Abstract
The accurate segmentation of small target buildings in high-resolution remote sensing images remains challenging due to two critical issues: (1) small target buildings often occupy few pixels in complex backgrounds, leading to frequent background confusion, and (2) significant intra-class variance complicates feature representation compared to conventional semantic segmentation tasks. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Foreground Perception Enhancement Network (MFFP-Net). This framework introduces three key innovations: (1) a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MFF) module that hierarchically aggregates shallow features through cross-level connections to enhance fine-grained detail preservation, (2) a Foreground Perception Enhancement (FPE) module that establishes pixel-wise affinity relationships within foreground regions to mitigate intra-class variance effects, and (3) a Dual-Path Attention (DPA) mechanism combining parallel global and local attention pathways to jointly capture structural details and long-range contextual dependencies. Experimental results demonstrate that the IoU of the proposed method achieves improvements of 0.44%, 0.98% and 0.61% compared to mainstream state-of-the-art methods on the WHU Building, Massachusetts Building, and Inria Aerial Image Labeling datasets, respectively, validating its effectiveness in handling small targets and intra-class variance while maintaining robustness in complex scenarios.
1. Introduction
With advancements in remote sensing technology, high-resolution satellite imagery has become indispensable in urban infrastructure development and environmental governance. As a crucial spatial element in urban remote sensing applications, the precise extraction and analysis of building features has emerged as a critical task with multi-dimensional implications. This technical requirement not only drives the iterative updating of geographic information systems (GIS) but also supports strategic urban planning and provides essential data support for disaster risk assessment and emergency management. Consequently, developing efficient and accurate methods for automated building feature extraction from complex remote sensing datasets has evolved into a cutting-edge research frontier.
Traditional image segmentation methods, such as threshold-based segmentation [1], region-based segmentation [2], and edge detection-based segmentation [3], have significant limitations in the task of remote sensing building extraction. The threshold-based method is vulnerable to differences in surface illumination and the diversity of building materials, and it is difficult to determine a universal segmentation threshold between the shadow area and the low-reflectivity roof. The region-based approach is prone to misjudging non-building features with similar textures (such as concrete pavements or regular farmland) as building units. Meanwhile, methods based on edge detection are sensitive to the fuzziness of building contours. Especially in low-resolution images, it is difficult to distinguish the transition areas between building edges and adjacent roads and vegetation, resulting in insufficient positioning accuracy for the target boundary. These flaws severely restrict the application efficiency of traditional image segmentation methods in highly heterogeneous urban remote sensing scenarios.
In recent years, with the rapid progress of deep learning (DL) technology, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) [4] have revolutionized this domain. The DL-based method with CNNs as the core significantly improved the segmentation accuracy through multi-level feature extraction. The fully convolutional network (FCN) [5], a pioneering framework for semantic segmentation, replaced traditional fully connected layers with fully convolutional layers to enable pixel-level prediction, marking a breakthrough in image parsing. Following the FCN’s success, CNN-based methods for remote sensing building extraction proliferated, significantly enhancing the accuracy and scalability of building segmentation in remote sensing imagery. Researchers further optimized network architectures by integrating advanced designs such as ResNet and DenseNet, which enhanced the feature extraction efficiency. Additionally, techniques like multi-scale feature fusion, attention mechanisms, and context-aware encoding improved the robustness in handling complex scenes and diverse remote sensing data. Today, building segmentation has not only achieved theoretical maturity but also demonstrates practical value in urban planning, disaster assessment, and environmental monitoring. In parallel, Vision Transformers (ViTs) [6] have extended the success of the Transformer architecture [7]—originally developed for natural language processing—to image analysis. By leveraging self-attention (SA) mechanisms, ViTs capture long-range dependencies within images, addressing challenges like occlusion and irregular building shapes in remote sensing data. Subsequent research has refined ViT-based approaches, achieving notable improvements in segmentation accuracy, computational efficiency, and adaptability to varying image resolutions. These advancements position ViTs as a vital complement to CNNs in remote sensing building segmentation, offering novel methodologies for feature learning. Beyond remote sensing, ViTs have inspired cross-disciplinary innovations, underscoring the broader potential of AI-driven solutions in geospatial analysis and related fields.
However, the precise segmentation of building targets in remote sensing images still faces severe challenges, mainly manifested in two aspects. Firstly, the intra-class variance of buildings is significant. Affected by factors such as the building types, materials, lighting conditions, and imaging angles, similar buildings show high heterogeneity in their shape, texture, and spectral characteristics. Secondly, the semantic confusion between complex surface backgrounds (such as dense vegetation, road networks, and shadow occlusion) and small and medium-sized building targets leads to difficulties in using segmentation models to effectively identify fine targets in low-contrast scenes. These bottleneck problems have severely restricted the practical application process of remote sensing building extraction technology.
To address these critical challenges, we present a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Foreground Perception Enhancement Network (MFFP-Net) for building segmentation in remote sensing images. The proposed architecture introduces three fundamental innovations: (1) hierarchical feature interaction for multi-scale object representation, (2) spatial–semantic correlation modeling for foreground disambiguation, and (3) hybrid attention mechanisms for efficient global–local context fusion. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate its state-of-the-art performance compared to existing mainstream methods. The main contributions of this paper are as follows.
- A Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MFF) module is proposed to improve the utilization efficiency of small target details in shallow features by constructing a hierarchical feature fusion mechanism, so that the network can pay more attention to shallow features containing more small target information.
- A Foreground Perception Enhancement (FPE) module is proposed, which introduces a scene-constrained affinity learning mechanism that dynamically constructs pixel-wise spatial–semantic correlations within predicted foreground regions. By integrating pyramid scene embedding and convolution-based relation mapping, FPE clearly models the intra-class context dependency relationship. Compared with the traditional framework, it can effectively reduce the false alarms caused by intra-class variance.
- A hybrid architecture in the form of a Dual-Path Attention (DPA) mechanism is designed, which combines the sparse self-attention (SA) of global context modeling with local attention based on strip convolution. This design strategically combines local details with global context dependency, reducing the computational complexity of the traditional SA and simultaneously improving the segmentation performance.
