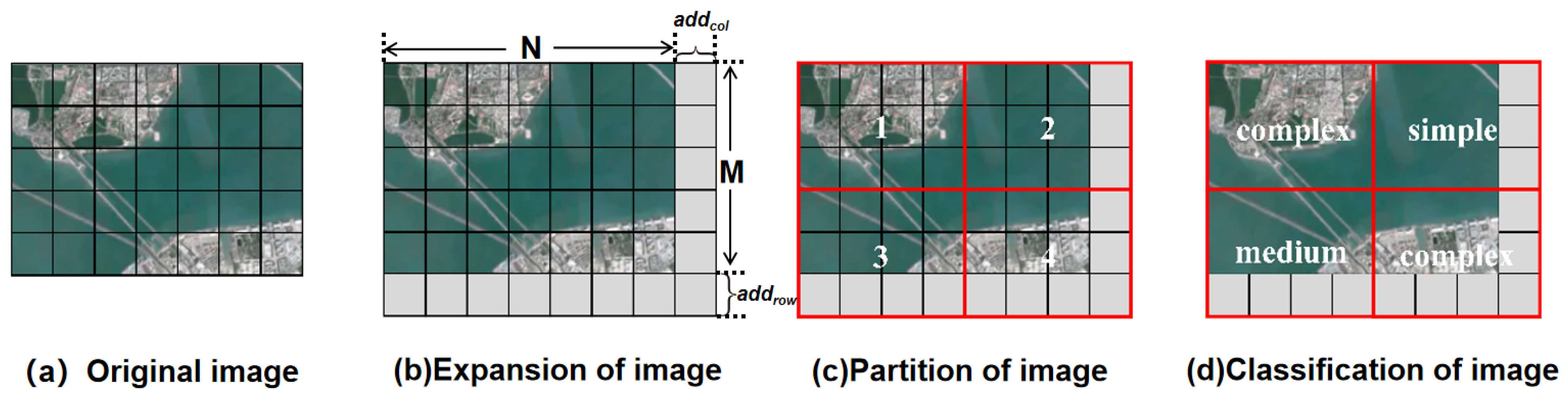
3.2.1. Partition and Texture Complexity Classification of RS Images
3.2.2. Initial Encryption Parameter Generation
3.2.3. Encryption of Image Blocks with a Texture-Adaptive Strategy
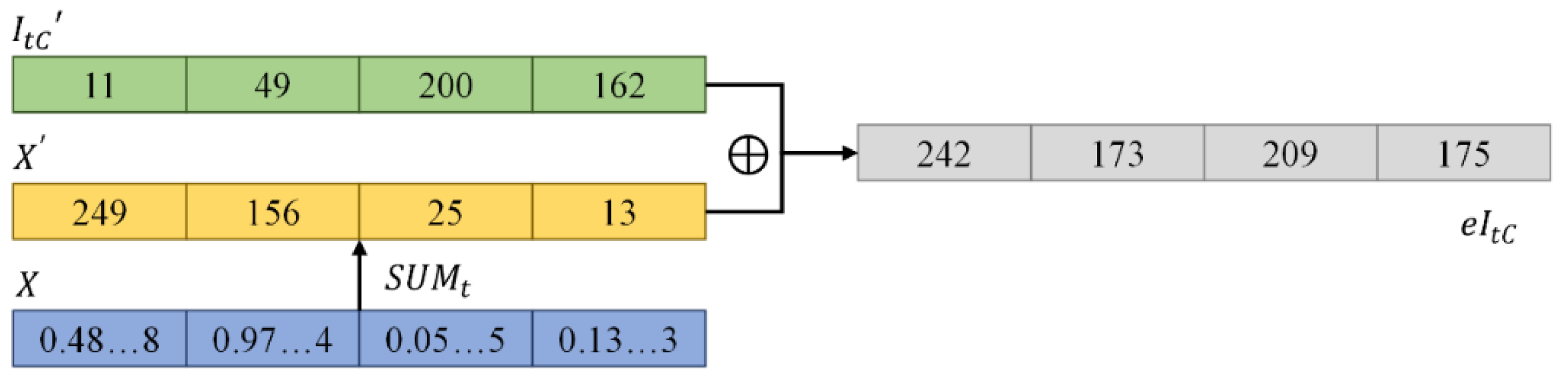
- Encryption of simple image block: The pixel values of the component matrices of the image block are encrypted by replacing the pixel values. The encryption steps for a simple image block component matrices (i.e., , and ) are as follows: First, is converted to a 1D image vector , where denotes the value of a component of the i-th pixel. The maximum value of i is the number of rows multiplied by the number of columns, w . Then, the 1D LTS initial parameters (, , and ) are calculated based on the passphrase P, related image block parameter , and using the method in Section 3.2. Further, according to Equation (16), the system is iterated () times to obtain a random sequence and remove the first random numbers to obtain . is processed according to Equation (22) to obtain the random vector , and pixel-wise XOR is performed on and to obtain the encrypted 1D vector .
