Using Multitask Machine Learning to Type Clouds and Aerosols from Space-Based Photon-Counting Lidar Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. CATS Data Products
2.2. CATS Operational Algorithm
2.3. CNN Multitask Learning Approach
2.4. Dataset Preparation
2.5. Model Optimization and Evaluation
2.6. Implementation Details
3. Results and Discussion
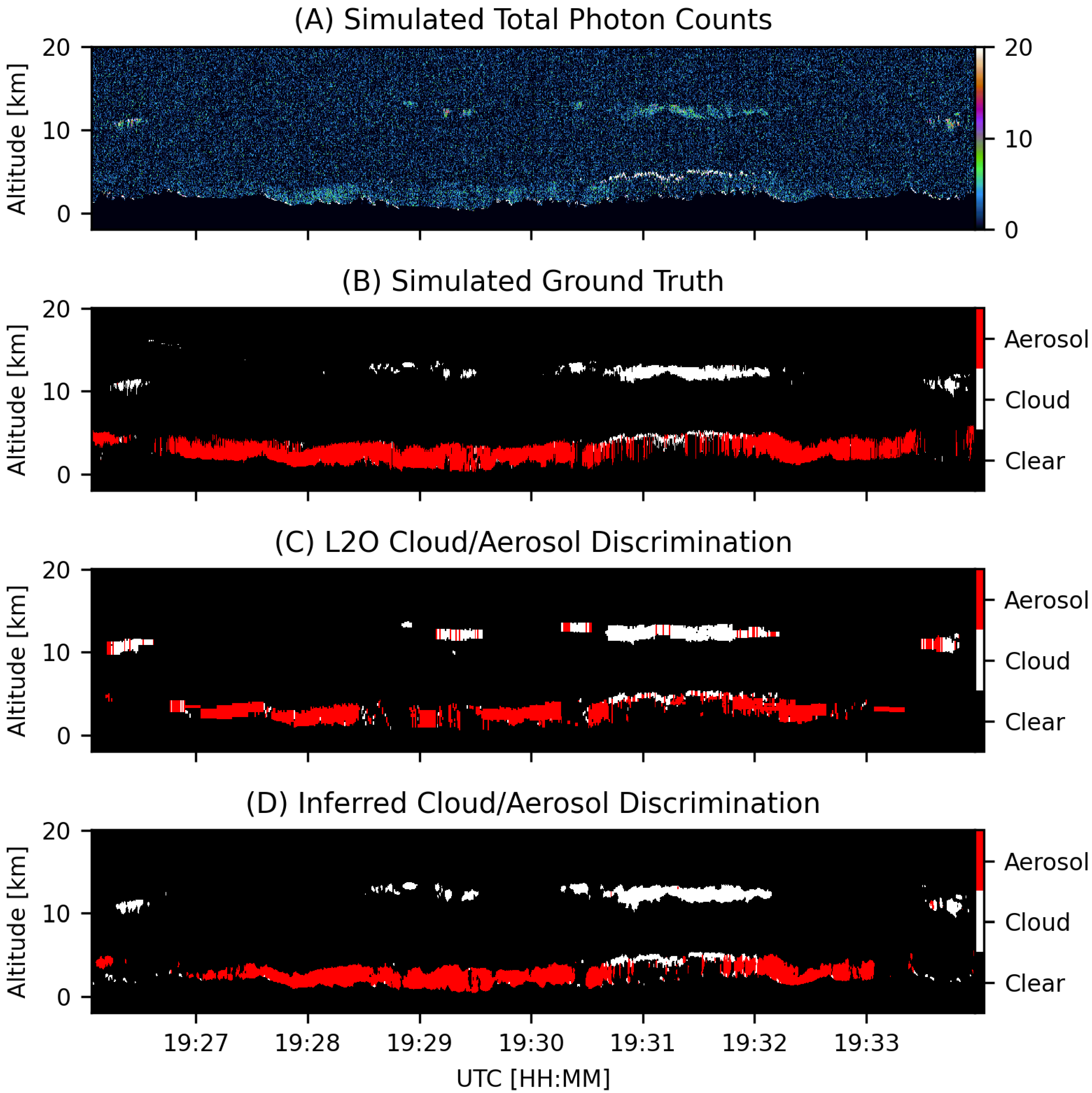
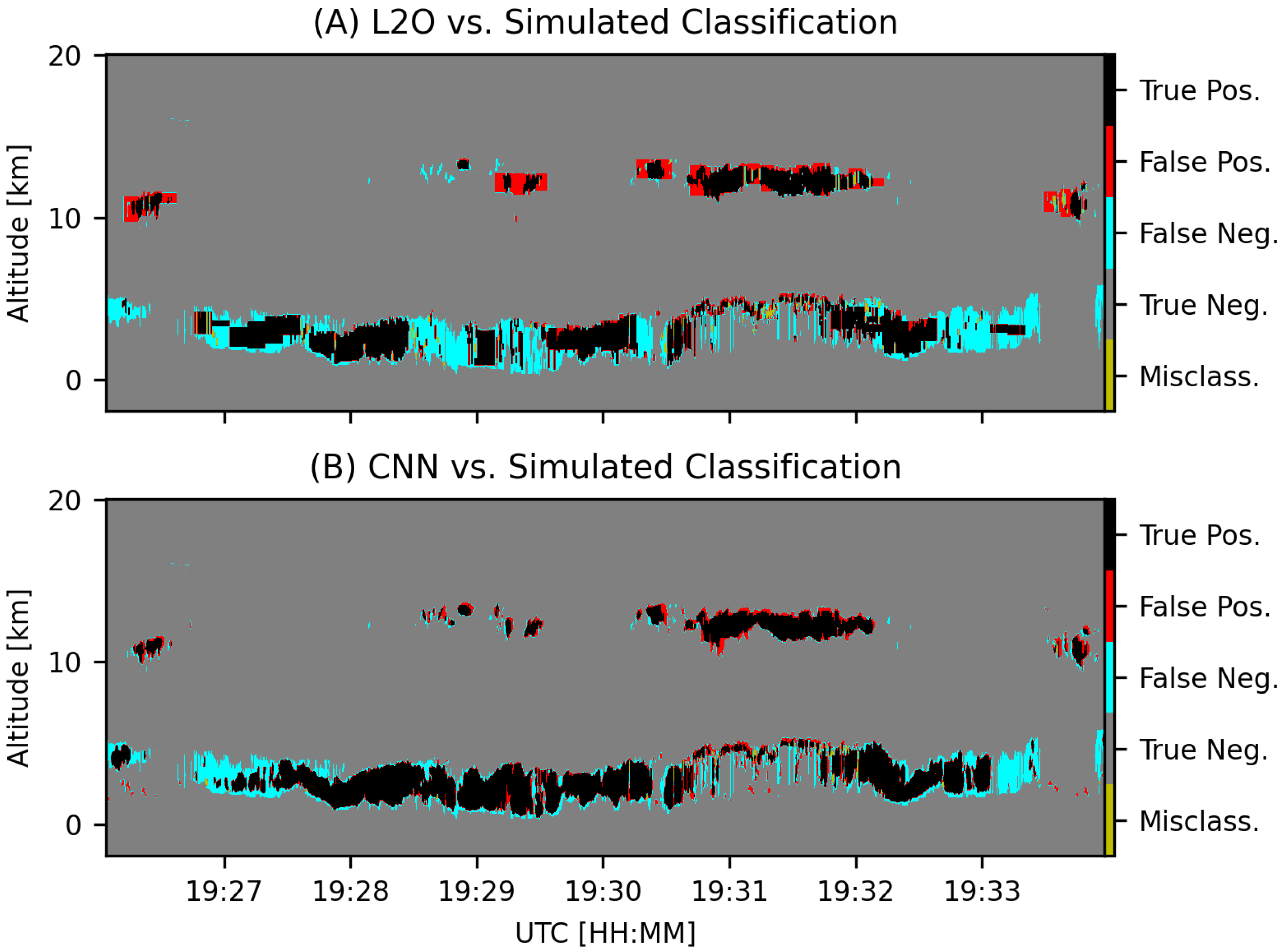
3.1. Layer Detection and CAD
3.2. Cloud Phase Typing
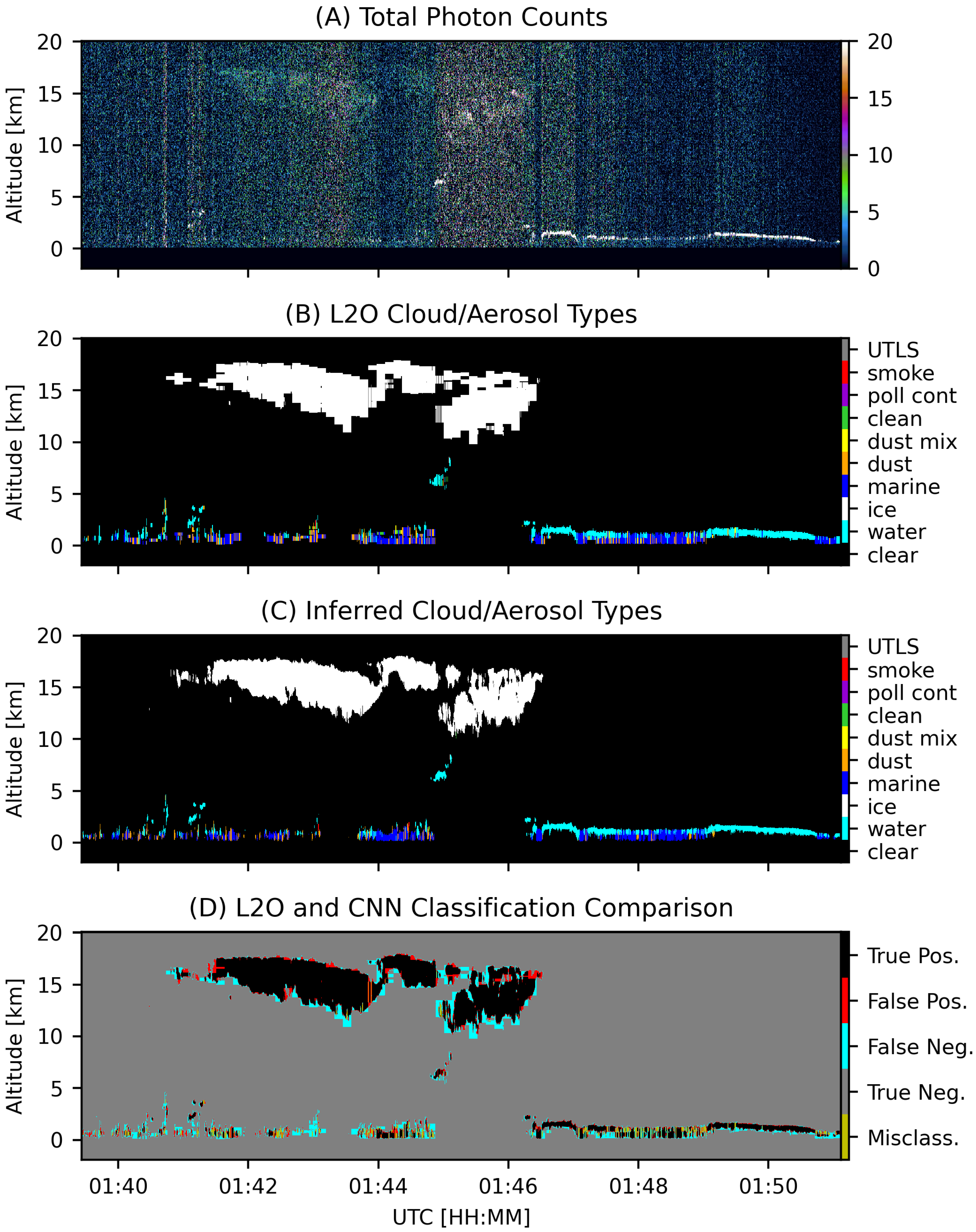
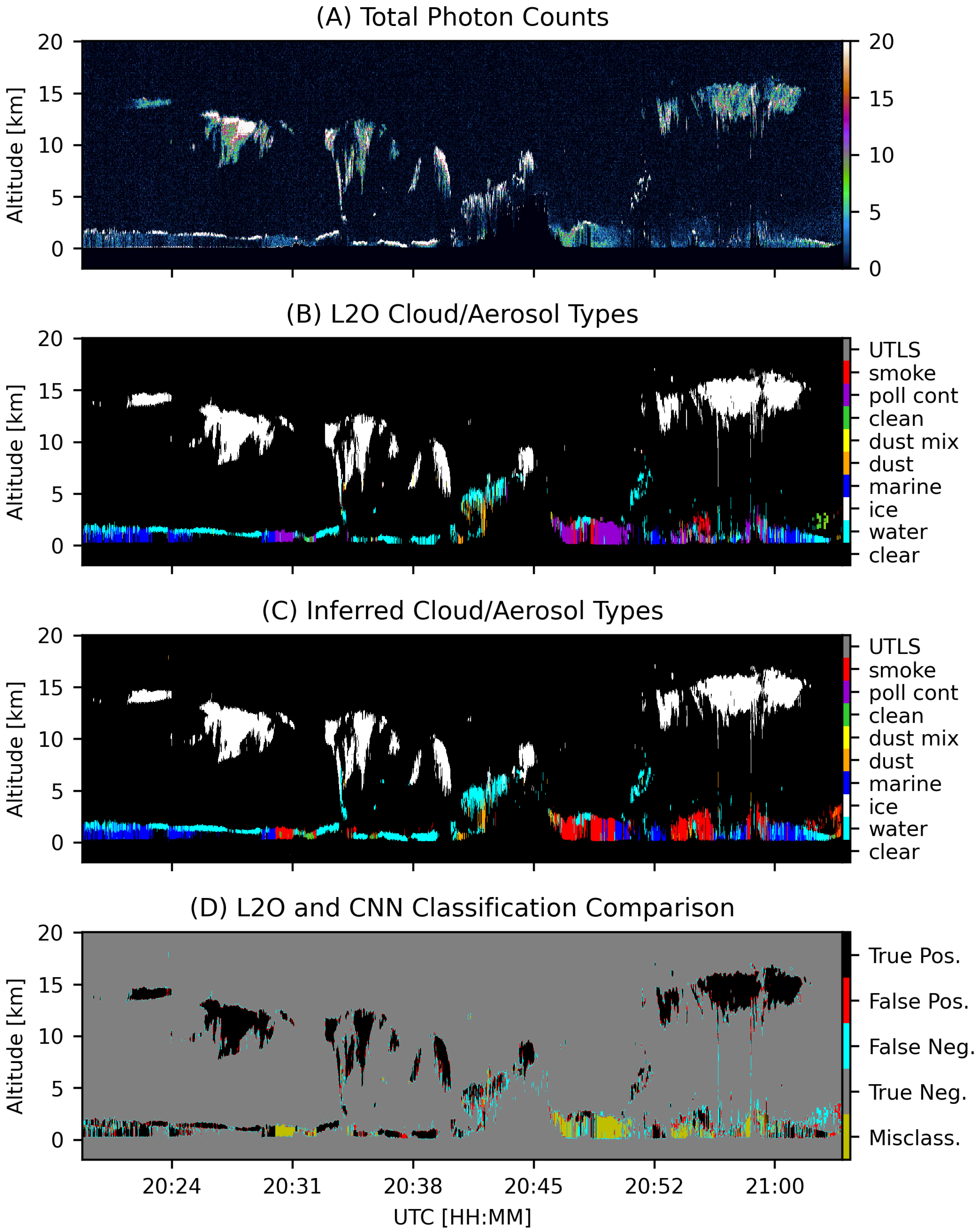
3.3. Aerosol Typing
3.4. Current Limitations
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACATS | Airborne Cloud–Aerosol Transport System |
| ATBD | Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document |
| CAD | Cloud–Aerosol Discrimination |
| CATS | Cloud–Aerosol Transport System |
| CALIPSO | Cloud–Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CPL | Cloud Physics Lidar |
| FN | false negative |
| FP | false positive |
| GEOS-5 | NASA Goddard Earth Observing System version 5 |
| ICESat-2 | Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite-2 |
| ISS | International Space Station |
| MERRA-2 | Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 |
| NRB | Normalized Relative Backscatter |
| Probability Density Function | |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| TN | true negative |
| TP | true positive |
| UTLS | Upper Troposphere Lower Stratosphere |
| VFM | Vertical Feature Mask |
References
