Enhancing Hyperlocal Wavelength-Resolved Solar Irradiance Estimation Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
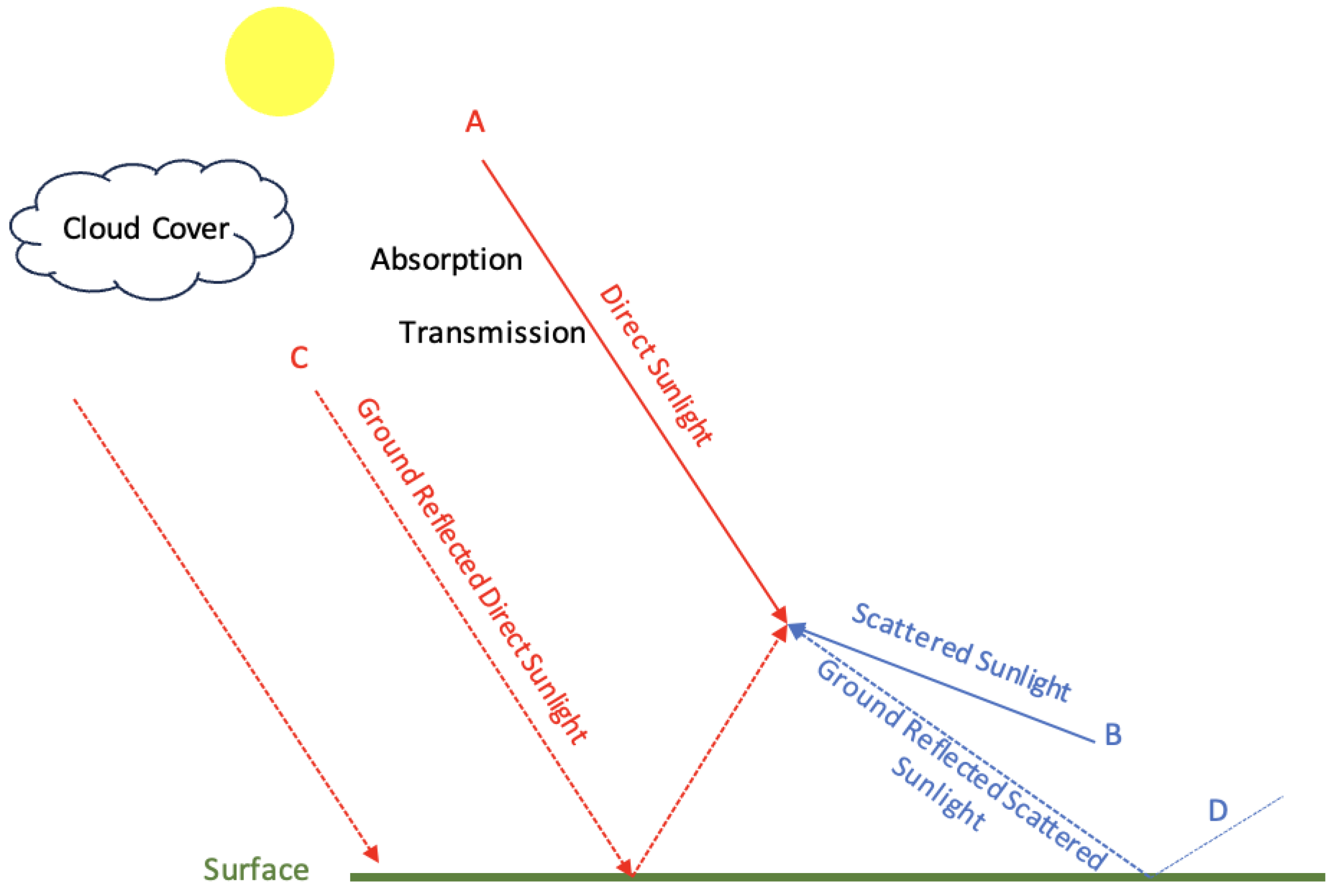
Quantifying the Surface Solar Irradiance Spectra
2. Materials and Methods
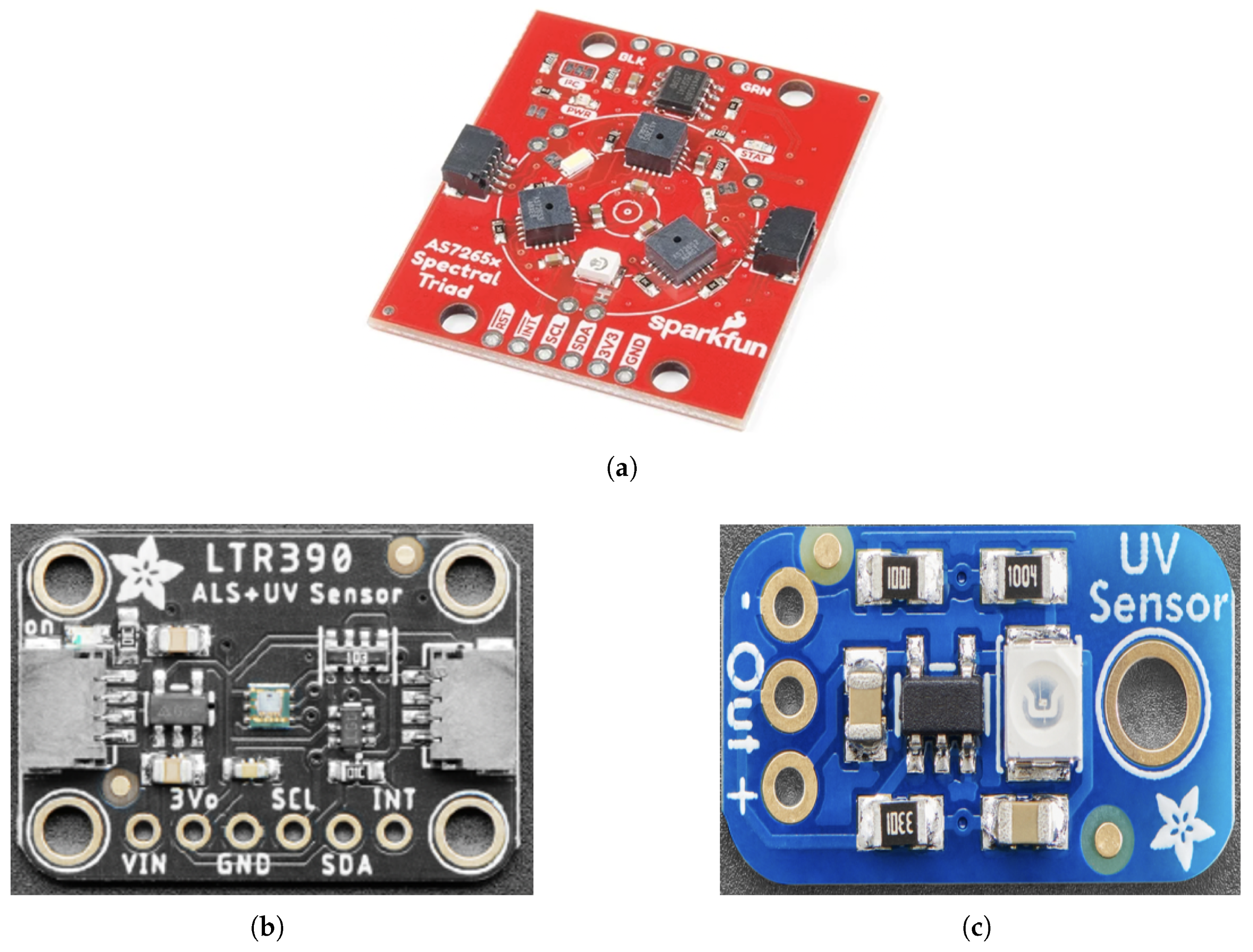
2.1. Low-Cost Sensor Module
2.2. Remote Sensing-Based Surface Reflectance Data
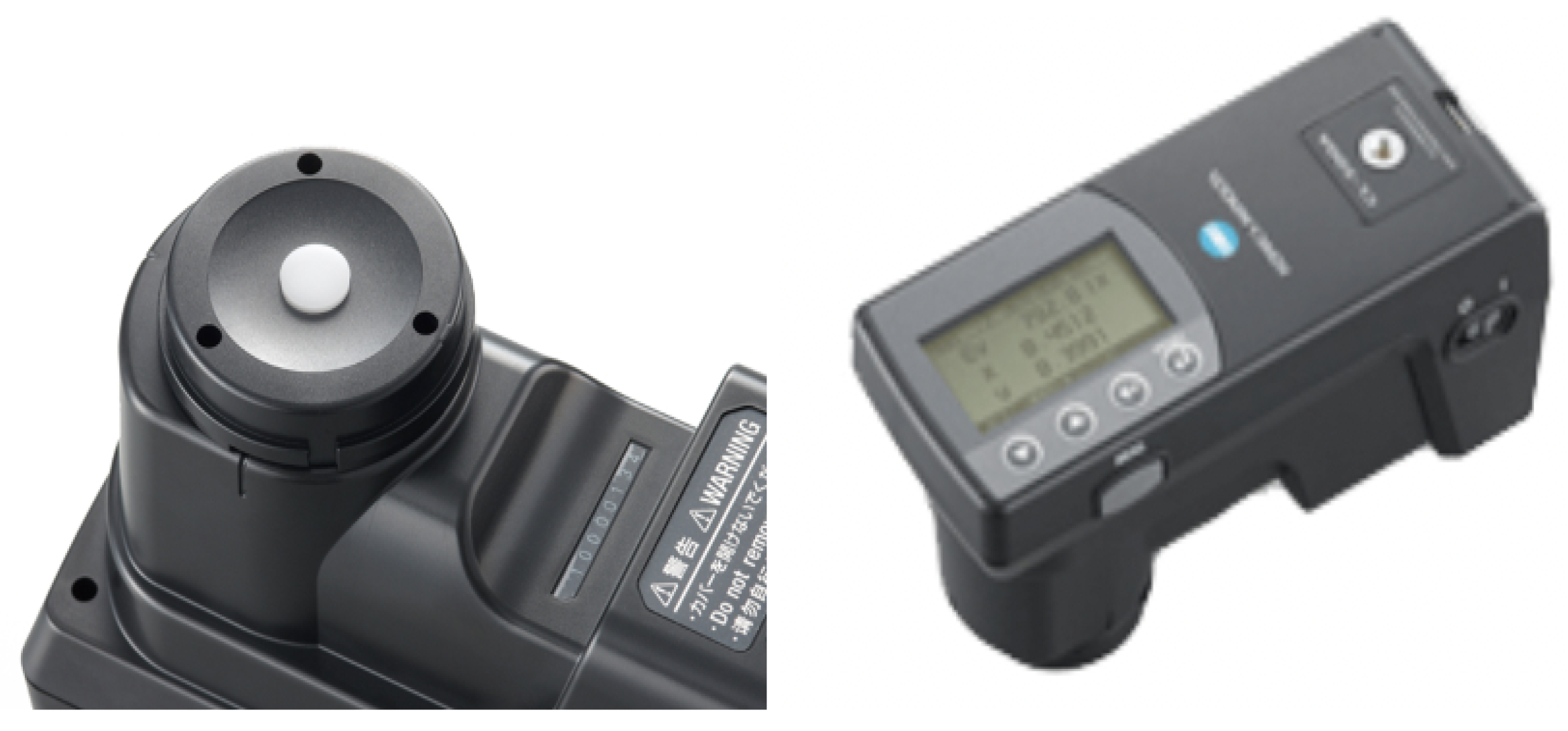
2.3. Reference Instrument
2.4. Machine Learning
2.5. Workflow
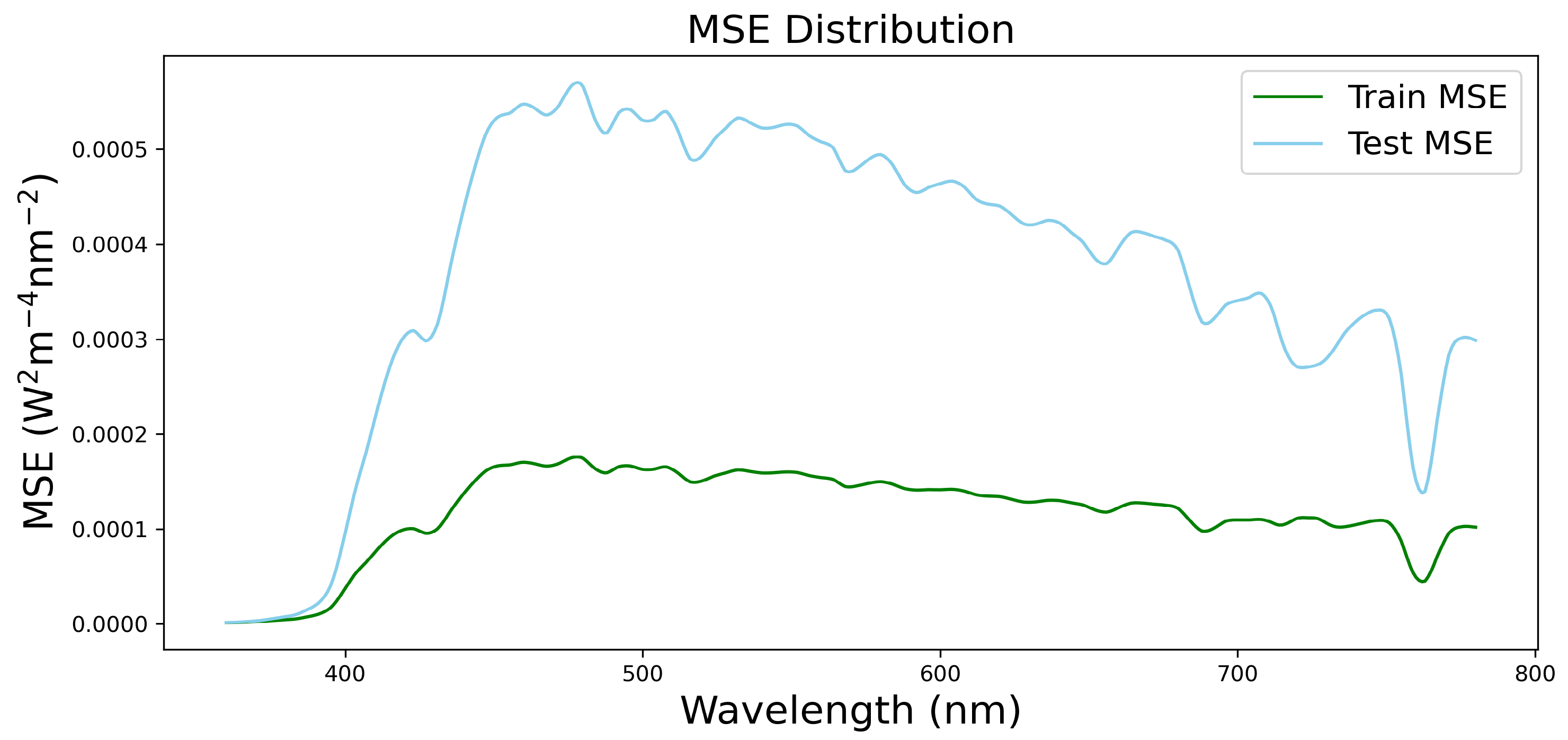
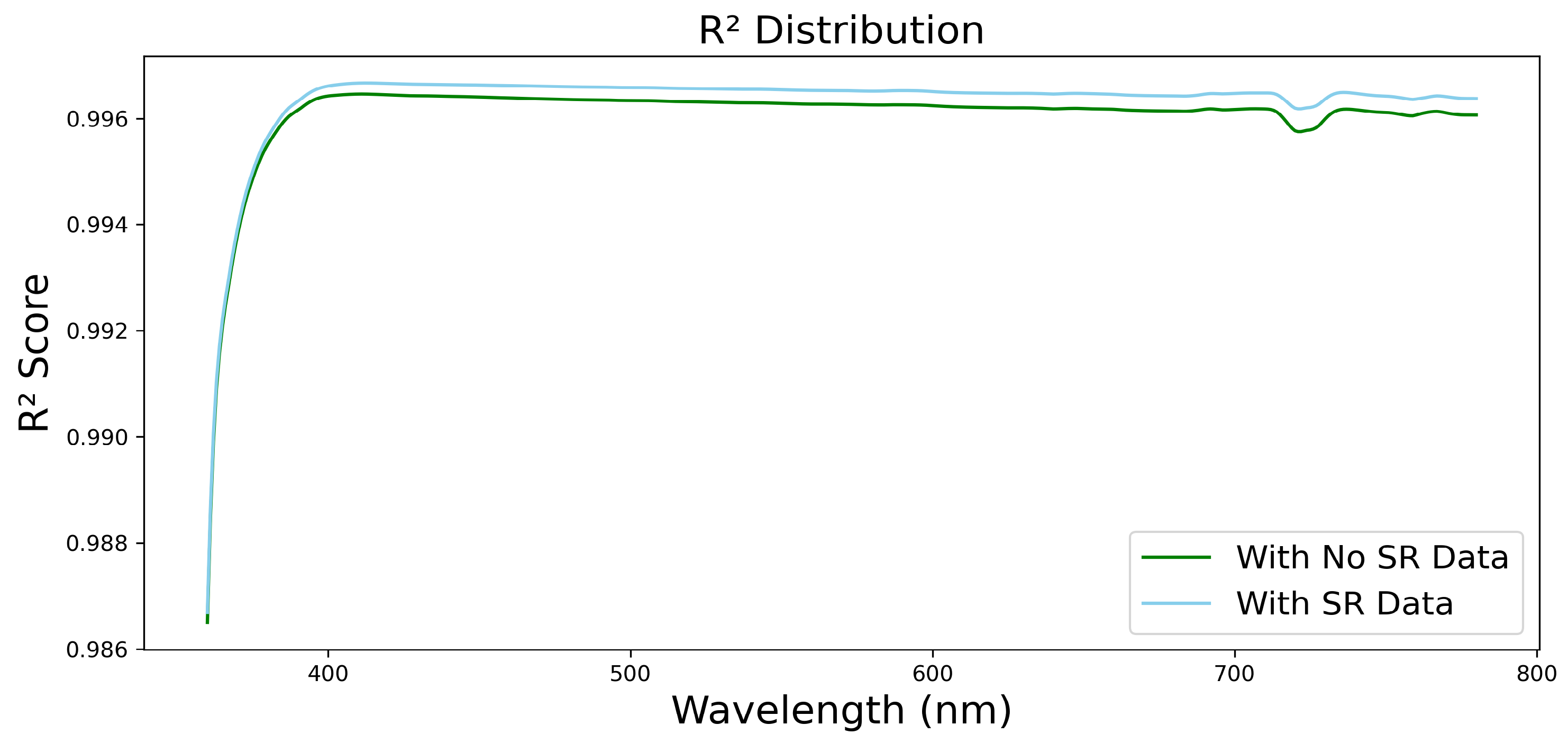
3. Results
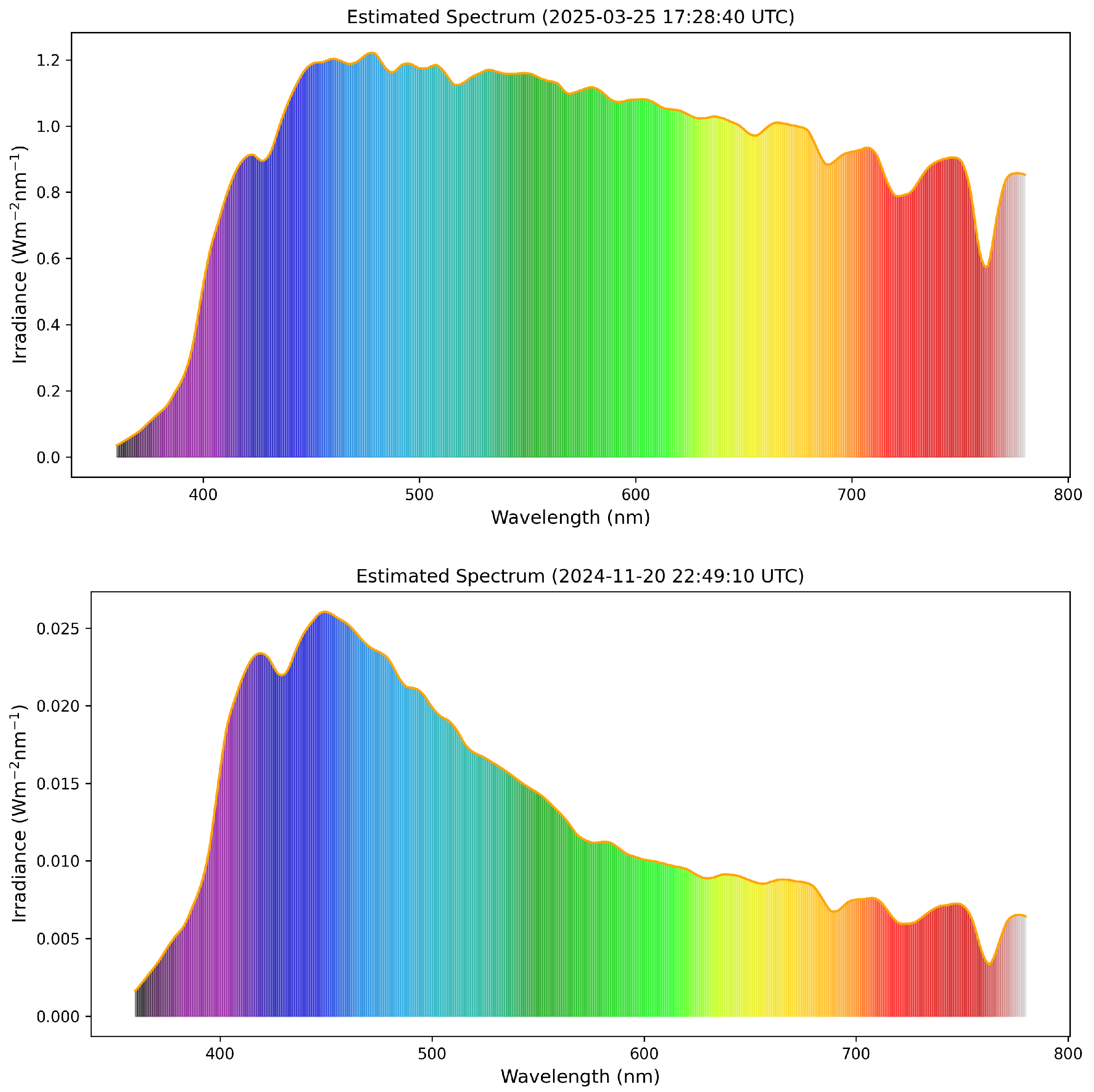
Application of the Model for Spectral Irradiance Estimation
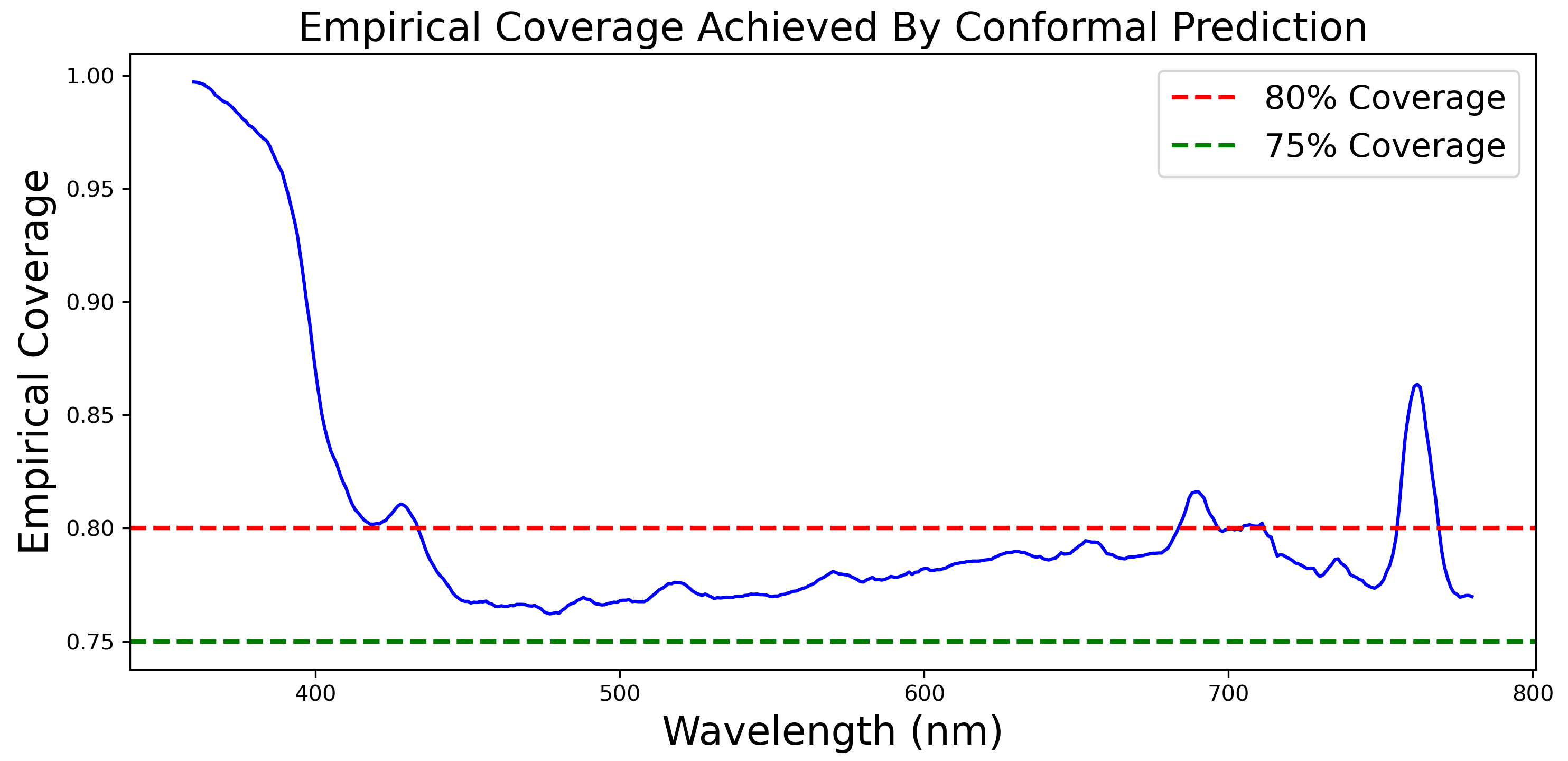
4. Extending the SSI Estimation Model to Incorporate Split Conformal Prediction for Principled Uncertainty Quantification
5. Societal Relevance and Significance
