Sensitive Object Trigger-Based Fragile Watermarking for Integrity Verification of Remote Sensing Object Detection Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose the first fragile watermarking method for RSOD models based on sensitive object triggers, enabling convenient and efficient black-box verification of model integrity.
- We design a target class feature-driven trigger initialization strategy, where a trained surrogate model guides the generation of the trigger using features of target class objects. This enables the initialized sensitive object trigger to possess weak semantic features of the target class.
- We introduce a joint optimization method based on the original model and a tampered model. The original model guides the trigger to maintain recognizability, while the tampered model encourages the trigger to remain sensitive to parameter changes. This dual supervision drives the trigger to gradually approach the model’s decision boundary.
- Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method enables convenient and reliable integrity verification across multiple representative RSOD models, exhibiting strong generalizability and practical applicability.
2. Related Works
2.1. Fragile Model Watermarking with White-Box Verification
2.2. Fragile Model Watermarking with Black-Box Verification
2.3. Remote Sensing Object Detection
3. Problem Statement and Threat Model
3.1. Problem Statement
3.2. Threat Model
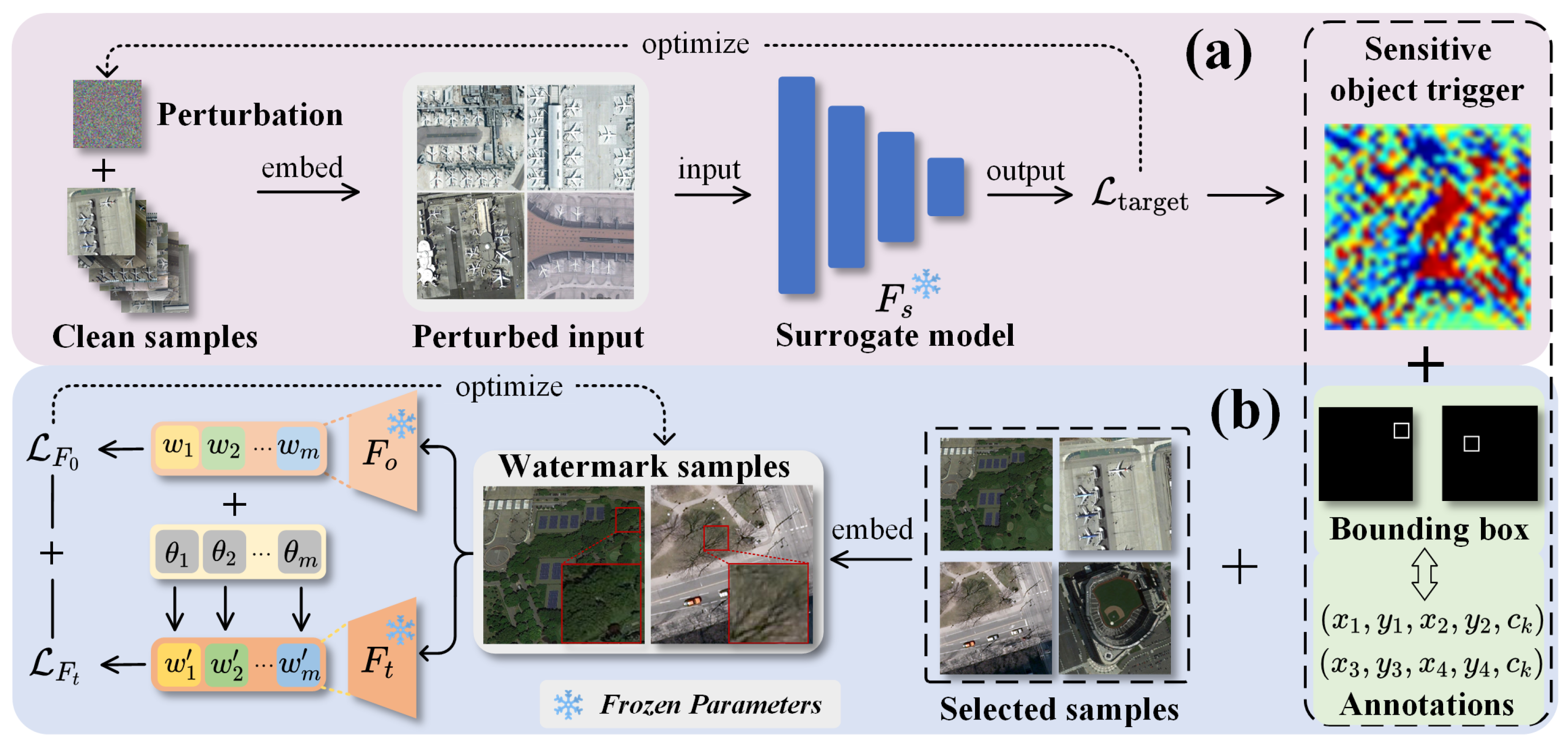
4. Proposed Method
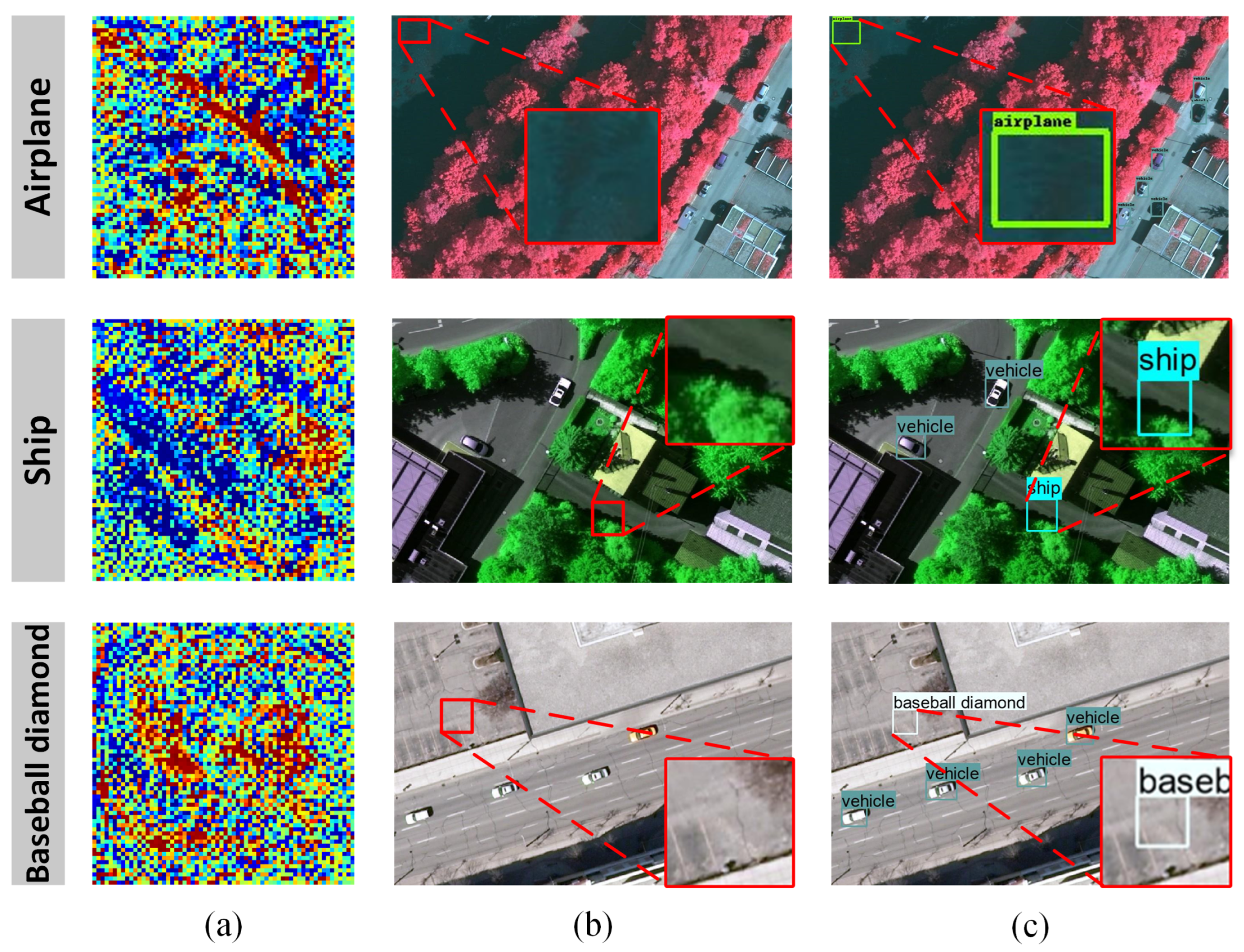
4.1. Fragile Watermark Verification Dataset Generation
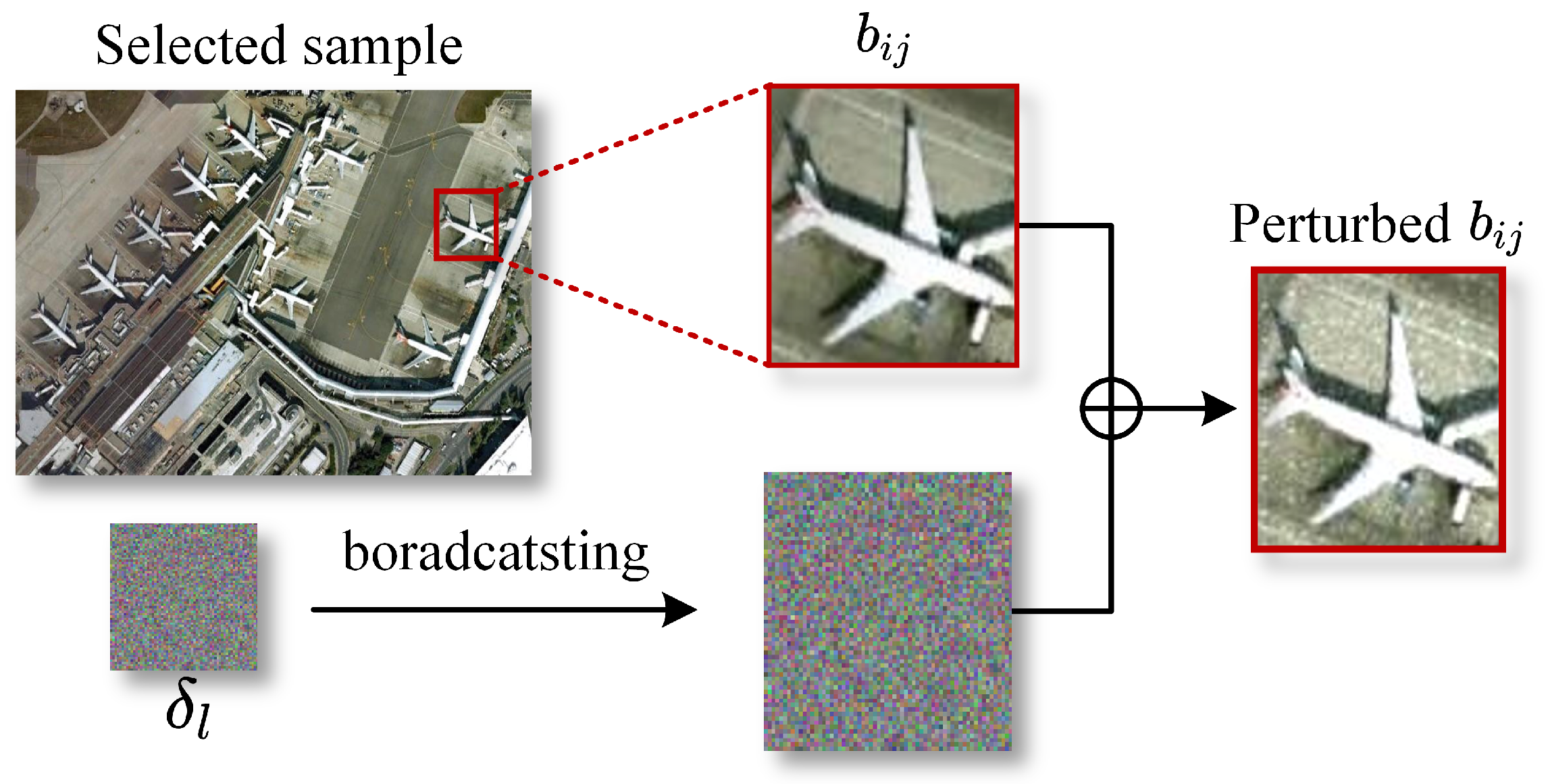
4.1.1. Generation of Initial Sensitive Object Trigger
4.1.2. Trigger Optimization
| Algorithm 1: Generation of initial sensitive object trigger |
 |
| Algorithm 2: Trigger optimization |
 |
4.2. Integrity Verification
5. Experimental Evaluation
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.2. Uniqueness Analysis
5.3. Effectiveness Analysis
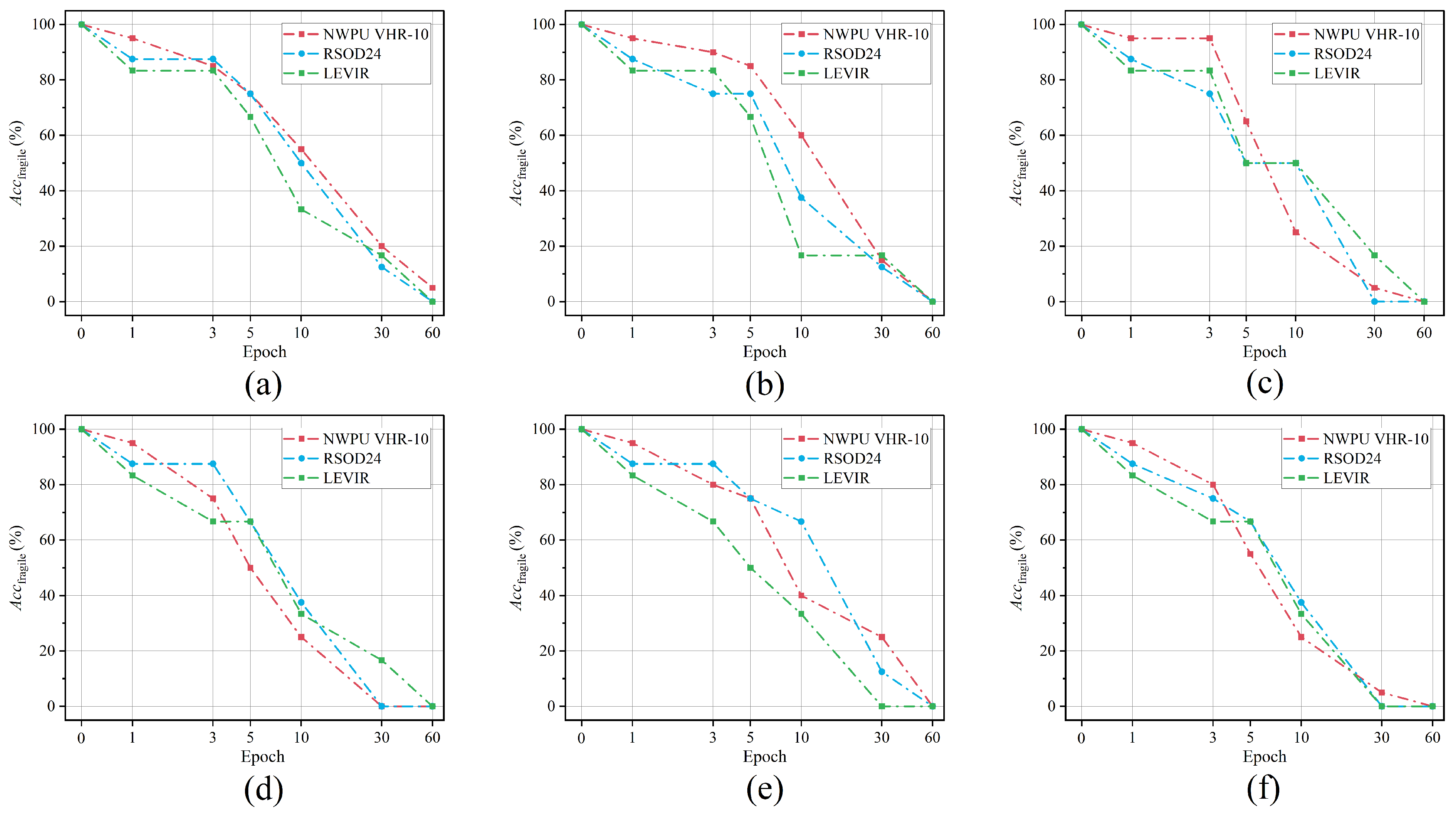
5.3.1. Backdoor Injection
5.3.2. Fine-Tuning
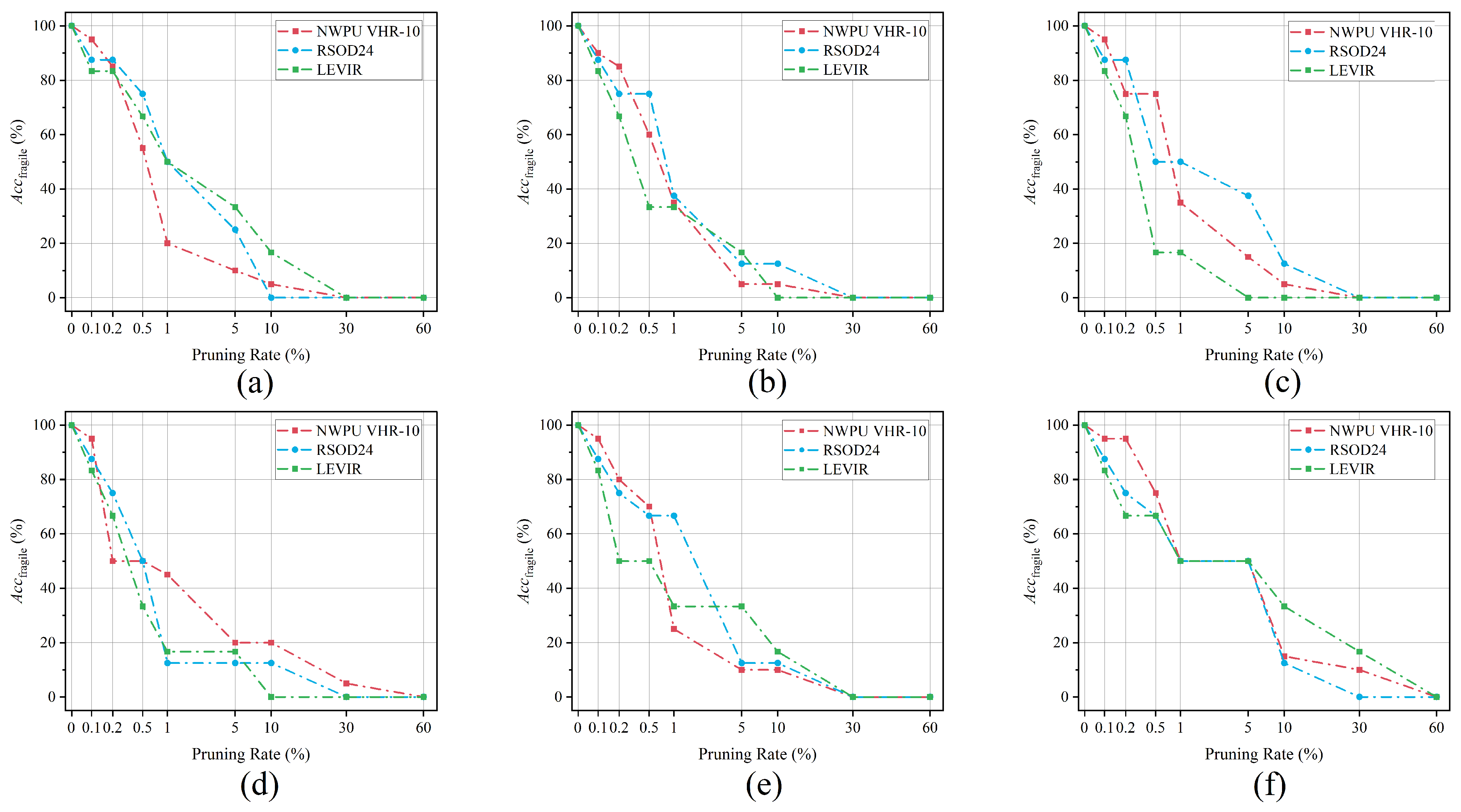
5.3.3. Pruning
5.3.4. Parameter Perturbation
5.3.5. Quantization Compression
