Spatial Parameter Identification for MIMO Systems in the Presence of Non-Gaussian Interference
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The proposed method introduces a new generalized correlation matrix, constructs a GMTFD matrix, analyzes the characteristics of the GMTFD matrix, characterizes the covariance matrix, and establishes a quasi-covariance matrix by using the GMTFD matrix.
- The similarity transformation of the quasi-covariance matrix is conducted based on the Gerschgorin disk criterion, and the objective function is constructed based on the radius and eigenvalues of the Gerschgorin disk to determine the number of transmit antennas in the MIMO system.
- Signal subspace and noise subspace are obtained by EVD of the quasi-covariance matrix, and the DOA estimation is carried out using the subspace method.
- The proposed method does not require prior information, such as channel coefficient, noise power, interference power, etc., and it can realize the joint estimation of the NTA and DOA for a MIMO system in the presence of Gaussian noise and non-Gaussian interference.
2. System Model
3. Generalized MTFD Matrix Construction
4. Joint Estimation Based on the Generalized MTFD Matrix
4.1. Estimation of the Number of Transmit Antennas
| Algorithm 1: Estimation of the NTA via the GMTFD matrix |
| Input: The GMTFD matrix |
| 1. The effective TF points of the GMTFD matrix are selected by Equation (20). |
| 2. The quasi-covariance matrix is constructed according to Equation (23). |
| 3. Perform a similar transformation on the matrix using Equation (30). |
| 4. Estimate the radius of the Gerschgorin disk according to Equation (31). |
| 5. Use the center of the Gerschgorin disk to compress the radius of the Gerschgorin disk. |
| Start iteration |
| 6. Construct the objective function based on the Gerschgorin disk criterion according to Equation (34). |
| 7. Update the objective function for . |
| 8. Until the objective function takes a non-negative value for the first time. |
| Terminate iteration |
| Output: |
4.2. DOA Estimation
4.2.1. MUSIC Algorithm
