DASeg: A Domain-Adaptive Segmentation Pipeline Using Vision Foundation Models—Earthquake Damage Detection Use Case
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Limitations of Aerial-Based Disaster Damage Assessment
2.2. Disaster Damage Assessment Studies on Social Media Images
2.3. Semantic Segmentation of SAM
2.4. Explainability in Computer Vision
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Preparation
3.1.1. EID Dataset
3.1.2. DSS Dataset
- 1.
- We relabeled entire buildings as Damaged Structure if any part of the building was originally labeled as Damaged Structure, shifting the focus from damaged subregions to the identification of the whole building.
- 2.
- We converted the original three-class labels into a binary classification task by merging the Damaged Structure and Debris categories into a single Damaged class, while treating all other pixels as Undamaged.
3.1.3. Bounding Box Annotation
- Preferably, each object (e.g., building or debris) should be enclosed by a single bounding box, with background pixels comprising no more than approximately 25% to 35% of the total bounding box area.
- Limit the labeling of each damaged structure to a maximum of two bounding boxes, with each box clearly containing a distinct, identifiable part of the structure. For debris objects with less defined boundaries, using more than two bounding boxes is permissible.
- Bounding boxes should be delineated based on objects as they visibly appear in the original image, rather than solely aligning with segmented mask labels.
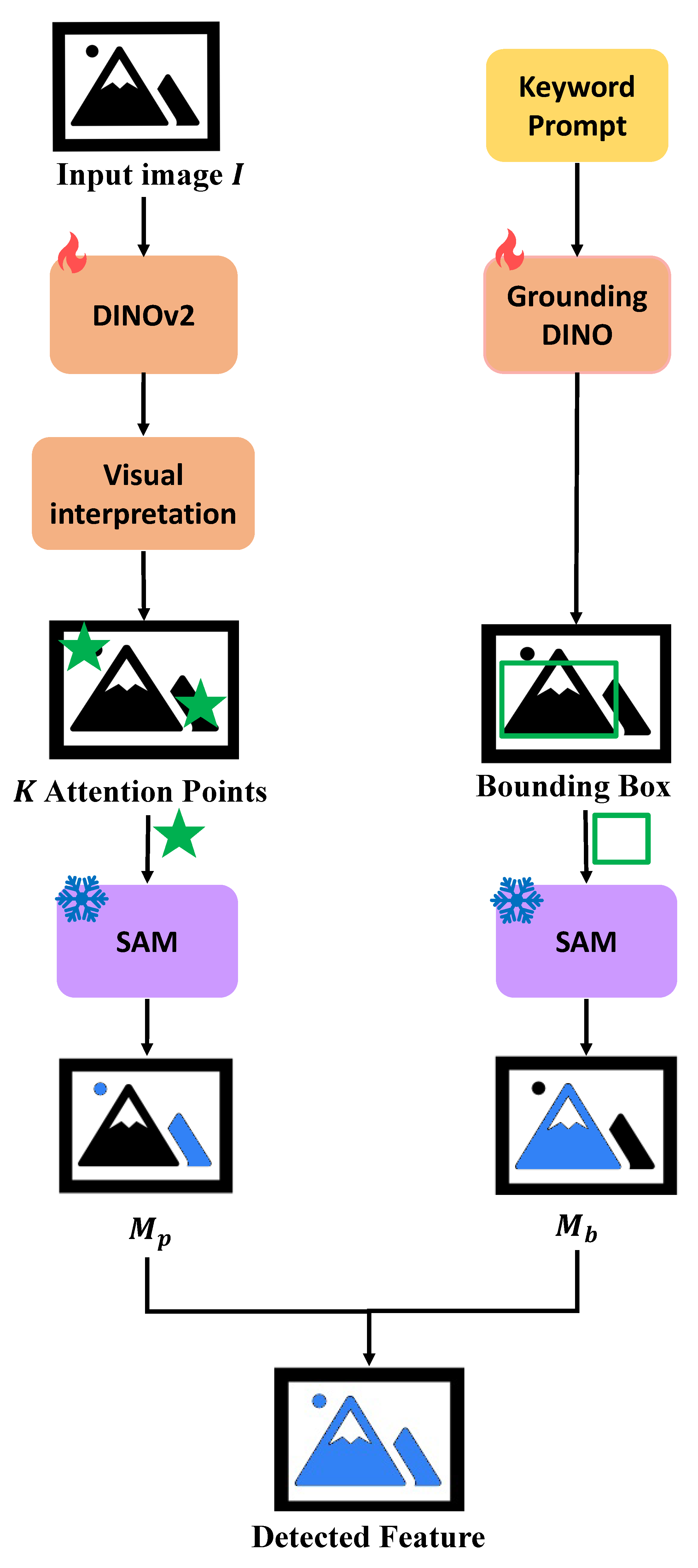
3.2. Point Prompt Generation from Saliency Map
3.3. Box Prompt Generation from Grounding DINO
3.4. Mask Fusion
3.5. Evaluation Metrics
4. Experimental Methodology
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Point Prompts Analysis
5.1.1. Number of Point Prompts
5.1.2. Threshold for Attention Map
5.1.3. Backbone Model Comparison
5.2. BBox Annotation Analysis
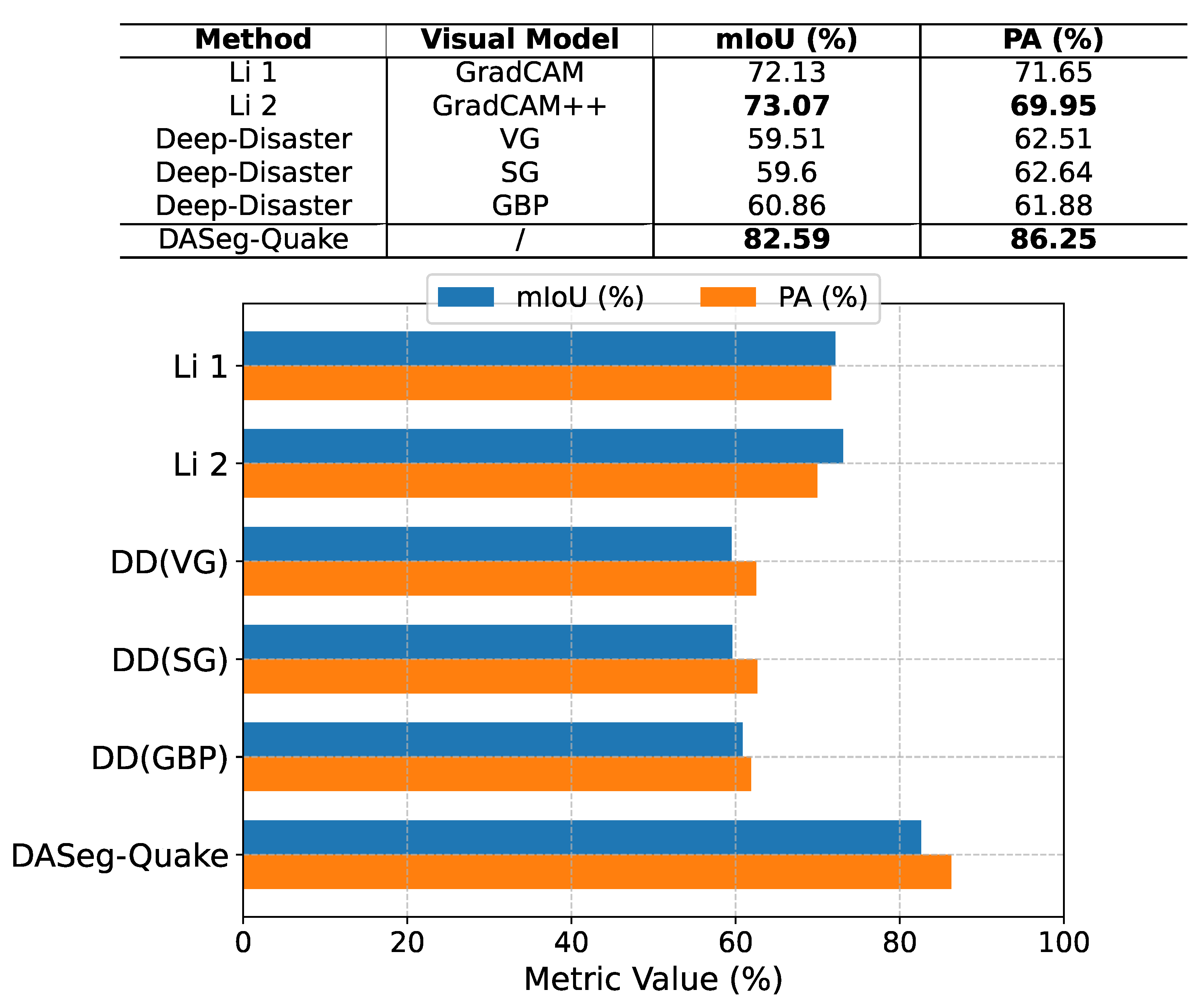
5.3. Comparison with Previous Related Work
- Deep-Disaster [41]: Employing Vanilla Gradient (VG), Smooth Gradient (SG), and Guided Back-Propagation (GBP) techniques based on a model trained with Knowledge Distillation (KD) methods.