6. Discussion and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSI | Surface solar irradiance |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| SR | Surface reflectance |
| GEE | Google Earth Engine |
| ML | Machine learning |
| RFR | Random forest regressor |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| RAE | Relative absolute error |
References
- Gessler, A.; Bugmann, H.; Bigler, C.; Edwards, P.; Guistina, C.D.; Kueffer, C.; Roy, J.; Resco de Dios, V. Light as a Source of Information in Ecosystems; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mellouki, A.; Wallington, T.; Chen, J. Atmospheric chemistry of oxygenated volatile organic compounds: Impacts on air quality and climate. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3984–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillman, S. The relation between ozone, NOx and hydrocarbons in urban and polluted rural environments. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1821–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, H., II. Photochemistry of the lower troposphere. Planet. Space Sci. 1972, 20, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wijeratne, L.O.H.; Talebi, S.; Lary, D.J. Machine learning for light sensor calibration. Sensors 2021, 21, 6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, D.L. Atmospheric radiative transfer and climate. Glob. Phys. Climatol. 2016, 2016, 49–94. [Google Scholar]
- Buehler, S.A.; Mendrok, J.; Eriksson, P.; Perrin, A.; Larsson, R.; Lemke, O. ARTS, the atmospheric radiative transfer simulator–version 2.2. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 1537–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lary, D.; Pyle, J. Diffuse radiation, twilight, and photochemistry—I. J. Atmos. Chem. 1991, 13, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lary, D.J.; Alavi, A.H.; Gandomi, A.H.; Walker, A.L. Machine learning in geosciences and remote sensing. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yan, G.; Wang, T.; Ren, H.; Calbó, J.; Zhao, J.; McKenzie, R. Estimation of surface shortwave radiation components under all sky conditions: Modeling and sensitivity analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, G.M.; Monahan, A.H.; Heinemann, D. Local short-term variability in solar irradiance. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6365–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solar Power Europe. Global Market Outlook for Solar Power 2015–2019. 2015. Available online: http://www.solarpowereurope.org/ (accessed on 7 September 2015).