| Algorithm 2: DOA estimation based on the GMTFD-MUSIC |
| Input: The GMTFD matrix |
| 1. The effective TF points of the GMTFD matrix are selected by Equation (20). |
| 2. The quasi-covariance matrix is constructed according to Equation (23). |
| 3. Do the EVD of according to Equation (36). |
| 4. Obtain the signal subspace and noise subspace according to the descending arrangement of the |
| eigenvalues. |
| Start iteration |
| 5. The signal direction is substituted into the spatial spectrum of the original data in turn. |
| 6. Search the spectrum peak to obtain the maximum matching angle as the DOA using Equation (41). |
| Terminate iteration |
| Output: |
4.2.2. ESPRIT Algorithm
| Algorithm 3: DOA estimation based on the GMTFD-ESPRIT |
| Input: The GMTFD matrix |
| 1. The effective TF points of the GMTFD matrix are selected by Equation (20). |
| 2. The quasi-covariance matrix is constructed according to Equation (23). |
| 3. Perform the EVD of according to Equation (36). |
| 4. Obtain the eigenvector corresponding to the signal subspace. |
| 5. Take the first rows and the last rows of to form the matrices and , |
| respectively. |
| 6. Use the least squares method to obtain the transformation matrix . |
| Start iteration |
| 7. Determine the eigenvalue of . |
| 8. Update the estimation of DOA according to Equation (44). |
| Terminate iteration |
| Output: |
4.3. Computational Complexity Analysis
- (1)
- The computation complexity of the GMTFD is , where L is the number of samples.
- (2)
- The MUSIC computation complexity is , where denotes the DOA search scope.
- (3)
- The ESPRIT computation complexity is .
- (4)
- The NTA estimation computation complexity based on the Gerschgorin disk principle is .
5. Simulations
5.1. Parameter Settings
5.2. Simulation Results
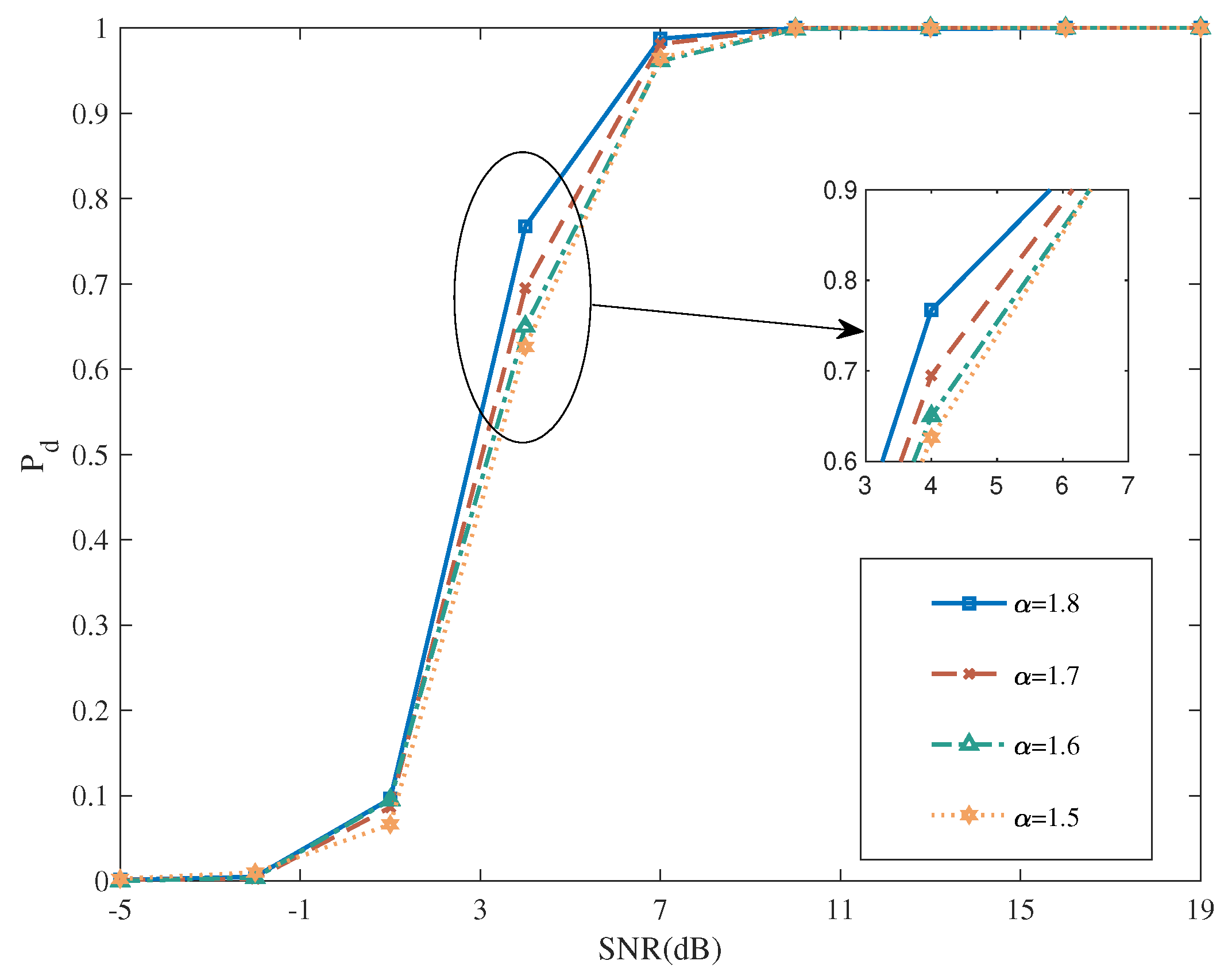
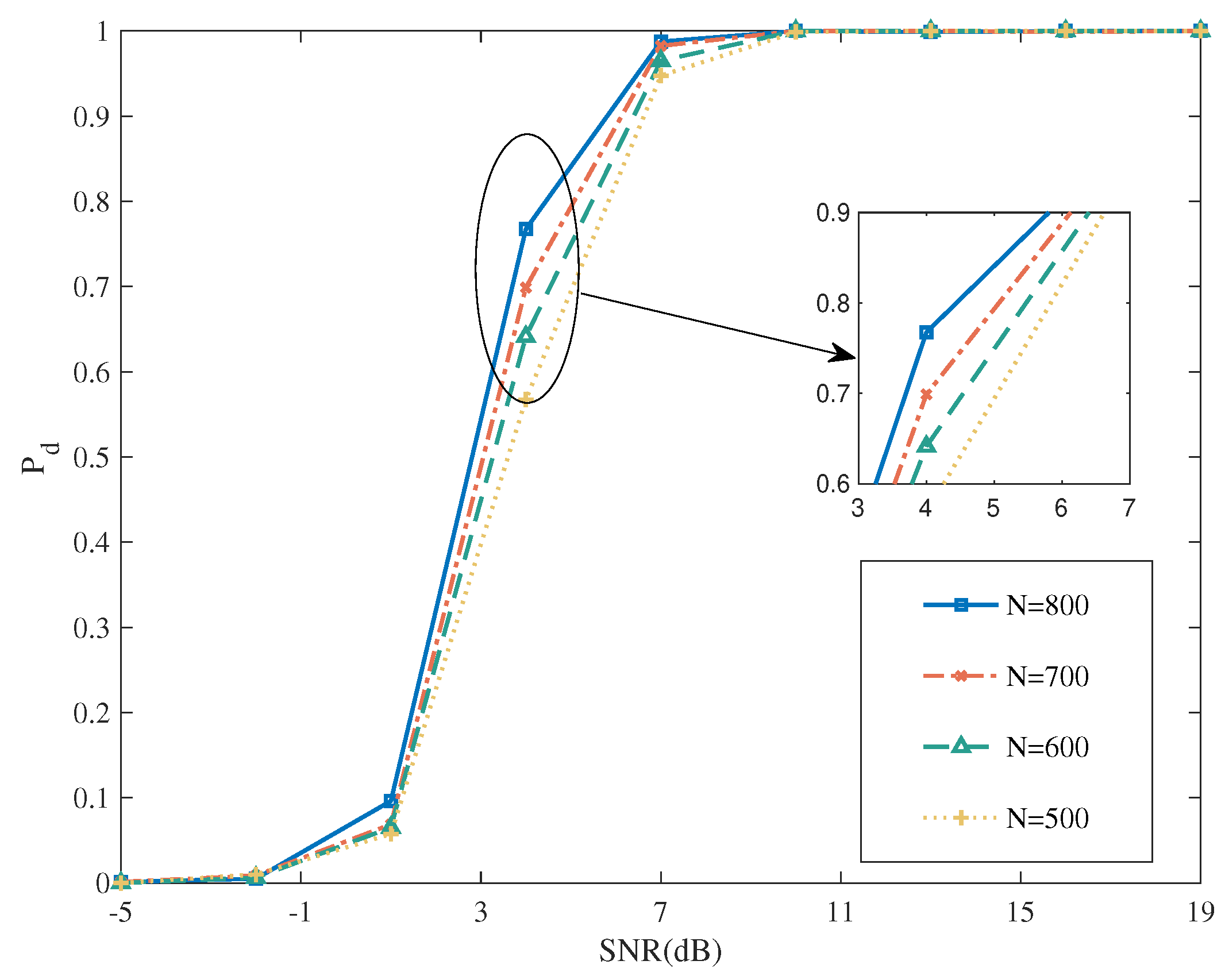
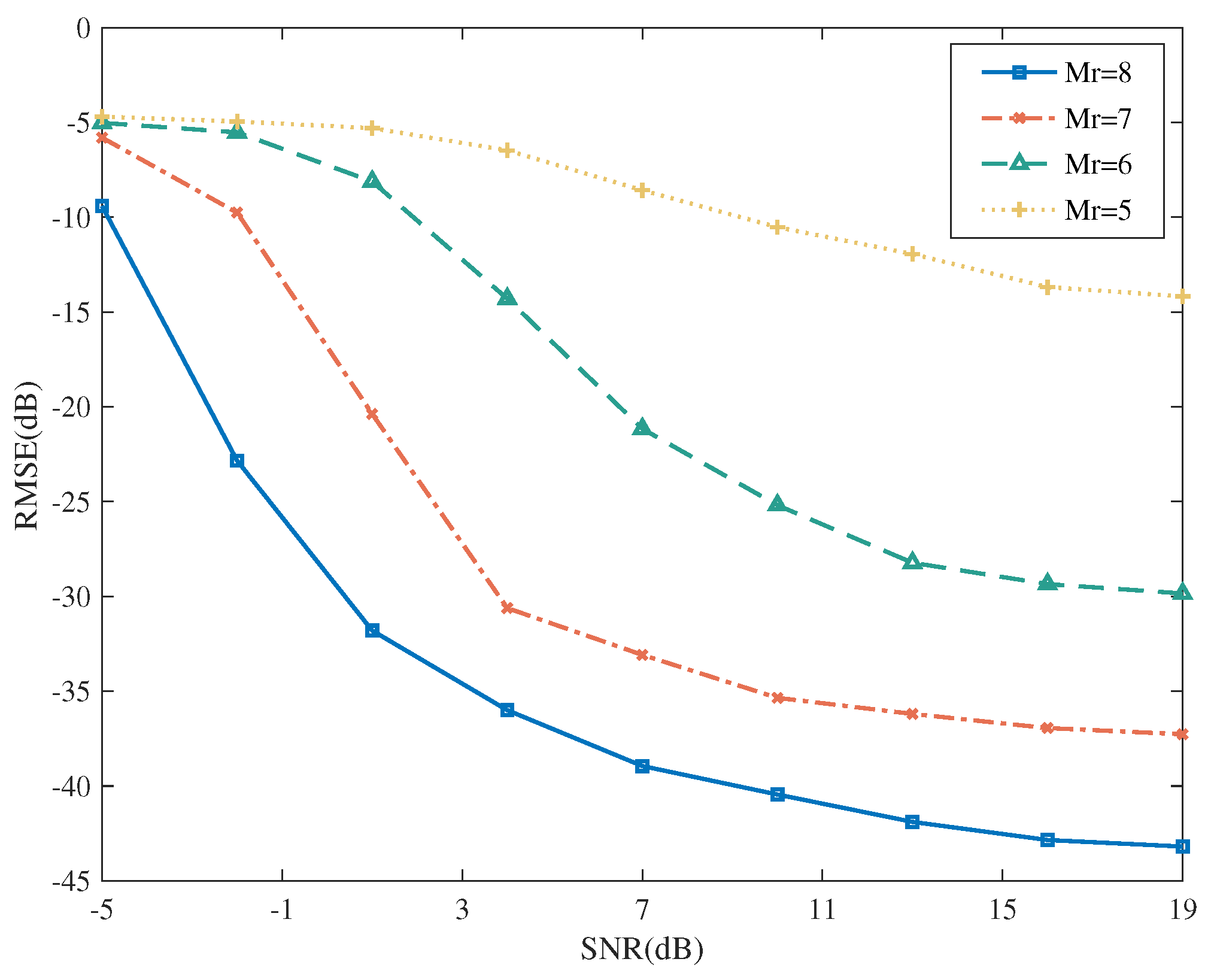
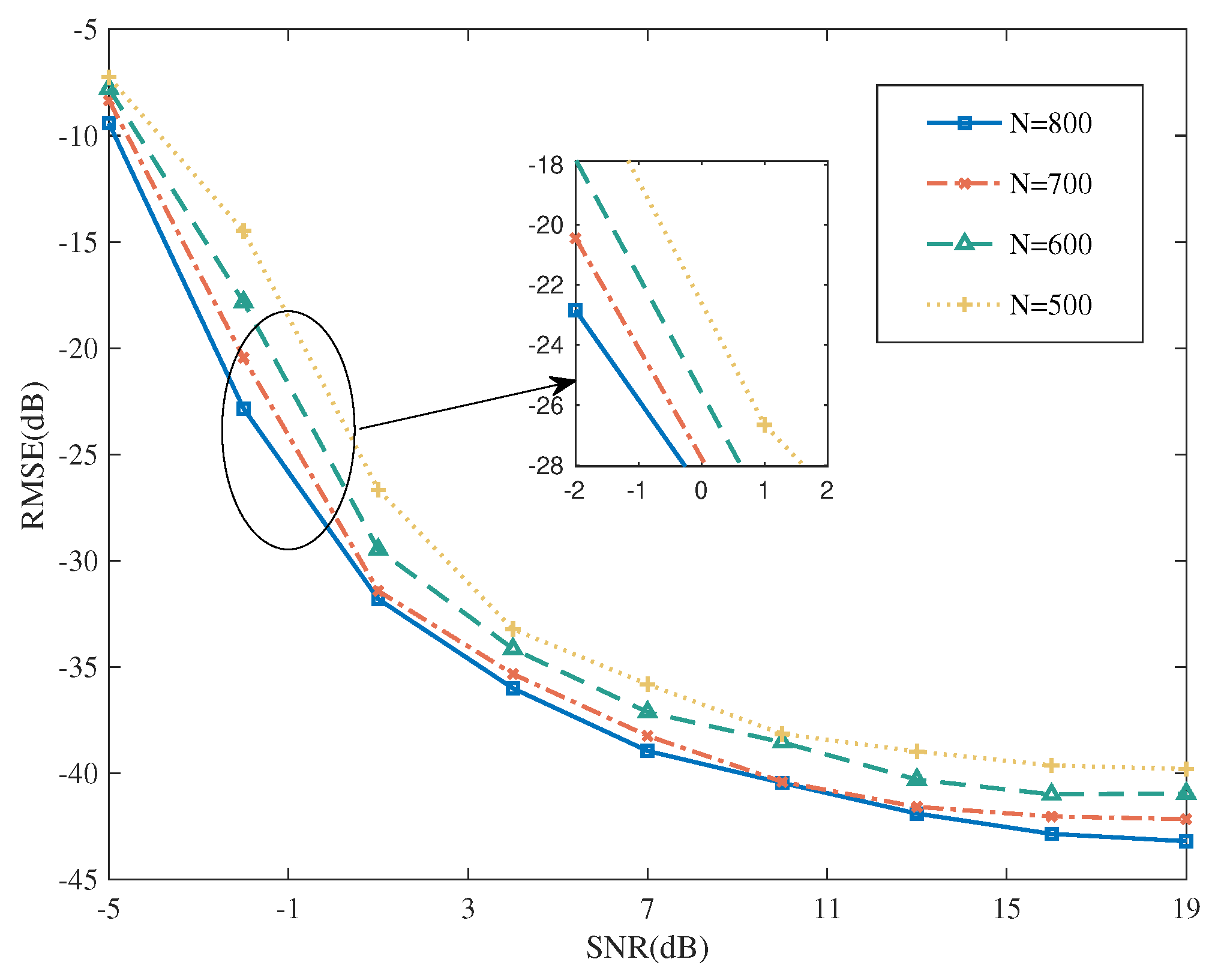
5.2.1. Performance for NTA Estimations
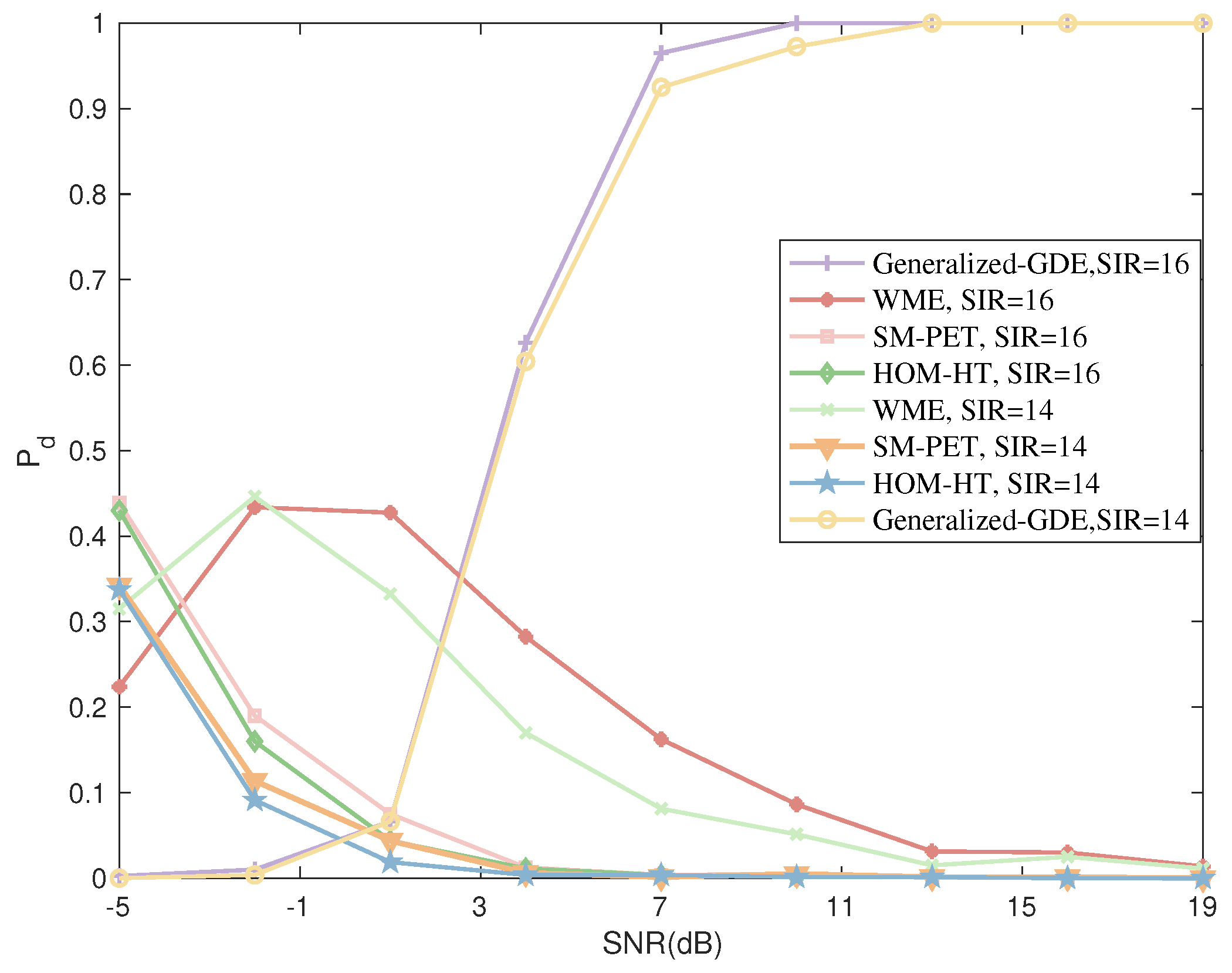
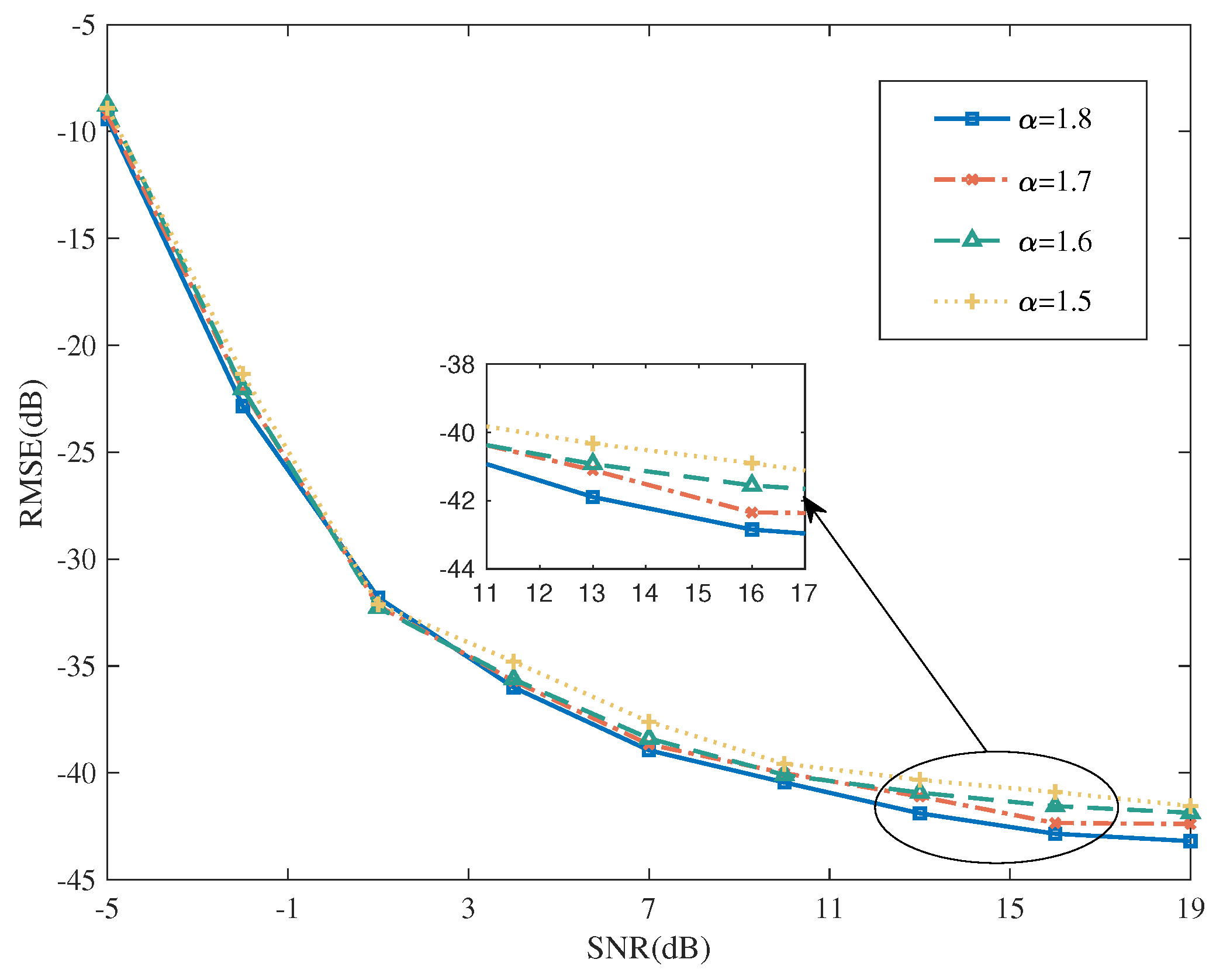
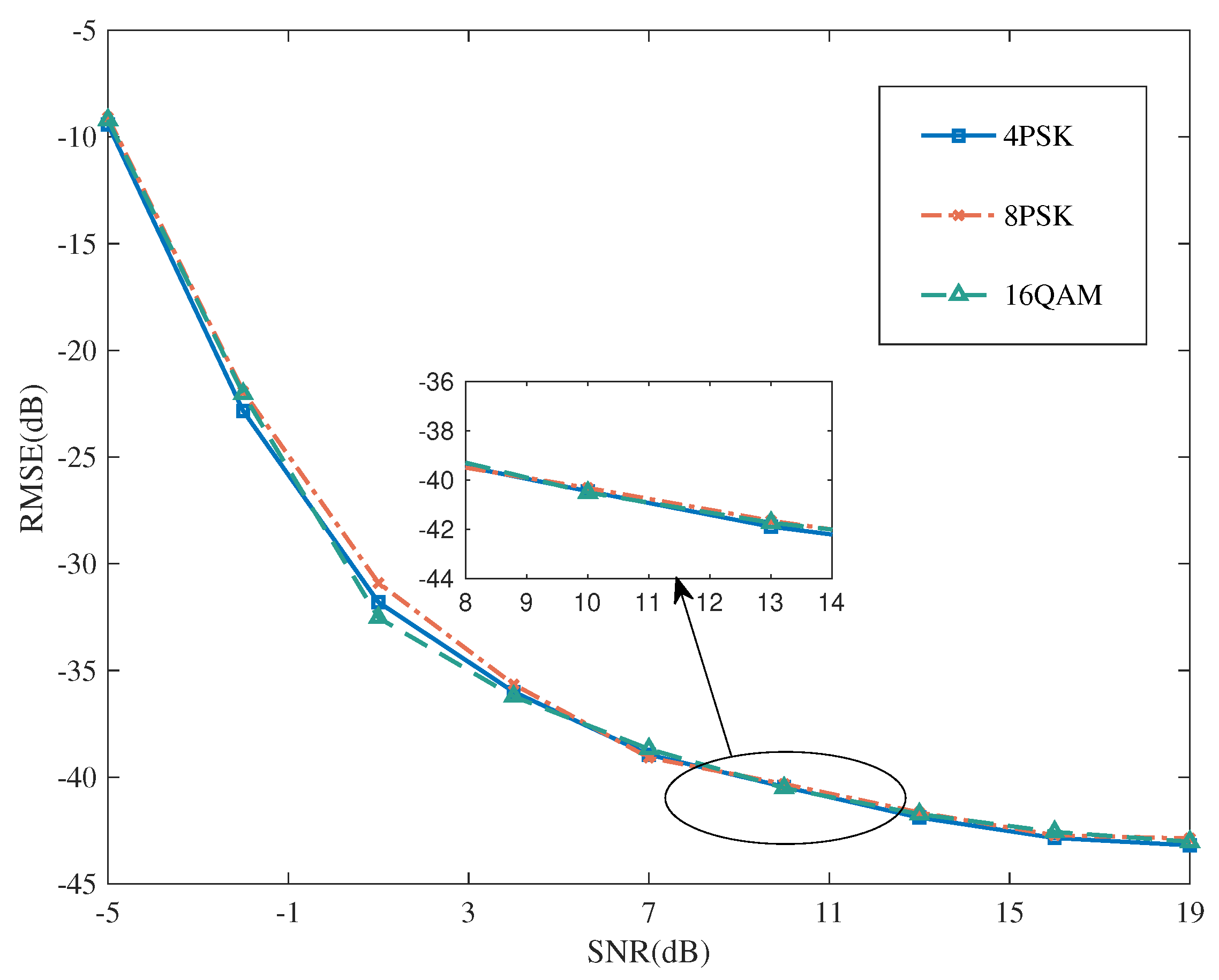
