Vertical Profiles of PM2.5 and O3 Measured Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and Their Relationships with Synoptic- and Local-Scale Air Movements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. UAV Measurement Location
2.2. UAV Measurement System
2.3. Principle and Correction of PM2.5 and O3 Measurements
2.4. Backward Trajectory Using the HYSPLIT Model
3. Results
3.1. Correction of AM520 and Series 500 Measurements
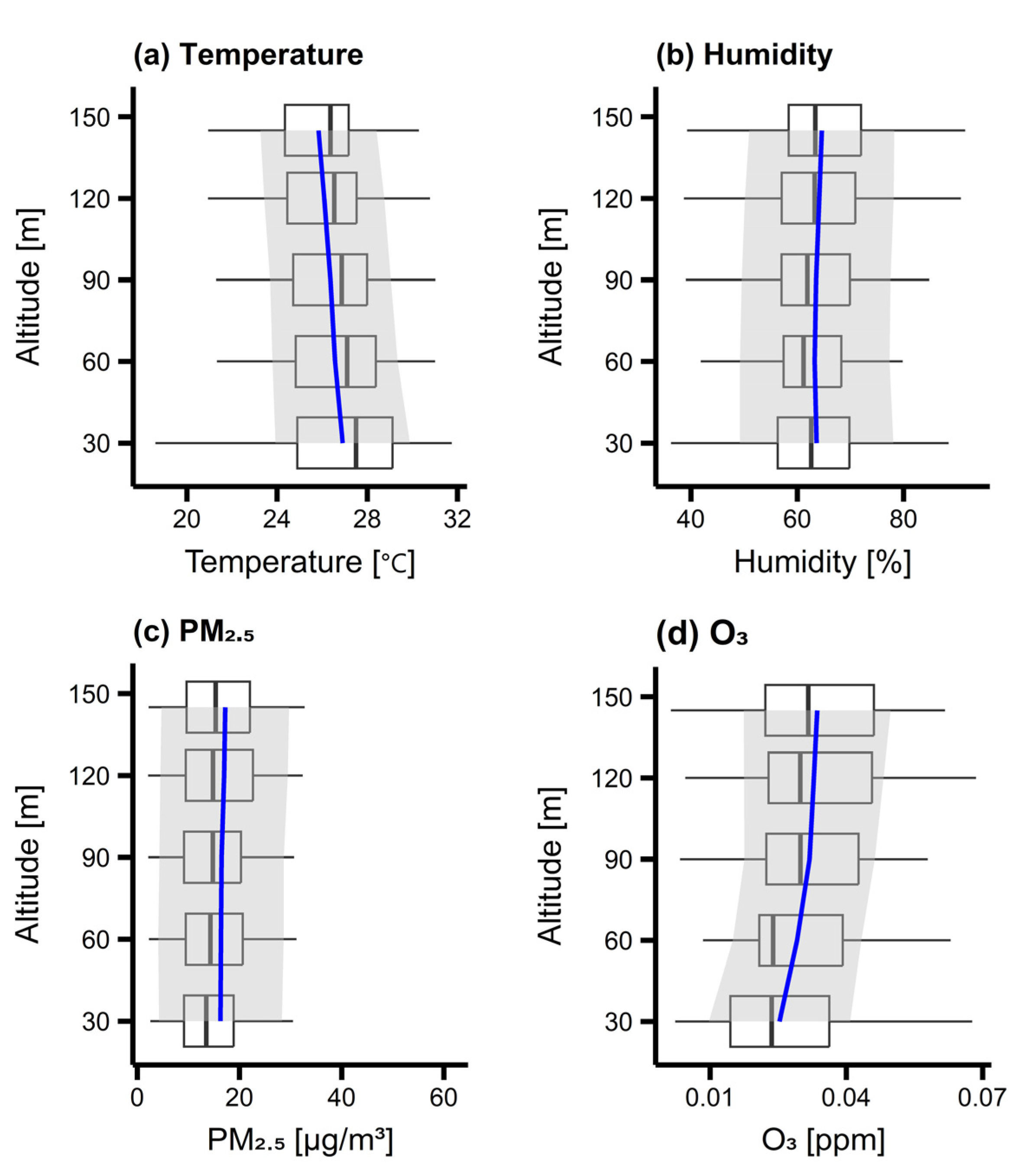
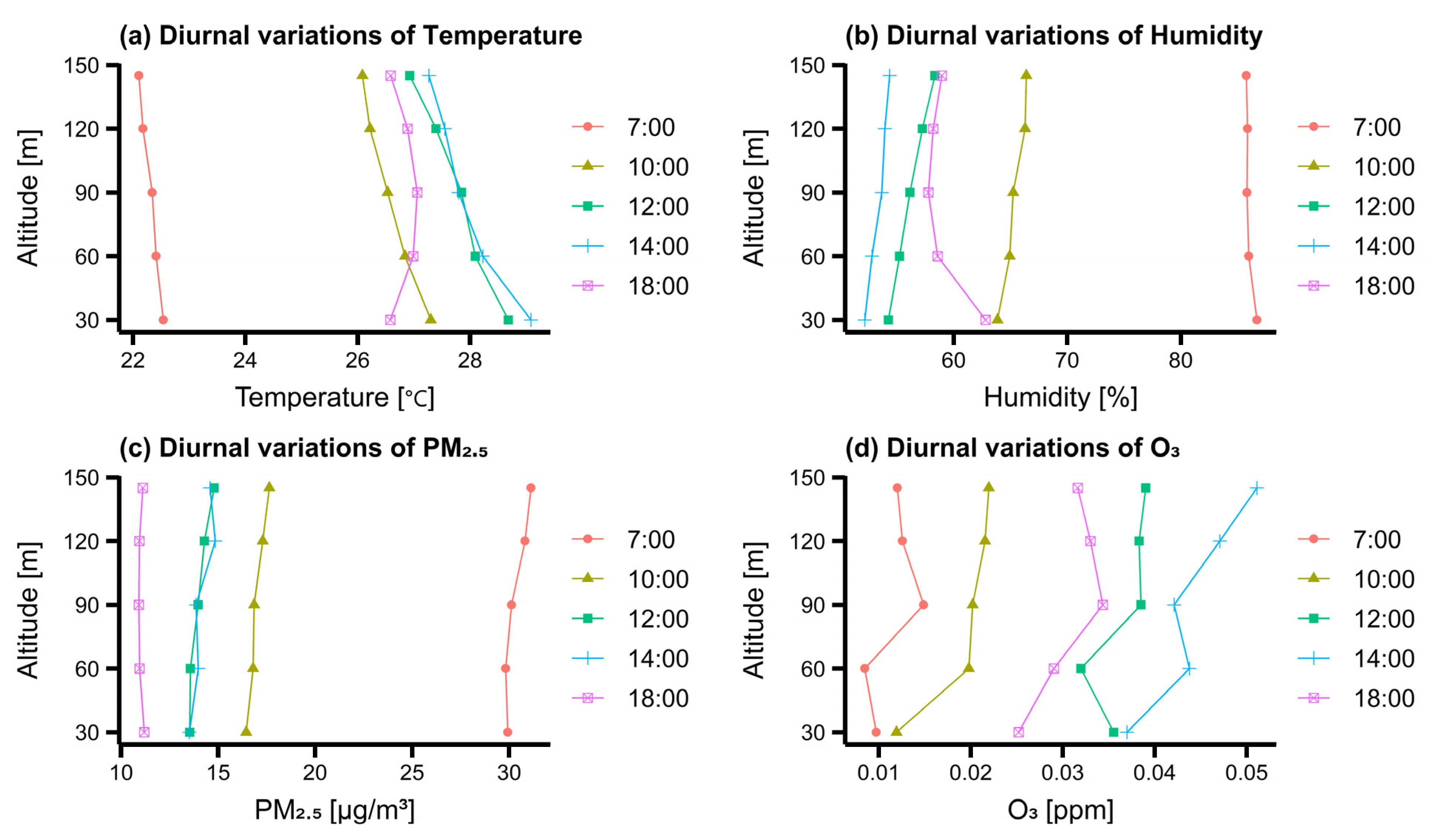
3.2. Characteristics of Measured Vertical Concentration Distribution
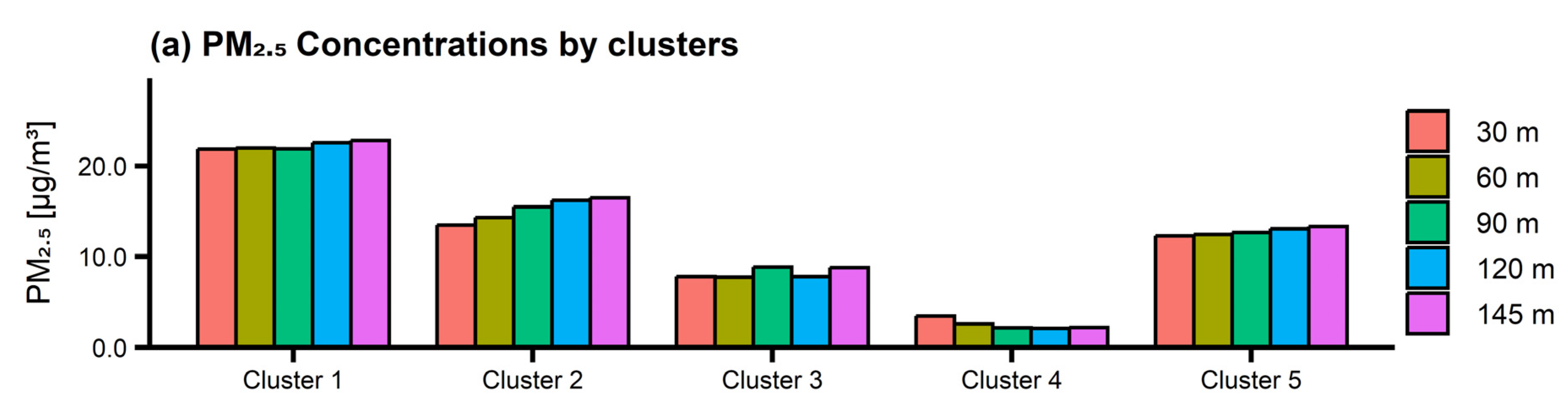
3.3. Long-Range Transport Cases in Summer of South Korea
3.4. Effect of Long-Range Transport of Air Pollutants on Vertical Profiles of PM2.5 and O3
3.5. Effect of Local Surface Wind on Vertical Profiles of PM2.5 and O3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fenger, J. Urban Air Quality. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4877–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopke, P.K.; Cohen, D.D.; Begum, B.A.; Biswas, S.K.; Ni, B.; Pandit, G.G.; Santoso, M.; Chung, Y.; Davy, P.; Markwitz, A. Urban Air Quality in the Asian Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, T.R.; Reddy, M.K.; Reddy, R.C.; Singh, R.N. Impact of an Industrial Complex on the Ambient Air Quality: Case Study using a Dispersion Model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5395–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.; Seo, Y.; Kim, J.; Baek, S. Monitoring of Particulate Hazardous Air Pollutants and Affecting Factors in the Largest Industrial Area in South Korea: The Sihwa-Banwol Complex. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 908–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J. The Effects of Transboundary Air Pollution from China on Ambient Air Quality in South Korea. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, M.; Gu, Y. Effects of Transboundary PM2. 5 Transported from China on the Regional PM2. 5 Concentrations in South Korea: A Spatial Panel-Data Analysis. PLoS ONE, 2023; 18, e0281988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Patra, A.K.; Nazneen. Vertical Profile of Particulate Matter: A Review of Techniques and Methods. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 979–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, N.H.; Kortoçi, P.; Su, X.; Lovén, L.; Hoel, H.K.; Haugsvær, S.B.; Srivastava, V.; Gulbrandsen, C.F.; Nurmi, P.; Tarkoma, S. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for Air Pollution Monitoring: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 21687–21704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthaus, S.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Collaud Coen, M.