Integrated Analysis of Satellite and Geological Data to Characterize Ground Deformation in the Area of Bologna (Northern Italy) Using a Cluster Analysis-Based Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
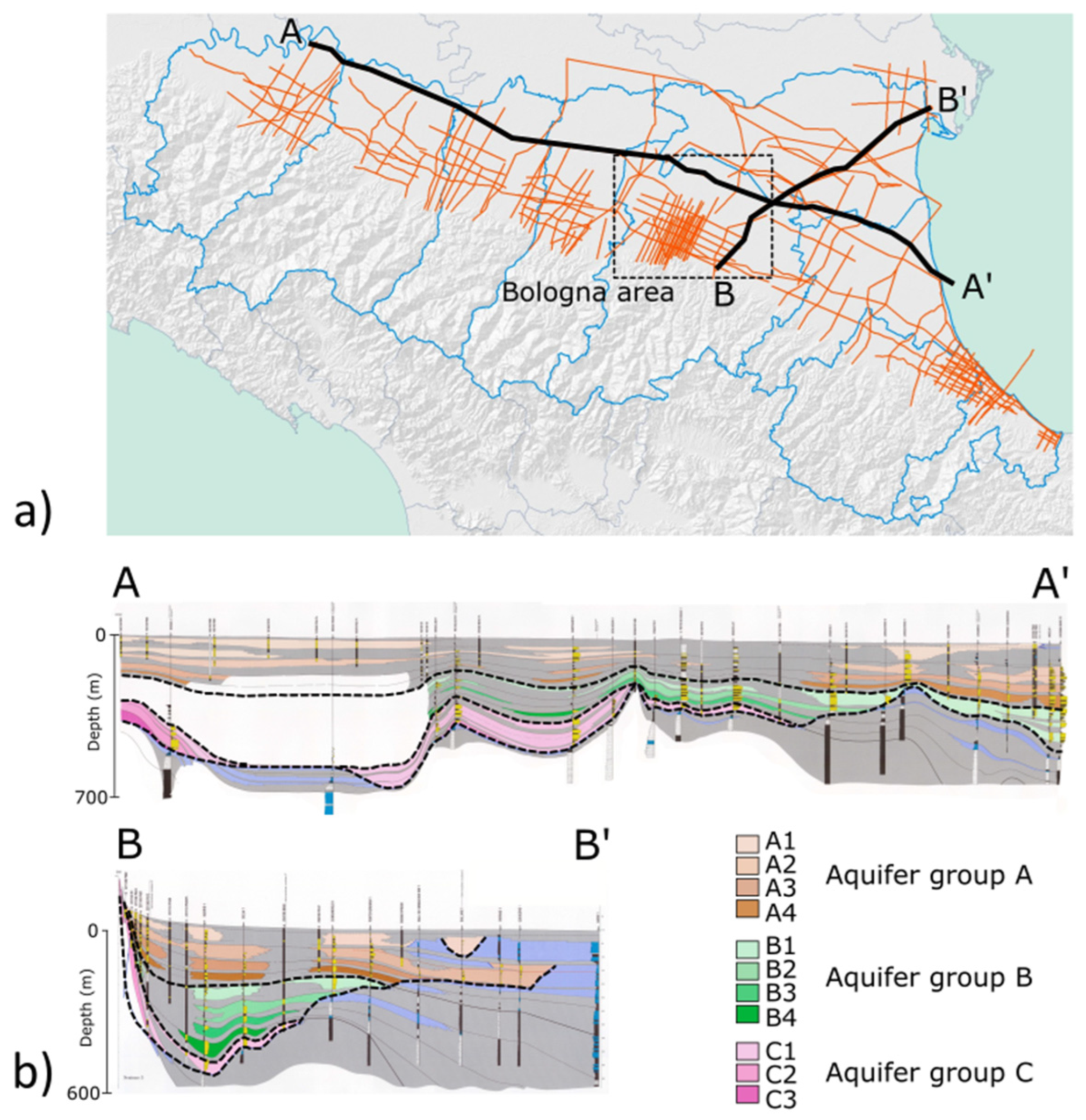
2.1. Geological Framework
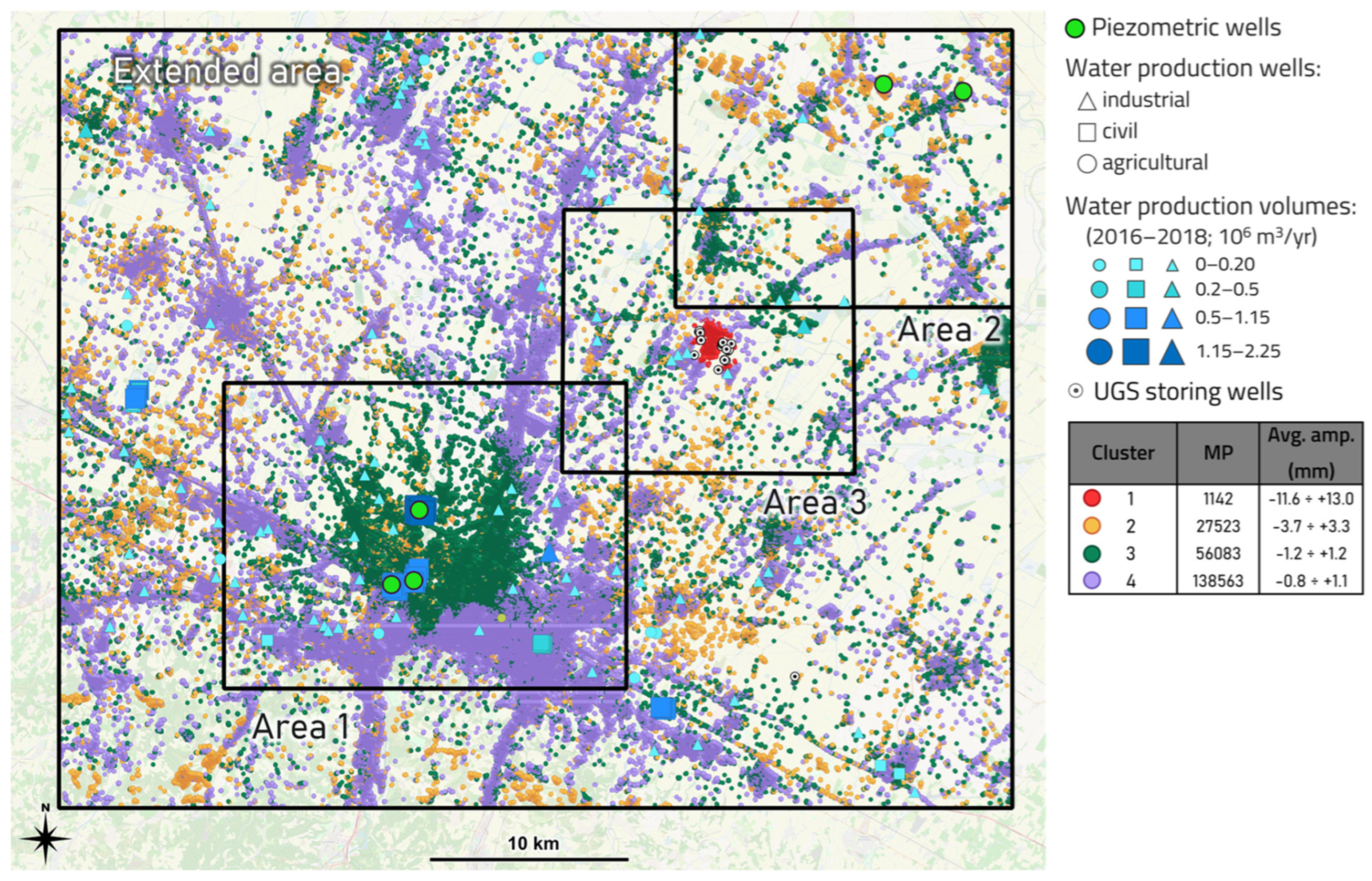
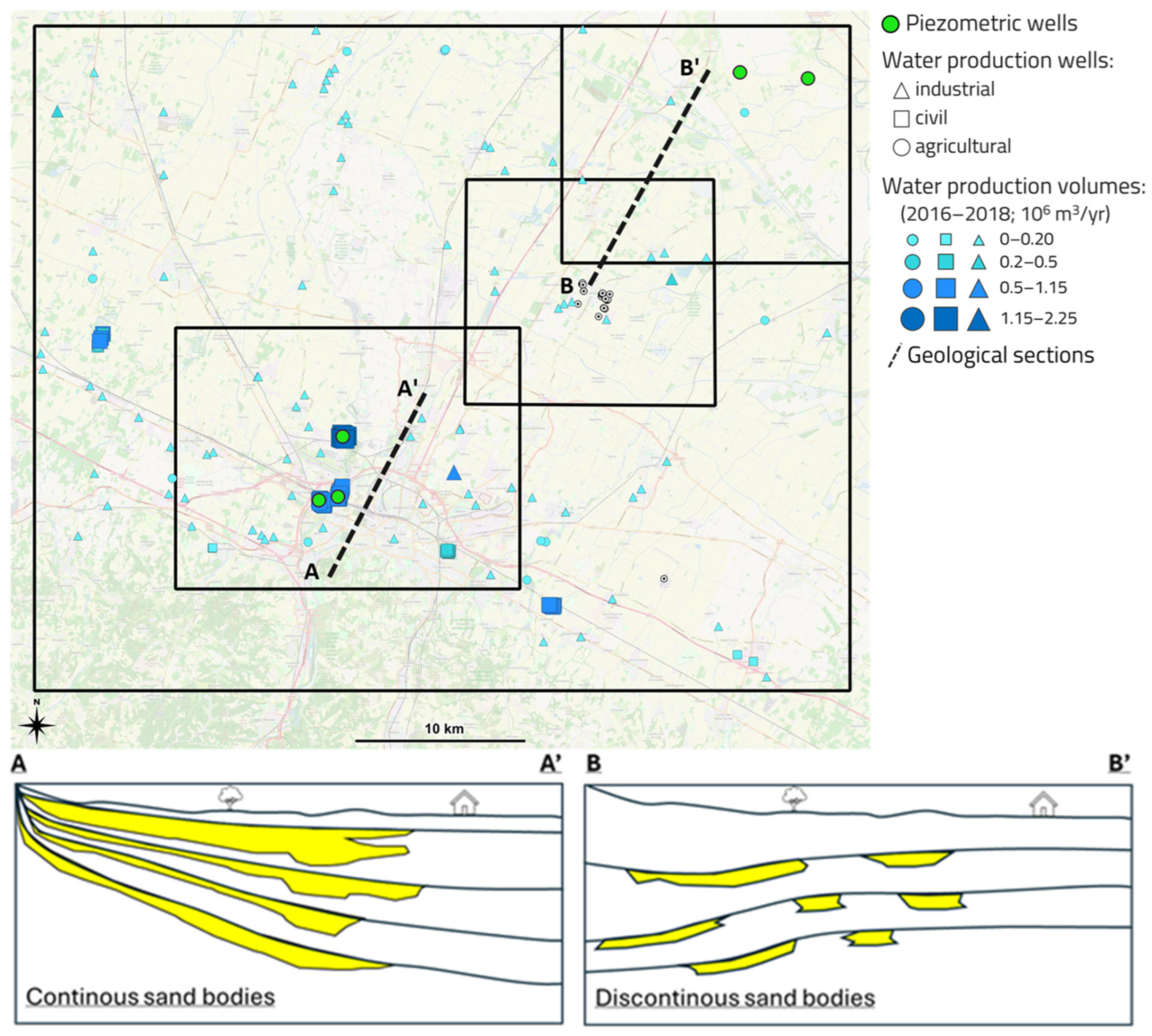