5.4. Comparison with Supervised Learning
5.5. Visualization of DASeg
5.6. DASeg for Earthquake-Induced Geo-Damage
5.7. Error Analysis and Limitations
- 1.
- False positives on unrelated objects: In Rows 1–2, DASeg-Quake mistakenly labels low-contrast foreground instances such as person and car as damaged regions. The underlying issue is the frozen Segment Anything (SAM) backbone: SAM’s embedding quality deteriorates on low-contrast features, leading to over-segmentation of irrelevant objects [14].
- 2.
- Missed damage along high-contrast boundaries: Rows 3–4 illustrate the opposite problem: debris and buildings that meet at a sharp edge are only partially covered. SAM treats this edge as an object boundary and truncates the mask, omitting the adjoining damaged pixels. In the DASeg-Quake result for Row 3, a distinct gap separates the debris region from the damaged building segment on the right.
5.8. Motivation for Fine-Tuning in Abnormal Pattern Segmentation
5.9. Robustness of Hyperparameter Selection
5.10. Annotation Efficiency and Computational Trade-Offs in DASeg-Quake
5.11. Potential Application for DASeg
6. Future Work
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Earle, P.S.; Wald, D.J.; Jaiswal, K.S.; Allen, T.I.; Hearne, M.G.; Marano, K.D.; Hotovec, A.J.; Fee, J.M. Prompt Assessment of Global Earthquakes for Response (PAGER): A System for Rapidly Determining the Impact of Earthquakes Worldwide; Open-File Report 2009–1131; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2009. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2009/1131/ (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- El-Tawil, S.; Aguirre, B.E. Search and rescue in collapsed structures: Engineering and social science aspects. Disasters 2010, 34, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Goodman, B.; Patel, N.; Hosfelt, R.; Sajeev, S.; Heim, E.; Doshi, J.; Lucas, K.; Choset, H.; Gaston, M. Creating xBD: A Dataset for Assessing Building Damage from Satellite Imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Ofli, F.; Imran, M.; Mitra, P. Damage assessment from social media imagery data during disasters. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), Sydney, Australia, 31 July–3 August 2017; Diesner, J., Ferrari, E., Xu, G., Eds.; Association for Computing Machinery, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the ECCV; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Ranzato, M., Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y., Liang, P., Vaughan, J.W., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Sydney, Australia, 2021; Volume 34, pp. 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-Attention Mask Transformer for Universal Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Dong, L.; Piao, S.; Wei, F. BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers. In Proceedings of the ICLR, Online, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Mai, G.; Hu, M.; Guan, Z.; Li, S.; Mu, L. Text2seg: Remote sensing image semantic segmentation via text-guided visual foundation models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.10597. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Qiao, Y.; Zheng, S.; Dam, S.K.; Zhang, M.; Kim, J.U.; Kim, S.T.; Choi, J.; et al. One small step for generative ai, one giant leap for agi: A complete survey on chatgpt in aigc era. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.06488. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; Haase-Schütz, C.; Rosenbaum, L.; Hertlein, H.; Gläser, C.; Timm, F.; Wiesbeck, W.; Dietmayer, K. Deep Multi-Modal Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation for Autonomous Driving: Datasets, Methods, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.; Touvron, H.; Misra, I.; Jegou, H.; Mairal, J.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A. Emerging Properties in Self-Supervised Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 9630–9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oquab, M.; Darcet, T.; Moutakanni, T.; Vo, H.V.; Szafraniec, M.; Khalidov, V.; Fernandez, P.; Haziza, D.; Massa, F.; El-Nouby, A.; et al. DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.07193. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 3992–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; Meila, M., Zhang, T., Eds.; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research (PMLR): Brookline, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 139, pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Puspitasari, F.D.; Zheng, S.; Li, C.; Qiao, Y.; Kang, T.; Shan, X.; Zhang, C.; Qin, C.; Rameau, F.; et al. A survey on segment anything model (sam): Vision foundation model meets prompt engineering. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.06211. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the ECCV; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Scene Parsing Through ADE20K Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Shi, J.; Gu, L. A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 169, 114417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghanaki, S.A.; Abhishek, K.; Cohen, J.P.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Hamarneh, G. Deep semantic segmentation of natural and medical images: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 54, 137–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; et al. Grounding dino: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.05499. [Google Scholar]
