Contrasting Impacts of Urbanization and Cropland Irrigation on Observed Surface Air Temperature in Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
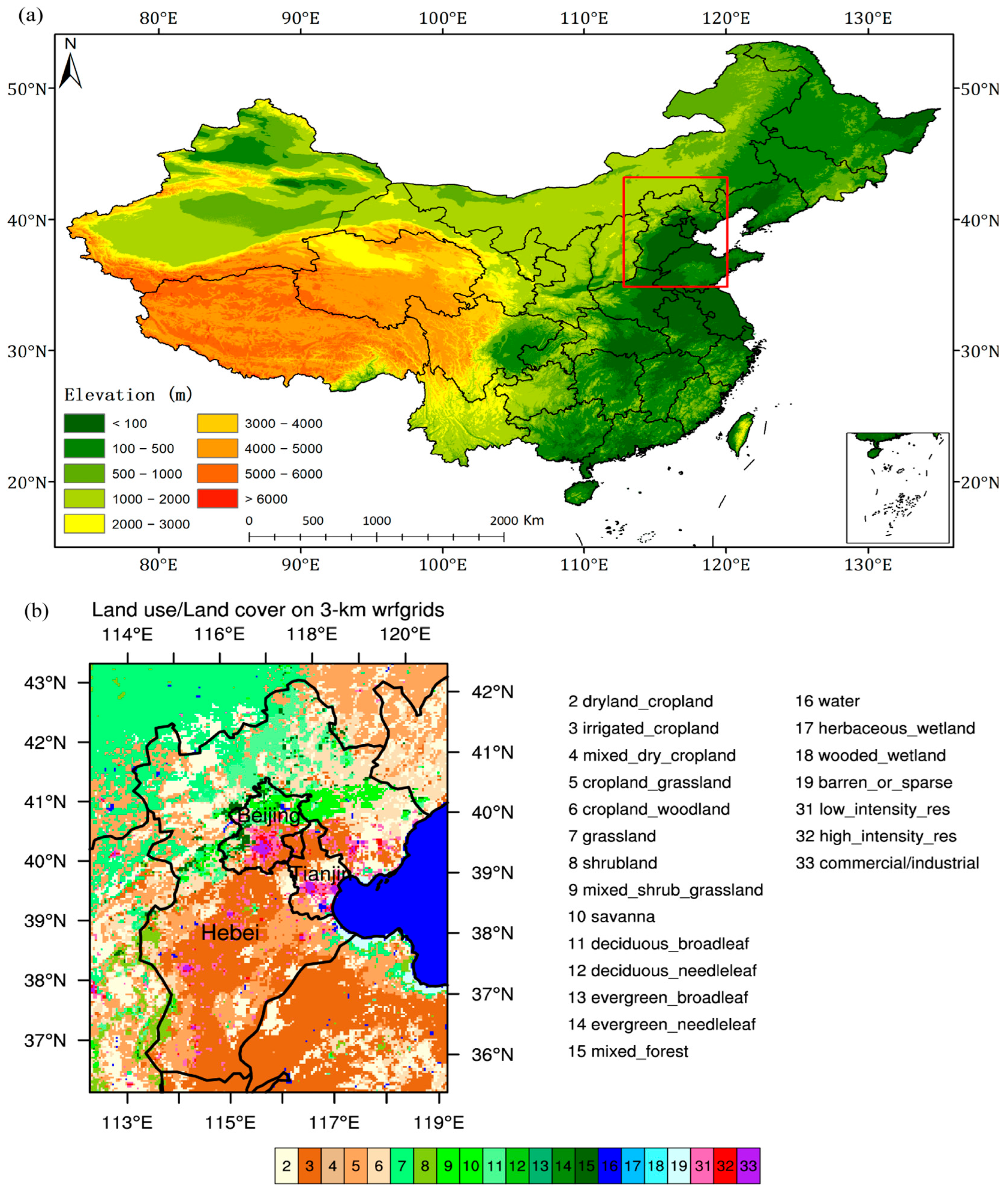
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data

2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Site Categorization
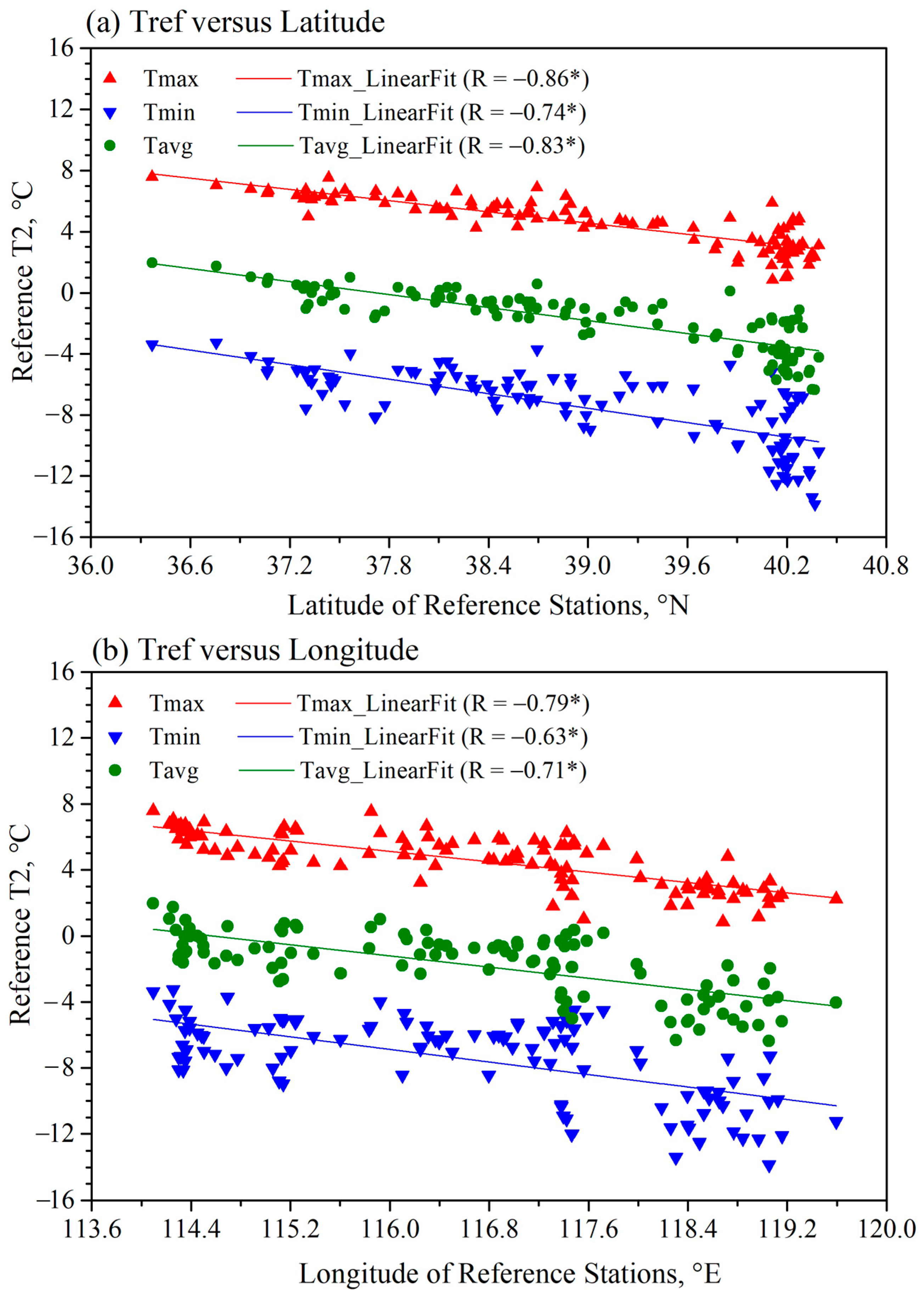
2.3.2. Estimation of Reference Temperatures
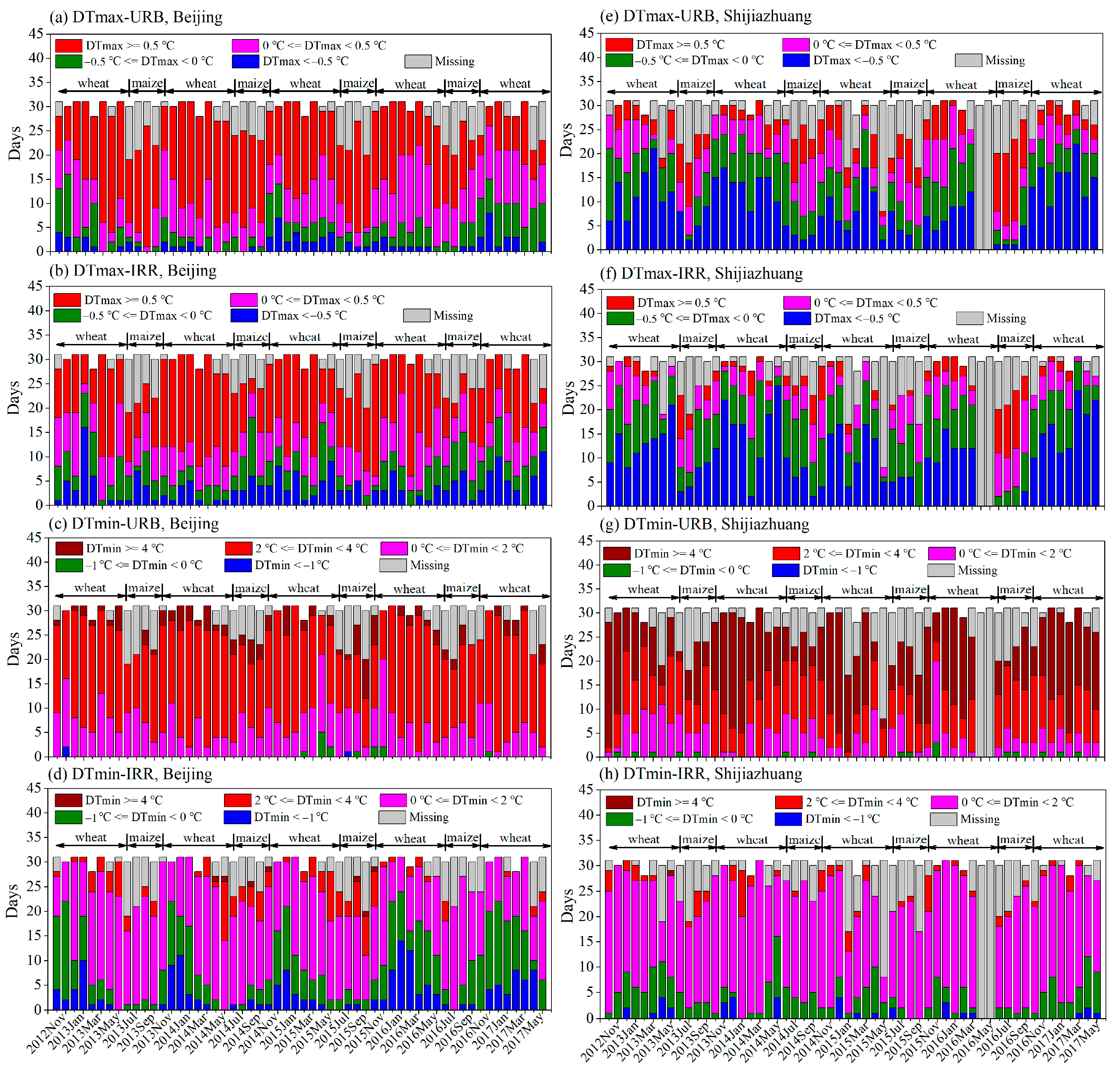
3. Results
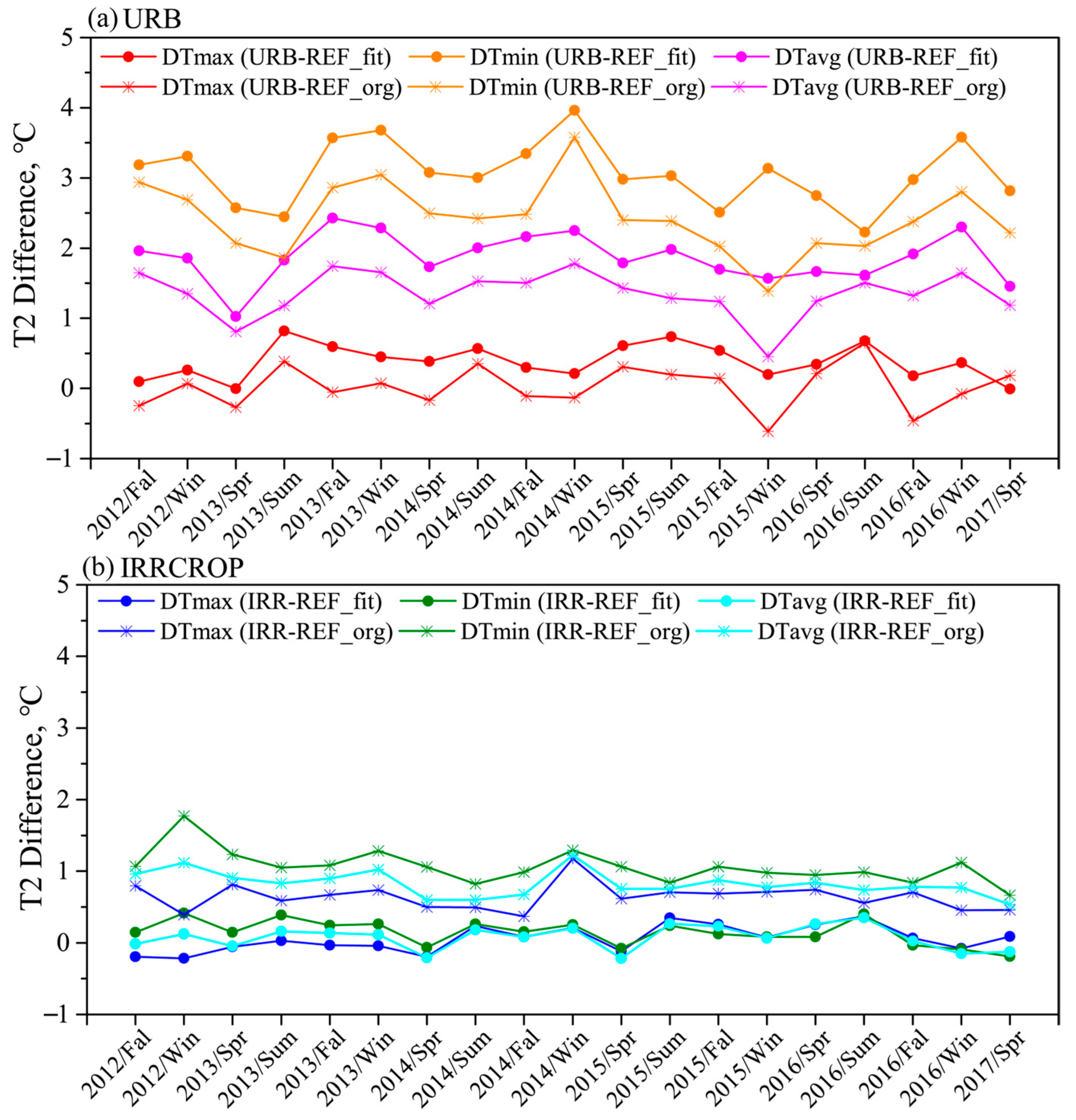
3.1. Temperature Effects over the Whole BTH Region
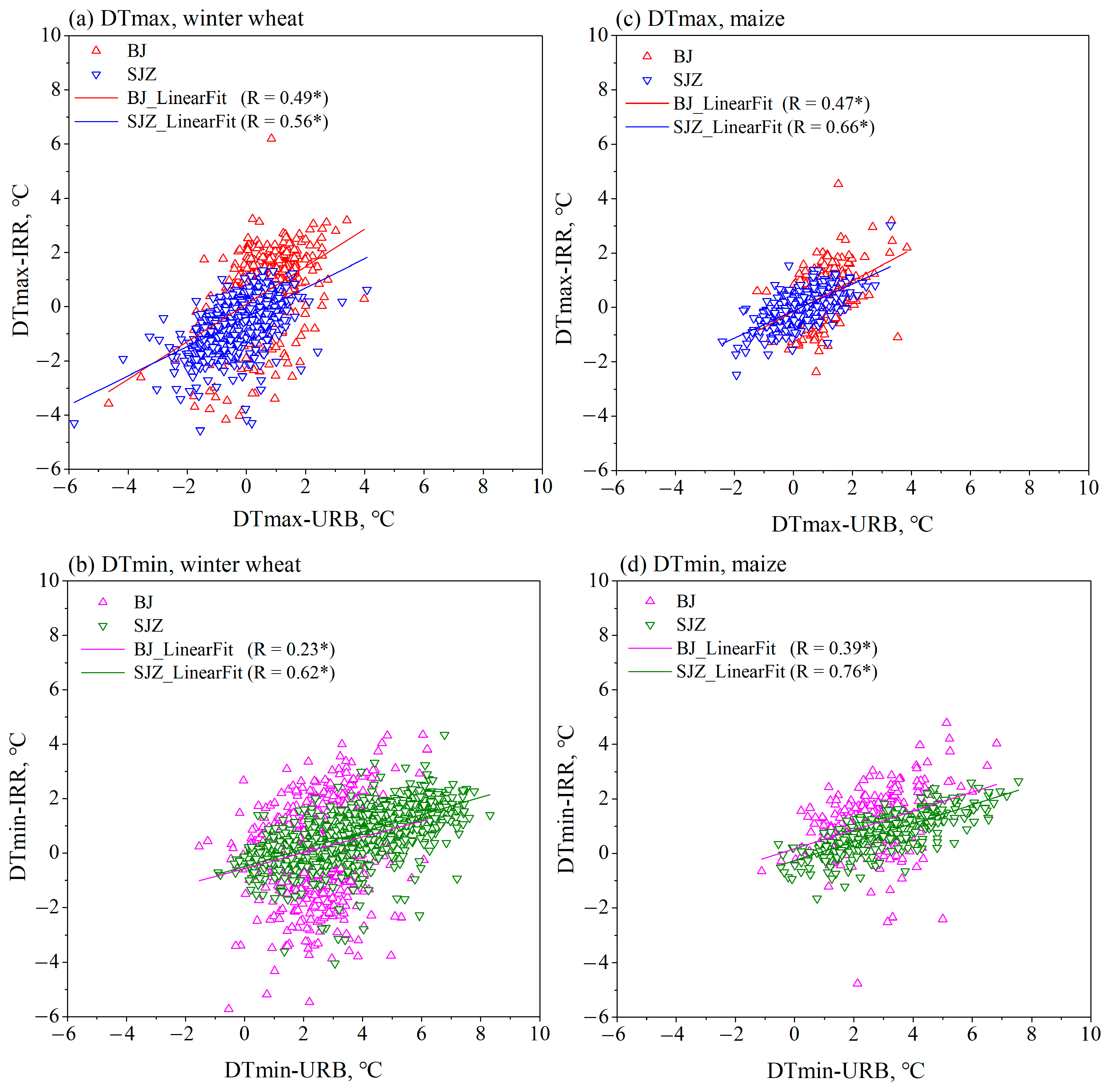
3.2. Differences in Temperature Effects Between Beijing and Shijiazhuang
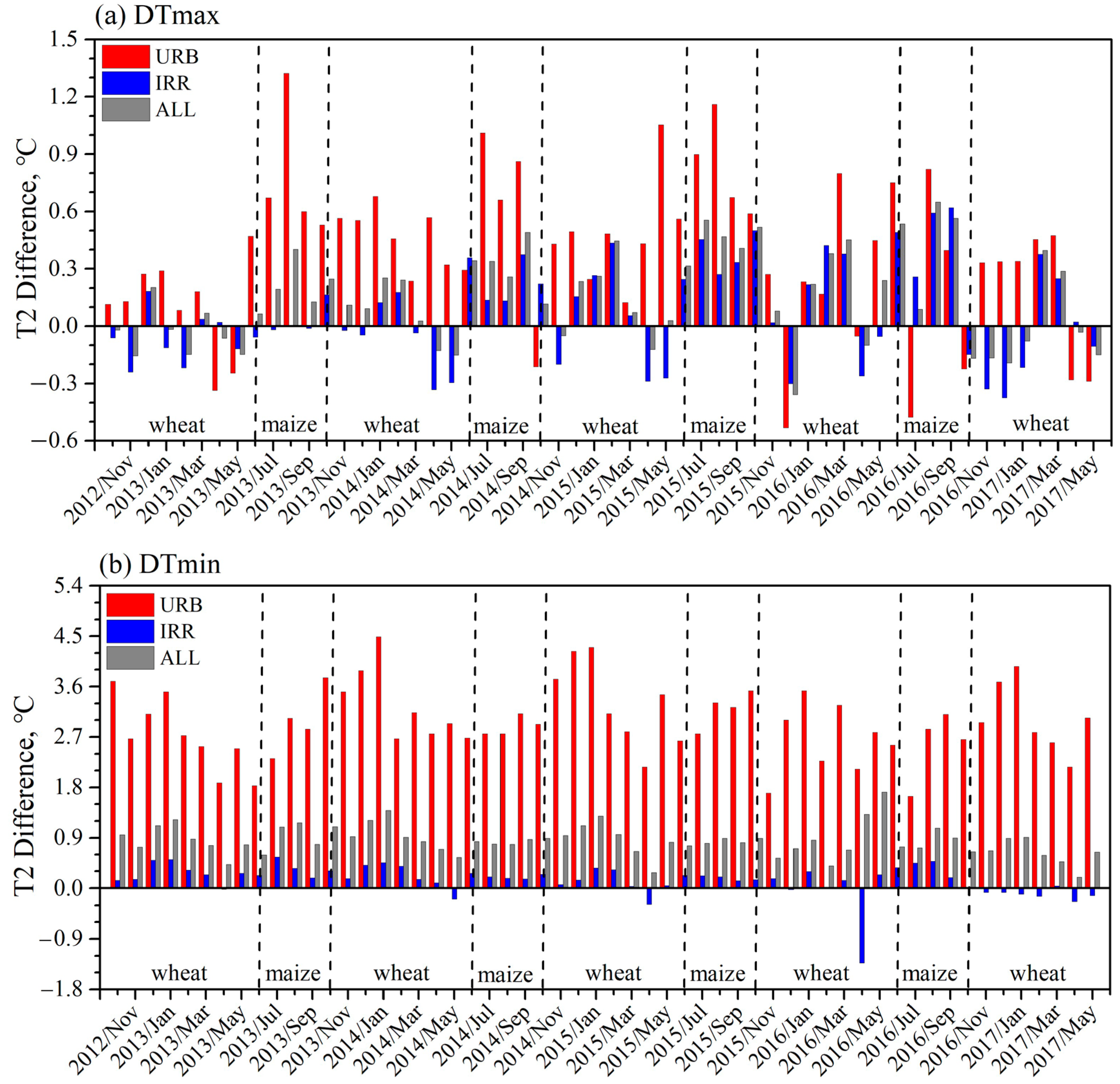
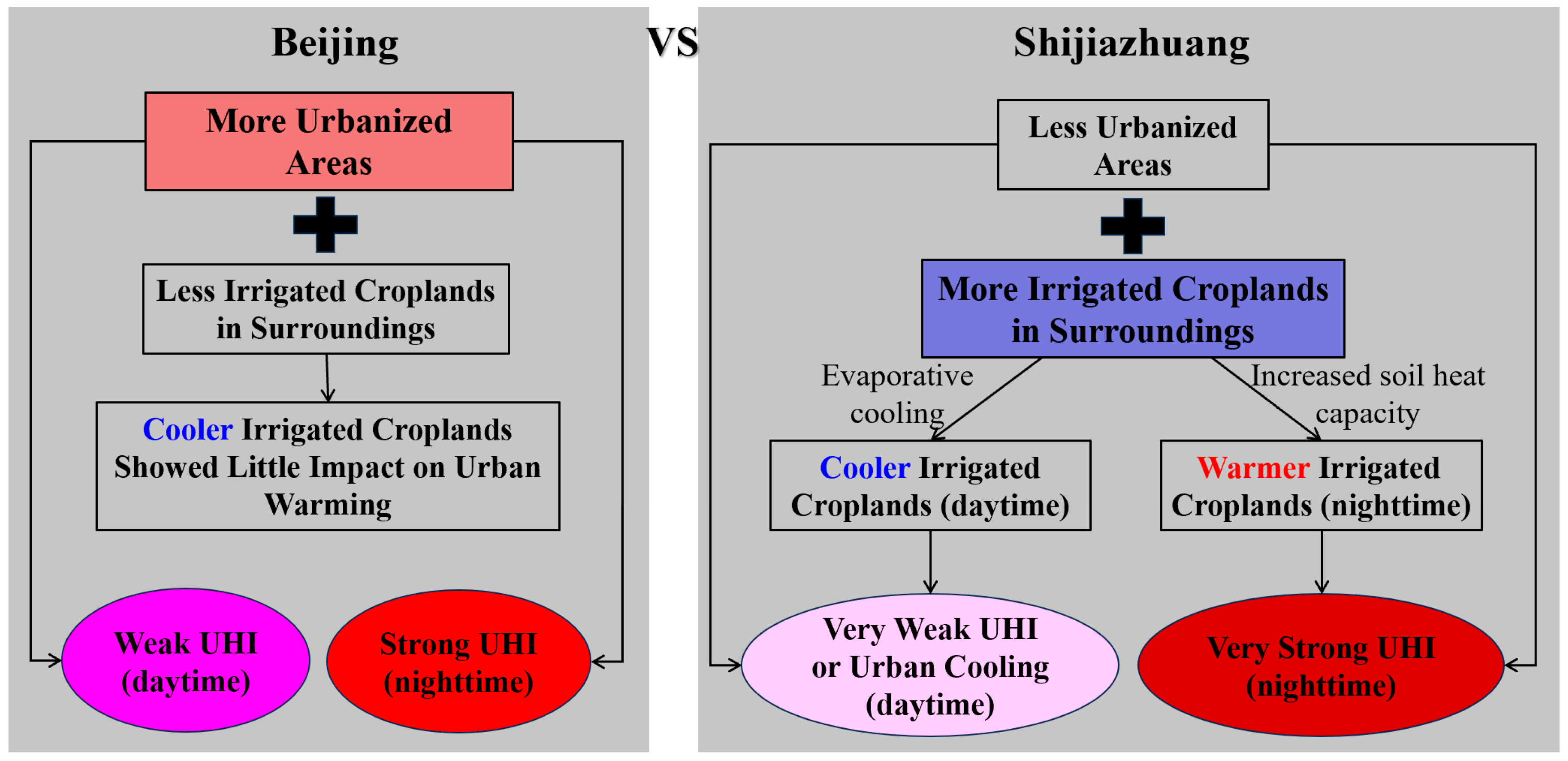
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Thermal Contrasts and Possible Implications
4.2. Uncertainties and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Snyder, M.A.; Kueppers, L.M.; Sloan, L.C.; Cayan, D.; Jin, J.; Kanamaru, H.; Kanamitsu, M.; Miller, N.L.; Tyree, M.; Du, H.; et al. Regional Climate Effects of Irrigation and Urbanization in the Western United States: A Model Intercomparison. California Energy Commission, PIER Energy-Related Environmental Research, CEC-500-2006-031. 2006. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3979q78z (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Ellis, E.C.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Siebert, S.; Lightman, D.; Ramankutty, N. Anthropogenic transformation of the biomes, 1700 to 2000. Global Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Kummu, M.; Porkka, M.; Döll, P.; Ramankutty, N.; Scanlon, B.R. A global data set of the extent of irrigated land from 1900 to 2005. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1521–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ciais, P.; Lin, P.; Gong, K.; Ziegler, A.D.; Chen, A.; et al. High-spatiotemporal-resolution mapping of global urban change from 1985 to 2015. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; O’Neill, B.C. Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puy, A.; Lo Piano, S.; Saltelli, A. Current models underestimate future irrigated areas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnfield, A.J. Two decades of urban climate research: A review of turbulence, exchanges of energy and water, and the urban heat island. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Chakraborty, T.C.; Li, J.; Li, D.; He, C.; Sarangi, C.; Chen, F.; Yang, X.; Leung, L.R. Urbanization Impact on Regional Climate and Extreme Weather: Current Understanding, Uncertainties, and Future Research Directions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 819–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, H.; Kimura, F. Thermal effects of urban canyon structure on the nocturnal heat island: Numerical experiment using a mesoscale model coupled with an urban canopy model. J. Appl. Meteor. 2004, 43, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmond, S. Urbanization and global environmental change: Local effects of urban warming. Geogr. J. 2007, 173, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Chen, F.; Li, Q.; Fan, S. Impacts of urban processes and urbanization on summer precipitation: A case study of heavy rainfall in Beijing on 1 August 2006. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2011, 50, 806–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Wang, Y.; Bornstein, R.D.; Miao, S. Observed Spatial Characteristics of Beijing Urban Climate Impacts on Summer Thunderstorms. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2015, 54, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. Analyzing the heat island magnitude and characteristics in one hundred Asian and Australian cities and regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfils, C.; Lobell, D. Empirical evidence for a recent slowdown in irrigation-induced cooling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13582–13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueppers, L.M.; Snyder, M.A.; Sloan, L.C. Irrigation cooling effect: Regional climate forcing by land use change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L03703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Bonfils, C. The Effect of Irrigation on Regional Temperatures: A Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Trends in California, 1934–2002. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, W.J.; Cook, B.I.; Buenning, N.; Levis, S.; Helkowski, J.H. Effects of global irrigation on the near-surface climate. Clim. Dynam. 2009, 33, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puma, M.J.; Cook, B.I. Effects of irrigation on global climate during the 20th century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Huang, M.; Tang, Q.; Sacks, W.J.; Lei, H.; Leung, L.R. Modeling the effects of irrigation on land surface fluxes and states over the conterminous United States: Sensitivity to input data and model parameters. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9789–9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Moore, N.; Zhong, S.; Kendall, A.D.; Gao, Z.; Hyndman, D.W. Effects of irrigation on summer precipitation over the United States. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 3541–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jeong, S. Irrigation enhances local warming with greater nocturnal warming effects than daytime cooling effects. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 24005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xu, X.; Barlage, M.; Rasmussen, R.; Shen, S.; Miao, S.; Zhou, G. Memory of irrigation effects on hydroclimate and its modeling challenge. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 64009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, F.; Barlage, M.; Gochis, D.; Miao, S.; Shen, S. Lessons learned from modeling irrigation from field to regional scales. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 2428–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Zhao, L.; Lin, A. Irrigation Cooling Effect on Local Temperatures in the North China Plain Based on an Improved Detection Method. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision (ST/ESA/SER.A/420); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Available online: https://population.un.org/wup/assets/WUP2018-Report.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Siebert, S.; Döll, P. Quantifying blue and green water uses and virtual water contents in global crop production as well as potential production losses without irrigation. J. Hydrol. 2010, 384, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.M.; Beltrán-Przekurat, A.; Niyogi, D.; Pielke, R.A.; Vörösmarty, C.J. The impact of agricultural intensification and irrigation on land–atmosphere interactions and Indian monsoon precipitation—A mesoscale modeling perspective. Global Planet. Change 2009, 67, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimberteau, M.; Laval, K.; Perrier, A.; Polcher, J. Global effect of irrigation and its impact on the onset of the Indian summer monsoon. Clim. Dynam. 2012, 39, 1329–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.P.; Puma, M.J.; Cook, B.I. The response of the South Asian Summer Monsoon circulation to intensified irrigation in global climate model simulations. Clim. Dynam. 