Dynamic Monitoring and Driving Factors Analysis of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Hindu Kush–Himalaya Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
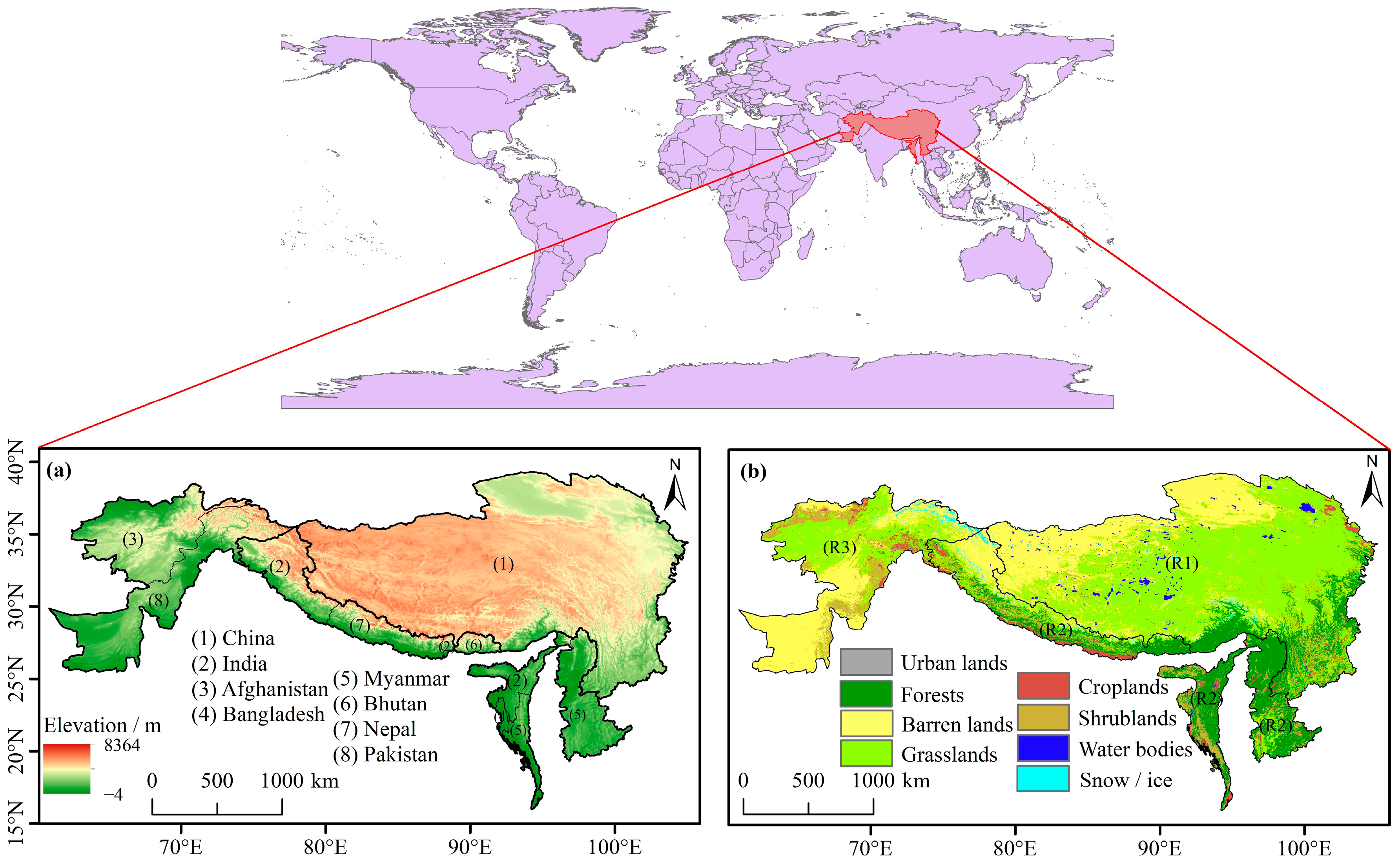
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Preprocessing
2.3. Method
2.3.1. RSEI Construction
2.3.2. Theil–Sen Estimation and Mann–Kendall Test
- (1)
- Theil–Sen Estimation
- (2)
- Mann–Kendall Test
2.3.3. Geodetector
3. Results
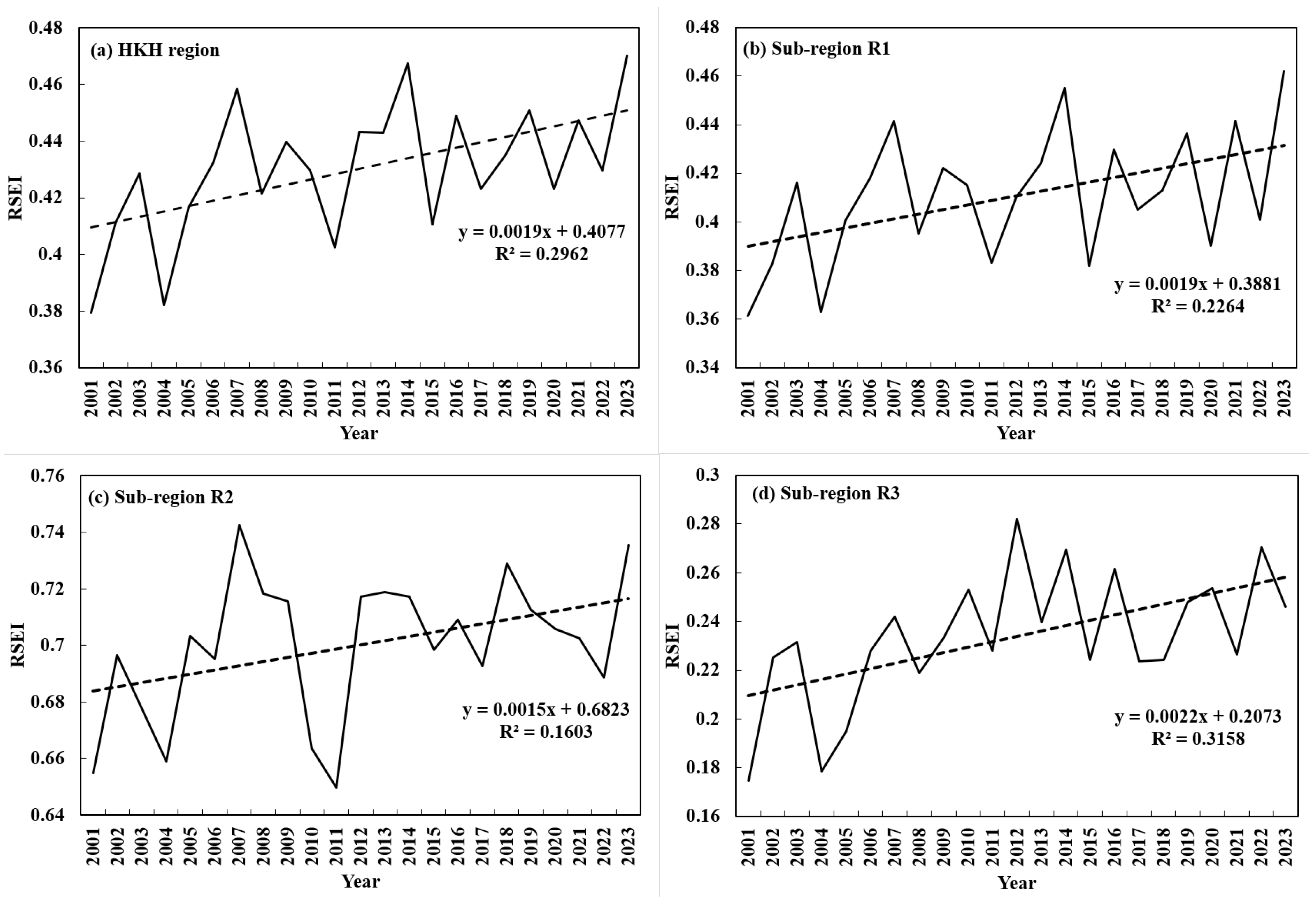
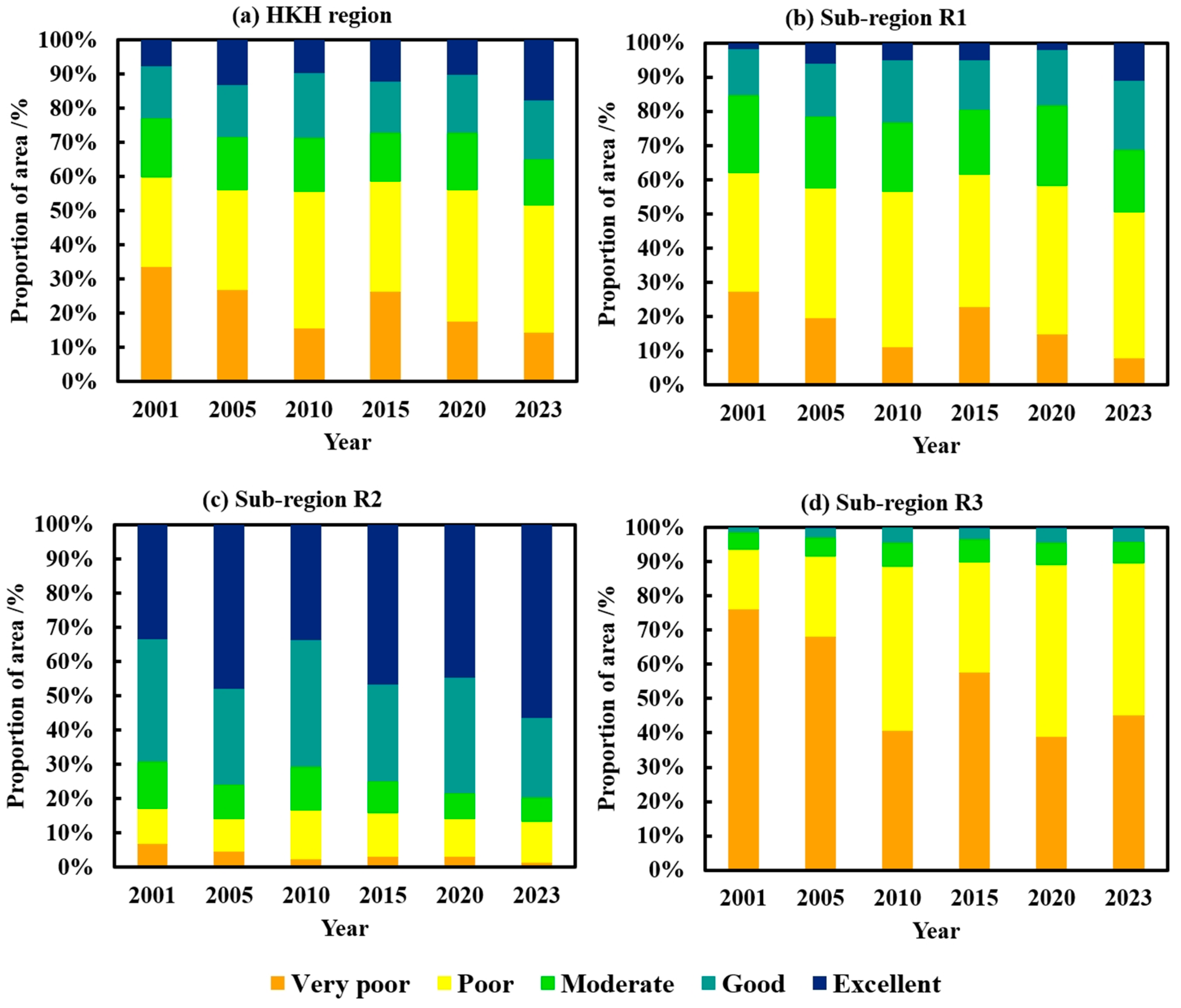
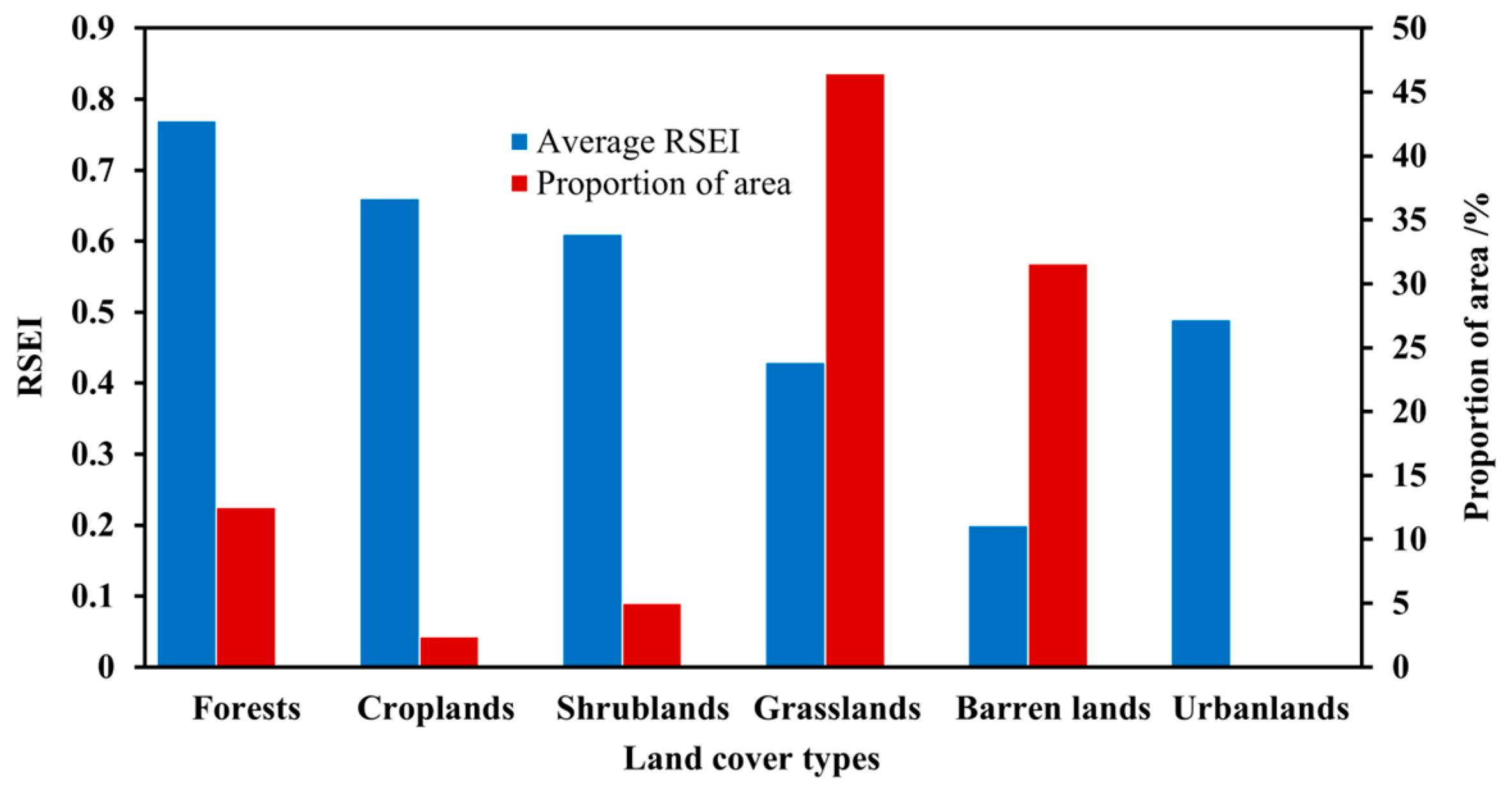
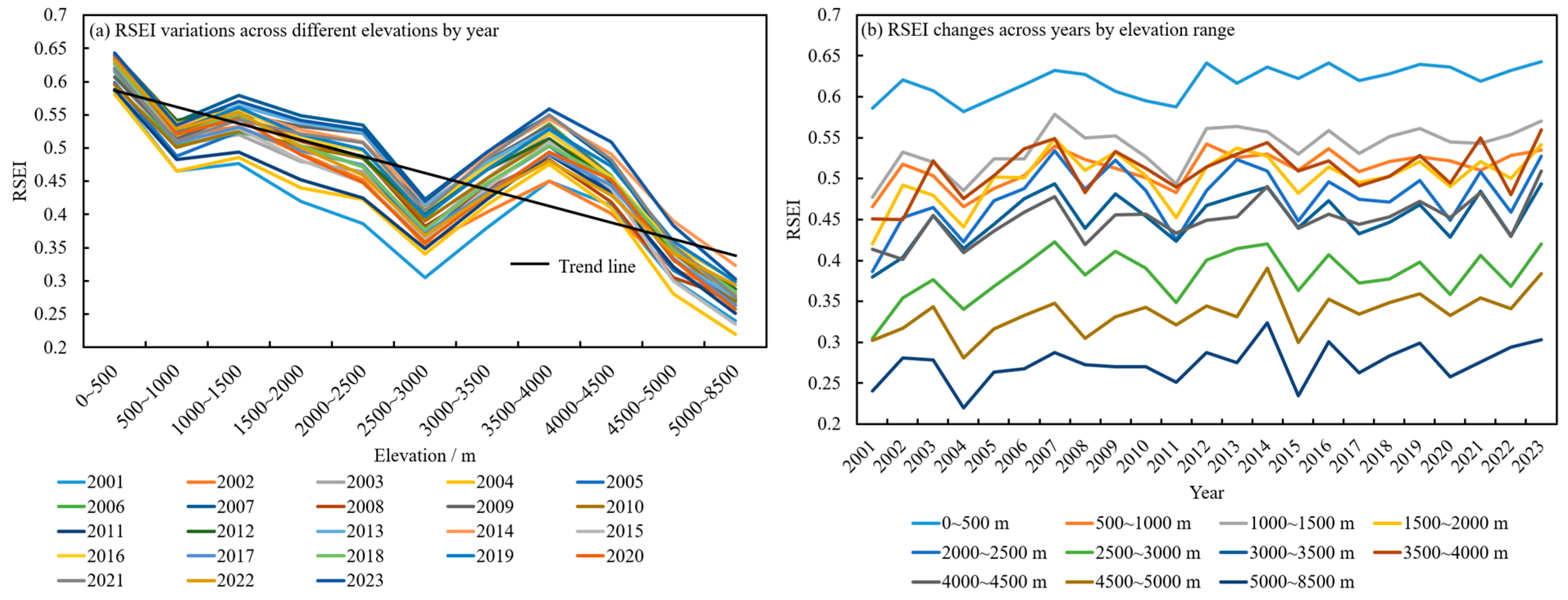
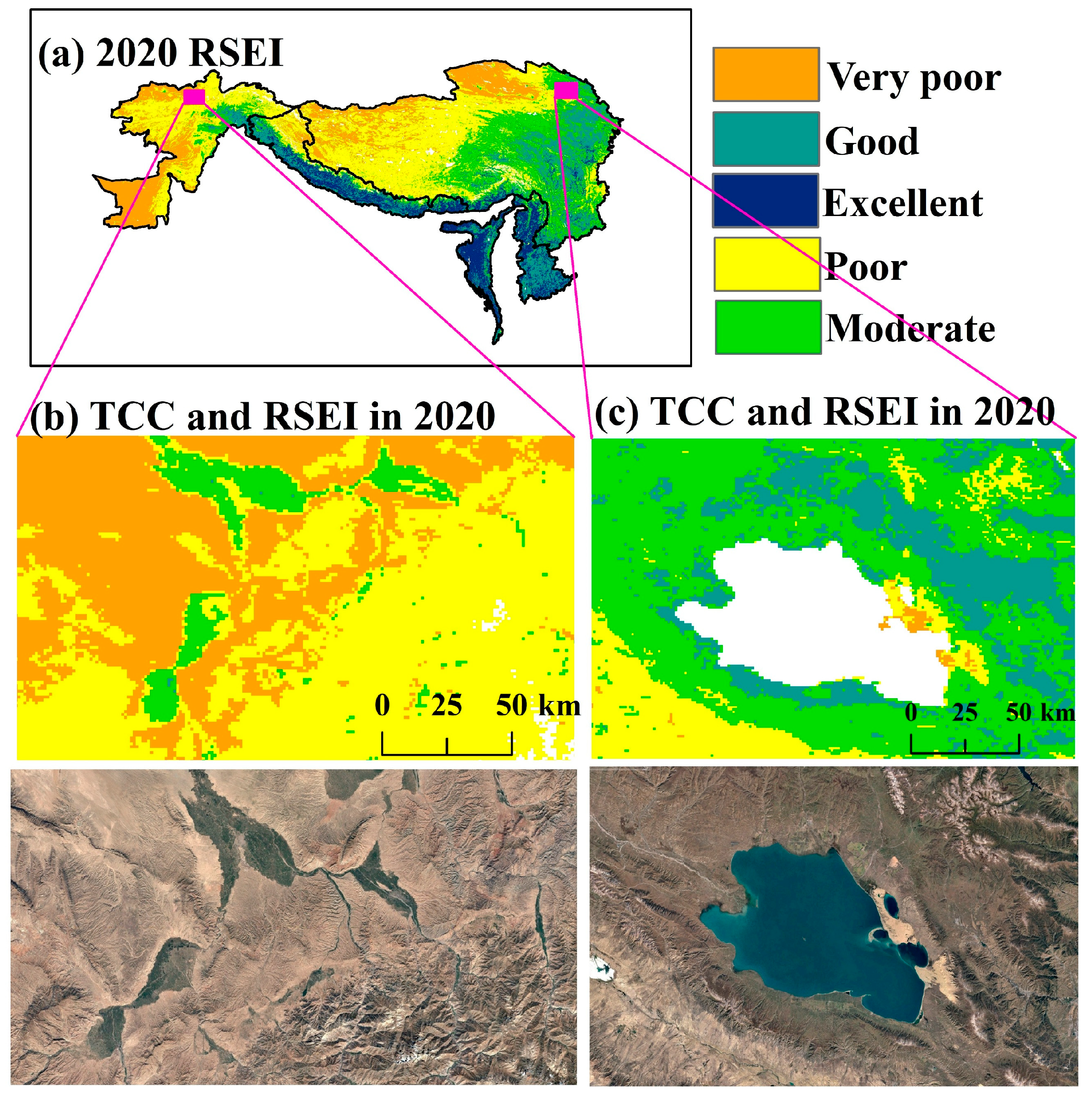
3.1. Overall Status of Eco-Environmental Quality
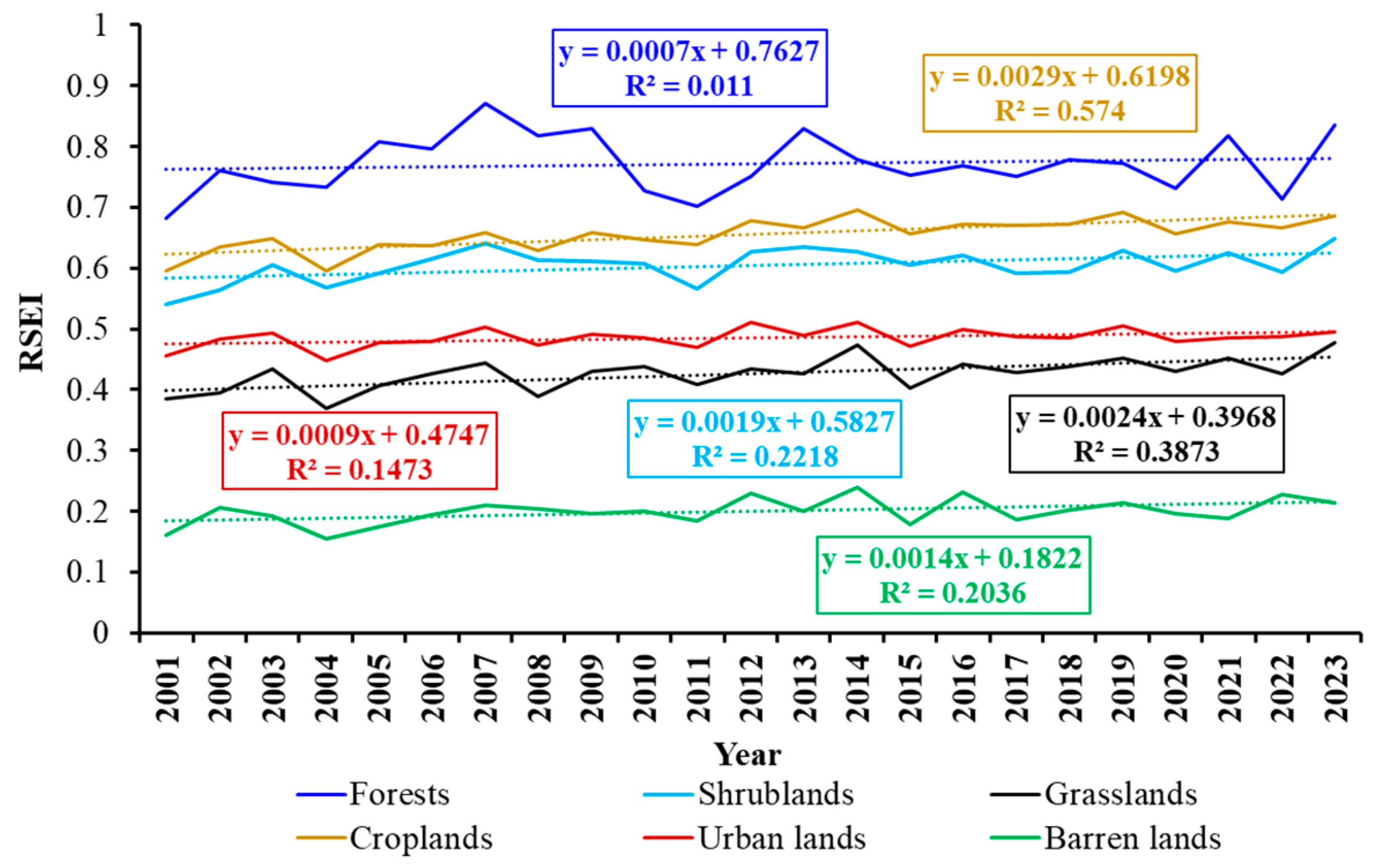
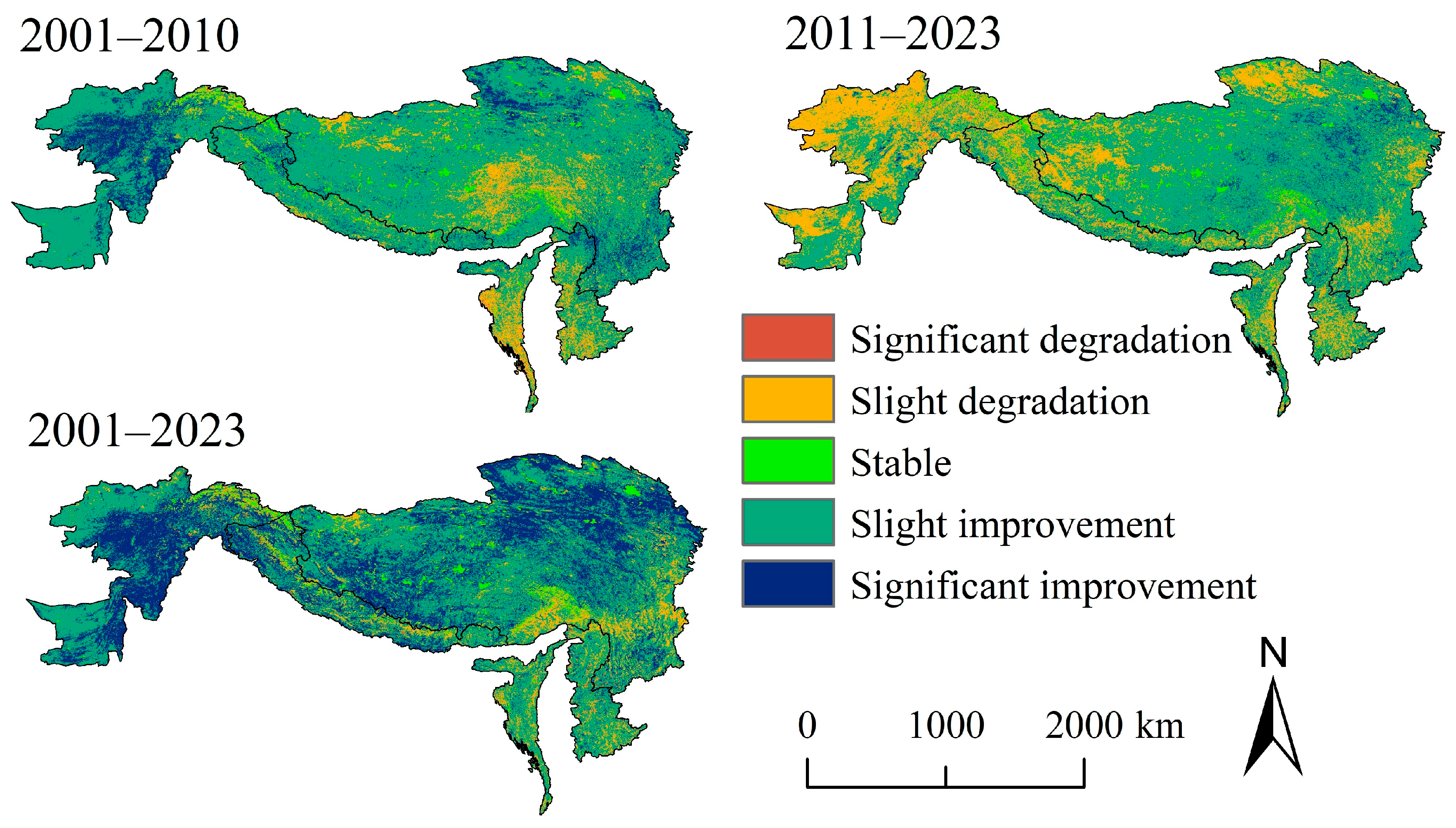
3.2. Eco-Environmental Quality Evolution
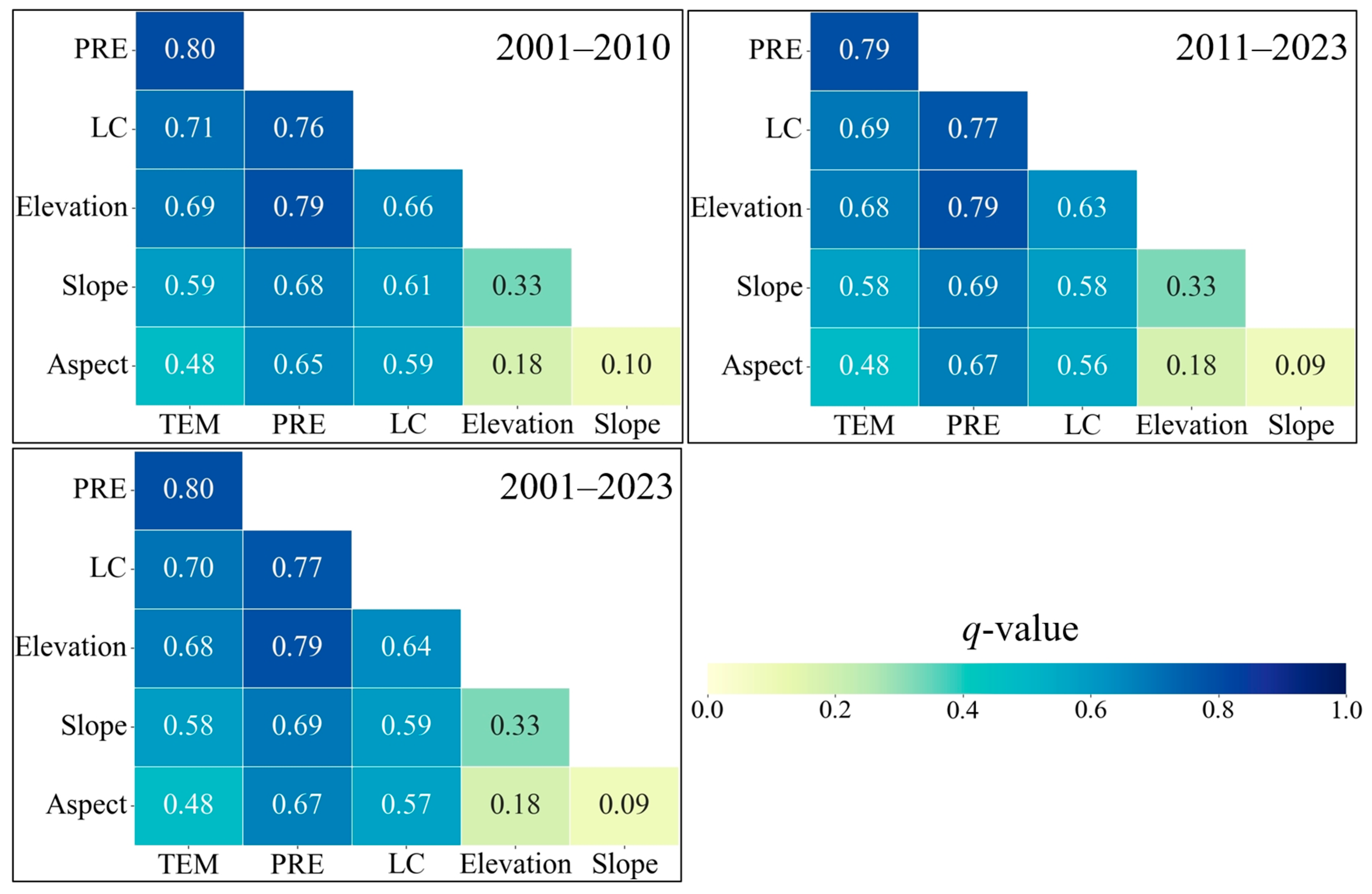
3.3. Driving Factors for Eco-Environmental Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Heterogeneity Characteristics and Regulation Strategies of Eco-Environmental Quality in the HKH Region
4.2. Limitations and Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Chen, D.; Piao, S. Reflections and future strategies for Third Pole Environment. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 608–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiutakes, J. Riding on the roof of the world. Nature 2007, 449, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S.; Shaw, R. Demographic changes, economic changes and livelihood changes in the HKH Region. In Mountain Hazards and Disaster Risk Reduction; Nibanupudi, H.K., Shaw, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; pp. 