On Flood Detection Using Dual-Polarimetric SAR Observation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dual-Pol Flood Detection Methods
2.1. Dual-Pol Scattering Observation
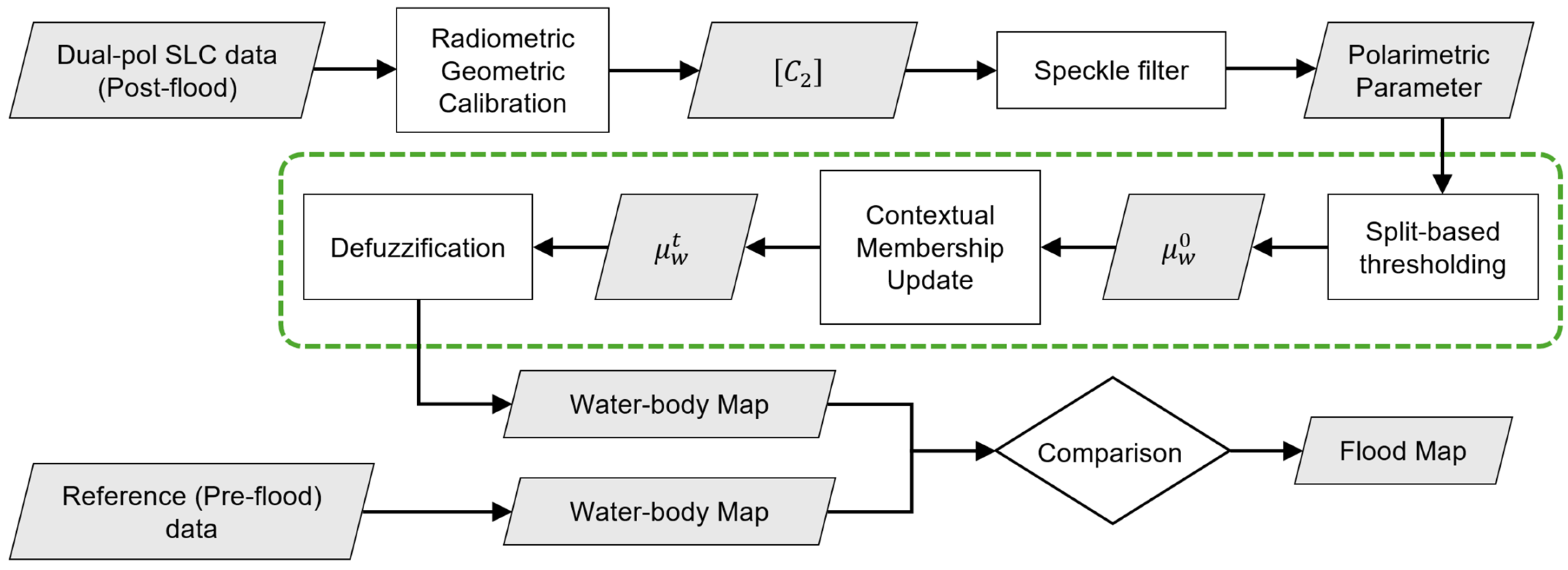
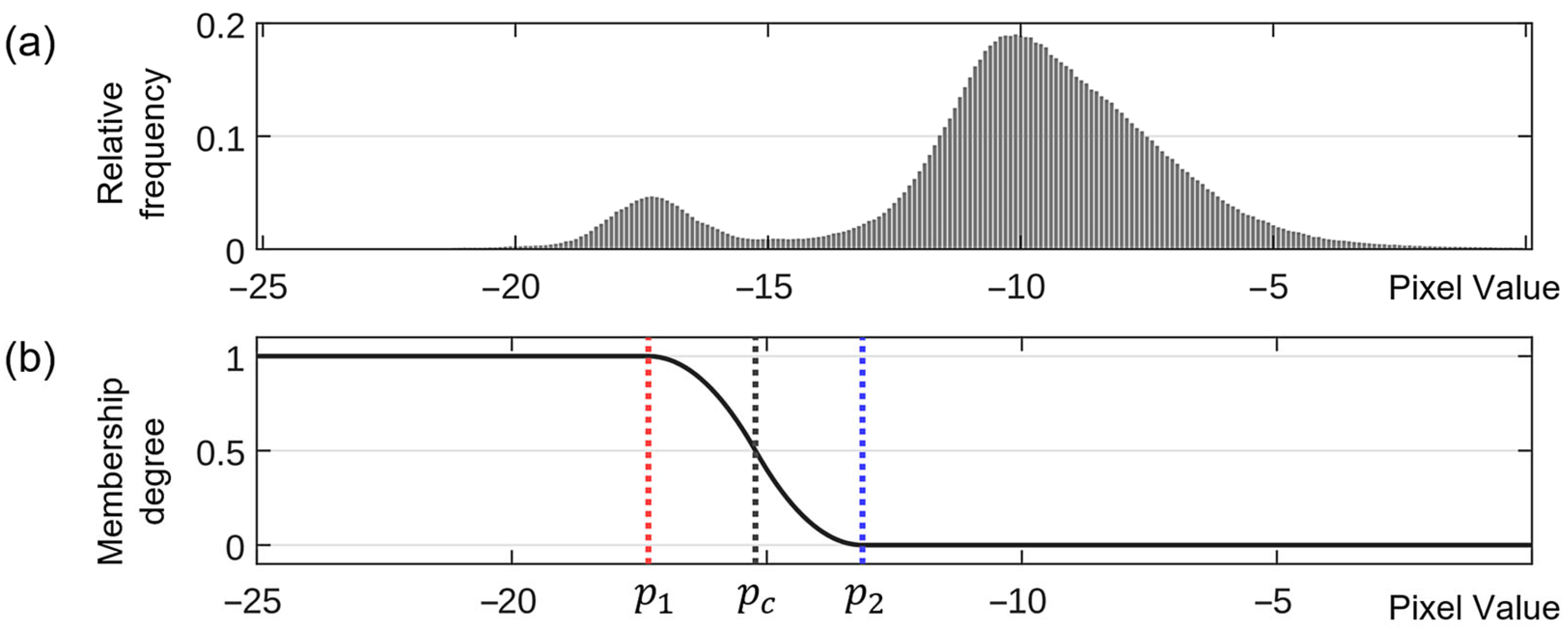
2.2. Flood Detection Using the Selected Dual-Pol Parameters
- (1)
- Split the entire image into non-overlapping subimages of user-defined size.
- (2)
- Apply a bimodality test, such as Hartigan’s dip statistic (HDS) [42], to each subimage.
- (3)
- Select subimages with a -value of HDS less than 0.01.
- (4)
- Define a new vector given by the union of pixel values of all the selected subimages.
- (5)
- Compute threshold value and the mean values associated with the water class, respectively, by applying the EM technique.
2.3. Flood Detection Using the Fusion of Dual-Pol Intensities
3. Experimental Results
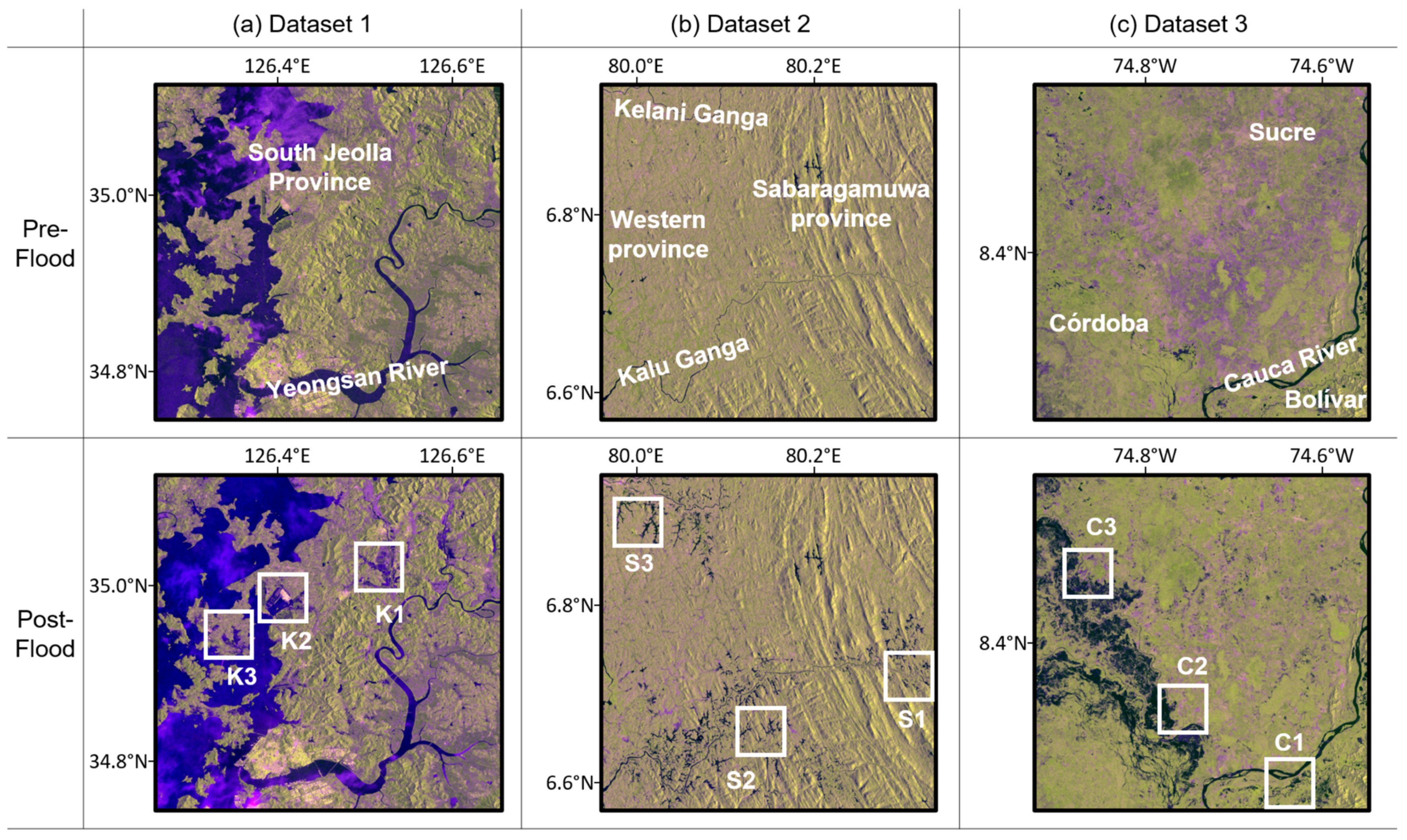
3.1. Datasets
3.1.1. Dataset 1: Korea
3.1.2. Dataset 2: Sri Lanka
3.1.3. Dataset 3: Colombia
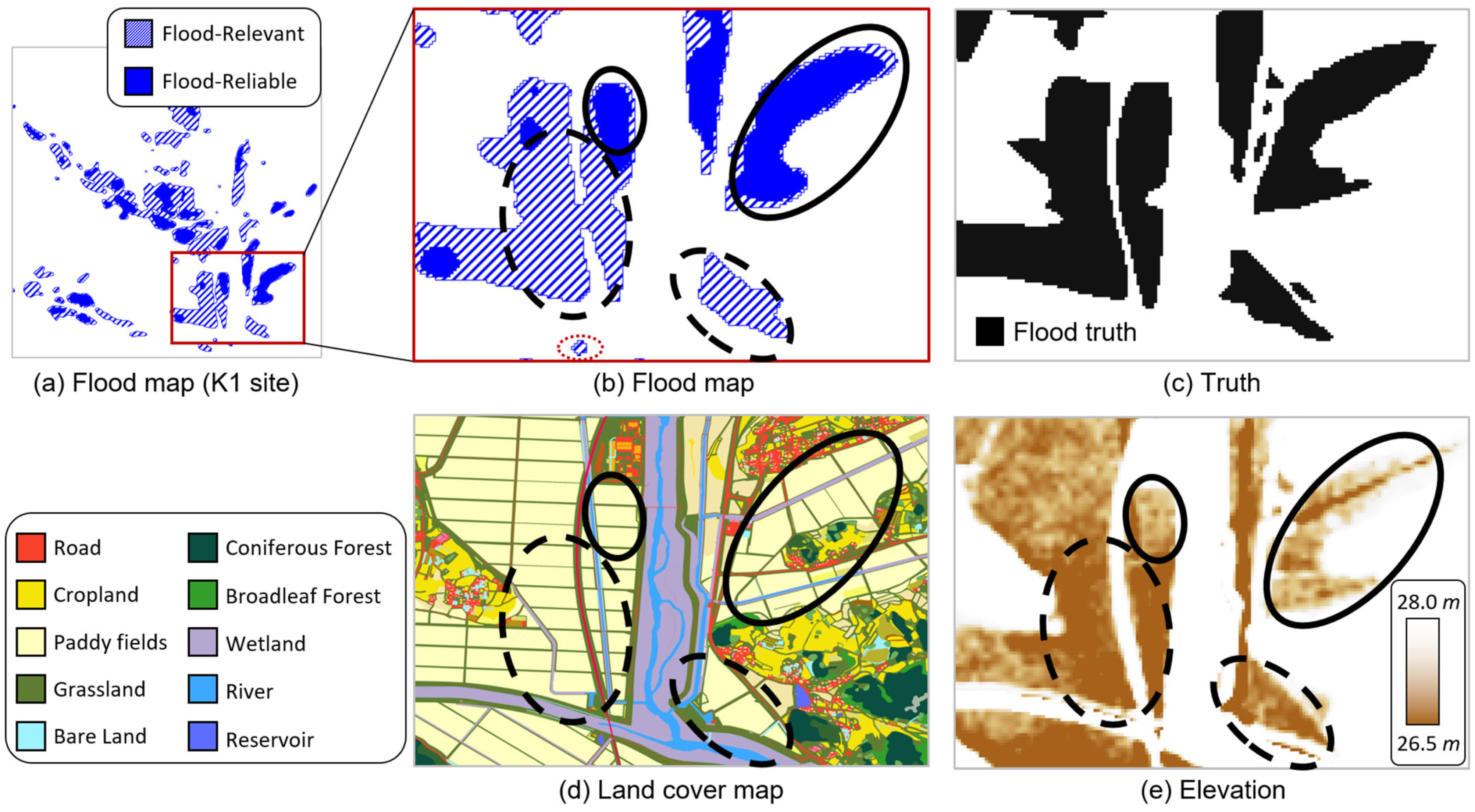
3.2. Flood Detection Results for Each Dataset
- (1)
- VV-pol intensity ()
- (2)
- VH-pol intensity ()
- (3)
- Span of the covariance matrix ()
- (4)
- Degree of polarization ()
- (5)
- Shannon entropy ()
- (6)
- Fuzzy intersection ()
- (7)
- Fuzzy union ()
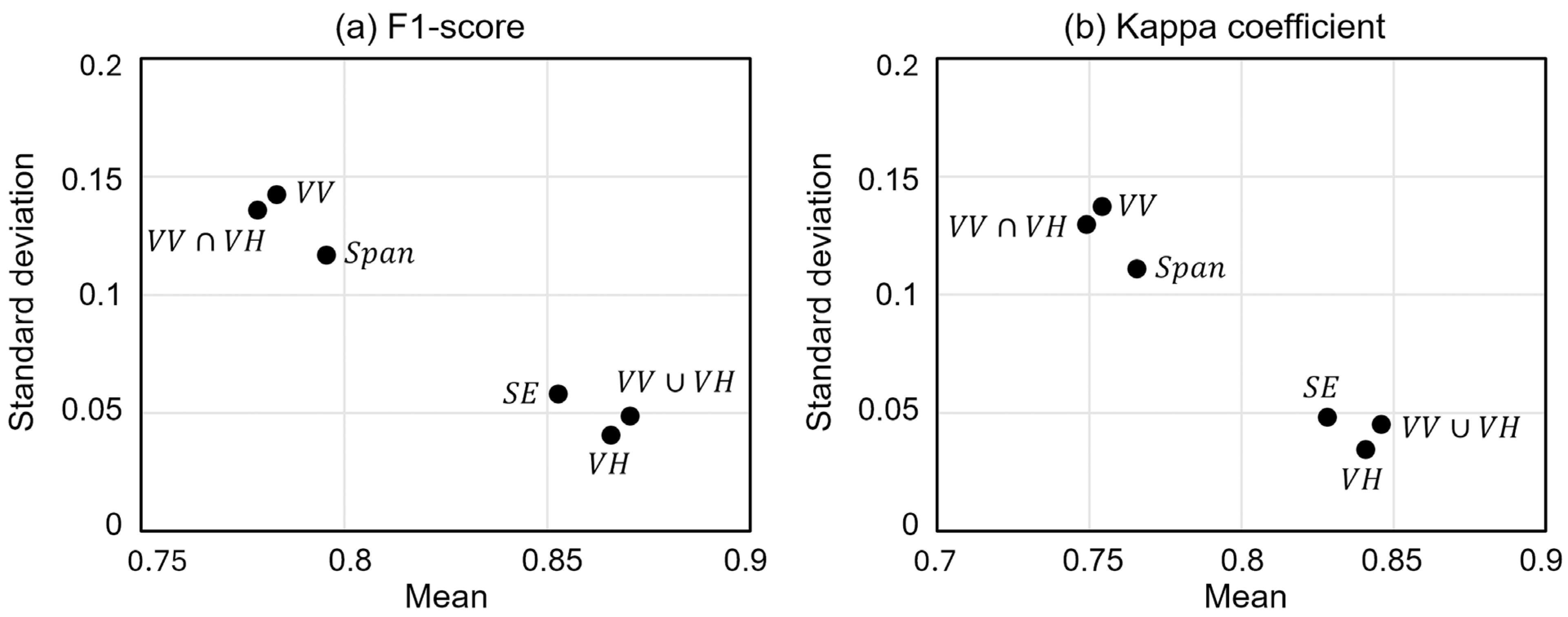
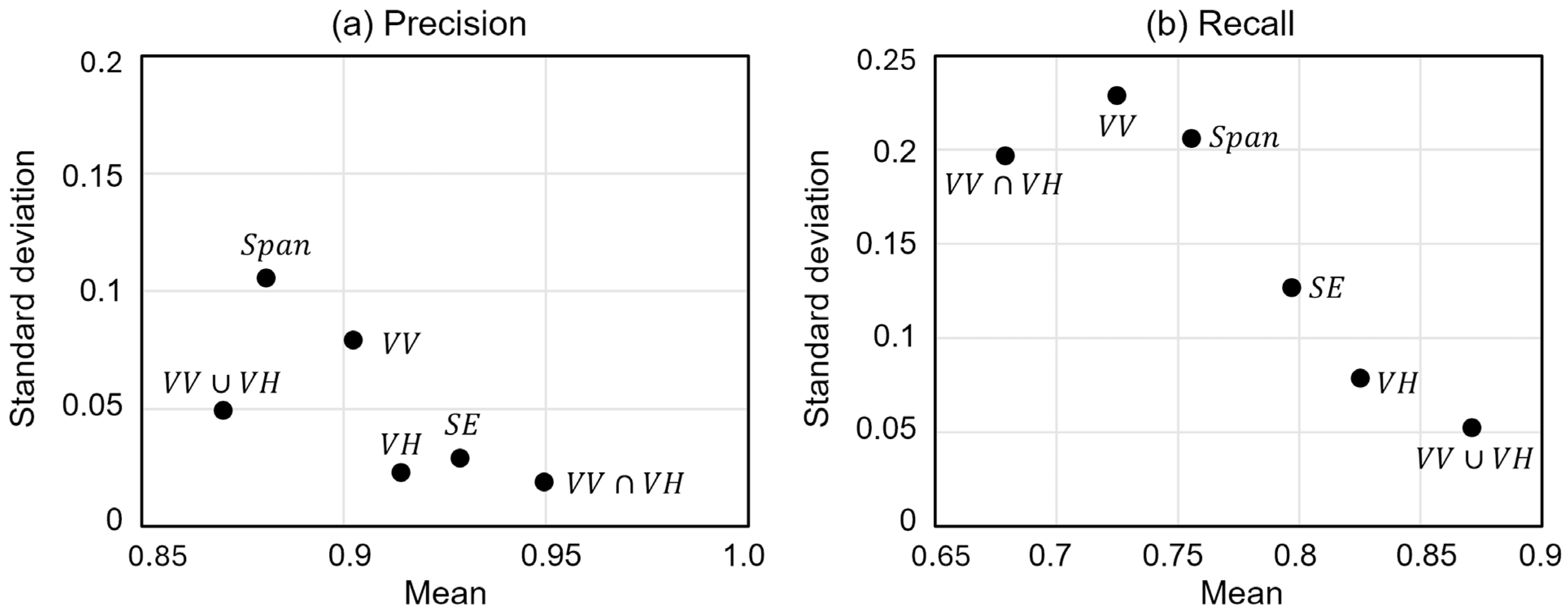
3.3. Overall Flood Detection Performance of Dual-Pol Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
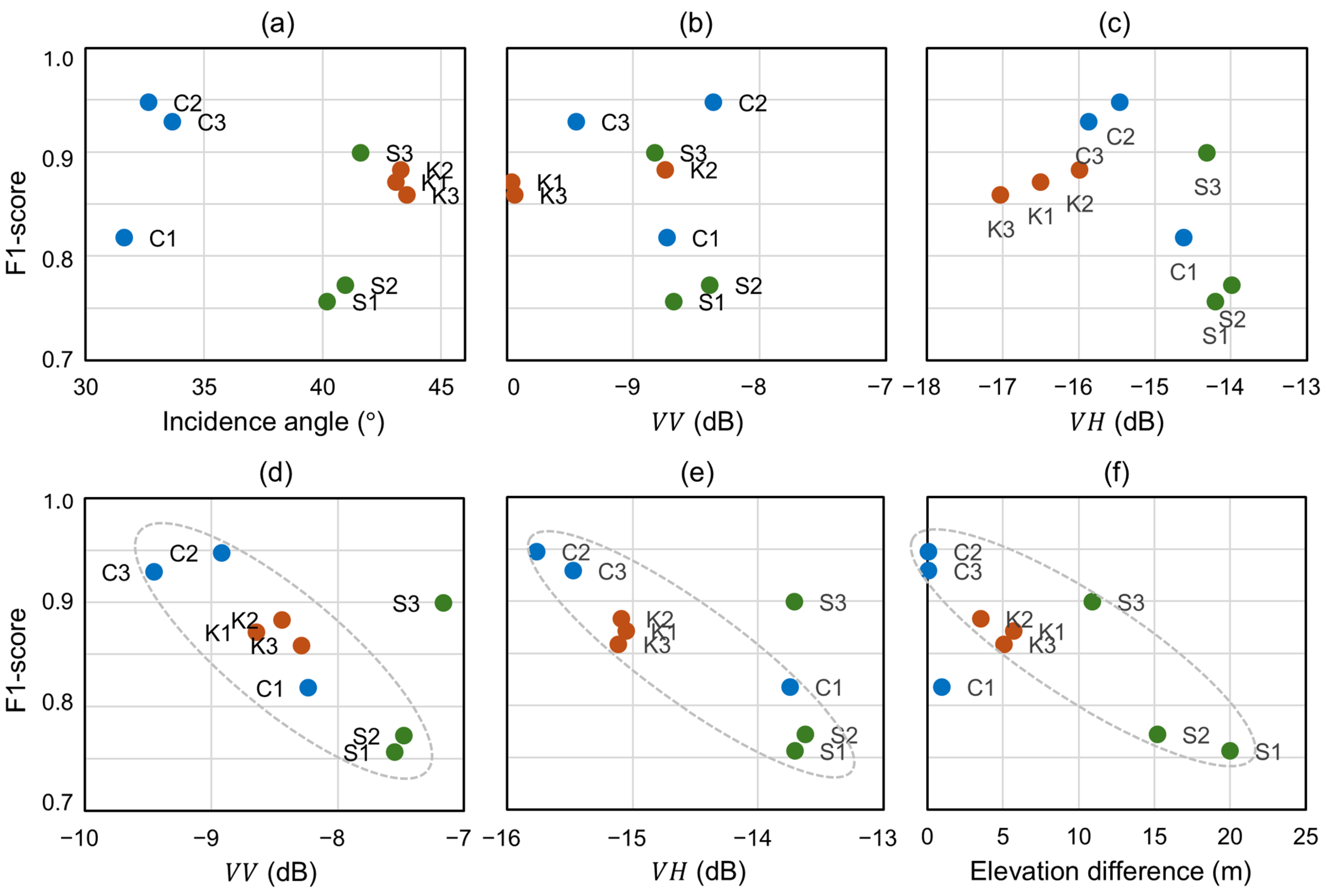