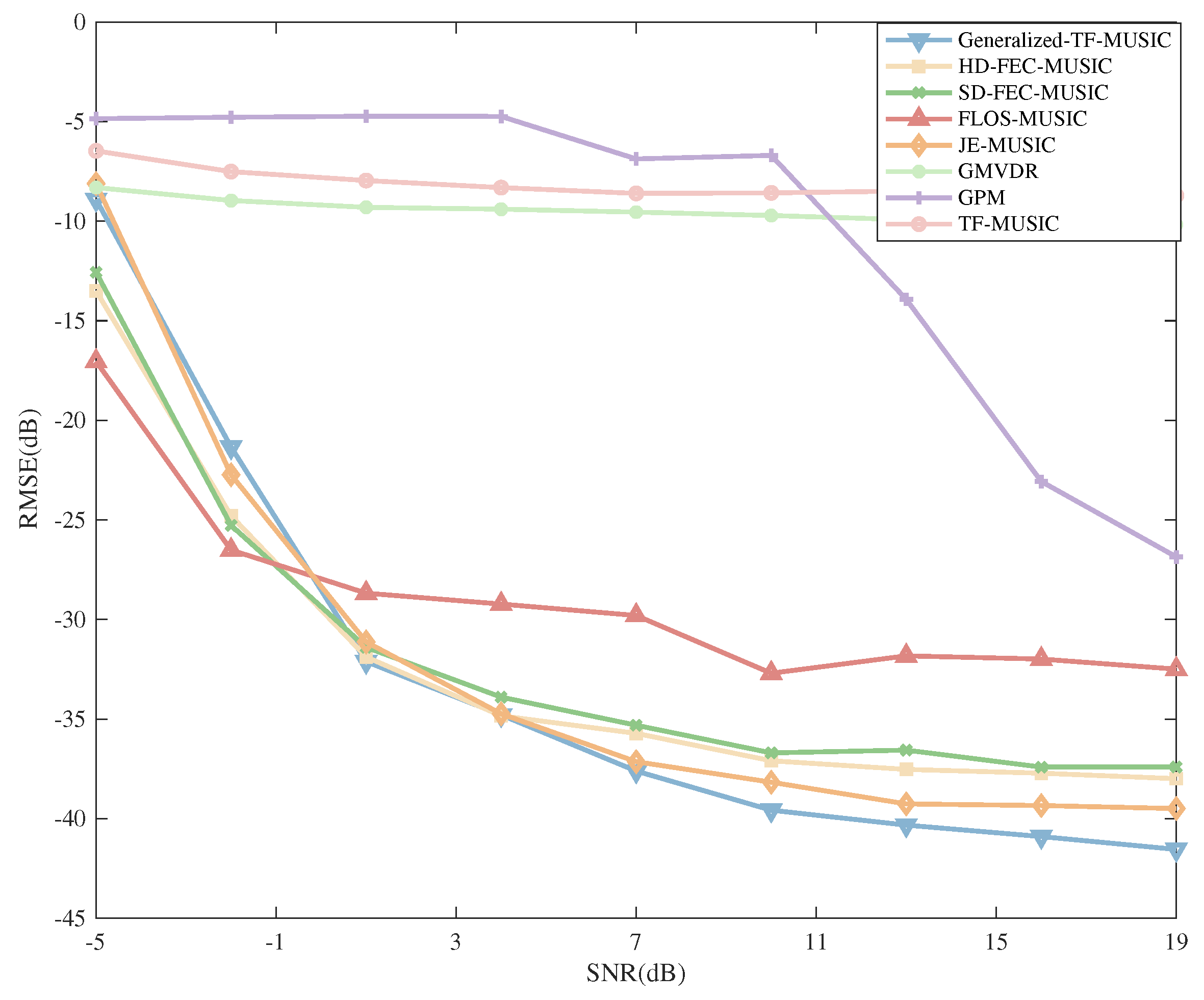
5.2.2. Performance for DOA Estimations
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Gao, Z.; Wan, Z.; Zheng, D.; Tan, S.; Masouros, C.; Ng, D.W.K.; Chen, S. Integrated sensing and communication with mmwave massive mimo: A compressed sampling perspective. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 1745–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhao, N. Adversarial attack and defense on deep learning for air transportation communication jamming. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wan, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.; Gen, M. Joint resource scheduling for uav-enabled mobile edge computing system in internet of vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 15624–15632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, K. Application of graph learning with multivariate relational representation matrix in vehicular social networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 2789–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, J.; Yin, X.; Yu, Z. Joint channel parameter estimation and scatterers localization. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 3324–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marey, M.; Dobre, O.A.; Mostafa, H. Cognitive Radios Equipped with Modulation and STBC Recognition Over Coded Transmissions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 1513–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, N. Attacking Modulation Recognition with Adversarial Federated Learning in Cognitive Radio-Enabled IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, A. Number of sources detection and aoa estimation of a wireless transmitter in multipath channels. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd URSI Atlantic and Asia Pacific Radio Science Meeting (AT-AP-RASC), Gran Canaria, Spain, 30 May–4 June 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Dong, Z. 2-d doa estimation of incoherently distributed sources considering gain-phase perturbations in massive mimo systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Xin, J.; Liu, C.; Zheng, N.; Sano, A. Improved capon estimator for high-resolution doa estimation and its statistical analysis. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica. 2023, 10, 1716–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.X.; Li, Z.T.; Tao, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.C. Quantum algorithm for music-based doa estimation in hybrid mimo systems. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2022, 7, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Vignesh, T.S.; Keshav, A.S.S.S.; Chandran, S.S.; Kirthiga, S. Parameter estimation and prediction using rotational invariant techniques in mimo system using usrp. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, 4–6 April 2019; pp. 833–837. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, Y.V.A.; Yuvaraj, R. Performance analysis of digital beamforming with modified esprit-music direction of arrival estimation algorithm for multi input multi output non orthogonal multiple access system over rayleigh fading channel. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Innovative Practices in Technology and Management (ICIPTM), Gautam Buddha Nagar, India, 23–25 February 2022; Volume 5, pp. 542–548. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, T.; Zhang, X.; Hassan, W.U. A higher-order propagator method for 2d-doa estimation in massive mimo systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurwanz, M.; Mietzner, J.; Hoeher, P.A. Improving estimation performance of compressive sensing- based multiple-input multiple-output radar using electronic beamsteering. IET Radar Sonar Nav. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wen, F. Phase compensation-based 2d-doa estimation for emvs-mimo radar. In IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems; IEEE: Toulouse, France, 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Ldnadmm-net: A denoising unfolded deep neural network for direction-of-arrival estimations in a low signal-to-noise ratio. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, W.; Li, Y.; Jin, M. Application of symplectic geometry mode decomposition based on gaussian process space angle in doa estimation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 8500712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Wang, H.; Gui, G.; Sari, H.; Adachi, F. Polarized intelligent reflecting surface aided 2d-doa estimation for nlos sources. In IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications; IEEE: Toulouse, France, 2024; p. 1-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, J.; Wang, X.; Lan, X.; Liu, W. A generalized noise reconstruction approach for robust doa estimation. IEEE Trans. Radar Syst. 2023, 1, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yang, D.; Mo, S. A doa estimation algorithm based on eigenvalues ranking problem. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Dong, J.; Jin, L.; Gao, F. Bayesian robust tensor factorization for angle estimation in bistatic mimo radar with unknown spatially colored noise. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 6051–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Sun, M.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Enhanced doa estimation with co-prime array in the scenario of impulsive noise: A pseudo snapshot augmentation perspective. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 11603–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Han, X.; Yin, J. Enhanced second-order off-grid doa estimation method via sparse reconstruction based on extended coprime array under impulsive noise. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 8500417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Yang, G.; Li, P.; Zhou, D.; Tian, L. Research on direction finding method under impulsive noise based on nonuniform linear array. J. Sens. 2024, 2024, 9936133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Tao, L.; Ren, H.; Wu, B.; Ye, L. Beyond 10log10m array gain: A beamforming method under non-gaussian noise and multi-sources. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Guo, Y. A bistatic mimo radar angle estimation method for coherent sources in impulse noise background. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 116, 3567–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Sun, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Enhanced bnc approach for noncircular signals direction finding with sparse array in the scenario of impulsive noise. IEEE Trans. Aero. Elec. Syst. 2023, 59, 6265–6277. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, S. Doa estimations with limited snapshots based on improved rank-one correlation model in unknown nonuniform noise. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 10308–10319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Xin, J.; Zheng, N.; Ohmori, H.; Sano, A. Subspace-based near-field source localization in unknown spatially nonuniform noise environment. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 4713–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somekh, O.; Simeone, O.; Bar-Ness, Y.; Su, W. Detecting the number of transmit antennas with unauthorized or cognitive receivers in mimo systems. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Military Communications Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 29–31 October 2007; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Bar-Ness, Y.; Su, W. Adaptive estimation of the number of transmit antennas. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Military Communications Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 29–31 October 2007; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, K.; Nz’eza, C.N.; Gautier, R.; Radoi, E.; Berbineau, M.; Dayoub, I. Blind detection of the number of transmitting antennas for spatially-correlated mimo systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 11th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications, St. Petersburg, Russia, 23–25 August 2011; pp. 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- Oularbi, M.R.; Gazor, S.; Aissa-El-Bey, A.; Houcke, S. Enumeration of base station antennas in a cognitive receiver by exploiting pilot patterns. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2013, 17, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkarimi, M.; Karami, E.; Dobre, O.A.; Win, M.Z. Number of transmit antennas detection using time-diversity of the fading channel. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 4031–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Cimini, L.J.; Zhang, H. Hypothesis testing based fast-converged blind estimation of transmit-antenna number for mimo systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 5084–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cimini, L.J.; Zhang, H. Estimation of mimo transmit-antenna number using higher-order moments-based hypothesis testing. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2018, 7, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, A. Joint Estimation of the Number of Antennas and AoA of a Wireless Communication Transmitter. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems & Technology (PAST), Waltham, MA, USA, 11–14 October 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Cimini, L.J.; Zhang, H. Blind estimation of transmit-antenna number for non-cooperative multiple-input multiple-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing systems. IET Commun. 2017, 11, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Hwang, S.S.; Shin, S.J.; Pyun, J.Y. Beamspace based aic and mdl algorithm for counting the number of signals in specific range. In Proceedings of the 2022 13th International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks, Barcelona, Spain, 5–8 July 2022; pp. 130–133. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Hu, G.; Zhou, H.; Guo, S. Research on underdetermined doa estimation method with unknown number of sources based on improved cnn. SENSORS 2023, 23, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, N.; Chen, Y.; Gong, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, N. Reliable detection of transmit- antenna number for mimo systems in cognitive radio-enabled internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 11324–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.A.; Yao, X. Multiobjective bilevel evolutionary approach