2.2. Study Area
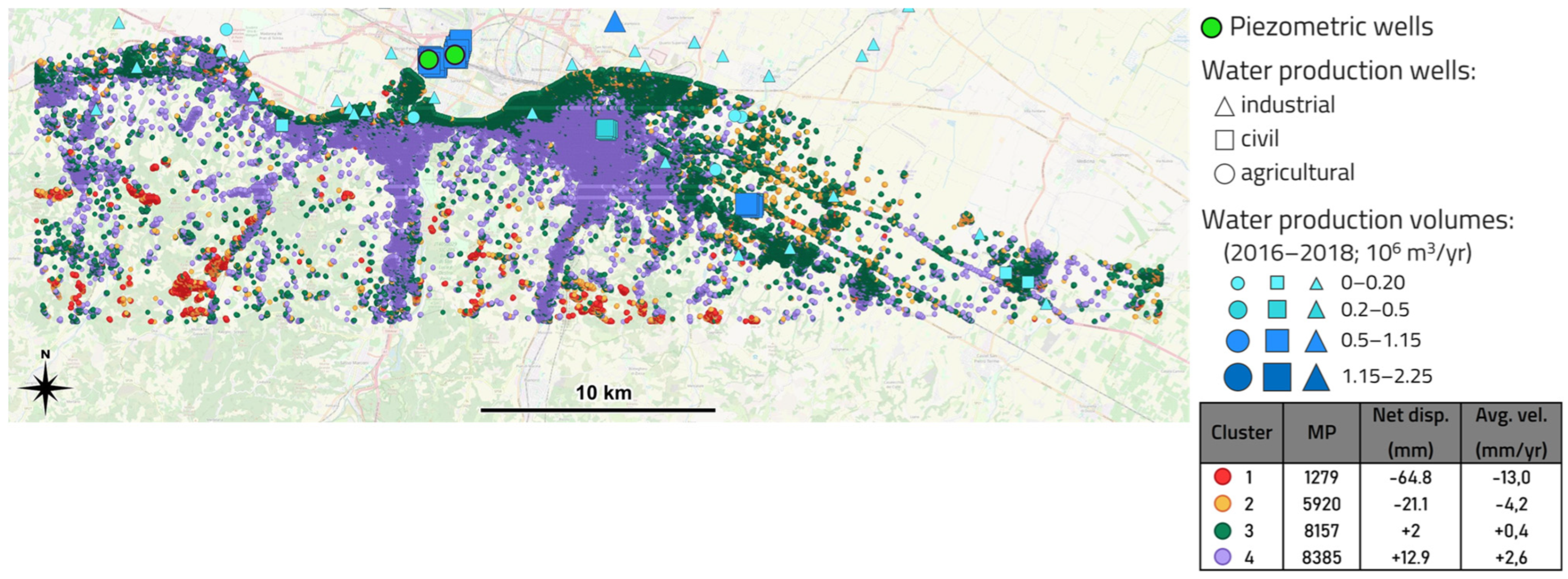
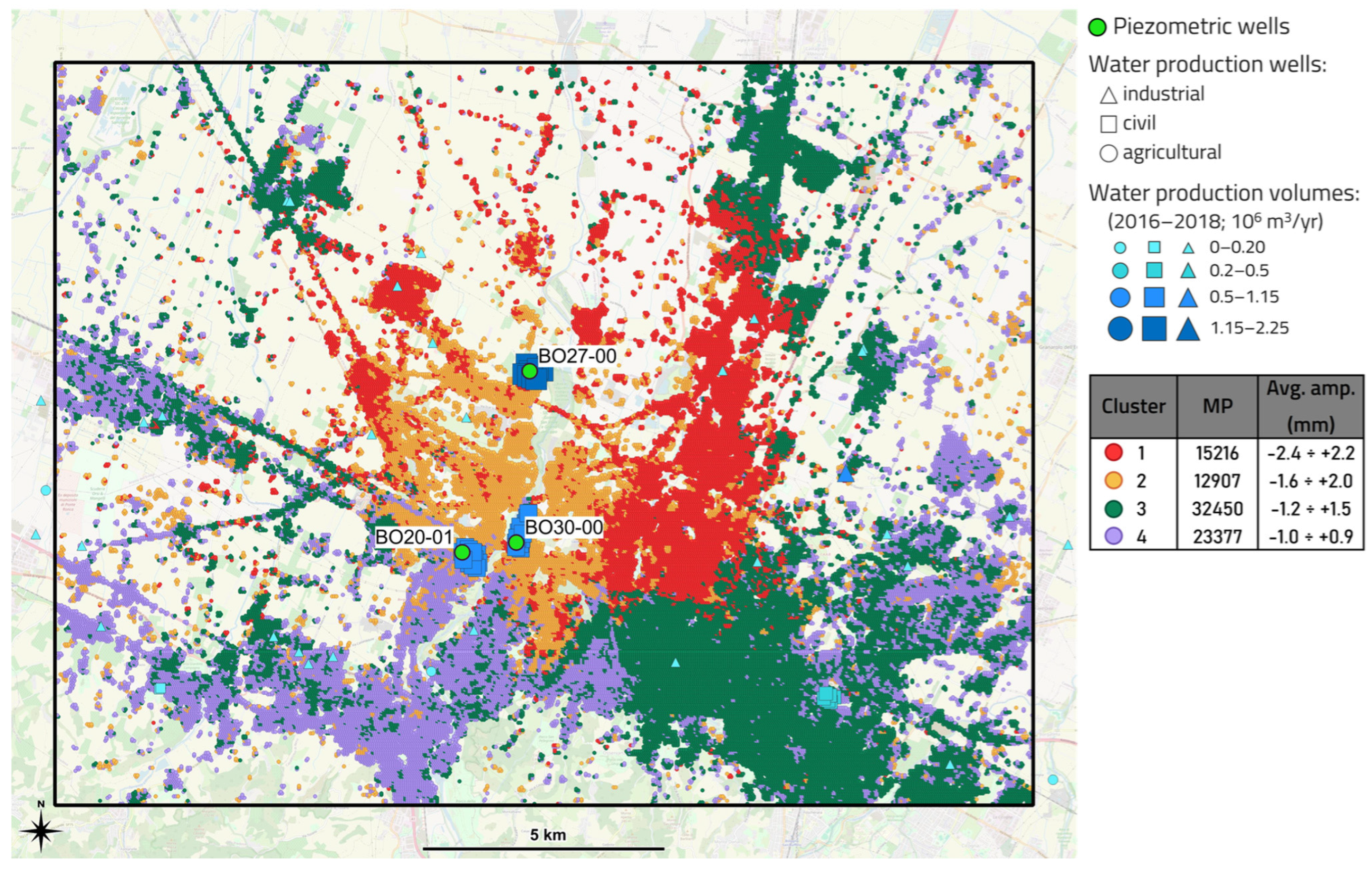
- “Area 1” focuses on the Metropolitan City of Bologna characterized by numerous industrial activities, a strong water production and a specific geological framework. It has been analyzed by numerous studies regarding the overall trend of ground deformation, focusing