2014, 42, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Tang, Q.; Xu, D.; Yang, Z. Impacts of urbanization and agricultural development on observed changes in surface air temperature over mainland China from 1961 to 2006. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Sun, G.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hao, L. Contrasting effects of urbanization and agriculture on surface temperature in eastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9597–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Hamdi, R.; He, H.; Yuan, X.; Yang, T.; Tang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Termonia, P.; Maeyer, P.D. Interplay between urbanization and irrigation on summer climate in the Huang-Huai-Hai plain, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Feng, Z.; Sarangi, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z. Impacts of large-scale urbanization and irrigation on summer precipitation in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL097845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Tao, F.; Liu, J. Regional temperature change over the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China: The roles of irrigation versus urbanization. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Shen, Y.J.; Stricevic, R.; Pei, H.; Sun, H.; Amiri, E.; Penas, A.; del Rio, S. Evaluation of the FAO AquaCrop model for winter wheat on the North China Plain under deficit irrigation from field experiment to regional yield simulation. Agr. Water Manag. 2014, 135, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, G.; Tan, K.; Zhou, L. Review on research of irrigation regime and its environmental effect in winter wheat field of North China Plain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 5979–5986, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, H.; Ma, L.; Ge, D.; Tu, S.; Qu, Y. Farmland function evolution in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain: Processes, patterns and mechanisms. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Verena, H.; Karen, F.; Jacob, B. Update of the Digital Global Map of Irrigation Areas to Version 5; Rheinische Frie-Drich-Wilhelms-Universität: Bonn, Germany; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Na-tions: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 10, pp. 2660–6728. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Chen, F.; Shen, S.; Miao, S.; Barlage, M.; Guo, W.; Mahalov, A. Using WRF-Urban to assess summertime air conditioning electric loads and their impacts on urban weather in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, W.P. Empirical estimation of urban effects on climate: A problem analysis. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1977, 16, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, Y.; Ohashi, Y.; Tsukamoto, O. Urban Cool Island in daytime-analysis by using thermal image and air temperature measurements. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Urban Climate, Yokohama, Japan, 29 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, Z.; Chan, P.W. The urban cool island phenomenon in a high-rise high-density city and its mechanisms. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 37, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, T.; Gough, W.A. Characterization and estimation of urban heat island at Toronto: Impact of the choice of rural sites. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 108, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lo, M.