- Stetz, T.; von Appen, J.; Niedermeyer, F.; Scheibner, G.; Sikora, R.; Braun, M. Twilight of the grids: The impact of distributed solar on Germany?s energy transition. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2015, 13, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buizer, J. Air quality. In Impacts, Risks, and Adaptation in the United States: Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume II; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Chapter 13; p. 516. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Wild, M.; Brunetti, M.; Guijarro, J.A.; Hakuba, M.Z.; Calbó, J.; Mystakidis, S.; Bartok, B. Reassessment and update of long-term trends in downward surface shortwave radiation over Europe (1939–2012). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9555–9569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.C.; Sohn, E.H.; Park, K.H. Estimating hourly surface solar irradiance from GK2A/AMI data using machine learning approach around Korea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzing, J.; Knap, W.; Stammes, P.; Apituley, A.; Bergwerff, J.; Swart, D.; Kos, G.; Ten Brink, H. Effect of aerosols on the downward shortwave irradiances at the surface: Measurements versus calculations with MODTRAN4. 1. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacovides, C.P.; Steven, M.D.; Asimakopoulos, D.N. Spectral solar irradiance and some optical properties for various polluted atmospheres. Sol. Energy 2000, 69, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, K.M.; Badarinath, K. Spectral solar attenuation due to aerosol loading over an urban area in India. Atmos. Res. 2005, 75, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, M.G.; Apell, J.N. Emerging investigator series: Quantifying the impact of cloud cover on solar irradiance and environmental photodegradation. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2021, 23, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueymard, C.A. Cloud and albedo enhancement impacts on solar irradiance using high-frequency measurements from thermopile and photodiode radiometers. Part 1: Impacts on global horizontal irradiance. Sol. Energy 2017, 153, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanov, G.H. A study of extreme overirradiance events for solar energy applications using NASA’s I3RC Monte Carlo radiative transfer model. Sol. Energy 2015, 122, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, W.B.; van Stratum, B.J.; Knap, W.H.; van Heerwaarden, C.C. Reconciling observations of solar irradiance variability with cloud size distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD037894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service. CAMS Solar Radiation Time-Series. Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) Atmosphere Data Store. 2020. Available online: https://ads.atmosphere.copernicus.eu/datasets/cams-solar-radiation-timeseries?tab=overview (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service. CAMS Gridded Solar Radiation. Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) Atmosphere Data Store, 2022. Available online: https://ads.atmosphere.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Pfeifroth, U.; Kothe, S.; Drücke, J.; Trentmann, J.; Schröder, M.; Selbach, N.; Hollmann, R. Surface Radiation Data Set—Heliosat (SARAH), 3rd ed.; Satellite Application Facility on Climate Monitoring (CM SAF): Offenbach, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOES-R Algorithm Working Group and GOES-R Program Office. NOAA GOES-R Series Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) Level 2 Downward Shortwave Radiation: Surface; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2017. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/metadata/landing-page/bin/iso?id=gov.noaa.ncdc:C01524 (accessed on 12 June 2025).
- Boudjella, M.Y.; Belbachir, A.H.; Dib, S.A.A.; Meftah, M. Calculation of surface spectral irradiance using the Geant4 Monte Carlo toolkit. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2023, 248, 106077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L.; Charlson, R.J.; Winker, D.M.; Ogren, J.A.; Holmén, K. Mesoscale variations of tropospheric aerosols. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitkreuz, H.; Schroedter-Homscheidt, M.; Holzer-Popp, T.; Dech, S. Short-range direct and diffuse irradiance forecasts for solar energy applications based on aerosol chemical transport and numerical weather modeling. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1766–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, S.; Schulz, M.; Textor, C.; Guibert, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Bauer, S.E.; Berntsen, T.; Berglen, T.F.; Boucher, O.; Chin, M.; et al. An AeroCom initial assessment—Optical properties in aerosol component modules of global models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2005, 5, 8285–8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.A.; Ruedy, R.; Hansen, J.E.; Aleinov, I.; Bell, N.; Bauer, M.; Bauer, S.; Cairns, B.; Canuto, V.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Present-day atmospheric simulations using GISS ModelE: Comparison to in situ, satellite, and reanalysis data. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 153–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ams OSRAM. ams AS7265x Smart Spectral Sensor. Available online: https://ams-osram.com/products/sensor-solutions/ambient-light-color-spectral-proximity-sensors/ams-as7265x-smart-spectral-sensor (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- SparkFun. SparkFun Triad Spectroscopy Sensor—AS7265x (Qwiic). Available online: https://www.sparkfun.com/sparkfun-triad-spectroscopy-sensor-as7265x-qwiic.html (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Adafruit. Adafruit LTR390 UV Light Sensor—STEMMA QT/Qwiic. Available online: https://www.adafruit.com/product/4831 (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Adafruit. Analog UV Light Sensor Breakout - GUVA-S12SD. Available online: https://www.adafruit.com/product/1918?srsltid=AfmBOopzuG3d4hTw_7uGepxUQev8_2LAAsoi3K-3PGq8Gp_u80qEr6yj (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Perez-Astudillo, D.; Bachour, D.; Martin-Pomares, L. Effect of Solar Position Calculations on Filtering and Analysis of Solar Radiation Measurements. In Proceedings of the ISES EuroSun 2018 Conference—12th International Conference on Solar Energy for Buildings and Industry, Rapperswil, Switzerland, 10–13 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA STAR Land Team. Surface Reflectance Product Overview, 2024. Available online: https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/smcd/emb/land/index.php?product=SR (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Burakowski, E.A.; Ollinger, S.V.; Lepine, L.; Schaaf, C.B.; Wang, Z.; Dibb, J.E.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Kim, J.; Erb, A.; Martin, M. Spatial scaling of reflectance and surface albedo over a mixed-use, temperate forest landscape during snow-covered periods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, R.; Khaki, M.; Saco, P.M.; Rodriguez, J.F. Monitoring and mapping vegetation cover changes in arid and semi-arid areas using remote sensing technology: A review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zeng, Y. Spatial Heterogeneity and Temporal Variation in Urban Surface Albedo Detected by High-Resolution Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Lee, E.; Jin, D.; Seong, N.H.; Jung, D.; Sim, S.; Han, K.S. Retrieval and uncertainty analysis of land surface reflectance using a geostationary ocean color imager. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union/ESA/Copernicus. Sentinel-2 MSI: MultiSpectral Instrument, Level-2A Surface Reflectance (SR). Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/COPERNICUS_S2_SR (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Park, S.S.; Yu, J.E.; Lim, H.; Lee, Y.G. Temporal variation of surface reflectance and cloud fraction used to identify background aerosol retrieval information over East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 309, 119916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KONICA MINOLTA. CL-500A Illuminance Spectrophotometer. Available online: https://sensing.konicaminolta.us/us/products/cl-500a-illuminance-spectrophotometer/ (accessed on 16 June 2025).