- Hunt, W.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Powell, K.A.; Lucker, P.L.; Weimer, C. CALIPSO Lidar Description and Performance Assessment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, T.; Neumann, T.; Martino, A.; Abdalati, W.; Brunt, K.; Csatho, B.; Farrell, S.; Fricker, H.; Gardner, A.; Harding, D.; et al. The Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2): Science requirements, concept, and implementation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.L.; Allen, R.J.; Li, K.F. California wildfire smoke contributes to a positive atmospheric temperature anomaly over the western United States. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 6937–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, Z.; DallaSanta, K.; Polvani, L.M.; Tsigaridis, K.; Orbe, C.; Bauer, S.E. Severe Global Cooling After Volcanic Super-Eruptions? The Answer Hinges on Unknown Aerosol Size. J. Clim. 2024, 37, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, M.A.; Powell, K.A.; Winker, D.M.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kuehn, R.E.; Hunt, W.H.; Getzewich, B.J.; Young, S.A.; Liu, Z.; McGill, M.J. Fully Automated Detection of Cloud and Aerosol Layers in the CALIPSO Lidar Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2034–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorks, J.E.; McGill, M.J.; Palm, S.P.; Hlavka, D.L.; Selmer, P.A.; Nowottnick, E.P.; Vaughan, M.A.; Rodier, S.D.; Hart, W.D. An overview of the CATS level 1 processing algorithms and data products. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4632–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestakis, E.; Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Binietoglou, I.; Ansmann, A.; Wandinger, U.; Hofer, J.; Yorks, J.; Nowottnick, E.; Makhmudov, A.; et al. EARLINET evaluation of the CATS Level 2 aerosol backscatter coefficient product. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11743–11764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.J.; Yorks, J.E.; Scott, V.S.; Kupchock, A.W.; Selmer, P.A. The Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS): A technology demonstration on the International Space Station. In Proceedings of the Lidar Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring XV, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 August 2015; Singh, U.N., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9612, p. 96120A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.; Hlavka, D.; Hart, W.; Scott, V.S.; Spinhirne, J.; Schmid, B. Cloud Physics Lidar: Instrument description and initial measurement results. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorks, J.E.; McGill, M.J.; Scott, V.S.; Wake, S.W.; Kupchock, A.; Hlavka, D.L.; Hart, W.D.; Selmer, P.A. The Airborne Cloud–Aerosol Transport System: Overview and Description of the Instrument and Retrieval Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 2482–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, R.M.; Yorks, J.E.; Hlavka, D.L.; McGill, M.J.; Amiridis, V.; Palm, S.P.; Rodier, S.D.; Vaughan, M.A.; Selmer, P.A.; Kupchock, A.W.; et al. Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS) 1064 nm calibration and validation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 6241–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorks, J.E.; Selmer, P.A.; Kupchock, A.; Nowottnick, E.P.; Christian, K.E.; Rusinek, D.; Dacic, N.; McGill, M.J. Aerosol and Cloud Detection Using Machine Learning Algorithms and Space-Based Lidar Data. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.J.