Abstract
Rapid urbanisation in the global south has often introduced substantial and rapid uncontrolled Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) changes, considerably affecting the Land Surface Temperature (LST) patterns. Understanding the relationship between LULC changes and LST is essential to mitigate such effects, considering the urban heat island (UHI). This study aims to elucidate the spatiotemporal variations and alterations of LST in urban areas compared to LULC changes. The study focused on a peripheral urban area of Phnom Penh (Cambodia) undergoing rapid urban development. Using Landsat images from 2000 to 2021, the analysis employed an exploratory time-series analysis of LST. The study revealed a noticeable variability in LST (20 to 69 °C), which was predominantly influenced by seasonal variability and LULC changes. The study also provided insights into how LST varies within different LULC at the exact spatial locations. These changes in LST did not manifest uniformly but displayed site-specific responses to LULC changes. This study accounts for changing land surfaces’ complex physical energy interaction over time. The methodology offers a replicable model for other similarly structured, rapidly urbanised regions utilising novel semi-automatic processing of LST from Landsat images, potentially inspiring future research in various urban planning and monitoring contexts.
1. Introduction
Land surface temperature (LST) is an essential parameter in understanding the balance of surface energy and the physical energy (heat) exchange between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere [1]. LST is a critical factor in determining the longwave radiation within land surface radiation and energy budgets. In simple terms, LST is the skin temperature of the surface. From a satellite’s perspective, the term “surface” refers to whatever it observes when peering through the atmosphere to the ground. This observation could encompass various elements such as snow and ice, grass on lawns, building rooftops, or forest canopy leaves. Consequently, it is essential to note that LST differs from the air temperature typically featured in daily weather reports [2]. However, previous studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between LST and air temperature in urban areas [3,4,5]. Moreover, LST is an essential input for climatic, hydrological, ecological, and biogeochemical models [6]. With rapid urbanisation, the built-up environment contributes to a significant increase in LST in an urban environment, thus accelerating the urban heat island (UHI) effect. UHI is a phenomenon where human activities and alterations in land use lead to higher temperatures in cities compared to neighbouring rural areas [7]. The UHI effect arises from reduced vegetation cover, increased impervious surfaces, and high energy consumption [8]. Urban environments have impervious surfaces, such as concrete and asphalt, with higher heat capacity and thermal conductivity than natural surfaces. As a result, they absorb and store more solar energy [9].
UHI has a multitude of negative impacts on the urban environment by affecting public health, local urban climate, ecosystem functions and biodiversity and also increasing pollution [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Understanding these effects of UHI is essential for urban planners, politicians and decision-makers to develop and implement effective mitigation strategies and counter-balancing measures, such as increasing green spaces, uncompacting and opening sealed surfaces, promoting energy-efficient buildings, and employing less emissive (colder) surface technologies [18].
A time-series analysis of LST provides a robust and geospatial explicit method for such understanding through the spatiotemporal patterns of urban LST and, thus, their thermal dynamics [19]. LST time series can reveal trends, seasonality, fluctuations, and considerable alterations in LST [20]. Time-series analysis involves examining data collected regularly over an extended period. The LST time series identifies areas with consistently high LST that have undergone significant LULC changes, detects changes in LST resulting from LULC changes, and evaluates the effectiveness of mitigation measures against the effects of UHI connected to LST [1,19,21,22,23,24]. Understanding the thermal dynamics of a city is critical for urban planners.
Several studies have investigated the connection between LST and LULC. Weng et al. (2008) analysed the spatial distribution of LST in various LULC types [25]. Their results indicated that highly urbanised areas with impervious surfaces and reduced vegetation cover experienced elevated LST. Similarly, Amiri et al. (2009) investigated the impact of different LULC types on LST using Landsat satellite data [26]. Their findings revealed that high-density urban areas with a predominance of concrete and asphalt surfaces exhibited higher LST values than low-density residential areas with more green and open ground spaces. The relationship between LST and different LULC types is often analysed using the LST and value from different spectral indices representative of different land covers [27,28,29,30]. Different spectral indices are used in these studies to identify the correlation between LST and different LULC classes. For vegetation, water and built-up areas, the widely used spectral indices are Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) and Normalised Difference Built-up Index (NDBI), respectively. However, Xu (2006) argued that a modified version of the NDWI, which is called the Modified Normalised Difference Index (MNDWI), produces better results compared to the NDWI [31]. Xu (2008) also argued that Indices-Based Built-up Index (IBI) is more accurate than NDBI in extracting built-up areas [32]. The impact of LULC changes on urban LST and UHI effect is recognised through different previous studies [3,33,34,35,36,37,38].
Karakuş (2019) investigated the relationship between LST and LULC by clustering the five LULC classes (agriculture, vegetation, built-up, water and bare land and studying the LST (minimum, mean and maximum) in different LULC classes [33]. While their study gave an overview of the LST in different LULC classes, they considered a long range from 1989 until 2015, but with only three images from three different Landsat satellites (4, 7 and 8). A similar approach study was conducted by Saha et al. (2021) with eight different LULC classes, and the relation between LST and LULC classes was also assessed [34]. However, the study only took three images from the same year, comparing three cities. Fatemi et al. (2019) used the NDVI and LST to monitor LULC changes and their impact on the LST, where six Landsat 5 images were considered throughout the study period from 1986 to 2011 [35]. Zhang et al. (2016) studied the dynamics of LST and its relation with LULC changes between 1989 and 2011 using two Landsat images and classifying them into six different LULC classes [36]. However, similar to Fatemi et al. (2019), Zhang et al. (2016) also emphasised the LST and NDVI relationship, expressing the spatiotemporal changes in LST and LULC. Using four Landsat images, Murtaza et al. (2023) studied the linkages between LULC changes and LST between 1992 and 2020 [38]. They also used LST and NDWI correlation to understand the relationship between these two variables. In a recent study, Lin et al. (2024) explored the connection between morphological characteristics of urban areas and UHI [39]. The last authors cited used Landsat 8 data from 2017, 2019 and 2021 to retrieve the LST among other data in their analysis. In their study, they divided the study area into eight different morphological classes, analysing how the morphological factors of urban areas affect the UHI. In another recent study, Saha et al. (2024) assessed the LST dynamics and LULC using eight Landsat images from Landsat-4, Landsat-5 and Landsat-8 over a long time frame [40]. While the studies mentioned above cover a more extended period and represent time series based on data from specific timestamps, building a long-term time series using the frequent data from the Landsat archive (16-day revisit time for Landsat) would enable more comprehensive insight into the thermal dynamics and an in-depth understanding of seasonal variability and longer trends and anomalies. In addition, the studies that conducted time series on LST focused on land use and land cover relations based on spectral indices often focused on descriptive statistics analysis without a visual interpretation [41,42,43]. Our hypothesis is that visual interpretation is essential, along with statistical analysis, to obtain a holistic picture.
This study conducted a detailed empirical spatiotemporal analysis of LST patterns through a time-series analysis and aspired to understand LST’s relation to LULC. The specific objectives of this research are to (1) analyse the statistical and temporal overview of LST distribution and ranges, (2) investigate the seasonal variation and trends of LST, and (3) examine the correlation between LST and different LULC classes, including vegetation, water, and built-up areas.
The article is structured as follows: following this introduction, Section 2 details the materials and methods, including the data sources, study area, and analytical methods. Section 3 presents the results, including statistical analysis and temporal patterns of LST. Section 4 discusses the study’s findings, methods, and limitations. Section 5 concludes the study with a summary of the findings and suggestions for future research.
