Study on the Aquaculture of Large Yellow Croaker in the Coastal Zone of Zhejiang Province Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
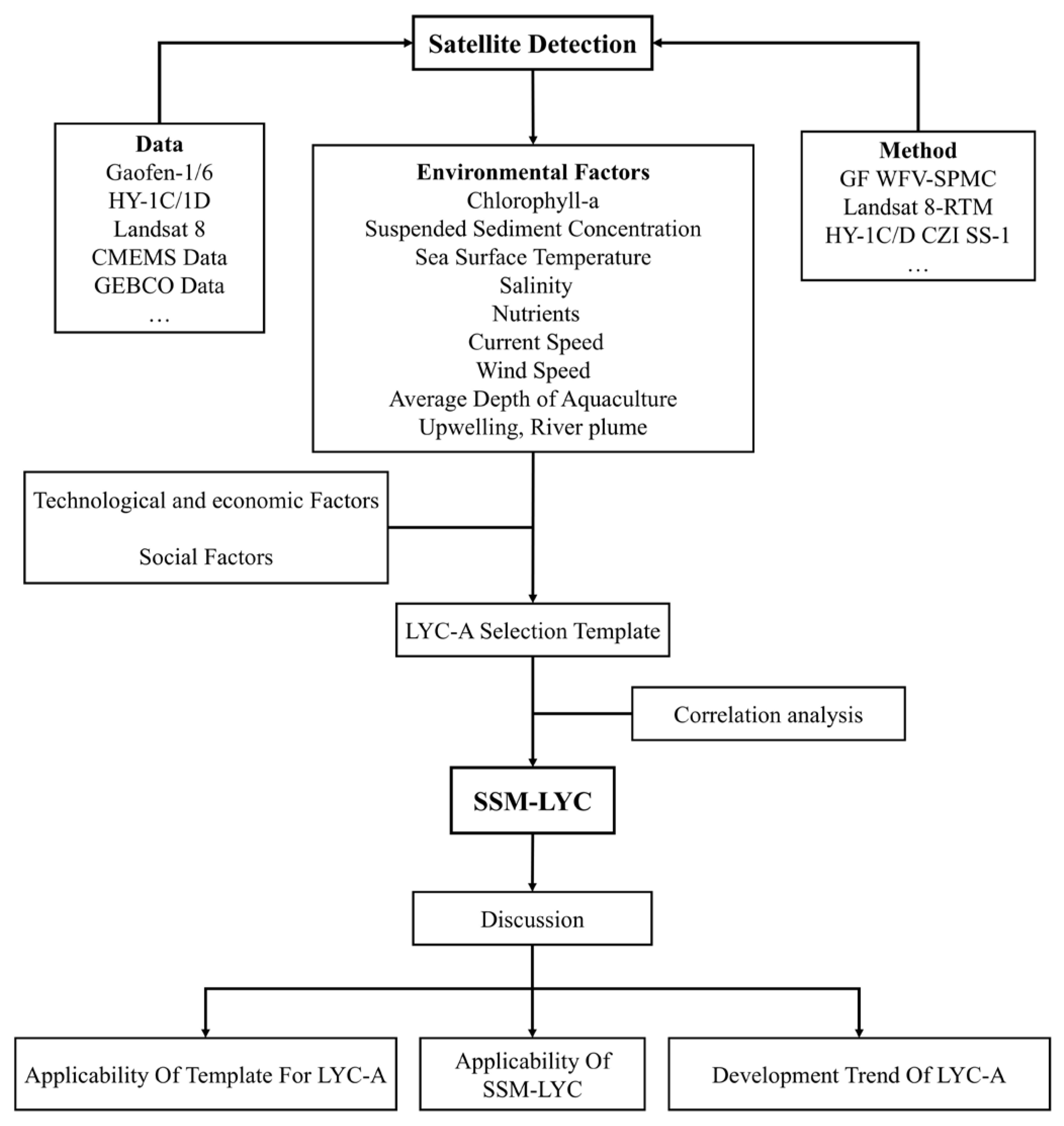
2. Data and Methods
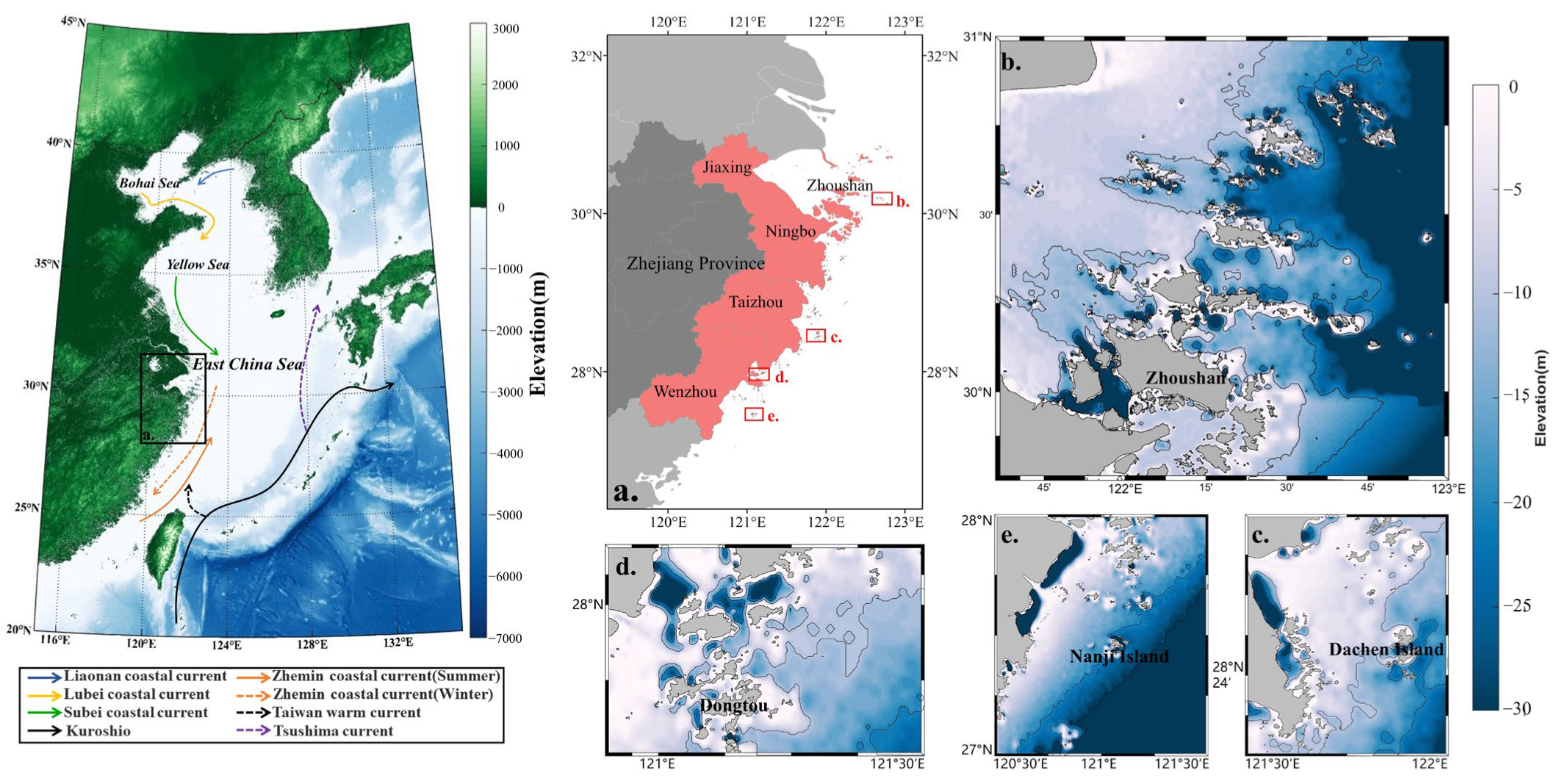
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite Data
2.2.1. HY-1C/HY-1D
2.2.2. Gaofen (GF) Series Satellite
2.2.3. Landsat 8
2.2.4. Other Sources of Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Large Yellow Croaker Culture Area Extraction: FRI 2 (Fishery Ranching Index 2)
2.3.2. New Site Selection Method for Large Yellow Croaker (SSM-LYC)
2.3.3. Satellite Inversion Method of Extracting Environmental Factors
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Large Yellow Croaker Aquaculture Area (LYC-A)
3.2. Template of Environmental Factors for LYC-A
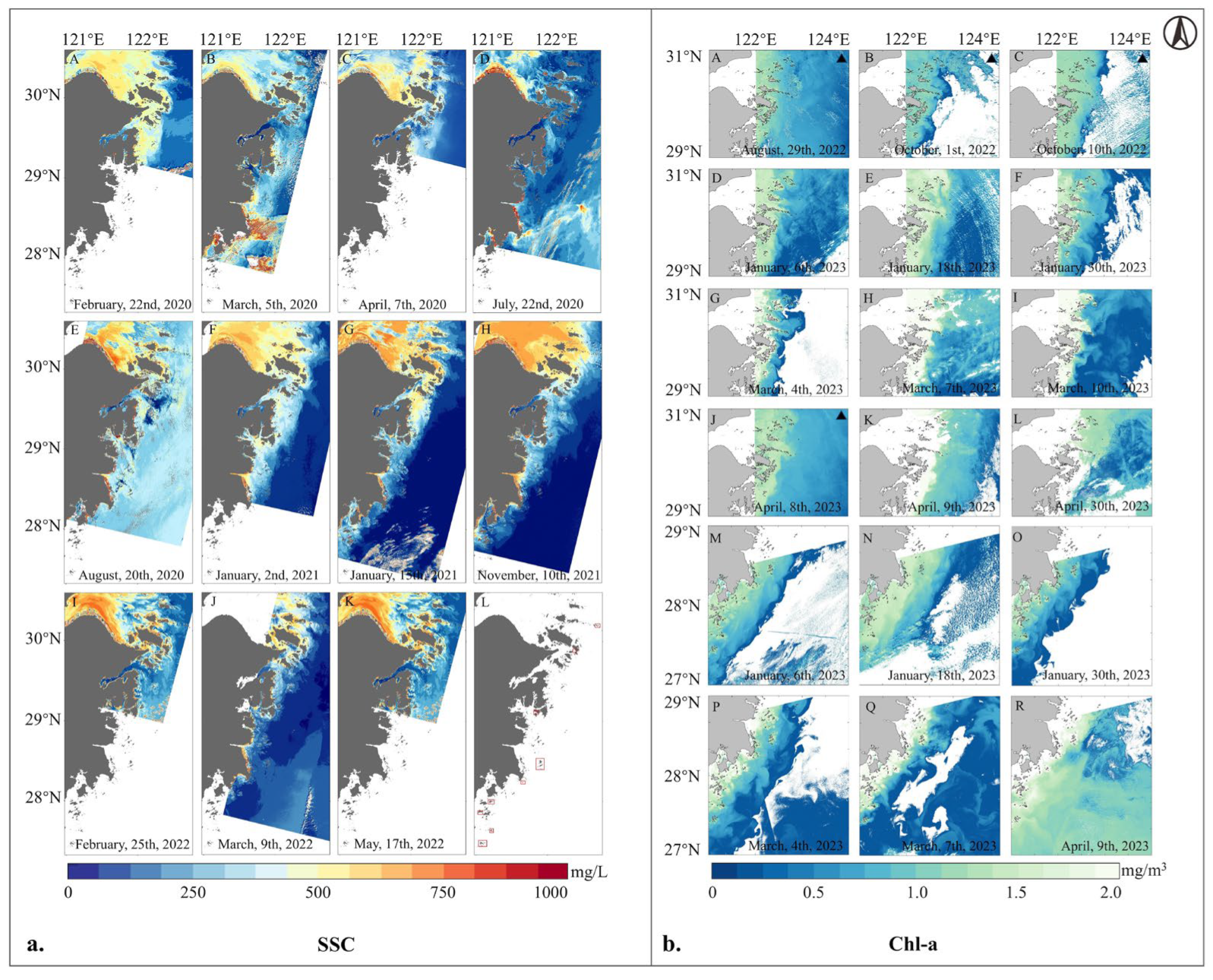
3.2.1. Water Color Factors Contributing to the Template for LYC-A
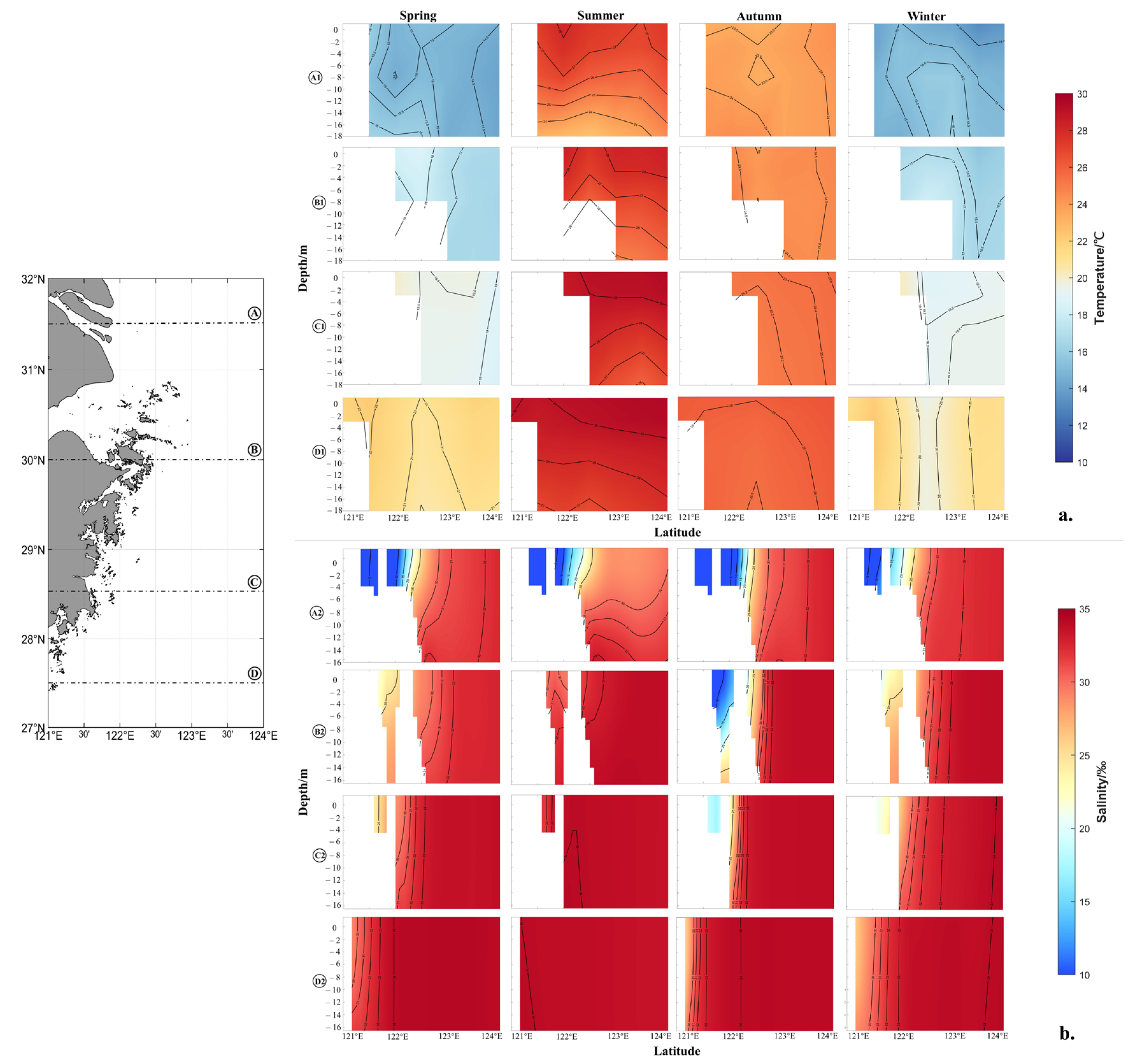
3.2.2. Marine Hydrological Factors Contributing to the Template for LYC-A
3.2.3. The Value of the Template for LYC-A
3.3. Potential Large Yellow Croaker Cage Aquaculture Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Applicability of Template of LYC-A
4.1.1. The Rationality Selection of Environmental Factors in the Template
4.1.2. Other Factors in the Template
4.2. Applicability of Site Selection Method for Large Yellow Croaker (SSM-LYC)
4.3. The Development Trend of Potential LYC-A from near Shore to Deep-Sea and Far-Sea
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ting, Y.L.; Yan, J.; Qing, X.; Mao, D.G.; Yi, C.X.; Min, L. Reproductive Dynamics of the Large Yellow Croaker Larimichthys crocea (Sciaenidae), A Commercially Important Fishery Species in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 868580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Analysis on the causes of resource change and reconstruction strategy of Daiqu large yellow croaker in East China Sea. J. Fish. China 2022, 46, 616–625. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, X. Reasons of Exhaustion of Resources of Pseudosciaenacrocea in Zhoushan Fishing Ground andthe Measures of Protection and Proliferation. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2002, 21, 160–165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aixia, D.; Yier, H. Experiment on breeding of large yellow croaker of Daiqu nationality in Zhoushan. China Fish. 2010, 2, 67–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hong, W.; Chen, X. Stock changes and resource protection of the large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) and ribbon fish (Trichiurus japonicus) in coastal waters of China. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2017, 36, 8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; You, G.; Kong, Z.; Xi, X.; Lei, L.; Zhao, D. Information Extraction of Sea-Enclosed Aquaculture Based on Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Images. Coast. Eng. 2022, 41, 173–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; You, S.; Zhang, S.; Cao, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Bi, X.; Gao, F.; Li, F. Marine aquaculture mapping using GF-1 WFV satellite images and full resolution cascade convolutional neural network. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2022, 15, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Boyd, C.E.; Odom, J. Identification of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) to rearing location using elemental profiling—ScienceDirect. Food Control 2014, 45, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitrago, J.; Rada, M.; Hernández, H.; Buitrago, E. A Single-Use Site Selection Technique, Using GIS, for Aquaculture Planning: Choosing Locations for Mangrove Oyster Raft Culture in Margarita Island, Venezuela. Environ. Manag. 2005, 35, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-González, J.; Angelats, E.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Diogene, J.; Alcaraz, C. First Results of Phytoplankton Spatial Dynamics in Two NW-Mediterranean Bays from Chlorophyll-a Estimates Using Sentinel 2: Potential Implications for Aquaculture. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.F.; Shen, W.L.; Liu, C.; Mu, D.L.; Wu, X.F.; Guo, N.G.; Zhu, J.Q. Effects of multi-environmental factors on physiological and biochemical responses of large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, G.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Q.; Gao, T. Assessment of fishery resources using environmental DNA: The large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in the East China Sea. Fish. Res. 2020, 235, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, Y.; Yang, L. Comparative Study of Distant Fishery Competitiveness of Zhejiang Province Based on the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Issues Agric. Econ. 2014, 35, 94–102+112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liang, J.; Bi, Y.; Feng, M.; Zhou, S.; Yu, B. Status and Prospects of Marine Ranching Construction in Zhejiang Province. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2016, 35, 181–185. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamin, S. Hydrological characteristics of Zhoushan Islands. J. China Hydrol. 2001, 06, 59–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q. A Research of the Transformation and Upgrading Path and the Development Bottlenecks of Fishery Industry in Zhejiang Province. Issues Agric. Econ. 2015, 36, 83–89+112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Yu, M.; Yan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S. HY-1C/D Reveals the Chlorophyll-a Concentration Distribution Details in the Intensive Islands’ Waters and Its Consistency with the Distribution of Fish Spawning Ground. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhou, M.; Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Ji, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zuo, J. HY-1C Coastal Zone Imager observations of the suspended sediment content distribution details in the sea area near Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge in China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, R.; Shen, F.; Liu, J. HY-1C/D CZI Image Atmospheric Correction and Quantifying Suspended Particulate Matter. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, J.; Liu, J.; Xia, G.; Yue, T.; Tong, R.; Tian, L.; Arai, K.; Wang, L. Atmospheric correction for HY-1C CZI images using neural network in western Pacific region. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 25, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xuan, F.; Dong, Y.; Su, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Zeng, Y.; Miao, S.; Li, J. Identifying Corn Lodging in the Mature Period Using Chinese GF-1 PMS Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Tian, Y. Estimation of Building Density with the Integrated Use of GF-1 PMS and Radarsat-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Tao, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, H.; Guan, X. A Novel Radiometric Cross-Calibration of GF-6/WFV with MODIS at the Dunhuang Radiometric Calibration Site. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Zhang, Z.; Long, T.; He, G.; Wang, G.; Peng, Y.; Xu, Z. High resolution (30 m) burned area product improves the ability for carbon emission estimation in Africa. Earth’s Future 2024, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, P. Application of Gaofen No.6 Satellite in Vegetation Ecological RemoteSensing Monitoring. J. Agric. 2021, 11, 56–59+111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsi, J.A.; Schott, J.R.; Hook, S.J.; Raqueno, N.G.; Markham, B.L.; Radocinski, R.G. Landsat-8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) Vicarious Radiometric Calibration. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Qiao, K.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Ji, G. Comparison of Three Single-window Algorithms for Retrieving Land-Surface Temperature with Landsat 8 TIRS Data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2017, 42, 869–876. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Yin, J.; Yan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, R.; Yu, M. The environmental analysis and site selection of mussel and large yellow croaker aquaculture areas based on high resolution remote sensing. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2024, 43, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cai, H.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y. Advance in grey incidence analysis modelling. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2013, 33, 2041–2046. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Tang, D.; Levy, G.; Liu, D. Remote sensing of the impacts of construction in coastal waters on suspended particulate matter concentration—The case of the Yangtze River delta. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 37, 2132–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Retrieval of the reflectance and land surface temperature of the newly-launched Landsat 8 satellite. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 741–747. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Fan, X. A comparison of two mono-window algorithms for retrieving sea surface temperature from Landsat8 data in coastal water of Hongyan River nuclear power station. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2018, 37, 164–174. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Boss, E.; Kiffney, T.; Hesketh, G.; Bourdin, G.; Fan, D.; Brady, D.C. Oyster Aquaculture Site Selection Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing: A Case Study in the Gulf of Maine, United States. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 802438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, D.C.; O’Malley, R.T.; Brodeur, R.D.; Churnside, J.H. Epipelagic fish distributions in relation to thermal fronts in a coastal upwelling system using high-resolution remote-sensing techniques. ICES J. Mar. Sci./J. Du Cons. 2011, 68, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Zou, B.; Ye, X. Study on the chlorophyll a concentration retrieved from HY-1C satelite coastal zone imager data. Haiyang Xuebao 2022, 44, 25–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, K.; Mélin, F. Variability of chlorophyll-a concentration in the Gulf of Guinea and its relation to physical oceanographic variables. Prog. Oceanogr. 