2. Related Works
CNNs have quickly become a mainstream technology in the field of image segmentation since they were proposed. With continuous research and innovation over the years, the application of CNNs to segment building objects in remote sensing images has been significantly improved and optimized. Early breakthroughs in natural image segmentation laid the foundational principles. For instance, U-Net [8] proposed a skip connection that connects the shallow layer and deep layer, so that the network can find the lost spatial information from the shallow layer. DeepLab [9] proposed Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) to obtain different receptive field information, so as to effectively capture image context information and adapt to different scale changes. DANet [10] uses the SA mechanism to establish the relationship between local pixels and global pixels by calculating the coefficient matrix of local pixels so as to obtain global pixel information, thus achieving good performance on urban landscape datasets. These methods have greatly promoted the progress of semantic segmentation, but domain-specific innovations have become critical to address the unique challenges of geospatial data. To address these domain-specific challenges, Guo et al. [11] proposed the Coarse-to-Fine Boundary Refinement Network, CBR-Net, which uses a boundary-refining module to sense the direction of each pixel in a remote sensing optical image regarding the center of the nearest object that it may belong to, aiming to improve construction prediction and effectively improve the performance of building segmentation in remote sensing images. MBR-HRNet [12] further advanced this paradigm by embedding boundary refinement modules and multi-scale context fusion. Zheng et al. [13] proposed a foreground perception relationship network, FarSeg++, which solved the problems of scale changes, large differences within background classes, and foreground–background imbalances in remote sensing images with high spatial resolutions. Ma et al. [14] proposed a multi-level weighted depth perception network to make full use of shallow feature information and improve the segmentation performance for small and medium-sized objects in remote sensing images. Chen et al. [15] proposed a lightweight convolutional neural network model, U-MGA, which solved problems such as high feature similarity, the insufficient utilization of multi-scale information, and insufficient fine-grained feature extraction in the recognition of cultivated land in remote sensing images. Zheng et al. [16] proposed an automatic extraction method, MA-FCN, for the construction of contours; this combines multi-scale aggregated fully convolutional networks and boundary regularization algorithms. The multi-scale information is fused through the feature pyramid, and the segmentation boundary is optimized by combining overlapping cutting and model voting strategies. The regularization algorithm generates a structured contour by using coarse adjustment to eliminate abnormal nodes and fine adjustment to align the main direction. SiU-Net [17] improves multi-scale building feature extraction by fusing the original and downsampled images. This method effectively integrates global and local information, providing high-quality benchmarks and efficient solutions for building segmentation in cross-sensor remote sensing images. SAU-Net [18] enhances semantic features through a residual channel attention module and a dense multi-dilated convolution module in the encoder. The decoder uses a supervised attention module to refine and integrate multi-scale features, enabling the refined extraction of building boundaries and small buildings in high-resolution remote sensing images. The NPSFF-Net [19] framework integrates multi-receptive field features via a hierarchical residual architecture, synergizing adaptive feature enhancement with dual-stream progressive fusion decoding. This configuration systematically mitigates detail degradation and contextual discontinuity in remote sensing building segmentation through complementary multi-scale representation learning. Although the above methods can effectively extract the target shape, texture, boundary, and other details, they are limited by the convolution window of the CNN, and they cannot establish a connection between the global contexts.
At present, most of the latest building segmentation methods in remote sensing image are hybrid structures consisting of CNNs and Transformers. Chen et al. [20] input the original image into a CNN for feature extraction and performed the patch embedding of the extracted features after linear projection; they then serialized the feature map, added the position code to it, and input it into the Transformer encoder to obtain more information and more accurate positioning. Segmenter [21] encodes the image block sequence through a global self-attention mechanism, generates pixel-level classification results by combining linear decoders or mask transformation decoders, and enhances the semantic feature reconstruction ability by using a pre-trained visual Transformer, effectively improving the segmentation accuracy in complex scenes. Zhang et al. [22] proposed a hybrid architecture in which a Swin Transformer backbone that captures remote dependencies is combined with a U-shaped decoder that employs ASPP blocks and SE blocks based on depth-separable convolution to better preserve local details in the remote sensing image. Swin-Unet [23] proposed a pure Transformer U-shaped network architecture for a Swin Transformer [24], modeled the global semantic association through a hierarchical window self-attention mechanism, and fused multi-scale features by combining the encoder–decoder structure and jump connections. Providing a convolution global context modeling scheme for remote sensing building image segmentation can enhance the semantic consistency of the edges of complex ground objects. Panboonyuen et al. [25] used a pre-trained Swin Transformer backbone and three decoder designs, namely U-Net, FPN, and PSPNet, to carry out the semantic segmentation of aerial remote sensing images and achieve improvements in multiple metrics. Wang et al. [26] combined the advantages of CNNs and ViTs and proposed a dual-path remote sensing building segmentation method, BuildFormer, including global context paths and spatial detail context paths, enabling the network to obtain global context dependence while retaining local detail information. Zhang et al. [27] further improved BuildFormer by designing DSFormer, a dual-path attention structure containing SA and local convolutional attention, and embedded it in the encoder and decoder structures; the feature alignment in the last layer of the decoder further improved the performance of building image segmentation. By using parallel multi-stage feature enhancement groups and global multi-scale attention mechanism, AFNet [28] extracts and fuses multi-scale features, so as to realize the efficient semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images. Zhao et al. [29] proposed a dual-branch network named SPNet, which can improve the semantic segmentation accuracy of buildings and water bodies in remote sensing images by combining spatial supplementary information. TCNet [30] proposes a multi-scale fusion architecture in parallel with a Transformer and CNN. Through Interactive Self-Attention (ISa) and Windowed Self-Attention Gating (WSaG), TCNet effectively integrates the global context and local details of building targets. Zhang et al. [31] proposed the SDSC-UNet model, which captures the multi-scale features of buildings in remote sensing images through a split-Transformer encoder. They also designed a double-jump connection encoder to synchronously transfer the internal self-attention map with the overall output to the decoder, and this was combined with the feature fusion module to strengthen the global dependency relationship. This solves the problems of scale differences and semantic information loss in the segmentation of buildings in complex scenarios. Although the above methods improve the performance of building segmentation in remote sensing images to a certain extent, they cannot effectively solve the problem of false positives caused by the fuzzy features of small and medium-sized target buildings and large intra-class variance in remote sensing images, and there are certain limitations.