- Shin, S.; Baek, K.; So, H. Rapid monitoring of indoor air quality for efficient HVAC systems using fully convolutional network deep learning model. Build. Environ. 2023, 234, 110191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindiran, G.; Hayder, G.; Kanagarathinam, K.; Alagumalai, A.; Sonne, C. Air quality prediction by machine learning models: A predictive study on the indian coastal city of Visakhapatnam. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; McGibbon, J.; Zhang, Y. Predicting high-resolution air quality using machine learning: Integration of large eddy simulation and urban morphology data. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 344, 123371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthick, K.; Aruna, S.K.; Dharmaprakash, R.; Ravindiran, G. Integrating machine learning techniques for Air Quality Index forecasting and insights from pollutant-meteorological dynamics in sustainable urban environments. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 3733–3748. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.; Liu, C.; Di, D.; Le, T.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, F.; Zhang, P.; Sohn, B.J. A multi-domain compression radiative transfer model for the Fengyun-4 Geosynchronous Interferometric Infrared Sounder (GIIRS). Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 1844–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.S.; Hansen, C.W.; Holmgren, W.F.; Jensen, A.R.; Mikofski, M.A.; Driesse, A. pvlib python: 2023 project update. J. Open Source Softw. 2023, 8, 5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- NBCDFW. March 25 Spring Storms Bring Hail to North Texas, 2025. Available online: https://www.nbcdfw.com/weather/weather-connection/march-25-spring-storms-hail/3800690/ (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- WeatherSpark. Historical Weather in November 2024 in Richardson, Texas, United States, 2024. Available online: https://weatherspark.com/h/m/8846/2024/11/Historical-Weather-in-November-2024-in-Richardson-Texas-United-States (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Mie, G. Beiträge zur Optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallösungen. Ann. Phys. 1908, 330, 377–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, J.W.S.B. On the Scattering of Light by Small Particles; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1871. [Google Scholar]
