Integrating Multi-Temporal Landsat and Sentinel Data for Enhanced Oil Palm Plantation Mapping and Age Estimation in Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. Satellite Imagery
2.2.2. Auxiliary Data
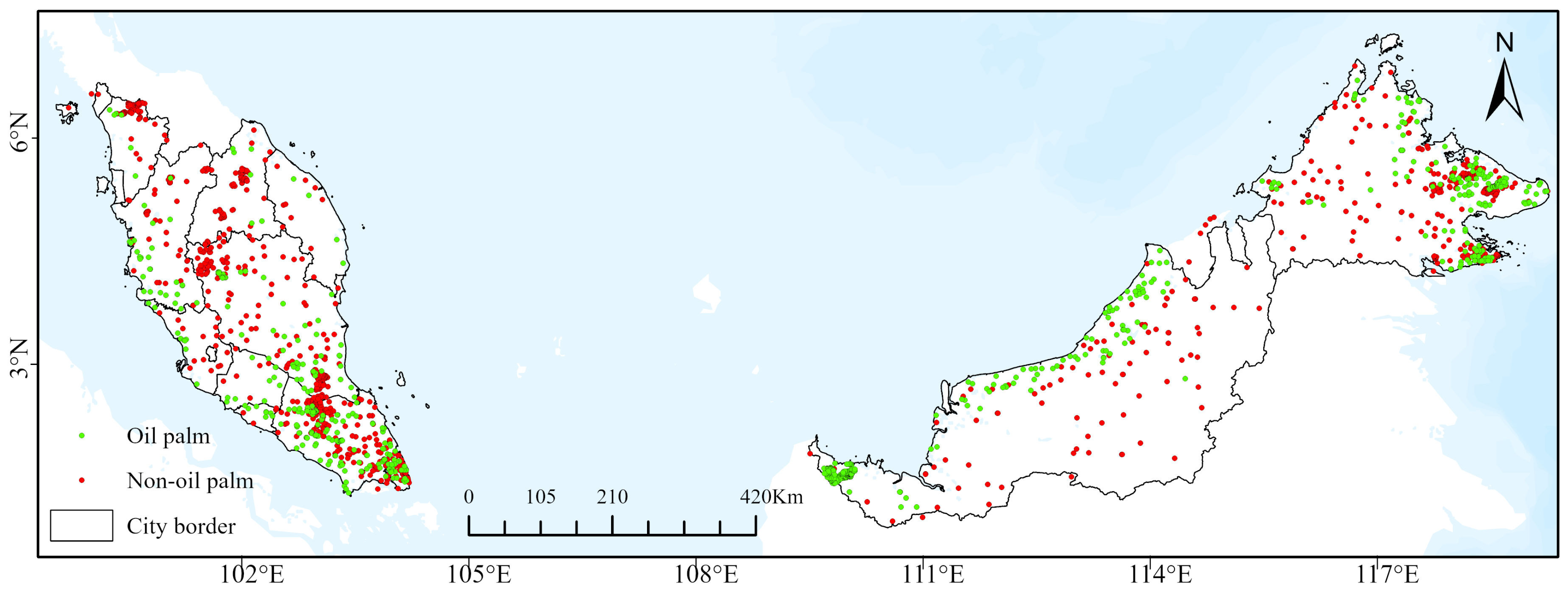
2.2.3. Ground Reference Data
2.2.4. Satellite Image Pre-Processing
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Method Overview
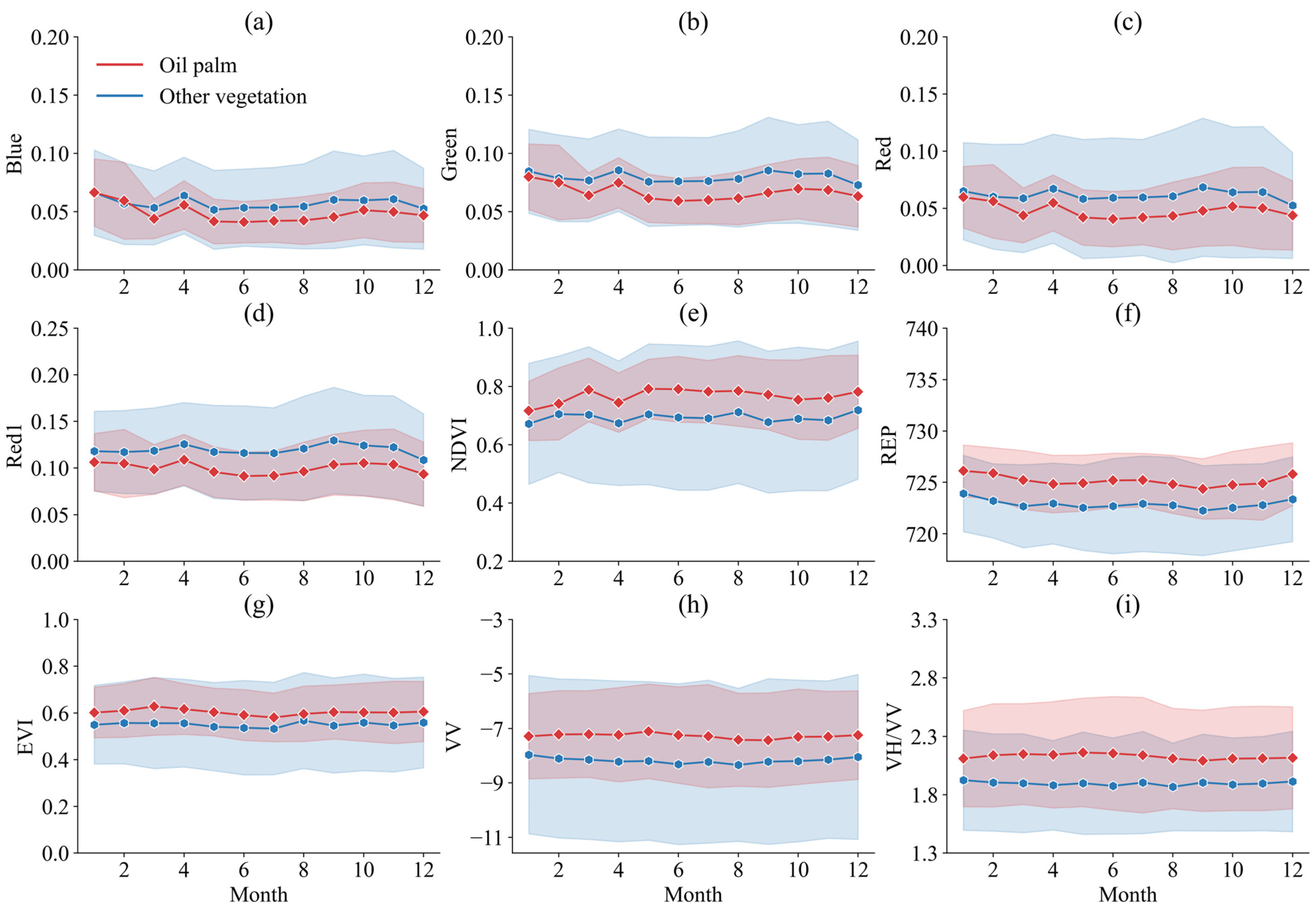
2.3.2. Feature Extraction and Data Synthesis
| Feature Variables | Reference | |
|---|---|---|
| Landsat 8/9 | Blue, Green, Red, NIR, SWIR1, SWIR2 | [28] |
| Sentinel-2 | Blue, Green, Red, NIR, SWIR1, SWIR2, RE1, RE2, RE3, RE4 * | [50] |
| Sentinel-1 | VH, VV, VH/VV | [3] |
| Vegetable Index | NDVI, LSWI, EVI, GRVI, REP | [51] |
| GLCM Texture Features | Angular Second Moment (ASM) | [51,52,53,54] |
| Contrast (CON) | ||
| Inverse Difference Moment (IDM) | ||
| Sum Average (SAVG) | ||
| Sum Entropy (SENT) | ||
| Entropy (ENT) | ||
| Difference Variance (DVAR) | ||
| Difference Entropy (DENT) | ||
| Information Measure of Corr. 1 (IMCORR1) | ||
| Information Measure of Corr. 2 (IMCORR2) | ||
| Dissimilarity (DISS) | ||
| Inertia |
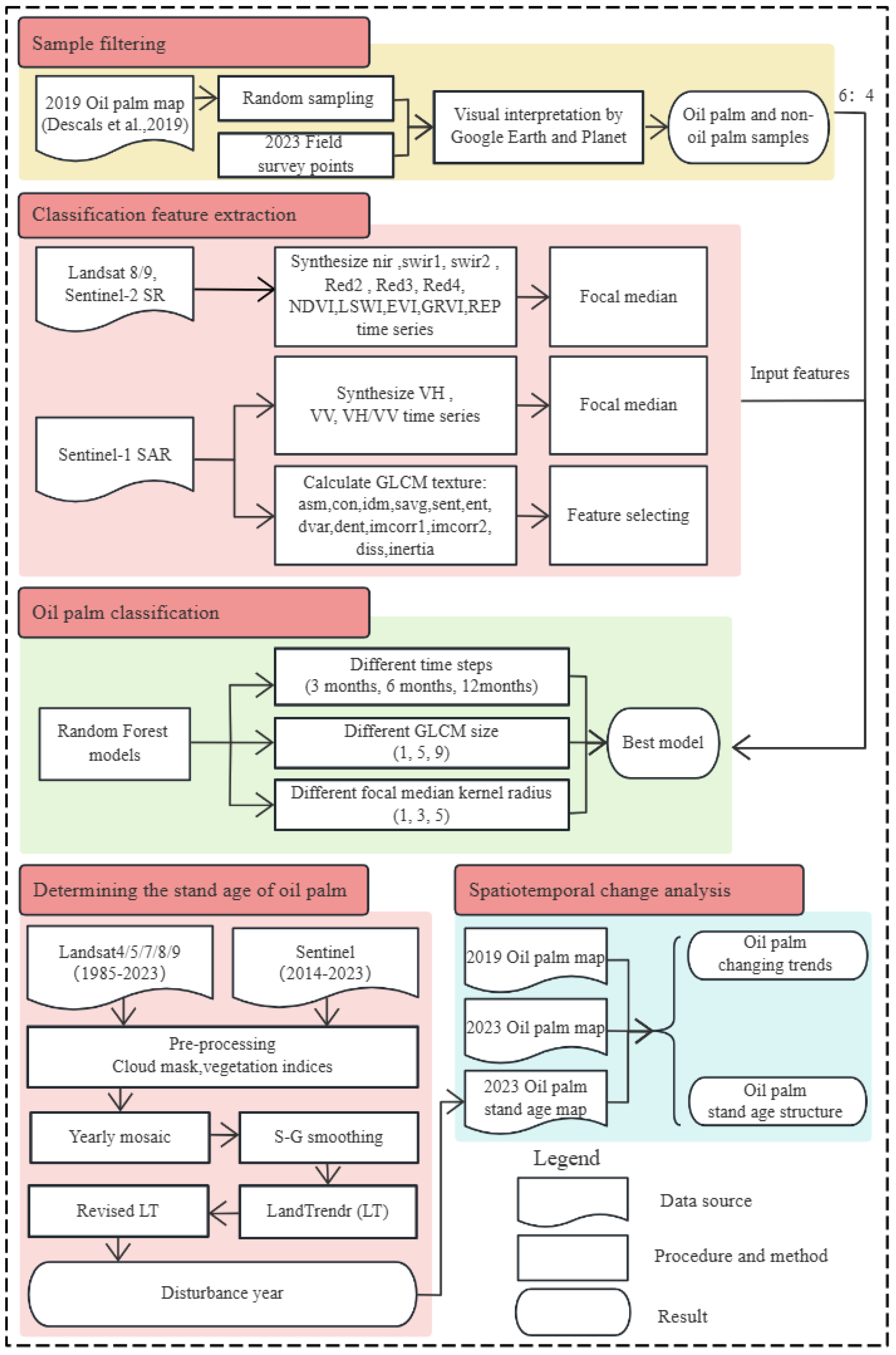
2.3.3. Model Construction
2.3.4. Determining the Plantation Establishment Year
2.3.5. Accuracy Assessment
2.3.6. Analysis of Spatial Temporal Dynamic Changes
2.3.7. Analysis of Oil Palm Stand Age Structure
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Parameter Selection on Oil Palm Identification Accuracy
3.2. Accuracy Assessment
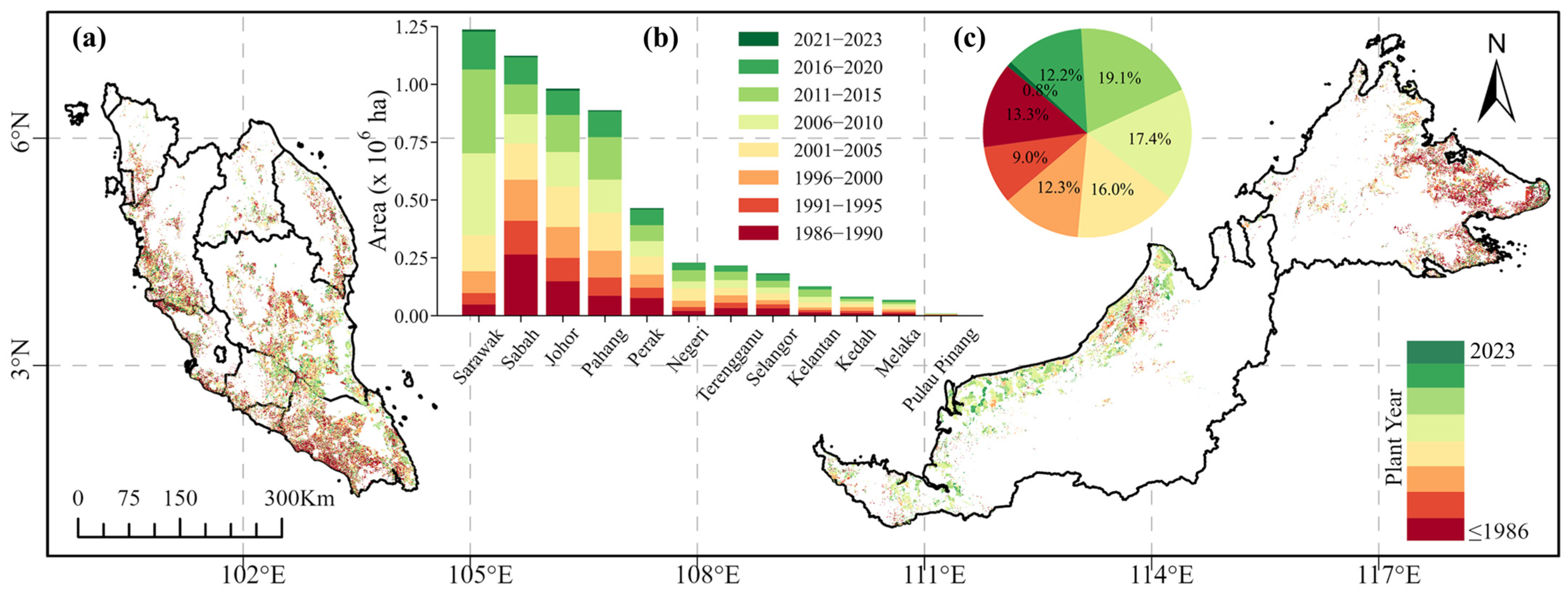
3.3. Spatiotemporal Changes of Oil Palms in Malaysia
3.4. Stand Age Structure of Oil Palm in Malaysia
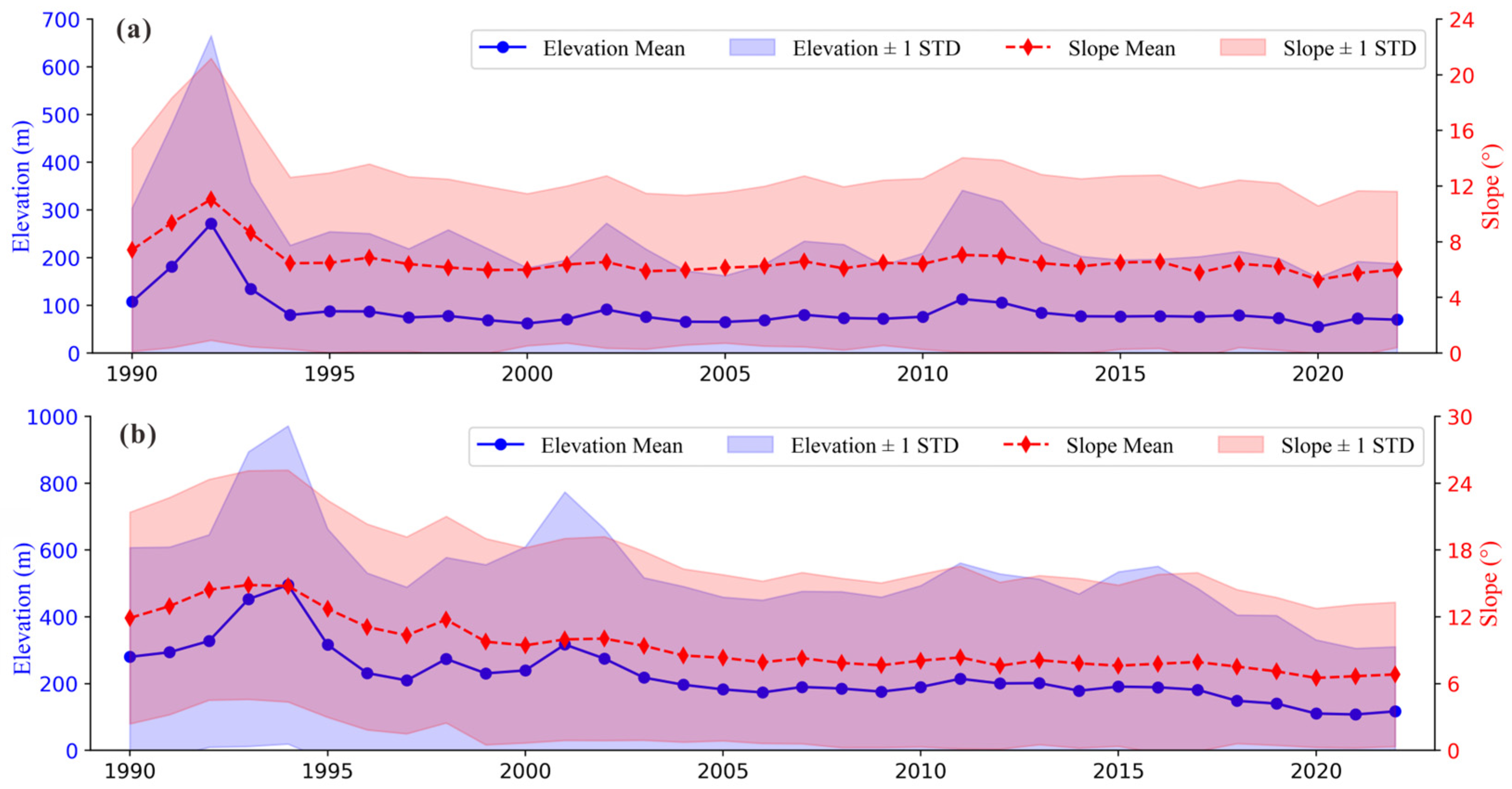
3.5. Trends in Topographic Characteristics of Oil Palm in Malaysia
4. Discussion
4.1. Methodological Advancements in Multi-Source Data Integration for Oil Palm Monitoring
4.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Regional Variability in Malaysian Oil Palm Development
4.3. Age Structure Analysis and Implications for Sustainable Management
4.4. Methodological Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chong, K.L.; Kanniah, K.D.; Pohl, C.; Tan, K.P. A review of remote sensing applications for oil palm studies. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 20, 184–200. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, R.; Reza, M.I.H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Yaakob, Z. Sustainable oil palm industry: The possibilities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danylo, O.; Pirker, J.; Lemoine, G.; Ceccherini, G.; See, L.; McCallum, I.; Hadi; Kraxner, F.; Achard, F.; Fritz, S. A map of the extent and year of detection of oil palm plantations in Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Fu, D.; Su, F.; Xiao, Y. Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Analysis of the Driving Force of Oil Palm Patterns in Malaysia from 2000 to 2018. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 280. [Google Scholar]
- Pin, K.L.; Wilcove, D.S. Is oil palm agriculture really destroying tropical biodiversity. Conserv. Lett. 2008, 1, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.H.; Wich, S.; Widayati, A.; Koh, L.P. Detecting industrial oil palm plantations on Landsat images with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2016, 4, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Meijaard, E.; Brooks, T.M.; Carlson, K.M.; Slade, E.M.; Garcia-Ulloa, J.; Gaveau, D.L.A.; Lee, J.S.H.; Santika, T.; Juffe-Bignoli, D.; Struebig, M.J.; et al. The environmental impacts of palm oil in context. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Choquette-Levy, N.; Wildemeersch, M.; Oppenheimer, M.; Levin, S.A. Risk transfer policies and climate-induced immobility among smallholder farmers. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Numata, I.; Andrew, J.E.; Mark, A.C.; Cangjiao, W.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, A.X. Deforestation, plantation-related land cover dynamics and oil palm age-structure change during 1990–2020 in Riau Province, Indonesia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 94024. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, L.; Ciais, P.; Li, W.; Santoro, M.; Yang, H.; Gong, P. Recent expansion of oil palm plantations into carbon-rich forests. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 574–577. [Google Scholar]