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3523–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmer, P.; Yorks, J.E.; Nowottnick, E.P.; Cresanti, A.; Christian, K.E. A Deep Learning Lidar Denoising Approach for Improving Atmospheric Feature Detection. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Fei, L.; Zheng, W.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, W.; Lin, C.W. Deep learning on image denoising: An overview. Neural Netw. 2020, 131, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorks, J.E.; Palm, S.P.; McGill, M.J.; Hlavka, D.L.; Hart, W.D.; Selmer, P.A.; Nowottnick, E.P. CATS Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; Technical report; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oladipo, B.; Gomes, J.; McGill, M.; Selmer, P. Leveraging Deep Learning as a New Approach to Layer Detection and Cloud–Aerosol Classification Using ICESat-2 Atmospheric Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J.; Takacs, L.; Liu, H.C.; Gu, W.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Koster, R.D.; Gelaro, R.; et al. The GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System-Documentation of Versions 5.0.1, 5.1.0, and 5.2.0; Technical Report NASA/TM-2008-104606-VOL-27; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Randles, C.; Da Silva, A.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part I: System description and data assimilation evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.J.; Selmer, P.A.; Kupchock, A.W.; Yorks, J.E. Machine learning-enabled real-time detection of cloud and aerosol layers using airborne lidar. Front. Remote Sens. 2023, 4, 1116817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CATS Data Release Notes: L1B Version 3.00, L2O Version 3.00. Available online: https://cats.gsfc.nasa.gov/media/docs/CATS_Release_Notes7.