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, B. Detection of dual effects of degradation of perennial snow and ice covers on the hydrologic regime of a Himalayan river basin by stream water availability modeling. J. Hydrol. 2012, 412, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.L.; Ren, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ren, Y.Y.; Sun, X.B.; Zhan, Y.J.; Shrestha, A.B.; Krishnan, R. An overview of studies of observed climate change in the Hindu Kush Himalayan (HKH) region. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2017, 8, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Appadurai, A.N.; Choudhury, D.; Regmi, B.R.; Kelkar, U.; Alam, M.; Chaudhary, P.; Mu, S.S.; Ahmed, A.U.; Lotia, H.; et al. Adaptation to climate change in the Hindu Kush Himalaya: Stronger action urgently needed. In The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment: Mountains, Climate Change, Sustainability and People; Philippus, W., Mishra, A., Mukherji, A., Shrestha, A.B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 457–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotru, R.K.; Shakya, B.; Joshi, S.; Gurung, J.; Ali, G.; Amatya, S.; Pant, B. Biodiversity conservation and management in the Hindu Kush Himalayan Region: Are transboundary landscapes a promising solution? Mt. Res. Dev. 2020, 40, A15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, P.; Mishra, A.; Mukherji, A.; Shrestha, A.B. The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment: Mountains, Climate Change, Sustainability and People; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Shi, T.; Guan, H.; Fang, C.; Lin, Z. Prediction of ecological effects