- Defourny, P.; Bontemps, S.; Bellemans, N.; Cara, C.; Dedieu, G.; Guzzonato, E.; Hagolle, O.; Inglada, J.; Nicola, L.; Rabaute, T. Near real-time agriculture monitoring at national scale at parcel resolution: Performance assessment of the Sen2-Agri automated system in various cropping systems around the world. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 551–568. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, P.; Nendel, C.; Hostert, P. Intra-annual reflectance composites from Sentinel-2 and Landsat for national-scale crop and land cover mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 220, 135–151. [Google Scholar]
- Blickensdörfer, L.; Schwieder, M.; Pflugmacher, D.; Nendel, C.; Erasmi, S.; Hostert, P. Mapping of crop types and crop sequences with combined time series of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 data for Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112831. [Google Scholar]
- Teluguntla, P.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Oliphant, A.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K.; Huete, A. A 30-m landsat-derived cropland extent product of Australia and China using random forest machine learning algorithm on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2018, 144, 325–340. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Fu, S.; Niu, Z.; Han, W.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, J.; Yuan, W. Early-season mapping of winter wheat in China based on Landsat and Sentinel images. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3081–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hou, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Mapping Maize Area in Heterogeneous Agricultural Landscape with Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images Based on Random Forest. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2988. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, S.; Zhao, L.; Huang, X.; Jiang, X. Parcel-based summer maize mapping and phenology estimation combined using Sentinel-2 and time series Sentinel-1 data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2022, 108, 102720. [Google Scholar]
- Claverie, M.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Dungan, J.L.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.; Skakun, S.V.; Justice, C. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Huang, W.; Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P. An evaluation of Landsat, Sentinel-2, Sentinel-1 and MODIS data for crop type mapping. Sci. Remote Sens. 2021, 3, 100018. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, H.; Cracknell, A.P.; Kanniah, K.; Gong, P. Mapping oil palm plantation expansion in Malaysia over the past decade (2007–2016) using ALOS-1/2 PALSAR-1/2 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7389–7408. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Najib, N.E.; Kanniah, K.D.; Cracknell, A.P.; Yu, L. Synergy of Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data for Effective Mapping of Oil Palm Plantation in Malaysia. Forests 2020, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descals, A.; Wich, S.; Meijaard, E.; Gaveau, D.L.A.; Peedell, S.; Szantoi, Z. High-resolution global map of smallholder and industrial closed-canopy oil palm plantations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 1211–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, D.; Yu, H.; Su, F.; Lyne, V.; Fan, R.; He, B.; Pan, T.; Tang, J. High-resolution global mature and young oil palm plantation subclass maps for 2020. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 2168–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, I.L.; Weston, C.J.; Newnham, G.J.; Volkova, L. Using Bayesian multitemporal classification to monitor tropical forest cover changes in Kalimantan, Indonesia. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 2061–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliman, S.; Rahman, S.A.; Bakar, S.A.; Busu, I. Segmentation of oil palm area based on GLCM-SVM and NDVI. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Region 10 Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 14–16 April 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 645–650. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ruzouq, R.; Shanableh, A.; Barakat, A.; Gibril, M.; Al-Mansoori, S. Image segmentation parameter selection and ant colony optimization for date palm tree detection and mapping from very-high-spatial-resolution aerial imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1413. [Google Scholar]
