Enhancing Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Single-Channel Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface via Phase Coding Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We establish a single receiving channel RIS-aided DOA estimation system model. Unlike existing works, which directly modeled the complex-valued received signals, we construct a power-based signal model by averaging the received signals. Based on this model, the DOA estimation problem is transformed into a sparse signal recovery problem in the framework of compressed sensing, where the far-field power radiation pattern of the RIS behaves as the measurement matrix.
- We derive the decoupled expression of the measurement matrix, which consists of the phase coding matrix, propagation phase shifts, and array steering matrix. Building on this, we formulate the phase coding design problem as the minimization of the mutual coherence of the measurement matrix. To overcome the challenges posed by the resulting non-convex optimization, we further transform the problem into minimizing the Frobenius norm between the Gram matrix of the measurement matrix and the identity matrix.
- We propose a deterministic phase coding design, where the phase coding is constructed based on the product of a unitary matrix and a partial Hadamard matrix. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed phase coding design significantly reduces the DOA estimation error and achieves a higher resolution probability compared with methods based on random phase coding.
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Signal Model
2.2. Sparse Representation for DOA Estimation
| Algorithm 1 OMP algorithm for DOA estimation. |
| Require: , , K. |
|
3. Proposed Phase Coding Design Method
3.1. Mutual Coherence of the Measurement Matrix
3.2. Proposed Phase Coding Design Method
| Algorithm 2 Proposed phase coding design algorithm. |
| Require: Initial matrix , . |
|
| Ensure: The optimized equivalent measurement matrix . |
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Details of Experiments
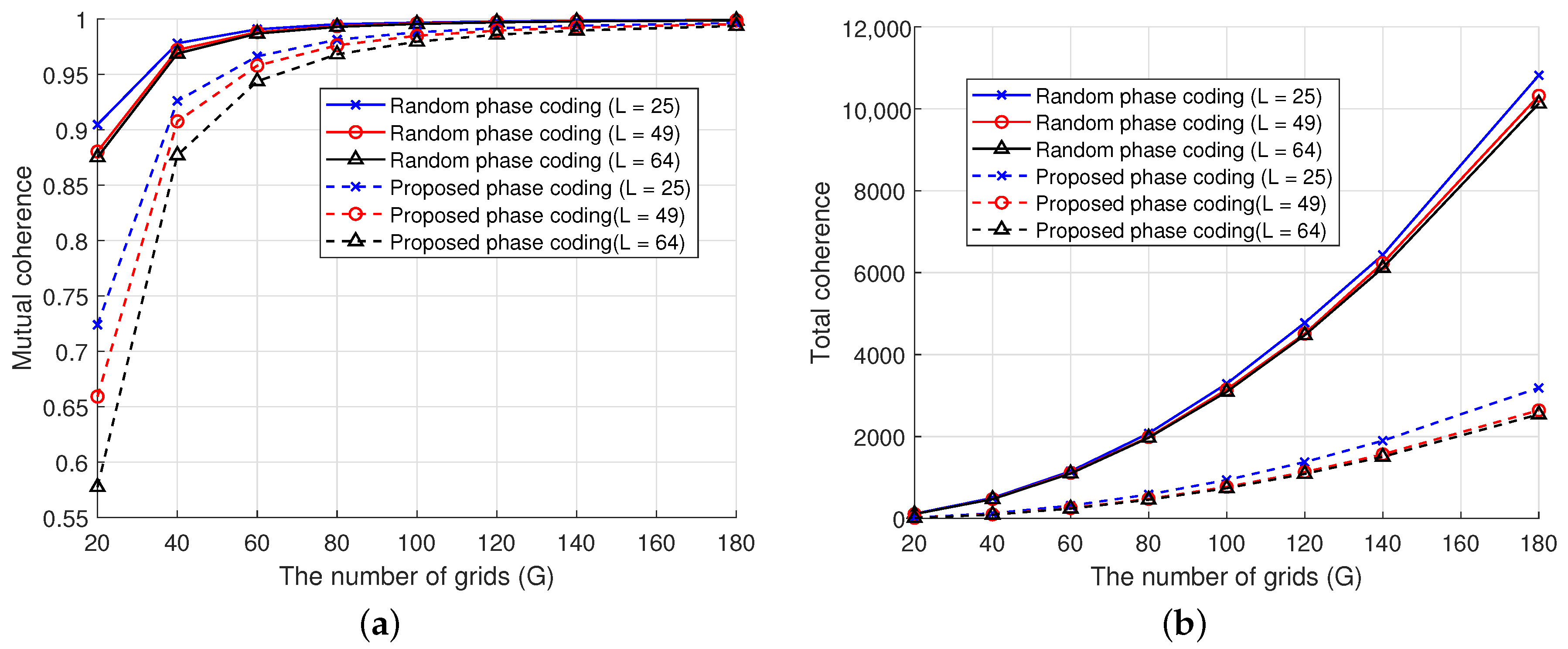
4.2. Validity Analysis
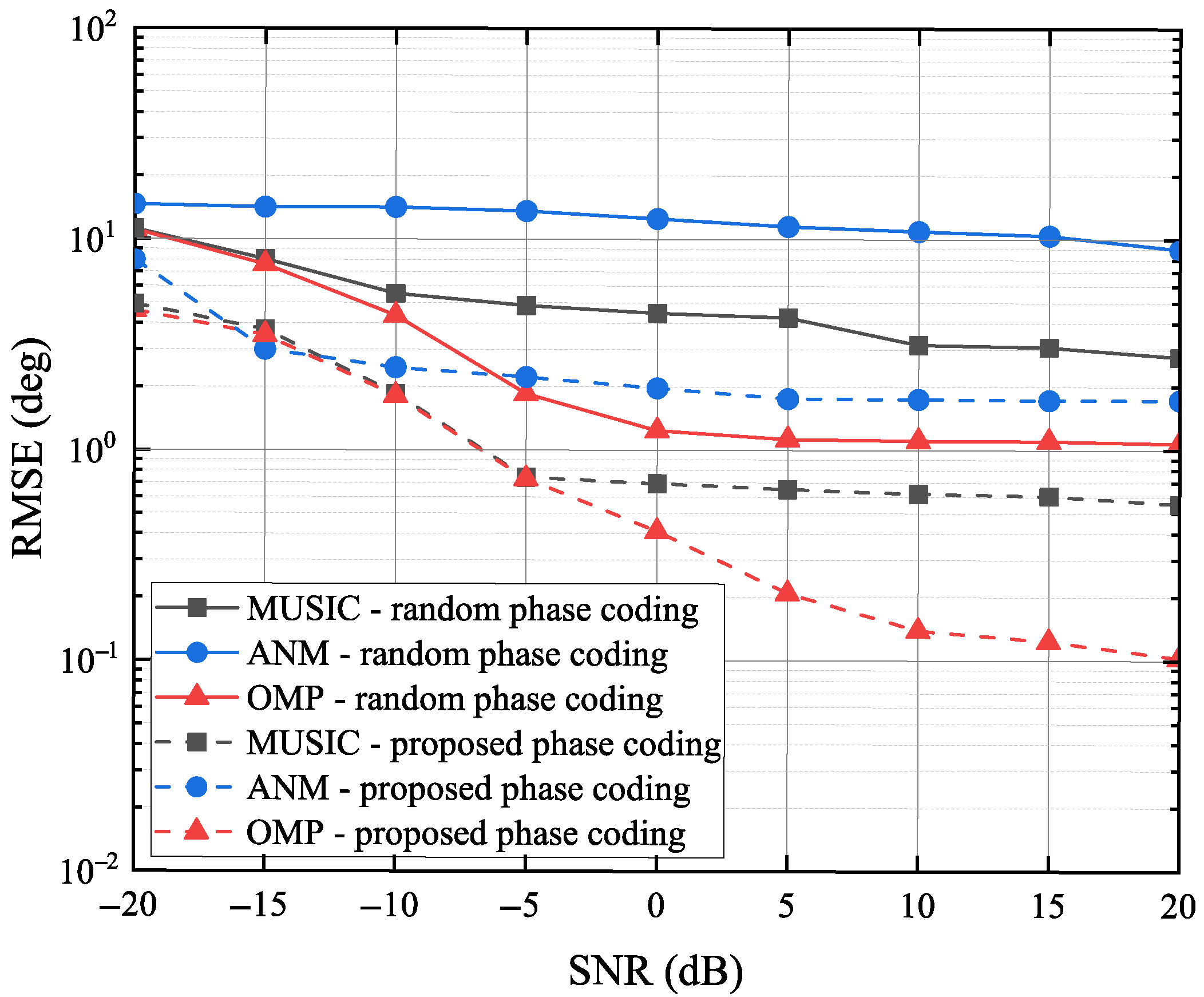