- Mendil, M.; Mossina, L.; Vigouroux, D. PUNCC: A Python Library for Predictive Uncertainty Calibration and Conformalization. In Proceedings of the Conformal and Probabilistic Prediction with Applications. PMLR, Limassol, Cyprus, 13–15 September 2023; pp. 582–601. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, H.; Proedrou, K.; Vovk, V.; Gammerman, A. Inductive confidence machines for regression. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning: ECML 2002: 13th European Conference on Machine Learning, Helsinki, Finland, 19–23 August 2002; Proceedings 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 345–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; G’Sell, M.; Rinaldo, A.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Wasserman, L. Distribution-free predictive inference for regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2018, 113, 1094–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, W.; Heusinkveld, B.; Mangan, M.R.; Hartogensis, O.; Veerman, M.; van Heerwaarden, C. Observed patterns of surface solar irradiance under cloudy and clear-sky conditions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2024, 150, 2338–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Weather Service (NWS). Dallas/Fort Worth Climate Narrative. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/fwd/dfw_narrative (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Wang, X.; Han, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Chen, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Hao, X. Cloud–snow confusion with MODIS snow products in boreal forest regions. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roßbach, P. Neural networks vs. random forests–does it always have to be deep learning. Ger. Frankf. Sch. Financ. Manag. 2018, 1–8. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:221088499 (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Wijeratne, L.O.; Kiv, D.R.; Aker, A.R.; Talebi, S.; Lary, D.J. Using machine learning for the calibration of airborne particulate sensors. Sensors 2019, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waczak, J.; Aker, A.; Wijeratne, L.O.; Talebi, S.; Fernando, A.; Dewage, P.M.; Iqbal, M.; Lary, M.; Schaefer, D.; Lary, D.J. Characterizing water composition with an autonomous robotic team employing comprehensive in situ sensing, hyperspectral imaging, machine learning, and conformal prediction. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, H.; Gammerman, A.; Vovk, V. Normalized nonconformity measures for regression conformal prediction. In Proceedings of the IASTED International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Applications (AIA 2008), Innsbruck, Austria, 11–13 February 2008; pp. 64–69. [Google Scholar]






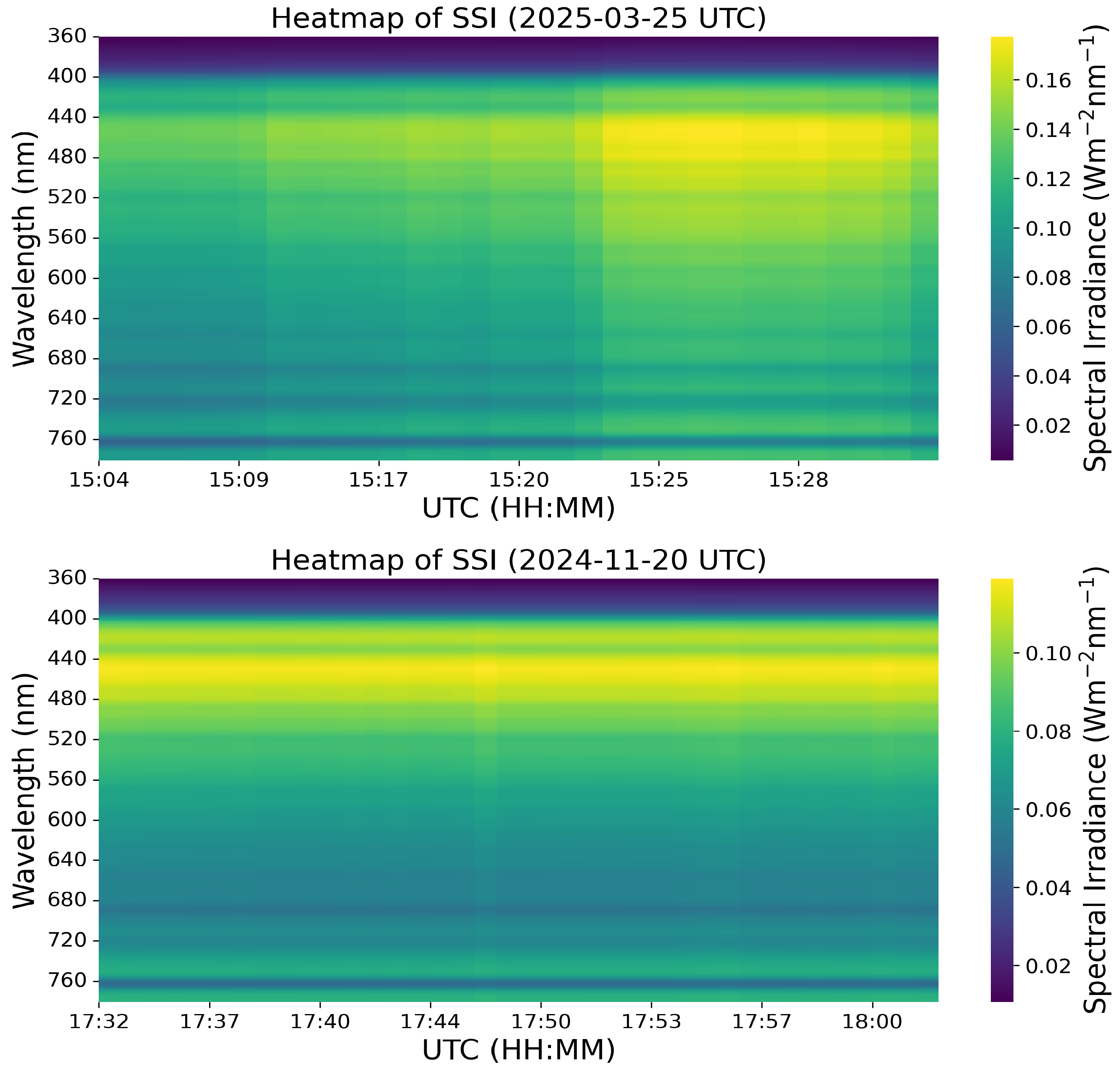


