Abstract
The application of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration datasets has become increasingly widespread, but the spatial precision verification at local scales is lacking. This study aims to investigate the consistency of PM2.5 concentration between remotely sensed data and ground-based data and optimize the accuracy of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data at the urban scale. Specifically, taking Changsha city as a case, four evaluation indices—R2, RMSE, uncertainty, and high deviation rate (HDR)—were employed to evaluate the credibility of remotely sensed data at national and dense ground-based stations, then analyze spatial variations of credibility and develop a Recursive Feature Elimination–Cross-Validation Random Forest (RFECV-RF) model to improve local fitting accuracy. Results show that remotely sensed data exhibit high credibility at national stations, while credibility at dense stations varies spatially and tends to decline with increasing distance from national stations. After optimizing by the RFECV-RF model, the credibility of remotely sensed data can be significantly improved, with R2 increasing from 0.87 to 0.98, RMSE decreasing from 8.59 µg/m3 to 3.08 µg/m3, HDR reducing from 2.01% to 0.04%, and uncertainty declining from 18.93% to 8.27%. Nevertheless, certain regions still require additional monitoring to further expand the credible spatial extent. These findings provide valuable insights for improving PM2.5 concentration remote sensing monitoring methods and designing the integrated “air–space–ground” observational network scheme.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of industrialization and urbanization, air pollution has become a globally recognized environmental issue [1,2,3]. Throughout this process, air quality monitoring methods have continuously improved, resulting in the emergence of various techniques, including ground-based monitoring stations, mobile on-road monitoring, ground-based radar, and satellite remote sensing [4,5]. Ground-based monitoring stations can provide high-precision data at point scale; however, their spatial coverage is limited, which makes it difficult to fully represent the spatial distribution of regional pollution [6,7,8]. Mobile on-road monitoring can detect pollution levels over a certain area and time span, but challenges remain in achieving large-scale continuous monitoring [9,10]. Ground-based radar can provide vertical atmospheric pollution data; however, it still faces significant limitations in terms of spatiotemporal continuity [11]. In contrast, remote sensing technology, with its significant advantages of high effectiveness, broad monitoring coverage, and low cost, has become an essential tool in large-scale air pollution monitoring [6,12,13]. However, against the background of the integrated “air–space– ground” monitoring system and the growing emphasis on “scientific and precise pollution control”, the accuracy of monitoring data is the challenge of remote sensing technology.
The advancement of long-term aerosol and PM2.5 concentration datasets has significantly expanded the possibilities for urban air quality research. Through the integration of remotely sensed data, numerical modeling, and ground-based monitoring data, researchers are now able to generate high-resolution, temporally continuous PM2.5 concentration datasets. These datasets have the potential to alleviate the spatial and temporal limitations of conventional monitoring methods, and can serve as a more comprehensive and accurate foundation for urban air quality assessment and management [14]. At present, several high-precision and spatiotemporal resolution PM2.5 concentration datasets have emerged, such as China High PM2.5 (CHAP) [15], the Long-term Gap-free High-resolution Air Pollutant Concentration Dataset (LGHAP) [16], Global Geophysical Satellite-Based PM2.5 (V5.GL.03) (GGS3) [17], and Tracking Air Pollution in China (TAP) [18]. The accuracy evaluation of these datasets is mainly based on ground monitoring data from national stations [19,20,21,22]. However, the research on the accuracy verification of local space is relatively scarce, especially in areas beyond national stations [23,24]. This limitation significantly constrains the role of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration datasets in identifying urban pollution hotspots and tracing pollution sources, thereby hindering their potential in air quality management and policy-making.
However, existing studies have demonstrated that the spatial distribution of PM2.5 pollutants within urban areas exhibits significant heterogeneity at finer spatial scales [25,26], indicating that the influence between factors and PM2.5 pollution distribution are more complex at the micro-environmental scale. Consequently, global models may not be universally applicable to all regions at the large scale, and local variations in PM2.5 pollution distribution and environmental characteristics cannot be ignored. Identifying these influencing factors and conducting local modeling or optimization has become critical for enhancing the credibility of remotely sensed data. Meanwhile, local modeling methods have been proven feasible in several studies and have demonstrated their potential to improve the credibility of remotely sensed data to some extent. For example, Xu et al. [27] developed a micro-environmental scenario-enhanced PM2.5 concentration spatial distribution fine simulation model, by integrating Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) with Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), based on PM2.5 concentrations from dense observations. Both fitting and validation accuracy of the model are better than those without scenario variables. Furthermore, integrating multi-source monitoring data and combining appropriate environmental factors for remotely sensed data correction provides new opportunities for further improving the credibility of remotely sensed data [28,29].
Thus, this study takes Changsha City as a case study and analyzes the consistency between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and ground-based monitoring data, exploring the spatial differentiation characteristics and variations in the credibility of remotely sensed data. Furthermore, the RFECV-RF model is utilized to correct the remotely sensed data, thereby improving its local fitting accuracy. Finally, based on the consistency analysis results of remotely sensed data before and after optimization, this study evaluates the local applicability of remote sensing methods for atmospheric pollution monitoring. The results are expected to provide references for the improvement of PM2.5 concentration remote sensing monitoring techniques and the optimization of the design of the integrated “air–space–ground” monitoring system.
2. Data and Methods
Figure 1 shows the flowchart of this study, including the processes of ① Data collection and preprocessing; ② Credibility evaluation of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data at station locations; ③ Analysis of credibility spatial variations; ④ Optimization of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data.
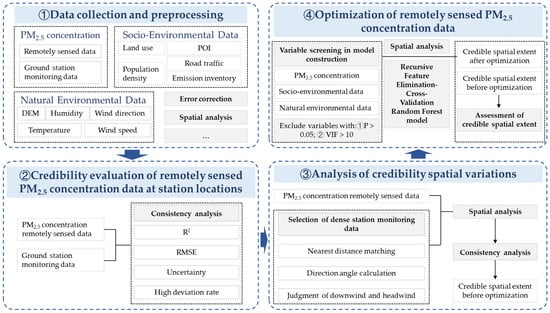
Figure 1.
The flowchart of this study.
2.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
2.1.1. Remotely Sensed PM2.5 Concentration Data
Table 1 shows information on typical remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration datasets in China. This study selects the CHAP dataset (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home) (accessed on 23 May 2025), which offers relatively high accuracy and spatiotemporal resolution. The dataset covers the period from 1 January 2019 to 31 December 2022.