-H.; Ryu, D.; Peel, M.; Zhang, Y. Possible increase of air temperature by irrigation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Oct | Nov | Dec | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| URB | 2012/2013 | dTmax | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.11 | 0.25 | −0.13 | −0.22 | 0.61 |
| dTmin | 4.17 | 3.10 | 3.33 | 3.80 | 3.03 | 2.73 | 1.97 | 2.70 | 2.03 | ||
| 2013/2014 | dTmax | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.56 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 0.74 | 0.24 | 0.30 | |
| dTmin | 3.79 | 3.75 | 4.27 | 4.72 | 2.87 | 3.31 | 2.71 | 3.13 | 2.73 | ||
| 2014/2015 | dTmax | −0.16 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.66 | 1.21 | 0.44 | |
| dTmin | 3.00 | 3.80 | 4.45 | 4.52 | 3.30 | 2.83 | 2.06 | 3.69 | 2.86 | ||
| 2015/2016 | dTmax | 0.61 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 1.15 | −0.10 | 0.34 | 1.27 | |
| dTmin | 3.60 | 1.74 | 3.13 | 3.59 | 2.38 | 3.03 | 1.90 | 2.52 | 2.46 | ||
| 2016/2017 | dTmax | −0.33 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.46 | 0.50 | −0.36 | −0.15 | / | |
| dTmin | 2.63 | 3.03 | 3.88 | 4.33 | 2.65 | 2.71 | 2.46 | 3.54 | / | ||
| AVG | dTmax | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.43 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.66 | |
| dTmin | 3.44 | 3.08 | 3.81 | 4.19 | 2.85 | 2.92 | 2.22 | 3.12 | 2.52 | ||
| IRR | 2012/2013 | dTmax | −0.04 | −0.34 | −0.04 | −0.27 | −0.38 | −0.06 | 0.09 | −0.10 | 0.17 |
| dTmin | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.23 | ||
| 2013/2014 | dTmax | 0.08 | −0.19 | −0.26 | −0.10 | 0.24 | −0.03 | −0.45 | −0.21 | 0.33 | |
| dTmin | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.06 | −0.07 | −0.25 | 0.29 | ||
| 2014/2015 | dTmax | 0.14 | −0.33 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.30 | 0.19 | −0.25 | −0.27 | 0.26 | |