- Kwang, C.S.; Abdul Razak, S.F.; Yogarayan, S.; Adli Zahisham, M.Z.; Tam, T.H.; Mohd Noor, M.K.; Abidin, H. Ganoderma Disease in Oil Palm Trees Using Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. J. Hum. Earth Future 2025, 6, 67–83. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Qian, J.; Hu, Z.; Duan, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Wei, S.; Xing, X. A New Machine Learning Approach in Detecting the Oil Palm Plantations Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Jarayee, A.N.; Shafri, H.Z.; Ang, Y.; Lee, Y.P.; Bakar, S.A.; Abidin, H.; Lim, H.S.; Abdullah, R.; Junaidi, U.U.; Samad, N. Oil palm age estimation using broad-band and narrow-band vegetation indices derived from Sentinel-2 data. Asia-Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 29, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Asari, N.; Suratman, M.N.; Jaafar, J. Modelling and mapping of above ground biomass (AGB) of oil palm plantations in Malaysia using remotely-sensed data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 4741–4764. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, T.T.; Sridhar, M.; Ju, J.; Zhou, Q.; Baker, B.; Freitag, B.; Olofsson, P.; Neigh, C.S.R. Continuous Change Detection and Classification (CCDC) Using NASA’s Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 (HLS) Data in Google Earth Engine (GEE). In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 June 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Shang, R.; Chen, J.M.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, G.R.; He, N.P.; Xu, L.; Jiao, W.Z. High-resolution forest age mapping based on forest height maps derived from GEDI and ICESat-2 space-borne lidar data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 339, 109592. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Du, H.; Mao, F.; Huang, Z.; Chen, C.; Hu, M.; Li, X. Improving forest age prediction performance using ensemble learning algorithms base on satellite remote sensing data. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Zan, M.; Ye, M.; Zhou, J.; Xue, C.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y. Time-series forest age estimation in Xinjiang based on forest disturbance and recovery detection. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Xu, K. Multi-Sensor Fusion and Machine Learning for Forest Age Mapping in Southeastern Tibet. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1926. [Google Scholar]
- Kardooni, R.; Yusoff, S.B.; Kari, F.B.; Moeenizadeh, L. Public opinion on renewable energy technologies and climate change in Peninsular Malaysia. Renew. Energ. 2018, 116, 659–668. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.H.D. Climate change in Malaysia: Trends, contributors, impacts, mitigation and adaptations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1858–1871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Awalludin, M.F.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Nadhari, W.N.A.W. An overview of the oil palm industry in Malaysia and its waste utilization through thermochemical conversion, specifically via liquefaction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Kovalskyy, V.; Zhang, H.K.; Vermote, E.F.; Yan, L.; Kumar, S.S.; Egorov, A. Characterization of Landsat-7 to Landsat-8 reflective wavelength and normalized difference vegetation index continuity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.K.; Roy, D.P.; Yan, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Vermote, E.; Skakun, S.; Roger, J.C. Characterization of Sentinel-2A and Landsat-8 top of atmosphere, surface, and nadir BRDF adjusted reflectance and NDVI differences. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 482–494. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Ma, J.; Yang, C.; Xiao, X.; Kou, W.; Wu, Z.; Yun, T.; Zaw, Z.; Nawan, P.; Sengprakhon, R.; et al. Diversified land conversion deepens understanding of impacts of rapid rubber plantation expansion on plant diversity in the tropics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poortinga, A.; Tenneson, K.; Shapiro, A.; Nquyen, Q.; San Aung, K.; Chishtie, F.; Saah, D. Mapping plantations in Myanmar by fusing Landsat-8, Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-1 data along with systematic error quantification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 831. [Google Scholar]
- Srestasathiern, P.; Rakwatin, P. Oil Palm Tree Detection with High Resolution Multi-Spectral Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9749–9774. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Johnson, B.A.; Tian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Verrelst, J.; Mu, X.; Gu, X. Remote sensing algorithms for estimation of fractional vegetation cover using pure vegetation index values: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2020, 159, 364–377. [Google Scholar]