Table 1.
Typical remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration datasets in China.
2.1.2. Station Monitoring Data of PM2.5 Concentration
The station monitoring data collected in this study primarily include hourly PM2.5 concentration data from 1 January 2019 to 31 December 2022. These data originate from 10 national stations (Table 2) managed by the China National Environmental Monitoring Center (https://air.cnemc.cn:18007/) and 157 dense stations operated by the Changsha Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Center in Hunan Province. Figure 2 shows the distribution of ground-based stations. Quality control of the PM2.5 ground monitoring data was conducted following the statistical validity requirements of China’s Ambient Air Quality Standard (GB3095-2012) [30]. Specifically, records with missing hourly concentrations or negative values were removed from the raw data. During the calculation of daily averages, records with fewer than 20 valid hourly values within a 24 h period were excluded.

Table 2.
Name and codes of national stations.
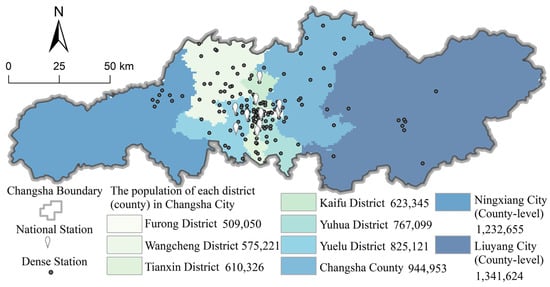
Figure 2.
Distribution of ground-based stations.
Due to limitations in instrument precision, maintenance conditions, and environmental interference, dense stations often exhibit inherent data biases, which may compromise their suitability for high-accuracy environmental analysis [31]. To mitigate such systematic errors caused by hardware constraints, this study employs an RF to calibrate data from dense stations using standardized measurements from nearby national stations [32]. National stations, with stricter quality control protocols and more stable instrument performance, provide data of higher accuracy and reliability. By establishing a nonlinear mapping relationship between the two datasets through machine learning, the proposed method can effectively correct measurement deviations arising from hardware disparities in dense stations, thereby enhancing the overall data quality of regional monitoring networks. The fitted model achieved an R2 of 0.99 and an RMSE of 2.88 µg/m3 on the training data, and an R2 of 0.92 and an RMSE of 7.69 µg/m3 on the test data, indicating reliable correction accuracy.
2.1.3. Other Modeling Data
Natural Environmental Data
The natural environmental data used in this study include meteorological data and Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data. The meteorological data were obtained from the Changsha Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Center in Hunan Province. Among the 157 dense stations, meteorological data were missing for 22 stations, leaving 135 stations with hourly observations of temperature, humidity, wind direction, and wind speed for the year 2022. The DEM data were sourced from the Geospatial Data Cloud platform (https://www.gscloud.cn/search) (accessed on 23 May 2025) and consist of 30 m resolution Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer Global Digital Elevation Model (ASTER GDEM) data.
Socio-Environmental Data
The selected socioeconomic and anthropogenic data include land use, population density, Points of Interest (POI), road traffic, and emission inventory data. Except for the emission inventory data, which corresponds to the year 2019, all other datasets are from 2022. The land use data were obtained from the China Land Cover Dataset (CLCD) (https://zenodo.org/records/12779975) (accessed on 23 May 2025), with a spatial resolution of 30 m, covering nine land cover types: cropland, forest, shrubland, grassland, water bodies, snow, barren land, impervious surfaces, and wetlands. The population density data, with a spatial resolution of 1 km, were sourced from Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) (https://www.ornl.gov/) (accessed on 23 May 2025). The POI data were provided by the Baidu Open Platform (http://lbsyun.baidu.com/) (accessed on 23 May 2025), encompassing 14 major categories, including transportation facilities, recreational activities, and public services. The road traffic data were downloaded from OpenStreetMap (https://download.geofabrik.de/) (accessed on 23 May 2025), while the emission inventory data were provided by the Changsha Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Center in Hunan Province.
Based on the aforementioned datasets, buffer zones with radii of 500 m, 1000 m, and 1500 m were established around each air quality monitoring station. Within each buffer zone, the proportion of different land use types, total population, number of POIs by category, road length, and the number of various emission sources were calculated.
2.2. Credibility Evaluation at Station Locations
The consistency between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and ground-based monitoring data was analyzed from two perspectives: fitting performance and deviation level. The credibility of remotely sensed data was assessed to quantify its suitability for local-scale monitoring. Fitting performance was evaluated using the coefficient of determination (R2) and root mean square error (RMSE), while deviation level was characterized by high deviation rate (HDR) and uncertainty.
2.2.1. Coefficient of Determination
The formula for calculating R2 to characterize the fitting performance between remotely sensed data and ground-based monitoring data is as follows:
where is the station monitoring data, is the mean of the station monitoring data, and is the remote sensing monitoring data.
2.2.2. Root Mean Square Error
RMSE was used to measure the fitting accuracy between remote sensing monitoring data and station monitoring data. The calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the sample size, denotes the station monitoring data, and represents the remote sensing monitoring data.
2.2.3. High Deviation Rate
The remote sensing monitoring data values at the monitoring station locations were extracted, and the deviation between the two datasets was calculated. All deviation values were then arranged in descending order, and the value at the 2% position (27.3) was taken as the threshold. Any deviation greater than this threshold was considered high deviation. The HDR refers to the ratio of the number of days during the statistical period D where the deviation between remote sensing monitoring data and station monitoring data exceeds 27.3, and the calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the HDR at station during the statistical period, and represents the number of days during which the deviation between remote sensing monitoring data and station monitoring data exceeds 27.3.
2.2.4. Uncertainty
The formula for calculating the uncertainty that represents the overall deviation level between remote sensing monitoring data and station monitoring data is as follows:
where represents the uncertainty at station on day , is the daily average of remotely sensed data at station on day , and is the daily average of station monitoring data at station on day .
The uncertainty for station is the average of all values over the total number of days D in the statistical period. The calculation formula is as follows:
2.3. Credibility Spatial Variation Analysis
To reveal the spatial variation characteristics of the credibility of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data, data collected when the dense stations were in downwind conditions relative to the national stations were selected based on the azimuth and wind direction between the national and dense stations. The data were classified into six categories based on the distance between the dense stations and the nearest national stations: ≤1 km, 1–5 km, 5–10 km, 10–15 km, 15–20 km, and >20 km. A consistency analysis was subsequently conducted between the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and the ground monitoring data from the dense stations in each category.
