First In-Orbit Validation of Interferometric GNSS-R Altimetry: Mission Overview and Initial Results
Abstract
1. Introduction
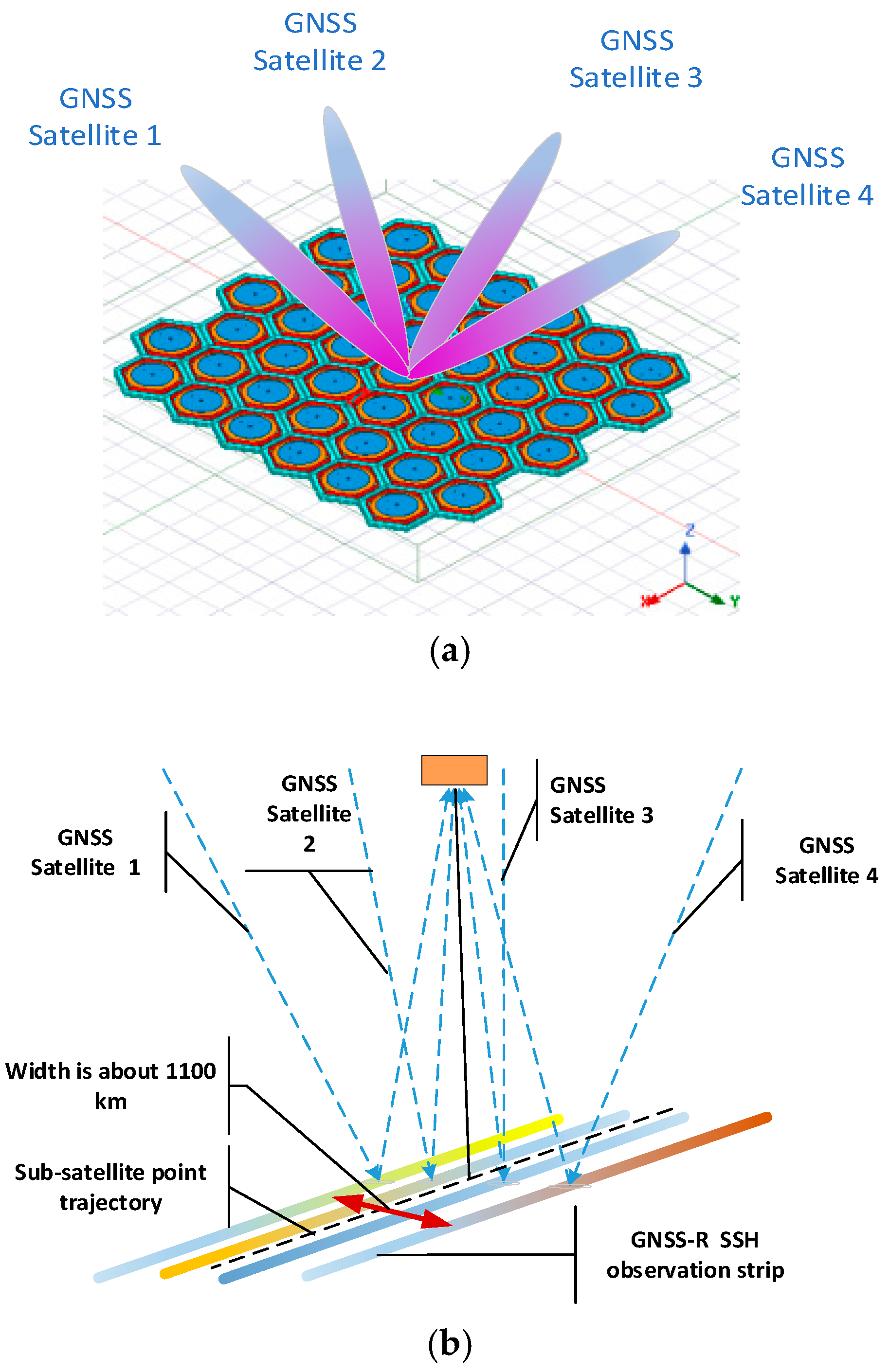
2. Mission Overview
2.1. Payload Design
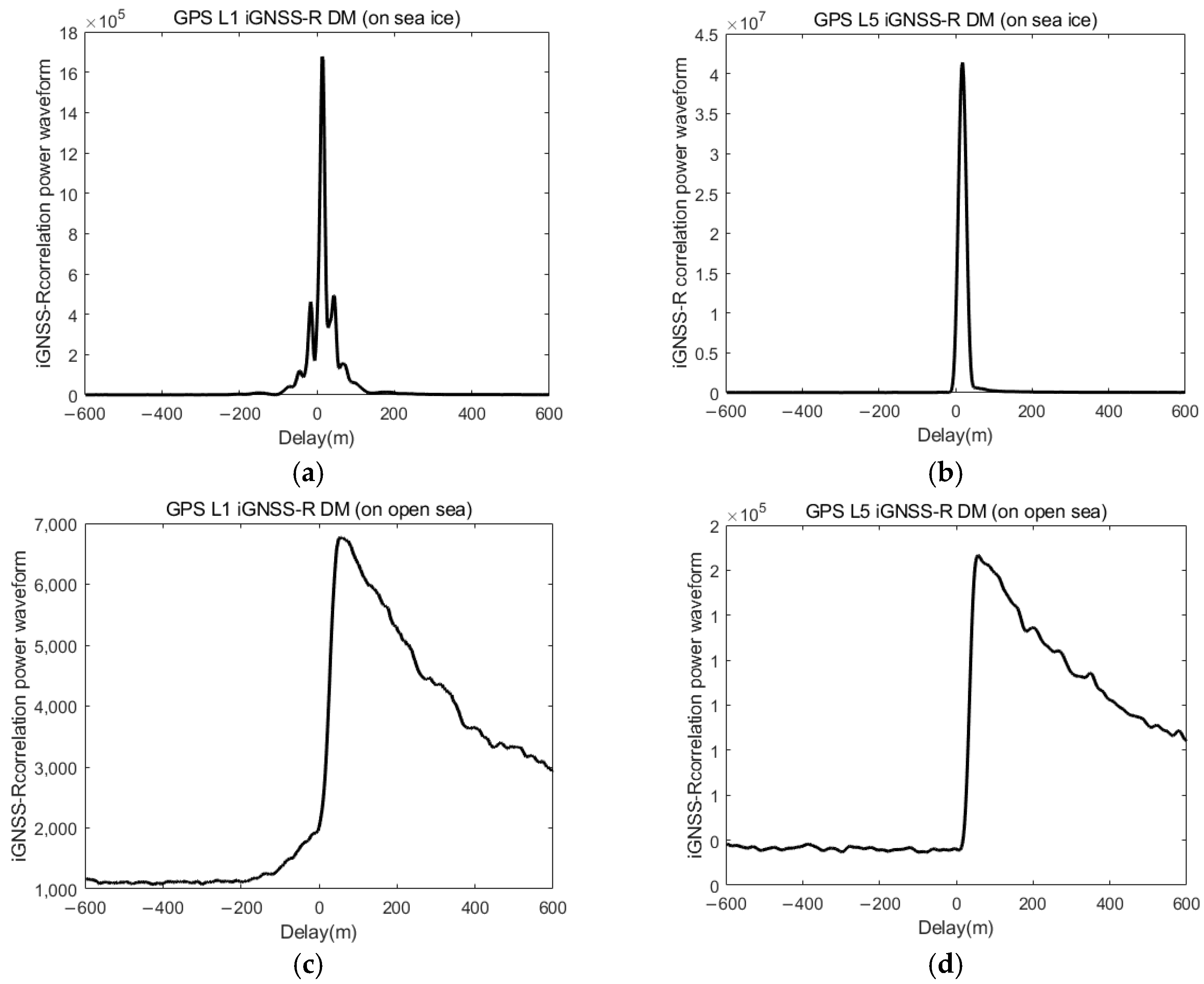
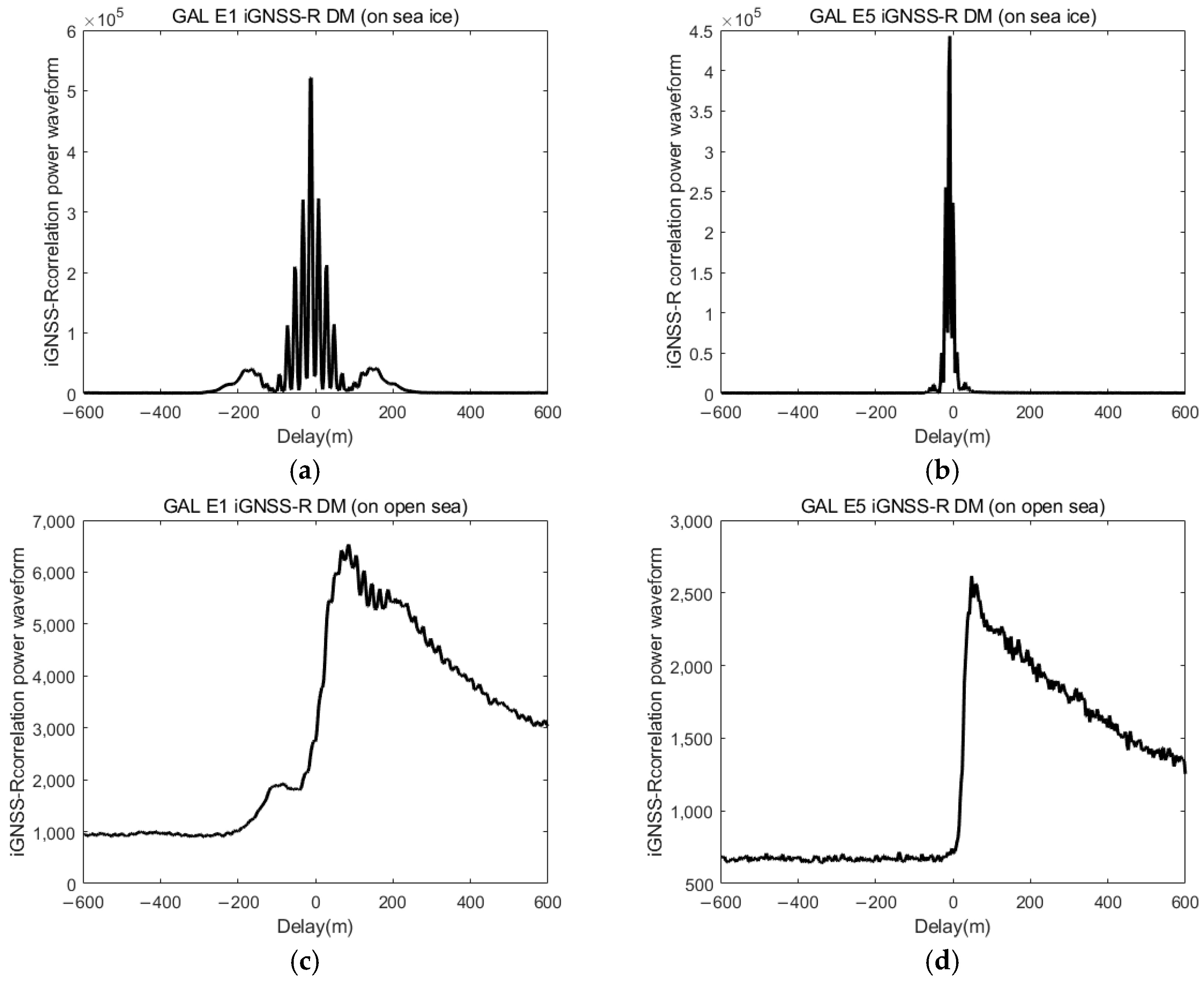
2.2. Interferometric Waveforms Description
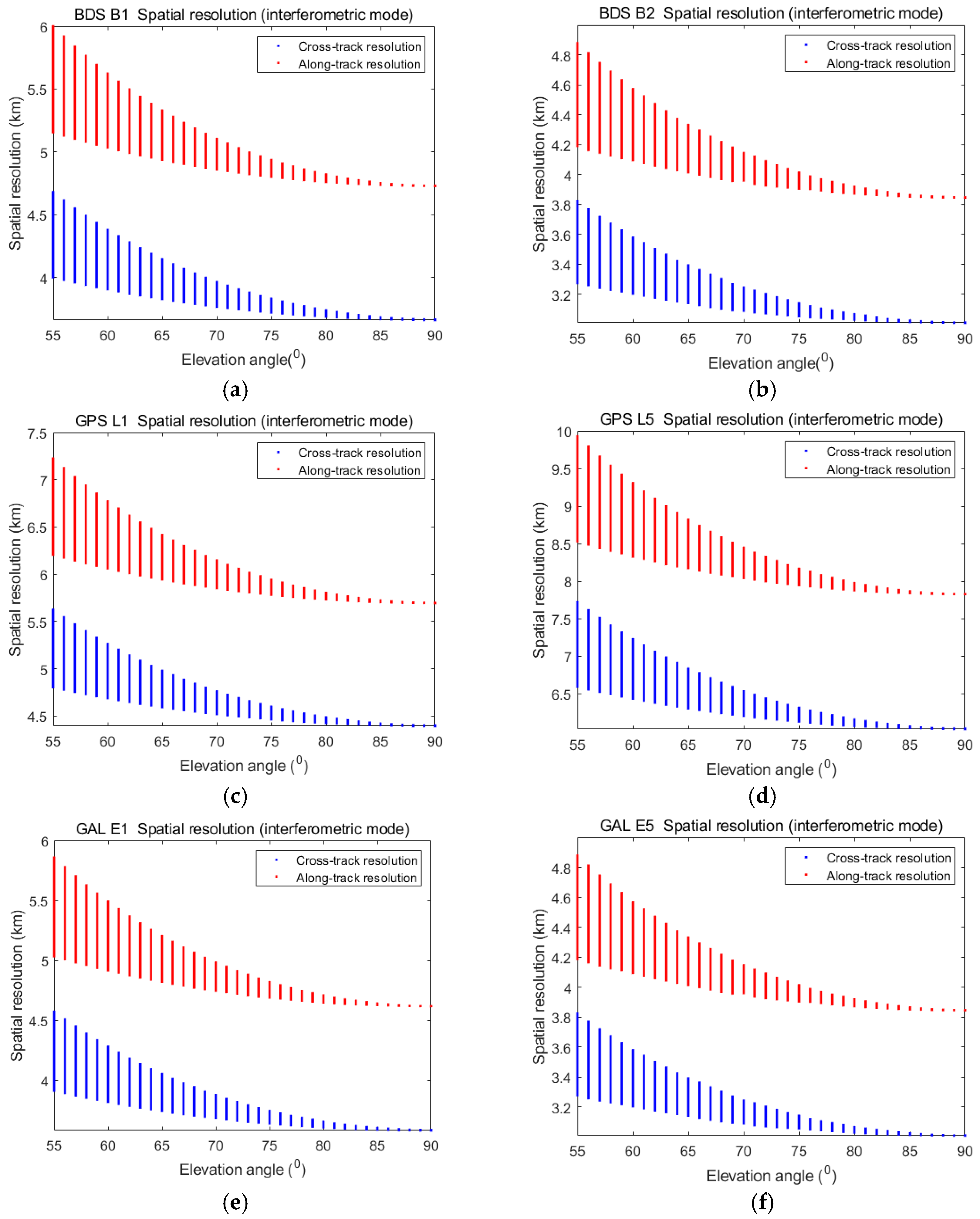
2.3. Spatial Resolution
2.4. iGNSS-R Sea Surface Height Retrieval
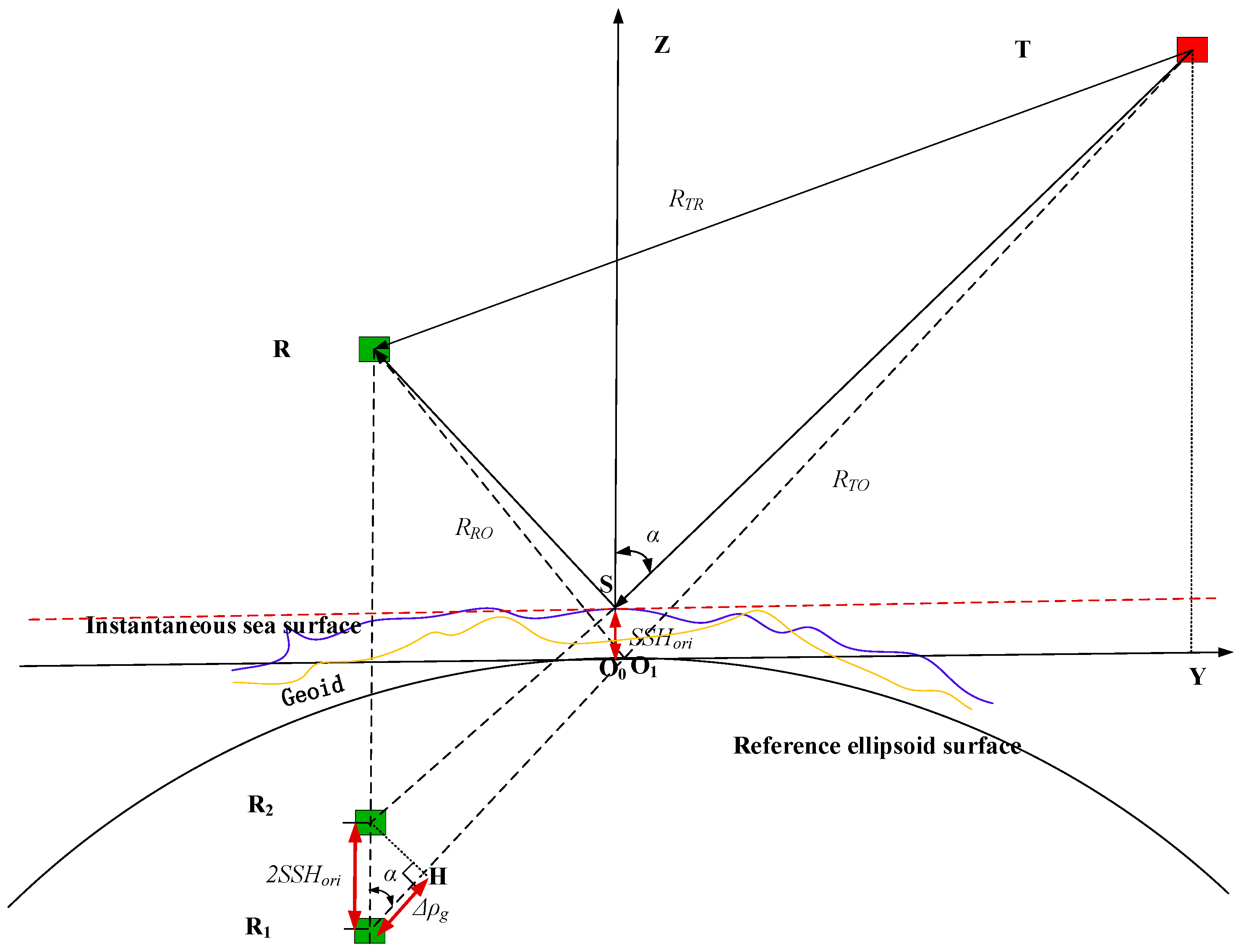
2.4.1. Geometry Model for iGNSS-R SSH Calculation
2.4.2. DM Waveform Matching
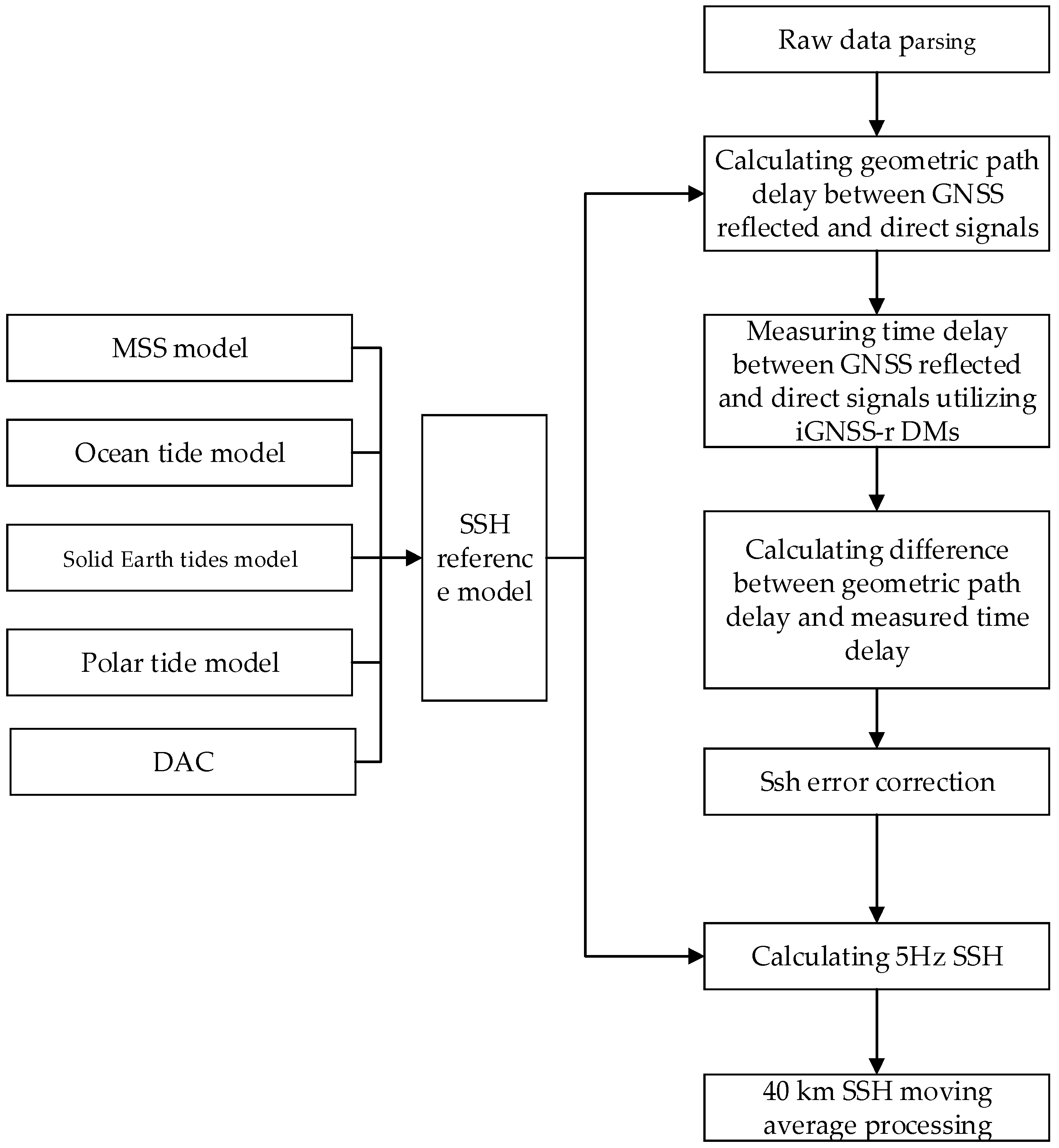
2.4.3. The Process of iGNSS-R SSH Retrieval
- (1)
- Data Parsing: Dual-frequency iGNSS-R DMs and auxiliary information are extracted from raw data packets.
- (2)
- Geophysical Path Delay Calculation: Utilizing the preliminary geolocation of the specular point calculated onboard, the SSH reference model is computed, incorporating the mean sea surface height, ocean tide, solid Earth tide, polar tide, and DAC. The specular point position