4.2. Flood Detection Performance in Terms of Local Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brivio, P.A.; Colombo, R.; Maggi, M.; Tomasoni, R. Integration of remote sensing data and GIS for accurate mapping of flooded areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.B.; Chastanet, P.; Fellah, K.; Desnos, Y.L. Envisat multi-polarized ASAR data for flood mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Henry, J.B.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Integration of SAR-derived river inundation areas, high-precision topographic data and a river flow model toward near real-time flood management. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.M.; Hambidge, C.H.; Brownett, J.M. Progress in operational flood mapping using satellite synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and airborne light detection and ranging (LiDAR) data. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 40, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roo, A.; Van Der Knijff, J.; Horritt, M.; Schmuck, G.; De Jong, S. Assessing flood damages of the 1997 Oder flood and the 1995 Meuse flood. In Proceedings of the Second International ITC Symposium on Operationalization of Remote Sensing, Enschede, The Netherlands, 16–20 August 1999; pp. 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, P.A. Estimating forest structure in wetlands using multitemporal SAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, P.D.; Horritt, M.S.; Smith, C.N.; Mason, D. Integrating remote sensing observations of flood hydrology and hydraulic modelling. Hydrol. Process. 1997, 11, 1777–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Horritt, M.S.; Dall’Amico, J.T.; Scott, T.R.; Bates, P.D. Improving river flood extent delineation from Synthetic Aperture Radar using airborne laser altimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3932–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Twele, A.; Voigt, S. Towards operational near real-time flood detection using a split-based automatic thresholding procedure on high resolution TerraSAR-X data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-W.; Liu, C.-C.; Cheng, I.-F.; Lee, Y.-R.; Shieh, M.-C. Rapid Response to a Typhoon-induced flood with an SAR-derived map of inundated areas: Case Study and Validation. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11954–11973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Kersten, J.; Twele, A. A fully automated TerraSAR-X based flood service. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.A.; Kilsby, C.G.; Moore, P. Multi-temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar flood mapping using change detection. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 152–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B. Operational flood detection using Sentinel-1 SAR data over large areas. Water 2019, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Fatoyinbo, T.E.; Policelli, F. Flood extent mapping for Namibia using change detection and thresholding with SAR. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. A split-based approach to unsupervised change detection in large-size multitemporal images: Application to tsunami-damage assessment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuaki, R.; Nagai, H. Synthetic Aperture Radar flood detection under multiple modes and multiple orbit conditions: A case study in Japan on typhoon Hagibis, 2019. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Speck, R.; Devereux, B.; Schumann, G.J.P.; Neal, J.C.; Bates, P.D. Flood detection in urban areas using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Chini, M.; Hostache, R.; Pappenberger, F.; Matgen, P. Flood hazard mapping combining hydrodynamic modeling and multi annual remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14200–14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaffer, S.; Matgen, P.; Hollaus, M.; Wagner, W. Flood detection from multi-temporal SAR data using harmonic analysis and change detection. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzine, A.; Saidi, S.; Hermassi, T.; Kammessi, I.; Darragi, F.; Rajhi, H. Flood mapping using hydraulic modeling and Sentinel-1 image: Case study of Medjerda Basin, northern Tunisia. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, L.; Schmitt, A.; Wendleder, A.; Roth, A. Monitoring of the Lac Bam Wetland Extent Using Dual-Polarized X-Band SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, K.; Braun, A.; Fotopoulos, G.; Roth, A.; Wessel, B. Assessing Single-Polarization and Dual-Polarization TerraSAR-X Data for Surface Water Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Duc, B.; Prigent, C.; Aires, F. Surface Water Monitoring within Cambodia and the Vietnamese Mekong Delta over a Year, with Sentinel-1 SAR Observations. Water 2017, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Matin, M.A.; Meyer, F.J. Operational Flood Mapping Using Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 SAR Images: A Case Study from Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, E. Coherence properties of partially polarized electromagnetic radiation. Nuovo Cim. 1959, 13, 