2.3.1. Nearest Distance Matching
By calculating the Haversine distance between each dense station and each national station, the nearest national station to each dense station was determined. The formula for distance calculation is as follows:
where represents the earth’s radius, and are the latitudes of the two points, and and represent the differences in latitude and longitude, respectively.
2.3.2. Direction Angle Calculation
The direction angle between the dense station and the nearest national station was calculated using the following formula:
Among them:
2.3.3. Estimation of Downwind and Upwind
Based on the direction angle between the national station and the dense station, as well as the wind direction, it is determined whether the dense station is in a downwind or upwind condition relative to the national station. The relationship between the wind direction angle and the direction angle is determined by the following rule: if the difference between the wind direction and the direction angle is less than 90° or greater than 270°, it is considered downwind; if the difference is between 90° and 270°, it is considered upwind. The calculation of the wind direction angle follows these rules: an east wind is assigned a value of 0°, and other wind directions increase in a clockwise direction.
2.4. Optimization of Remotely Sensed PM2.5 Concentration Data
2.4.1. Data Preprocessing and Variable Screening
The dependent variable used for model construction is the deviation between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data, while the independent variables consist of the natural and social environmental data from the aforementioned data preprocessing step.
Prior to model construction, data cleaning was performed on the deviation between the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration and dense station observations. The 3.5×interquartile range (IQR) criterion was adopted to identify and remove outliers, eliminating 0.87% of abnormal residuals to enhance model robustness and reliability. To ensure consistent distributions of key variables in both training and test sets, a stratified random sampling strategy was applied, partitioning the dataset into a training set (90%) and a test set (10%). Figure 3 shows the data distribution of training set and test set. The test set was exclusively reserved for final model evaluation and was not involved in any training process.
Figure 3.
Data distribution of training set and test set.
To reduce unnecessary noise, avoid multicollinearity, and enhance model accuracy, a preliminary screening of the modeling variables was performed using significance analysis and collinearity tests: ① Variables with p-value > 0.05 were excluded; ② Variables with variance inflation factor (VIF) > 10 were excluded.
2.4.2. RFECV-RF Model
Random forest is an ensemble learning method based on decision trees. It enhances the model’s generalization ability and accuracy by constructing multiple decision trees and combining their predictions [33].
Feature Importance Calculation
In random forest, feature importance reflects the contribution of each feature in reducing the model’s error. This is achieved by assessing the impact of each feature on the decision tree node splits. For each feature, its importance is the sum of the mean squared errors (MSEs) reduced during the splitting process across all trees. The calculation formula is as follows:
where represents the sample size, denotes the true value of the sample, and represents the predicted value of the sample.
where refers to the mean squared error of the node before splitting, and refers to the mean squared error of the node after splitting.
where represents the number of trees in the forest, and denotes the contribution of feature in tree .
Feature Selection
To further enhance the model accuracy, Recursive Feature Elimination with Cross-Validation (RFECV) was used for feature selection. Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) calculates the importance of each feature by repeatedly constructing models and progressively eliminating the least important features until the optimal feature subset is identified. After each feature elimination, cross-validation (CV) is performed to evaluate the model error for the current feature subset. The feature subset with the lowest cross-validation error is selected. The specific modeling process is as follows:
- ①
- Train the model using all features;
- ②
- Calculate the importance of each feature and remove the least important feature;
- ③
- Perform cross-validation;
- ④
- Repeat the above steps until the model error reaches its minimum value.
Hyperparameter Optimization and Final Training
To further optimize model performance, Bayesian Optimization was used to search for the optimal combination of hyperparameters. Bayesian Optimization is a global optimization technique based on a probabilistic surrogate model, often a Gaussian Process. At each iteration, it uses the surrogate model to propose the most promising hyperparameter configuration, balancing exploration and exploitation. This method significantly reduces the number of evaluations needed to find optimal parameters [34].
For each proposed hyperparameter set, 10-fold cross-validation [35] was performed to assess model performance. The combination yielding the lowest validation error was selected as the final hyperparameter configuration. In addition, an early stopping strategy was implemented to avoid overfitting and improve training efficiency: model training was terminated early when the MSE no longer showed significant improvement over several iterations. The optimal number of trees determined through this process was 1500 (Figure 4). The final model, trained using the optimized parameters and the selected features, achieved an R2 of 0.92 and an RMSE of 2.37 µg/m3 on the training set, and an R2 of 0.79 and an RMSE of 3.46 µg/m3 on the test set.
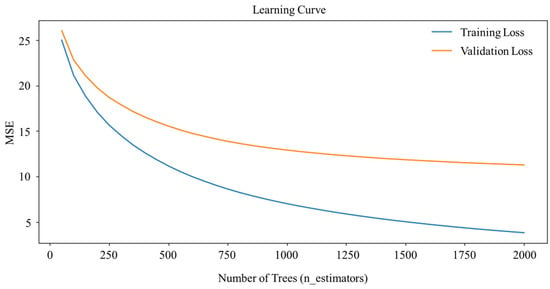
Figure 4.
Learning curve of model.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Remotely Sensed PM2.5 Concentration Data Credibility at Station Locations
3.1.1. National Station-Based Evaluation
Figure 5 illustrates the overall fitting results of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and the national station monitoring data over the period from 2019 to 2022. The fitting degree between the two datasets is high, with an R2 of 0.94 and an RMSE of 6.24 µg/m3, indicating a significant correlation. The scatter plot reveals a distinct clustered distribution, particularly within the concentration range of 0–50 µg/m3, where the remotely sensed data closely aligns with the national station monitoring data. Further consistency analysis indicates that the uncertainty between the two datasets is 6.10%, with a low HDR of 1.83%, suggesting minimal bias and strong consistency of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data.
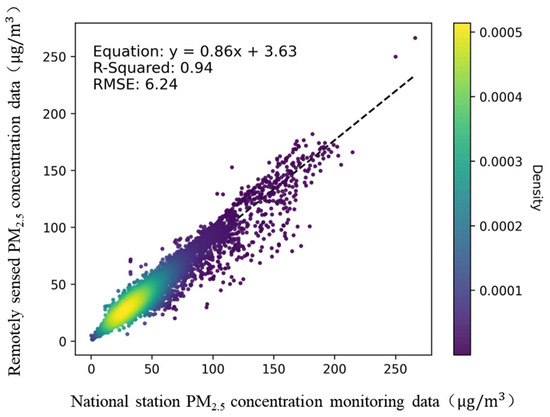
Figure 5.