3. Method
3.1. The Overall Structure of MFFP-Net
To address the aforementioned critical challenges, we propose a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Foreground Perception Enhancement Network (MFFP-Net), whose overall structure is shown in Figure 1. Here, ConvNeXt [32]—a convolutional neural network that re-examines and optimizes traditional design principles—serves as the backbone feature extractor. This architecture achieves performance comparable to that of Transformer-based models while retaining the advantages of convolutional networks, such as reduced computational costs and fewer parameters, making it well suited for efficient segmentation tasks. First, to enhance the network’s ability to capture small targets, we propose a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MFF) module. This module integrates shallow features (rich in fine-grained details) with deeper, higher-level features extracted by ConvNeXt, thereby improving the utilization of small target information across scales. Second, we introduce the Foreground Perception Enhancement (FPE) module. By explicitly modeling relationships between foreground classes (e.g., buildings), this module strengthens intra-class feature coherence and suppresses false positives caused by visually similar backgrounds. Finally, to harmonize local detail extraction with global context modeling, we design a Dual-Path Attention (DPA) mechanism. The DPA consists of two parallel branches: (1) the Local Path Attention (LPA), which employs convolutional layers to focus on fine-grained spatial patterns, and (2) the Global Path Attention (GPA), which uses SA to capture long-range dependencies. By synergizing these complementary pathways, the network simultaneously leverages the strengths of CNNs and ViTs for robust feature learning.
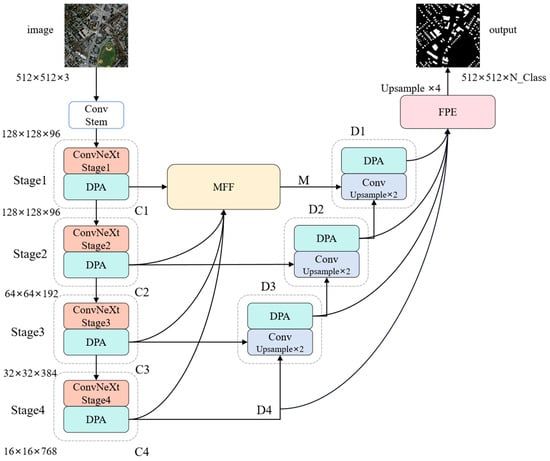
Figure 1.
The overall structure of MFFP-Net.
The process of MFFP-Net is as follows. The input image is first preprocessed to a size of 512 × 512 × 3 before being fed into the feature extraction network. Features are then extracted using the ConvNeXt backbone network. As shown in Figure 1, the output feature maps from the four stages of the ConvNeXt network are labeled as C1, C2, C3, and C4. These feature maps are then input into the MFF module, where they are fused with shallow features to generate the decoder feature maps D1, D2, D3, and D4, corresponding to C1, C2, C3, and C4, respectively. Subsequently, D1, D2, D3, and D4 are passed through the FPE module to enhance the correlation between foreground classes. Finally, the refined feature map is upsampled to the size of the input image, and the final prediction image is generated. Additionally, DPA is embedded throughout the network to capture rich local information and establish global context dependencies for the output feature maps at each stage.
3.2. Dual-Path Attention (DPA)
The ViT’s superior performance is primarily attributed to its innovative use of SA to process image data. This mechanism enables ViTs to comprehensively consider the complex interactions between various regions in an image, effectively capturing global context information during image classification and other visual tasks. The introduction of the self-attention mechanism not only enhances the model’s ability to capture long-distance dependencies but also achieves efficient parameter utilization through parameter sharing. These factors collectively contribute to ViTs’ powerful performance across multiple visual tasks.
In SA, each element in the input sequence is mapped to three vectors—a query (), key (), and value ()—which are typically derived by training learnable weight matrices , , and . These weight matrices multiply the embedded vectors of the input sequence. For each element, the similarity between its query vector and all key vectors is computed via the dot product. These similarity scores represent the degrees of importance that the model assigns to other elements in the sequence within the current context. To stabilize the training process, the scores are normalized and converted into an attention probability distribution. Each value vector is then weighted according to its corresponding attention probability. Finally, the weighted value vectors are summed to produce the self-attention output—a vector containing information about all elements in the sequence.
The key advantage of SA lies in its ability to consider all elements in a sequence simultaneously and capture long-distance dependencies. However, SA requires computing attention scores between each element and all others, resulting in a computational cost that is proportional to the square of the sequence length. To address this, some ViT-based methods employ spatial reduction (SR) operations, which reduce the sequence length during SA computation. For instance, the PVT [33] reduces the sequence lengths of keys and values using convolution operations. While this method reduces the computational cost to some extent, maintaining full-resolution queries to preserve the output size incurs high computational costs. Furthermore, it does not resolve the common issue of missing local information in SA.
Based on the aforementioned challenges in capturing global context dependences and supplementing local information for the Transformer-based SA mechanism, we propose the Dual-Path Attention (DPA) mechanism, building upon the PVT. The key innovation of DPA is to reduce the resolution of feature maps after the SR operation, thereby further decreasing the sequence length and enabling the extraction of coarse global context dependencies at a lower computational cost. To address the potential loss of local details, we incorporate attention-based convolution to refine the feature representation. As illustrated in Figure 2, DPA consists of two parallel branches: Global Path Attention (GPA) and Local Path Attention (LPA). In the GPA branch, the input feature map undergoes SR followed by four applications of 4×4 convolution downsampling, which reduces the computational complexity and establishes coarse-grained global context dependencies. In the LPA branch, multi-scale local features are extracted through a combination of 3 × 3 standard convolution and strip convolutions (including 1 × 3, 3 × 1, 1 × 5, 5 × 1, 1 × 7, and 7 × 1 kernels). These features are then fused, added together, and dot-multiplied with the original input to capture fine local spatial details and complement the global context captured by GPA. Strip convolution is employed for two reasons. First, it is computationally efficient, as it mimics the effect of a 7 × 7 convolution kernel using pairs of 7 × 1 and 1 × 7 kernels, significantly reducing the computational overhead compared to standard 2D convolutions. Second, in the context of building segmentation in remote sensing images, many buildings exhibit elongated, strip-like shapes, making strip convolution particularly effective in capturing such features. Finally, the global and local feature representations obtained from GPA and LPA are concatenated and fed into a feedforward neural network (FFN) for further feature fusion and refinement. The overall calculation process of DPA can be expressed as follows:
where represents the input feature map, represents the output of the GPA branch, represents the output of the LPA branch, Conv1×1( ) represents 1 × 1 convolution, and represents the final output of the DPA.