| dTmin | 0.24 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.02 | −0.32 | 0.04 | 0.24 | ||
| 2015/2016 | dTmax | 0.52 | −0.21 | −0.33 | 0.19 | 0.35 | 0.35 | −0.14 1 | −0.17 1 | 0.54 | |
| dTmin | 0.19 | 0.09 | −0.08 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.11 | −1.38 1 | 0.10 1 | 0.31 | ||
| 2016/2017 | dTmax | −0.11 | −0.33 | −0.58 | −0.16 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.01 | −0.12 | / | |
| dTmin | −0.06 | −0.10 | −0.17 | 0.04 | −0.14 | −0.08 | −0.25 | −0.26 | / | ||
| AVG | dTmax | 0.12 | −0.28 | −0.21 | −0.04 | 0.15 | 0.13 | −0.15 | −0.18 | 0.33 | |
| dTmin | 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.32 | 0.15 | 0.07 | −0.15 | −0.06 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Miao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, J. Contrasting Impacts of Urbanization and Cropland Irrigation on Observed Surface Air Temperature in Northern China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132256
Xu X, Miao S, Zhang Y, Dou J. Contrasting Impacts of Urbanization and Cropland Irrigation on Observed Surface Air Temperature in Northern China. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(13):2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132256
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaoyu, Shiguang Miao, Yizhou Zhang, and Jingjing Dou. 2025. "Contrasting Impacts of Urbanization and Cropland Irrigation on Observed Surface Air Temperature in Northern China" Remote Sensing 17, no. 13: 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132256
APA StyleXu, X., Miao, S., Zhang, Y., & Dou, J. (2025). Contrasting Impacts of Urbanization and Cropland Irrigation on Observed Surface Air Temperature in Northern China. Remote Sensing, 17(13), 2256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132256