of potential population and impervious surface increases using a remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghua, L.; Yingjuan, H.; Hui, Z.; Yunxia, W. Analysis on spatial-temporal variation characteristics and driving factors of fractional vegetation cover in Ningxia based on geographical detector. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 31, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, F.; Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal change and driving factors of the Eco-Environment quality in the Yangtze River Basin from 2001 to 2019. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, S.X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, R.; Han, X.D. The application of ecological environment index model on the national evaluation of ecological environment quality. Remote Sens. Inf. 2012, 27, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Performance Index. EPI Framework [EB/OL]. Available online: https://epi.yale.edu/ (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Ye, Y.P.; Liu, L.J. A preliminary study on assessment indicator system of provincial eco environmental quality in China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2000, 13, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.T.; Mendes, J.F.G. City Noise-Air: An environmental quality index for cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2012, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Jiang, W. Evaluation of the spatiotemporal variations in the eco-environmental quality in China based on the remote sensing ecological index. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Du, Y. Analysis of ecological quality in Lhasa Metropolitan Area during 1990–2017 based on remote sensing and Google Earth Engine platform. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Cui, Y.W.; Tang, W.J.; Li, S. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of ecological quality changes across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under the influence of climate factors and human activities. Res. Cold Arid Reg. 2024, 16, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chai, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; He, H. Monitoring and Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality in the Tianshan Mountains of China Using Remote Sensing from 2001 to 2020. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of spatial–temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Xue, P.; Wang, J. Assessment of optimal seasonal selection for RSEI construction: A case study of ecological environment quality assessment in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from 2001 to 2020. Geocarto Int. 2024, 39, 2311224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Guo, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X. Assessment of eco-environmental quality changes and spatial heterogeneity in the Yellow River Delta based on the remote sensing ecological index and geo-detector model. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M. Evolutionary characteristics of carbon sources/sinks in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems regarding to temporal effects and geographical partitioning. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, N.; Shrestha, A.B.; Sharma, E. Climate change trends and ecosystem resilience in the Hindu Kush Himalayas. In Himalayan Weather and Climate and Their Impact on the Environment; Dimri, A.P., Bookhagen, B., Stoffel, M., Yasunari, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 525–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q.; Deng, W.H. Rationality analysis of MRSEI and its difference with RSEI. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2022, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Dozier, J. A generalized split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobser, S.E.; Cohen, W.B. MODIS tasselled cap: Land cover characteristics expressed through transformed MODIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5079–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, H. A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Han, D.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F. Spatiotemporal variations in ecological quality of Otindag Sandy Land based on a new modified remote sensing ecological index. J. Arid Land 2023, 15, 920–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, A.; Cheng, X. Landsat-based monitoring of landscape dynamics in arctic permafrost region. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 2022, 9765087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; He, H.; Xu, J.; Jin, Y. Detecting global vegetation changes using Mann-Kendal (MK) trend test for 1982–2015 time period. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Meng, J.; Zhu, L. Applying Geodetector to disentangle the contributions of natural and anthropogenic factors to NDVI variations in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, F.; Xu, C.; Li, B.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z. Evaluating the suitability of urban development land with a Geodetector. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Che, M.; Shang, Z.; Degen, A.A. Tracking of Vegetation Carbon Dynamics from 2001 to 2016 by MODIS GPP in HKH Region. In Carbon Management for Promoting Local Livelihood in the Hindu Kush Himalayan (HKH) Region; Shang, Z., Degen, A.A., Rafiq, M.K., Squires, V.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Gong, J. Spatial–Temporal Changes and Driving Mechanisms of Ecological Environmental Quality in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Land 2024, 13, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Park, T.; Chen, C.; Lian, X.; He, Y.; Bjerke, J.W.; Chen, A.; Ciais, P.; Tømmervik, H. Characteristics, drivers and feedbacks of global greening. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, E.; Wu, S.; Fan, R.; Xu, L.; Ning, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal dynamics of ecological condition in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on remotely sensed ecological index. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Ijaz, M.; Aziz, M.; Hassan, M.; Ahmed, A.M.; Soomro, D.M.; Ali, S. Locust attack: Managing and control strategies by the government of Pakistan: A review on locust attack in Pakistan. Proc. Pak. Acad. Sci. B Life Environ. Sci. 2022, 59, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ecological Protection Level of Sanjiangyuan National Park Continues to Improve [EB/OL]. Available online: http://www.qinghai.gov.cn/dmqh/system/2023/11/13/030029577.shtml (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Airiken, M.; Li, S. The