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Feng, R.; et al. A survey of machine learning and deep learning in remote sensing of geological environment: Challenges, advances, and opportunities. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 202, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, C.; Chen, M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, F.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Artificial intelligence for geoscience: Progress, challenges and perspectives. Innovation 2024, 5, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Song, S.; Qin, R.; Tang, Y. Remote sensing object detection in the deep learning era—A review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Wu, L. Lightweight attention-guided YOLO with level set layer for landslide detection from optical satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 3543–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X. TFGNet: Traffic salient object detection using a feature deep interaction and guidance fusion. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 3020–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, T.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gou, C.; Wang, X.; Yao, F.; Sun, C. A parallel teacher for synthetic-to-real domain adaptation of traffic object detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2022, 7, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Qin, W.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, X.; Deng, X.; Ouyang, Y. Real-time object detection network in UAV-vision based on CNN and transformer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, P.Y.; Kim, Y.G. Real-time abnormal object detection for video surveillance in smart cities. Sensors 2022, 22, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, A.; Aved, A.; Blasch, E. Situational awareness: Techniques, challenges, and prospects. AI 2022, 3, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bai, T.; Yu, W.; Chang, S.; Atkinson, P.M.; Ghamisi, P. AI security for geoscience and remote sensing: Challenges and future trends. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2023, 11, 60–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, E.; Lin, J.; Runfola, D. Susceptibility & defense of satellite image-trained convolutional networks to backdoor attacks. Inf. Sci. 2022, 603, 244–261. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, P. A comprehensive survey of deep learning-based lightweight object detection models for edge devices. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, H.; Chakraborty, C.; Khosravi, M.R.; Berretti, S.; Wan, S. Edge computing driven low-light image dynamic enhancement for object detection. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 3086–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, W.; Hong, D.; Tao, R.; Du, Q. Deep learning for unmanned aerial vehicle-based object detection and tracking: A survey. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 10, 91–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jia, X.; Hu, J.; Tan, K. Moving vehicle detection for remote sensing video surveillance with nonstationary satellite platform. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5185–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wu, H.; Zhen, L.; Hua, Q.; Garg, S.; Kaddoum, G.; Hassan, M.M.; Yu, K. Edge YOLO: Real-time intelligent object detection system based on edge-cloud cooperation in autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 25345–25360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhou, M.; Gong, Z.; Abusorrah, A.; Lin, C.; Huang, Z. Making accurate object detection at the edge: Review and new approach. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 2245–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivas, K.; Kamkshi Prasad, V. Fragile watermarking schemes for image authentication: A survey. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2018, 9, 1193–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, C. A fragile watermarking in ciphertext domain based on multi-permutation superposition coding for remote sensing image. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 5664–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Renza, D.; Ballesteros L., D.M.; Lemus, C. Authenticity verification of audio signals based on fragile watermarking for audio forensics. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 91, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberna, P.; Agilandeeswari, L. Digital image and video watermarking: Methodologies, attacks, applications, and future directions. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 5531–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, Z. A survey of fragile model watermarking. Signal Process. 2025, 238, 110088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Feng, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, N. Reversible watermarking in deep convolutional neural networks for integrity authentication. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 2273–2280. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Qin, C.; Yao, H.; Han, Y. DNN self-embedding watermarking: Towards tampering detection and parameter recovery for deep neural network. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2022, 164, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuadbba, A.; Kim, H.; Nepal, S. DeepiSign: Invisible fragile watermark to protect the integrity and authenticity of CNN. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, Virtual, 22–26 March 2021; pp. 952–959. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Zhang, T.; Lee, R. Sensitive-sample fingerprinting of deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4729–4737. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Tang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Wu, B.; Lu, Y. Fragile Model Watermark for integrity protection: Leveraging boundary volatility and sensitive sample-pairing. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhang, X. Neural network fragile watermarking with no model performance degradation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Bordeaux, France, 16–19 October 2022; pp. 3958–3962. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Abuadbba, S.; Agarwal, S.; Moore, K.; Sun, R.; Xue, M.; Nepal, S.; Camtepe, S.; Kanhere, S. Publiccheck: Public integrity verification for services of run-time deep models. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2023; pp. 1348–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Qin, C. Black-box Lossless Fragile Watermarking Based on Hidden Space Search for DNN Integrity Authentication. In Proceedings of the 2023 Asia Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Taipei, Taiwan, 31 October–3 November 2023; pp. 450–455. [Google Scholar]