2017, 151, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Tang, R.; Yan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yu, M. The spatial-temporal consistency of chlorophyll-a and fishery resources in the water of the Zhoushan archipelago revealed by high resolution remote sensing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1022375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlusty, M.F.; Wikgren, B.; Lagueux, K.; Kite-Powell, H.; Jin, D.; Hoagland, P.; Kenney, R.D.; Kraus, S.D. Co-Occurrence Mapping of Disparate Data Sets to Assess Potential Aquaculture Sites in the Gulf of Maine. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 25, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Cui, J.; Tian, Y.; Xu, X. Analysis of aquaculture safety in marine cage culture area of Maniao bay under the effect of typhoon. Appl. Ocean Res. 2024, 144, 103902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Z.; Xu, W. Effects of Low Temperature Stress Periods on Serum Biochemical Indexes in Large Yellow Croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.L.; Wan, F.G.; Chen, Y.L.; Jiang, L.H.; Zhan, Q.H.; Chen, T.H.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Q.L.; Li, W.Y.; Liu, Y.F. Comparative study on the morphological characteristics, nutritional quality, and tastes of large yellow croaker from five cage culture areas: Relay farming improved fish quality. Aquaculture 2024, 590, 741030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermgassen, P.S.E.Z.; Bonai, K.; Boudry, P.; Bromley, C.A.; Cameron, T.C.; Colsoul, B.; Coolen, J.W.P.; Franki, A.; Hancock, B.; Have, T.M.V.D. Forty questions of importance to the policy and practice of native oyster reef restoration in Europe. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2020, 30, 2038–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, D.; Juell, J.E.; Oppedal, F.; Stiansen, J.E.; Ruohonen, K. The influence of the pycnocline and cage resistance on current flow, oxygen flux and swimming behaviour of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in production cages. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Xu, X.; Cui, L.; Chen, Y.; Shang, J.; Yuan, X. Study on ecological risk evaluation method of mariculture zones. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 915–920. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.F.; Fang, X.H. Efficiency Analysis of China Deep-Sea Cage Aquaculture Based on the SBM–Malmquist Model. Fishes 2023, 8, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; Xu, J.; Haegen, G.V. Supplementing Marine Capture Fisheries in the East China Sea: Sea Ranching of Prawn Penaeus orientalis, Restocking of Large Yellow Croaker Pseudosciaena crocea, and Cage Culture. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2008, 16, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jin, X.; Yang, J.; Han, Z.; Su, F. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors for marine fisheries industry ecosystem vulnerability in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 4273–4283. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, W.; Sun, X. The present and future of the European Copernicus Project. Satell. Appl. 2024, 3, 53–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Lian, A.; Yuan, T.; Pang, G.; Huang, X. Deep Learning-Based Fish Detection Using Above-Water Infrared Camera for Deep-Sea Aquaculture: A Comparison Study. Sensors 2024, 24, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhen, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. Hydrodynamic Characteristics Analysis and Mooring System Optimization of an Innovative Deep-Sea Aquaculture Platform. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 12, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-P.; Liu, H.-F.; Bi, C.-W.; Cui, Y.; Guan, C.-T. Numerical study on the flow field inside and around a semi-submersible aquaculture platform. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 114, 102932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Zhao, T.H.; Liu, Y. Investigation on dynamic performance of semi-submersible aquaculture platform in two mooring forms. Ocean Eng. 2024, 297, 117092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.F.; Liu, Y. Numerical investigation on the dynamic response of the semi-submersible aquaculture platform in regular waves. Ocean Eng. 2024, 294, 116718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.W.; Jiang, J.Q.; Yue, W.Z.; Li, Y.Z.; Wang, W.S.; Sheng, S.W.; Chen, M. Numerical Study on Hydrodynamic Performance of a New Semi-Submersible Aquaculture Platform. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Wang, W.; Sheng, S.; Ye, Y.; Hong, T. Analysis of the wave load and dynamic response of a new semi-submersible wave-energy-powered aquaculture platform. Ocean Eng. 2022, 248, 110346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-F.; Bi, C.-W.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.