on the city of Bologna, which has been affected by intensive subsidence related to groundwater exploitation, e.g., [31,32,33].
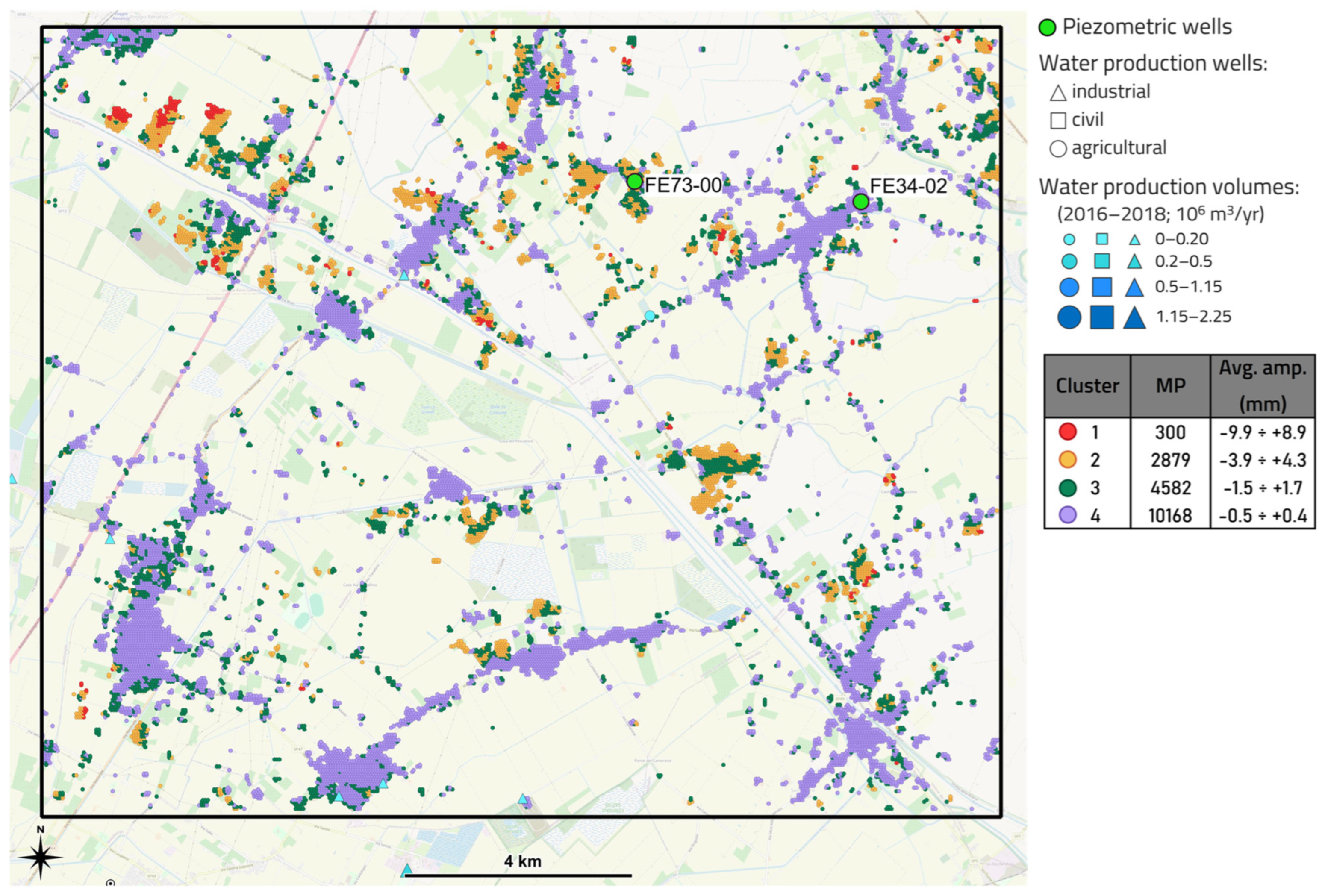
- “Area 2” is located to the NE of Bologna and is characterized by a low concentration of urban areas and industrial activities, and by negligeable water production, suggesting a stable condition.