4.3. Performance Analysis Under Different SNRs
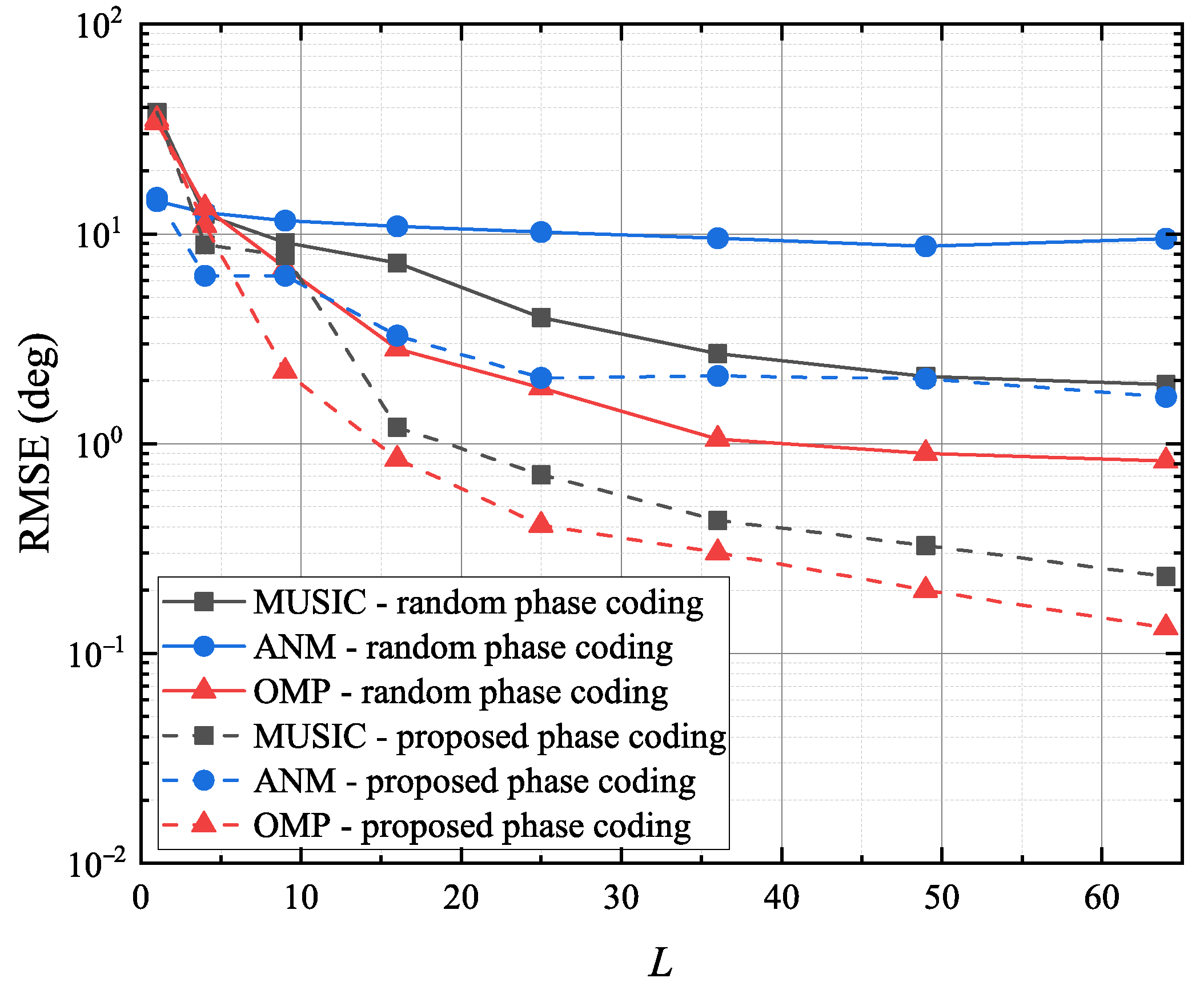
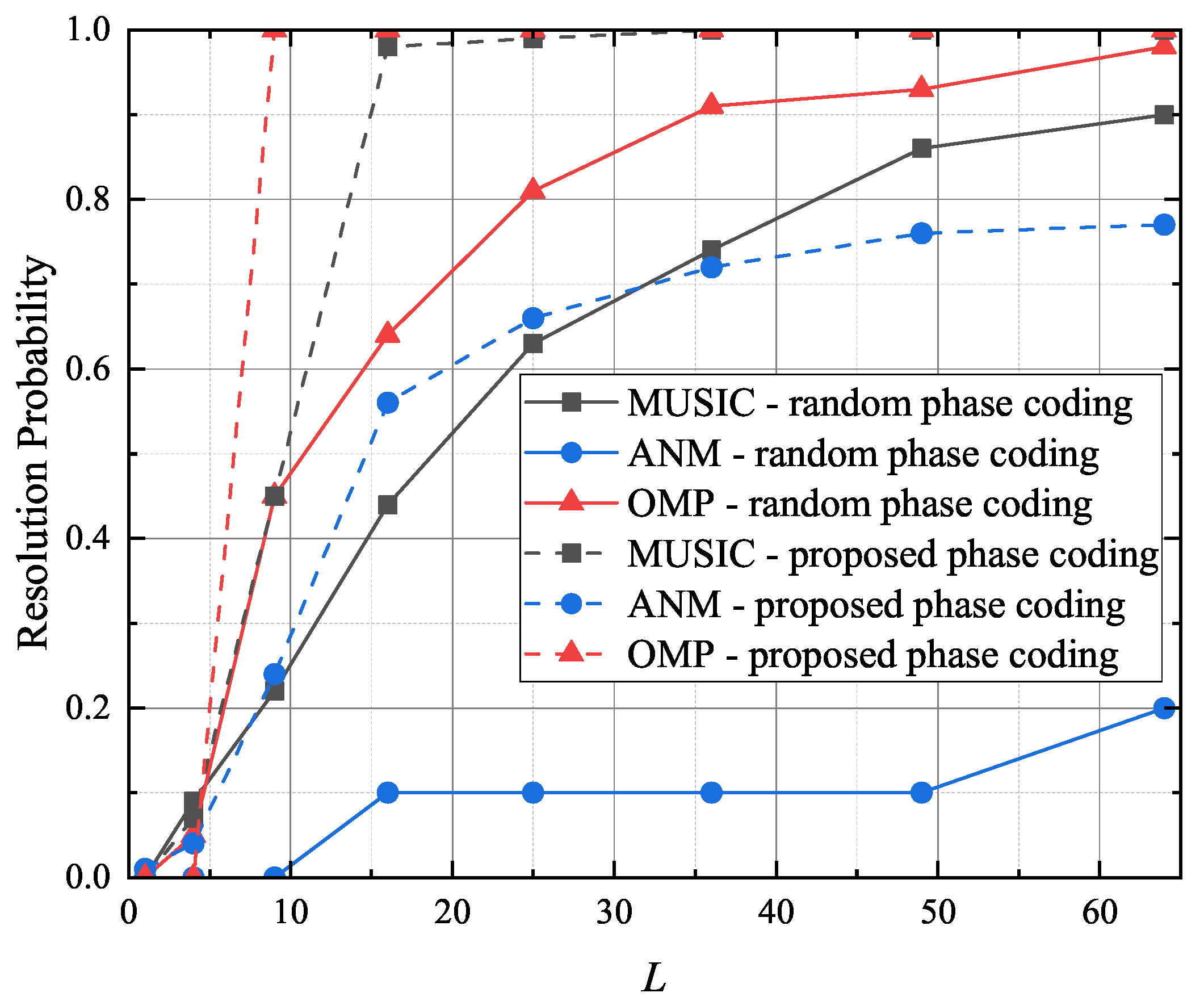
4.4. Performance Analysis Under Different L Values
4.5. Performance Analysis Under Different Angles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Proof of Lemma 1
Appendix B. The Proof of Lemma 2
Appendix C. The Proof of Lemma 3
References
- Luo, X.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, R.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, M. ISAC—A Survey on Its Layered Architecture, Technologies, Standardizations, Prototypes and Testbeds. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shim, B.; Zhao, H. Downlink Compressive Channel Estimation with Phase Noise in Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 5534–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, M.; Lan, X.; Sun, L. Tensor-Based Reduced-Dimension MUSIC Method for Parameter Estimation in Monostatic FDA-MIMO Radar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Thomas Hou, Y.; Lou, W. A Real-time Super-resolution DoA Estimation Algorithm for Automotive Radar Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 37947–37961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shen, X.; Shang, Z.; Ding, G.; Wu, H.; Qiao, X. An Open-Set Few-Shot Class Incremental Learning Framework for Specific Emitter Identification. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cheng, L.; Wang, S.; Lou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, W.; Ng, D.W.K. Integrated Sensing and Communication with Massive MIMO: A Unified Tensor Approach for Channel and Target Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 8571–8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X.; Cai, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R. Channel Estimation for Movable-Antenna MIMO Systems Via Tensor Decomposition. IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett. 2024, 13, 3089–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Kailath, T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W. Research on super resolution angle measurement based on esprit algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2646, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Park, Y.; Gerstoft, P. Gridless DOA Estimation and Root-MUSIC for Non-Uniform Linear Arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Y.D.; Huang, Y. Rank Minimization-Based Toeplitz Reconstruction for DoA Estimation Using Coprime Array. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2265–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Off-Grid DOA Estimation Using Sparse Bayesian Learning in MIMO Radar with Unknown Mutual Coupling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H. Block Bayesian matching pursuit based channel estimation for FDD massive MIMO system. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 93, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Pan, J. Direction of Arrival Estimation by a Modified Orthogonal Propagator Method with Spline Interpolation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 11389–11393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, F.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Blum, R.S. Super-Resolution Compressed Sensing for Line Spectral Estimation: An Iterative Reweighted Approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 4649–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chi, Y. Off-the-Grid Line Spectrum Denoising and Estimation with Multiple Measurement Vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, Y.D.; Chen, T. DOA estimation using compressed sparse array. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 4133–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, W.; Chen, X.; Gao, Z.; Cai, Y. Terahertz Integrated Sensing and Communication-Empowered UAVs in 6G: A Transceiver Design Perspective. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2025, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shim, B.; Wu, W. Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Large Antenna Arrays with Hybrid Analog and Digital Architectures. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, R.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cai, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, J. Improving Age of Information for Covert Communication with Time-Modulated Arrays. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 1718–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.J. Microwave metamaterials. Nat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Tang, J.; Zhang, S.; So, D.K.; Dobre, O.A.; Wong, K.K.; Chambers, J. Reconfigurable-Intelligent-Surface-Assisted B5G/6G Wireless Communications: Challenges, Solution, and Future Opportunities. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2023, 61, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeywickrama, S.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Yuen, C. Intelligent Reflecting Surface: Practical Phase Shift Model and Beamforming Optimization. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 5849–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, G.; Cheng, L.; Guan, X.; Wu, Q.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R. Tensor-based Channel Estimation for Extremely Large-Scale MIMO-OFDM with Dynamic Metasurface Antennas. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2025, 24, 6052–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Miao, C.; Ma, Y.; Wu, W. Energy-Efficient Beamforming for Downlink Multi-User Systems with Dynamic Metasurface Antennas. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2025, 29, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kim, S.; Shim, B. Energy-Efficient Power Control and Beamforming for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Uplink IoT Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 10162–10176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Wang, H.; Gui, G.; Sari, H.; Adachi, F. Polarized Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided 2D-DOA Estimation for NLoS Sources. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 8085–8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.J.; Qi, M.Q.; Wan, X.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Q.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, S.; Guo, L.J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Xue, H.; Liu, G.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, T.J. Accurate 2-D DoA estimation based on active metasurface with nonuniformly periodic time modulation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Technol. 