-P. Hydrodynamic assessment of a semi-submersible aquaculture platform in uniform fluid environment. Ocean Eng. 2021, 235, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatziantoniou, A.; Spondylidis, S.C.; Zachou, O.S.; Papandroulakis, N.; Topouzelis, K. Dissolved oxygen estimation in aquaculture sites using remote sensing and machine learning. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 28, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernez, P.; Palmer, S.C.J.; Thomas, Y.; Forster, R. Editorial: Remote Sensing for Aquaculture. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 638156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Shi, S.; Li, L.; Tian, X.; Gao, Q.; Dong, S. Effects of deep-sea cage culture on water quality and stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes of suspended particulate organic matter in the Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayode-Afolayan, S.D.; Ahuekwe, E.F.; Nwinyi, O.C. Impacts of pharmaceutical effluents on aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, 01288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Z.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, M. Modeling impact of culture facilities on hydrodynamics and solute transport in marine aquaculture waters of North Yellow Sea. Water Sci. Eng. 2023, 16, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, C. Remote Sensing Analysis of Typhoon-Induced Storm Surges and Sea Surface Cooling in Chinese Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, C.; Cheng, B.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W.; Jia, N. Storm Surge Damage Interpretation by Satellite Imagery: Case Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




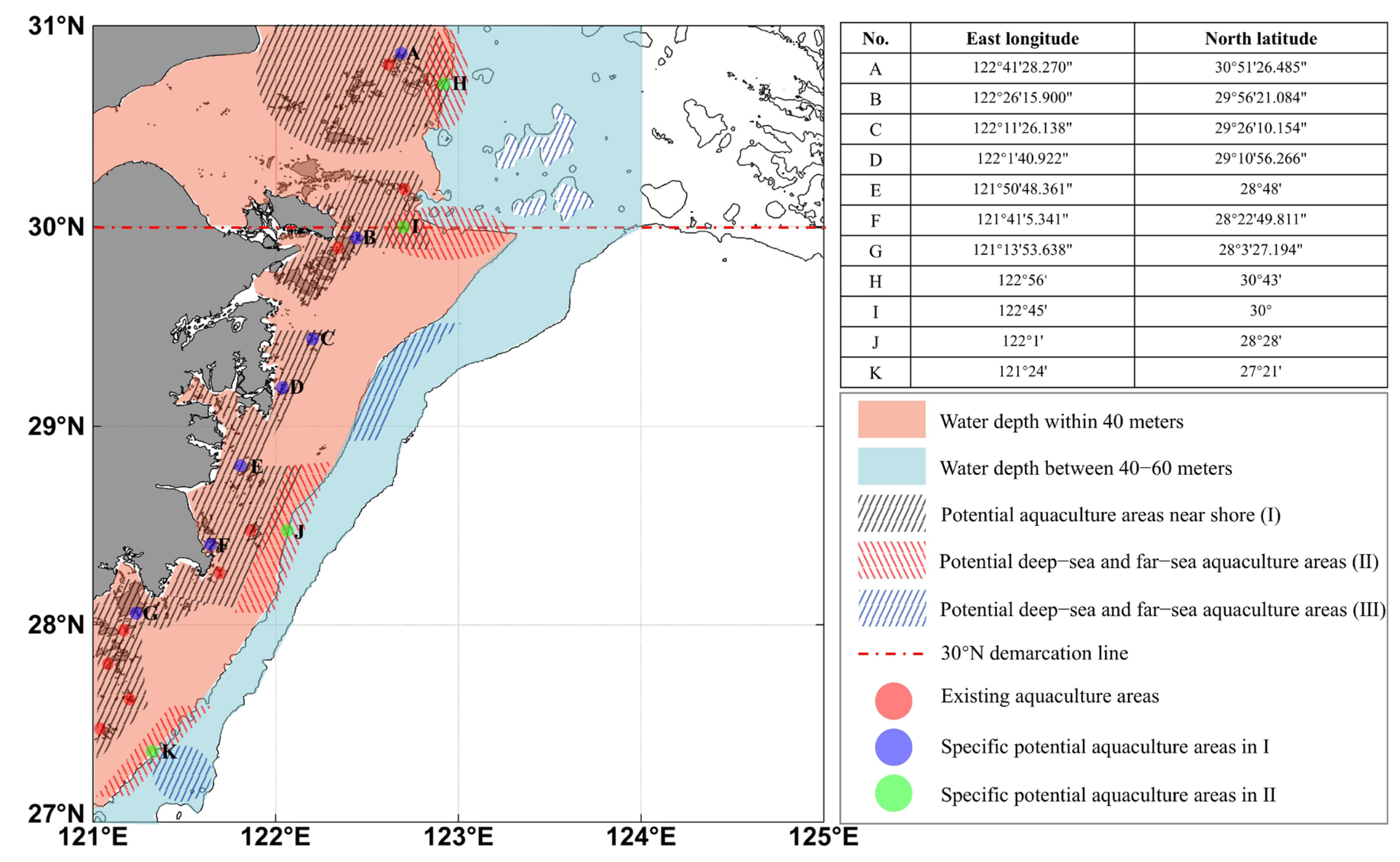

| Sensor | Band No. | Spectral Range/μm | Spatial Resolution/m | Width/km | Orbit Period/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZI | 1 | 0.42–0.50 | 50 | 950 | 100.34 |
| 2 | 0.52–0.60 | ||||
| 3 | 0.61–0.69 | ||||
| 4 | 0.76–0.89 |
| Sensor | Band No. | Spectral Range/μm | Spatial Resolution/m | Width/km | Orbit Period/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMS | 1 | 0.45–0.90 | 2 | 60 | 100.34 |
| 2 | 0.45–0.52 | 8 | |||
| 3 | 0.52–0.59 | ||||
| 4 | 0.63–0.69 | ||||
| 5 | 0.77–0.89 | ||||
| WFV | 1 | 0.45–0.52 | 16 | 800 | |
| 2 | 0.52–0.59 | ||||
| 3 | 0.63–0.69 | ||||
| 4 | 0.77–0.89 |
| Sensor | Band No. | Spectral Range/μm | Spatial Resolution/m | Width/km | Orbit Period/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIRS | 10 | 10.60–11.19 | 100 | 185 | 98.9 |
| 11 | 11.50–12.51 | 100 | 185 |
| Field (Units) | Data Source | Spatiotemporal Resolution | Resourses |
|---|---|---|---|