- Sarzynski, T.; Giam, X.; Carrasco, L.; Lee, J.S.H. Combining radar and optical imagery to map oil palm plantations in Sumatra, Indonesia, using the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1220. [Google Scholar]
- Clevers, J.; De Jong, S.M.; Epema, G.F.; Van Der Meer, F.D.; Bakker, W.H.; Skidmore, A.K.; Scholte, K.H. Derivation of the red edge index using the MERIS standard band setting. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3169–3184. [Google Scholar]
- Nurmasari, Y.A.A.W. Oil palm plantation detection in Indonesia using Sentinel-2 and Landsat-8 optical satellite imagery (case study: Rokan Hulu regency, Riau Province). Int. J. Remote Sens. Earth Sci. (IJRESES) 2021, 18, 3537. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, S.; Ishii, R.; Suhaili, A.B.; Kobayashi, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Ichie, T.; Motohka, T.; Kendawang, J.J.; Suzuki, R. Usability of noise-free daily satellite-observed green–red vegetation index values for monitoring ecosystem changes in Borneo. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 7910–7926. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanaiah, P.; Sathyanarayana, P.; GuruKumar, L. Image texture feature extraction using GLCM approach. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2013, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Tan, M.L.; Tew, Y.L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, T.; Samat, N.; Tangang, F.; Yusop, Z. Optimization of Open-Access Optical and Radar Satellite Data in Google Earth Engine for Oil Palm Mapping in the Muda River Basin, Malaysia. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Ledoux, L.; Salas, W.; Zhao, M. Regional Mapping of Plantation Extent Using Multisensor Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. On. Syst. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar]
- Conners, R.W.; Trivedi, M.M.; Harlow, C.A. Segmentation of a high-resolution urban scene using texture operators. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1984, 25, 273–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descals, A.; Szantoi, Z.; Meijaard, E.; Sutikno, H.; Rindanata, G.; Wich, S. Oil Palm (Elaeis guineensis) Mapping with Details: Smallholder versus Industrial Plantations and their Extent in Riau, Sumatra. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.P.; Kanniah, K.D.; Cracknell, A.P. Use of UK-DMC 2 and ALOS PALSAR for studying the age of oil palm trees in southern peninsular Malaysia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7424–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, N.; Dong, J. Examining earliest identifiable timing of crops using all available Sentinel 1/2 imagery and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2020, 161, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Dong, J.; Thi Thu Hien, T.; Yun, T.; Kou, W.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, G.; Lai, H.; Liu, R. A full time series imagery and full cycle monitoring (FTSI-FCM) algorithm for tracking rubber plantation dynamics in the Vietnam from 1986 to 2022. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2025, 220, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Gorelick, N.; Braaten, J.; Cavalcante, L.; Cohen, W.B.; Healey, S. Implementation of the LandTrendr algorithm on google earth engine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, E.T.S.; Simatupang, A.F.; Waluyo, S.; Indradewa, D. The growth of one year-old oil palms intercropped with soybean and groundnut. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, S. Analysis of a Pineapple-Oil Palm Intercropping System in Malaysia. Master’s Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, H.; Cracknell, A.P.; Kanniah, K.; Gong, P. Towards global oil palm plantation mapping using remote-sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5891–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizan, F.A.; Kiloes, A.M.; Astuti, I.S.; Abdul Aziz, A. Application of optical remote sensing in rubber plantations: A systematic review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Schwartz, M.D.; Fei, S. Validating satellite phenology through intensive ground observation and landscape scaling in a mixed seasonal forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Jacob, F.; Duveiller, G. Remote sensing for agricultural applications: A meta-review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, W.; Ciais, P.; Cheng, Y.; Gong, P. Annual oil palm plantation maps in Malaysia and Indonesia from 2001 to 2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Huang, J.; Tang, X. An effective and objective criterion for evaluating the performance of denoising filters. Pattern Recogn. 2012, 45, 2743–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhang, L.; Song, C.; Zhang, D.; Gao, H. Gradient histogram estimation and preservation for texture enhanced image denoising. IEEE T. Image Process 2014, 23, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar]