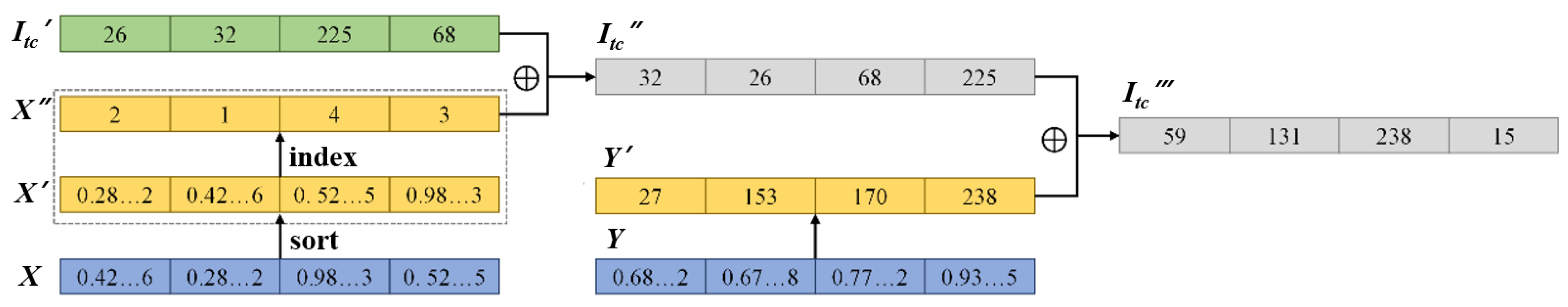
- Encryption of medium image block: The encryption steps for the medium image block are more complex compared to that for simple blocks; first, convert one component matrix into a 1D image vector . According to the parameters , , and passphrase P, calculate the 2D LASM initial parameters (, , and ) using the method in Section 3.2. According to Equation (19), iterate the system () times to obtain two groups of random sequences; remove the first random numbers from each group to generate two 1D random sequences and . Then, sort in ascending order to obtain the sorted sequence and index sequence , and perform a position permutation on according to Equation (23) to obtain . Sequence obtains a new 1D random sequence . Perform pixel-wise XOR between and according to Equation (23) to obtain the encrypted 1D vector :
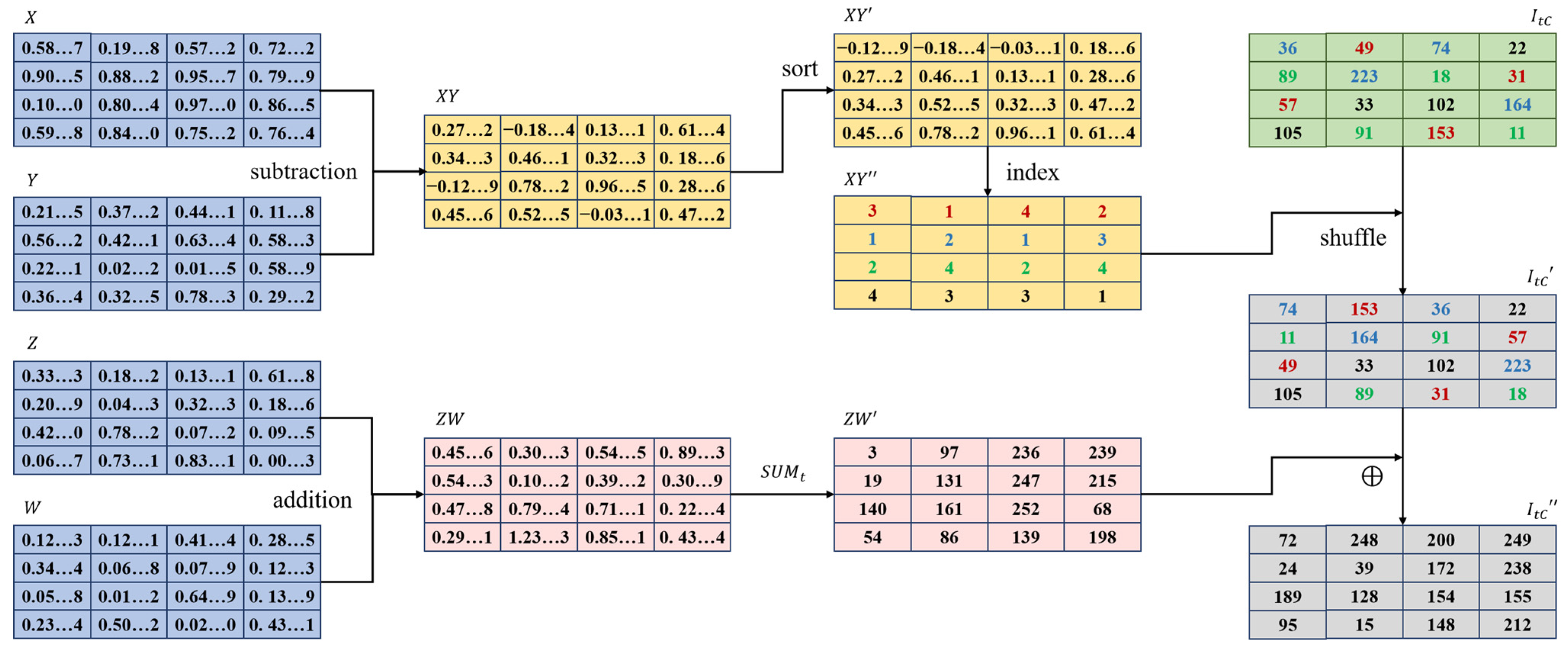
- Encryption of complex image block: The encryption steps for complex image blocks also take the pixel values of the component matrices as encryption objects, but the process of generating scrambling and substitution matrices is more complicated. The encryption steps for difficult image block ’s one-component matrices are as follows: First, calculate the 4D hyperchaotic system initial parameters (, , , and ) based on , , and passphrase P using the method in Section 3.2. According to Equation (20), iterate the system () to generate four groups of random sequences, remove the first k random numbers from each group, and use the remaining random numbers in each group to generate four 2D random matrices , , , and respectively. Then, perform one-to-one subtraction on matrices and to obtain the index matrix , and perform one-to-one addition on and to obtain the scrambling matrix and the scramble matrix according to the index matrix using the chaos magic transformation method (CMT) proposed by [91] to obtain the scrambled matrix . Further, perform pixel-wise XOR operations between and according to Formula (24) to obtain the encrypted component matrix .
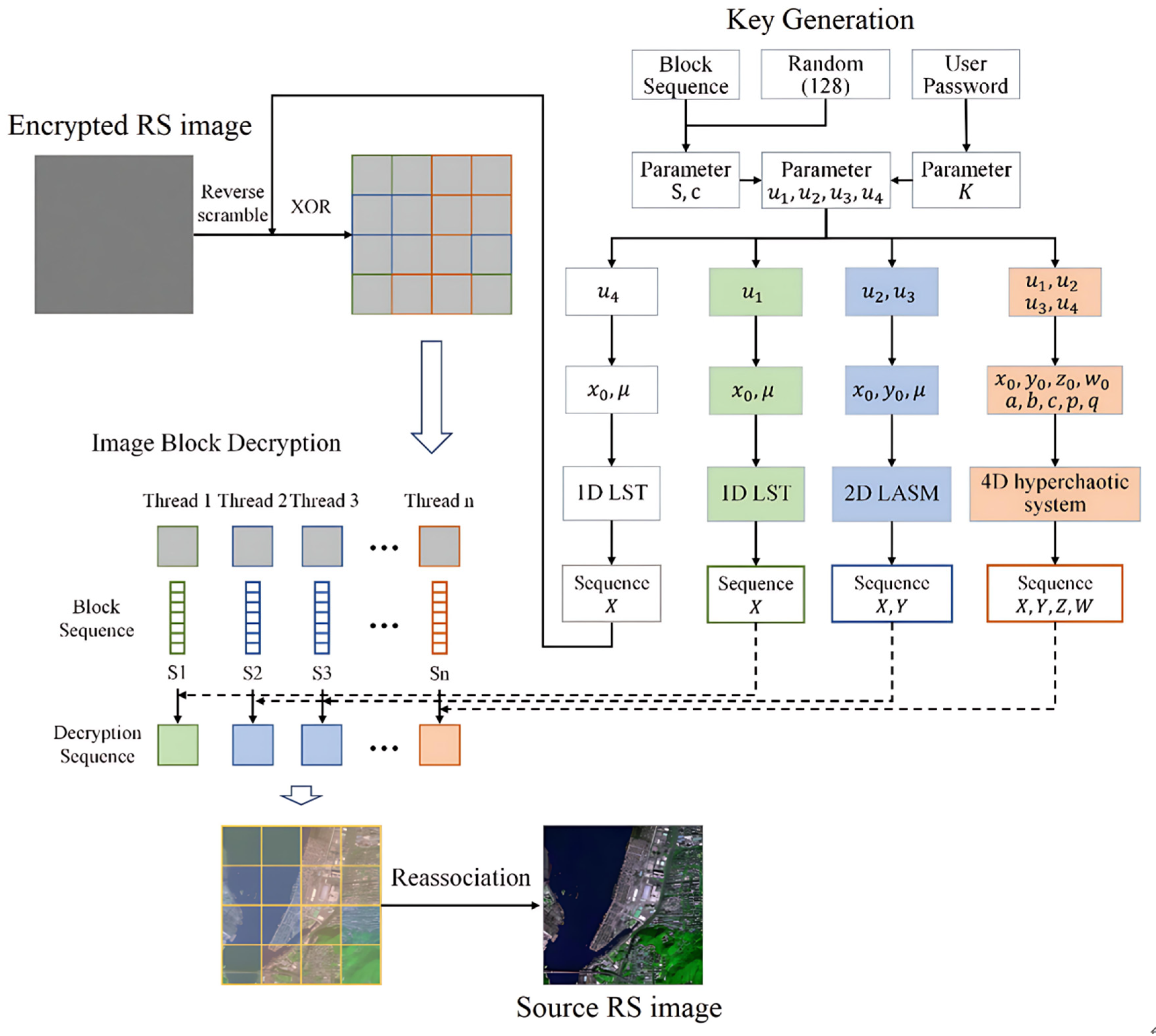
3.3. Encrypted Image Decryption
4. Experiment
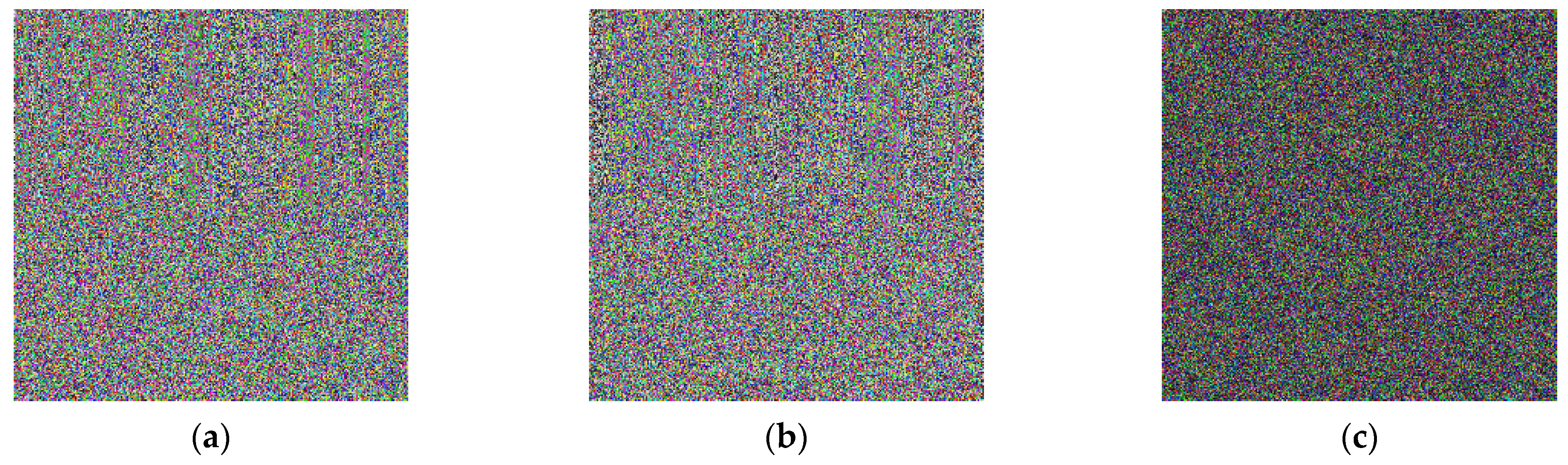
4.1. Encryption of Image Blocks
4.2. Comparative Analysis of Efficiency
4.3. Key Security Analysis
4.4. Information Entropy Analysis
4.5. Correlation Analysis of Adjacent Pixels
4.6. Analysis of Resistance to Differential Attack
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, Y.; Ma, A.; Ong, Y.S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L. Computational intelligence in optical remote sensing image processing. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 64, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, S.; You, S.; Zhang, L. Learning transferable deep models for land-use classification with high-resolution remote sensing images. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.05713. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; An, J.; Rahaman, M.M.; Chen, L.; Zhou, X.; Guan, Q. A Land Cover Classification Method for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on NDVI Deep Learning Fusion Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, H.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X. Intelligent Mapping of Urban Forests from High-Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery Using Object-Based U-Net-DenseNet-Coupled Network. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.-Y.; Xia, G.-S.; Lu, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, S.; You, S.; Zhang, L. Land-cover classification with high-resolution remote sensing images using transferable deep models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Research advances in remote sensing monitoring of sea ice in the Bohai sea. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. Advances in spaceborne hyperspectral remote sensing in China. Geospat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 24, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; Foody, G.M.; Boyd, D.S. Applications in Remote Sensing to Forest Ecology and Management. One Earth 2020, 2, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Dong, X.; Li, W.; Lu, P.; Zheng, W.; Zhu, Y. Remote sensing for landslide investigations: A progress report from China. Eng. Geol. 2023, 321, 107156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Content security protection for remote sensing images integrating selective content encryption and digital fingerprint. J. Appl. Remote Sens. (JARS) 2012, 6, 063505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Hao, Q. Digital watermarking secure scheme for remote sensing image protection. China Commun. 2020, 17, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Leng, X.; Yu, T.; Gu, X.; Liu, Q. A Joint Encryption and Compression Algorithm for Multiband Remote Sensing Image Transmission. Sensors 2023, 23, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SaberiKamarposhti, M.; Ghorbani, A.; Yadollahi, M. A comprehensive survey on image encryption: Taxonomy, challenges, and future directions. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 178, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guan, N. A novel chaotic image encryption algorithm based on extended Zigzag confusion and RNA operation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 131, 106366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, J. Optical image encryption algorithm based on hyper-chaos and public-key cryptography. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 127, 106171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y. Chaotic image encryption algorithm based on hybrid multi-objective particle swarm optimization and DNA sequence. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 137, 106393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Xiao, D.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, T. An image coding scheme using parallel compressive sensing for simultaneous compression-encryption applications. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2017, 44, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Lu, M.; Qin, L.; Han, J.; Fang, X. Asymmetric encryption and signature method with DNA technology. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2010, 53, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, H.R.; Harkut, D.G. Classical and Quantum Cryptography for Image Encryption & Decryption. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Research in Intelligent and Computing in Engineering (RICE), San Salvador, El Salvador, 22–24 August 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, M.Y.; Iqbal, A.; Mahmood, Z.; Ghafoor, A. Analysis of classical encryption techniques in cloud computing. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2016, 21, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankpal, P.R.; Vijaya, P.A. Image Encryption Using Chaotic Maps: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 2014 Fifth International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Bangalore, India, 8 January 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, S.; Punithavathi, P.; Infanteena, A.M.; Sindhu, S.S.S. A Literature Review on Image Encryption Techniques. Int. J. Inf. Secur. Priv. (IJISP) 2018, 12, 42–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiken, C.; Samli, R. A Comprehensive Review About Image Encryption Methods. Harran Üniversitesi Mühendislik Derg. 2022, 7, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, L.; Zhao, H. Fast image encryption algorithm based on parallel computing system. Inf. Sci. 2019, 486, 340–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneja, K.; Dua, S.; Dua, M. A Review of Chaos based Image Encryption. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 27–29 March 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.S.; Kayhan, S.K. Chaos and compressive sensing based novel image encryption scheme. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2021, 58, 102711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Saxena, A.; Vuppala, S.S. A Survey on Chaos Based Image Encryption Techniques. In Multimedia Security Using Chaotic Maps: Principles and Methodologies; Hosny, K.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshadian, S.; Ebrahimzade, A.; Kazemitabar, S.J. Optimizing chaos based image encryption. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 25569–25590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-K.; Phan, R.C.-W.; Yap, W.-S.; Goi, B.-M. SPRING: A novel parallel chaos-based image encryption scheme. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 92, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maazouz, M.; Toubal, A.; Bengherbia, B.; Houhou, O.; Batel, N. FPGA implementation of a chaos-based image encryption algorithm. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34 Pt B, 9926–9941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, A.; Wang, X. A novel block-based image encryption scheme using a new Sine powered chaotic map generator. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 21955–21978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikbal, F.; Gopikakumari, R. Image block generation from block-based SMRT in colour image encryption and its performance analysis. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34 Pt A, 8459–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Vaish, A. Block based visually secure image encryption algorithm using 2D-Compressive Sensing and nonlinearity. Optik 2023, 272, 170341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faragallah, O.S.; Afifi, A.; El-Sayed, H.S.; Khedr, A.E.; Alharbi, A.G.; El-Shafai, W.; Abd El-Samie, F.E. Block-Based Optical Color Image Encryption Based on Double Random Phase Encoding. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 4184–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, D.; Mou, H.; Lu, D.; Peng, M. A Compressive Sensing Based Image Encryption and Compression Algorithm With Identity Authentication and Blind Signcryption. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 211676–211690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, E.; Zhao, B. Image Encryption Scheme with Compressed Sensing Based on a New Six-Dimensional Non-Degenerate Discrete Hyperchaotic System and Plaintext-Related Scrambling. Entropy 2021, 23, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadkhan, S.B. Information Security based on DNA—Importance and Future Trends. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Communication & Information Technology (ICICT), Basrah, Iraq, 5–6 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, A.; Samsudin, A.; Akhshani, A. Cryptanalysis of an image encryption algorithm based on DNA encoding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 95, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Deng, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, C. Image Encryption Scheme Based on Newly Designed Chaotic Map and Parallel DNA Coding. Mathematics 2023, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, J.; Mandal, M.K. Chaos-based Image Encryption using Integer Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 27–28 February 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, C. New insights into the existing image encryption algorithms based on DNA coding. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, D.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Alvarez, G.; Halang, W.A. Cryptanalysis of an image encryption scheme based on a new total shuffling algorithm. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 41, 2613–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Hu, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y. Fingerprint images encryption via multi-scroll chaotic attractors. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 185, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloom, S.; Eftekhari-Moghadam, A.M. Color image encryption based on Coupled Nonlinear Chaotic Map. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 42, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Remote-sensing image encryption algorithm using the advanced encryption standard. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, W. A fast image encryption scheme based on AES. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Chengdu, China, 2–4 June 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrich, J. Symmetric Ciphers Based on Two-Dimensional Chaotic Maps. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1998, 08, 1259–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Jin, F.; Xu, B.; Huang, H. 2D Logistic-Sine-coupling map for image encryption. Signal Process. 2018, 149, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y. 2D Logistic-Modulated-Sine-Coupling-Logistic Chaotic Map for Image Encryption. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 14081–14098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, C.; Huang, L. A new color image encryption using combination of the 1D chaotic map. Signal Process. 2017, 138, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, J.; Guo, S.; Ding, Q.; Wang, E. Image Encryption Scheme with Compressed Sensing Based on New Three-Dimensional Chaotic System. Entropy 2019, 21, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim, A.H.; Ali Pacha, A.; Hadj Said, N. Image encryption based on compressive sensing and chaos systems. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 132, 106489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, D. An efficient double-image encryption and hiding algorithm using a newly designed chaotic system and parallel compressive sensing. Inf. Sci. 2022, 610, 300–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Zheng, X.; Gan, Z.; Han, D.; Chen, Y. An image encryption algorithm based on chaotic system and compressive sensing. Signal Process. 2018, 148, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Pan, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhou, Z. Image compression–encryption scheme based on hyper-chaotic system and 2D compressive sensing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 82, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Jiang, D.; An, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. A novel double-image encryption algorithm based on Rossler hyperchaotic system and compressive sensing. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 41704–41716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Mou, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Yan, H. Characteristic analysis of the fractional-order hyperchaotic complex system and its image encryption application. Signal Process. 