- Englebert, A.; Stassin, S.; Nanfack, G.; Mahmoudi, S.A.; Siebert, X.; Cornu, O.; De Vleeschouwer, C. Explaining Through Transformer Input Sampling. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 806–815. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, C.M.; Blair, J.; Nevill-Manning, C.; Smith, D.; Soroker, D.; Valero, M.; Wilkin, P. Next-generation geospatial-temporal information technologies for disaster management. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2020, 64, 5:1–5:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, B.J.; Karimi, H.A. Deep learning-enabled semantic inference of individual building damage magnitude from satellite images. Algorithms 2020, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxar. Open Data Program. 2025. Available online: https://www.maxar.com/open-data (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Geotechnical Extreme Events Reconnaissance (GEER) Association. Geotechnical Extreme Events Reconnaissance (GEER) Association. 2025. Available online: https://www.geerassociation.org/ (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)—National Geodetic Survey. Emergency Response Imagery Online Viewer. 2025. Available online: https://storms.ngs.noaa.gov/ (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Da, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, Y. Building damage assessment based on Siamese hierarchical transformer framework. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, F.; Galasso, C.; Cremen, G.; Dall’Asta, A.; Di Sarno, L.; Giaralis, A.; Gutiérrez-Urzúa, F.; Málaga-Chuquitaype, C.; Mitoulis, S.; Petrone, C.; et al. Innovations in earthquake risk reduction for resilience: Recent advances and challenges. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 60, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEER Association; EERI Learning From Earthquakes Program. 2023 Türkiye Earthquake Sequence: Preliminary Virtual Reconnaissance Report; Virtual Reconnaissance Report GEER-082; Geotechnical Extreme Events Reconnaissance (GEER) Association & Earthquake Engineering Research Institute (EERI), Kahramanmaraş: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023; Report date: 6 May 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEER Association; EERI Learning From Earthquakes Program. February 6, 2023 Türkiye Earthquakes: Reconnaissance Report on Geotechnical and Structural Impacts; Full Reconnaissance Report GEER-082; Geotechnical Extreme Events Reconnaissance (GEER) Association & Earthquake Engineering Research Institute (EERI): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Gupta, R.; Fobi Nsutezo, S.; Pound, E.; Ortiz, A.; Rosa, M.; White, K.; Dodhia, R.; Zolli, A.; Birge, C.; et al. Turkey Earthquake Report; Technical Report MSR-TR-2023-7; Microsoft: Redmond, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, F.; Imran, M.; Ofli, F. Image4Act: Online Social Media Image Processing for Disaster Response. In Proceedings of the2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 31 July–3 August 2017; pp. 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Alam, F.; Ofli, F.; Imran, M. Automatic Image Filtering on Social Networks Using Deep Learning and Perceptual Hashing During Crises. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.02602. [Google Scholar]
- Nia, K.R.; Mori, G. Building Damage Assessment Using Deep Learning and Ground-Level Image Data. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 16–19 May 2017; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, F.; Alam, T.; Hasan, M.A.; Hasnat, A.; Imran, M.; Ofli, F. MEDIC: A Multi-Task Learning Dataset for Disaster Image Classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Masalava, A.; Roozbahani, M.M.; Roy, N.; Frost, J.D. Enhancing the Fidelity of Social Media Image Data Sets in Earthquake Damage Assessment. Earthq. Spectra 2025, 41, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Caragea, D.; Zhang, H.; Imran, M. Localizing and quantifying damage in social media images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), Barcelona, Spain, 28–31August 2018; pp. 194–201. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Caragea, D.; Zhang, H.; Imran, M. Localizing and quantifying infrastructure damage using class activation mapping approaches. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2019, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekarizadeh, S.; Rastgoo, R.; Al-Kuwari, S.; Sabokrou, M. Deep-Disaster: Unsupervised Disaster Detection and Localization Using Visual Data. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 2814–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Alam, T.; Ofli, F.; Imran, M. Social Media Images Classification Models for Real-time Disaster Response. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.04184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, H.; Smith, N.S.; Roy, N.; Frost, J.D. From Pixels to Damage Severity: Estimating Earthquake Impacts Using Semantic Segmentation of Social Media Images. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.02781. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M., Lin, H., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Sydney, Australia, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-Resolution Image Synthesis With Latent Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, K.; Huang, C.; Loy, C.C. Open-Vocabulary DETR with Conditional Matching. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, N.; Gabeur, V.; Hu, Y.T.; Hu, R.; Ryali, C.; Ma, T.; Khedr, H.; Rädle, R.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; et al. Sam 2: Segment anything in images and videos. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.00714. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Osco, L.P. samgeo: A Python package for segmenting geospatial data with the Segment Anything Model (SAM). J. Open Source Softw. 2023, 8, 5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. RSPrompter: Learning to Prompt for Remote Sensing Instance Segmentation Based on Visual Foundation Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4701117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Y.; Diao, W.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. RingMo-SAM: A Foundation Model for Segment Anything in Multimodal Remote-Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5625716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Jia, H.; Zheng, L.; Wang, F.; Xu, F. ClassWise-SAM-Adapter: Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Adapts Segment Anything to SAR Domain for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Pu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, F. Tuning a SAM-Based Model With Multicognitive Visual Adapter to Remote Sensing Instance Segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Feng, J.; Liang, X.; Cheng, M.M.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, S. Object Region Mining with Adversarial Erasing: A Simple Classification to Semantic Segmentation Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1568–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.T.; Zhang, C.B.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M.; Wei, Y. LayerCAM: Exploring Hierarchical Class Activation Maps. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 5875–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, W. Deep Graph Cut Network for Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 130105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, À.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.04150. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhay, A.; Sarkar, A.; Howlader, P.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Grad-CAM++: Generalized Gradient-Based Visual Explanations for Deep Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 839–847. [Google Scholar]
- Abnar, S.; Zuidema, W. Quantifying Attention Flow in Transformers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.00928. [Google Scholar]
- Voita, E.; Talbot, D.; Moiseev, F.; Sennrich, R.; Titov, I. Analyzing Multi-Head Self-Attention: Specialized Heads Do the Heavy Lifting, the Rest Can Be Pruned. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.09418. [Google Scholar]
- Chefer, H.; Gur, S.; Wolf, L. Generic Attention-Model Explainability for Interpreting Bi-Modal and Encoder-Decoder Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 397–406. [Google Scholar]
- Chefer, H.; Gur, S.; Wolf, L. Transformer Interpretability Beyond Attention Visualization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 782–791. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Li, X.H.; Cao, C.C.; Zhang, N.L. ViT-CX: Causal Explanation of Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Thirty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-23, Macao, 19–25 August 2023; Elkind, E., Ed.; pp. 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.I.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The PASCAL Visual Object Classes Challenge 2011 (VOC2011) Results. Available online: http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2011/guidelines.html (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 4 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. A k-means clustering algorithm. JSTOR Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.14030. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Sabuncu, M.R. Generalized Cross Entropy Loss for Training Deep Neural Networks with Noisy Labels. In Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2018), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab Detection Toolbox and Benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. BreastSAM: A Study of Segment Anything Model for Breast Tumor Detection in Ultrasound Images. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.12447. [Google Scholar]