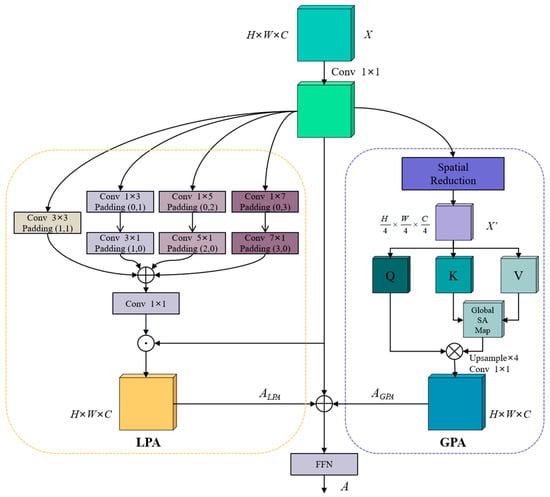
Figure 2.
The structure of DPA.
3.3. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MFF)
The recognition and segmentation of building objects in remote sensing images are more challenging than in common images because they usually contain more segmented objects and more complex backgrounds. In particular, small building objects in remote sensing images may occupy only a few pixels, and their fuzzy features and susceptibility to background interference make it difficult for existing building segmentation models to effectively extract the semantic information of these small target buildings, resulting in poor performance and obvious limitations in the recognition and segmentation of small buildings. In order to overcome this challenge, improve the recognition ability of the network for small target buildings, and then improve the segmentation performance of the model, a Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MFF) module is proposed in this paper, and its structure is shown in Figure 3.
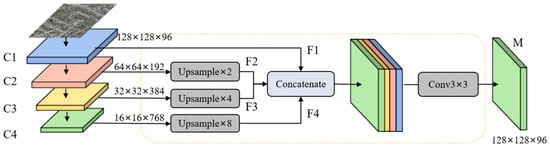
Figure 3.
The structure of the MFF module.
The main idea of MFF is to enhance shallow feature information through fusion at multiple stages of the network, enabling the network to better focus on the important semantic information of small targets for more accurate detection. This is because, in image segmentation networks, shallow features contain more accurate target details and preserve richer information about small objects compared to deep features. By fusing these features at different levels, we can significantly improve the network’s ability to effectively capture small objects, resulting in enhanced overall performance in image segmentation tasks. Specifically, its main processes are as follows. First of all, in order to fuse low-resolution deep-layer features with high-resolution shallow features, the , , and feature maps are, respectively, sampled to the same size as . Then, the sampled , , and are processed to obtain smooth features of the same size as follows:
where Upsample( ) represents the upsampling operation, and Conv3×3( ), BN( ), and ReLU( ) represent 3 × 3 convolution, batch normalization, and ReLU activation functions, respectively. Then, the smooth feature is concatenated, the dimension of the concatenated feature map is reduced, and the feature map after multi-scale feature fusion is output as follows:
where Concatenate( ) indicates that is concatenated by the channel dimension.
3.4. Foreground Perception Enhancement (FPE)
The intricate backgrounds of remote sensing images often lead to significant visual disparities among objects of the same category. For instance, the visual attributes of identical buildings can vary drastically across different geographical settings and under various imaging conditions, such as variations in lighting, shadows, and seasonal transitions. Such intra-class variance can make it difficult for recognition or segmentation models based on image features to accurately distinguish between the object and the background, which can lead to false positives in the model’s prediction, where the background is mistakenly classified as the target object. The problem of false positives is particularly serious in remote sensing image analysis, because remote sensing images often cover a wide geographic area and contain a variety of different surface types and scenes, which can increase the intra-class variance and make it difficult to achieve high-precision segmentation or recognition, even for models targeted at specific categories. To address this issue, we propose a novel Foreground Perception Enhancement (FPE) module. By leveraging the foreground context information related to the object–scene relationship, the network’s ability to discriminate foreground features is enhanced, thereby improving the segmentation performance of the model. FPE consists of a pyramid structure similar to the FPN and scene embedding (SE), the structure of which is shown in Figure 4.
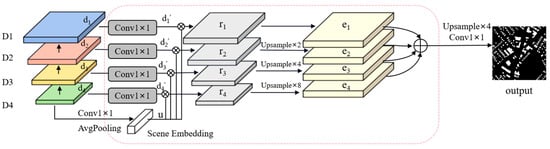
Figure 4.
The structure of the FPE module.
The main idea of FPE is to first explicitly model the relationships between objects and scenes and then use potential scene embedding to associate the foreground with the relevant context; finally, we re-weight the input feature map through relational mapping to enhance the distinction between the foreground feature and the background feature, thereby improving the network’s ability to discriminate the foreground features. In other words, the feature map with an enhanced foreground relationship can be obtained by re-encoding the feature map and then using relational mapping to re-weight it. Specifically, firstly, the feature graph is converted to by 1 × 1 convolution, batch normalization, and ReLU activation functions as follows:
where ; the “i” in the subsequent formula also presents a similar meaning. Conv1×1( ), BN( ), and ReLU( ) represent 1 × 1 convolution, batch normalization, and ReLU activation functions, respectively. Then, is used to compute the geospatial scene representation with the foreground via a learnable 1 × 1 convolution layer and adaptive global average pooling as follows:
where Pavg( ) denotes adaptive global average pooling. Then, the scene embedding vector and are calculated via the dot product to obtain a similar estimation as follows:
where represents the pointwise dot product. Finally, the calculation method for the pre-background feature graph for relationship enhancement is as follows:
where is an encoder with a learnable parameter with input feature mapping . The encoder is designed to introduce an additional nonlinear unit to avoid feature degradation, which is implemented in this paper using 1 × 1 convolution, batch normalization, and a ReLU activation function. Finally, the final output result is obtained after feature weighting and the upsampling of as follows:
where denotes the element-wise summation of the feature maps.
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, experiments are conducted on the following three publicly available semantic segmentation datasets for remote sensing buildings.
- Massachusetts: The Massachusetts Building dataset is a collection of 151 aerial RGB images of different buildings in a 340-square-kilometer area of Boston, with a size of 1500 × 1500 pixels and a ground sampling distance of 1 m. The dataset contains both urban and suburban scenarios, where the buildings vary in size, shape, texture, and color, so the dataset is very challenging and is suitable for verifying the validity of the module. In this experiment, 131 images are used for training, 4 for verification, and 10 for testing. We expand the images to 1536 × 1536 pixels and then crop them to 512 × 512 pixels.