2020, 169, 107373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tong, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M. Uniform non-degeneracy discrete chaotic system and its application in image encryption. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 108, 653–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Mou, J.; Xiong, L.; Banerjee, S.; Liu, T.; Han, X. Dynamical analysis of a new chaotic system: Asymmetric multistability, offset boosting control and circuit realization. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 103, 2867–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y. Sine-transform-based chaotic system with FPGA implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.S.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, J.G.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, H.D. Color image encryption based on programmable complemented maximum length cellular automata and generalized 3-D chaotic cat map. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 22825–22842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Yi, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, H. Cross-plane colour image encryption using a two-dimensional logistic tent modular map. Inf. Sci. 2021, 546, 1063–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tong, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M. Efficient high nonlinearity S-box generating algorithm based on third-order nonlinear digital filter. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 150, 111109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Yi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, Y. Designing hyperchaotic cat maps with any desired number of positive Lyapunov exponents. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 48, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Fan, C.; Ding, Q. Constructing discrete chaotic systems with positive Lyapunov exponents. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2018, 28, 1850084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Construction of a class of high-dimensional discrete chaotic systems. Mathematics 2021, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tong, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y. Image compression and encryption algorithm based on uniform non-degeneracy chaotic system and fractal coding. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 8771–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M. Yet new extreme multi-stable chaotic system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 3124–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.M.A.; Sriram, S.; Natiq, H.; Ahmadi, A.; Rajagopal, K.; Jafari, S. A novel multi-stable sinusoidal chaotic map with spectacular behaviors. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2023, 75, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, H. A novel 3D non-degenerate hyperchaotic map with ultra-wide parameter range and coexisting attractors periodic switching. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Mou, J.; Xiong, L.; Banerjee, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J. A novel chaotic circuit with coexistence of multiple attractors and state transition based on two memristors. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 152, 111363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, H.; He, S. A class of novel discrete memristive chaotic map. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 174, 113791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, M.; Forti, M.; Pancioni, L.; Tesi, A. New class of discrete-time memristor circuits: First integrals, coexisting attractors and bifurcations without parameters. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2024, 34, 2450001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Su, Y. Image encryption based on compressed sensing and DNA encoding. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2021, 95, 116246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X. A RGB image encryption algorithm based on DNA encoding and chaos map. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2012, 38, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X. Image encryption algorithm based on DNA biological properties and chaotic systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Bio-Inspired Computing: Theories and Applications (BIC-TA), Liverpool, UK, 8–10 September 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasimov, V.A.; Mammadov, J.I. DNA-based image encryption algorithm. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 734, 012162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; McCarthy, Z.; Jow, O.; Lee, D.; Chen, X.; Goldberg, K.; Abbeel, P. Deep Imitation Learning for Complex Manipulation Tasks from Virtual Reality Teleoperation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 5628–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, S. A remote sensing image encryption method combining chaotic neuron and tent map. J. Comput. (Taipei) 2021, 32, 108–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, G.; Huang, X. A novel block chaotic encryption scheme for remote sensing image. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 11433–11446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensikaddour, E.-H.; Bentoutou, Y.; Taleb, N. Embedded implementation of multispectral satellite image encryption using a chaos-based block cipher. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 32, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yang, Z. Method of remote sensing image detail encryption based on symmetry algorithm. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, Q.; Qin, Q. A Multilevel Convolution Pyramid Semantic Fusion Framework for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification and Annotation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 18195–18208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Peng, C. Content-Oriented Multilevel Security Authorization of Images. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Mechatronics, Control and Electronic Engineering (MCE-14), Shenyang, China, 29–31 March 2014; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, L.; Sharmila, T.S. Optimized Feature Integration and Minimized Search Space in Content Based Image Retrieval. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 165, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bao, L.; Chen, C.P. A new 1D chaotic system for image encryption. Signal Process. 2014, 97, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, Y. Image encryption using 2D Logistic-adjusted-Sine map. Inf. Sci. 2016, 339, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laarem, G. A new 4-D hyper chaotic system generated from the 3-D Rösslor chaotic system, dynamical analysis, chaos stabilization via an optimized linear feedback control, it’s fractional order model and chaos synchronization using optimized fractional order sliding mode control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 152, 111437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertaul, L.; Kaur, M.; Gudise, V.A.K.R. Implementation and performance analysis of pbkdf2, bcrypt, scrypt algorithms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Networks (ICWN), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–28 July 2016; The Steering Committee of The World Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering and Applied Computing (WorldComp): Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Pun, C.