Scatter plot of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and all national station monitoring data.
Figure 6 shows the fitting degree between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and ground monitoring data of each national station. The fitting degrees of all stations are generally high, although some differences are observed. Most stations demonstrate high consistency, with 5 out of 10 stations achieving the R2 of 0.95, suggesting that remotely sensed data can effectively reflect the variations in PM2.5 concentration at these locations. Specifically, the monitoring stations at 1342A and 1340A exhibit the highest accuracy, with the R2 of 0.95, RMSE of 5.25 µg/m3 and 5.98 µg/m3, and relatively low uncertainty and HDR. Notably, even at stations with relatively lower consistency, such as the 1344A, the R2 still reaches 0.92, with the RMSE of 6.89 µg/m3. This indicates that remotely sensed data maintains a high level of consistency at all national station locations.
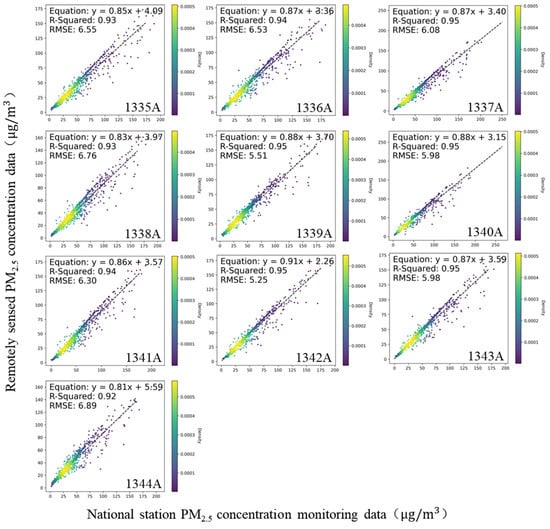
Figure 6.
Scatter plots of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and monitoring data of each national station.
3.1.2. Dense Station-Based Evaluation
The fitting results between the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and the dense station monitoring data are shown in Figure 7. The overall fitting performance is relatively good, with an R2 of 0.87, an RMSE of 8.59 μg/m3, an uncertainty of 18.93%, and an HDR of 2.01%. However, compared to the fitting results of national station monitoring data, the fitting degree with the dense station monitoring data is notably weaker, as reflected by the deterioration in all evaluation indicators, particularly a significant increase in uncertainty. Although the scatter plot indicates that the data points are generally aligned with the fitting line, their distribution appears more dispersed. It shows greater variability especially in high-concentration areas, where the increased dispersion results in poorer fitting performance.
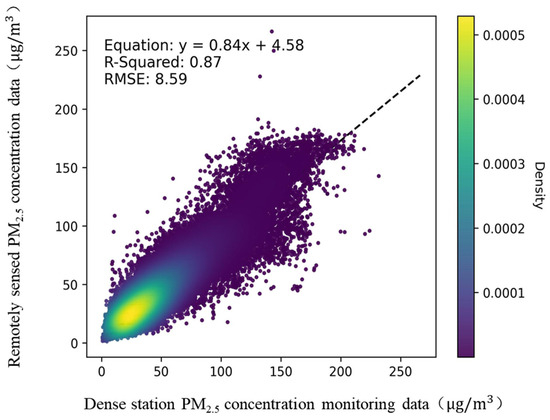
Figure 7.
Scatter plot of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data.
The consistency analysis results between the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and the dense station monitoring data are illustrated in the violin plot in Figure 8. The R2 values exhibit a positively skewed distribution, with most data points concentrated between 0.80 and 0.93, indicating that the remotely sensed data are highly accurate at the majority of dense station locations. However, the extended tail of the distribution suggests that at certain locations, the R2 values are lower, highlighting limitations in the fitting performance of the remotely sensed data in these areas. Among the 157 dense stations, 10.83% exhibit R2 values above 0.90, demonstrating strong consistency, while 10.83% have R2 values below 0.80, indicating relatively poor fit. The majority of the stations have R2 values concentrated between 0.80 and 0.90. Notably, the station in Yuhua District–Gaoqiao Street achieves the highest R2 value of 0.93, while the station in Liuyang Industrial Park has the lowest R2 value of 0.64.
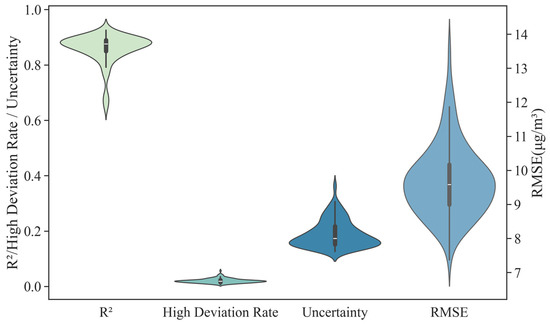
Figure 8.
Violin plot of consistency between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data. The curved sections on both sides of the violin plot represent the density of the data distribution. The wider sections indicate a higher frequency of data points around that value. The white line in the center of each violin plot represents the median (50th percentile) of the data, while the box represents the interquartile range (Q1 and Q3), which corresponds to the 25th and 75th percentiles of the data.
Overall, the HDR values are concentrated, with most of them falling within a lower range. The station with the highest HDR is Jinjing Town 2nd Site, Changsha County, reaching 5.66%, while the lowest is at Dongfanghong Street, High-tech Zone, with 0.69%. Among all stations, 42.68% exhibit a HDR higher than the overall level of 2.01%, and 9.55% exceed 3%, indicating a poor fit of the remotely sensed data at these stations.
The median uncertainty of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data is approximately 20%, which is significantly higher than the 6.10% uncertainty observed at national stations. The range of uncertainty is between 12.64% and 36.50%, with the highest value at Guankou Street, Liuyang City, and the lowest at Gaoqiao Street, Yuhua District. Among all stations, 14.65% have uncertainty exceeding 25%, indicating significant data deviation, while 22.29% have uncertainty below 15%, where the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data are relatively reliable.
The distribution of RMSE values is widely dispersed, following a positively skewed distribution. Most data points are concentrated in the lower range, although extreme values are also present. Among all dense stations, 10.19% have RMSE values exceeding 11 μg/m3, indicating a substantial discrepancy between the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data. In contrast, 14.01% of stations exhibit RMSE values below 8.59 μg/m3. The station with the highest RMSE is Jinjing Town 2nd Site, Changsha County, at 13.67 µg/m3, while the station with the lowest RMSE is Quantang Street 1st Site, Changsha County, at 7.37 µg/m3.