- Inria: The Inria Aerial Image Labeling dataset consists of a total of 360 images collected from different scenes in 5 cities, each with a size of 5000 × 5000 pixels. Following official recommendations, 155 of the images are used for training, 25 for verification, and the rest for testing. We expand the original 5000 × 5000-pixel images to 5120 × 5120 pixels and then crop them into 512 × 512-pixel images.
- WHU: The Wuhan University Building dataset contains two kinds of images: aerial images and satellite images. The WHU aerial image subset covers buildings in an area of more than 450 square kilometers and contains a total of about 22,000 building targets, each with a size of 512 × 512 pixels and a spatial resolution of 0.3 m. The dataset has a total of 8189 images, of which 4736 are used for training, 1036 for verification, and 2416 for testing.
4.2. Experimental Setup and Evaluation Metrics
Following the baseline DSATNet [27] and most of the comparison methods, we train the models using the AdamW optimizer with the cosine strategy on a single NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 GPU (12 GB memory). The model training spans 105 epochs and the batch size is 4. The initial learning rate is set to 0.0001, and the learning rate is reduced by a factor of 0.5 when the IoU does not improve in five consecutive epochs on the validation set during the training process. The weights of the filters are initialized with a normal distribution and the bias is zero. For all training cases, random flips, random rotation, and random brightness and contrast changing are applied to increase the data diversity. For the sake of fairness, all experiments are carried out under the same experimental conditions as described above.
In terms of evaluation metrics, precision, recall, the F1 score (F1), and the intersection over union (IoU) are used in this paper; these are widely used in building segmentation in remote sensing images. The calculations of these metrics are shown as follows:
where TP, FP, and FN indicate true positives, false positives, and false negatives, respectively.
4.3. Performance Comparison
In order to verify the performance of the proposed method, we conduct a comparison experiment with the current mainstream state-of-the-art building segmentation methods for remote sensing images. The comparison methods include CNN-based methods, namely CBR-Net [11], MBR-HRNet [12], MA-FCN [16], SiU-Net [17], SAU-Net [18], and NPSFF-Net [19], and hybrid methods based on the CNN–Transformer: Segmenter [21], TransUNet [20], Swin-Unet [23], TCNet [25], BuildFormer [26], and DSATNet [27]. The experimental results are shown in Table 1 (including the metrics for computational complexity and the experimental results on the Massachusetts Building dataset) and Table 2 (including the experimental results on the WHU Building and Inria Aerial Image Labeling datasets). All results listed in the table are provided in the literature corresponding to the methods.

Table 1.
Performance comparison of different methods on the Massachusetts dataset (%).

Table 2.
Performance comparison of different methods on the WHU and Inria datasets (%).
As shown in Table 1, MFFP-Net achieved the best performance while maintaining relatively low computational complexity among the listed methods on the Massachusetts dataset in terms of the IoU (76.30%), F1 (86.57%), and precision (87.78%). Compared to the baseline method DSATNet, MFFP-Net improved the results by 0.98%, 0.65%, and 0.39%, respectively. Although MFFP-Net only ranked third in recall, the methods with superior recall performance (TCNet and Swin-Unet) were outperformed by MFFP-Net in terms of the IoU, F1, and precision. As shown in Table 2, on the WHU dataset, MFFP-Net was slightly inferior to TCNet in terms of recall by a narrow margin of 0.13%, but it achieved the best performance in terms of the IoU (91.85%), F1 (95.75%), and precision (96.08%). Compared to DSATNet, MFFP-Net improved the results by 0.44%, 0.24%, and 0.26%, respectively. Furthermore, on the Inria dataset, MFFP-Net achieved the best results in all four metrics: the IoU (83.17%), F1 (90.81%), Precision (92.21%), and recall (89.50%). Compared to DSATNet, the improvements were 0.61%, 0.36%, 0.45%, and 0.33%, respectively. The superior performance of MFFP-Net can be attributed to three key factors: (1) MFF’s efficient utilization of shallow features, (2) FPE’s enhanced association between foreground classes, and (3) DPA’s ability to capture local information while establishing global context dependencies. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of MFFP-Net in improving the building segmentation performance in remote sensing images.
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method and further verify our conclusions, we conducted visual comparisons by randomly selecting three images from the test set of each dataset: Massachusetts, WHU, and Inria. These images were segmented using the proposed method and several representative mainstream state-of-the-art methods, including DSATNet, BuildFormer, and CBRNet. We present the visualization results of these three representative methods based on the following considerations. Firstly, these three methods represent the current mainstream processing paradigms (CNN-based methods and the hybrid structure based on CNN–Transformer), and their visual comparisons have been able to clearly show the essential differences in the performance of building segmentation in remote sensing images among different methods. Secondly, the detailed quantitative metrics provided in Table 1 cover all of the comparison methods and form a complete chain of evidence with the visualization results. Finally, to avoid the core conclusion being dispersed due to too many visual images, we adopt the same presentation strategy of “representative methods + comprehensive data” as in most of the literature. For the results shown in Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 (corresponding to the Massachusetts, WHU, and Inria datasets, respectively).
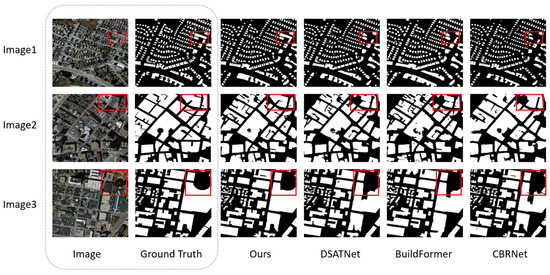
Figure 5.
Visual comparison of building segmentation on the Massachusetts dataset (red boxes highlight the areas where the improvements are most evident).
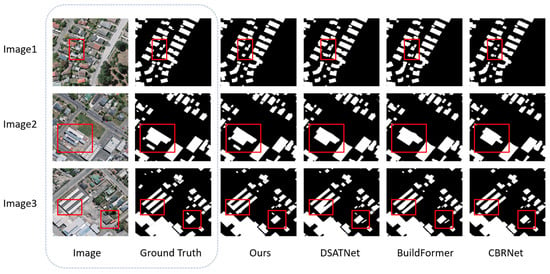
Figure 6.