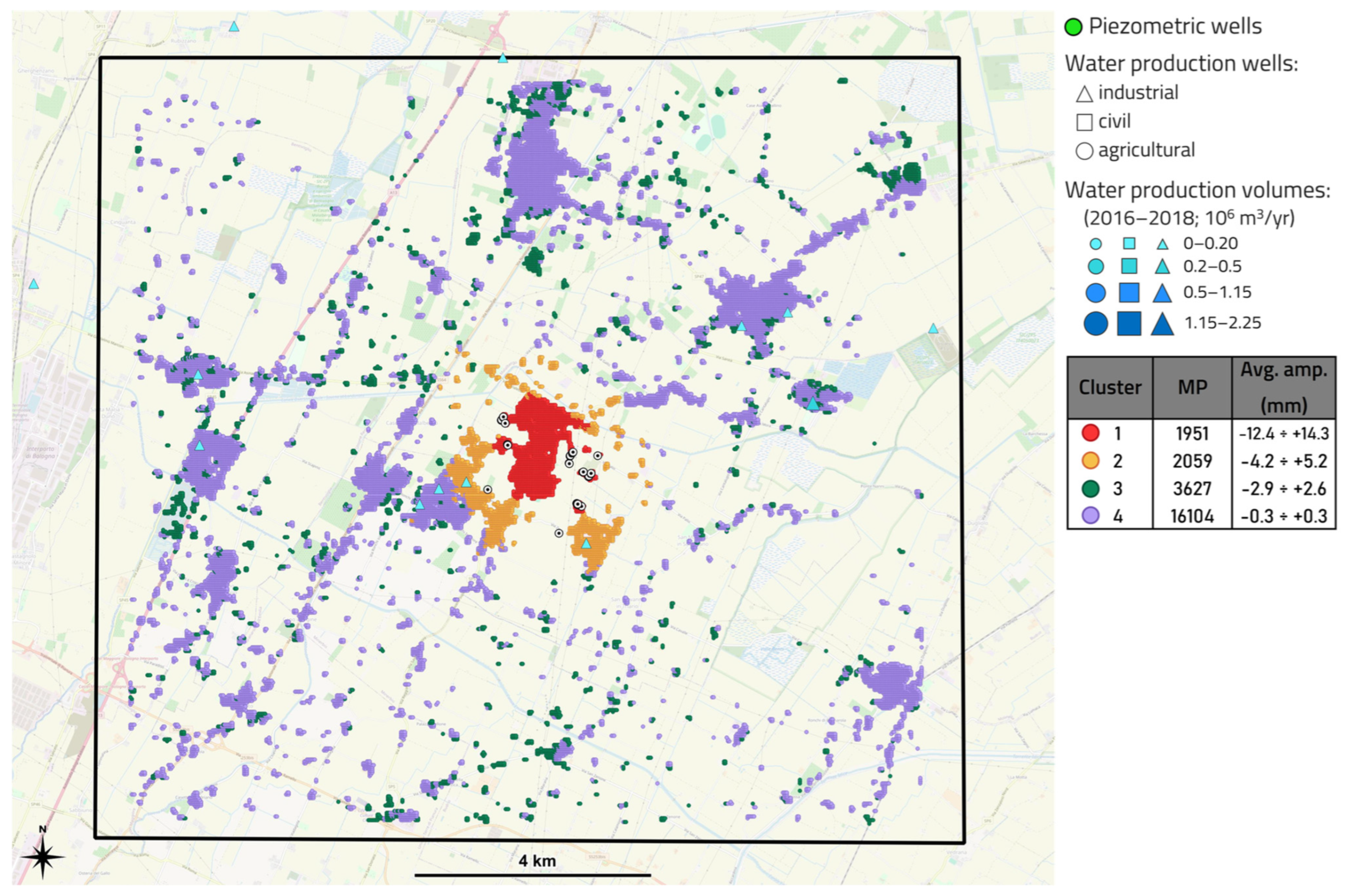
- “Area 3”, in between, shows poor and scattered urban and industrial areas, numerous widespread water production wells with average production volume, and is marked by the presence of a UGS system. It represents a transition zone with superimposed effects from superficial aquifer exploitation and deep subsurface operations.
2.3. Datasets
- Land use maps from the geoportal of Regione Emilia-Romagna;
- Ground movement surveys:
- Groundwater production volumes (in 106 m3/yr) in the time frame 2016–2018, and well positions;
- Well use: for agricultural, civil, and industrial purposes;
- piezometric data measurements publicly available on the Open Data portal of ARPAE (Agenzia Prevenzione Ambiente Energia Emilia-Romagna);
- Geological data collected from technical literature and the geoportal of Regione Emilia-Romagna:
- Geological cross-sections;
- Hydrodynamic aquifer parametrization.
2.4. P-SBAS DInSAR
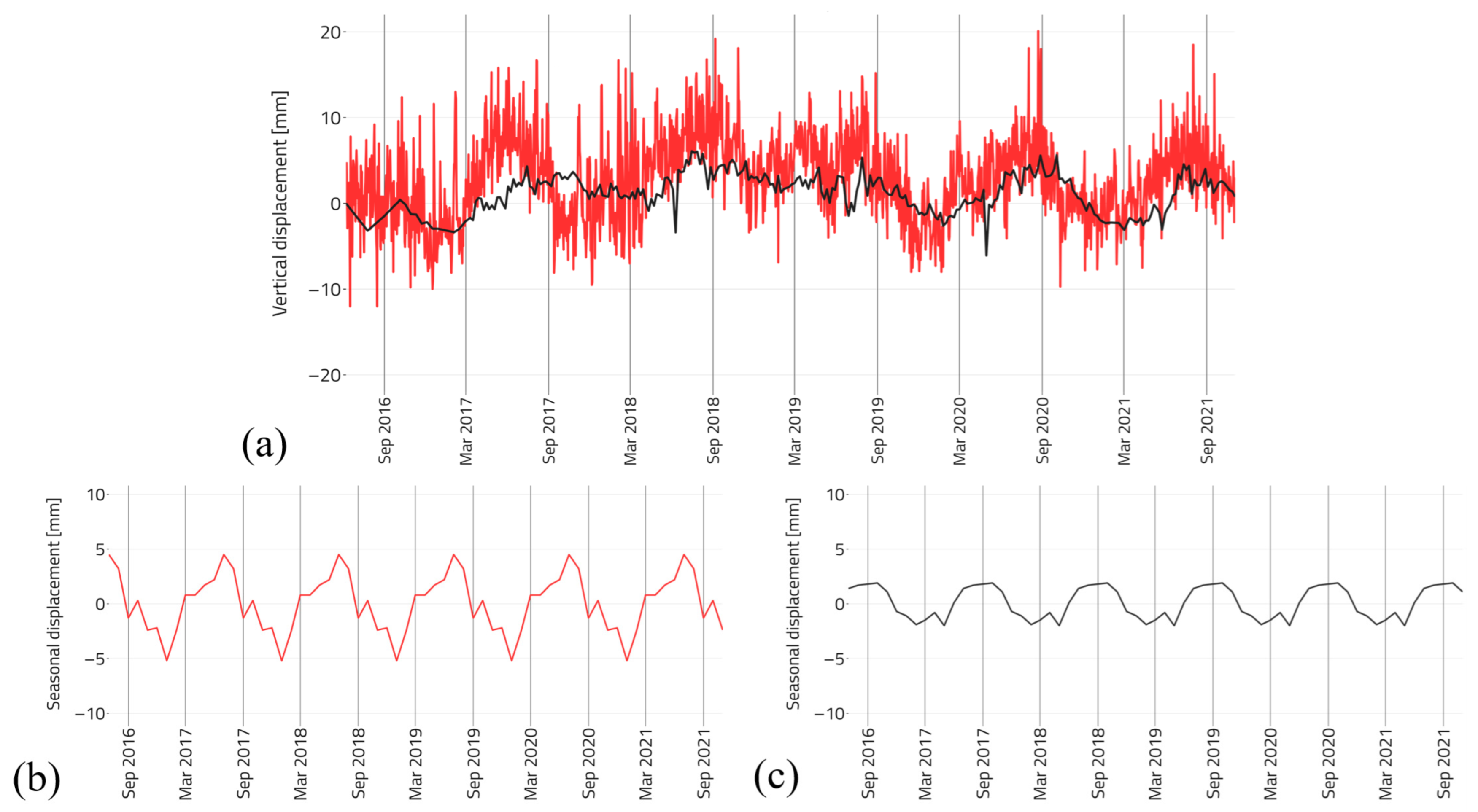