- Aramoon, O.; Chen, P.Y.; Qu, G. Aid: Attesting the integrity of deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 58th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 December 2021; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, P.; Li, P. DeepAuth: A DNN authentication framework by model-unique and fragile signature embedding. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 9595–9603. [Google Scholar]
- Coatrieux, G.; Pan, W.; Cuppens-Boulahia, N.; Cuppens, F.; Roux, C. Reversible watermarking based on invariant image classification and dynamic histogram shifting. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 8, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Fragile watermarking with error-free restoration capability. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2008, 10, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, M.; Cavagnino, D.; Esposito, R. NeuNAC: A novel fragile watermarking algorithm for integrity protection of neural networks. Inf. Sci. 2021, 576, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rakin, A.S.; He, Z.; Fan, D.; Chakrabarti, C. Radar: Run-time adversarial weight attack detection and accuracy recovery. In Proceedings of the 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Virtual, 1–5 February 2021; pp. 790–795. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, D. Convolutional neural networks tamper detection and location based on fragile watermarking. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 24056–24067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yin, Z.; Zhan, H.; Yin, H.; Lu, Y. Adaptive watermarking with self-mutual check parameters in deep neural networks. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2024, 180, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, H.; Ren, H.; Sun, J.; Xu, S.; Ning, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, K.; Deng, R.H. Secure and verifiable inference in deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 784–797. [Google Scholar]