- de Araujo, A.F.; Constantinou, C.E.; Tavares, J.M.R. Smoothing of ultrasound images using a new selective average filter. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2016, 60, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayitakire, F.; Hamel, C.; Defourny, P. Retrieving forest structure variables based on image texture analysis and IKONOS-2 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüera, F.; Aguilar, F.J.; Aguilar, M.A. Using texture analysis to improve per-pixel classification of very high resolution images for mapping plastic greenhouses. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2008, 63, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampun, A.; Strange, H.; Zwiggelaar, R. Texture segmentation using different orientations of GLCM features. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Vision/Computer Graphics Collaboration Techniques and Applications, Berlin, Germany, 6–7 June 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Fu, H.; Yu, L.; Cracknell, A. Deep Learning Based Oil Palm Tree Detection and Counting for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarak, K.; Witayangkurn, A.; Kritiyutanont, K.; Arunplod, C.; Shibasaki, R. Oil palm tree detection and health classification on high-resolution imagery using deep learning. Agriculture 2021, 11, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttinaovarat, S.; Horkaew, P. Deep and machine learnings of remotely sensed imagery and its multi-band visual features for detecting oil palm plantation. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019, 12, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemura, A.; van Duren, I.; van Leeuwen, L.M. Determination of the age of oil palm from crown projection area detected from WorldView-2 multispectral remote sensing data: The case of Ejisu-Juaben district, Ghana. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2015, 100, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, E.; Convery, I.; Ramsey, A.D.; Simmons, E. Changing place: Palm oil and sense of place in Borneo. Hum. Geogr. J. Stud. Res. Hum. Geogr. 2012, 6, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.T.F.; Sims, J.P.; Ouyang, H.; Komšić, F.; Bettani, S.A. Nusantara’s Northern Neighbors: Brunei, Sabah, Sarawak, and the Prospects of a Pan-Borneo Railway in ASEAN. Unnes Political Sci. J. 2024, 8, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordway, E.M.; Naylor, R.L.; Nkongho, R.N.; Lambin, E.F. Oil palm expansion and deforestation in Southwest Cameroon associated with proliferation of informal mills. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaveau, D.L.; Sheil, D.; Husnayaen; Salim, M.A.; Arjasakusuma, S.; Ancrenaz, M.; Pacheco, P.; Meijaard, E. Rapid conversions and avoided deforestation: Examining four decades of industrial plantation expansion in Borneo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charters, L.J.; Aplin, P.; Marston, C.G.; Padfield, R.; Rengasamy, N.; Bin Dahalan, M.P.; Evers, S. Peat swamp forest conservation withstands pervasive land conversion to oil palm plantation in North Selangor, Malaysia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 7409–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, J.; Ghazoul, J.; Nelson, P.; Klintuni Boedhihartono, A. Oil palm expansion transforms tropical landscapes and livelihoods. Glob. Food Secur. 2012, 1, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosnier, A.; Boere, E.; Reumann, A.; Yowargana, P.; Pirker, J.; Havlík, P.; Pacheco, P. Palm Oil and Likely Futures: Assessing the Potential Impacts of Zero Deforestation Commitments and a Moratorium on Large-Scale Oil Palm Plantations in Indonesia; No. 51; CIFOR: Bogor, Indonesia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Colchester, M. Do commodity certification systems uphold indigenous peoples’ rights? Lessons from the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil and Forest Stewardship Council. Policy Matters 2016, 21, 150–165. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzherbert, E.B.; Struebig, M.J.; Morel, A.; Danielsen, F.; Brühl, C.A.; Donald, P.F.; Phalan, B. How will oil palm expansion affect biodiversity? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MS 2530:2022; Malaysian Sustainable Palm Oil (MSPO). Department of Standards Malaysia: Cyberjaya, Malaysia, 2022.