All the stations mentioned in the above are showed in the Figure 9.
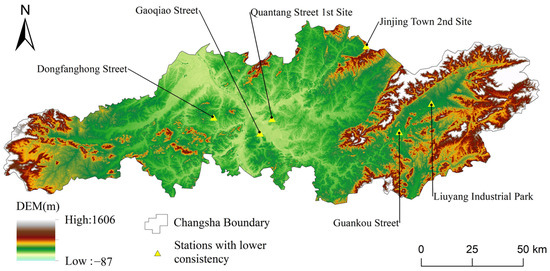
Figure 9.
Distribution of stations with lower consistency.
3.2. Spatial Variability Pattern of Credibility
The spatial distribution of the consistency analysis results between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and monitoring data from various dense stations is presented in Figure 10. The points in the figure indicate the locations of the dense stations, and the shading of each point reflects the value of the consistency measurement indicators, representing the fitting degree between remotely sensed data and the dense station monitoring data. It is clearly evident from the figure that the fitting degree between the two datasets is significantly correlated with the distance between the dense station and the national station. Specifically, remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data exhibit a higher fitting degree at dense stations located closer to the national stations, and lower at those located farther.
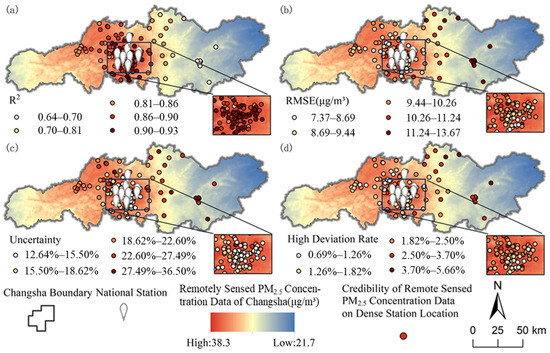
Figure 10.
Spatial distribution of consistency between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data. (a) R2 of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data; (b) RMSE of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data; (c) Uncertainty of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data; (d) HDR of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data.
To clarify the relationship between the accuracy of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and the distance to national stations, a further investigation into the spatial variation characteristics of the credibility was conducted. As shown in Figure 11, the credibility of remotely sensed data gradually declines as the distance increases from national stations. In particular, the trends of R2 and uncertainty are particularly evident, showing a stepwise deterioration. The following three credible intervals can be roughly divided from the results: ① high credible range (0–1 km): R2 maintains superior performance (>0.90), indicating high credibility of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data; ② transitional stability range (1–15 km): exhibiting stabilized yet diminished measurement indicators of credibility; ③ critical decay boundary (>15 km): a phase transition manifests through precipitous quality deterioration, characterized by the uncertainty surge to 20% and R2 decline to 0.86. The credibility of the remotely sensed data significantly decreases when the distance from national stations is over 15 km, making it difficult to meet the needs of accurate PM2.5 monitoring.
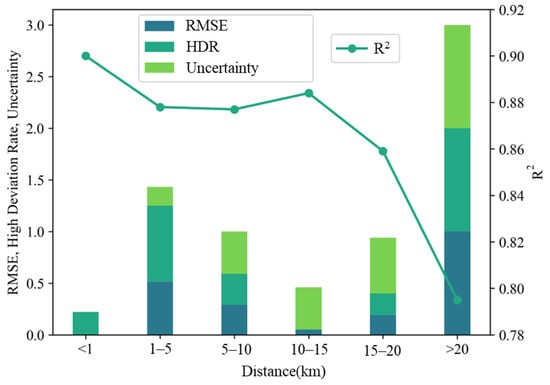
Figure 11.
Credibility changes in remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data in different ranges around national stations. To facilitate the visual comparison of data at different magnitudes, RMSE, uncertainty, and HDR were standardized using min–max normalization, while R2 values were plotted using the original data.
The spatial variability of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data credibility is also associated with the distribution of PM2.5 pollution concentration. As shown in Figure 12, the R2 of PM2.5 remotely sensed data with ground-based monitoring data shows a significant positive correlation with the range, mean, and variance of the ground-based monitoring data. This suggests that in areas with more severe pollution, where the concentration range and fluctuations are larger and more intense, the credibility of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data is higher.
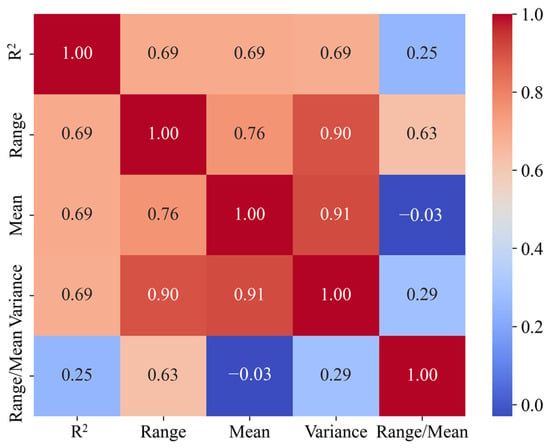
Figure 12.
Heatmap of R2 values with dense station monitoring data statistics (range/mean/variance/range–mean ratio). Both the x-axis and the y-axis represent the statistics of the dense station monitoring data.
Therefore, to explore the spatial variability of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data credibility from the perspective of geographic environmental factors influencing PM2.5 pollution distribution, as illustrated in Figure 13, the spatial variability of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data credibility is pronounced. Areas with higher credibility are concentrated in the city center, whereas areas at the urban periphery demonstrate lower credibility of the remotely sensed data. In regions with the lower credibility of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data, several geographic and environmental factors appear to contribute to this reduced credibility. These areas are typically characterized by greater topographic variation, higher vegetation coverage, and more complex land use types. Moreover, pollution emission sources in these regions are relatively dispersed, and such areas are often located at the periphery of the urban core. These peripheral zones are more susceptible to the influence of external pollution transport, which may cause significant vertical stratification of aerosols. As a result, the accuracy of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration tends to decrease in these areas.