- Kuttichira, D.P.; Gupta, S.; Nguyen, D.; Rana, S.; Venkatesh, S. Verification of integrity of deployed deep learning models using Bayesian optimization. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 241, 108238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yin, Z.; Gao, Z.; Su, H.; Zhang, X.; Luo, B. FTG: Score-based black-box watermarking by fragile trigger generation for deep model integrity verification. J. Inf. Intell. 2024, 2, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Z. Semi-fragile neural network watermarking for content authentication and tampering localization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 236, 121315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Z. Semi-Fragile Neural Network Watermarking Based on Adversarial Examples. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 8, 2775–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faster, R. Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 9199, 2969239–2969250. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G. Ultralytics YOLOv5 2020. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 18 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLOv8 2023. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov8/ (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wei, G.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Peng, H.; She, Y. Clean-Label Backdoor Watermarking for Dataset Copyright Protection via Trigger Optimization. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wan, G.; Cheng, G.; Meng, L.; Han, J. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bai, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Ren, P. Multiscale visual attention networks for object detection in VHR remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Q. Accurate object localization in remote sensing images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2486–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Random access memories: A new paradigm for target detection in high resolution aerial remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.H.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J. Baddet: Backdoor attacks on object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 396–412. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Huang, R. Backdoor attacks with wavelet embedding: Revealing and enhancing the insights of vulnerabilities in visual object detection models on transformers within digital twin systems. Adv. Eng. Informatics 2024, 60, 102355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Cao, X.; Tao, D. Pre-trained trojan attacks for visual recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2025, 133, 3568–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dataset | Backdoor Attack Types | (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5l | YOLOv5n | YOLOv5s | YOLOv8 | SSD | Faster-RCNN | ||
| NWPU VHR-10 | BadDet | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BAWE | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 10 | |
| PTAVR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| RSOD24 | BadDet | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.5 |
| BAWE | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | 0 | 25 | |
| PTAVR | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | |
| LEVIR | BadDet | 33.33 | 0 | 0 | 16.67 | 0 | 33.33 |
| BAWE | 33.33 | 0 | 0 | 33.33 | 16.67 | 50 | |
| PTAVR | 16.67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16.67 | |
| Dataset | Perturbation Target | Gaussian Noise Intensity | (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5l | YOLOv5n | YOLOv5s | YOLOv8 | SSD | Faster-RCNN | |||
| NWPU VHR-10 | BN Layer | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 30 | 20 | 25 | 35 | 30 | 35 | |||
| 25 | 15 | 15 | 30 | 25 | 25 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Conv Layer | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 20 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 20 | |||
| 5 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| RSOD24 | BN Layer | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 37.5 | 0 | 37.5 | |||
| 12.5 | 0 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 0 | 12.5 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Conv Layer | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 25 | 12.5 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 25 | |||
| 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| LEVIR | BN Layer | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 50 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 33.33 | 16.67 | 66.67 | |||
| 33.33 | 0 | 0 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 33.33 | |||