- Koh, P.L.; Wilcove, D.S.; Yu, H.; Fu, D.; Yuan, Z.; Tang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Kang, L.; Lyne, V.; Su, F. Regimes of global and national oil palm cultivations from 2001 to 2018. Glob. Environ. Change 2024, 86, 102845. [Google Scholar]
- Mansor, S.A.; Sarker, M.L.R. Remote sensing technique for estimating the age of oil palm using high resolution image. In Proceedings of the 36th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing 2015, Quezon, Phillipines, 24–28 October 2015; pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gaveau, D.; Locatelli, B.; Salim, M.A.; Husnayaen; Manurung, T.; Descals, A.; Angelsen, A.; Meijaard, E.; Sheil, D. Slowing deforestation in Indonesia follows declining oil palm expansion and lower oil prices. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e266178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aholoukpè, H.; Dubos, B.; Flori, A.; Deleporte, P.; Amadji, G.; Chotte, J.; Blavet, D. Estimating aboveground biomass of oil palm: Allometric equations for estimating frond biomass. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 292, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardana, I.K.; Wulandari, S.; Hartati, R.S. Urgency to accelerate replanting of Indonesian oil palm: A review of the role of seed institutions. Iop Conf. Series. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 974, 12104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hati, D.P.; Mulyani, A.; Nugroho, E.S. An estimation method for oil palm replanting potential in Kampar Regency, Province of Riau. Iop Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 757, 12034. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Elmore, A.J.; Lee, J.S.H.; Numata, I.; Zhang, X.; Cochrane, M.A. Replanting and yield increase strategies for alleviating the potential decline in palm oil production in Indonesia. Agric. Syst. 2023, 210, 103714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Navarrete, A.; Jansen, K. Oil palm expansion without enclosure: Smallholders and environmental narratives. In