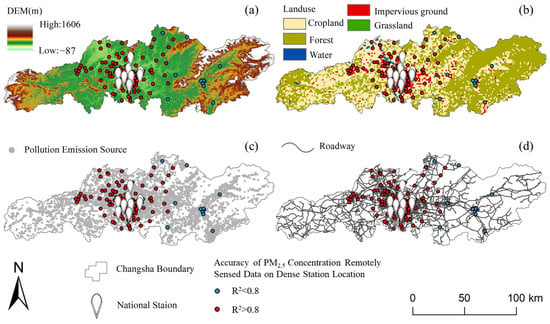
Figure 13.
Spatial distribution of R2 values between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and ground-based monitoring data in relation to geographical environmental factors. (a) Distribution of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data credibility with elevation; (b) Distribution of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data credibility with land use; (c) Distribution of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data credibility with pollution emission source; (d) Distribution of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data credibility with roadway.
Figure 14 quantitatively illustrates the relationship between various geographical factors and the HDR. The y-axis represents various geographic environmental variables surrounding each station, including elevation, road length within a 1500 m buffer (1500_rl), water area within a 1000 m buffer (1000_wa), and the number of pollution source within a 1000 m buffer (1000_psn). To facilitate comparison within a single figure, the values of these geographic factors were normalized and divided into five groups as the x-axis. The color of each point indicates the sample amount, and the size of each point reflects the HDR. The figure clearly demonstrates that both elevation and the number of pollution sources are significantly associated with the probability of large deviations in remote sensing data. Specifically, higher elevations and greater numbers of pollution sources correspond to a markedly increased probability of high deviation, indicating reduced credibility of remotely sensed data under such geographic conditions.
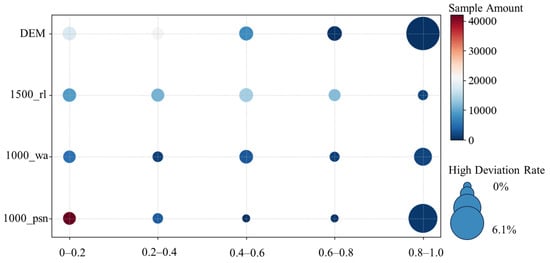
Figure 14.
The relationship between geographical factors and high deviation rate.
3.3. Assessment of Credibility Spatial Extent
The RFECV-RF model was conducted to further improve the fitting accuracy of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data in areas not covered by national stations. The model is based on the residuals between the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and the dense station monitoring data, as well as geographic environmental data.
After optimization, the local fitting ability of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data improve significantly (Figure 15). All the consistency indicators exhibit great enhancement, with the R2 increasing from 0.87 to 0.98, RMSE decreasing from 8.59 µg/m3 to 3.06 µg/m3, HDR reducing from 2.01% to 0.04%, and uncertainty declining from 18.93% to 8.27%.
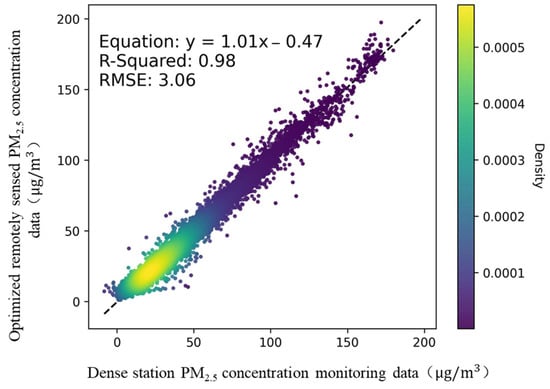
Figure 15.
Scatter plot of overall optimized remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data.
Specifically, the number of stations with increased R2 value reaches 134, and the proportion of stations with an R2 greater than 0.90 significantly increases from 10.83% before optimization to 97.78%, indicating a substantial improvement in the fitting degree between the corrected remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and dense station monitoring data. The most notable improvement is observed in the HDR indicator, with all the stations showing a decrease in HDR. The proportion of stations with an HDR greater than 2.01% decreased from 42.68% to 0. Moreover, it is noteworthy that 93.33% of the stations experienced a reduction in the HDR to 0, effectively mitigating the occurrence of extreme deviations. The number of stations with reduced uncertainty is also large (135 stations), and the proportion of stations with uncertainty values below 15% increases from 22.29% to 94.07%. Additionally, at all the stations (135 stations), the RMSE value decreases, and the proportion of stations with an RMSE value below 8.59 µg/m3 significantly increases from 14.01% to 99.26%.
Figure 16a shows the changes in R2 values before and after the optimization of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data within varying ranges from national stations. After optimization, the reliable radius of the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data (R2 > 0.90) expands from 1 km to over 25 km. The farthest distance between the dense station and the nearest national station is 68 km. At the location of this station, the optimized remotely sensed data still have a very high credibility, and the R2 is above 0.95. Although the R2 value still exhibits a decreasing trend with increasing distance from the national stations, the optimized data maintain a stable fitting accuracy. And even beyond 25 km, it remains above 0.95. Figure 16b presents the changes in the other consistency indicators before and after optimization. All the three indicators show a great decline after optimization, especially the significant reduction in HDR, indicating a substantial improvement in the credibility of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data after optimization.
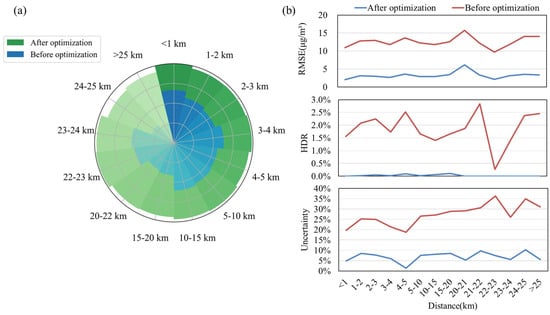
Figure 16.
Credibility change plot of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data in a certain range around national stations before and after optimization. (a) Changes in R2 values of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data before and after optimization; (b) Changes in RMSE, HDR, uncertainty of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data before and after optimization. (a) shows the radial range of R2 value changes, with the horizontal axis (in angular direction) representing different distance intervals from the national stations.
Remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data demonstrate acceptable credibility for PM2.5 concentration monitoring a big range of over 25 km from national stations, indi-cating its potential as a supplementary monitoring approach.
The credibility and optimization of remotely sensed data are further constrained by the spatial distribution of dense stations. Notably, 59.87% of dense stations are located within 5 km of national stations, indicating a highly clustered distribution pattern. Consequently, in regions beyond 25 km, the limited density of monitoring stations (only 15.29% of total dense stations) may compromise the accuracy of credibility calculations in these peripheral areas. The credible spatial range depicted in Figure 17, derived from the farthest dense station from national station with the R2 > 0.90, may have a certain margin of error.