The study employs an innovative approach using time-series analysis to comprehensively investigate thermal dynamics in the context of urban planning and monitoring. Furthermore, the study’s methodology represents a methodological advancement by employing a semi-automatic process for analysing similar approaches in other urban areas, which utilises easily reproducible monitoring techniques. This approach enables a more subtle analysis of the impact of urbanisation on environmental parameters, setting the stage for the development of spatially focused, data-driven urban planning and environmental policies. The findings of this study are poised to offer valuable insights for urban planners, environmental scientists, and policy-makers, contributing to the use of remote sensing in sustainable urban planning and monitoring. While rooted in Phnom Penh, Cambodia, our methodology and findings offer critical insights and a methodological framework that can be adapted and applied in diverse urban settings globally.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Chbar Ampov District, located in the southeast region of Phnom Penh, Cambodia, is a rapidly developing urban area with a mix of residential and commercial zones. The Mekong River borders the district from the north, the Meanchey District to the west, the Kien Svay District to the east and the Bassac River to the south (Figure 1). Phnom Penh has experienced rapid growth over the past two decades, which has resulted in significant changes to the built environment, particularly in the former suburban areas like Chbar Ampov [44]. This transformation is driven by a surge in investments in real estate, commercial ventures, and infrastructure projects, which have propelled the district into a dynamic urban centre.
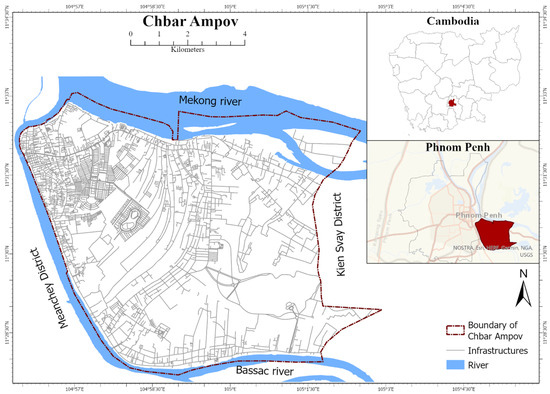
Figure 1.
Location of the study area. (data sources: open street map, USGS for background map).
The strategic location of Chbar Ampov, alongside the Mekong River, has made it an attractive site for both local and international investors, fostering a diverse economic landscape. As Chbar Ampov transitions from a predominantly rural area formerly dominated by the backwaters of the Bassac River and a larger extent of peri-urban smallholder agriculture to a densely urbanised area with a large amount of new landfilling the swamps, such rapid urban growth presents challenges and opportunities for climate resilience measures, including housing, infrastructure, and environmental sustainability issues. This ongoing evolution underscores the district’s role in the broader narrative of Cambodia’s development, marking it as a microcosm of the country’s ambitions and complexities in the face of globalisation and economic integration [44]. Spanning approximately 62.52 square kilometres, Chbar Ampov is home to an estimated population of 164,379 people, according to the 2019 population census [45]. The district has a tropical wet and dry climate, characterised by distinct wet (May to October) and dry (November to April) seasons, with an average annual air temperature of around 27.8 °C with a difference in rainfall between the months receiving the least and the most precipitation is 246 mm or 10 inches (data considered from 1991 to 2021) [46]. The area features a predominantly flat topography reaching a lower elevation of about 10 m above sea level [47] and only several decimetres above the Mekong peak flood level of 10.30 at the Chaktumuk gauging station [48]. The physiography of Chbar Ampov consists mainly of lowland plains and backwater swamps of the interconnected Mekong and Tonle Bassac floodplains. In tandem with its rapid urbanisation, Phnom Penh is experiencing urban heat island (UHI) effects, exacerbating the environmental and health challenges within the city, including in districts like Chbar Ampov. Previous study suggested that Phnom Penh’s UHI effect contributes significantly to increased energy consumption, elevated greenhouse gas emissions, and heightened vulnerability to heat-related illnesses among its population [49].
2.2. Data and Initial Processing
This study introduces a novel methodological framework that combines the semi-automatic image processing of Landsat data across Landsat sensor types, time-series analysis, and visual interpretation to dissect the spatiotemporal relationship between LST and LULC changes, enabling a comprehensive approach to urban environmental analysis.
We used collection-1 Tier 1 data from Landsat 5, 7 and 8. Both surface reflectance (SR) and top-of-atmosphere (TOA) data via Google Earth Engine image archive data are provided by the NASA/USGS Landsat program [50]. For image data dating from 2000 to 2021, a 60% maximum cloud filter and a cloud mask is applied to filter out the existing cloudy pixels using the C-Function-of Mask (CFMask) algorithm [51]. Radiometric calibration (details in Section 2.5, Equation (9)) and thermal calibration (details in Section 2.5, Equation (10)) were performed before LST retrieval as part of preprocessing. After retrieving LST, a 20 °C (for minimum LST) filter was applied to avoid further cloud contamination, which was undetected by cloud masking. After all the initial processing and data filtering, 425 images were selected for this study (Figure 2). Figure 3 shows the distribution of selected 425 images according to the day of the year from 2000 to 2021. We used Google Earth Engine (GEE) to process the images. It is important to mention that no classification-based LULC mapping was performed in this study. Google Earth images are used to understand the LULC changes visually. The spectral indices (Table 1) are used to numerically draw correlations between LST and different LULC classes.
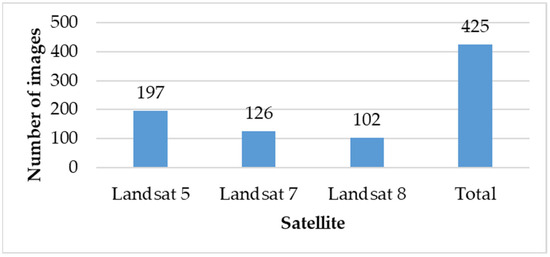
Figure 2.
Different Landsat satellite-wise number of images.
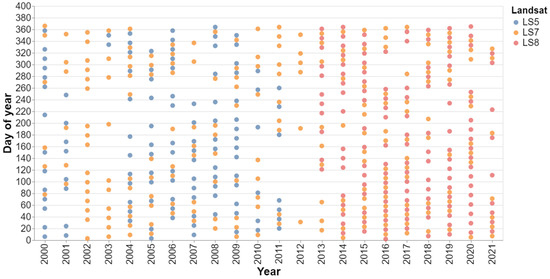
Figure 3.
Distribution of selected 425 images based on the day of the year and Landsat satellite type.

Table 1.
Different spectral indices used in the study and their respective LULC classes.
2.3. Spectral Indices Retrieval
We used three different spectral indices in this study called NDVI, MNDWI and IBI using Equations (1)–(3) [31,32,52].
where NIR is the near-infrared, R is the visible red, G is the visible green, swir1 is the shortwave infrared (band 5 in Landsat 5, 7 and band 6 in Landsat 8) band.
NDVI = (NIR − R)/(NIR + R)
MNDWI = (G − SWIR1)/(G + SWIR1)
IBI = (2 SWIR1/(SWIR1 + NIR1) − [NIR (NIR + R) + G/(G + SWIR1)])/(2 SWIR1/(SWIR1 + NIR1) + [NIR (NIR + R) + G/(G + SWIR1)])
2.4. Proportion of Vegetation and Emissivity Calculation
The proportion of vegetation (P_v) can help account for the effects of vegetation on the thermal radiation emitted from the land surface. By incorporating P_v information into LST estimation models, LST estimation accuracy can improve, particularly in areas with high vegetation cover [53]. Pv was calculated using Equation (4).
where NDVI_v and NDVI_s was chosen as 0.86 and −0.64, respectively, considering the NDVI range (maximum and minimum value) for the study area.