Global Land Grabbing and Political Reactions ‘from Below’; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 325–350. [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar, A.; Kasim, S.; Ishak, M.Y.; Uddin, M.K. Maximizing Oil Palm Yield: Innovative Replanting Strategies for Sustainable Productivity. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 5, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhebergen, T.; Fairhurst, T.; Whitbread, A.; Giller, K.E.; Zingore, S. Yield gap analysis and entry points for improving productivity on large oil palm plantations and smallholder farms in Ghana. Agr. Syst. 2018, 165, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, D.; Cheng, A.; Wei, H.; Stanley, D. Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2013, 80, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.N.; Ge, Y.; An, R.; Chen, Y. Enhancing land cover mapping through integration of pixel-based and object-based classifications from remotely sensed imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghraoui, K.; Sebari, I.; Bensiali, S.; El Kadi, K.A. Can Pixel-Based Approach Achieve Similar Performance to Area-Based Approach in Crop Yield Forecasting Using Sentinel-2 Imagery and Deep Neural Networks? A Probabilistic Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Technology Innovation and Its Applications (ICTIIA), Medan, Indonesia, 12–13 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pouyanfar, S.; Sadiq, S.; Yan, Y.; Tian, H.; Tao, Y.; Reyes, M.P.; Shyu, M.L.; Chen, S.C.; Iyengar, S.S. A survey on deep learning: Algorithms, techniques, and applications. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2018, 51, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargan, S.; Kumar, M.; Ayyagari, M.R.; Kumar, G. A survey of deep learning and its applications: A new paradigm to machine learning. Arch. Comput. Method Eng. 2020, 27, 1071–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gu, X.; Tang, L.; Yin, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y. Application of machine learning, deep learning and optimization algorithms in geoengineering and geoscience: Comprehensive review and future challenge. Gondwana Res. 2022, 109, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