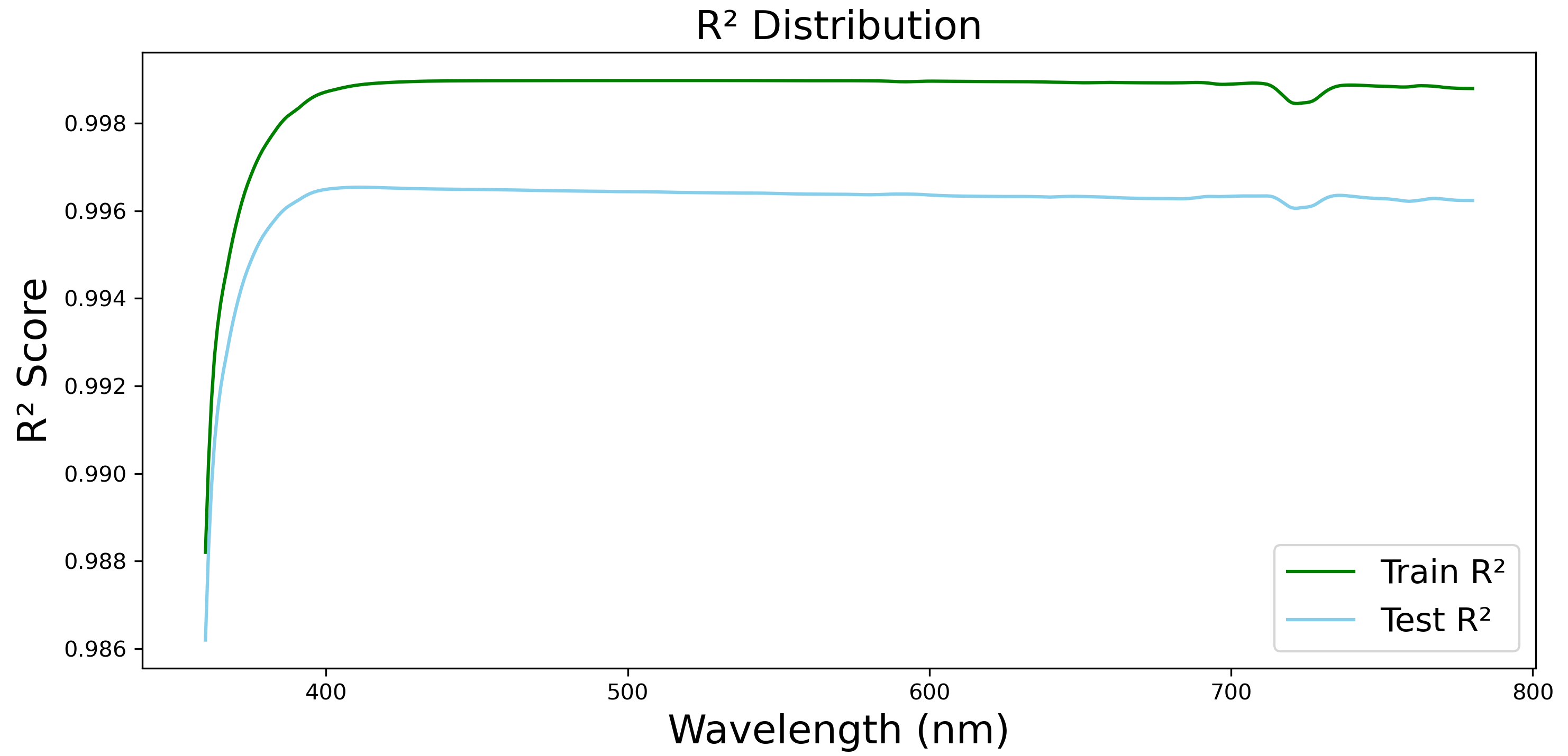

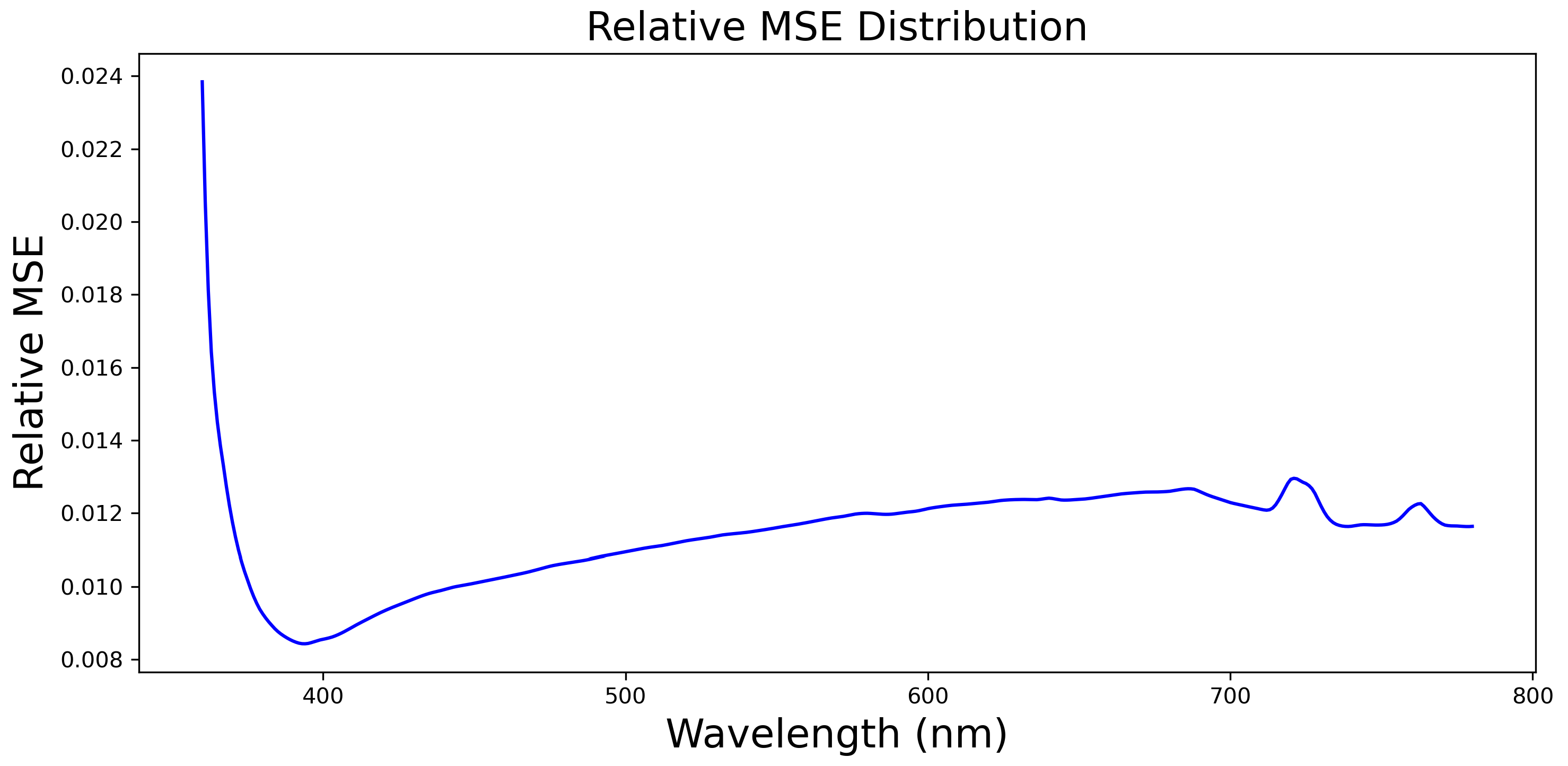
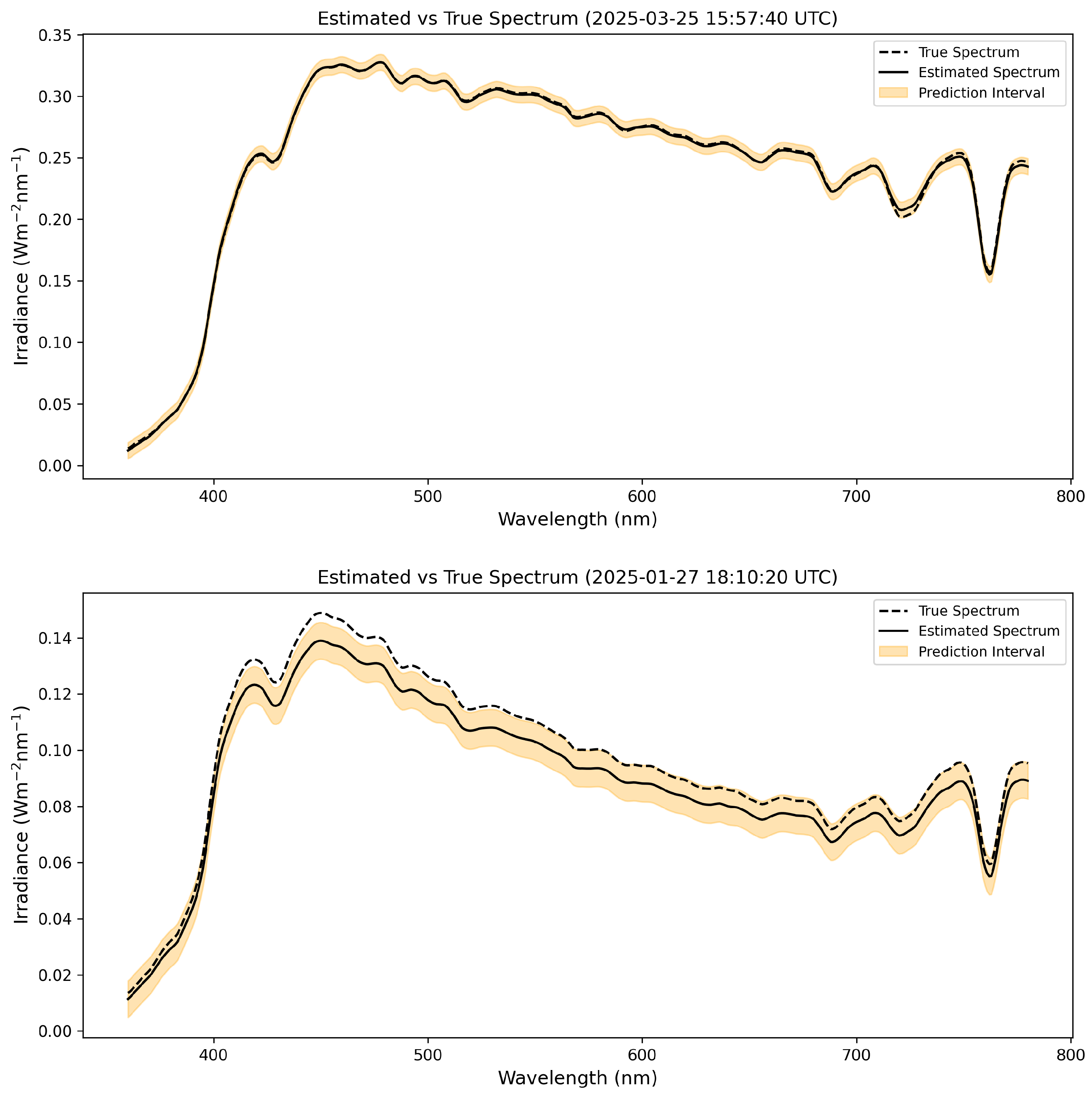

| Feature | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Channel 410 nm | Counts | AS7265X |
| Channel 435 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 460 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 485 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 510 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 535 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 560 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 585 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 610 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 645 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 680 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 705 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 730 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 760 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 810 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 860 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 900 nm | Counts | |
| Channel 940 nm | Counts | |
| Ambient Light Level Reading | Unitless | LTR390 |
| UVA Level Reading | Unitless | |
| UV Level Proxies | Volt | GUVA-S12SD |
| Solar Zenith Angle | Degrees | Calculated |
| Solar Azimuth Angle | Degrees | |
| Sentinel-2 Surface Reflectance (Spectral Bands B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B8A) | Unitless | Harmonized Sentinel-2 MSI: MultiSpectral Instrument, Level-2A (SR) Product |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sooriyaarachchi, V.; Wijeratne, L.O.H.; Waczak, J.; Patra, R.; Lary, D.J.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing Hyperlocal Wavelength-Resolved Solar Irradiance Estimation Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162753
Sooriyaarachchi V, Wijeratne LOH, Waczak J, Patra R, Lary DJ, Zhang Y. Enhancing Hyperlocal Wavelength-Resolved Solar Irradiance Estimation Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162753
Chicago/Turabian StyleSooriyaarachchi, Vinu, Lakitha O. H. Wijeratne, John Waczak, Rittik Patra, David J. Lary, and Yichao Zhang. 2025. "Enhancing Hyperlocal Wavelength-Resolved Solar Irradiance Estimation Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162753
APA StyleSooriyaarachchi, V., Wijeratne, L. O. H., Waczak, J., Patra, R., Lary, D. J., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Enhancing Hyperlocal Wavelength-Resolved Solar Irradiance Estimation Using Remote Sensing and Machine Learning. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162753