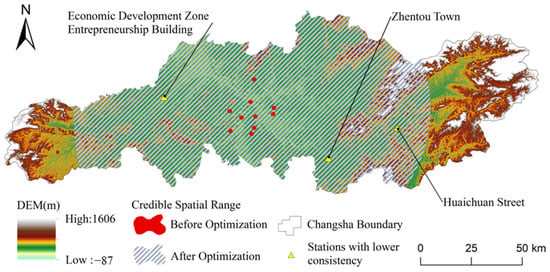
Figure 17.
Lower-consistency station locations and spatial distribution of credible coverage changes in remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data before and after optimization.
Moreover, the credibility of remotely sensed PM2.5 data is influenced by environmental factors such as terrain and land use. Even within the generally credible range, some stations (Figure 17) demonstrate relatively poor consistency due to such factors. In addition, in regions where dense stations are absent, particularly those far from national stations, the reliability of remotely sensed data remains unknown. To further assess and improve the credibility of remotely sensed PM2.5 data, it is recommended to enhance supplementary measurements.
4. Discussion
While the overall fitting degree between remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and ground-based data is strong, notable variations are observed across different stations, as demonstrated in Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7. Specifically, the remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data exhibit a high degree of consistency with the national station at the aggregate level (Figure 5), however, the consistency exhibits significant spatial heterogeneity across the national stations (Figure 6), and further declines when compared with dense station monitoring data (Figure 7).
One key reason for the reduced consistency at dense stations is the modeling data selection of the CHAP dataset. The model was constructed exclusively using data from national stations, which are relatively sparse and unevenly distributed, typically located in areas designed to represent broader regional air quality conditions. As a result, the consistency of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data can achieve a high degree on the national stations and their surroundings, but the learning and optimization of models are limited to these regional environments. When applied to dense stations, which are constructed in complex urban microenvironments and often influenced by emission sources such as traffic, cooking fumes, or nearby construction, the consistency deteriorates due to the different environment between national and dense stations.
The differences in model performance across individual stations may be due to the spatial heterogeneity of influencing factors. It is important to note that the CHAP dataset model was constructed at a large scale that primarily incorporates indicators such as aerosol optical depth (AOD), meteorological parameters, elevation, and normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) [15]. These variables are effective in capturing large scale variations in PM2.5 concentrations; however, they are less sensitive at the local scale. As noted in the introduction, PM2.5 distribution exhibits significant heterogeneity at finer spatial scales. But the model does not incorporate finer resolution variables such as the density and type of POI, road network distribution, or distance to local pollution sources, all of which can significantly affect PM2.5 concentration in local scale. The omission of these fine-scale variables in the modeling process may cause the variability in consistency across different monitoring stations, even within the same city.
Although the CHAP dataset demonstrates relatively high estimation accuracy among existing PM2.5 datasets (as shown in Table 1), notable uncertainties remain, primarily due to error propagation from aerosol optical depth (AOD) inversion. AOD plays a critical role in model accuracy. Studies have shown that a 1% systematic error in AOD can result in an approximate 0.27% error in PM2.5 estimation [15]. This effect is partly attributed to the limited ability of AOD to represent the vertical distribution of aerosols, particularly in regions with substantial variability in planetary boundary layer height or complex vertical pollution profiles [36]. Therefore, despite the superior overall performance of the CHAP product compared to similar datasets, its strong sensitivity to AOD, and the inherent limitations of AOD inversion remain major factors influencing the accuracy of PM2.5 estimations.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically evaluated the credibility of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and proposed an optimization strategy for enhancing its localized application in urban air quality monitoring. Results show that the fitting degree of PM2.5 concentration data from remote sensing and national station is relatively good, but there is some spatial variation between different stations. In regions outside the national station, the credibility of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data exhibits significant spatial heterogeneity, gradually declining with increasing distance from the national stations. Integrating dense station monitoring data with geographic environmental factors can effectively enhance the local fitting accuracy of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data and expand its credible range. These findings can effectively enhance the credibility of remotely sensed data, facilitating its application in high-resolution urban air pollution monitoring. This research provides both a foundation and a promising perspective for the potential replacement of certain ground-based stations as a primary monitoring approach and for the establishment of the integrated “air–space–ground” monitoring system in the future.
Although our study found that fusing dense station PM2.5 concentration data and geographic environmental factors can significantly improve the credibility of remotely sensed data in regions outside national stations, this research was validated only in Changsha city. Different cities exhibit variations in the number of dense stations, layout environments, pollution sources, and topography. Given these differences in pollution dispersion mechanisms, whether remotely sensed data credibility can be similarly improved through model optimization in other cities remains to be further verified [37,38].
Furthermore, while more dense stations can generate more precise and spatially comprehensive PM2.5 concentration monitoring, many cities lack the conditions to establish dense stations, because it would incur substantial financial burdens. These realities underscore the critical need to enhance the precision of remotely sensed data through optimal utilization of limited ground-based stations, thereby improving their local scale credibility for urban fine resolution air quality assessments.