Visual comparison of building segmentation on the WHU dataset (red boxes highlight the areas where the improvements are most evident).
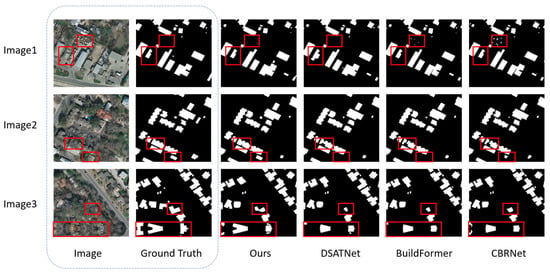
Figure 7.
Visual comparison of building segmentation on the Inria dataset (red boxes highlight the areas where the improvements are most evident).
Figure 5 visually compares the segmentation performance across the methods on the Massachusetts dataset. In Image1 (Figure 5, the largest cuboid building), DSATNet, BuildFormer, and CBRNet erroneously classify most pixels as background, whereas MFFP-Net achieves accurate segmentation. Image2 (the red-boxed building) reveals that the same three methods omit the left portion, while MFFP-Net captures the complete structure. Image3 (the curved edge of a building) demonstrates that BuildFormer struggles with the curved edge, misclassifying foreground pixels as background. This issue becomes more severe in DSATNet and CBRNet. In contrast, MFFP-Net precisely identifies the arc-shaped boundary, ensuring accurate segmentation.
Similar trends are observed on the WHU dataset (Figure 6). In Image1, DSATNet, BuildFormer, and CBRNet incorrectly label concrete ground as buildings due to its height similarity with the target structure, while MFFP-Net avoids this confusion. Image2 highlights the challenge of debris in the lower-left red box: conventional methods fail to segment the obscured building. However, MFFP-Net not only identifies the target but also maintains a high-quality mask. Image3 shows that DSATNet, BuildFormer, and CBRNet misclassify a bus as a building and incorrectly exclude a shaded green hut due to tree and shadow interference. MFFP-Net, however, resists these distractions to segment the buildings accurately.
For the Inria dataset (Figure 7), Image1 contains tents resembling buildings, misleading BuildFormer and CBRNet into false classifications. Images2 and 3 illustrate that dense tree canopy occlusion causes DSATNet, BuildFormer, and CBRNet to misclassify foreground pixels as background. MFFP-Net overcomes these challenges, producing precise segmentation masks despite the strong interference.
Collectively, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7 demonstrate notable improvements over the mainstream state-of-the-art methods in terms of segmentation accuracy, particularly in regions with complex boundaries and occlusion. These results validate that the synergistic integration of Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MFF), Foreground Perception Enhancement (FPE), and Dual-Path Attention (DPA) enhances the model’s robustness to complex scenarios, including occlusion, edge ambiguities, and background interference.
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. Ablation of Different Modules
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed modules, we conducted ablation experiments on the Massachusetts dataset and analyzed the results. We chose the Massachusetts Building dataset for the ablation experiment because it contains most of the common complex scenes in the building segmentation of remote sensing images and is one of the most representative datasets for building segmentation in remote sensing images. Compared with the WHU Building dataset and the Inria Aerial Image Labeling dataset, the Massachusetts Building dataset is more challenging and can better validate the effectiveness of the modules. The results of the ablation of various modules are shown in Table 3. “No. 1” signifies the experimental result corresponding to the combination of the FPE module and the DPA mechanism (exclusion of solely the MFF module). “No. 2” denotes the experimental result related to the combination of the MFF module and the DPA mechanism (exclusion of solely the FPE module). “No. 3” represents the experimental result for the combination of the MFF module and the FPE module (omission of solely the DPA mechanism). “No. 4” reflects the experimental result pertaining to the complete MFFP-Net methodology proposed in this study.

Table 3.
Ablation experiment results for MFFP-Net on the Massachusetts dataset (%).
As shown in Table 3, Experiment No. 4 achieved the best results. Comparing Experiment No. 1 to No. 4, the IoU and F1 scores decreased by 0.12% and 0.09%, respectively. This difference is attributed to the fact that, in the DL-based image segmentation feature network, shallow features better capture target intricacies and include a greater variety of small target information compared to deeper features. When the MFF module is removed, the feature network progressively focuses on higher-level semantic information during downsampling, leading to a reduction in detail and small target information in the shallow features. This further demonstrates the importance and effectiveness of the MFF module. Similarly, comparing Experiment No. 2 to No. 4, the IoU and F1 scores dropped by 0.33% and 0.21%, respectively. This is due to the inherent complexity of remote sensing images, which have more intricate backgrounds than conventional images. Additionally, certain target foreground pixels are close to background pixels, making them difficult to distinguish and reducing the segmentation accuracy. The FPE module addresses this by establishing relationships between objects and scenes, leveraging contextual elements to better discern foreground features confused with the background, thereby improving the segmentation performance. These results clearly confirm the effectiveness of the FPE module. Finally, comparing Experiment No. 3 to No. 4, the IoU and F1 decreased by 0.70% and 0.46%, respectively. This is because the absence of the DPA mechanism prevents the network from adequately capturing local details, resulting in a lack of global contextual information. Consequently, the model may fail to focus on certain building targets during segmentation, negatively impacting its performance. This further highlights the efficacy and superiority of the DPA mechanism in improving the model’s segmentation capabilities.
To more intuitively verify the effectiveness of the modules proposed in this paper, we randomly selected three images from the test set of the Massachusetts dataset for visual analysis, as illustrated in Figure 8. Image3 in Figure 8 clearly shows that, after removing FPE, the buildings in the central region of the red box exhibit significant foreground error segmentation into the background, primarily due to substantial intra-class variance. As shown in Image1, the elimination of MFF results in the failure to accurately identify the small buildings located between the two rows of larger structures within the red box, caused by insufficient feature information. Furthermore, Image2 demonstrates that removing FPE leads to erroneous segmentation in the central region of the red box, incorrectly classifying foreground elements as background. Image3 also reveals that removing DPA causes the building in the upper-left corner of the red box to be misclassified as foreground, as the convolutional network fails to adequately model the global contextual information. These segmentation outcomes strongly demonstrate the efficacy and superiority of each module proposed in this paper. Specifically, MFF, which integrates shallow features across different levels, allows the network to focus more on shallow features that are rich in small target information, thereby improving the ability to extract small target buildings. FPE effectively mitigates the adverse effects of significant intra-class variance on model performance by strengthening the correlation among foreground classes and reducing false positives. DPA, on the other hand, enables the simultaneous acquisition of local information and establishment of global contextual dependencies, providing the model with more effective feature information for the target being segmented. Collectively, these three components work synergistically to enhance the model’s segmentation performance.