is recalculated using the SSH reference model, precise GNSS ephemeris, and precise orbit determination files. Phase center corrections are applied to direct and reflected GNSS signals using satellite attitude information, and the geometry model delay difference between the GNSS reflected and direct signals is calculated.
- (3)
- Measuring Time Delay: The waveform-matching method is employed to determine the measured delay difference between GNSS reflected and direct signals. Corrections are applied, using a hardware delay lookup table, to the measured time delay difference between the reflected and direct GNSS signals.
- (4)
- Calculating the Delay Difference: The difference between the geophysical path delay and the measured time delay is calculated.
- (5)
- SSHori Error Correction and Calibration: The instantaneous sea surface height (SSHori) is calculated using (1). To eliminate the impact of ionospheric bias, a dual-frequency combination technique is employed. The dry and wet tropospheric delays are computed using the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) reanalysis data (temperature, humidity, and air pressure) through ray-tracing techniques that account for atmospheric variations along the reflection path. In [47,48], Ghavidel et al. utilized numerical simulations to calculate the electromagnetic (EM) bias of L-band waves using the physical optics (PO) method under the Kirchhoff approximation (KA). They examined the impacts of several factors, including the incidence angle, wind speed, rain, swell, and surface currents. Their findings indicate that significant wave height, sea surface wind speed, and the incidence angle are the main contributors to EM bias, with the effect of the incidence angle being well-described by a cosine function. Based on these results, we developed an EM bias lookup table to correct for sea state bias. After correcting for the aforementioned errors, the residual error compared with radar altimeter data are modeled according to the cosine function of the incidence angle to calibrate the SSHori.