P_v = ((NDVI − NDVI_s)/(NDVI_v − NDVI_s))^2
Emissivity (E_m) is a physical property of a material’s surface that measures its ability and effectiveness in emitting energy as thermal radiation. In this study, land surface emissivity was calculated using the Simplified NDVI Threshold Method (SNDVITHM) from Equation (5) [54].
where E_s and E_v are the emissivity of soil and vegetation. For this study, the emissivity of soil and vegetation were selected as 0.97 and 0.985 following a previous study [55].
E_m = E_s (1 − P_v) + E_v × P_v
2.5. LST Retrieval
This study utilised a Single-Channel (SC) algorithm to obtain LST that includes the surface emissivity and atmospheric conditions (Equation (6)) [56]. This approach was selected due to its simplicity when the relevant parameters are known and its accuracy for sensors equipped with a single thermal band.
where γ and δ are the parameters dependent on Planck’s function and calculated from Equations (7) and (8) [43], L is spectral radiance at the sensor (Equation (9)), E_m is surface emissivity, and ψ values are the atmospheric functions based on the amount of atmospheric water vapour using a second-degree polynomial approximation (for details, see [56,57]).
where BT represents the brightness temperature, and b represents a sensor-specific constant, which is 1256 K, 1277 K, and 1324 K for Landsat 5, 7 and 8, respectively [57]. ML is the band-specific multiplicative factor; AL is the band-specific additive factor.
LST = γ [1/E_m × (ψ_1 × L + ψ_2) + ψ_3] + δ
γ = (BT)^2/(b_γ × L)
δ = BT − (BT)^2/b_γ
L = ML × DN + AL
BT was measured from the TOA product using thermal calibration constants from the metadata of the respective image collection and based on Planck’s law Equation (10) [58].
where BT is the brightness temperature, L is the radiance and K_1 and K_2 are the band-specific thermal calibration constants.
BT = K_2/(ln(K_1/L + 1)) − 273.15
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The minimum, mean, and maximum values of LST were extracted through the reducer function of GEE, and all the values were stored in a data frame for descriptive statistical analysis [59]. The statistical analysis comprises descriptive analysis, calendar heatmaps and trend analysis based on descriptive analysis. Boxplots and histograms are plotted to illustrate the data distribution. Calendar heatmaps are used, which provide information about seasonal trends, a yearly comparison of LST distribution, anomalies and extreme events, and consistency of the LST range [60,61]. Trend analysis is conducted by drawing simple line charts of minimum, mean and maximum LST. Correlation tests between LST and values extracted from different spectral indices (IBI, MNDWI and NDVI) have been performed by drawing 400 random points (Appendix A) instead of using descriptive statistics. In the case of LST and NDVI correlations, points having less than 0.2 NDVI values are omitted because the lower NDVI points represent water pixels, which appear to have both lower NDVI and colder LST, affecting the true nature of the statistical and physical relationship. For a similar reason, vegetation pixels were omitted for LST and MNDWI correlation.
2.7. Visual Interpretation
Images from different years from February to April (dry season) are compared to visually illustrate the LST distribution and changes in the study area over the entire study period. From the visual illustration of the previous steps, five points (Appendix B) were identified to observe the response of LST in different LULCs. We took five points to see examples of how LST and LULC changes interact instead of a rigorous study on identifying critical interventions areas. In these spots, the LST values over time are extracted and compared visually with images from Google Earth to acquire an impression of how LST responds to different LULC and LULC changes. However, only one point (point 4) is illustrated in the result. Images from each month of 2015 are plotted together to help visualise the seasonal variation in LST. The year 2015 was selected for this because this year had more cloud-free data than other years during the study period.
2.8. Overview of the Overall Methodology
It should be noted that descriptive statistics (minimum, mean and maximum) were used in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2 in this study. For the calendar heatmap in Section 3.1, we used mean LST. Absolute LST values were used for the visual interpretation in Section 3.3, including the example how LST responds to different LULC in a certain point. For the correlation analysis in Section 3.4, we used absolute LST values in 400 random points (for details, see Table A1 in Appendix C). In each case, whether the LST values used are descriptive or absolute is also explicitly mentioned in the relevant sections. A graphical overview of the entire methodical workflow is provided below to illustrate the methodological steps in this study (Figure 4).
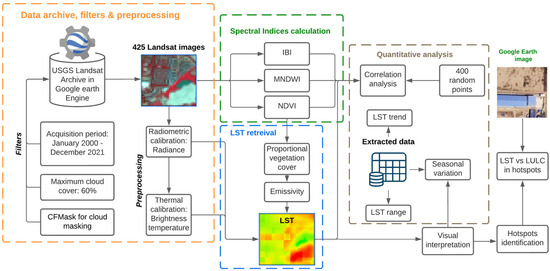
Figure 4.
Graphical overview of the methodical overview.
3. Results
3.1. LST Distribution and Range
Figure 5 indicates that the study area experiences wide LST variation. We assumed this was likely due to daily or seasonal changes or different land cover types, which is further examined in the later part of the result section. There is a greater spread of maximum LST values than minimum and mean LST. This greater spread indicates that the maximum LST is influenced by more factors or is less consistent than the minimum and mean LST. The presence of outliers in the mean LST and maximum LST denotes the extreme values that deviate significantly from the central tendency of the respective categories.
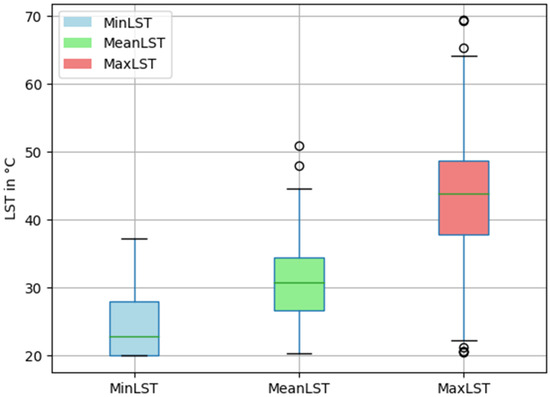
Figure 5.
Boxplot of minimum, mean and maximum LST (number of observation (N) = 425).
The calendar heatmap (Figure 6) of mean LST was created to obtain a temporal overview of LST in the study area. Figure 6 also provides information about the following two precise points: seasonal trends and anomalies and extreme events.
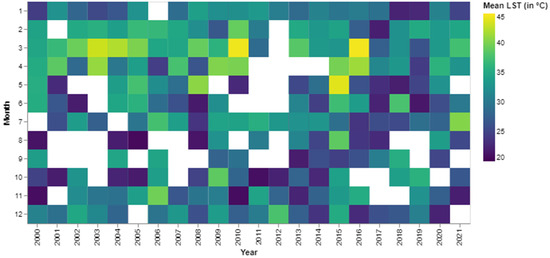
Figure 6.
Calendar heatmap of mean LST (white boxes inside the figure represent no data).
3.1.1. Seasonal Trends
Mean LST are comparatively higher from November to April, indicating the area’s dry season. Among these months, February to April consistently showed a higher mean LST. However, in some months and years, May also has a higher LST. The rest of the months (June to October) have lower LST, apart from a few exceptions in specific years and months.
3.1.2. Anomalies and Extreme Events
Mean LST has four distinctive high values across the entire observation period, three of which are in March 2003, 2010, and 2016, when the values are 43.10 °C, 44.43 °C, and 44.58 °C. The fourth value in May 2015 peaks out at 43.86 °C LST.
3.2. Consistency of LST Range and Trend of LST
The study area has experienced a wide range of LST (minimum, mean, and maximum), which is categorically visible in the different levels of spreads (Figure 7). The overall LST range is 20 to 69.40 °C, and there are outliers. Maximum LST has the widest range. The years 2003, 2008, 2015 and 2016 have a wider range than other years. The median lines within each boxplot are relatively stable over the years, which suggests that despite yearly fluctuations, the central tendency of LST has not changed dramatically.