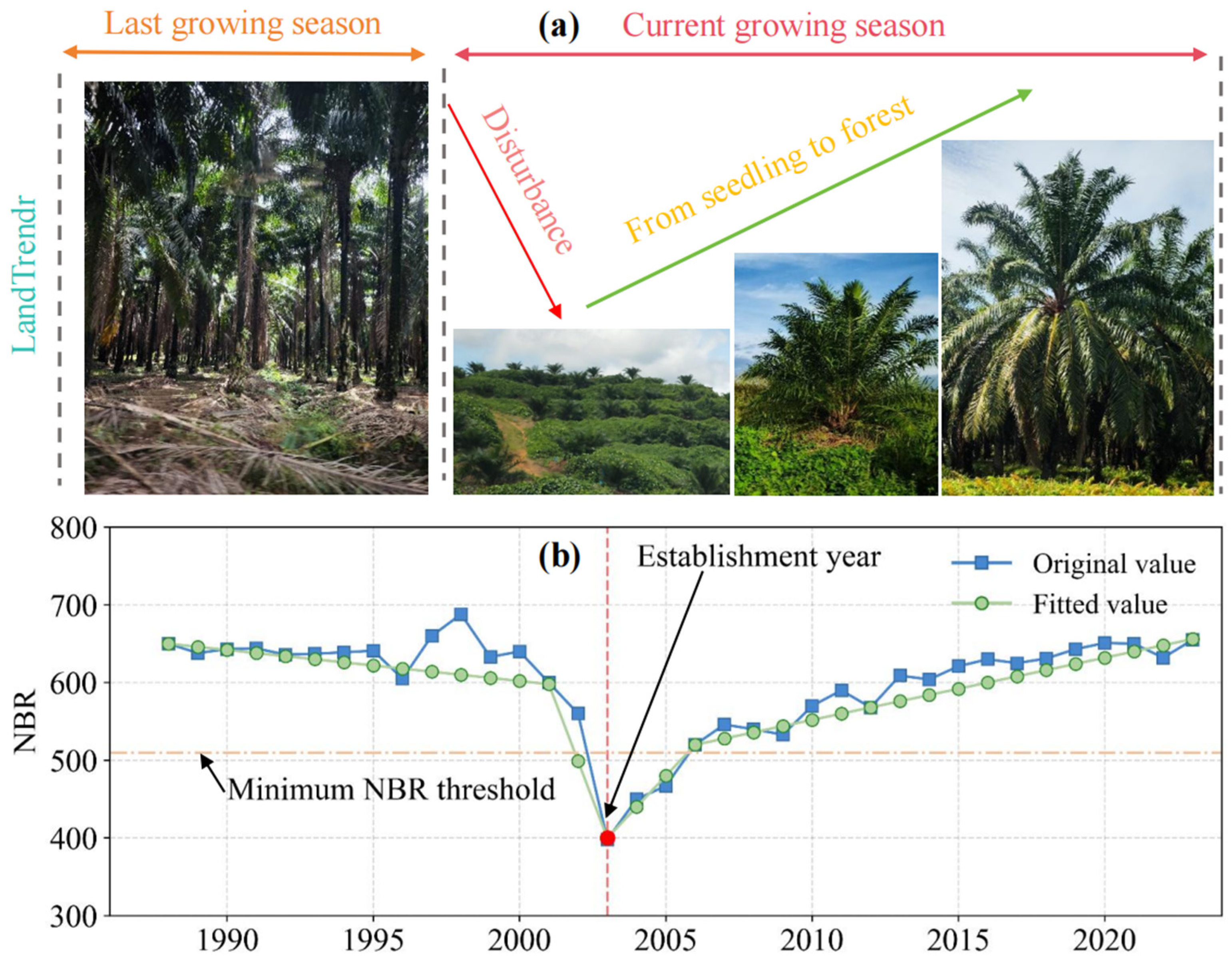
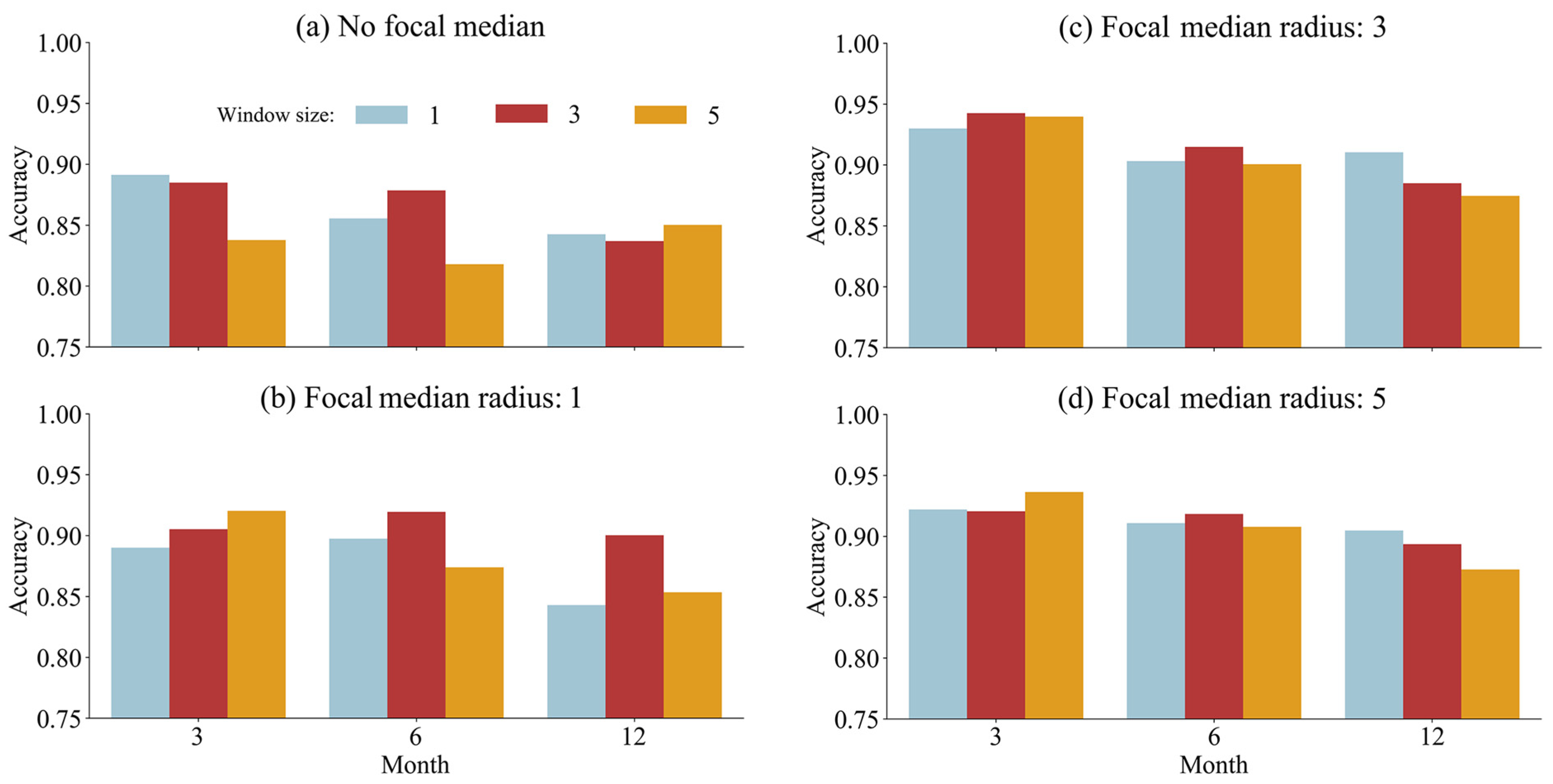
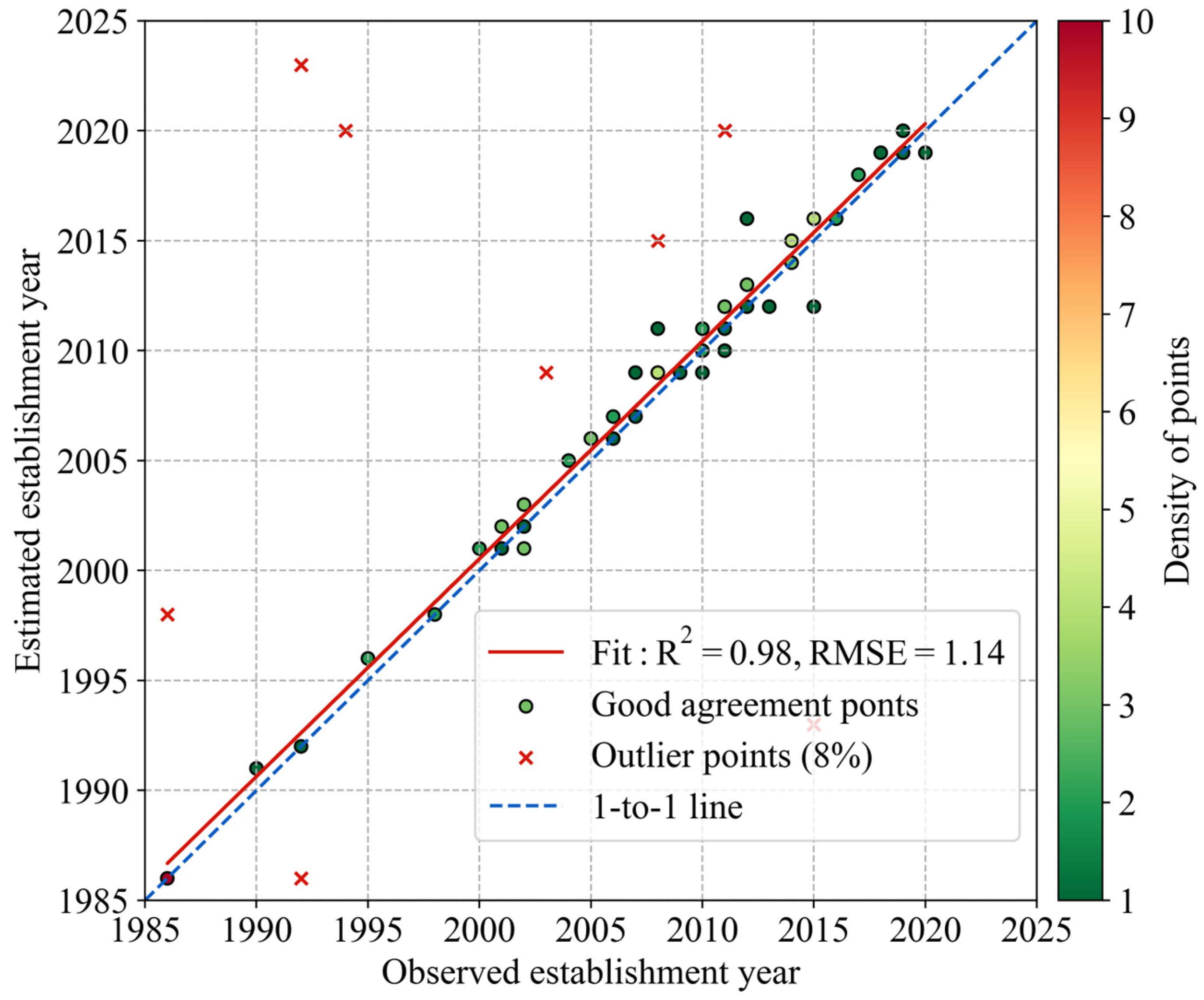
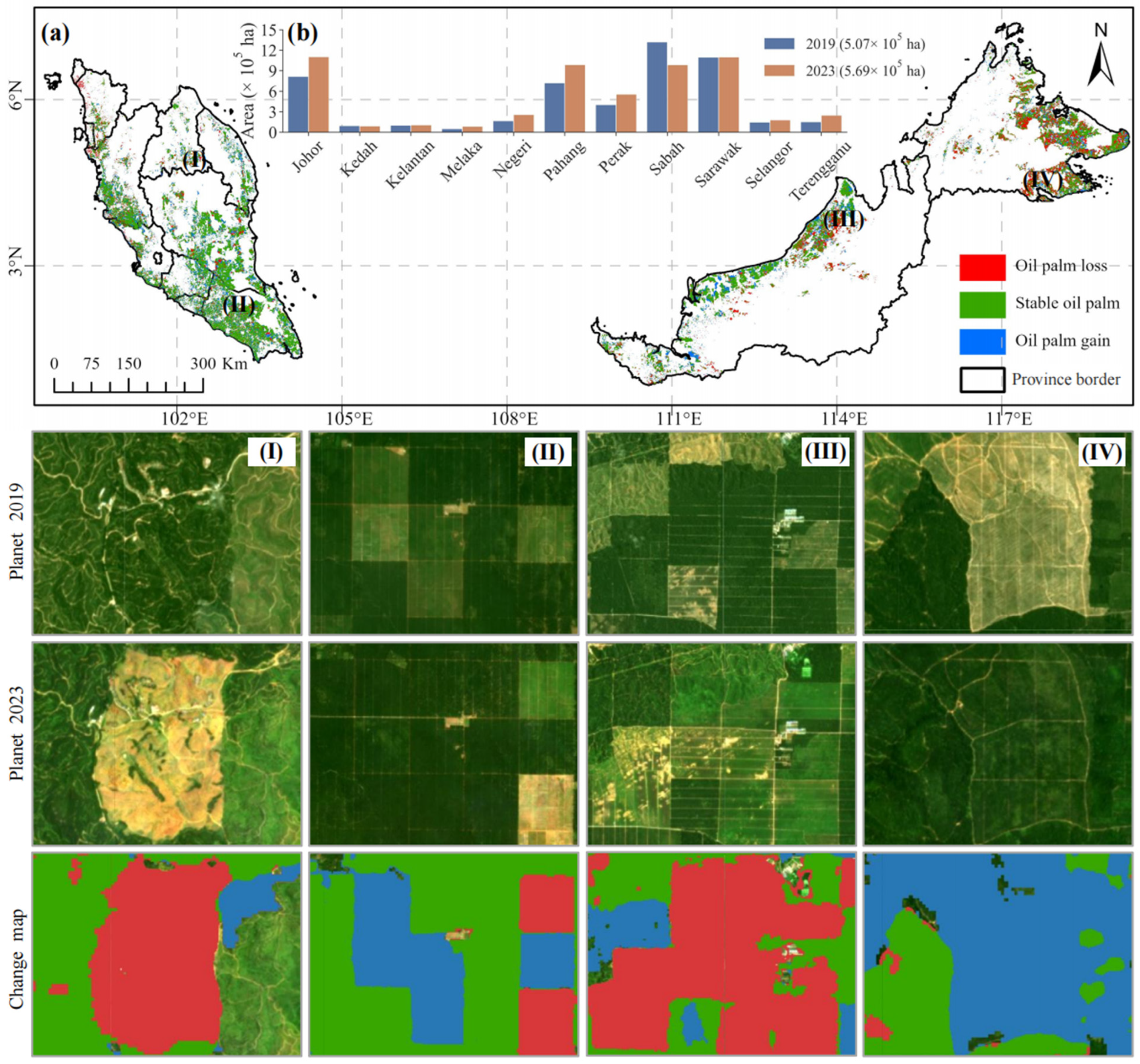
| Sample | User’s Acc. | Overall Acc. | Kappa | F1-Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil Palms | Non-Oil Palms | Total | |||||||
| 2023 | Classification | Oil Palms | 1594 | 88 | 1682 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.89 |
| Non-Oil Palms | 114 | 1916 | 2030 | 0.94 | |||||
| Total | 1708 | 2004 | 3712 | ||||||
| Producer’s Acc. | 0.93 | 0.96 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Ong-Abdullah, M.; Wu, Z.; Lan, G.; Azmi Tohiran, K.; Amit, B.; Lai, H.; Wang, G.; et al. Integrating Multi-Temporal Landsat and Sentinel Data for Enhanced Oil Palm Plantation Mapping and Age Estimation in Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162908
Li C, Chen B, Wang X, Ong-Abdullah M, Wu Z, Lan G, Azmi Tohiran K, Amit B, Lai H, Wang G, et al. Integrating Multi-Temporal Landsat and Sentinel Data for Enhanced Oil Palm Plantation Mapping and Age Estimation in Malaysia. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162908
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Caihui, Bangqian Chen, Xincheng Wang, Meilina Ong-Abdullah, Zhixiang Wu, Guoyu Lan, Kamil Azmi Tohiran, Bettycopa Amit, Hongyan Lai, Guizhen Wang, and et al. 2025. "Integrating Multi-Temporal Landsat and Sentinel Data for Enhanced Oil Palm Plantation Mapping and Age Estimation in Malaysia" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162908
APA StyleLi, C., Chen, B., Wang, X., Ong-Abdullah, M., Wu, Z., Lan, G., Azmi Tohiran, K., Amit, B., Lai, H., Wang, G., Yun, T., & Kou, W. (2025). Integrating Multi-Temporal Landsat and Sentinel Data for Enhanced Oil Palm Plantation Mapping and Age Estimation in Malaysia. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162908












