Research on Key Sand Generating Parameters and Remote Sensing Traceability of Dust Storms in the Taklamakan Desert
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
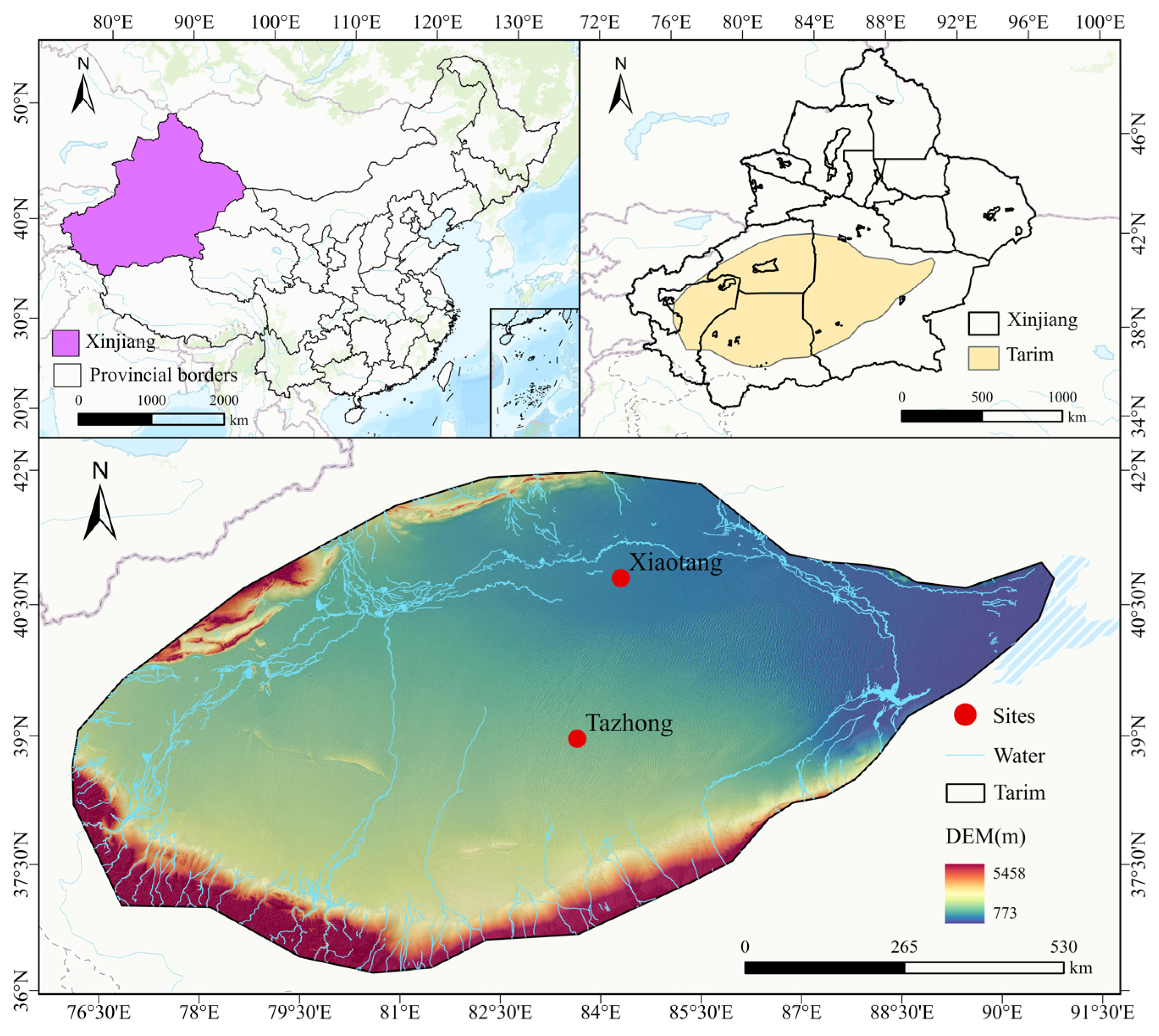
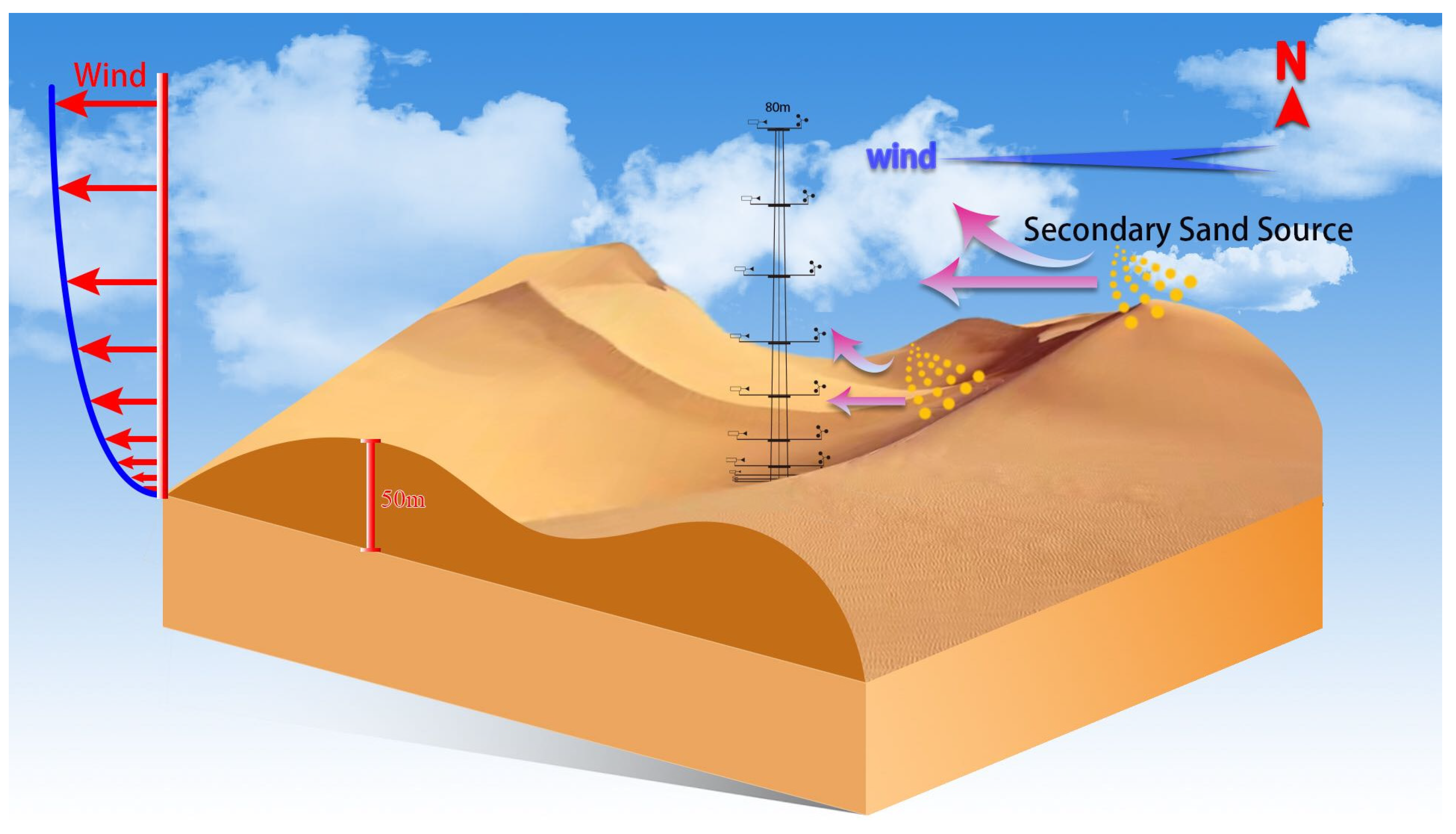
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Observational Data
2.2.1. Methods for Acquiring and Analyzing Horizontal Dust Flux (Q)
2.2.2. Methods for Acquiring and Analyzing Vertical Dust Flux (F)
2.3. Remote Sensing Monitoring Data
Introduction to Remote Sensing Satellite Data Background
2.4. Introduction to the Backward Trajectory Tracing Method
3. Results
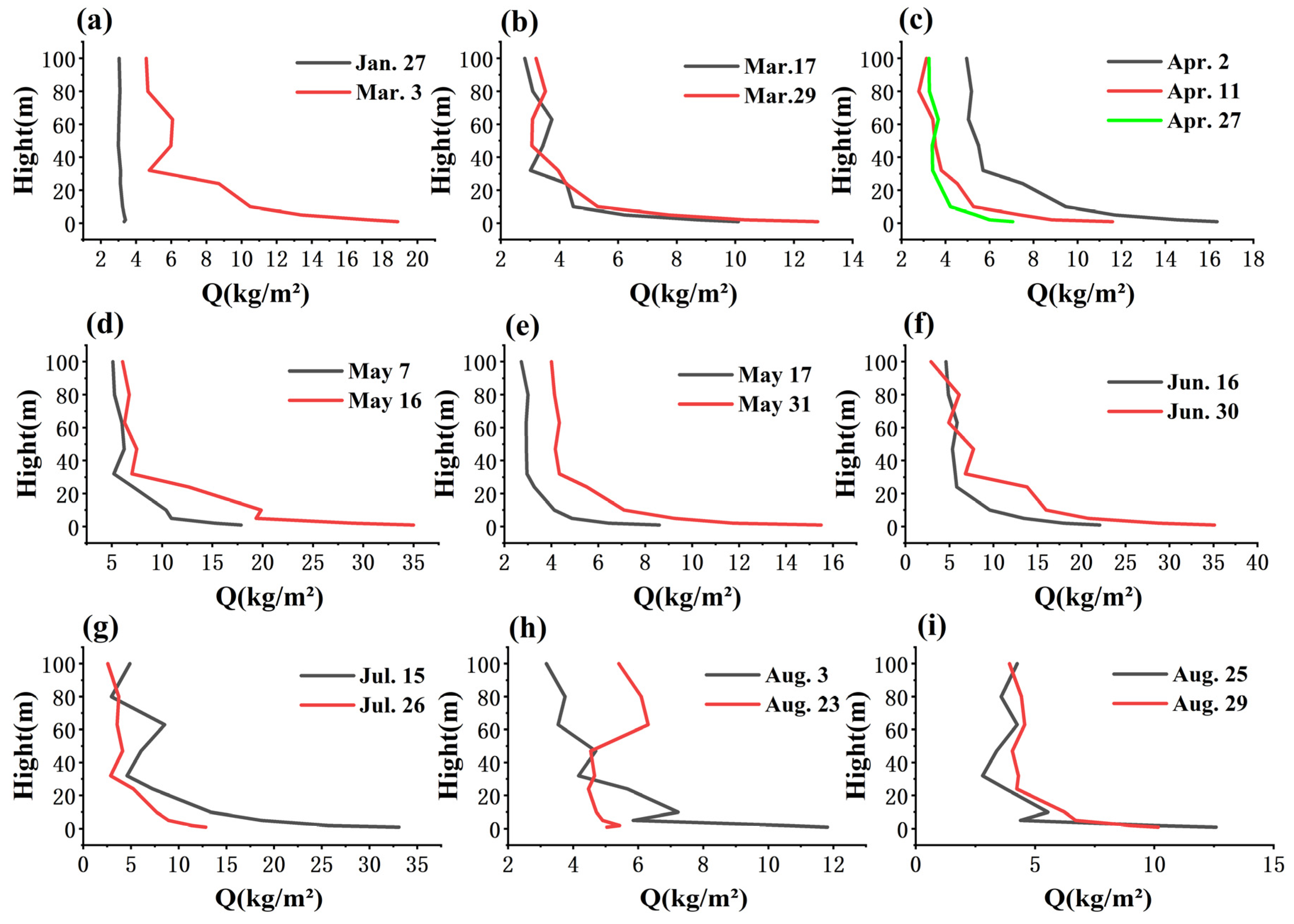
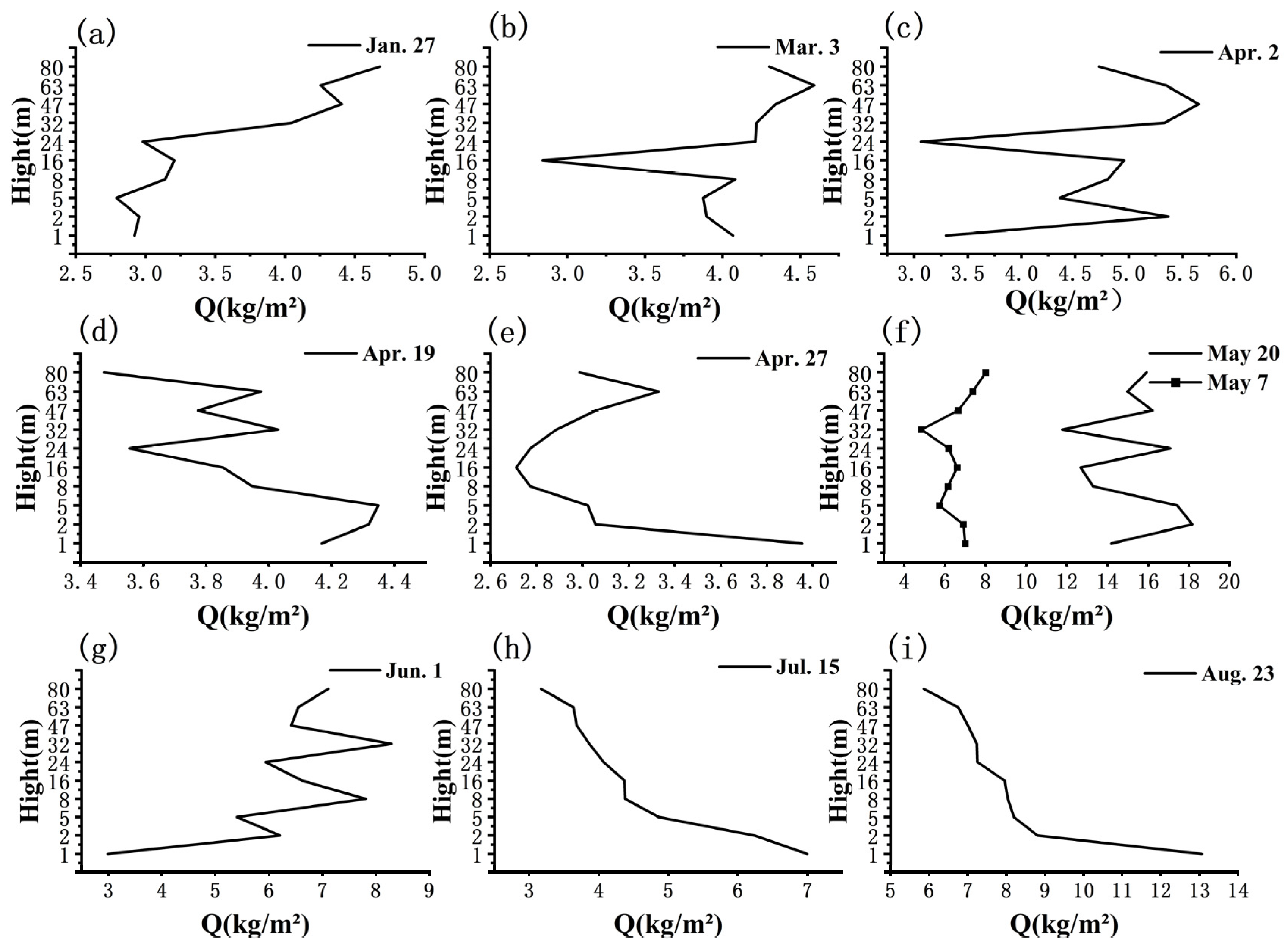
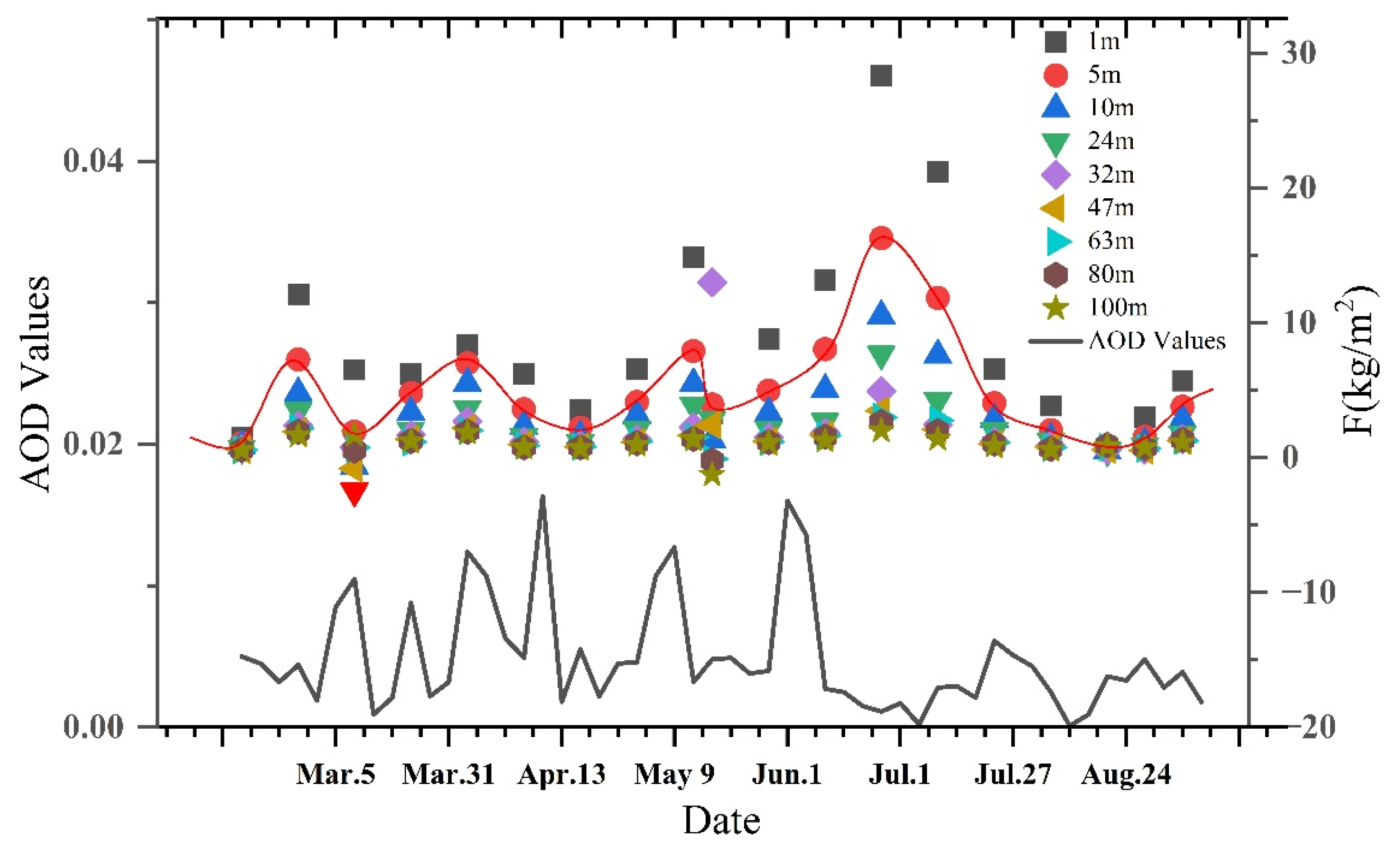
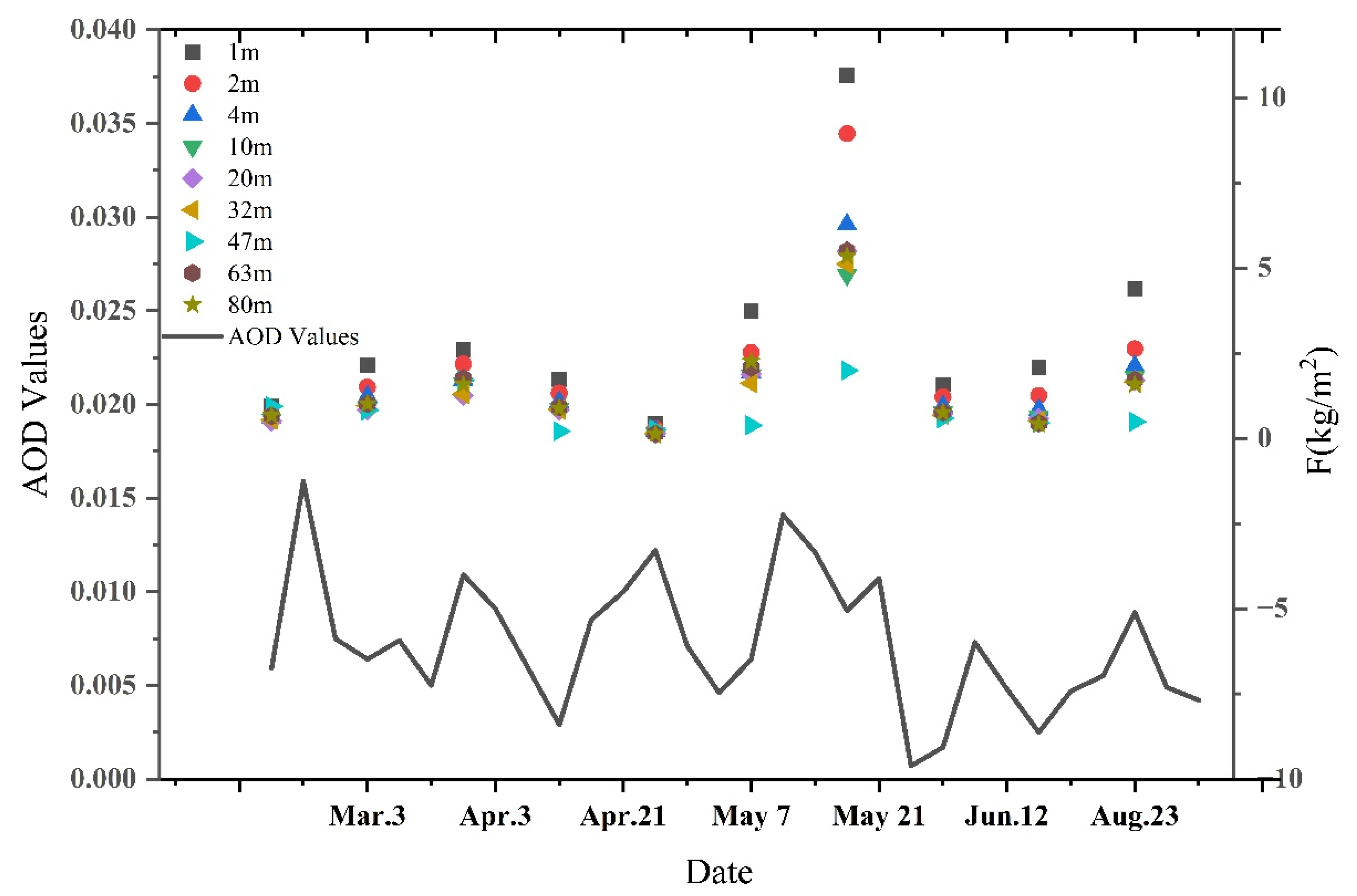
3.1. Variation Trend of Q at Different Heights
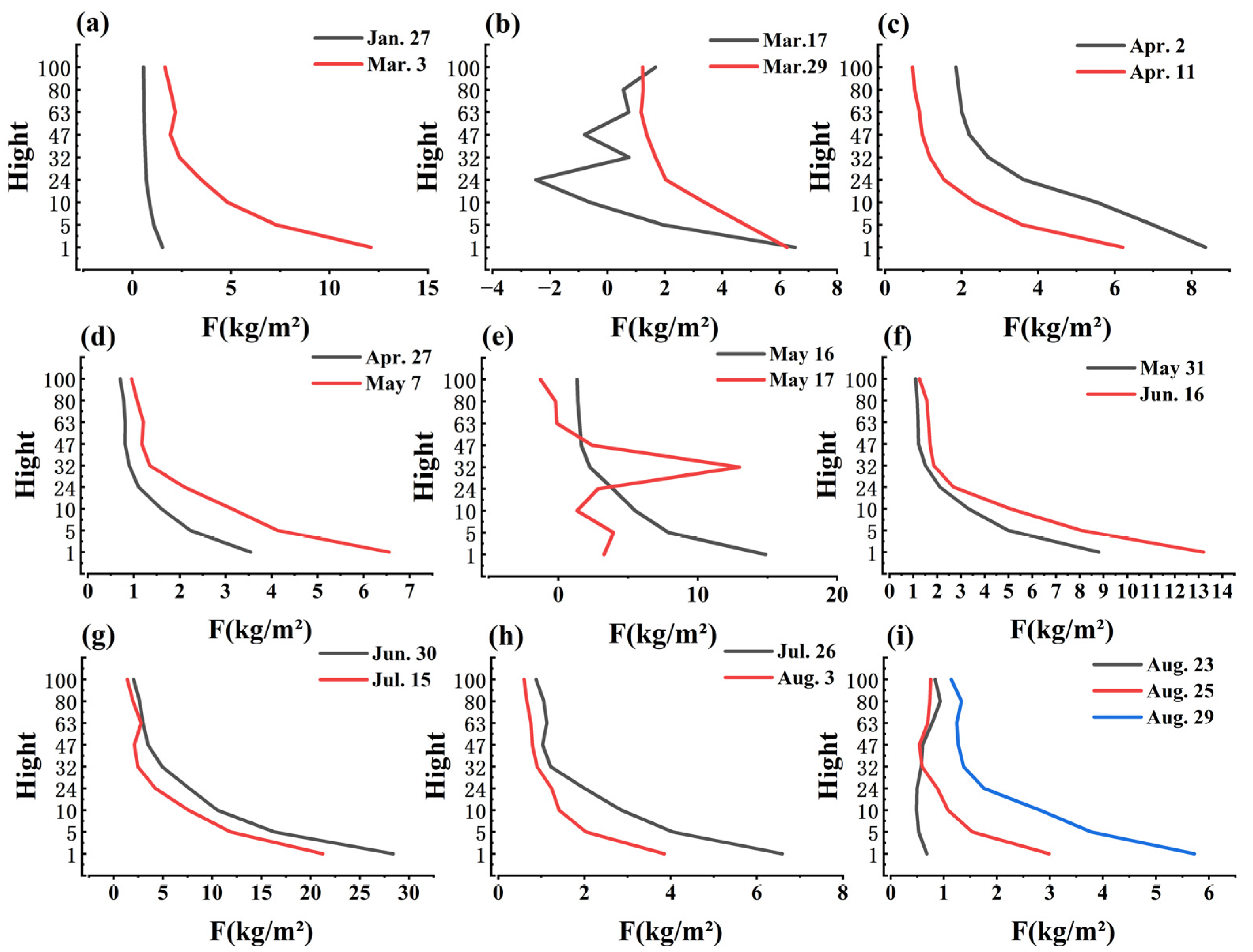
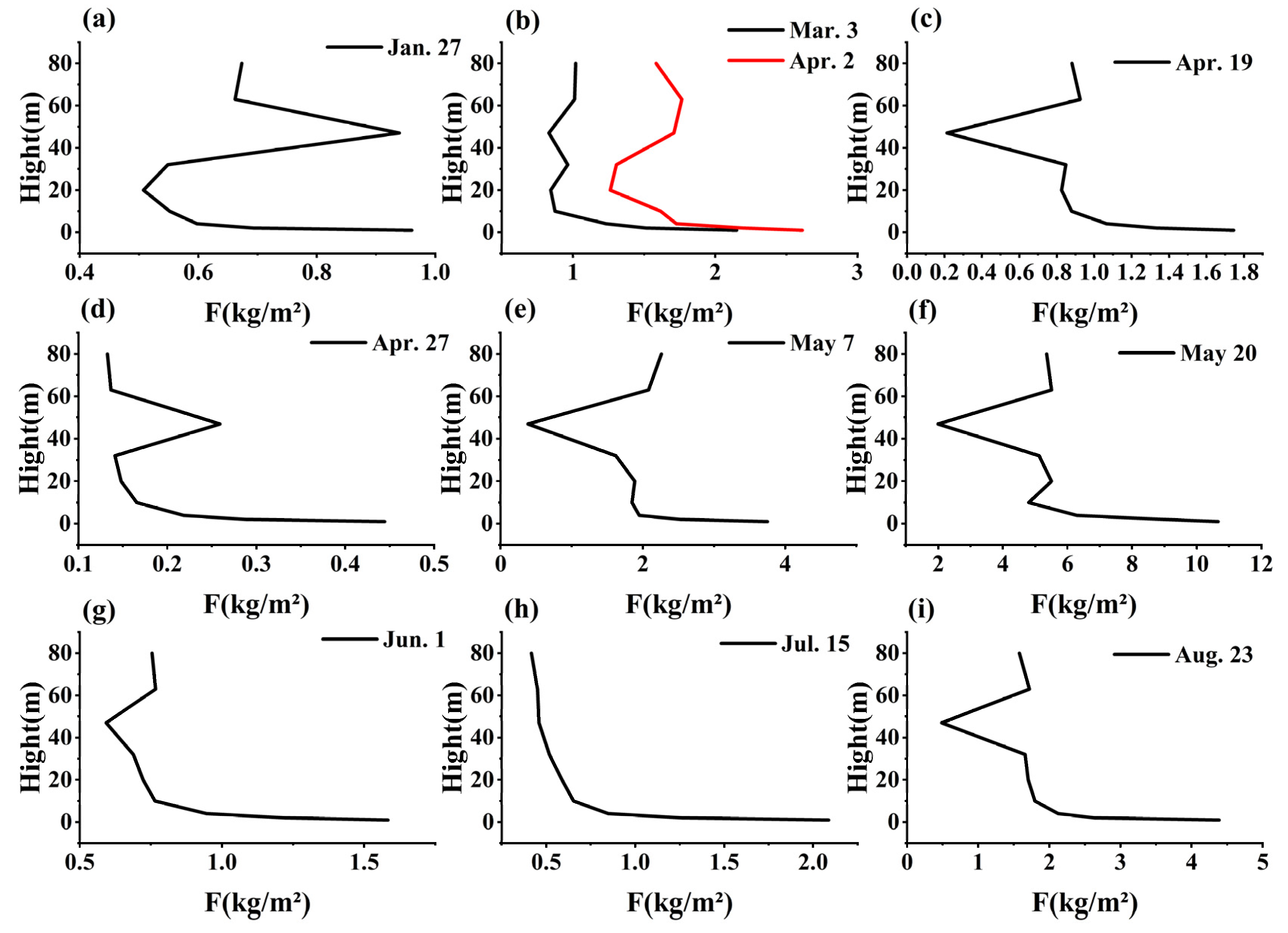
3.2. Variation Trend of F at Different Heights
3.3. Satellite Image Analysis of Dust Storms
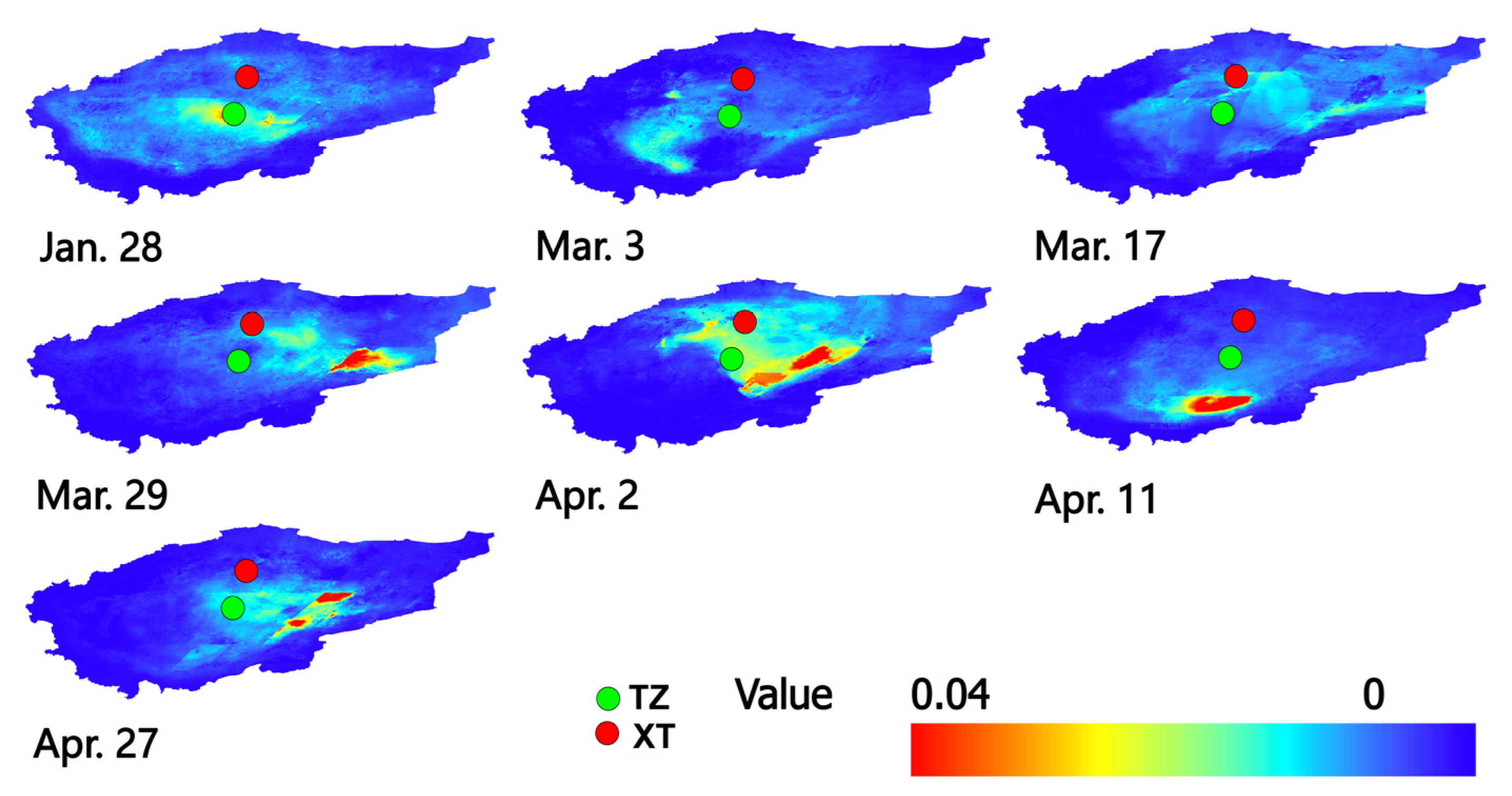
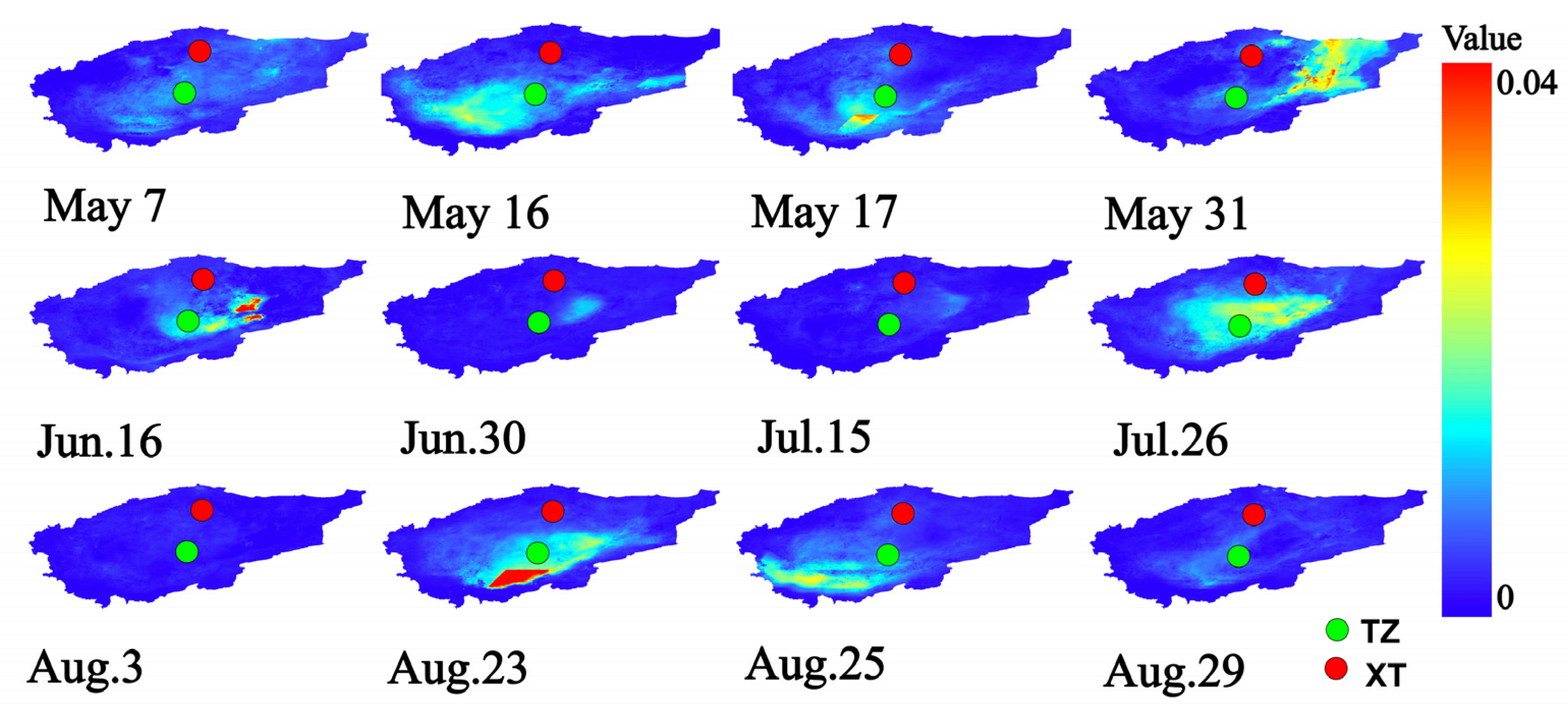
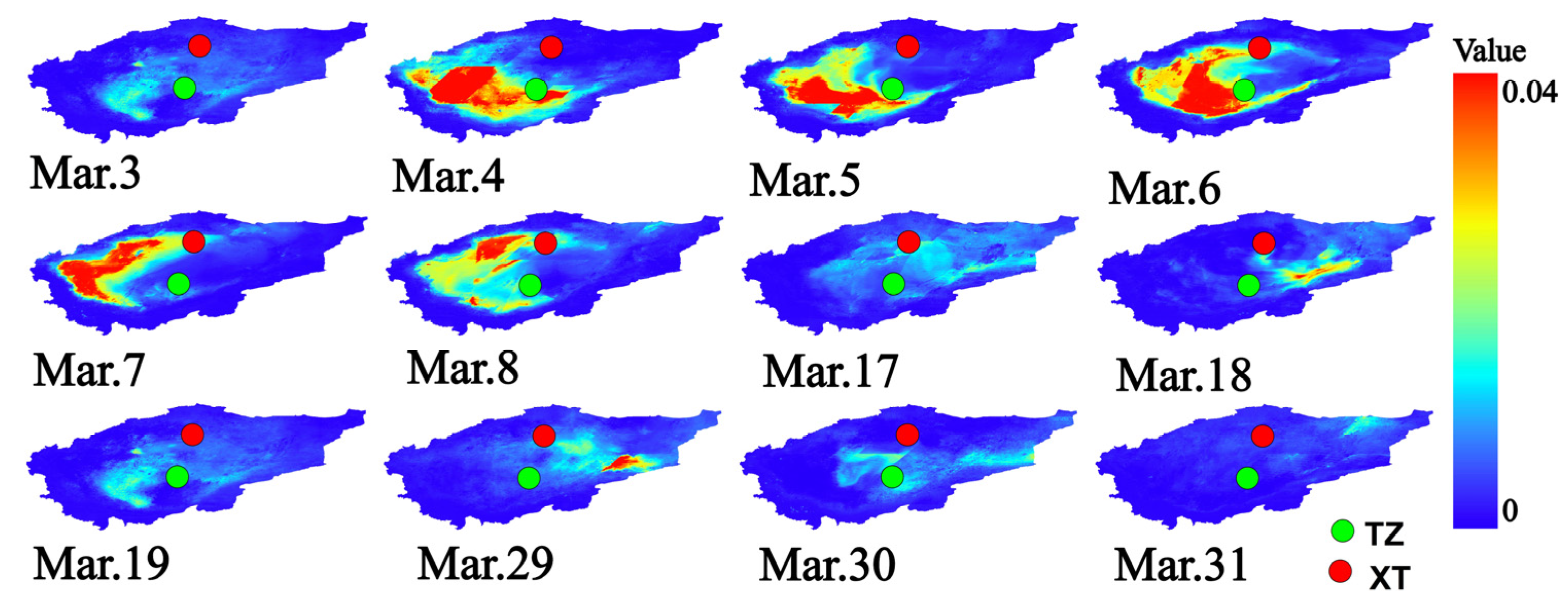
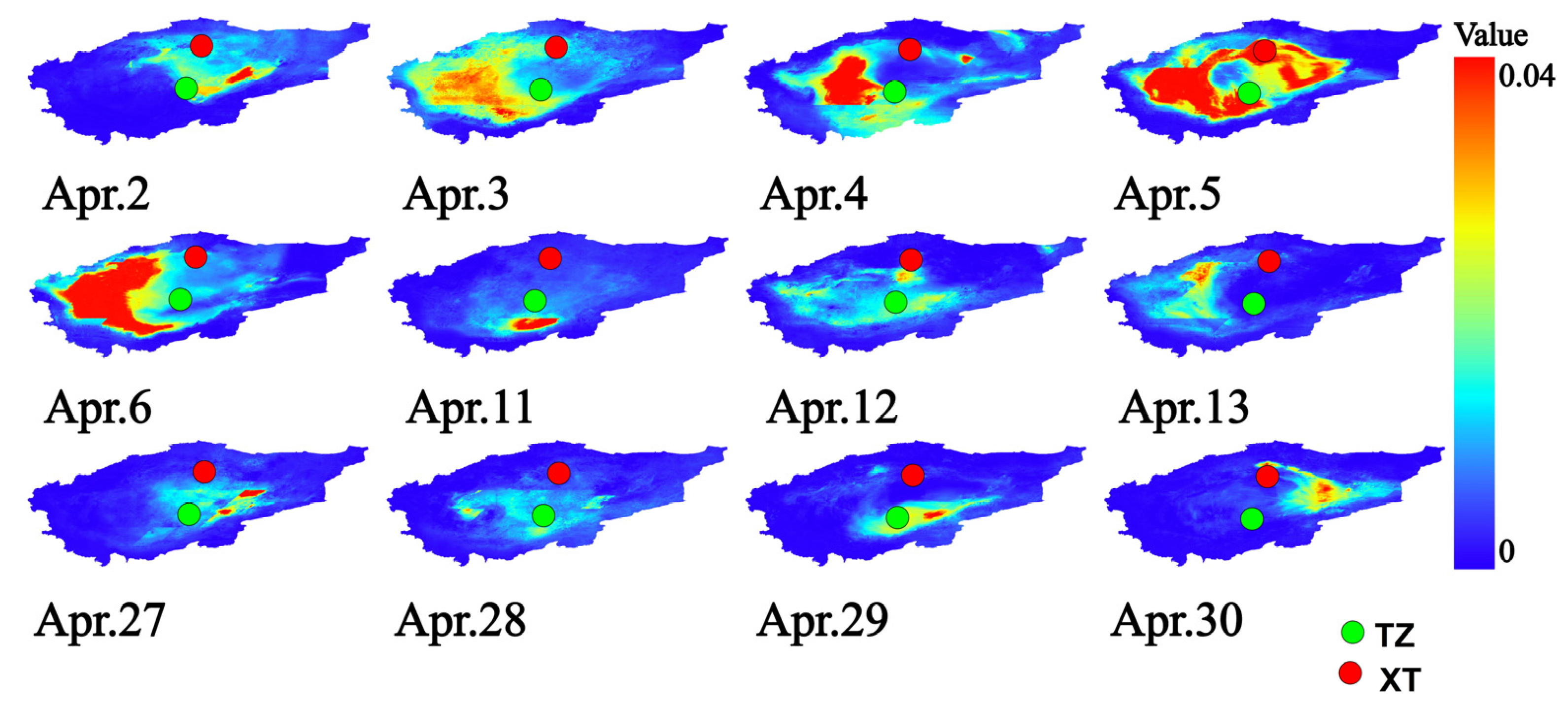
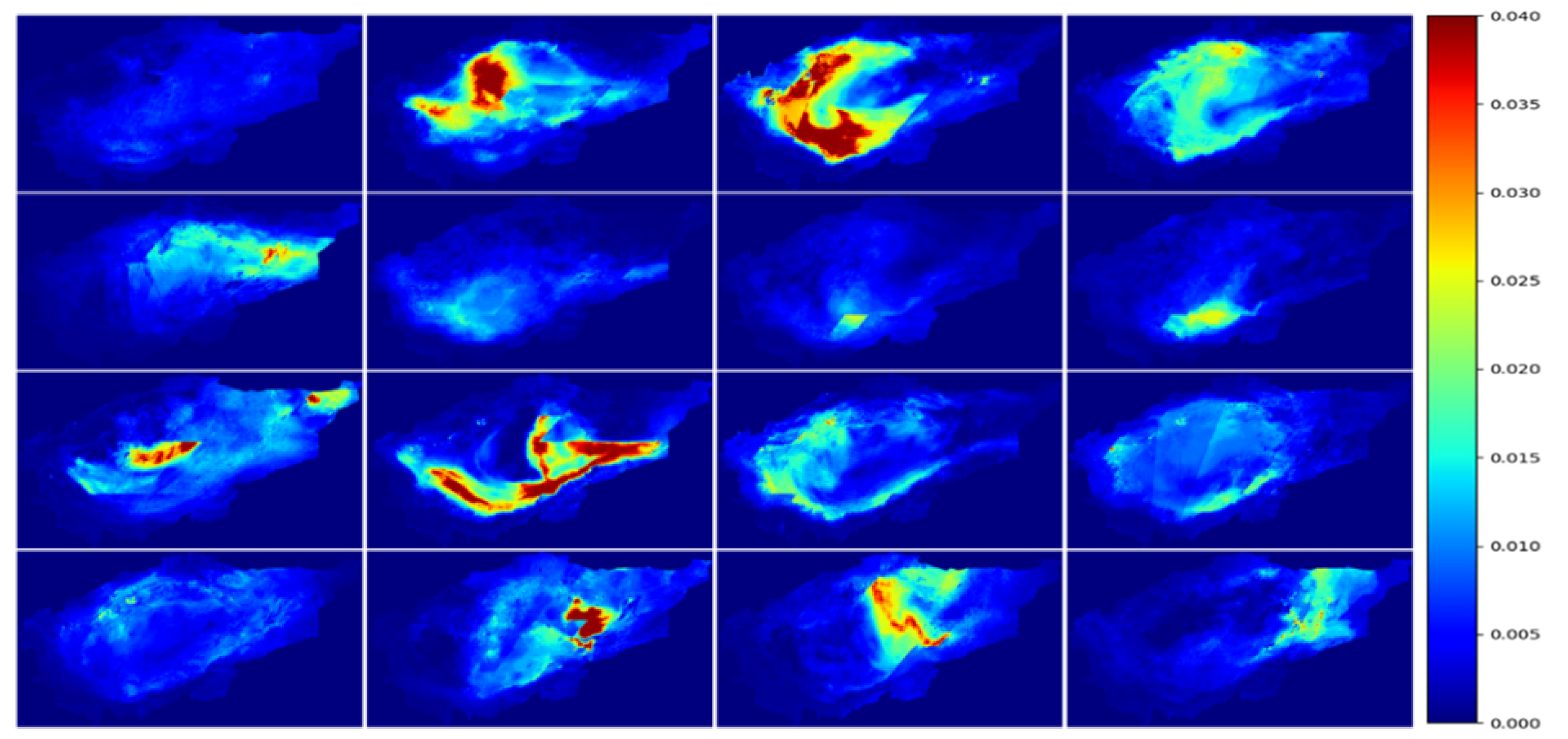
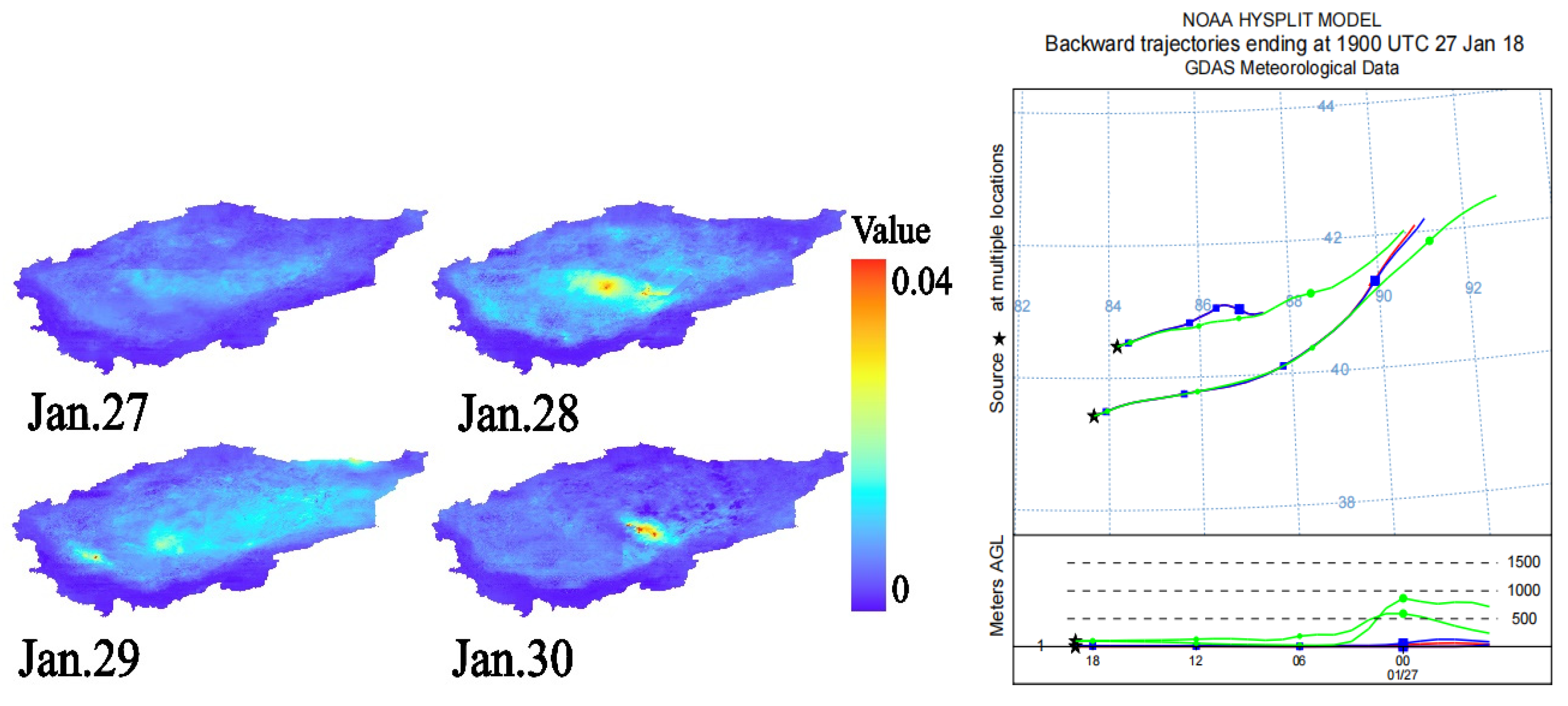
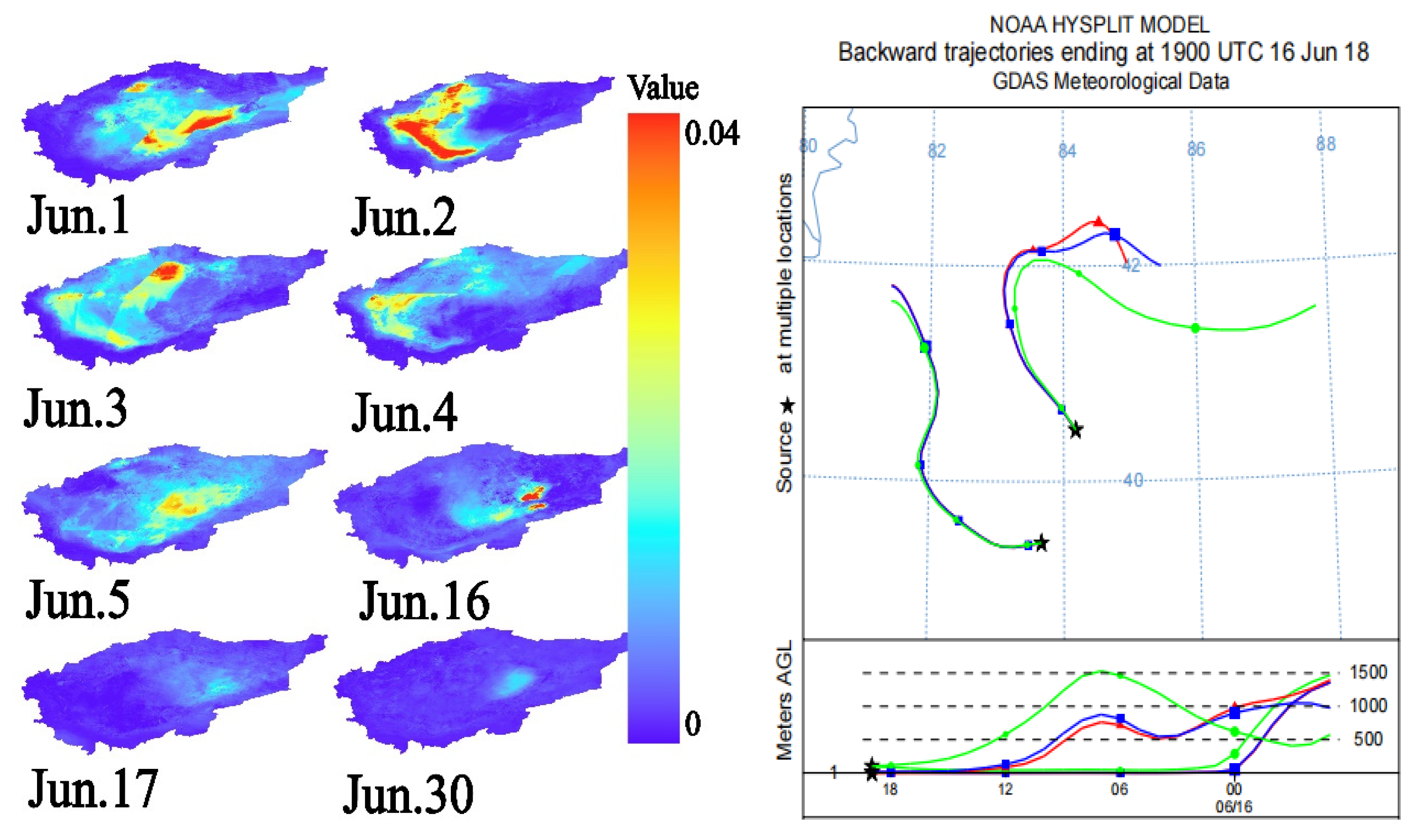
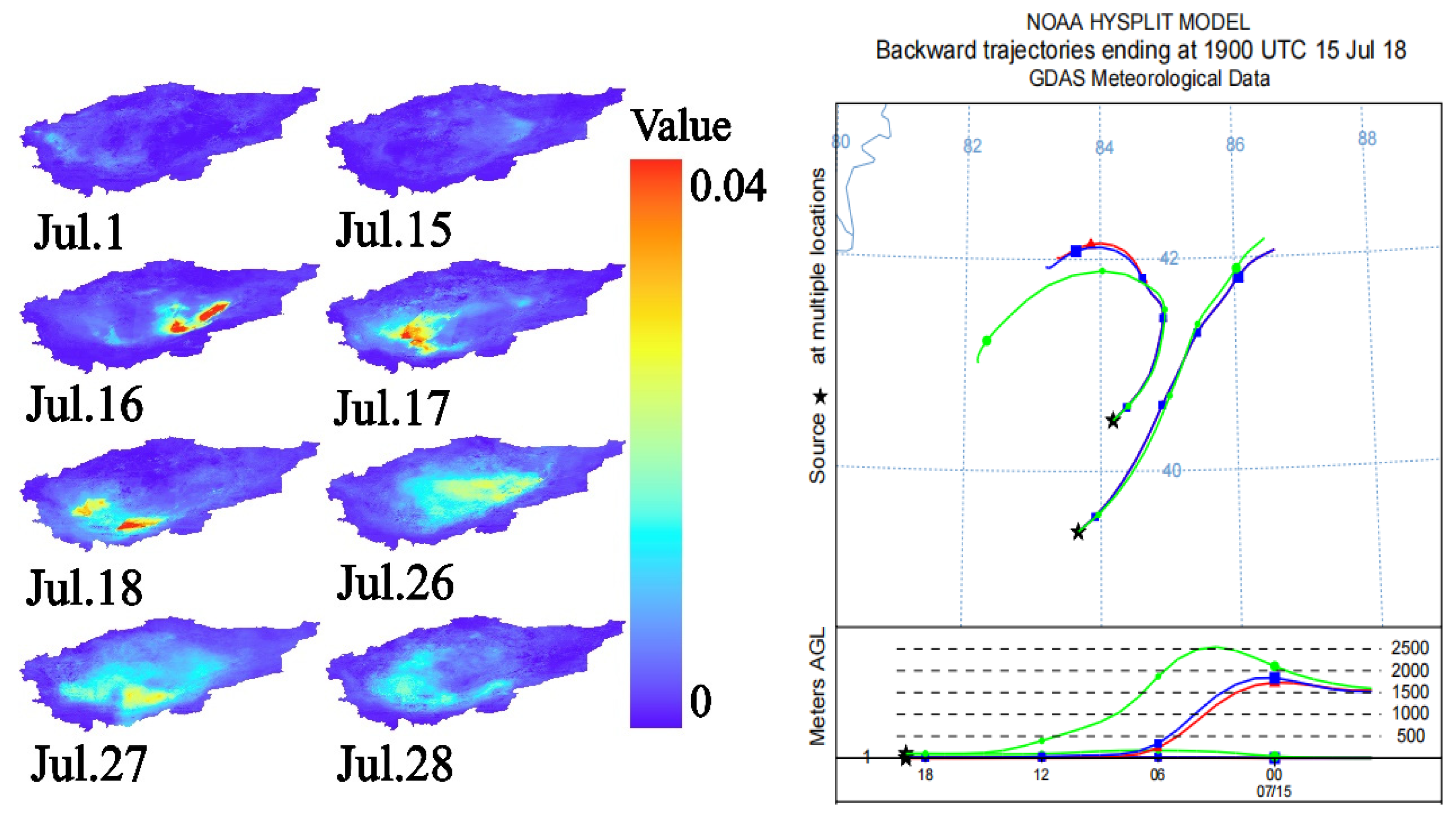
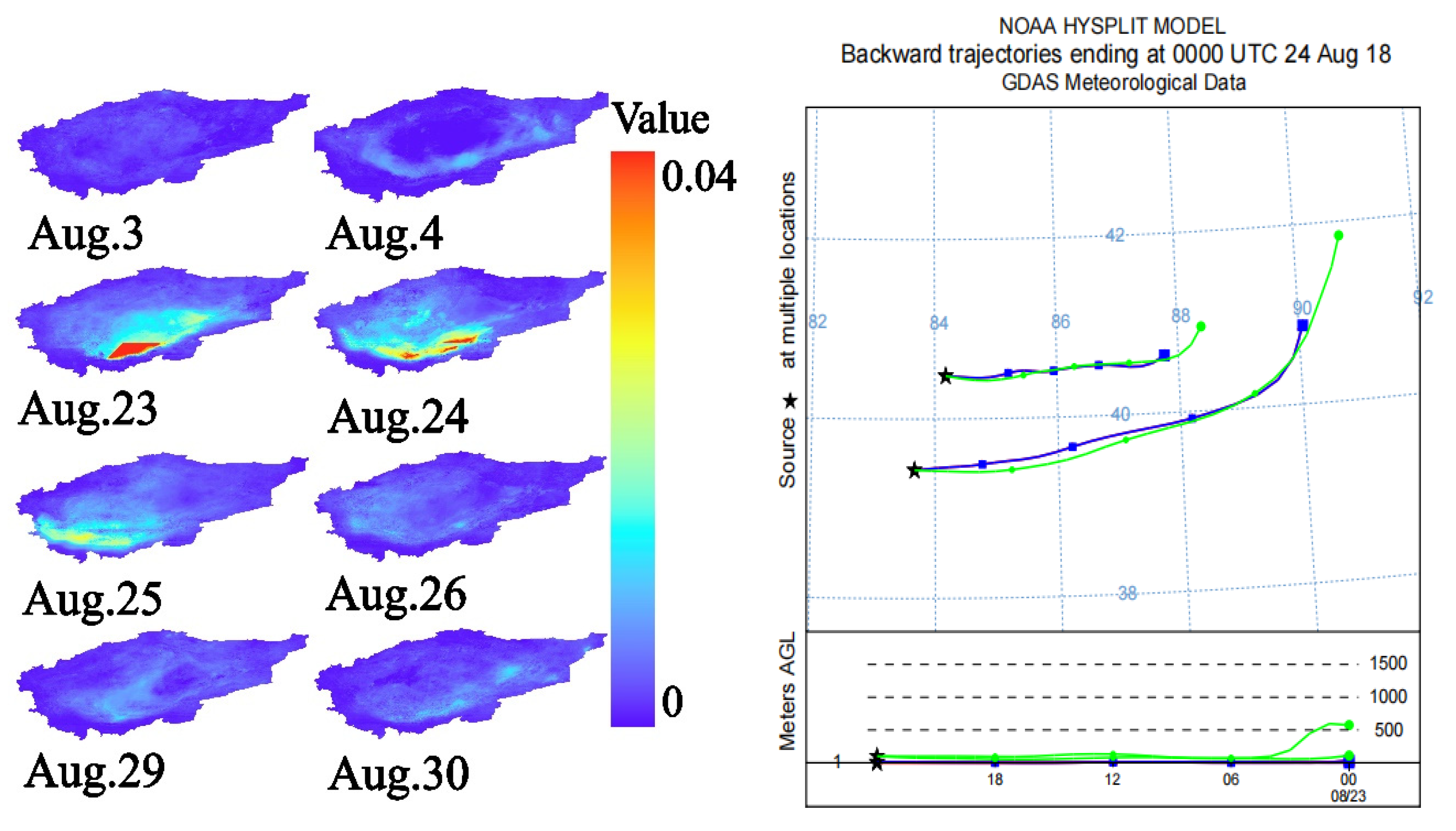
3.3.1. AOD Dust Storm Monitoring and Analysis of the Taklamakan Desert
3.3.2. Analysis of the Relationship Between Dust Flux and Dust Storm Dispersion Process
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goudie, A.S. Dust Storms: Recent Developments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaseelan, I.; Bhaskar, B.V.; Muthuchelian, K. The Effect of Aerosol Optical Depth on Rainfall with Reference to Meteorology over Metro Cities in India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8188–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Li, X. Interannual Variations of Dust Events in the Xinjiang Region. In Proceedings of the SPIE Conference on Ecosystems Dynamics, Ecosystem-Society Interactions, and Remote Sensing Applica-tions for Semi-Arid and Arid Land, Hangzhou, China, 23–27 October 2002; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; Volume 4890, pp. 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, T.R.; Matthews, H.D.; Simmons, C.; Leduc, M. Quantifying Changes in Extreme Weather Events in Response to Warmer Global Temperature. Atmos.-Ocean. 2015, 53, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.; Briottet, X. North Africa and Saudi Arabia Day/Night Sandstorm Survey (NASCube). Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H. Seasonal Variations in Dust Concentration and Dust Emission Observed over Horqin Sandy Land Area in China from December 2010 to November 2011. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, R.; Jia, S. Dynamic Monitoring of the Strong Sandstorm Migration in Northern and Northwestern China via Satellite Data. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 3244–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; He, Q.; Li, Z.; Deng, M.; Abbas, A. Variation Characteristics of Dust in the Taklimakan Desert. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 2129–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Oanh, N.T.K.; Abuduwaili, J. Variation Trends of Dust Storms in Relation to Meteorological Conditions and Anthropogenic Impacts in the Northeast Edge of the Taklimakan Desert, China. Open J. Air Pollut. 2016, 5, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Kang, L.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, T.; Yang, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, G. Emission, Transport, and Radiative Effects of Mineral Dust from the Taklimakan and Gobi Deserts: Comparison of Measurements and Model Results. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2401–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Huang, N.; Zhu, Y. Analysis of Wind-Blown Sand Movement over Transverse Dunes. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, K.R.; Mikkelsen, H.E. On the Efficiency of Vertical Array Aeolian Field Traps. Sedimentology 1998, 45, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G. Modeling the Atmospheric Dust Cycle: 1. Design of a Soil-Derived Dust Emission Scheme. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 16415–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Raupach, M.; Leys, J. A Model for Predicting Aeolian Sand Drift and Dust Entrainment on Scales from Paddock to Region. Soil Res. 1996, 34, 309–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Shao, Y. A New Model for Dust Emission by Saltation Bombardment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 16827–16842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Chin, M.; Tegen, I.; Prospero, J.M.; Holben, B.; Dubovik, O.; Lin, S.-J. Sources and Distributions of Dust Aerosols Simulated with the GOCART Model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 20255–20273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y. Physics and Modelling of Wind Erosion; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 37, ISBN 978-1-4020-8894-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Methuen: London, UK, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, R. Study on Sand Movement by Wind; Reports of the Institute of Science and Technology; University of Tokyo: Tokyo, Japan, 1972; Volume 5, pp. 95–112. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, P.R. Saltation of Uniform Grains in Air. J. Fluid Mech. 1964, 20, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.R. Soil Transport by Winds on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1979, 84, 4643–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A.; Passi, R. Modeling Dust Emission Caused by Wind Erosion. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1988, 93, 14233–14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, M. An Analytic Model of Wind-Blown Sand Transport. In Aeolian Grain Transport; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-U.; Park, M.-S.; Chun, Y. A Parameterization of Dust Concentration (PM10) of Dust Events Observed at Erdene in Mongolia Using the Monitored Tower Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2951–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, J.D.; White, B.R. Saltation Threshold on Earth, Mars and Venus. Sedimentology 1982, 29, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swet, N.; Katra, I. Reduction in Soil Aggregation in Response to Dust Emission Processes. Geomorphology 2016, 268, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate Effects of Dust Aerosols over East Asian Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11398–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Bi, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Tsay, S.-C.; Shi, J. Dust Aerosol Vertical Structure Measurements Using Three MPL Lidars during 2008 China-U.S. Joint Dust Field Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D00K12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, N.B.; Nair, V.S.; Suresh Babu, S. Vertical Structure of Aerosols and Mineral Dust Over the Bay of Bengal from Multisatellite Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 12845–12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiao, R.; He, Q.; Huo, W.; Yang, F.; Ai, L. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Dust Flux Based on High-Resolution Observations. J. Earth Environ. 2020, 11, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offer, Z.Y.; Goossens, D. Thirteen Years of Aeolian Dust Dynamics in a Desert Region (Negev Desert, Israel): Analysis of Horizontal and Vertical Dust Flux, Vertical Dust Distribution and Dust Grain Size. J. Arid. Environ. 2004, 57, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attiya, A.A.; Jones, B.G. Investigation of Severe Dust Storms Over Baghdad City by Using Remote Sensing Measurements and Ground Data. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1215, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari Alamdarloo, E.; Khosravi, H.; Abolhasani, A. Chapter 5—Dust-Source Monitoring Using Remote Sensing Techniques. In Remote Sensing of Soil and Land Surface Processes; Melesse, A.M., Rahmati, O., Khosravi, K., Petropoulos, G.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 99–111. ISBN 978-0-443-15341-9. [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos, P.; Colarco, P.; Espinosa, W.R.; Guzewich, S.D.; Levy, R.C.; Miller, R.L.; Chin, M.; Kahn, R.A.; Kemppinen, O.; Moosmüller, H.; et al. Mineral Dust Optical Properties for Remote Sensing and Global Modeling: A Review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 303, 113982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostad-Ali-Askari, K.; Rahimi, N.; Ashrafi, P.; Gholami, H.; Ashrafi, A.-H.; Dehghan, S. Assessment of Dust Event by RS, GIS, MODIS and Statistical Methods Among Satellite Images. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2021, 14, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, Z. Sand Dust Image Visibility Enhancement Algorithm via Fusion Strategy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Meng, Z.; Li, H.; Cai, J.; Qin, L. Changes in Landscape Ecological Risk in the Beijing-Tianjin Sandstorm Source Control Project Area from a Spatiotemporal Perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Yao, W.; Che, H.; An, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Record-Breaking Dust Loading during Two Mega Dust Storm Events over Northern China in March 2021: Aerosol Optical and Radiative Properties and Meteorological Drivers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 7905–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qu, J. Detection of Asian Dust Storm Using MODIS Measurements. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Prasad, A.K.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Sinha, P.R.; Kharol, S.K.; Gupta, P.; El-Askary, H.M.; Kafatos, M. Synergistic Use of Remote Sensing and Modeling for Tracing Dust Storms in the Mediterranean. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 861026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attiya, A.A.; Jones, B.G. An Extensive Dust Storm Impact on Air Quality on 22 November 2018 in Sydney, Australia, Using Satellite Remote Sensing and Ground Data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkop, A.; Pietruczuk, A. Analysis of Aerosol Transport over Southern Poland in August 2015 Based on a Synergy of Remote Sensing and Backward Trajectory Techniques. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 016039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowden, M.; Mueller, U.; Blake, D. Review of Surface Particulate Monitoring of Dust Events Using Geostationary Satellite Remote Sensing. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 183, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Askary, H.; Gautam, R.; Kafatos, M. Remote Sensing of Dust Storms over the Indo-Gangetic Basin. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2004, 32, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarakat, R.; Lakshmi, V. Monitoring Dust Storms in Iraq Using Satellite Data. Sensors 2019, 19, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Mohammadi, F.; Ghiasi, S.S.; Tiefenbacher, J.; Moghaddam, D.D.; Coulon, F.; Nalivan, O.A.; Tien Bui, D. Identifying Sources of Dust Aerosol Using a New Framework Based on Remote Sensing and Modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Mesbahzadeh, T.; Masoudi, R.; Zehtabian, G.; Amouei Torkmahalleh, M. Dust Storm Surveying and Detection Using Remote Sensing Data, Wind Tracing, and Atmospheric Thermodynamic Conditions (Case Study: Isfahan Province, Iran). Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broomandi, P.; Mohammadpour, K.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Fathian, A.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Maslov, V.A.; Nikfal, A.; Jahanbakhshi, A.; Aubakirova, B.; Kim, J.R.; et al. A Synoptic- and Remote Sensing-Based Analysis of a Severe Dust Storm Event over Central Asia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 220309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Hybrid Methods’ Integration for Remote Sensing Monitoring and Process Analysis of Dust Storm Based on Multi-Source Data. Atmosphere 2022, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ji, C.; Mao, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Gao, L.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, T. Downdraft Influences on the Differences of PM2.5 Concentration: Insights from a Mega Haze Evolution in the Winter of Northern China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 19, 014042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkikas, A.; Basart, S.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Kazadzis, S.; Pey, J.; Querol, X.; Jorba, O.; Gassó, S.; et al. Mediterranean Intense Desert Dust Outbreaks and Their Vertical Structure Based on Remote Sensing Data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 8609–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, W. Scaling of Vertical Coherence and Logarithmic Energy Profile for Wall-Attached Eddies during Sand and Dust Storms. J. Fluid Mech. 2024, 996, A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guehaz, R.; Sivakumar, V.; Mbatha, N. A Case Study on the Dust Storm That Occurred on March 13–18, 2022, over the Algerian Sahara, Using Satellite Remote Sensing. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2024, 264, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D.; Martínez, G.M.; Sebastián, E.; Lemmon, M.T.; Atwood, S.A.; Toledo, D.; Viúdez-Moreiras, D.; Stcherbinine, A.; Rodriguez-Manfredi, J.A.; de la Torre Juárez, M. The Diurnal Variation of Dust and Water Ice Aerosol Optical Depth at Jezero Crater Observed by MEDA/TIRS over a Full Martian Year. Icarus 2025, 425, 116313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haitham, A.; Mohammed, F.S. Optical Simulation of the Soil Effect on Solar Photovoltaic Systems for Low Buildings. J. Opt. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashi, Y.; Chamard, P.C.; Courel, M.-F.; Tiyip, T.; Tuerxun, Y.; Drake, S. The Recent Evolution of the Oasis Environment in the Taklimakan Desert, China. In Water and Sustainability in Arid Regions: Bridging the Gap Between Physical and Social Sciences; Schneier-Madanes, G., Courel, M.-F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 51–74. ISBN 978-90-481-2776-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.M.; Huang, J.P.; Xu, C.P.; Qi, Y.L.; Liu, H.Y. Characteristics of Taklimakan Dust Emission and Distribution: A Satellite and Reanalysis Field Perspective. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11772–11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X. Health Effects of Dust Storms on the South Edge of the Taklimakan Desert, China: A Survey-Based Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Shen, S.; Yang, F.; He, Q.; Ali, M.; Huo, W.; Liu, X. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Blowing Dust Events in the Taklimakan Desert. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 125, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Lü, P.; Cao, M.; Yu, J.; Xia, Z. Morphological and Sedimentary Characteristics of Raked Linear Dunes in the Southeastern Taklimakan Desert, China. Aeolian Res. 2024, 67–69, 100923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; He, Q.; Jiang, H.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, S.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Observations of the Vertical Distribution of Particulate Matter in the Surface Layer of the Taklimakan Desert in China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Yang, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhi, X.; Song, M.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; MamtiMin, A.; He, Q.; Wen, C.; et al. Influence of Topographic Relief on Sand Transport in the Near-Surface Layer During Dust Storms in the Taklimakan Desert. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 931529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H. Observation of Surface Sand Entrainment and Improvement of Sand Entrainment Parameterization Scheme in the Taklimakan Desert. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schepanski, K. Transport of Mineral Dust and Its Impact on Climate. Geosciences 2018, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Representations of Dynamics Size Distributions of Mineral Dust over East Asia by a Regional Sand and Dust Storm Model. Atmos. Res. 2021, 250, 105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.R. Light Scattering for Particle Characterization. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1999, 25, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, R.; Kakroodi, A.A.; Soleimani, M.; Karami, L.; Amiri, F.; Alavipanah, S.K. Identifying Sand and Dust Storm Sources Using Spatial-Temporal Analysis of Remote Sensing Data in Central Iran. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Che, H.; Xue, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, H.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Sand and Dust Storm Events in East Asia from 2007 to 2016: Relationships with Surface Conditions and Climate Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Quan, L.; Shi, S. Variations of the Dust Storm in China and Its Climatic Control. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, B.H. Characteristics and Meteorological Causes of Dust Transport Pathways in China from 2000 to 2021. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 4450–4458. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Shang, K. Regional Characteristics of Three Kinds of Dust Storm Events in China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Song, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhi, X.; Yang, F.; Ma, M.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Mamtimin, A.; He, Q. Relationships between Near-Surface Horizontal Dust Fluxes and Dust Depositions at the Centre and Edge of the Taklamakan Desert. Land 2022, 11, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Xu, H.; Xu, Q.; Liu, K. Aeolian Dust Movement and Deposition under Local Atmospheric Circulation in a Desert-Oasis Transition Zone of the Northeastern Taklimakan Desert. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, W. Observational Study on Salt Dust Aerosol Optical Properties Using Ground-Based and Satellite Remote Sensing. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 21, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P. Remote Sensing Approaches for Meteorological Disaster Monitoring: Recent Achievements and New Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Meskhidze, N.; Rasheeda Satheesh, A.; Petters, M.D. Turbulent Flux Measurements of the Near-Surface and Residual-Layer Small Particle Events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Facility | Observation Levels (m) | Other Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| XT Observation Station | 1, 2, 5, 10, 24, 32, 47, 63, 80, 100 | |