-M.; Chen, C.P. 2D Sine Logistic modulation map for image encryption. Inf. Sci. 2015, 297, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q. A Secure Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Composite Chaos Theory. Trait. Du Signal 2019, 36, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, S.; Feng, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H. Remote sensing image compression and encryption based on block compressive sensing and 2D-LCCCM. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 108, 2705–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Noonan, J.P.; Agaian, S. NPCR and UACI randomness tests for image encryption. Cyber J. Multidiscip. J. Sci. Technol. J. Sel. Areas Telecommun. (JSAT) 2011, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar]



| Methods | Size | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 256 × 256 | 512 × 512 | 1024 × 1024 | 2048 × 2048 | 4096 × 4096 | |
| Encryption method based on composite chaos [92] | 1996 | 2248 | 2974 | 5163 | 13,909 |
| Encryption method based on chaotic system and AES [46] | 2736 | 3251 | 4616 | 8961 | 32,163 |
| Global encryption method based on 1D LTS | 1916 | 2005 | 2697 | 5159 | 12,652 |
| Global encryption method based on 4D hyperchaotic system | 2075 | 2366 | 3003 | 6378 | 24,807 |
| Our method | 1947 | 2249 | 2649 | 4480 | 9014 |
| Name | Size | Information Entropy of the Source RS Image | Information Entropy of the Encrypted RS Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test1.tif | 256 × 256 | 5.66774 | 7.99717 |
| Test2.tif | 512 × 512 | 6.95465 | 7.99929 |
| Test3.tif | 1024 × 1024 | 5.94480 | 7.99982 |
| Test4.tif | 2048 × 2048 | 6.41338 | 7.99995 |
| Test5.tif | 4096 × 4096 | 6.42870 | 7.99998 |
| Image | Component | Horizontal Direction | Vertical Direction | Diagonal Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source RS image | R | 0.9569 | 0.9393 | 0.9363 |
| G | 0.9615 | 0.9338 | 0.9325 | |
| B | 0.9826 | 0.9698 | 0.9672 | |
| Encrypted RS image | R | −0.0181 | 0.0149 | 0.0141 |
| G | −0.0069 | −0.0031 | −0.0090 | |
| B | 0.0097 | −0.0163 | 0.0028 |
| Size of the RS Image | NPCR | UACI |
|---|---|---|
| 256 × 256 | 99.6205% | 33.5417% |
| 512 × 512 | 99.6066% | 33.4559% |
| 1024 × 1024 | 99.6054% | 33.4659% |
| 2048 × 2048 | 99.6095% | 33.4514% |
| 4096 × 4096 | 99.6112% | 33.4690% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Jiang, X.; Huang, C.; Ding, C.; Deng, M.; Huang, Z.; Duan, J.; Zhu, X. Texture-Adaptive Hierarchical Encryption Method for Large-Scale HR Remote Sensing Image Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172940
Tang J, Jiang X, Huang C, Ding C, Deng M, Huang Z, Duan J, Zhu X. Texture-Adaptive Hierarchical Encryption Method for Large-Scale HR Remote Sensing Image Data. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(17):2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172940
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jianbo, Xingxiang Jiang, Chaoyi Huang, Chen Ding, Min Deng, Zhengyuan Huang, Jia Duan, and Xiaoye Zhu. 2025. "Texture-Adaptive Hierarchical Encryption Method for Large-Scale HR Remote Sensing Image Data" Remote Sensing 17, no. 17: 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172940
APA StyleTang, J., Jiang, X., Huang, C., Ding, C., Deng, M., Huang, Z., Duan, J., & Zhu, X. (2025). Texture-Adaptive Hierarchical Encryption Method for Large-Scale HR Remote Sensing Image Data. Remote Sensing, 17(17), 2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17172940