1165–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réfrégier, P.; Morio, J. Shannon entropy of partially polarized and partially coherent light with Gaussian fluctuations. JOSA A 2006, 23, 3036–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, C.; Pottier, E.; Hubert-Moy, L.; Rapinel, S. One year wetland survey investigations from quad-pol RADARSAT-2 time-series SAR images. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 38, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.T.; Park, S.E.; Baek, C.S.; Kim, D.H. Evaluation of polarimetric parameters for flood detection using PALSAR-2 quad-pol data. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2018, 34, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Betbeder, J.; Rapinel, S.; Corgne, S.; Pottier, E.; Hubert-Moy, L. TerraSAR-X dual-pol time-series for mapping of wetland vegetation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 107, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Hostache, R.; Schumann, G.; Pfister, L.; Hoffmann, L.; Savenije, H.H.G. Towards an automated SAR-based flood monitoring system: Lessons learned from two case studies. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.J.P.; Bates, P.D.; Mason, D.C. A change detection approach to flood mapping in urban areas using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Giustarini, L.; Xiong, B.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Kuang, G. Automated flood detection with improved robustness and efficiency using multi-temporal SAR data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanama, V.S.K.; Rao, Y.S.; Bhatt, C.M. Change detection based flood mapping using multi-temporal Earth Observation satellite images: 2018 flood event of Kerala, India. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Twele, A. A hierarchical spatio-temporal Markov model for improved flood mapping using multi-temporal X-band SAR data. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2240–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Chini, M.; Guerriero, L. An algorithm for operational flood mapping from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data using fuzzy logic. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Rosenfeld, A. Image enhancement and thresholding by optimization of fuzzy compactness. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1988, 7, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1977, 39, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, L.; Prieto, D.F. Automatic analysis of the difference image for unsupervised change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E. Detection of water bodies from Kompsat-5 SAR data. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2016, 32, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Hartigan, P.M. The dip test of unimodality. Ann. Stat. 1985, 13, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaiman, B.; Pierce, L.; Ulaby, F. Multisensor data fusion using fuzzy concepts: Application to land-cover classification using ERS-1/JERS-1 SAR composites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twele, A.; Cao, W.; Plank, S.; Martinis, S. Sentinel-1-based flood mapping: A fully automated processing chain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2990–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, V.; Tamkuan, N.; Nagai, M. Near-real-time flood mapping using off-the-shelf models with SAR imagery and deep learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereczky, M.; Wieland, M.; Krullikowski, C.; Martinis, S.; Plank, S. Sentinel-1-based water and flood mapping: Benchmarking convolutional neural networks against an operational rule-based processing chain. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Garg, S.; Motagh, M.; Martinis, S. Automatic flood detection from Sentinel-1 data using a nested UNet model and a NASA benchmark dataset. PFG J. Photogram. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2024, 92, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive. Volume 2-Radar Remote Sensing and Surface Scattering and Emission Theory; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]

| Dataset 1 (Korea) | Dataset 2 (Sri Lanka) | Dataset 3 (Colombia) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Flood | Post-Flood | Pre-Flood | Post-Flood | Pre-Flood | Post-Flood | |
| Polarization | VV-VH | VV-VH | VV-VH | |||
| Orbit | Ascending | Descending | Descending | Descending | Descending | Descending |
| IW sub-swath | IW1 | IW3 | IW2 | IW2 | IW1 | IW1 |
| Acquisition Date (UTC) | 23 July 2023 09:33 | 23 July 2023 21:31 | 5 April 2024 00:25 | 4 June 2024 00:25 | 25 April 2024 10:50 | 19 May 2024 10:50 |
| Parameter | OA | F1 | Kappa | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9451 | 0.6287 | 0.6029 | 0.9711 | 0.4648 | |
| 0.9747 | 0.8711 | 0.8571 | 0.8878 | 0.8551 | |
| 0.9508 | 0.6810 | 0.6569 | 0.9700 | 0.5247 | |
| 0.8925 | 0.0783 | 0.0513 | 0.2754 | 0.0456 | |
| 0.9670 | 0.8102 | 0.7926 | 0.9542 | 0.7040 | |
| 0.9450 | 0.6285 | 0.6027 | 0.9709 | 0.4646 | |