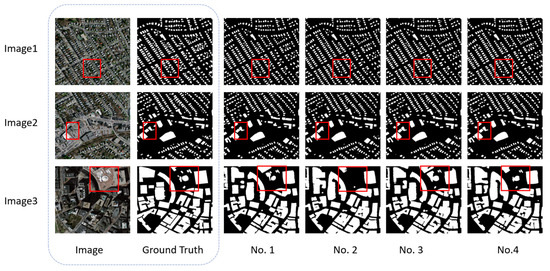
Figure 8.
Visual comparison of ablation experiment of MFFP-Net on the Massachusetts dataset (red boxes indicate the areas where the differences are most obvious).
4.4.2. Ablation Experiment of DPA
To systematically evaluate the individual contributions of the GPA and LPA branches within the DPA mechanism, controlled ablation studies were conducted through progressive component removal. The experimental results are shown in Table 4. Here, “MFFP-Net w/o DPA” indicates the model without the DPA mechanism. “MFFP-Net w/o GPA” indicates the model with only the GPA branch removed from the DPA mechanism. “MFFP-Net w/o LPA” indicates the model with only the LPA branch removed from the DPA mechanism.

Table 4.
Ablation experiment results of DPA on the Massachusetts dataset (%).
As demonstrated in Table 4, the exclusion of DPA led to a decline in the IoU and F1 metrics by 0.70% and 0.46%, respectively. When only the GPA branch was removed while retaining the LPA branch of DPA, the IoU and F1 metrics dropped by 0.32% and 0.21%, respectively. In the scenario where only the LPA branch was removed and the GPA branch of DPA was preserved, the IoU and F1 metrics decreased by 0.60% and 0.39%, respectively. Furthermore, as illustrated in Table 4, removing only the GPA branch of DPA resulted in IoU and F1 metrics that were 0.38% and 0.25% higher, respectively, compared to the complete removal of DPA; similarly, removing only the LPA branch of DPA led to IoU and F1 metrics that were 0.10% and 0.07% higher than those associated with the complete removal of DPA. These experimental findings demonstrate that, in the context of segmentation tasks in remote sensing images, the performance can be enhanced by effectively extracting local target information and establishing global context dependencies. By integrating these two methodologies, the DPA mechanism proposed in this study not only improves the network’s ability to acquire local information but also effectively models global context dependencies. As a result, this integration leads to a more significant enhancement in performance while reducing the computational demands. These results comprehensively demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the DPA mechanism, which includes the GPA and LPA branches.
The aforementioned conclusions are further substantiated by Figure 9. In Image1, heavy misassignment is observed when comparing “MFFP-Net w/o LPA” to MFFP-Net, as the foreground is erroneously segmented into the background. In Image2, where the strip-like building is highly similar to the background, “MFFP-Net w/o DPA”, “MFFP-Net w/o GPA”, and “MFFP-Net w/o LPA” fail to achieve complete separation from the background, whereas MFFP-Net successfully segments the building’s main body. In Image3, shadow interference causes “MFFP-Net w/o DPA” and “MFFP-Net w/o LPA” to incorrectly include shadow regions in the building’s foreground. In contrast, MFFP-Net effectively mitigates this interference, enabling the more accurate segmentation of building targets.

Figure 9.
Visual comparison of ablation experiment on DPA on the Massachusetts dataset (red boxes indicate the areas where the differences are most obvious).
5. Discussion
5.1. Model Parameters and FLOPs
Table 1 provides comprehensive results regarding the model parameters and FLOPs for various models. Below is an analysis of the key findings.
CNN-based models: CNN-based models generally have fewer parameters. Among them, the parameter count of NPSFF-Net is the lowest, which is 13.21 M. The parameter counts of CBR-Net and MBR-HRNet are 22.68 M and 31.02 M, respectively. These models are more suitable for deployment on resource-constrained embedded devices but may not perform as well in intensive tasks. Furthermore, the FLOPs value of NPSFF-Net is the highest, at 219.96 G, followed by CBR-Net, at 185.87 G. This is usually related to complex operations (such as large convolution kernels). Excessively high FLOPs means an increase in the time consumption of a single inference, making it difficult to meet the real-time requirements.
Hybrid models based on CNN–Transformer: The models that introduce Transformer usually have a relatively high parameter count. After introducing the Transformer structure into the traditional U-Net, TransUNet achieved a maximum of 105.91 M. The performance of most hybrid models will be improved to a certain extent after the introduction of Transformer, but it is usually accompanied by a greater computational cost. Swin-Unet optimizes the computational efficiency through window attention and has smaller parameter and FLOPs values compared with TransUNet. DSATNet further compresses the computational load through sparse attention, with the parameters and FLOPs amounting to 48.50 M and 57.75 G, respectively. However, when the number of parameters is small, the resulting effect is significantly diminished.
These findings highlight the trade-offs between model complexity, computational requirements, and task performance. The proposed MFFP-Net model stands out by achieving the best performance while maintaining moderate parameters and FLOPs.
5.2. The Cost–Performance Balance in Building Segmentation
The comparative experiments demonstrate that MFFP-Net outperforms other competing methods in terms of building segmentation accuracy, while maintaining a moderate number of parameters and FLOPs. In certain aspects, the enhancements introduced by MFFP-Net are notably remarkable.
Precision Sensitivity: In applications necessitating high-precision building segmentation, even incremental gains in accuracy can yield substantial advantages. For critical scenarios, nuanced improvements can profoundly affect decision-making processes. For instance, highly accurate building segmentation facilitates meticulous urban planning and governance, serving as an essential tool for precise land use distribution, infrastructure development, and policy formulation. In tasks demanding stringent standards for edge delineation, structural integrity, and the extraction of small-scale targets, MFFP-Net demonstrates superior efficacy compared to other models.