2.5. Seasonal and Trend Decomposition Using Loess
2.6. Cluster Analysis—K-Means
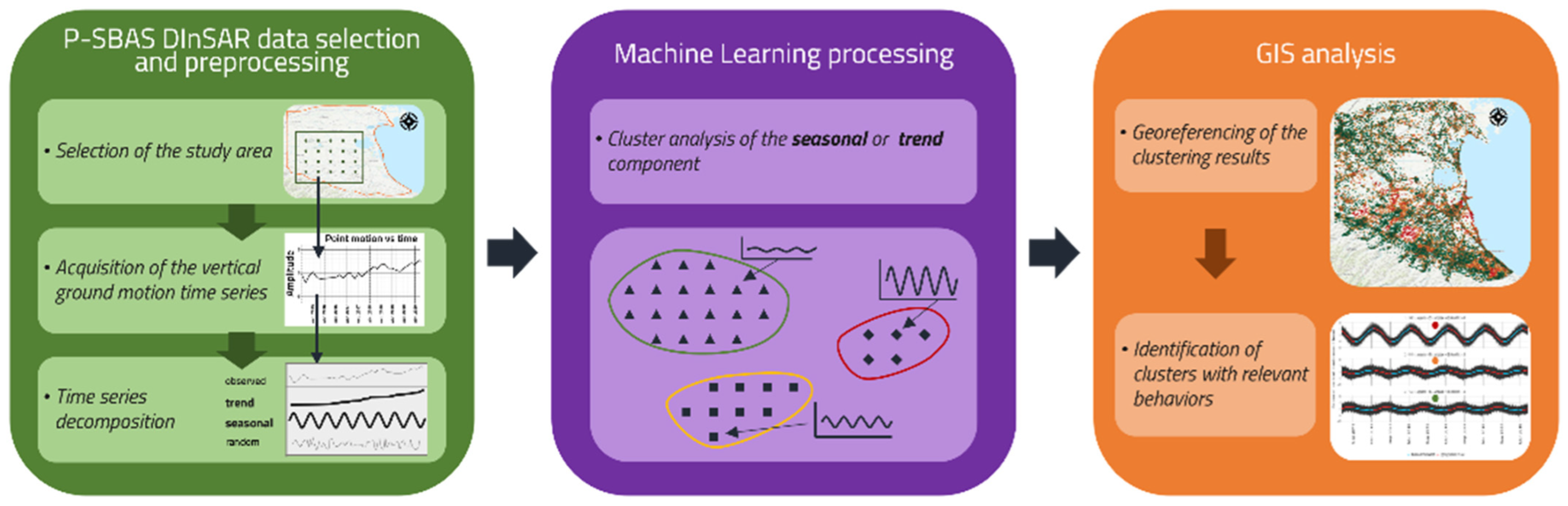
2.7. Methodology
- The relative P-SBAS DInSAR vertical measurements were compared with the GNSS absolute vertical measurements from the “BOLG00ITA” station located close to the city of Bologna (Figure 3);
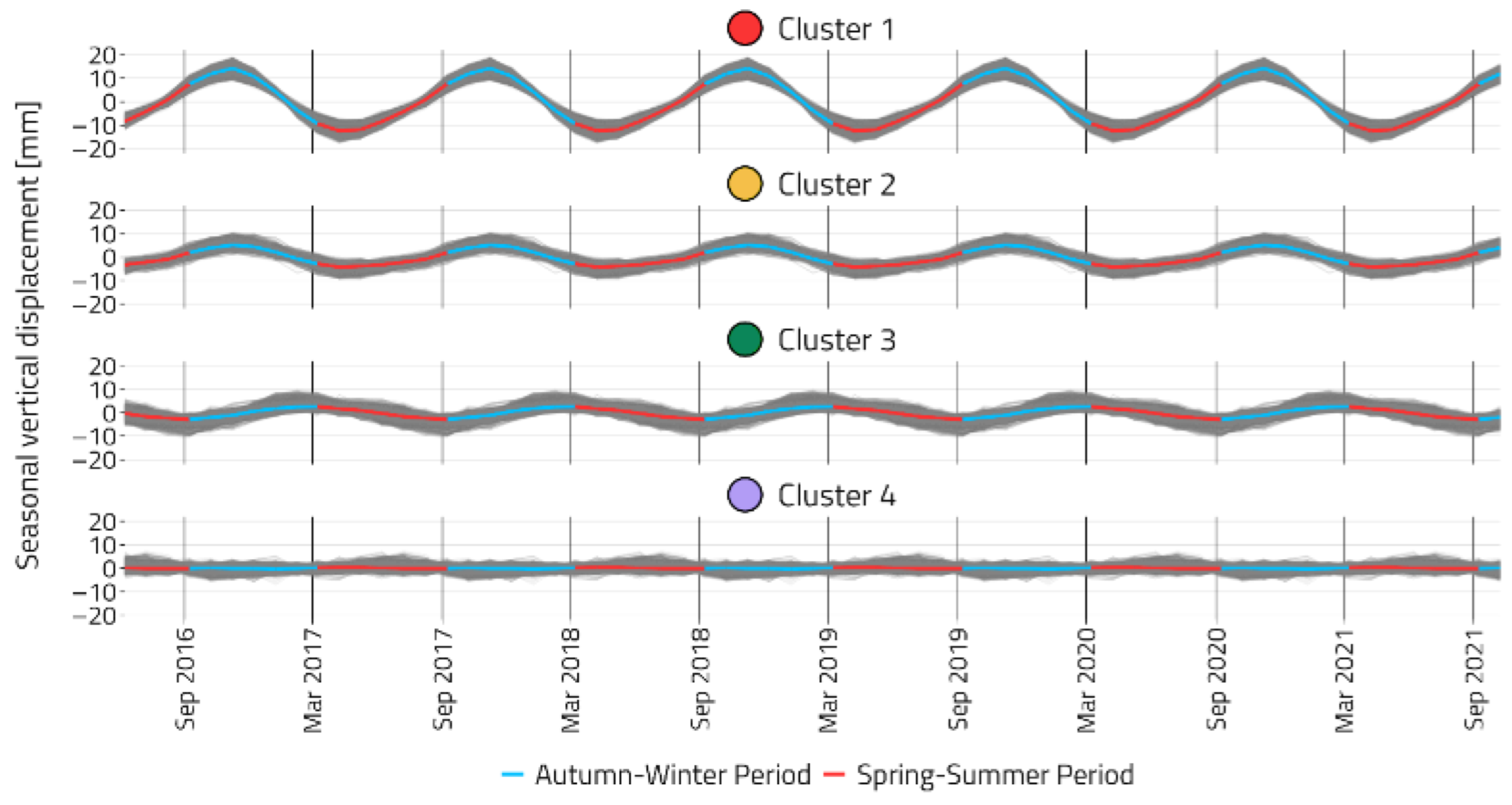
- P-SBAS DInSAR vertical time-series were processed through STL and successive cluster analysis on seasonal and trend components using the methodology developed by [18];
- The behavior and magnitude of the identified clusters (where a cluster groups objects based on the similarity of some shared properties or features [41]) were compared with both groundwater production and UGS information;
- The geological framework of the superficial aquifers from [4] was further investigated for the specific area under analysis and, together with the general geological framework of the Po Plain, they were related to the phenomena identified by the cluster analysis output.