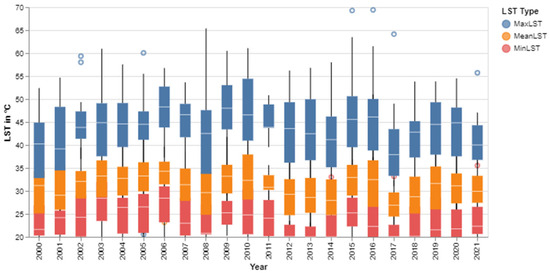
Figure 7.
Boxplot of yearly minimum, mean and maximum LST.
The following line chart represents the minimum, mean and maximum LST trend from 2000 to 2021 (Figure 8). The 20 °C flatline at the bottom results from the minimum filter applied to the data. The maximum LST is usually below 60 °C apart from a few years in 2008, 2015, 2016, and 2017. Regular fluctuation exists due to the seasonal variation explained in the previous section. However, the noticeable LST spikes in each category seem symmetrical. When the maximum LST spiked, the mean and minimum also seemed to be spiked in most cases. However, no visible long-term trend in LST appeared parallel to Figure 7 above.
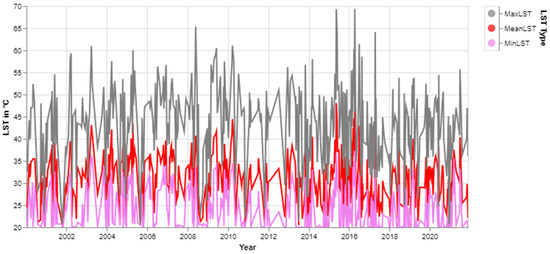
Figure 8.
Total time series of minimum, mean and maximum LST (2000–2021).
3.3. Results from the Visual Interpretations
Images from different months from the same year (2015) have been visually inspected and compared to understand the seasonal and spatial variation of LST (Figure 9).
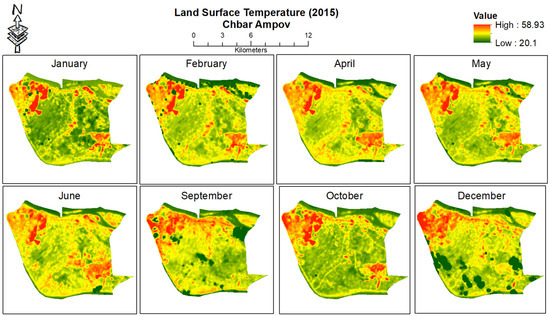
Figure 9.
LST (in °C) in different months from 2015 (images in March, July, August and November were heavily contaminated from cloud).
There is a seasonal variability of LST as it shows different ranges and distributions of LST within different months of the same year. For example, a noticeable difference between January and April is also reflected similarly in the calendar heatmap previously (Figure 6). The minimum, mean, and maximum LST values of the LST images from Figure 8 are visualised together to understand this variability (Figure 10).
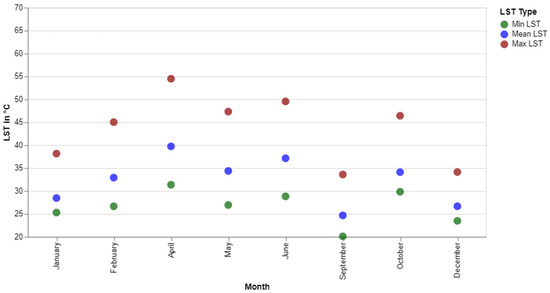
Figure 10.
Monthly minimum, mean and maximum LST in 2015.
There is a visible fluctuation between different months in the same year (2015) regarding minimum, mean and maximum LST. The maximum difference in all values appears between April and September. All LST values are lower in September but comparatively higher in the immediate next month (October) (Figure 10). Upon visual investigation, it appears that the cloud affected certain areas with consistently higher LST (Figure 11). Hence, instead of September, October was taken as an example, along with April, to understand the seasonal variability.
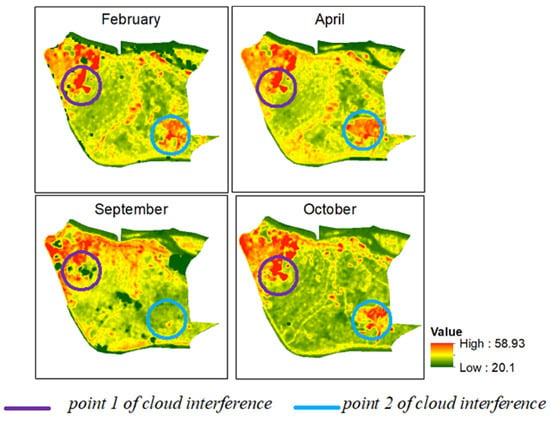
Figure 11.
Example of how visual interpretation provides additional input.
Another reason behind choosing these two months is that both images are entirely cloud-free, which enabled a good comparison, and the distance between the two months is adequate to represent different seasons in this area. Between April and October, the difference in minimum, mean, and maximum LST is 1.5, 5.6 and 8.1 °C, respectively. This seasonal variability is essential to understand the long-term trend of LST, especially when data from different seasons are considered in a time series.
The LST values from each year are visualised in Figure 12 together to observe the changes in LST visually. All images are taken from February to April to ensure coherence in seasonal fluctuation.
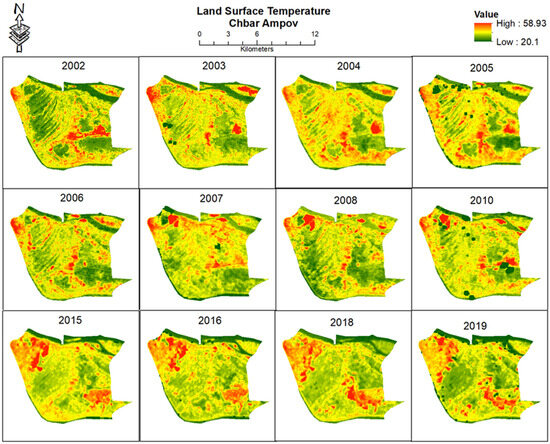
Figure 12.
LST (in °C) in 2000–2021.
Anniversary images (taken on the same day of the year) from each year would have been ideal for this analysis. However, this was not possible due to different image acquisition dates and cloud cover. This representation shows how LST has changed over the years in some areas, specifically in the northwest and southeast of the study area. An increase in the northeast can be linked to the urban expansion of the built-up area and the urban fabric of Phnom Penh City. A golf course is being built in the southeastern part of the study area, starting the conversion of land in 2015. This means a visible connection between LULC change and LST is apparent from both areas visually compared (Figure 13).
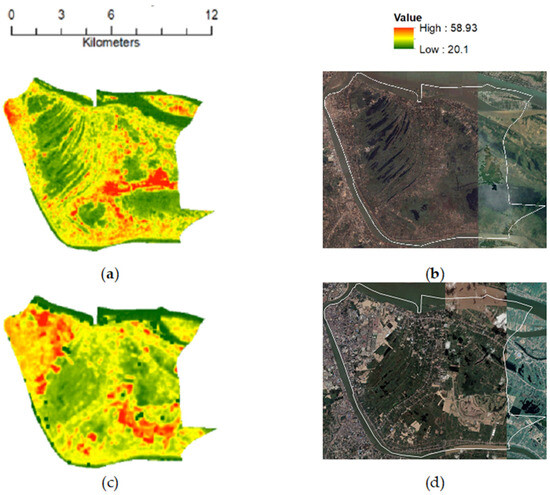
Figure 13.