| SST (°C) | GLOBAL_ANALYSIS_FORECAST_PHY_001_024 | 0.083°/1 month | https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00016 |
| Salinity (‰) | GLOBAL_ANALYSIS_FORECAST_PHY_001_024 | 0.083°/1 month | https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00016 |
| Nutrients (mmol/m3) | GLOBAL_ANALYSISFORECAST_BGC_001_028 | 0.25°/1 month | https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00015 |
| Wind (m/s) | WIND_GLO_PHY_L3_NRT_012_002 | 0.125°/1 day | https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00182 |
| Water Depth (m) | GEBCO (2023) | 15″ | https://doi.org/10.5285/f98b053b-0cbc-6c23-e053-6c86abc0af7b |
| ≥30°N | <30°N | |||||||||
| Season | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||
| SST (°C) | 12–13 | 25–26 | 24–25 | 11–12 | 13–14 | 25–27 | 25–26 | 11–12 | ||
| Salinity (‰) | 25–32 | 32–33 | 27–29 | 29–30 | 29–31 | 33–35 | 20–21 | 21–23 | ||
| Chl-a (mg/m3) | 1–1.5 | 0.8–1.0 | 1.2–1.4 | 2–2.2 | 0.8–1.0 | 1.1–1.3 | 0.7–0.9 | 1.5–1.7 | ||
| Nutrients (mmol/m3) | NO3⁻ | 2–3 | 1–2 | 5–6 | 4–5 | 5–6 | 1–2 | 5–6 | 6–7 | |
| Si | 6–7 | 7–8 | 6–7 | 8–9 | 14–14.5 | 12.5–13 | 10–10.5 | 11–11.5 | ||
| SSC (mg/L) | 130–150 | 260–300 | 150–180 | 170–200 | ||||||
| Current (m/s) | 0.07–0.09 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.2–0.24 | 0.17–0.26 | 0.04–0.05 | 0.1–0.16 | 0.11–0.14 | 0.12–0.14 | ||
| Wind (m/s) | 3–3.6 | 6–7 | 7–8 | 8–9 | 2–3 | 4–5 | 8–9 | 9–10 | ||
| Disaster Frequency (Times/year) | 1.3 | 2.3 | ||||||||
| Average Depth of Aquaculture (m) | 10–60 | |||||||||
| Market Proximity * | ≤50 km | |||||||||
| Marine Traffic * | No Obstruction of Marine Traffic | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Cai, L.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; Zhang, B. Study on the Aquaculture of Large Yellow Croaker in the Coastal Zone of Zhejiang Province Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010009
Yin J, Cai L, Li J, Yan X, Zhang B. Study on the Aquaculture of Large Yellow Croaker in the Coastal Zone of Zhejiang Province Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jie, Lina Cai, Jiahua Li, Xiaojun Yan, and Beibei Zhang. 2025. "Study on the Aquaculture of Large Yellow Croaker in the Coastal Zone of Zhejiang Province Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 17, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010009
APA StyleYin, J., Cai, L., Li, J., Yan, X., & Zhang, B. (2025). Study on the Aquaculture of Large Yellow Croaker in the Coastal Zone of Zhejiang Province Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 17(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17010009