- (6)
- Calculation of 5 Hz SSH: After SSHori error correction and calibration, the GOT4.10 model is used to correct for ocean tides. Polar tides, which are tidal phenomena caused by the centrifugal effect due to the motion of the Earth’s poles, are corrected using the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) polar tide model. Solid Earth tides are corrected using the tidal response analysis proposed in [49]. DAC is applied using the DAC data released by AVISO (https://www.aviso.altimetry.fr/en/data.html (accessed on 20 May 2025)).
- (7)
- 40 km SSH Moving Average Processing: Utilizing the 5 Hz SSH data, 40 km along-track averaging is implemented to achieve the final SSH products. The main steps of the along-track averaging are as follows: First, the difference between the 5 Hz sea surface height measurements and the corresponding mean sea surface height model is calculated. Next, this difference is smoothed to a 40 km resolution. Finally, the smoothed difference is added back to the mean sea surface height model value to obtain the 40 km sea surface height product.
2.5. Inter-Satellite Cross-Validation Method
2.5.1. iGNSS-R Altimeter Products
2.5.2. Jason-3 Satellite Radar Altimeter Products
2.5.3. Sensial-6 Satellite Radar Altimeter Products
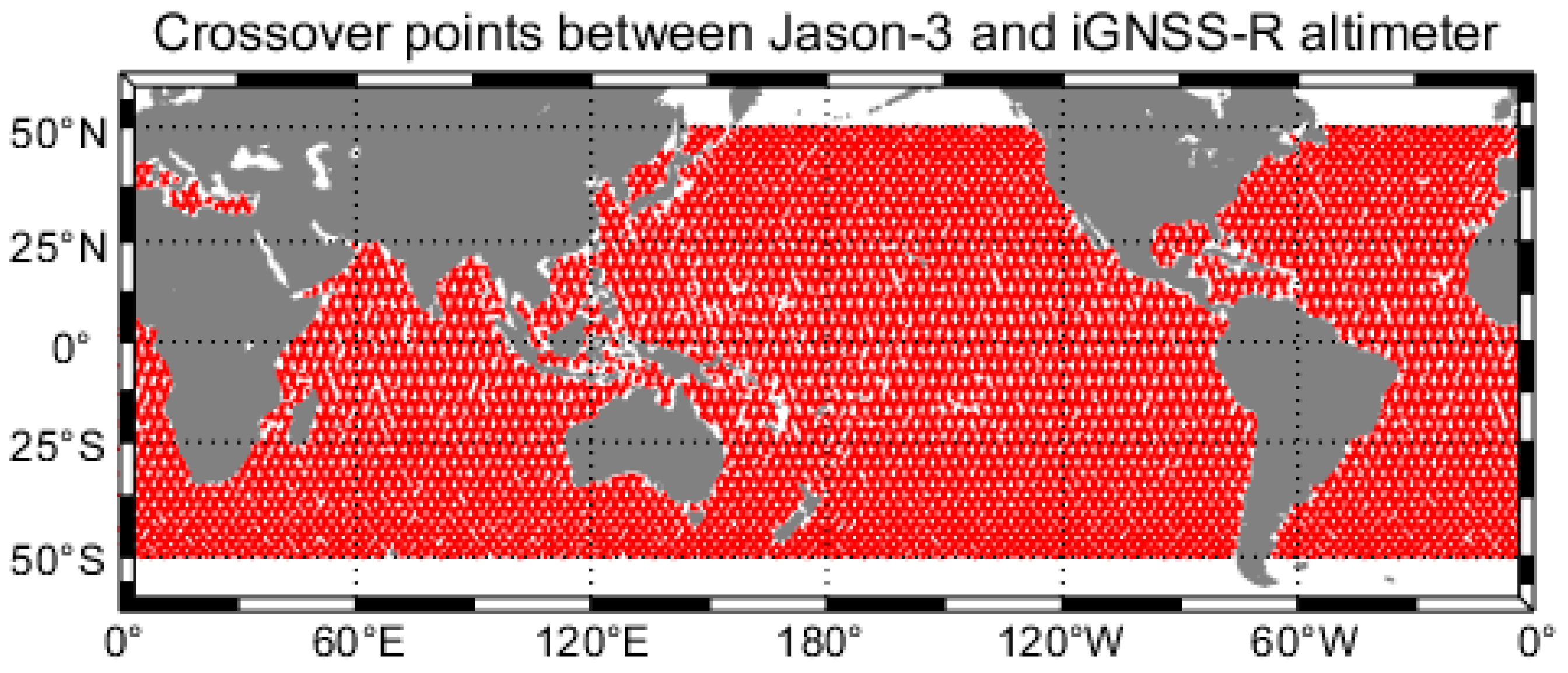
2.5.4. Crossover Data Calculation Method
3. Results
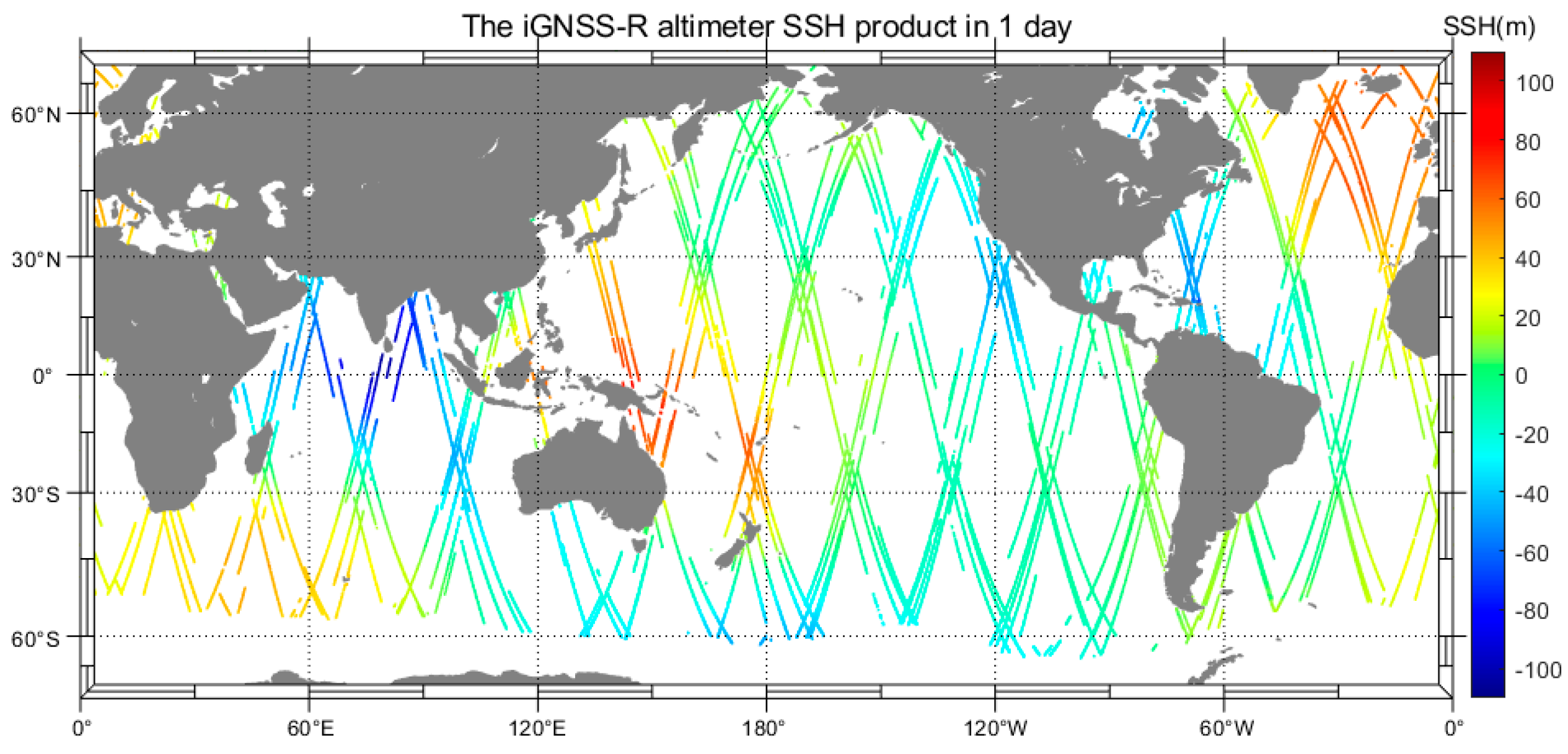
3.1. Routine Daily SSH Products from iGNSS-R Altimeter
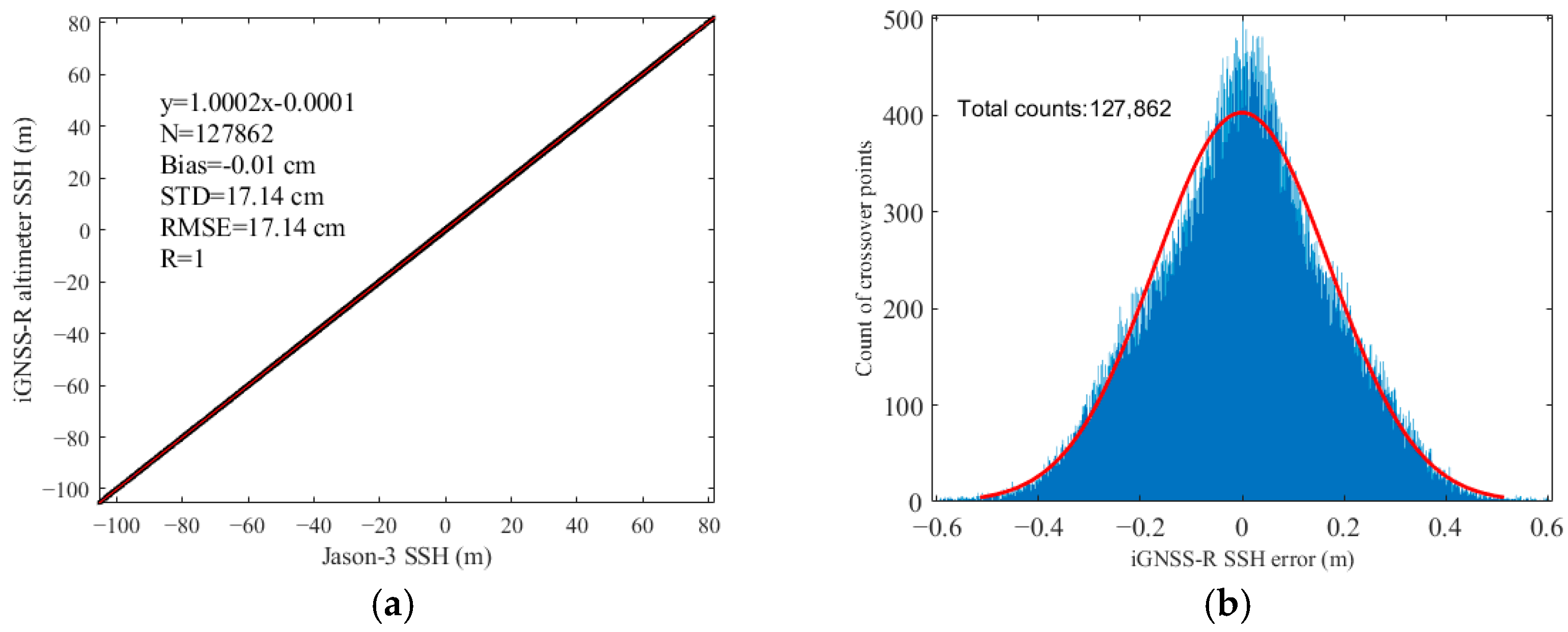
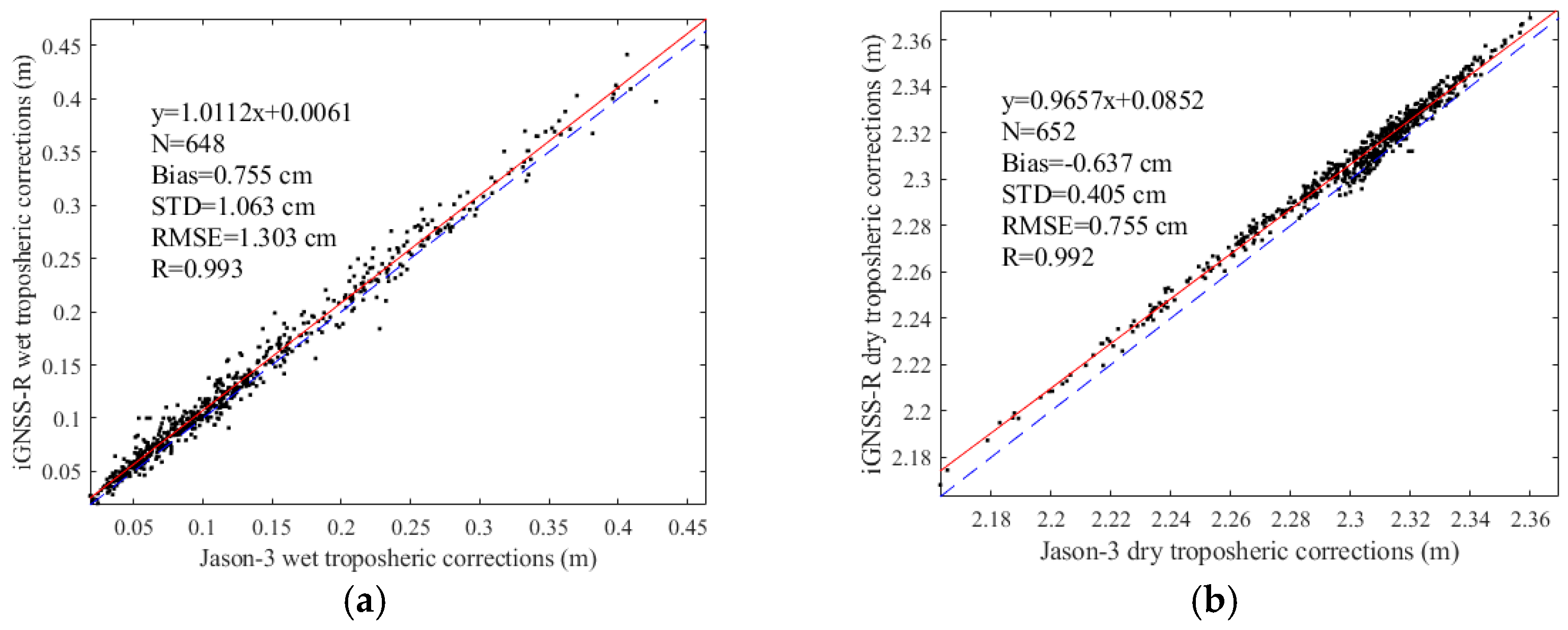
3.2. Intercomparisons with Jason-3 SSH Products
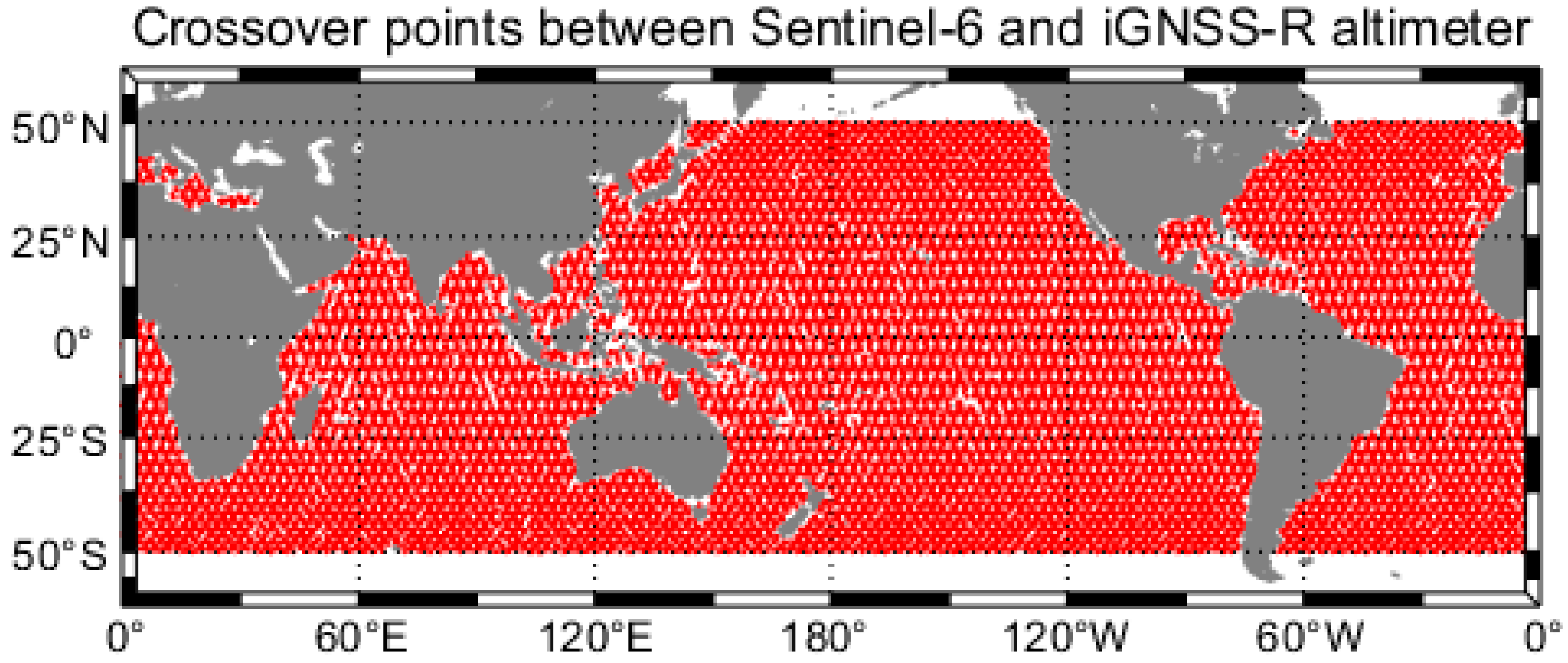
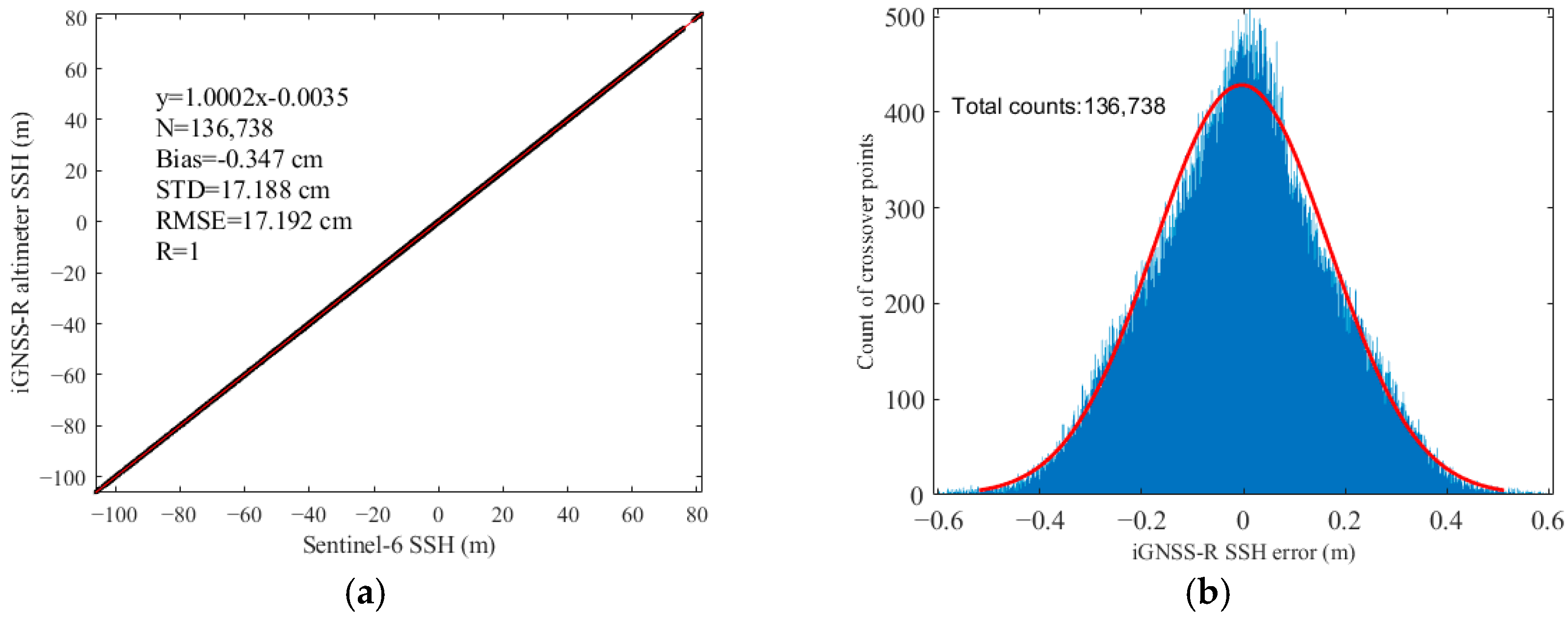
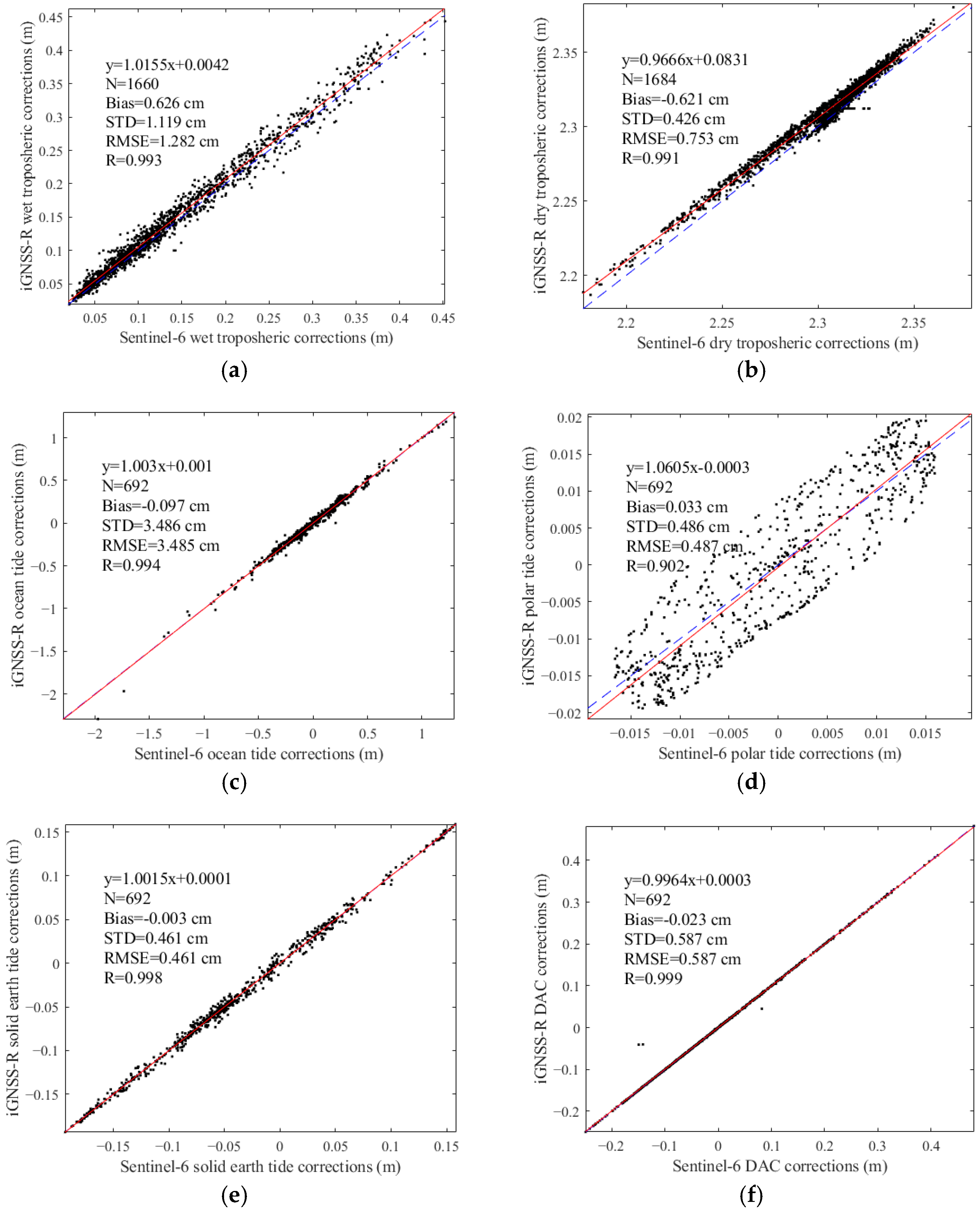
3.3. Intercomparisons with Sentinel-6 SSH Products
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SSH | sea surface height |
| GNSS | global navigation satellite system |
| GNSS-R | global navigation satellite system reflectometry |
| iGNSS-R | interferometric global navigation satellite system reflectometry |
| BDS | BeiDou Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| GAL | Galileo Satellite Navigation System |
| DM | delay mapping |
| SWOT | Surface Water and Ocean Topography |
| CYGNSS | Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System |
| SPIR | software-defined interferometric receiver |
| UPC | Technical University of Catalonia |
| MIR | microwave interferometric reflectometer |
| PARIS-IOD | Passive Reflectometry and Interferometry System In-Orbit Demonstration |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| ISS | International Space Station |
| GEROS-ISS | GNSS Reflectometry, Radio Occultation, and Scatterometry on the International Space Station |
| G-TERN | GNSS Transpolar Earth Reflectometry exploriNg |
| NSSC | National Space Science Center |
| CAS | Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| DDM | Delay–Doppler Mapping |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| C/A | Coarse/Acquisition |
| DAC | dynamic atmospheric correction |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| IERS | International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service |
| PO | physical optics |
| KA | Kirchhoff approximation |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| EUMETSAT | European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites |
| CNES | Centre National d’Études Spatiales |
| GDR | Geophysical Data Records |
| NRT | Near-Real-Time |
| STC | Short-Time-Critical |
| NTC | Non-Time-Critical |
| STD | standard deviation |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| R | correlation coefficient |
References