| 16.67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Conv Layer | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 50 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 33.33 | 33.33 | 33.33 | |||
| 16.67 | 0 | 0 | 16.67 | 0 | 16.67 | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Dataset | Quantization Compression | (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5l | YOLOv5n | YOLOv5s | YOLOv8 | SSD | Faster-RCNN | ||
| NWPU VHR-10 | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 16-bit | 15 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 20 | |
| 8-bit | 10 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 10 | |
| RSOD24 | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 16-bit | 25 | 0 | 12.5 | 25 | 12.5 | 37.5 | |
| 8-bit | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | |
| LEVIR | Original | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 16-bit | 33.33 | 0 | 16.67 | 33.33 | 16.67 | 33.33 | |
| 8-bit | 16.67 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16.67 | 16.67 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Tang, W.; Ren, N.; Zhu, C. Sensitive Object Trigger-Based Fragile Watermarking for Integrity Verification of Remote Sensing Object Detection Models. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142379
Xu X, Wang Z, Chen W, Tang W, Ren N, Zhu C. Sensitive Object Trigger-Based Fragile Watermarking for Integrity Verification of Remote Sensing Object Detection Models. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(14):2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142379
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xin, Zihao Wang, Weitong Chen, Wei Tang, Na Ren, and Changqing Zhu. 2025. "Sensitive Object Trigger-Based Fragile Watermarking for Integrity Verification of Remote Sensing Object Detection Models" Remote Sensing 17, no. 14: 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142379
APA StyleXu, X., Wang, Z., Chen, W., Tang, W., Ren, N., & Zhu, C. (2025). Sensitive Object Trigger-Based Fragile Watermarking for Integrity Verification of Remote Sensing Object Detection Models. Remote Sensing, 17(14), 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17142379