2022, 71, 3424–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, P.; Guo, Z.; Ni, D. Low-Cost Beamforming and DOA Estimation Based on One-Bit Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 2397–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Su, X.; He, L.; Guan, D.; Liu, Z. Coherent Signal DOA Estimation Method Based on Space–Time–Coding Metasurface. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Xu, M.; Wan, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Deng, B.; Guan, D.; Zha, S. Single Sensor to Estimate DOA with Programmable Metasurface. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 10187–10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Wan, X.; Cui, T. High-Precision Direction-of-Arrival Estimations Using Digital Programmable Metasurface. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, B.; Wang, X. Efficient DOA Estimation Method for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces Aided UAV Swarm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ren, L.; Ma, Z.; Fan, P. RIS Aided Gridless 2D-DOA Estimation via Decoupled Atomic Norm Minimization. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 15733–15738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Shang, X.; Han, C.; Zhang, Y. Robust sensing matrix design for the Orthogonal Matching Pursuit algorithm in compressive sensing. Signal Process. 2025, 227, 109684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Gil, G.T.; Lee, Y.H. Channel Estimation via Orthogonal Matching Pursuit for Hybrid MIMO Systems in Millimeter Wave Communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 64, 2370–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Shen, W.; Xing, C.; Zhao, L.; An, J. Training Beam Design for Channel Estimation in Hybrid mmWave MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 7121–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Shen, J.C.; Zhang, J.; Letaief, K.B. Alternating minimization algorithms for hybrid precoding in millimeter wave MIMO systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2016, 10, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.F.; Eldar, Y.C. Structured Compressed Sensing: From Theory to Applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 4053–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.T.; Wang, L. Orthogonal Matching Pursuit for Sparse Signal Recovery with Noise. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 2011, 57, 4680–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| the complex conjugate of a matrix | |
| the transpose of a matrix | |
| the complex conjugate transpose of a matrix | |
| tr() | the trace of a matrix |
| diag() | the diagonal matrix with elements in vector as the diagonals |
| the mathematical expectation of a function | |
| the Kronecker product of two matrices and | |
| the Khatri–Rao product of two matrices and | |
| the Frobenius norm of a matrix | |
| the -norm of a vector | |
| the absolute value of a scalar a | |
| the identity matrix of dimensions |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Sima, B.; Ma, Y.; Miao, C.; Kang, W. Enhancing Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Single-Channel Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface via Phase Coding Design. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142394
Hu C, Zhang R, Wang J, Sima B, Ma Y, Miao C, Kang W. Enhancing Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Single-Channel Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface via Phase Coding Design. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142394
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Changcheng, Ruoyu Zhang, Jingqi Wang, Boyu Sima, Yue Ma, Chen Miao, and Wei Kang. 2025. "Enhancing Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Single-Channel Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface via Phase Coding Design" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142394
APA StyleHu, C., Zhang, R., Wang, J., Sima, B., Ma, Y., Miao, C., & Kang, W. (2025). Enhancing Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Single-Channel Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface via Phase Coding Design. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142394