- Raveendran, S.; Patil, M.D.; Birajdar, G.K. Underwater image enhancement: A comprehensive review, recent trends, challenges and applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 5413–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. GPT-4V(ision) Technical Report. 2023. Available online: https://openai.com/research/gpt-4v-system-card (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Xiong, C.; Hoi, S.C. BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 12885–12900. [Google Scholar]
- Minderer, M.; Gritsenko, A.A.; Stone, A.; Neumann, M.; Weissenborn, D.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Mahendran, A.; Arnab, A.; Dehghani, M.; Shen, Z.; et al. Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.06230. [Google Scholar]
- Tangkaratt, V.; Han, B.; Khan, M.E.; Sugiyama, M. VILD: Variational Imitation Learning with Diverse-quality Demonstrations. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.; Hwang, J.N.; et al. Grounded Language-Image Pre-training. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, L.H.; Dai, X.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L.; Hwang, J.N.; Gao, J. GLIPv2: Unifying Localization and Vision-Language Understanding. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.05836. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, A.; Singh, M.; LeCun, Y.; Misra, I.; Synnaeve, G.; Carion, N. MDETR–Modulated Detection for End-to-End Multi-Modal Understanding. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.12763. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Li, X.-H.; Cao, C.C.; Zhang, N.L. ViT-CX: Causal Explanation of Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Vienna, Austria, 23–29 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, S.; Binder, A.; Montavon, G.; Klauschen, F.; Müller, K.R.; Samek, W. On pixel-wise explanations for non-linear classifier decisions by layer-wise relevance propagation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfeld, Z.; van den Berg, E.; Greenewald, K.; Melnyk, I.; Nguyen, N.; Kingsbury, B.; Polyanskiy, Y. Estimating Information Flow in Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.05728. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Fang, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, P.; Zang, Y.; Kong, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D.; Wang, J. Alpha-CLIP: A CLIP Model Focusing on Wherever You Want. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.03818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Dataset | Image Source(s) | Disaster Events (year) | #Classes | #Images | Task | Resolution Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EID [38] | X (Twitter) | Nepal (2015) Illapel (2015) Ecuador (2016) Mexico (2017) Iran–Iraq (2017) | 4 | 13,513 | Classification | 48 × 48– 7191 × 4571 pixels |
| DSS [43] | Wenchuan (2008) Haiti (2010) Nepal (2015) Türkiye (2023) Morocco (2023) | 3 | 607 | Semantic segmentation | 250 × 213– 8258 × 5505 pixels |
| R | Annotator A% | Annotator B% | Avg% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0∼5% | 83.3 | 82.6 | 83.0 |
| 25∼35% | 85.5 | 86.5 | 86.0 |
| 45∼55% | 83.8 | 85.5 | 84.7 |
| 75∼85% | 83.3 | 83.4 | 83.4 |
| 95∼100% | 84.3 | 84.9 | 84.6 |
| Threshold | mIoU (%) | PA (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 80.8 | 84.3 |
| 0.6 | 81.1 | 84.7 |
| 0.7 | 81.2 | 85.0 |
| 0.8 | 82.6 | 86.3 |
| 0.9 | 80.5 | 84.9 |
| Model Variant | Num of Blocks | Acc (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DINOv2-S | 1 | 90.7 | 90.1 |
| – | 3 | 91.3 | 90.8 |
| – | 5 | 91.0 | 90.5 |
| – | All | 91.0 | 90.7 |
| DINOv2-B | 1 | 91.6 | 91.3 |
| – | 3 | 92.1 | 92.2 |
| – | 5 | 91.7 | 91.6 |
| – | All | 91.6 | 91.3 |
| DINOv2-L | 1 | 90.3 | 89.8 |
| – | 3 | 91.6 | 91.2 |
| – | 5 | 90.4 | 89.9 |
| – | All | 90.4 | 89.7 |
| mIoU (%) | PA (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Annotator A | 79.86 | 87.86 |
| Annotator B | 79.82 | 87.89 |
| Final BBox | 81.56 | 88.19 |
| Disaster Type | Annotator A vs. B | DASeg-Quake (Zero-Shot) vs. B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mIoU (%) | PA (%) | mIoU (%) | PA (%) | ||
| Lateral Spreading | 79.87 | 83.31 | 68.41 | 83.81 | |
| Rupture | 82.03 | 85.29 | 69.24 | 81.47 | |
| Landslide | 81.59 | 84.38 | 74.98 | 92.15 | |
| Sinkhole | 92.22 | 95.93 | 87.49 | 95.98 | |
| Average | 83.93 | 87.23 | 75.03 | 88.35 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, D.; Roozbahani, M.M.; Frost, J.D. DASeg: A Domain-Adaptive Segmentation Pipeline Using Vision Foundation Models—Earthquake Damage Detection Use Case. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162812
Huang H, Zhang A, Zhang D, Roozbahani MM, Frost JD. DASeg: A Domain-Adaptive Segmentation Pipeline Using Vision Foundation Models—Earthquake Damage Detection Use Case. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162812
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Huili, Andrew Zhang, Danrong Zhang, Max Mahdi Roozbahani, and James David Frost. 2025. "DASeg: A Domain-Adaptive Segmentation Pipeline Using Vision Foundation Models—Earthquake Damage Detection Use Case" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162812
APA StyleHuang, H., Zhang, A., Zhang, D., Roozbahani, M. M., & Frost, J. D. (2025). DASeg: A Domain-Adaptive Segmentation Pipeline Using Vision Foundation Models—Earthquake Damage Detection Use Case. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162812