dynamic monitoring and driving forces analysis of ecological environment quality in the Tibetan Plateau based on the Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zeng, W.; Ma, B. Roadmap for coordinated development of economic construction and ecological protection in protected areas: Take Sanjiangyuan area as an example. Biodivers. Sci. 2022, 30, 21225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Shang, Z.; Gao, J.; Boone, R.B. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 287, 106684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.; Chand, N.; Shrestha, A.; Dhakal, N.; Karki, K.B.; Shrestha, H.L.; Bhandari, P.L.; Adhikari, B.; Shrestha, S.K.; Regmi, S.P. How policy and development agencies led to the degradation of indigenous resources, institutions, and social-ecological systems in Nepal: Some insights and opinions. Conservation 2022, 2, 134–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, D.; Meyfroidt, P.; Lambin, E.F. Forest cover changes in Bhutan: Revisiting the forest transition. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 67, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP. Building Resilience in the Hindu Kush Himalayan Region [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.undp.org/nepal/events/building-resilience-in-himalayan-region (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- UNDP and ICIMOD sign an agreement to build resilience in the Hindu Kush Himalayan countries [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.undp.org/nepal/press-releases/undp-and-icimod-sign-agreement-build-resilience-hindu-kush-himalayan-countries (accessed on 9 June 2022).