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Costa, M.J.; Cimini, D.; O’Connor, E.J.; Hervo, M.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Jiménez-Portaz, M. Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height from Ground-Based Remote Sensing: A Review of Capabilities and Limitations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 433–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, G.; Orr, G. Atmospheric and Radiation Effects on Balloon Performance-A Review and Comparison of Flight Data and Vertical Performance Analysis Results. In Proceedings of the International Balloon Technology Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–5 June 1997; p. 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, K.A.; Prather, K.A. Aircraft Measurements of Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Mixing States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevlin, A.G.; Li, Y.; Collett, J.L.; McDuffie, E.E.; Fischer, E.V.; Murphy, J.G. Tall Tower Vertical Profiles and Diurnal Trends of Ammonia in the Colorado Front Range. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 12,468–12,487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kwak, K. Assessing 3-D Spatial Extent of Near-Road Air Pollution Around a Signalized Intersection using Drone Monitoring and WRF-CFD Modeling. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Hwang, H.; Lee, J.Y. Vertical Measurements of Roadside Air Pollutants using a Drone. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Stehr, J.W.; Marufu, L.T.; Li, Z.; Dickerson, R.R. Aircraft Measurements of SO2 and Aerosols Over Northeastern China: Vertical Profiles and the Influence of Weather on Air Quality. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassol, H.L.; Domingues, L.G.; Sanchez, A.H.; Basso, L.S.; Marani, L.; Tejada, G.; Arai, E.; Correia, C.; Alden, C.B.; Miller, J.B. Determination of Region of Influence obtained by Aircraft Vertical Profiles using the Density of Trajectories from the HYSPLIT Model. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Chang, C.; Wang, J.; Lin, M.; Ou-Yang, C.; Pan, H.; Chen, Y. A Study of Atmospheric Mixing of Trace Gases by Aerial Sampling with a Multi-Rotor Drone. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 184, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, B.; Huang, Y.; An, J.; Xu, J. PM2. 5 Vertical Variation during a Fog Episode in a Rural Area of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X.; Chen, W.; Lin, M.; Ho, Y.; Chuang, M.; Liu, W.; Chang, C. A Study of the Vertical Homogeneity of Trace Gases in East Asian Continental Outflow. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 134165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Z.; Wang, D. Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle to Investigate the Vertical Distribution of Fine Particulate Matter. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, N.L.; Zhao, D.; Sellier, M.; Liu, X. Experimental Investigation on Turbulence Effects on Unsteady Aerodynamics Performances of Two Horizontally Placed Small-Size UAV Rotors. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 108535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Norton, T.; Chen, J.; Tan, Y. The Computational Fluid Dynamic Modeling of Downwash Flow Field for a Six-Rotor UAV. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Aggarwal, S.G. A Technical Overview on Beta-Attenuation Method for the Monitoring of Particulate Matter in Ambient Air. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 220195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M. Evaluation of Physical and Chemical Parameters Effects on Different Ozone Monitoring Technologies. Master’s Thesis, Concordia University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Lee, S.; Yeo, M.; Rim, D. Field and Laboratory Evaluation of PurpleAir Low-Cost Aerosol Sensors in Monitoring Indoor Airborne Particles. Build. Environ. 2023, 234, 110127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R. HYSPLIT (Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model. 2003. Available online: https://www.ready.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Dong, D.; Huang, G.; Qu, X.; Tao, W.; Fan, G. Temperature Trend–altitude Relationship in China during 1963–2012. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 122, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebende, G.F.; Brito, A.A.; Silva Filho, A.M.; Castro, A.P. ρDCCA Applied between Air Temperature and Relative Humidity: An Hour/Hour View. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 494, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, O.; Akimoto, H. Intercontinental Transport of Ozone and its Precursors in a Three-dimensional Global CTM. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 27729–27744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, K.; Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y. Effect of Urban Underlying Surface on PM2. 5 Vertical Distribution Based on UAV in Xi’an, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kang, D.; Jung, H.Y.; Jeon, J.; Lee, J.Y. Review of Smog Chamber Experiments for Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Pang, X.; Li, J.; Xing, B.; An, T.; Yuan, K.; Dai, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q. Vertical Profiles of O3, NO2 and PM in a Major Fine Chemical Industry Park in the Yangtze River Delta of China Detected by a Sensor Package on an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, I.; Langner, J.; Soto, C.; Monroy-Sahade, E.A.; Espinosa-Calderón, A.; Pérez, P.; Rubio, M.A.; Arellano, A.; Gramsch, E. Vertical Distribution of PM2. 