Balancing Cost and Overall Efficiency: When marginal increases in model accuracy can reduce downstream operational expenses or enhance task throughput, a moderate rise in the parameter count is justifiable. In critical applications such as urban planning, resource allocation, and disaster monitoring, automated building segmentation constitutes a critical preliminary step. Enhanced model precision reduces the need for extensive post-processing, thereby optimizing the segmentation workflow and conserving computational and human resources. MFFP-Net’s superior precision minimizes the post-processing requirements so as to improve the efficiency of the building segmentation process while saving additional computing resources and human resources.
Multi-Scale Feature Representation Capabilities: Complex remote sensing environments characterized by small target structures and substantial intra-class variability necessitate accurate multi-scale localization and detailed texture preservation. MFFP-Net achieves a more advanced representation of multi-scale features through the synergistic integration of the MFF and FPE modules. Moreover, the dual capabilities of global context modeling and localized detail refinement, afforded by the DPA mechanism, empower the model to more effectively prioritize salient features. This architectural advantage endows MFFP-Net with heightened adaptability to diverse feature distributions in heterogeneous scenes, resulting in consistently superior segmentation outcomes.
The method proposed in this paper provides an innovative solution and feasible technical approach to building segmentation in remote sensing images. However, in practical applications, there is no one-size-fits-all answer regarding the selection of building segmentation models. The key lies in choosing the appropriate model based on the goals and resource constraints of the specific task and achieving a balance between the computational cost and performance.
6. Conclusions
In order to address the challenges of complex backgrounds and numerous objects in remote sensing images, particularly the difficulties in segmenting small target buildings and the issue of large intra-class variance, we propose an innovative Multi-Scale Feature Fusion and Foreground Perception Enhancement Network (MFFP-Net) for building segmentation. Our framework achieves a performance breakthrough through three core modules: (1) the Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MFF) module enhances the utilization efficiency of small target details in shallow features by constructing a hierarchical feature fusion mechanism; (2) the Foreground Perception Enhancement (FPE) module, based on spatial context modeling, establishes semantic associations between foreground pixels, significantly alleviating the false positive problem caused by intra-class variance; (3) the Dual-Path Attention (DPA) mechanism effectively combines local attention and self-attention, capturing both local structural features and global context dependencies. The proposed method demonstrates excellent performance on the WHU Building, Massachusetts Building, and Inria Aerial Image Labeling datasets, proving its effectiveness in handling small targets and intra-class variance while maintaining robustness in complex scenarios.
While the proposed method demonstrates promising performance, this study has several limitations that warrant further investigation. For example, following common practices in the existing literature and constrained by limited computational resources, our ablation experiments were conducted exclusively on the Massachusetts Building dataset. Our future work will focus on (1) extending the ablation experiments to the WHU Building dataset and the Inria Aerial Image Labeling dataset to verify the robustness of each component under different geographical features and image resolutions; (2) exploring the integration of large models (such as SAM_MLoRA) with our architecture and utilizing the general segmentation priors of buildings (such as shape, texture, and shadow) learned through their pre-training to enhance the generalization capabilities of our model regarding irregular buildings and fog-obscured areas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.X. and Q.H.; formal analysis, H.X. and G.N.; methodology, Q.H.; project administration, H.X.; software, Q.H.; supervision, H.X.; validation, H.X., H.L. and G.N.; visualization, Q.H.; writing—original draft, Q.H.; writing—review and editing, H.X., H.L. and W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2024JJA170106), the Key Research and Development Program of Guangxi (Grant No. AD25069071), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52169021).
Data Availability Statement
The authors can supply the datasets related to this article upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sahoo, P.; Soltani, S.; Wong, A. A survey of thresholding techniques. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1988, 41, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Bischof, L. Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, M.; Biasotti, S.; Giorgi, D.; Patane, G.; Spagnuolo, M. Discrete Laplace–Beltrami operators for shape analysis and segmentation. Comput. Graph. 2009, 33, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenborn, T.; Leitloff, J.; Schiefer, F.; Hinz, S. Review on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in vegetation remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tan, X.; Guo, B.; Zhu, K.; Liao, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X. SDFCNv2: An Improved FCN Framework for Remote Sensing Images Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Su, X. A coarse-to-fine boundary refinement network for building footprint extraction from remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 183, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Jing, H.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; He, S. Enhancing Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images: Advanced Multi-Scale Boundary Refinement with MBR-HRNet. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, A.; Zhang, L. FarSeg++: Foreground-Aware Relation Network for Geospatial Object Segmentation in High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13715–13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Liu, B.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Q. MwdpNet: Towards improving the recognition accuracy of tiny targets in high-resolution remote sensing image. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, L. U-MGA: A Multi-Module Unet Optimized with Multi-Scale Global Attention Mechanisms for Fine-Grained Segmentation of Cultivated Areas. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ji, S.; Lu, M. Toward Automatic Building Footprint Delineation from Aerial Images Using CNN and Regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. Fully Convolutional Networks for Multisource Building Extraction from an Open Aerial and Satellite Imagery Data Set. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Mao, T.; Wu, J.; Du, R.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, L. SAU-Net: A Novel Network for Building Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images by Reconstructing Fine-Grained Semantic Features. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 6747–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Jiang, M.; Hu, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, R.; Luo, J. NPSFF-Net: Enhanced Building Segmentation in Remote Sensing Images via Novel Pseudo-Siamese Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Strudel, R.; Garcia, R.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Segmenter: Transformer for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 7242–7252. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, C. Transformer and CNN Hybrid Deep Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation of Very-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-Unet: Unet-Like Pure Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Panboonyuen, T.; Jitkajornwanich, K.; Lawawirojwong, S.; Srestasathiern, P.; Vateekul, P. Transformer-Based Decoder Designs for Semantic Segmentation on Remotely Sensed Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fang, S.; Meng, X.; Li, R. Building Extraction with Vision Transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G. DSAT-Net: Dual Spatial Attention Transformer for Building Extraction from Aerial Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, S. AFENet: An Attention-Focused Feature Enhancement Network for the Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xia, M.; Weng, L.; Hu, K.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. SPNet: Dual-Branch Network with Spatial Supplementary Information for Building and Water Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Gong, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Ren, T. TCNet: Multiscale Fusion of Transformer and CNN for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 3123–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G. SDSC-UNet: Dual Skip Connection ViT-Based U-Shaped Model for Building Extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid Vision Transformer: A Versatile Backbone for Dense Prediction Without Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).