Visible connection between LST (in °C) and LULC changes elaborating spatial changes: (a) LST in March 2003; (b) Google Earth RGB image in February 2003; (c) LST in March 2019; (d) Google Earth RGB image in February 2019.
Based on visual observation, five specific points are identified to examine further to observe how LST responds to different LULCs (Appendix B). One point (point 4) is elaborately discussed here (Figure 14). Point 4 has undergone large-scale LULC changes, resulting in a noticeable LST change.
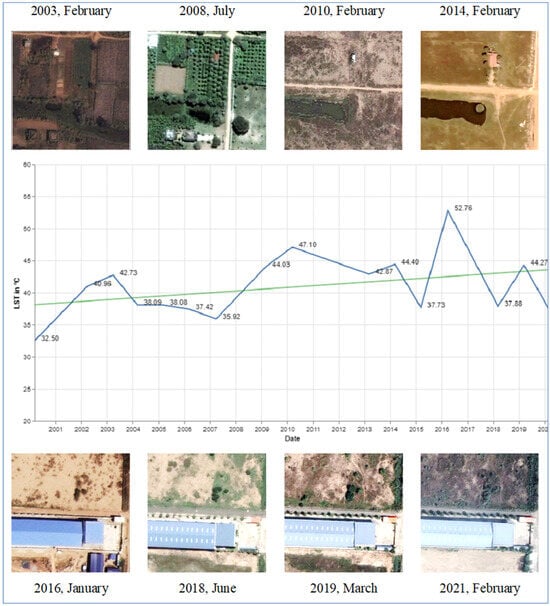
Figure 14.
LST and LULC changes in point 4 (The blue line is the line graph of LST data in the time series, and the green line is a statistical trendline showing the upward trend of LST at this specific point).
The area used to be a peri-urban agricultural land characterised by a spatial intermixture of some vegetation cover interrupted by small, shallow linear waterbodies in the Mekong–Tonle Bassac flood plain in 2003. By 2008, the area had become lush green (probably an orchard) with several newly planted medium-sized trees, and it was covered by dense vegetation, which was reflected by the downward spike in LST. However, by 2010, the area lost all the trees and vegetation due to its preparation to become an urban built-up area, thus creating an upward spike in LST. The area with the highest LST in 2016 was where a large building with a potential metal roof cover was located, and the soil was mostly exposed and dry. Overall, the area shows a visible upward trend in LST.
3.4. Correlation between LST and Different Land Covers
The correlation matrix in Figure 15 is generated to understand the correlation between different parameters, including LST, IBI, MNDWI, and NDVI, in 400 random points (Appendix A). IBI, representing built-up areas, shows a strong positive correlation. NDVI and MNDWI, representing vegetation and water, show a strong negative correlation.
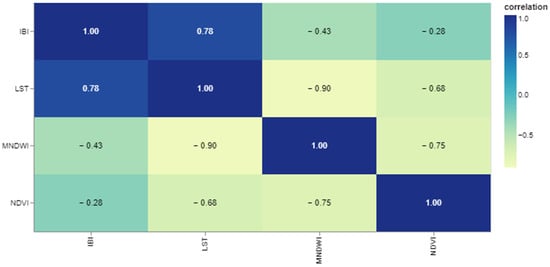
Figure 15.
Correlation matrix between LST, IBI, MNDWI and NDVI in 400 random points.
The correlation matrix indicates a strong positive correlation between the built-up area and LST. This relationship appears to be linear (Figure 16). This statistically explains the increase in LST over the year in the northwestern and southeastern parts of the study area over the entire time series.
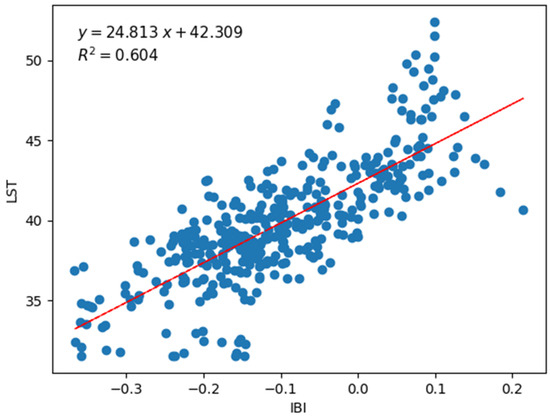
Figure 16.
Linear relationship between built-up area and LST (in °C).
Figure 17 illustrates the relationship between LST and vegetation as well as LST and open water. In the lower NDVI range, where it is more likely bodies of water, both NDVI and LST values are lower, which creates a contradiction in expressing the relationship (Figure 17a). Hence, only vegetation samples were considered to show the relationship between LST and NDVI (Figure 17b). Similarly, in the vegetation pixels, which have a lower value in MNDWI, both the MNDWI and LST values are low (Figure 17c). Hence, all the vegetation samples are removed to demonstrate the true relationship between LST and MNDWI (Figure 17d).
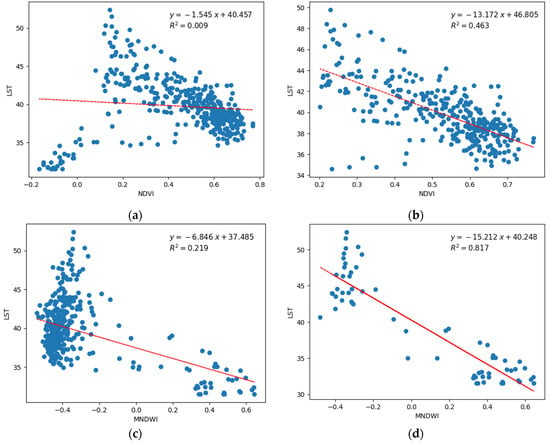
Figure 17.
Relationship between LST and NDVI and MNDWI: (a) LST vs. NDVI with all 400 samples; (b) LST vs. NDVI with only points that have ≥ 0.2 NDVI values (only vegetation samples); (c) LST vs. MNDWI with all 400 samples; (d) LST vs. MNDWI with only points that has ≤0.2 NDVI (without vegetation samples).
4. Discussion
The study area is prone to be affected by lots of clouds. This made it difficult to find images from the same day of the year to compare LST precisely. Hence, such a yearly comparison of LST might have introduced some inconsistencies in absolute LST measurement due to variations in image acquisition dates. LST in a city like Phnom Penh can be influenced by extreme weather and environmental phenomena such as monsoon rain, heatwaves, flooding, droughts, and global climatic phenomena like El Niño and La Niña events. While it was not within the scope of the study to integrate such meteorological variables into the analysis, this kind of extreme event usually creates unusual values in long-term trends, which were not visible in the study findings. Hence, we would argue that the analysis and results of the study are meaningful and valuable, but it cannot be said that the changes in LST were attributed only to LULC changes.
The study aimed to examine the spatiotemporal patterns of LST in the study area and to analyse seasonal variability, LST trends over time and the response of LST to different LULC types at specific sites. By combining semi-automated processing, in-depth spatio-temporal analysis, and visual land cover interpretation, our study advances the methodological approach available to researchers and planners, providing scalable solutions from semi-automated LST monitoring over time to the challenges posed by urbanisation. Key findings from the study include a noticeable seasonal influence on LST, with the maximum regional difference in values occurring between April and October, which can be interpreted as the regional peak dry season and close to the regional peak rainy season. Previous similar studies also indicated the seasonal variability of LST and highlighted the importance of considering seasonal variability in LST time-series analysis [62,63]. While the study found fluctuations in LST, no long-term trends, such as an increase in LST (minimum, mean, maximum), were evident in the data. A strong positive correlation between built-up areas and LST was observed, while a strong negative correlation between LST and water was found. The correlation between LST and vegetation was also found to be strongly negative. The study also found a visual link between LST and LULC changes, supporting the above-mentioned LST vs. spectral indices correlation results.