5 in Santiago De Chile Studied with an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and Dispersion Modelling. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 310, 119947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, B.; Huangfu, Y.; Fan, G.; Wang, H.; Lou, S. Vertical Distributions of Boundary-Layer Ozone and Fine Aerosol Particles during the Emission Control Period of the G20 Summit in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Alvarez Florez, D.; Chourdakis, I.; Vogt, U. Concept of using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) for 3D Investigation of Air Quality in the Atmosphere—example of Measurements Near a Roadside. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumthaler, M.; Ambach, W.; Ellinger, R. Increase in Solar UV Radiation with Altitude. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1997, 39, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlback, A.; Gelsor, N.; Stamnes, J.J.; Gjessing, Y. UV Measurements in the 3000–5000 M Altitude Region in Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Bae, G.; Lee, Y.; Moon, K.; Choi, M. Correlation between Light Intensity and Ozone Formation for Photochemical Smog in Urban Air of Seoul. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2010, 10, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, J. Bypassing the NOx Titration Trap in Ozone Pollution Control in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viallon, J.; Moussay, P.; Flores, E.; Wielgosz, R.I. Ozone Cross-Section Measurement by Gas Phase Titration. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10720–10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumi, Y.; Kawasaki, M. Photolysis of Atmospheric Ozone in the Ultraviolet Region. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4767–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solberg, S.; Stordal, F.; Hov, ø. Tropospheric Ozone at High Latitudes in Clean and Polluted Air Masses, a Climatological Study. J. Atmos. Chem. 1997, 28, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Hopke, P.K.; Yi, S. Source Apportionment of PM 2.5 in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4957–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, M.; Bu, R.; Chang, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, W. Characterization of Air Pollution Index and its Affecting Factors in Industrial Urban Areas in Northeastern China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1579–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.W.; Kim, Y.P.; Yeo, M.J. Estimation of Air Pollutant Emissions from Heavy Industry Sector in North Korea. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 230066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.; Lee, S.; Cho, Y.; Kim, J.; Koo, J.; Kim, Y.P.; Kim, Y.; Woo, J.; Ahn, D.H. Assessment of Air Quality in North Korea from Satellite Observations. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Wee, D.; Kim, Y.P. Estimation of the Contribution of Biomass Fuel Burning Activities in North Korea to the Air Quality in Seoul, South Korea: Application of the 3D-PSCF Method. Atmos. Res. 2019, 230, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Chang, C.; Chuang, M.; Chou, C.C.; Pan, X.; Ho, Y.; Ou-Yang, C.; Liu, W.; Chang, C. Using Drone Soundings to Study the Impacts and Compositions of Plumes from a Gigantic Coal-Fired Power Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, K.C. Estimation of Atmospheric Mixing Layer Height from Radiosonde Data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, P.; Chan, D.; Kodikara, J. Ground–atmosphere Interaction Modelling for Long-Term Prediction of Soil Moisture and Temperature. Can. Geotech. J. 2012, 49, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrendele, C.; Audy, O.; Hofman, J.; Kucerik, J.; Kukucka, P.; Mulder, M.D.; Pribylova, P.; Prokes, R.; Sanka, M.; Schaumann, G.E. Diurnal Variations of Air-Soil Exchange of Semivolatile Organic Compounds (PAHs, PCBs, OCPs, and PBDEs) in a Central European Receptor Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4278–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, H.; Lee, J.E.; Shin, S.A.; You, C.R.; Shin, S.H.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, J.Y. Vertical Profiles of PM2.5 and O3 Measured Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and Their Relationships with Synoptic- and Local-Scale Air Movements. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091581
Hwang H, Lee JE, Shin SA, You CR, Shin SH, Park J-S, Lee JY. Vertical Profiles of PM2.5 and O3 Measured Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and Their Relationships with Synoptic- and Local-Scale Air Movements. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(9):1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091581
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Hyemin, Ju Eun Lee, Seung A. Shin, Chae Rim You, Su Hyun Shin, Jong-Sung Park, and Jae Young Lee. 2024. "Vertical Profiles of PM2.5 and O3 Measured Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and Their Relationships with Synoptic- and Local-Scale Air Movements" Remote Sensing 16, no. 9: 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091581
APA StyleHwang, H., Lee, J. E., Shin, S. A., You, C. R., Shin, S. H., Park, J.-S., & Lee, J. Y. (2024). Vertical Profiles of PM2.5 and O3 Measured Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and Their Relationships with Synoptic- and Local-Scale Air Movements. Remote Sensing, 16(9), 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16091581