| 0.9747 | 0.8713 | 0.8573 | 0.8880 | 0.8552 |
| Parameter | OA | F1 | Kappa | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9552 | 0.8135 | 0.7881 | 0.8155 | 0.8116 | |
| 0.9616 | 0.8221 | 0.8009 | 0.9304 | 0.7364 | |
| 0.9479 | 0.7913 | 0.7616 | 0.7643 | 0.8204 | |
| 0.9288 | 0.5893 | 0.5567 | 0.9640 | 0.4244 | |
| 0.9630 | 0.8291 | 0.8086 | 0.9343 | 0.7452 | |
| 0.9607 | 0.8152 | 0.7937 | 0.9399 | 0.7197 | |
| 0.9565 | 0.8208 | 0.7960 | 0.8139 | 0.8278 |
| Parameter | OA | F1 | Kappa | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9464 | 0.9088 | 0.8709 | 0.9198 | 0.8981 | |
| 0.9439 | 0.9035 | 0.8639 | 0.9236 | 0.8842 | |
| 0.9490 | 0.9147 | 0.8783 | 0.9082 | 0.9214 | |
| 0.7932 | 0.4835 | 0.3900 | 0.9371 | 0.3258 | |
| 0.9505 | 0.9187 | 0.8832 | 0.8971 | 0.9414 | |
| 0.9392 | 0.8928 | 0.8505 | 0.9373 | 0.8523 | |
| 0.9512 | 0.9188 | 0.8839 | 0.9079 | 0.9299 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.-E. On Flood Detection Using Dual-Polarimetric SAR Observation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111931
Kim S-Y, Lee Y, Park S-E. On Flood Detection Using Dual-Polarimetric SAR Observation. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(11):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111931
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Su-Young, Yeji Lee, and Sang-Eun Park. 2025. "On Flood Detection Using Dual-Polarimetric SAR Observation" Remote Sensing 17, no. 11: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111931
APA StyleKim, S.-Y., Lee, Y., & Park, S.-E. (2025). On Flood Detection Using Dual-Polarimetric SAR Observation. Remote Sensing, 17(11), 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111931