The greater spread in the maximum LST values may be physically connected to the physical emissivity of certain materials and their specific emissivity under tropical conditions; however, this requires further examination. The study also recorded a noticeable difference between maximum and minimum temperature (49 °C). This range between minimum and maximum LST in similar studies varies in the findings of different studies. Karakuş (2019) [33] found that the spread between minimum and maximum LST is 16.82 °C, whereas Saha et al. (2024) [40] found this difference to be 14.69 °C. The analysis also revealed a recurring temperature anomaly every six or seven years, predominantly in the dry season. It is evident that these anomalies recur every sixth or seventh year during the dry season, which is parallel to the identified El Niño phases since 1910 [64]. Although a more extended period of data is required to confirm this, the evidence strongly suggests a correlation between the two to be tested and elaborated in more detail in further studies. The example shown in the result section (Section 3.3, Figure 11) argues that it is essential to have a visual interpretation that validates our hypothesis regarding the importance of parallel visual interpretation along with statistical analysis. Otherwise, we may overlook certain pertinent information, thus leading to misinterpretation of the thermal dynamics. The studies on time series of LST often produce a visible trend [65]. While it has been observed visually that there is a noticeable spread of higher LST over the study area during the study period, there is an absence of a clear long-term trend in LST in the trend analysis. Karakuş (2019) [33] also observed this absence of a long-term trend while observing the period of 1989 to 2015 in LST changes based on descriptive statistics similar to the current study. This outcome suggests that trend analysis based on descriptive statistics (minimum, mean and maximum) might not provide a complete picture. The study results demonstrated that LULC changes in an exact location visually connect with LST changes. Our study’s example shows that an area changing from vegetation to built-up can be connected to the largest LST change, which is a finding supported by a previous study conducted by Amiri et al. (2009) [26].
Weng et al. (2008) found that biophysical factors were the most influential in accounting for the spatial differences in LST compared to the other LULC variables [25]. This echoes our findings that LST and water have a strong correlation. However, we found that built-up areas also have a strong positive correlation with LST, similar to Weng (2001) [63], indicating that urbanisation and the expansion of built-up areas in suburban areas contribute to higher LST values. A strong negative correlation was observed between LST and vegetation, which was similar to previous studies [27,33,35]. Fatemi et al. (2019) pointed out that the LST and NDVI relationships vary throughout different seasons and attributed this difference in different seasons to the quality of the vegetation [35]. In addition, the study tried to understand the LULC–LST relationship based on LST and NDVI where the authors tried to understand different LULC classes by using only NDVI. As we explained in the results (Figure 17) of the current study, the lowest NDVI value representing water can create a contradiction in expressing the relationship between LST and NDVI; this was not addressed in the study carried out by Fatemi et al. (2019), which might also be a reason for these seasonal differences in LST–NDVI correlations. However, the strong negative correlation between LST and water, as well as vegetation, suggests that the presence of water bodies or green spaces helps moderate local LST. The negative correlation between LST and water is also similar to the findings from previous studies, as water bodies tend to have lower LST due to their high heat capacity and evaporative cooling [31]. Promoting significant urban green spaces can be an effective mitigation measure for reducing the urban heat island. This is because the negative correlation between land surface temperature (LST) and vegetation can be attributed closely to the cooling effect of vegetation through shade and evapotranspiration [66,67]. Therefore, integrated urban planning and greening initiatives are crucial for mitigating the UHI effect and achieving environmental sustainability and climate resilience in Phnom Penh City.
A combination of imagery from different Landsat sensors (5, 7, 8) was required to establish the long-term LST timeline of this study. However, this combination of sensors also poses specific issues that need to be considered during analysis. In the case of Landsat, all Landsat sensors have a 16-day revisit schedule according to their timeline. Hence, obtaining images from the same day of each season and year is only possible in some cases when it comes to the cross-combination of different sensors over time. Landsat-5 has a spatial resolution of 120 m in the thermal band, which is 60 m for Landsat-7 and 100 m for Landsat-8. While all the thermal bands are re-sampled into 30 m pixel resolution due to their inherent difference in their actual spatial resolution pixel to pixel-to-pixel, comparison lacks a certain degree of coherence.
The Scan Line Corrector (SLC), a component of Landsat-7 ETM+, failed on 31 May 2003 [68]. As a result, instead of scanning a continuous swath of the Earth’s surface, the sensor began to capture a series of parallel scans with gaps in between. This failure of SLC resulted in a pattern of data gaps or “stripes” in each Landsat 7 scene, affecting the quality and usability of the satellite’s data, which also applied to this research area. Gap filling of SLC-off LS 7 data has not been considered in this study, since we were interested in spatially explicit LST data in the considerably small research area The Landsat 8 experienced unanticipated calibration inconsistencies of one of its thermal infrared sensor bands—Band 11 that impacted the data’s accuracy, creating a bias in the recorded land surface temperatures [69]. These technical issues are also critical aspects of constructing an LST timeline using data from these sensors and all other long-term time series data sets derived from the Landsat archive.
There are several different algorithms and techniques to estimate LST from Landsat data. The study used the single-channel algorithm considering the sensor variation because it requires only one thermal band [56]. Since Landsat-5 and Landsat-7 have only one thermal band, producing the time series analysed from Landsat 5, 7 and 8 together using a single thermal band was logical. However, the atmospheric information and emissivity values of the primary surfaces that are being inspected need to be considered. These parameters can influence the accuracy and quality of the output LST data. If the local atmospheric data are available, the radiative transfer equation (RTE) algorithm can be an alternative for a high degree of accuracy [70]. If the time series length and study period can be covered by the sensors that have more than one thermal band, the split-window algorithm can be a better choice over the single-channel algorithm because this technique is better at dealing with the atmospheric effects, especially in humid areas [54].
5. Conclusions and Outlook
In addition, our study not only highlights the complex dynamics between LST and LULC changes in Phnom Penh but also provides a methodological blueprint for analysing and mitigating urban heat island effects in cities worldwide. Thus, it contributes to urban planning and environmental science and suggests that investments in urban blue–green infrastructure of densely built-up areas in tropical agglomerations should be considered to improve urban climate resilience. In addition, our study not only highlights the complex dynamics between LST and LULC changes in Phnom Penh but also provides a methodological blueprint for analysing and mitigating urban heat island effects in cities worldwide. Thus, it contributes to urban planning and environmental science and suggests that investments in urban blue–green infrastructure of densely built-up areas in tropical agglomerations should be considered to improve urban climate resilience.
Based on the current study, we suggest several future research directions to advance further the analysis of thermal dynamics and the understanding of the relationships between LST and LULC changes. While the spectral indices-based approach provides a means to compare LST and different indices values quantitatively, an additional detailed LULC analysis would significantly help to interpret this relationship and even more profoundly explain the influences of the spatial pattern of land use on LST. A further study to identify thermal hotspots will support identifying critical regions in an urban area for interventions in the urban blue and green infrastructure. For example, a pixel-by-pixel analysis of the study area can be conducted to see which pixels show up in the upper range of LST during a study period. Future research could benefit from developing more sophisticated models incorporating a more comprehensive range of weather variables and adapting LST values, accordingly, providing a more sophisticated understanding of LST variations in the context of climate variability and change.