- Dhungel, D.N.; Pun, S.B. The Nepal-India Water Relationship: Challenges; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, U.; Anjum, S.; Sabir, S. Armed conflict, militarization and ecological footprint: Empirical evidence from South Asia. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 281, 125299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Pereira, P. The impact of the armed conflict in Afghanistan on vegetation dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharat, M. Water management in the Indus Basin in Pakistan: Challenges and opportunities. In Indus River Basin: Water Security and Sustainability; Khan, S.I., Adams, T.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Shi, W.; Hao, M.; Zhu, X. FSDAF 2.0: Improving the performance of retrieving land cover changes and preserving spatial details. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Fawcett, D.; Cugulliere, A.; Benford, S.; Jones, D.; Leng, R. Vegetation expansion in the subnival Hindu Kush Himalaya. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 1608–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, F.; Godinho, S.; Ferraz, G.; Pita, R.; Gameiro, J.; Silva, B.; Marques, A.T.; Silva, J.P. Multi-temporal remote sensing of inland surface waters: A fusion of Sentinel-1&2 data applied to small seasonal ponds in semiarid environments. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 135, 104283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Greenness (NDVI) | Heat (LST) | Wetness (WET) | Dryness (NDBSI) | Eigenvalue | Explained Variance/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 0.83 | −0.36 | −0.38 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 71.60 |
| 2002 | 0.91 | −0.25 | −0.28 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 61.17 |
| 2003 | 0.89 | −0.32 | −0.27 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 75.31 |
| 2004 | 0.84 | −0.27 | −0.42 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 76.04 |
| 2005 | 0.83 | −0.40 | −0.33 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 72.32 |
| 2006 | 0.90 | −0.30 | −0.26 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 75.27 |
| 2007 | 0.90 | −0.32 | −0.26 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 75.47 |
| 2008 | 0.88 | −0.28 | −0.33 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 68.44 |
| 2009 | 0.90 | −0.32 | −0.24 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 71.69 |
| 2010 | 0.93 | −0.22 | −0.24 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 73.14 |
| 2011 | 0.90 | −0.29 | −0.27 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 72.04 |
| 2012 | 0.91 | −0.29 | −0.23 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 73.34 |
| 2013 | 0.92 | −0.25 | −0.23 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 71.50 |
| 2014 | 0.90 | −0.25 | −0.32 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 69.84 |
| 2015 | 0.92 | −0.21 | −0.28 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 76.82 |
| 2016 | 0.91 | −0.25 | −0.27 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 70.29 |
| 2017 | 0.93 | −0.23 | −0.23 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 72.52 |
| 2018 | 0.91 | −0.26 | −0.26 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 72.58 |
| 2019 | 0.89 | −0.25 | −0.32 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 72.35 |
| 2020 | 0.92 | −0.23 | −0.26 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 76.28 |
| 2021 | 0.93 | −0.20 | −0.27 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 74.13 |
| 2022 | 0.90 | −0.28 | −0.27 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 69.27 |
| 2023 | 0.90 | −0.30 | −0.22 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 76.10 |
| Average | 0.90 ± 0.01 | −0.28 ± 0.015 | −0.28 ± 0.015 | 0.18 ± 0.016 | 0.07 ± 0.003 | 72.50 ± 0.64 |
| Grades | 2001–2010 | 2011–2023 | 2001–2023 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area/km2 | Proportion/% | Area/km2 | Proportion/% | Area/km2 | Proportion/% | |
| Significant degradation | 16,762 | 0.42 | 19,901 | 0.50 | 28,049 | 0.70 |
| Slight degradation | 613,338 | 15.38 | 1,276,095 | 32.00 | 431,574 | 10.82 |
| Stable | 115,790 | 2.90 | 117,364 | 2.94 | 118,309 | 2.97 |
| Slight improvement | 2,740,568 | 68.73 | 2,396,252 | 60.10 | 2,043,860 | 51.26 |
| Significant improvement | 500,843 | 12.56 | 177,689 | 4.46 | 1,365,509 | 34.25 |
| Factor Type | 2001–2010 | 2011–2023 | 2001–2023 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q-Value | Sort | q-Value | Sort | q-Value | Sort | |
| Temperature | 0.47 | 3 | 0.47 | 3 | 0.47 | 3 |
| Precipitation | 0.65 | 1 | 0.67 | 1 | 0.66 | 1 |
| Elevation | 0.16 | 4 | 0.17 | 4 | 0.17 | 4 |
| Slope | 0.09 | 5 | 0.08 | 5 | 0.09 | 5 |
| Aspect | 0.01 | 6 | 0.01 | 6 | 0.01 | 6 |
| Land cover type | 0.59 | 2 | 0.55 | 2 | 0.57 | 2 |
| Factor Type | Sub-Region R1 | Sub-Region R2 | Sub-Region R3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q-Value | Sort | q-Value | Sort | q-Value | Sort | |
| Temperature | 0.64 | 1 | 0.64 | 2 | 0.10 | 4 |
| Precipitation | 0.51 | 2 | 0.48 | 4 | 0.50 | 1 |
| Elevation | 0.33 | 4 | 0.64 | 3 | 0.06 | 5 |
| Slope | 0.19 | 5 | 0.11 | 5 | 0.19 | 3 |
| Aspect | 0.01 | 6 | 0.00 | 6 | 0.01 | 6 |
| Land cover type | 0.51 | 3 | 0.66 | 1 | 0.31 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, Z. Dynamic Monitoring and Driving Factors Analysis of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Hindu Kush–Himalaya Region. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132141
Zhang F, Wang X, Yu J, Yu H, Yu Z. Dynamic Monitoring and Driving Factors Analysis of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Hindu Kush–Himalaya Region. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(13):2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132141
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fangmin, Xiaofei Wang, Jinge Yu, Huijie Yu, and Zhen Yu. 2025. "Dynamic Monitoring and Driving Factors Analysis of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Hindu Kush–Himalaya Region" Remote Sensing 17, no. 13: 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132141
APA StyleZhang, F., Wang, X., Yu, J., Yu, H., & Yu, Z. (2025). Dynamic Monitoring and Driving Factors Analysis of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Hindu Kush–Himalaya Region. Remote Sensing, 17(13), 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17132141