| TZ Observation Station | 1, 2, 5, 8, 16, 24, 32, 47, 63, 80 | |
| Dust Inlet | Width: 2 cm, Height: 5 cm | Covered with a 60-mesh screen on top for air filtration and dust particle collection |
| Particle Size Range (μm) | Main Characteristics | Scattering Energy Concentration Direction | Absorption and Extinction Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01–5 | Very small, similar to atmospheric background | Random | Low |
| 5–20 | Medium particle size, significant impact | Forward scattering tends to increase | Moderate |
| Project | Detailed Dataset Name |
|---|---|
| China 1 km Resolution Daily Seamless Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Dataset | |
| Time Range | 2000–2020 (2018 data used in this study) |
| Time Resolution | Daily |
| Spatial Resolution | 1 km |
| Longitude Range | 71–139°E |
| Latitude Range | 15–56°N |
| Product Validation Accuracy | ≥0.90 |
| Data Source | National Earth System Science Data Center (https://www.geodata.cn) |
| China 1 km Resolution Daily Seamless Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Dataset | |
| Time Range | 2000–2020 (2018 data used in this study) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maihamuti, M.; Huo, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Mamtimin, A. Research on Key Sand Generating Parameters and Remote Sensing Traceability of Dust Storms in the Taklamakan Desert. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111870
Maihamuti M, Huo W, Liu Y, Wang Y, Yang F, Zhou C, Yang X, Mamtimin A. Research on Key Sand Generating Parameters and Remote Sensing Traceability of Dust Storms in the Taklamakan Desert. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(11):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111870
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaihamuti, Mayibaier, Wen Huo, Yongqiang Liu, Yifei Wang, Fan Yang, Chenglong Zhou, Xinghua Yang, and Ali Mamtimin. 2025. "Research on Key Sand Generating Parameters and Remote Sensing Traceability of Dust Storms in the Taklamakan Desert" Remote Sensing 17, no. 11: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111870
APA StyleMaihamuti, M., Huo, W., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Yang, F., Zhou, C., Yang, X., & Mamtimin, A. (2025). Research on Key Sand Generating Parameters and Remote Sensing Traceability of Dust Storms in the Taklamakan Desert. Remote Sensing, 17(11), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111870