The results of this study emphasised adopting a subtle and context-dependent approach to LST analysis, which can ultimately lead to more effective urban planning and management strategies. The study’s implications demonstrate the potential for developing new theories, frameworks, methods, or models that account for the complex interplay between LST and LULC changes in different settings. The methodology employed in this study can be applied to other areas and serve as a foundation for future research. The technical framework of the study may inspire the development of new techniques and applied methods that can help monitor and mitigate LST changes more effectively. For instance, advancements in remote sensing and GIS technologies could enable more precise tracking of LULC changes and LST dynamics at local and regional scales.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, G.M.; methodology, G.M. and J.-P.M.; software, G.M.; formal analysis, G.M.; investigation, G.M.; resources, G.M., J.-P.M. and G.M.; writing—original draft preparation, G.M.; writing—review and editing, G.M. and J.-P.M.; visualisation, G.M. and J.-P.M.; supervision, J.-P.M.; project administration, J.-P.M.; funding acquisition, J.-P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Build4People Project under the funding priority SURE, Sustainable Development of Urban Regions, of the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), funding support code (FKZ): 01LE1908D1 and the APC was funded by J.-P. Mund and Eberswalde University for Sustainable Development (HNEE).
Data Availability Statement
The data and code used in this study can be accessed at: https://github.com/mohigeo33/thermal_dynamics (accessed on 31 December 2023).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Hor Sanara, Chea Chetha, Eun Sambath from the Royal University of Agriculture (RUA) in Phnom Penh, Cambodia, and the Buidl4people Project team members for their continuous academic discussion and support. Additionally, the authors would like to acknowledge the cooperation of the public authorities of the Phnom Penh municipality (PPCH) during the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
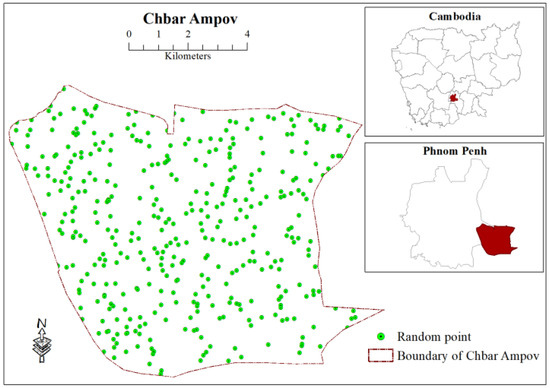
Figure A1.
Location 400 random points considered for correlation test between LST and LULC.
Appendix B
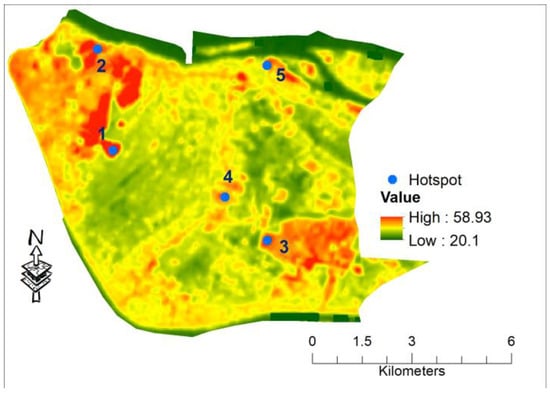
Figure A2.
Location of identified five points to examine LST and LULC interactions (background map is LST (in °C) from April 2015).
Appendix C

Table A1.
Type of LST values used in different results.
Table A1.
Type of LST values used in different results.
| Section | Content | Type of LST Value |
|---|---|---|
| 3.1 | Boxplot (Figure 5) | Minimum, mean and maximum |
| 3.1 | Calendar heatmap (Figure 6) | Mean |
| 3.2 | Boxplot (Figure 7) | Minimum, mean and maximum |
| 3.2 | Line chart (Figure 8) | Minimum, mean and maximum |
| 3.3 | Seasonal variability map (Figure 9) | Absolute |
| 3.3 | Point chart (Figure 10) | Minimum, mean and maximum |
| 3.3 | Cloud contamination example map (Figure 11) | Absolute |
| 3.3 | Visual timeline of LST (Figure 12) | Absolute |
| 3.3 | Visible connection between LST (in °C) and LULC changes elaborating spatial changes (Figure 13) | Absolute |
| 3.3 | Point specific LST and LULC connection (Figure 14) | Absolute |
| 3.4 | LST and LULC correlation scatterplots (Figure 16 and Figure 17) | Absolute |
References
- Weng, Q. Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing for Urban Climate and Environmental Studies: Methods, Applications, and Trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. Land Surface Temperature. NASA Earth Observatory. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). 2024. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/global-maps/MOD_LSTD_M (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Yang, C.; Yan, F.; Zhang, S. Comparison of Land Surface and Air Temperatures for Quantifying Summer and Winter Urban Heat Island in a Snow Climate City. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Bedra, K.B.; Ouyang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J. Spatial and Seasonal Differences between near Surface Air Temperature and Land Surface Temperature for Urban Heat Island Effect Assessment. Urban Clim. 2023, 52, 101745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, E.J.; Aldred, F.M.; Ghent, D.J.; Veal, K.L.; Jimenez, C. An Analysis of the Stability and Trends in the LST_cci Land Surface Temperature Datasets Over Europe. Earth Space Sci. 2022, 9, e2022EA002317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, J. Chapter 7—Land Surface Temperature and Thermal Infrared Emissivity. In Advanced Remote Sensing, 2nd ed.; Liang, S., Wang, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 251–295. [Google Scholar]
- Oke, T.R.; Cleugh, H.A. Urban Heat Storage Derived as Energy Balance Residuals. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1987, 39, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnfield, A.J. Two Decades of Urban Climate Research: A Review of Turbulence, Exchanges of Energy and Water, and the Urban Heat Island. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. (Ed.) Energy and Climate in the Urban Built Environment; James & James: London, UK, 2001; ISBN 978-1-873936-90-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kovats, R.S.; Hajat, S. Heat Stress and Public Health: A Critical Review. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondula, D.M.; Georgescu, M.; Balling, R.C. Challenges Associated with Projecting Urbanization-Induced Heat-Related Mortality. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, J.A.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Holloway, T.; Foley, J.A. Impact of Regional Climate Change on Human Health. Nature 2005, 438, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. On the Energy Impact of Urban Heat Island and Global Warming on Buildings. Energy Build. 2014, 82, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Imhoff, M.L.; Wolfe, R.E.; Bounoua, L. Characterizing Urban Heat Islands of Global Settlements Using MODIS and Nighttime Lights Products. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.J.; Winner, D.A. Effect of Climate Change on Air Quality. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickett, S.T.A.; Cadenasso, M.L.; Grove, J.M. Resilient Cities: Meaning, Models, and Metaphor for Integrating the Ecological, Socio-Economic, and Planning Realms. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 69, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Pomerantz, M.; Taha, H. Cool Surfaces and Shade Trees to Reduce Energy Use and Improve Air Quality in Urban Areas. Sol. Energy 2001, 70, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.; Glenn, E.; Nguyen, U.; Scott, R.; Doody, T. Estimating Riparian and Agricultural Actual Evapotranspiration by Reference Evapotranspiration and MODIS Enhanced Vegetation Index. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3849–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, 5th ed.; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Erell, E.; Pearlmutter, D.; Williamson, T.J. Urban Microclimate: Designing the Spaces between Buildings, 1st ed.; Earthscan: London, UK; Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Santamouris, M. Cooling the Cities—A Review of Reflective and Green Roof Mitigation Technologies to Fight Heat Island and Improve Comfort in Urban Environments. Sol. Energy 2014, 103, 682–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajat, S.; O’Connor, M.; Kosatsky, T. Health Effects of Hot Weather: From Awareness of Risk Factors to Effective Health Protection. Lancet 2010, 375, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleerekoper, L.; Van Esch, M.; Salcedo, T.B. How to Make a City Climate-Proof, Addressing the Urban Heat Island Effect. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 64, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Liu, H.; Liang, B.; Lu, D. The Spatial Variations of Urban Land Surface Temperatures: Pertinent Factors, Zoning Effect, and Seasonal Variability. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2008, 1, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Weng, Q.; Alimohammadi, A.; Alavipanah, S.K. Spatial–Temporal Dynamics of Land Surface Temperature in Relation to Fractional Vegetation Cover and Land Use/Cover in the Tabriz Urban Area, Iran. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2606–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Gillies, R.R.; Perry, E.M. A Method to Make Use of Thermal Infrared Temperature and NDVI Measurements to Infer Surface Soil Water Content and Fractional Vegetation Cover. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 9, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M. Combining Multifrequency Microwave and Optical Data for Crop Management. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. A Verification of the “triangle” Method for Obtaining Surface Soil Water Content and Energy Fluxes from Remote Measurements of the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Surface e. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 3145–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholt, I.; Rasmussen, K.; Andersen, J. A Simple Interpretation of the Surface Temperature/Vegetation Index Space for Assessment of Surface Moisture Status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) to Enhance Open Water Features in Remotely Sensed Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A New Index for Delineating Built-up Land Features in Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakuş, C.B. The Impact of Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) Changes on Land Surface Temperature in Sivas City Center and Its Surroundings and Assessment of Urban Heat Island. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 55, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Saha, A.; Das, M.; Saha, A.; Sarkar, R.; Das, A. Analyzing Spatial Relationship between Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) and Land Surface Temperature (LST) of Three Urban Agglomerations (UAs) of Eastern India. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 22, 100507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, M.; Narangifard, M. Monitoring LULC Changes and Its Impact on the LST and NDVI in District 1 of Shiraz City. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tiyip, T.; Kung, H.; Johnson, V.C.; Maimaitiyiming, M.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J. Dynamics of Land Surface Temperature (LST) in Response to Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) Changes in the Weigan and Kuqa River Oasis, Xinjiang, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, P. Correlation Analysis of Land Surface Temperature and Topographic Elements in Hangzhou, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, K.O.; Shafai, S.; Shahid, P.; Romshoo, S.A. Understanding the Linkages between Spatio-Temporal Urban Land System Changes and Land Surface Temperature in Srinagar City, India, Using Image Archives from Google Earth Engine. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 107281–107295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Wei, K.; Guan, Z. Exploring the Connection between Morphological Characteristic of Built-Up Areas and Surface Heat Islands Based on MSPA. Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.; Ria, S.S.; Sultana, J.; Shima, U.A.; Hasan Seyam, M.M.; Rahman, M.M. Assessing Seasonal Dynamics of Land Surface Temperature (LST) and Land Use Land Cover (LULC) in Bhairab, Kishoreganj, Bangladesh: A Geospatial Analysis from 2008 to 2023. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, S.M.; De Lorenzi, F.; Menenti, M. Mapping Air Temperature Using Time Series Analysis of LST: The SINTESI Approach. Nonlin. Process. Geophys. 2013, 20, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Weng, Q. A Time Series Analysis of Urbanization Induced Land Use and Land Cover Change and Its Impact on Land Surface Temperature with Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nill, L.; Ullmann, T.; Kneisel, C.; Sobiech-Wolf, J.; Baumhauer, R. Assessing Spatiotemporal Variations of Landsat Land Surface Temperature and Multispectral Indices in the Arctic Mackenzie Delta Region between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, F.; Beckwith, L.; Ngin, C. People and Politics: Urban Climate Resilience in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Front. Sustain. Cities 2023, 4, 972173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asia. (City District, Cambodia)—Population Statistics, Charts, Map and Location. 2024. Available online: https://www.citypopulation.de/en/cambodia/phnompenh/admin/1212__chbar_ampov/ (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Phnom Penh Climate (Cambodia). Phnom Penh Climate: Weather Phnom Penh & Temperature by Month. 2024. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/asia/cambodia/phnom-penh/phnom-penh-4857/ (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Touch, S.; Likitlersuang, S.; Pipatpongsa, T. 3D Geological Modelling and Geotechnical Characteristics of Phnom Penh Subsoils in Cambodia. Eng. Geol. 2014, 178, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phnom Penh (Bassac). Regional Flood Management and Mitigation Centre. Mekong River Commision. 2024. Available online: http://ffw.mrcmekong.org/stations.php?StCode=PPB&StName=Phnom%20Penh%20(Bassac) (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Bunleng, S.; Katzschner, L. Will Cities Survive? Urban Climate Recommendations for Urban Planning in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. In Proceedings of the PLEA SANTIAGO 2022W, Santiago, Chile, 22–25 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- GEE. Landsat Collections in Earth Engine|Earth Engine Data Catalog|Google for Developers. Google Earth Engine. Google. 2024. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/landsat (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Foga, S.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dilley, R.D.; Beckmann, T.; Schmidt, G.L.; Dwyer, J.L.; Joseph Hughes, M.; Laue, B. Cloud Detection Algorithm Comparison and Validation for Operational Landsat Data Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W., Jr.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring the Vernal Advancement and Retrogradation (Green Wave Effect) of Natural Vegetation (No. NASA-CR-132982); NTRS: Washington, DC, USA, 1973.
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the Relation between NDVI, Fractional Vegetation Cover, and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Soria, G.; Romaguera, M.; Guanter, L.; Moreno, J.; Plaza, A.; Martinez, P. Land Surface Emissivity Retrieval From Different VNIR and TIR Sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-Derived Land Surface Temperature: Current Status and Perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Cristobal, J.; Sobrino, J.A.; Soria, G.; Ninyerola, M.; Pons, X.; Pons, X. Revision of the Single-Channel Algorithm for Land Surface Temperature Retrieval From Landsat Thermal-Infrared Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Skokovic, D.; Mattar, C.; Cristobal, J. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval Methods From Landsat-8 Thermal Infrared Sensor Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1840–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of Current Radiometric Calibration Coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI Sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reducer Overview of Google Earth Engine Algorithms. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/guides/reducers_intro (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Simpson, R.B.; Zhou, B.; Alarcon Falconi, T.M.; Naumova, E.N. An Analecta of Visualizations for Foodborne Illness Trends and Seasonality. Sci Data 2020, 7, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, S. Impact of Climate Change on Hiking: Quantitative Evidence through Big Data Mining. Curr. Issues Tour. 2021, 24, 3040–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. A Remote Sensing? GIS Evaluation of Urban Expansion and Its Impact on Surface Temperature in the Zhujiang Delta, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, X. A New Index for Mapping Built-up and Bare Land Areas from Landsat-8 OLI Data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Often do El Niño and La Niña Typically Occur? Climate Prediction Center—Enso FAQ. National Weather Service. 2024. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20090827143632/http:/www.cpc.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ensofaq.shtml#HOWOFTEN (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ottle, C.; Bréon, F.-M.; Nan, H.; Zhou, L.; Myneni, R.B. Surface Urban Heat Island Across 419 Global Big Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, G.B. Ecological Climatology: Concepts and Applications, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-107-04377-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zomer, R.J.; Trabucco, A.; Bossio, D.A.; Verchot, L.V. Climate Change Mitigation: A Spatial Analysis of Global Land Suitability for Clean Development Mechanism Afforestation and Reforestation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 126, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wei, C.; Jin, Y.; Li, Z.; Tong, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Filling Gaps in Landsat ETM+ SLC-off Images with Sentinel-2 MSI Images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 101, 102365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, M.; Barsi, J.; Lunsford, A.; Rohrbach, S.; Markham, B. Performance of the Thermal Infrared Sensor On-Board Landsat 8 over the First Year On-Orbit; Butler, J.J., Xiong, X., Gu, X., Eds.; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; p. 921817. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Ren, H.; Qin, Q.; Meng, J.; Zhao, S. A Practical Split-Window Algorithm for Estimating Land Surface Temperature from Landsat 8 Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).