3. Results
3.1. Analyses of Ground Movement Survey Data: P-SBAS DInSAR and GNSS
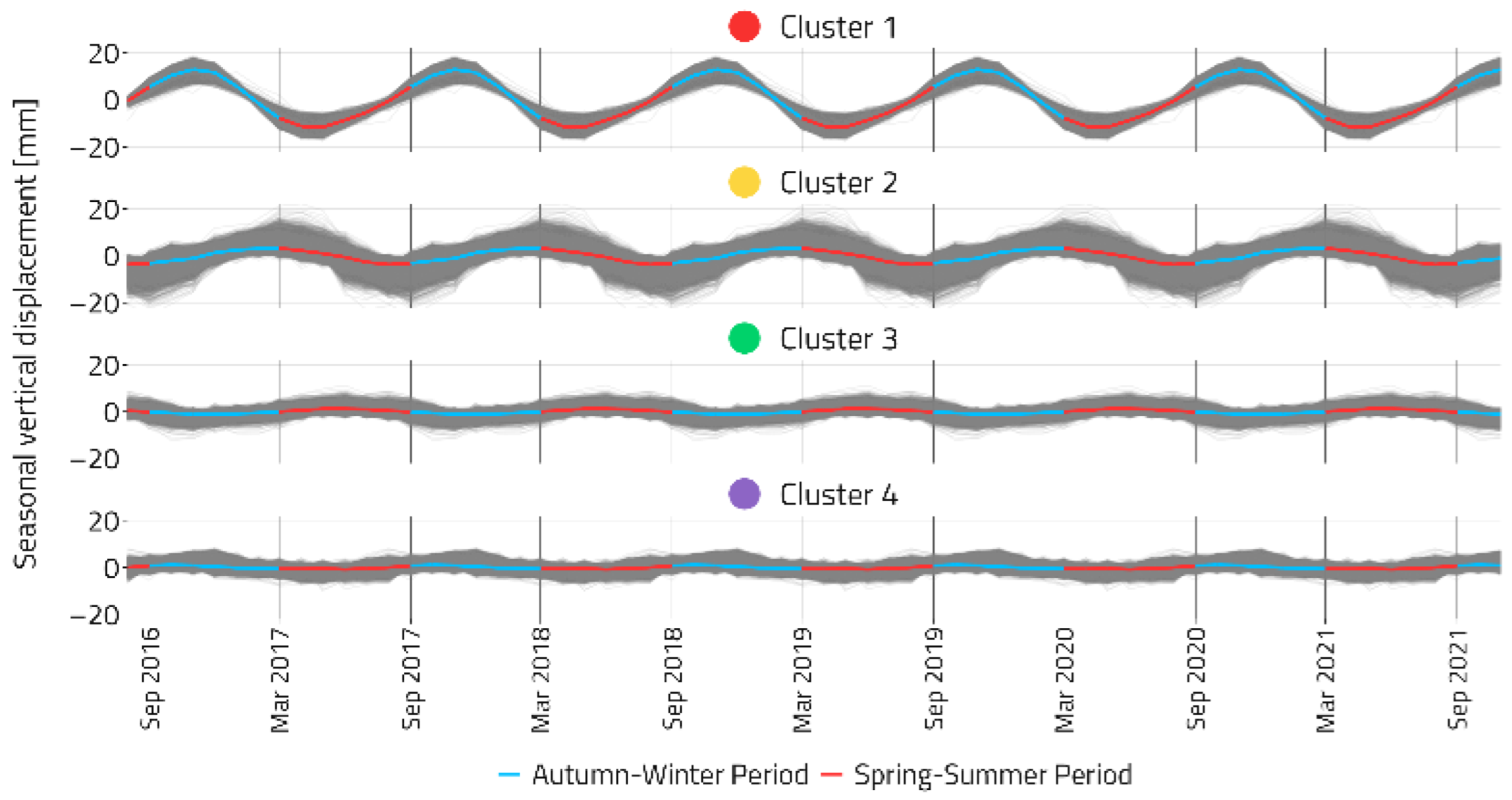
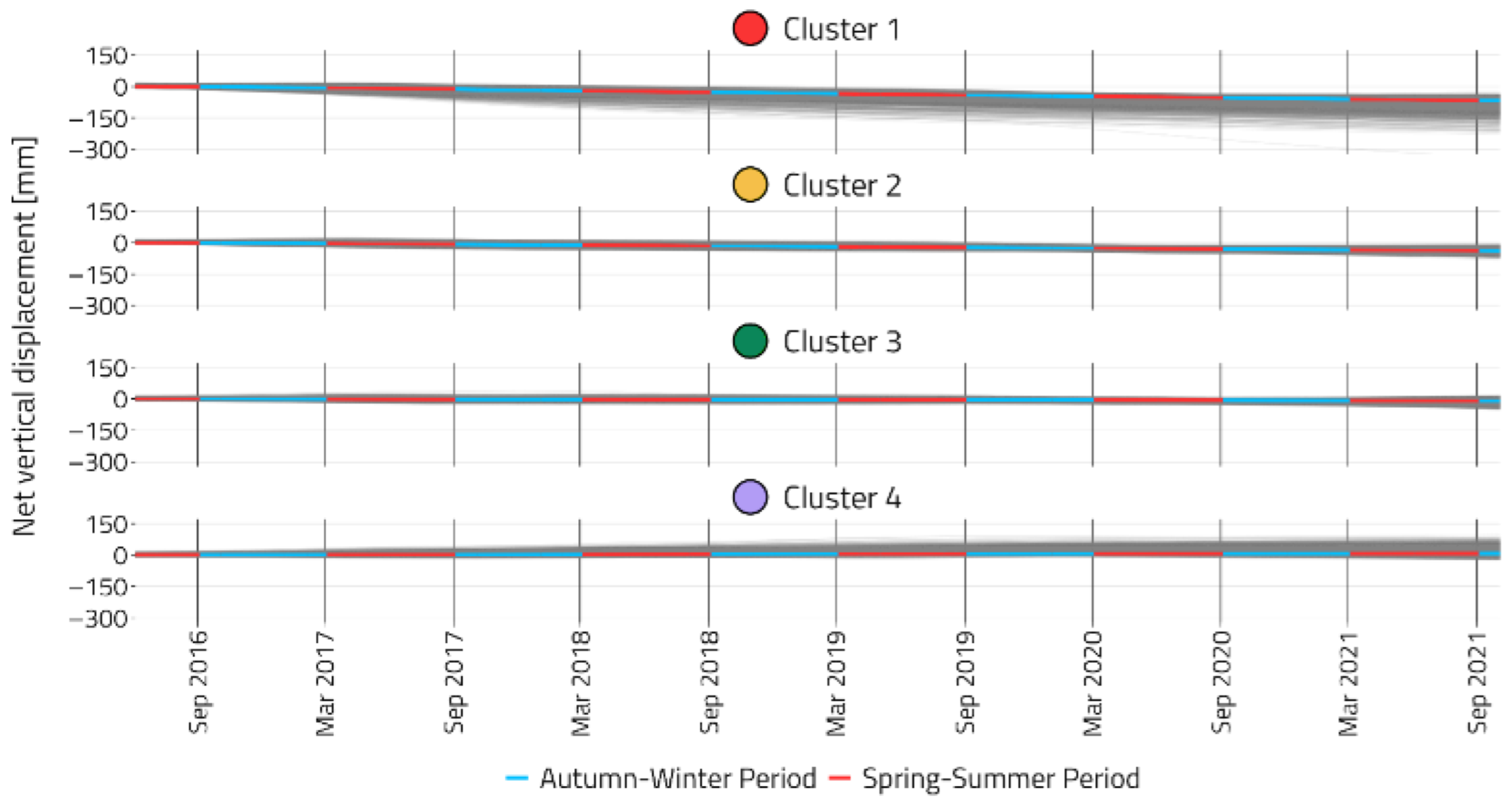
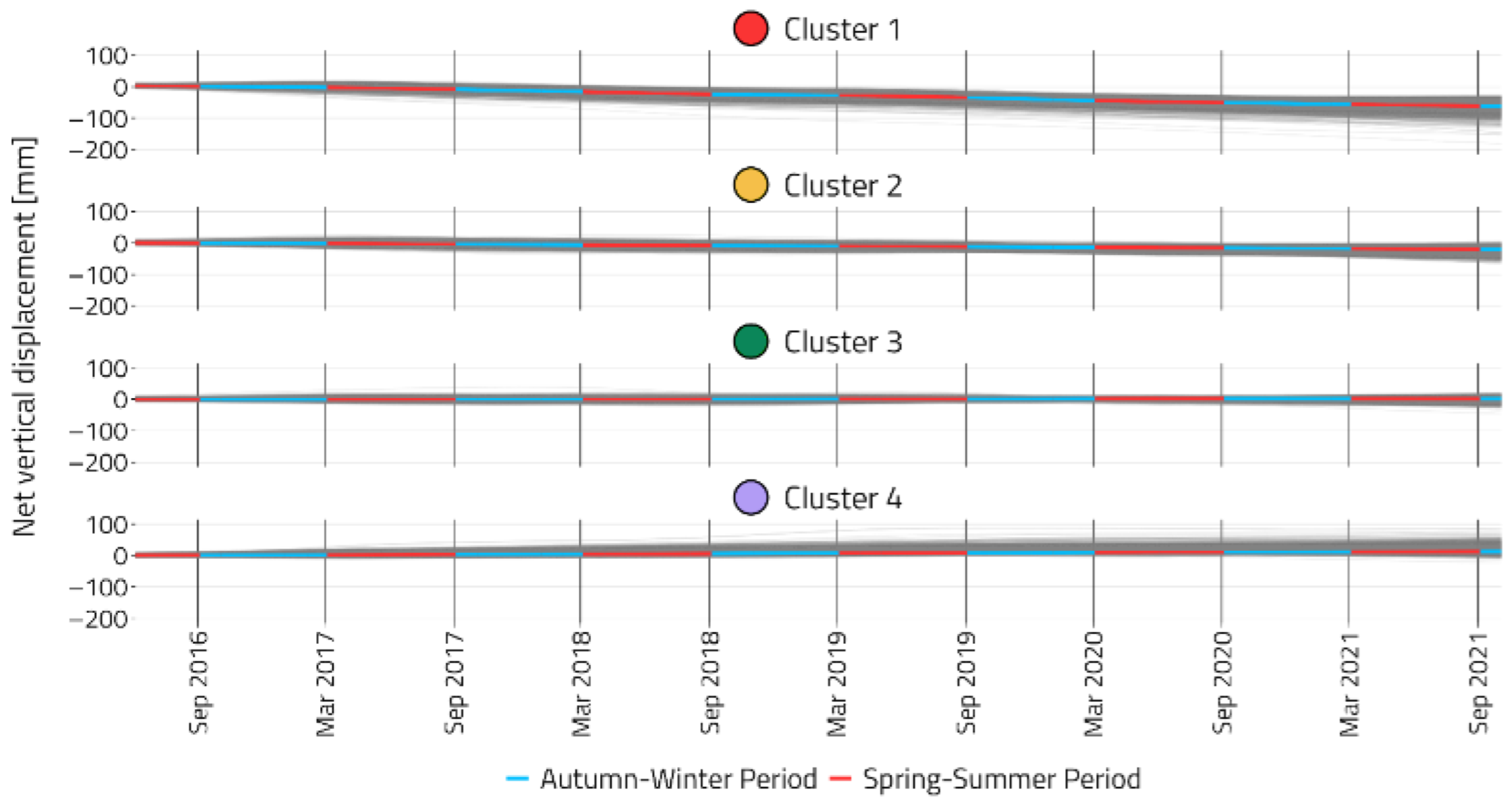
3.2. Analyses of Seasonal and Trend Behavior of Ground Movements: Regional Scale
3.3. Analyses of Seasonal and Trend Behavior of Ground Movements: Local Scale
3.3.1. Area 1
3.3.2. Area 2
3.3.3. Area 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARPAE | Agenzia Prevenzione Ambiente Energia Emlia-Romagna |
| CNR-IREA | National Research Council—Institute for the Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment |
| DInSAR | Diferential Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| EPN | EUREF Permanent Network |
| EUREF | Regional Reference Frame Sub-Commission for Europe |
| GIS | Geographic Information Systems |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite Systems |
| INGV | Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia |
| IWS | Interferometric Wide Swath |
| LOS | Line of Sight |
| MP | Measuring point |
| NE | North East |
| NW | North West |
| P-SBAS | Parallel Computing Small BAseline Subset |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| SBAS | Small BAseline Subset |
| STL | Seasonal and Trend decomposition by Loess |
| UGS | Underground Gas Storage |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1

Appendix A.2

Appendix A.3

References
- Kooi, H.; Vries, J.J. Land Subsidence and Hydrodynamic Compaction of Sedimentary Basins. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 1998, 2, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barends, F.B.J.; Brouwer, F.J.J.; Schroder, F.H. Land Subsidence: Natural Causes, Measuring Techniques, the Groningen Gasfields; IAHS Publications: Wallingford, UK, 1995; Volume 234, p. 409. [Google Scholar]
- Coda, S.; Tessitore, S.; Martire, D.; Calcaterra, D.; Vita, P.; Allocca, V. Coupled Ground Uplift and Groundwater Rebound in the Metropolitan City of Naples (Southern Italy). J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, C.; Benetatos, C.; Rocca, V. Fluid Production Dataset for the Assessment of the Anthropogenic Subsidence in the Po Plain Area (Northern Italy). Resources 2022, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Erkens, G.; Kuniansky, E.L.; Rowland, J.C. Preface: Land Subsidence Processes. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, M.; Pieri, L.; Unguendoli, M. Geometric investigation of the subsidence in the Po Delta. Boll. Geod. Teor. Appl. 1970, 13, 187–207. [Google Scholar]
- Arca, S.; Beretta, G. Prima sintesi geodetico-geologica sui movimenti verticali del suolo nell’Italia Settentrionale (1897–1957). Boll. Geod. Sci. Affin. 1985, 44, 125–156. [Google Scholar]
- Carminati, E.; Martinelli, G. Subsidence Rates in the Po Plain, Northern Italy: The Relative Impact of Natural and Anthropogenic Causation. Eng. Geol. 2002, 66, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitelli, G.; Bonsignore, F.; Del Conte, S.; Franci, F.; Lambertini, A.; Novali, F.; Severi, P.; Vittuari, L. Updating the Subsidence Map of Emilia-Romagna Region (Italy) by Integration of SAR Interferometry and GNSS Time Series: The 2011–2016 Period. Proc. IAHS 2020, 382, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminati, E.; Donato, G. Separating Natural and Anthropogenic Vertical Movements in Fast Subsiding Areas: The Po Plain (N. Italy) Case. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teatini, P.; Ferronato, M.; Gambolati, G.; Gonella, M. Groundwater Pumping and Land Subsidence in the Emilia-Romagna Coastland, Italy: Modeling the Past Occurrence and the Future Trend. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbini, S.; Richter, B.; Rocca, F.; Dam, T.; Matonti, F. A Combination of Space and Terrestrial Geodetic Techniques to Monitor Land Subsidence: Case Study, the Southeastern Po Plain, Italy. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, 5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, P.; Bonvalot, S.; Borghi, A.; Brancolini, G.; Carminati, E.; Cavaliere, A.; Teatini, P. La Subsidenza nell’italia Centro-Settentrionale da Misure GPS; Gruppo Nazionale di Geofisica della Terra Solida: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cenni, N.; Fiaschi, S.; Fabris, M. Monitoring of Land Subsidence in the Po River Delta (Northern Italy) Using Geodetic Networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Saroli, M.; Tolomei, C.; Moro, M.; Doumaz, F.; Pesci, A.; Loddo, F.; Baldi, P.; Boschi, E. Surface Movements in Bologna (Po Plain, Italy) Detected by Multitemporal DInSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nespoli, M.; Cenni, N.; Belardinelli, M.E.; Marcaccio, M. The Interaction between Displacements and Water Level Changes Due to Natural and Anthropogenic Effects in the Po Plain (Italy): The Different Point of View of GNSS and Piezometers. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confuorto, P.; Del Soldato, M.; Solari, L.; Festa, D.; Bianchini, S.; Raspini, F.; Casagli, N. Sentinel-1-Based Monitoring Services at Regional Scale in Italy: State of the Art and Main Findings. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Navarro, A.M.; Rocca, V.; Capozzoli, A.; Chiosa, R.; Verga, F. Investigation of Ground Movements Induced by Underground Gas Storages via Unsupervised ML Methodology Applied to InSAR Data. Gas Sci. Eng. 2024, 125, 205293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S.; McRae, J.E.; Terpenning, I. STL: A Seasonal-Trend Decomposition Procedure Based on Loess (with Discussion). J. Stat. Softw. 1990, 6, 3–73. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinno, I. A First Assessment of the P-SBAS DInSAR Algorithm Performances within a Cloud Computing Environment. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4675–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Elefante, S.; Imperatore, P.; Zinno, I.; Manunta, M.; Luca, C.; Lanari, R. SBAS-DInSAR Parallel Processing for Deformation Time-Series Computation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrini, C. Influence of Structural Inheritance on Foreland-Foredeep System Evolution. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 376–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doglioni, C. Some Remarks on the Origin of Foredeeps. Tectonophysics 1993, 288, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrato, P.; Ciucci, F.; Valensise, G. An Inventory of River Anomalies in the Po Plain, Northern Italy: Evidence for Active Blind Thrust Faulting. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 46, 865–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, M.; Groppi, G. Progetto Finalizzato Geodinamica. In Subsurface Geological Structure of the Po Plain, Italy; CNR Publication: Rome, Italy, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Area Geologia, Suoli e Sismica-Settore Difesa del Territorio-Regione Emilia-Romagna. Riserve Idriche Sotterranee Della Regione Emilia-Romagna; Selca: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, M.; Marcaccio, M.; Zavatti, A. Esperienze e Prospettive Nel Monitoraggio Delle Acque Sotterranee: Il Contributo Dell’emilia-Romagna; Pitagora Editrice: Bologna, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, G.; Minissale, A.; Verrucchi, C. Geochemistry of Heavily Exploited Aquifers in the Emilia-Romagna Region (Po Valley, Northern Italy. Environ. Geol. 1998, 36, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Dadomo, A.; Italiano, F.; Petrini, R.; Slejko, F.F. Geochemical Monitoring of the 2012 Po Valley Seismic Sequence: A Review and Update. Chem. Geol. 2017, 469, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modoni, G.; Darini, G.; Spacagna, R.L.; Saroli, M.; Russo, G.; Croce, P. Spatial-Temporal Analysis of the Subsidence in the City of Bologna. In Geotechnical Engineering for the Preservation of Monuments and Historic Sites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alessi, R. La subsidenza nel centro storico della città di Bologna. Il grado di dissesto dei fabbricati nella zona di via Zamboni. Inarcos 1985, 456. [Google Scholar]
- Darini, G.; Modoni, G.; Saroli, M.; Croce, P. Land Subsidence Induced by Groundwater Extraction: The Case of Bologna. In Proceedings of the IEMSs 2008: International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software, Barcelona, Spain, 3 July 2008; pp. 1386–1393. [Google Scholar]
- Bruyninx, C.; Legrand, J.; Fabian, A.; Pottiaux, E. GNSS Metadata and Data Validation in the EUREF Permanent Network. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetatos, C.; Codegone, G.; Ferraro, C.; Mantegazzi, A.; Rocca, V.; Tango, G.; Trillo, F. Multidisciplinary analysis of ground movements: An underground gas storage case study. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar Interferometry and Its Application to Changes in the Earth’s Surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry to Measure Earth’s Surface Topography and Its Deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Casu, F.; Ventura, G.; Zeni, G.; Borgström, F.; Berardino, P.; Del Gaudio, C.; Lanari, R. Surface Deformation Analysis in the Ischia Island (Italy) Based on Spaceborne Radar Interferometry. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2006, 151, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.; Zinno, I.; Manunta, M.; Lanari, R.; Casu, F. Large Areas Surface Deformation Analysis through a Cloud Computing P-SBAS Approach for Massive Processing of DInSAR Time Series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, C.D.; Valerio, E.; Giudicepietro, F.; Macedonio, G.; Casu, F.; Lanari, R. Pre- and Co-Eruptive Analysis of the September 2021 Eruption at Cumbre Vieja Volcano (La Palma, Canary Islands) Through DInSAR Measurements and Analytical Modeling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Steinbach, M.; Karpatne, A.; Kumar, V. Introduction to Data Mining, 2nd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Morissette, L.; Chartier, S. The K-Means Clustering Technique: General Considerations and Implementation in Mathematica. Tutor. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2013, 9, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A K-Means Clustering Algorithm. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 1979, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice; OTexts: Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zinno, I.; Casamento, F.; Lanari, R. On The Exploitation of Etad Data for the Atmospheric Phase Screen Filtering of Medium/High Resolution Dinsar Products. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023—2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 7882–7885. [Google Scholar]
- Verga, F. What’s Conventional and What’s Special in a Reservoir Study for Underground Gas Storage. Energies 2018, 11, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severi, P. Soil Uplift in the Emilia-Romagna Plain (Italy) by Satellite Radar Interferometry. Bull. Geophys. Oceanogr. 2021, 62, 527–542. [Google Scholar]
- Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia. Concessione di Stoccaggio di Gas Naturale “MINERBIO Stoccaggio” (BO) Relazione Finale; Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Giacomelli, S.; Zuccarini, A.; Amorosi, A.; Bruno, L.; Paola, G.; Martini, A.; Severi, P.; Berti, M. 3D Geological Modelling of the Bologna Urban Area (Italy). Eng. Geol. 2023, 324, 107242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argnani, A.; Barbacini, G.; Bernini, M.; Camurri, F.; Ghielmi, M.; Papani, G.; Rizzini, F.; Rogledi, S.; Torelli, L. Gravity Tectonics Driven by Quaternary Uplift in the Northern Apennines: Insights from the La Spezia-Reggio Emilia Geo-Transect. Quat. Int. 2003, 101–102, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletti, M.; Corti, G.; Martelli, L. Recent and Active Tectonics of the External Zone of the Northern Apennines (Italy). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 100, 1331–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Category | Extended Area | Area 1 | Area 2 | Area 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural and green areas | 81.6 | 61.5 | 88.8 | 86.0 |
| Urban areas | 10.5 | 21.4 | 6.2 | 6.9 |
| Industrial areas | 2.5 | 6.0 | 0.6 | 1.3 |
| Road and railway networks | 2.8 | 7.4 | 1.2 | 1.5 |
| Others | 2.6 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 4.4 |
| Covered Area (km × km) | Number of Measuring Points (MPs) | MPs Density (MP/km2) | Grid Spatial Resolution (m × m) | Satellite | Processing Algorithm | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1850 | 223,311 | 121 | 40 × 30 | Sentinel 1 | Parallel SBAS Interferometry Chain (*) | June–2016 October–2021 |
| Azimuth Multilook Factor (Pixels) | Range Multilook Factor (Pixels) | Maximum Temporal Baseline (Days) | Maximum Spatial Baseline (m) | Temporal Coherence Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 20 | 360 | 200 | 0.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro, A.M.G.; Eid, C.; Rocca, V.; Benetatos, C.; De Luca, C.; Onorato, G.; Lanari, R. Integrated Analysis of Satellite and Geological Data to Characterize Ground Deformation in the Area of Bologna (Northern Italy) Using a Cluster Analysis-Based Approach. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152645
Navarro AMG, Eid C, Rocca V, Benetatos C, De Luca C, Onorato G, Lanari R. Integrated Analysis of Satellite and Geological Data to Characterize Ground Deformation in the Area of Bologna (Northern Italy) Using a Cluster Analysis-Based Approach. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(15):2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152645
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro, Alberto Manuel Garcia, Celine Eid, Vera Rocca, Christoforos Benetatos, Claudio De Luca, Giovanni Onorato, and Riccardo Lanari. 2025. "Integrated Analysis of Satellite and Geological Data to Characterize Ground Deformation in the Area of Bologna (Northern Italy) Using a Cluster Analysis-Based Approach" Remote Sensing 17, no. 15: 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152645
APA StyleNavarro, A. M. G., Eid, C., Rocca, V., Benetatos, C., De Luca, C., Onorato, G., & Lanari, R. (2025). Integrated Analysis of Satellite and Geological Data to Characterize Ground Deformation in the Area of Bologna (Northern Italy) Using a Cluster Analysis-Based Approach. Remote Sensing, 17(15), 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152645