- Srinivasan, M.; Tsontos, V. Satellite Altimetry for Ocean and Coastal Applications: A Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lin, L.N.; Fan, L.; Liu, N.; Huang, L.Y.; Xu, Y.S.; Mertikas, S.P.; Jia, Y.J.; Lin, M.S. Satellite Altimetry: Achievements and Future Trends by a Scientometrics Analysis. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Q.; Xu, N.; Wang, M.R.; Liu, T.; Lu, H.; Cao, Y.Q.; Tang, X.M.; Mo, F.; Chang, H.Y.; Gong, H.Y.; et al. SWOT satellite for global hydrological applications: Accuracy assessment and insights into surface water dynamics. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2472924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Neira, M.; D’Addio, S.; Buck, C.; Floury, N.; Prieto-Cerdeira, R. The PARIS Ocean Altimeter In-Orbit Demonstrator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2209–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.X.; Xia, J.M.; Yin, C.; Zhai, X.C.; Yang, G.L.; Bai, W.H.; Sun, Y.Q.; Du, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Qiu, T.S.; et al. Spaceborne GNSS Reflectometry With Galileo Signals on FY-3E/GNOS-II: Measurements, Calibration, and Wind Speed Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 3501505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.; Al-Khaldi, M.; Asharaf, S.; Balasubramaniam, R.; Mckague, D.; Pascual, D.; Russel, A.; Twigg, D.; Warnock, A. Characterization of CYGNSS Ocean Surface Wind Speed Products. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, D.K.; Yang, L. Retrieval and Assessment of Significant Wave Height from CYGNSS Mission Using Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Du, Q.F.; Xia, J.M.; Huang, F.X.; Yin, C.; Meng, X.F.; Bai, W.H.; Sun, Y.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Duan, L.C.; et al. Comparative Analysis of SWH Retrieval Between BDS-R and GPS-R Utilizing FY-3E/GNOS-II Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 6520–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Cardellach, E.; Fabra, F.; Ribo, S.; Rius, A. Assessment of Spaceborne GNSS-R Ocean Altimetry Performance Using CYGNSS Mission Raw Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Han, Y.L.; Yang, S.H.; Hong, Z.H.; Ma, D.H.; Meng, W.T. Machine Learning Methods for Spaceborne GNSS-R Sea Surface Height Measurement From TDS-1. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Hua, X.F.; Yan, Q.Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wickert, J. Sea Ice Detection from GNSS-R Data Based on Local Linear Embedding. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Xia, J.M.; Huang, F.X.; Li, W.; Bai, W.H.; Sun, Y.Q.; Liu, C.L.; Yang, G.L.; Hu, X.Q.; Xiao, X.J.; et al. Sea Ice Detection with Fy3e Gnos Ii Gnss Reflectometry. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Specialist Meeting on Reflectometry Using GNSS and Other Signals of Opportunity 2021 (Gnss+R 2021), Virtual, 14–17 September 2021; pp. 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Yan, Q.Y.; Huang, W.M. Retrieval of sea ice thickness from FY-3E data using Random Forest method. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.J.; Yan, Q.Y. Retrieval of sea ice thickness using FY-3E/GNOS-II data. Satell. Navig 2024, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.J.; Zhu, Y.C.; Qu, X.C.; Tao, T.Y. Spaceborne GNSS-R for Sensing Soil Moisture Using CYGNSS Considering Land Cover Type. Water Resour. Manag. 2025, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Huang, F.X.; Xia, J.M.; Bai, W.H.; Sun, Y.Q.; Yang, G.L.; Zhai, X.C.; Xu, N.; Hu, X.Q.; Zhang, P.; et al. Soil Moisture Retrieval from Multi-GNSS Reflectometry on FY-3E GNOS-II by Land Cover Classification. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, M.P.; Ruf, C.; Cipollini, P.; Zuffada, C. First spaceborne observation of sea surface height using GPS-Reflectometry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, E.; Mashburn, J.; O’Brien, A.; Axelrad, P.; Zuffada, C.; Li, Z.J. Towards an Ocean Altimetry Product Using CYGNSS. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 8700–8702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Johnson, J.T.; O’Brien, A.; Lowe, S.T. Studies of Tds-1 GNSS-R Ocean Altimetry Using a “Full Ddm” Retrieval Approach. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 5625–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Wu, F.; Xu, A.G.; Zhu, H.Z.; Liu, Z.Q. A New GNSS-R Altimetry Algorithm Based on Machine Learning Fusion Model and Feature Optimization to Improve the Precision of Sea Surface Height Retrieval. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 730565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Jin, Q.; Meng, W.T.; Yang, S.H.; Huang, S.; Han, Y.L.; Hong, Z.H.; Chen, Z.S.; Liu, W.L. Global Sea Surface Height Measurement From CYGNSS Based on Machine Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendia, R.N.; Tabibi, S.; Francis, O. Exploring grazing angle GNSS-R for precision altimetry: A comparative study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 318, 114604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Li, W.Q.; Wan, W.; Lu, F.; Niu, X.L.; Chen, X.W.; Rius, A.; Cardellach, E.; Ribó, S.; Liu, B.J.; et al. A review of the BuFeng-1 GNSS-R mission: Calibration and validation results of sea surface and land surface. Geo.-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 27, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Neira, M. Considerations on Gnss-R Carrier Phase Altimetry. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 8299–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellach, E.; Li, W.Q.; Rius, A.; Semmling, M.; Wickert, J.; Zus, F.; Ruf, C.S.; Buontempo, C. First Precise Spaceborne Sea Surface Altimetry With GNSS Reflected Signals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.A.; Nogués-Correig, O.; Yuasa, T.; Masters, D.; Irisov, V. Initial GNSS Phase Altimetry Measurements From the Spire Satellite Constellation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, A.; Park, H.; Domènech, E.V.I.; Pascual, D.; Martin, F.; Rius, A.; Ribo, S.; Benito, J.; Andrés-Beivide, A.; Saameno, P.; et al. Optimization and Performance Analysis of Interferometric GNSS-R Altimeters: Application to the PARIS IoD Mission. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1436–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, A.; Pascual, D.; Park, H.; Martin, F.; Rius, A.; Ribo, S.; Benito, J.; Andrés, A.; Saameno, P.; Staton, G.; et al. Altimetry Performance and Error Budget of the PARIS In-Orbit Demonstration Mission. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addio, S.; Martín, F.; Park, H.; Camps, A.; Martin-Neira, M. Height Precision Prediction of the Paris in Orbit Demonstrator Based on Cramer-Rao Bound Analysis. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 7063–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addio, S.; Martin-Neira, M.; Buck, C. End-to-End Performance Analysis of a Paris in-Orbit Demostrator Ocean Altimeter. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 4387–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Zuffada, C.; Lowe, S.T.; Lee, T.; Zlotnicki, V. Analysis of GNSS-R Altimetry for Mapping Ocean Mesoscale Sea Surface Heights Using High-Resolution Model Simulations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4631–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, A.; Park, H.; Sekulic, I.; Rius, J.M. GNSS-R Altimetry Performance Analysis for the GEROS Experiment on Board the International Space Station. Sensors 2017, 17, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellach, E.; Wickert, J.; Baggen, R.; Benito, J.; Camps, A.; Catarino, N.; Chapron, B.; Dielacher, A.; Fabra, F.; Flato, G.; et al. GNSS Transpolar Earth Reflectometry exploriNg System (G-TERN): Mission Concept. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 13980–14018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stosius, R.; Beyerle, G.; Helm, A.; Hoechner, A.; Wickert, J. Simulation of space-borne tsunami detection using GNSS-Reflectometry applied to tsunamis in the Indian Ocean. Nat. Hazard Earth Syst. 2010, 10, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.G. Weak Tsunami Detection Using GNSS-R-Based Sea Surface Height Measurement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogués-Correig, O.; Ribó, S.; Arco, J.C.; Cardellach, E.; Rius, A.; Valencia, E.; Tarongí, J.M.; Camps, A.; van der Marel, H.; Martín-Neira, M. The Proof of Concept for 3-Cm Altimetry Using the Paris Interferometric Technique. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3620–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius, A.; Nogués-Correig, O.; Ribó, S.; Cardellach, E.; Oliveras, S.; Valencia, E.; Park, H.; Tarongí, J.M.; Camps, A.; van der Marel, H.; et al. Altimetry with GNSS-R interferometry: First proof of concept experiment. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellach, E.; Rius, A.; Martín-Neira, M.; Fabra, F.; Nogués-Correig, O.; Ribó, S.; Kainulainen, J.; Camps, A.; D’Addio, S. Consolidating the Precision of Interferometric GNSS-R Ocean Altimetry Using Airborne Experimental Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4992–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribó, S.; Arco-Fernández, J.C.; Nogués-Correig, O.; Fabra, F.; Cardellach, E.; Rius, A.; Martín-Neira, M. The Software Paris Interferometric Receiver. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 5593–5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, D.; Onrubia, R.; Querol, J.; Alonso-Arroyo, A.; Park, H.; Camps, A. First Delay Doppler Maps Obtained with the Microwave Inteferometric Reflectometer (Mir). Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 1993–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogues, O.C.I.; Munoz-Martin, J.F.; Park, H.; Camps, A.; Onrubia, R.; Pascual, D.; Rüdiger, C.; Walker, J.P.; Monerris, A. Improved GNSS-R Altimetry Methods: Theory and Experimental Demonstration Using Airborne Dual Frequency Data from the Microwave Interferometric Reflectometer (MIR). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickert, J.; Cardellach, E.; Martín-Neira, M.; Bandeiras, J.; Bertino, L.; Andersen, O.B.; Camps, A.; Catarino, N.; Chapron, B.; Fabra, F.; et al. GEROS-ISS: GNSS REflectometry, Radio Occultation, and Scatterometry Onboard the International Space Station. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4552–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Neira, M.; Li, W.Q.; Andrés-Beivide, A.; Ballesteros-Sels, X. “Cookie”: A Satellite Concept for GNSS Remote Sensing Constellations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4593–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, S.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Yang, R.; Du, Q.; Huang, Z. Accurate verification and evaluation of on-board GNSS-R interferometric altimetry under on-shore conditions. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2024, 53, 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, J.; Xue, S.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Luo, Z.; et al. Research progress of geodesy in China (2019–2023). Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2023, 52, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, W.H.; Xia, J.M.; Zhao, D.Y.; Sun, Y.Q.; Meng, X.G.; Liu, C.L.; Du, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, D.W.; Wu, D.; et al. Greeps: An Gnss-R End-to-End Performance Simulator. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 4831–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavidel, A.; Camps, A. Impact of Rain, Swell, and Surface Currents on the Electromagnetic Bias in GNSS-Reflectometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4643–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavidel, A.; Schiavulli, D.; Camps, A. Numerical Computation of the Electromagnetic Bias in GNSS-R Altimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, D.E.; Edden, A.C. Corrected Tables of Tidal Harmonics. Geophys. J. Int. 1973, 33, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.W.; Jia, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.G. Measurement analyses and evaluations of sea-level heights using the HY-2A satellite’s radar altimeter. Acta Ocean. Sin. 2019, 38, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, F.; Camps, A.; Park, H.; D’Addio, S.; Martín-Neira, M.; Pascual, D. Cross-Correlation Waveform Analysis for Conventional and Interferometric GNSS-R Approaches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, F.; D’Addio, S.; Camps, A.; Martín-Neira, M. Modeling and Analysis of GNSS-R Waveforms Sample-to-Sample Correlation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Pascual, D.; Camps, A.; Martin, F.; Alonso-Arroyo, A.; Carreno-Luengo, H. Analysis of Spaceborne GNSS-R Delay-Doppler Tracking. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Valencia, E.; Camps, A.; Rius, A.; Ribó, S.; Martín-Neira, M. Delay Tracking in Spaceborne GNSS-R Ocean Altimetry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, D.; Park, H.; Camps, A.; Arroyo, A.A.; Onrubia, R. Simulation and Analysis of GNSS-R Composite Waveforms Using GPS and Galileo Signals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Arroyo, A.; Querol, J.; Lopez-Martinez, C.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Park, H.; Pascual, D.; Onrubia, R.; Camps, A. SNR and Standard Deviation of cGNSS-R and iGNSS-R Scatterometric Measurements. Sensors 2017, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Q.; Rius, A.; Fabra, F.; Cardellach, E.; Ribó, S.; Martín-Neira, M. Revisiting the GNSS-R Waveform Statistics and Its Impact on Altimetric Retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2854–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, D.; Camps, A.; Martin, F.; Park, H.; Arroyo, A.A.; Onrubia, R. Precision Bounds in GNSS-R Ocean Altimetry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Frequency | GPS L1/L5, BDSB1/B2, GAL E1/E5 |
| Beam | 16 (4 direct L1/B1/E1, 4 direct L5/E5/B2, 4 reflected L1/B1/E1, 4 reflected L5/E5/B2) |
| DMs | 5 Hz 448 delay tags Delay coverage: ±600 m Delay tag interval: 2.6767 m (112 MHz) |
| Coherent time | 1 ms |
| Incoherent times | 200 |
| Band width | B1: 32 MHz, B2: 44 MHz L1: 26 MHz, L5: 20 MHz E1: 32 MHz, E5: 44 MHz |
| Validation Parameters | STD (cm) | Bias (cm) | RMSE (cm) | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSH | 17.140 | −0.010 | 17.140 | 1 |
| Wet tropospheric delay * | 1.063 | 0.755 | 1.303 | 0.993 |
| Dry tropospheric delay * | 0.405 | −0.637 | 0.755 | 0.992 |
| Ocean tide | 3.225 | −0.219 | 3.230 | 0.994 |
| Polar tide | 0.492 | −0.003 | 0.492 | 0.902 |
| Solid earth tide | 0.435 | −0.002 | 0.434 | 0.998 |
| DAC | 0.390 | −0.013 | 0.390 | 1 |
| Validation Parameters | STD (cm) | Bias (cm) | RMSE (cm) | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSH | 17.188 | −0.347 | 17.192 | 1 |
| Wet tropospheric delay * | 1.119 | 0.626 | 1.282 | 0.993 |
| Dry tropospheric delay * | 0.426 | −0.621 | 0.753 | 0.991 |
| Ocean tide | 3.486 | −0.097 | 3.485 | 0.994 |
| Polar tide | 0.486 | 0.033 | 0.487 | 0.902 |
| Solid Earth tide | 0.461 | −0.003 | 0.461 | 0.998 |
| DAC | 0.587 | −0.023 | 0.587 | 0.999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xia, J.; Huang, L.; Du, Q.; Bai, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Cai, Y.; Duan, L.; et al. First In-Orbit Validation of Interferometric GNSS-R Altimetry: Mission Overview and Initial Results. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111820
Sun Y, Sun Y, Xia J, Huang L, Du Q, Bai W, Wang X, Wang D, Cai Y, Duan L, et al. First In-Orbit Validation of Interferometric GNSS-R Altimetry: Mission Overview and Initial Results. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(11):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111820
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yixuan, Yueqiang Sun, Junming Xia, Lingyong Huang, Qifei Du, Weihua Bai, Xianyi Wang, Dongwei Wang, Yuerong Cai, Lichang Duan, and et al. 2025. "First In-Orbit Validation of Interferometric GNSS-R Altimetry: Mission Overview and Initial Results" Remote Sensing 17, no. 11: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111820
APA StyleSun, Y., Sun, Y., Xia, J., Huang, L., Du, Q., Bai, W., Wang, X., Wang, D., Cai, Y., Duan, L., Zhai, Z., Guan, B., Huang, Z., Li, S., Huang, F., Yin, C., & Liu, R. (2025). First In-Orbit Validation of Interferometric GNSS-R Altimetry: Mission Overview and Initial Results. Remote Sensing, 17(11), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17111820