Although the local fitting accuracy of remotely sensed PM2.5 concentration data can theoretically be improved through optimized models, it is important to acknowledge that remotely sensed data are not universally applicable due to current limitations in spatial resolution and revisit period. Specifically, this study identifies areas where the optimization model does not significantly improve the credibility of remotely sensed data, thereby necessitating supplementary ground-based monitoring. Additionally, remotely sensed data are ineffective during nighttime or under adverse weather conditions [39]. Given these constraints, a promising avenue for future research is the integration of remotely sensed data, ground-based data, and model-based simulations to enhance urban air quality monitoring.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.Z. and S.L.; Methodology, Z.Z.; Software, Z.Z.; Validation, Z.Z.; Formal analysis, Z.Z.; Investigation, Z.Z.; Resources, B.Z. and S.L.; Data curation, Z.Z.; Writing—original draft, Z.Z.; Writing—review & editing, B.Z. and S.L.; Visualization, Z.Z.; Project administration, B.Z. and S.L.; Funding acquisition, B.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42301497), National Natural Science Foundation of China (42271440), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFE0117100).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zou, B.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Wang, B.; Cao, S.; Zhao, X.; Peng, F.; Qin, N.; Guo, Q. Efforts in Reducing Air Pollution Exposure Risk in China: State versus Individuals. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ebenstein, A.; Greenstone, M.; Li, H. Evidence on the Impact of Sustained Exposure to Air Pollution on Life Expectancy from China’s Huai River Policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12936–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y. Review of Research on the Impacts of Atmospheric Pollution on the Health of Residents. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousis, I.; Manni, M.; Pisello, A.L. Environmental Mobile Monitoring of Urban Microclimates: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.; Xue, B.; Xu, Z.; Wu, J. Development of Ecological Environment Monitoring Network System in China. Strateg. Study Chin. Acad. Eng. 2024, 26, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Progress of environmental remote sensing monitoring technology in China and some related frontier issues. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Gao, C.; Cao, S.; Yan, L.; Meng, Z.; Tian, H.; Liu, M. Spatial representative evaluation of ambient air quality monitoring stations in the Yangtze River Delta: Taking PM2.5 as an example. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2021, 41, 4377–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, C.; Jiao, P. Estimation of nighttime PM2.5 concentration in Shanghai based on NPP/VIIRS Day_Night Band data. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2019, 39, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; He, H.-D.; Huang, H.-C.; Yang, J.-M.; Peng, Z.-R. High-Resolution Spatiotemporal Prediction of PM2.5 Concentration Based on Mobile Monitoring and Deep Learning. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 364, 125342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, K. Development of Urban Air Monitoring with High Spatial Resolution Using Mobile Vehicle Sensors. Environ. Monit Assess 2021, 193, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. An Atmospheric Correction Method for Ground-Based Radar Under Complex Environment. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 48, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, P.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Mao, H.; et al. Systematics of Atmospheric Environment Monitoring in China via Satellite Remote Sensing. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, F.T.; Shah, S.R.; Nidamanuri, R.R. Applications of Remote Sensing Vis-à-Vis Machine Learning in Air Quality Monitoring and Modelling: A Review. Environ. Monit. Assess 2023, 195, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salcedo-Bosch, A.; Zong, L.; Yang, Y.; Cohen, J.B.; Lolli, S. Forecasting Particulate Matter Concentration in Shanghai Using a Small-Scale Long-Term Dataset. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2025, 37, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-Km-Resolution High-Quality PM2.5 Data Records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal Variations and Policy Implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Li, K.; Ma, M.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Chang, N.-B.; Tan, Z.; Han, D. LGHAP: The Long-Term Gap-Free High-Resolution Air Pollutant Concentration Dataset, Derived via Tensor-Flow-Based Multimodal Data Fusion. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 907–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Hammer, M.S.; Bindle, L.; Brauer, M.; Brook, J.R.; Garay, M.J.; Hsu, N.C.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Kahn, R.A.; Lee, C.; et al. Monthly Global Estimates of Fine Particulate Matter and Their Uncertainty. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15287–15300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Geng, G.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Q. Spatiotemporal continuous estimates of daily 1-km PM2.5 from 2000 to present under the Tracking Air Pollution in China (TAP) framework. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 13229–13242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N. Seamless Fine Simulation and Forecast of Real-Time PM2.5 Concentration Using Mutlimodal Data Fusion. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Baodong, X.U.; Jing, L.I.; Qinhuo, L.I.U.; Xiaozhou, X.I.N.; Yelu, Z.; Gaofei, Y.I.N. Review of Methods for Evaluating Representativeness of Ground Station Observations. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 19, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Z. Estimations of PM2.5 concentrations based on the method of geographically weighted regression. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Park, R.J. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 Using Aerosol Optical Depth Determined from Satellite Remote Sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, N.; Zou, B.; Xiong, L. Uncertainty Analysis of Premature Death Estimation Under Various Open PM2.5 Datasets. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 934281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Boys, B.L. Use of Satellite Observations for Long-Term Exposure Assessment of Global Concentrations of Fine Particulate Matter. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, J.S.; Messier, K.P.; Gani, S.; Brauer, M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Lunden, M.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Portier, C.J.; Vermeulen, R.C.H.; Hamburg, S.P. High-Resolution Air Pollution Mapping with Google Street View Cars: Exploiting Big Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6999–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zou, B.; Li, S.; Duan, X.; Zhou, X. Spatial heterogeneity analysis of PM2.5 concentrations in intra-urban microenvironments. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zou, B.; Hu, C. Urban scene-oriented simulation of the spatial distribution of PM2.5 concentration in an intra-urban area at fine scale. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 4570–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, B.; Li, S.; Tian, R.; Zhang, B.; Feng, H.; Tang, Y. A Hierarchical Residual Correction-Based Hyperspectral Inversion Method for Soil Heavy Metals Considering Spatial Heterogeneity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 479, 135699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Waller, L.A.; Lyapustin, A. Estimating Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentrations in the Southeastern United States Using MAIAC AOD Retrievals and a Two-Stage Model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3095−2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Yan, X.; Zhang, G.; Feng, D.; Tian, Y.; Shen, S.; Yang, Z.; Dong, M.; Zhao, H. Data Correction of Grid Air Quality Monitor Based on CIWOA—BP Neural Network. Instrum. Tech. Sens. 2024, 55, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zou, B.; Liu, N.; Feng, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H. Simulation of PM2.5 Concentration Based on Optimized Indexes of 2D/3D Urban Form. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4425–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xie, B. A review of random forest methods. Stat. Inf. Forum 2011, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Shahriari, B.; Swersky, K.; Wang, Z.; Adams, R.P.; de Freitas, N. Taking the Human Out of the Loop: A Review of Bayesian Optimization. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 148–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R. A Study of Cross-Validation and Bootstrap for Accuracy Estimation and Model Selection. In Proceedings of the IJCAI’95: Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QB, Canada, 20 August 1995; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Martin, R.V.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Hammer, M.S.; Li, C.; Meng, J.; Oxford, C.R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; et al. Importance of Aerosol Composition and Aerosol Vertical Profiles in Global Spatial Variation in the Relationship between PM2.5 and Aerosol Optical Depth. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 11565–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, G.; Fu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Kong, X. Spatial Homogeneity-Aware Transfer Learning for Urban Flow Prediction. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2025, 67, 4349–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Feng, X.; He, Y. Transfer Learning Method for Plastic Pollution Evaluation in Soil Using NIR Sensor. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmajeed, A.Y.A.; Juszczak, R. Challenges and Limitations of Remote Sensing Applications in Northern Peatlands: Present and Future Prospects. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).