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Nowottnick, E.P.; Christian, K.E.; Yorks, J.E.; McGill, M.J.; Midzak, N.; Selmer, P.A.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Salinas, S.V. Aerosol Detection from the Cloud Aerosol Transport System on the International Space Station: Algorithm Overview and Implications for Diurnal Sampling. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.; Winker, D.; Kittaka, C.; Getzewich, B.; Kuehn, R.; Omar, A.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Hostetler, C. The CALIPSO Lidar Cloud and Aerosol Discrimination: Version 2 Algorithm and Initial Assessment of Performance. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1198–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorks, J.E.; Hlavka, D.L.; Hart, W.D.; McGill, M.J. Statistics of cloud optical properties from airborne lidar measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, C.; Delanoë, J.; Groß, S.; Ewald, F.; Tridon, F.; Jourdan, O.; Mioche, G. Lidar–radar synergistic method to retrieve ice, supercooled water and mixed-phase cloud properties. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2024, 17, 3863–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.P.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kittaka, C.; Rogers, R.R.; et al. The CALIPSO automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchard, V.; Randles, C.; Da Silva, A.; Darmenov, A.; Colarco, P.; Govindaraju, R.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; Beyersdorf, A.; Ziemba, L.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part II: Evaluation and case studies. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6851–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Crawshaw, M. Multi-Task Learning with Deep Neural Networks: A Survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.09796. [Google Scholar]
- Loveland, T.R.; Reed, B.C.; Brown, J.F.; Ohlen, D.O.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, L.; Merchant, J.W. Development of a global land cover characteristics database and IGBP DISCover from 1 km AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 1303–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, C.H.; Li, W.; Vercauteren, T.; Ourselin, S.; Jorge Cardoso, M. Generalised dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: Third International Workshop, DLMIA 2017, and 7th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Québec City, QC, Canada, 14 September 2017; Proceedings 3. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 240–248. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nowottnick, E.P.; Yorks, J.E.; McGill, M.J.; Selmer, P.A.; Christian, K.E. A Simulation Capability Developed for NASA GSFC’s Spaceborne Backscatter Lidars: Overview and Projected Performance for the Upcoming AOS Mission. In Proceedings of the 30th International Laser Radar Conference, Virtual, 26 June 2022; Sullivan, J.T., Leblanc, T., Tucker, S., Demoz, B., Eloranta, E., Hostetler, C., Ishii, S., Mona, L., Moshary, F., Papayannis, A., et al., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 675–681. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.A.; Vaughan, M.A. The Retrieval of Profiles of Particulate Extinction from Cloud-Aerosol Lidar Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) Data: Algorithm Description. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1105–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutro, R. Several Washington State Fires Rage; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y. Depolarization ratio–effective lidar ratio relation: Theoretical basis for space lidar cloud phase discrimination. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illingworth, A.J.; Barker, H.W.; Beljaars, A.; Ceccaldi, M.; Chepfer, H.; Clerbaux, N.; Cole, J.; Delanoë, J.; Domenech, C.; Donovan, D.P.; et al. The EarthCARE Satellite: The Next Step Forward in Global Measurements of Clouds, Aerosols, Precipitation, and Radiation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1311–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yao, Q.; Liu, T.; Niu, G.; Tsang, I.W.; Kwok, J.T.; Sugiyama, M. A Survey of Label-noise Representation Learning: Past, Present and Future. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.04406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenay, B.; Verleysen, M. Classification in the Presence of Label Noise: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 25, 845–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolnick, D.; Veit, A.; Belongie, S.; Shavit, N. Deep Learning is Robust to Massive Label Noise. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
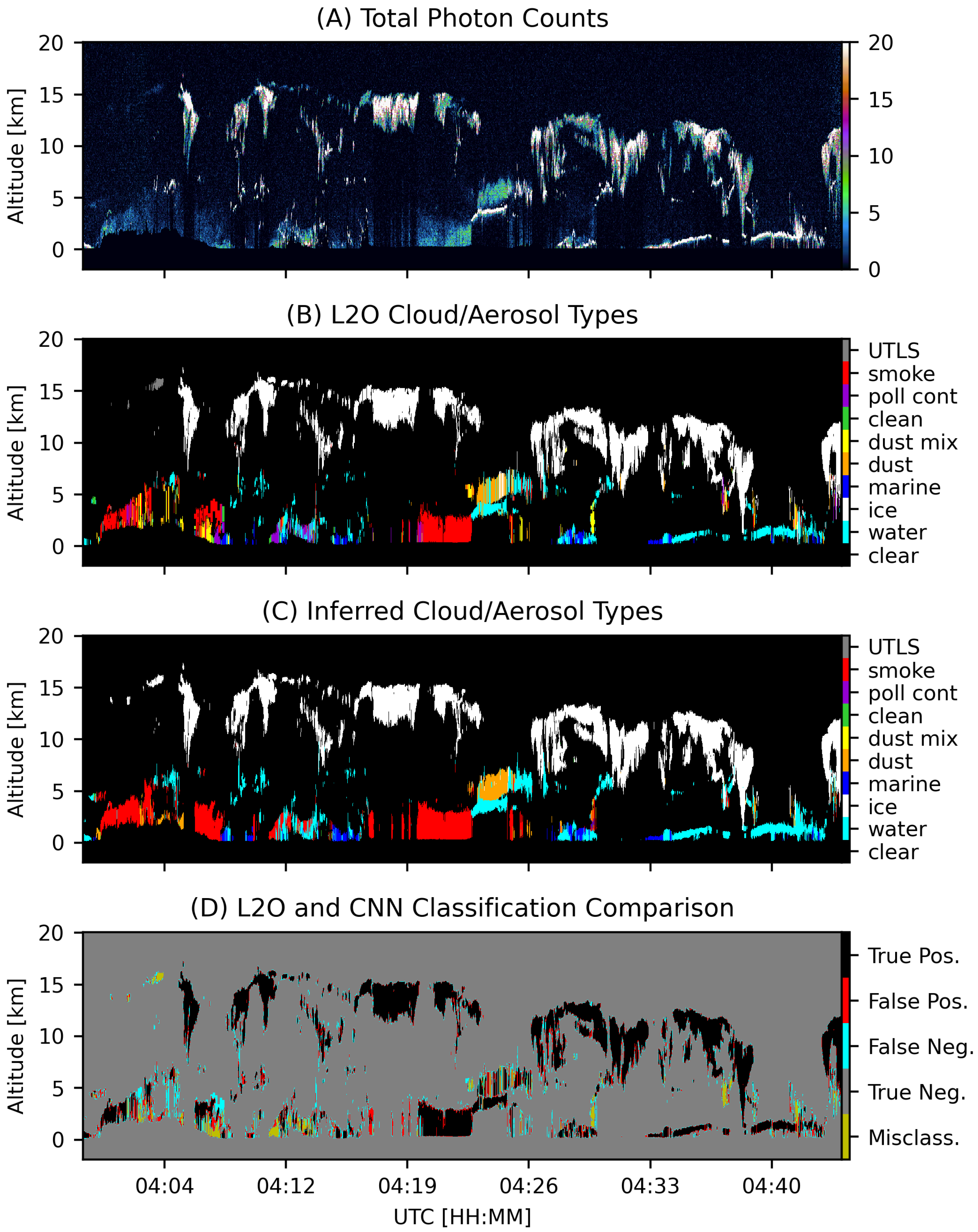
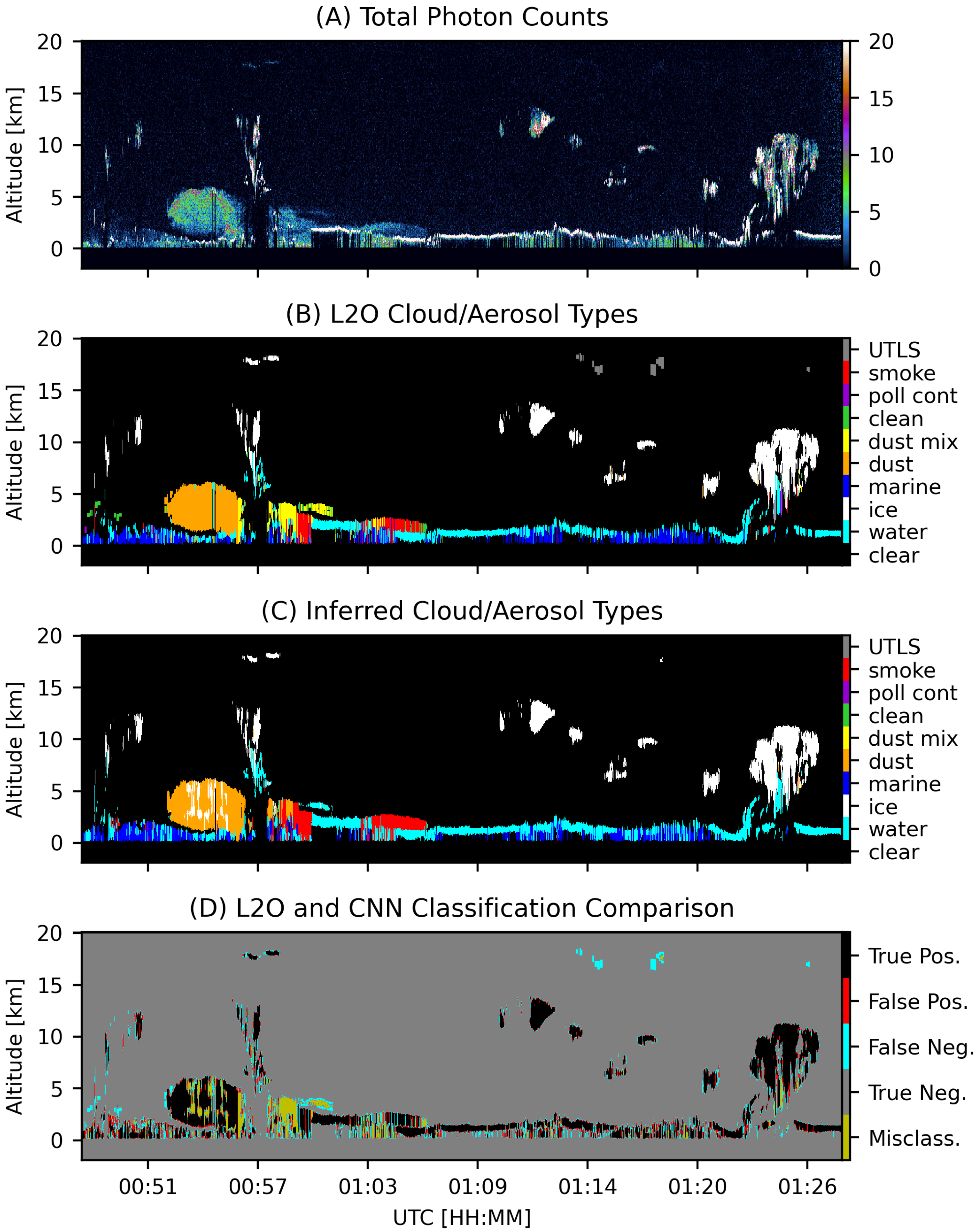
| Clear | Water | Ice | Marine | Dust | Mix | Clean | Poll | Smoke | UTLS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.9 × | 1.6 × | 8.7 × | 3.7 × | 5.7 × | 1.5 × | 7.6 × | 8.7 × | 3.3 × | 1.6 × |
| Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Support | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clear Sky | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 9,406,732 | |
| L2O | Cloud | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.69 | 195,664 |
| Aerosol | 0.73 | 0.45 | 0.56 | 286,353 | |
| Clear Sky | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 9,406,732 | |
| CNN | Cloud | 0.67 | 0.75 | 0.71 | 195,664 |
| Aerosol | 0.87 | 0.61 | 0.71 | 286,353 |
| Clear | Water | Ice | Marine | Dust | Mix | Clean | Poll | Smoke | UTLS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mix | 71,765 | 34,020 | 4053 | 39,841 | 10,692 | 0 | 148 | 0 | 3225 | 0 |
| poll | 65,148 | 8899 | 23,505 | 1833 | 24,755 | 0 | 1238 | 0 | 5372 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fuller, C.A.; Selmer, P.A.; Gomes, J.; McGill, M.J. Using Multitask Machine Learning to Type Clouds and Aerosols from Space-Based Photon-Counting Lidar Measurements. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162787
Fuller CA, Selmer PA, Gomes J, McGill MJ. Using Multitask Machine Learning to Type Clouds and Aerosols from Space-Based Photon-Counting Lidar Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162787
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuller, Chase A., Patrick A. Selmer, Joseph Gomes, and Matthew J. McGill. 2025. "Using Multitask Machine Learning to Type Clouds and Aerosols from Space-Based Photon-Counting Lidar Measurements" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162787
APA StyleFuller, C. A., Selmer, P. A., Gomes, J., & McGill, M. J. (2025). Using Multitask Machine Learning to Type Clouds and Aerosols from Space-Based Photon-Counting Lidar Measurements. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162787