for off-grid direction-of-arrival estimation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 113, 107954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, N.D.; Andersson, M.H.; Box, T.; Courtois, F.L.; Cronin, D.; Holdsworth, N.; Kinneging, N.; Mendes, S.; Merck, T.; Mouat, J.; et al. Impulsive noise pollution in the northeast atlantic: Reported activity during 2015–2017. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Mao, X.P.; Qian, C.; Liu, Y.T. Robust relaxation for coherent doa estimation in impulsive noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boashash, B.; Aïssa-El-Bey, A. Robust multisensor time-frequency signal processing: A tutorial review with illustrations of performance enhancement in selected application areas. Digit. Signal Process. 2018, 77, 153–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sa’d, M.; Boashash, B.; Gabbouj, M. Design of an optimal piece-wise spline wigner-ville distribution for tfd performance evaluation and comparison. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 3963–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; He, Q.; Peng, Z. Parameterized resampling time-frequency transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 5791–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh-Trung, N.; Belouchrani, A.; Abed-Meraim, K.; Boashash, B. Separating more sources than sensors using time–frequency distributions. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2005, 17, 845079. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Shi, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Spatial Parameter Identification for MIMO Systems in the Presence of Non-Gaussian Interference. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071243
Zhang J, Shi Z, Chen Y, Liu M. Spatial Parameter Identification for MIMO Systems in the Presence of Non-Gaussian Interference. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(7):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071243
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junlin, Zihui Shi, Yunfei Chen, and Mingqian Liu. 2024. "Spatial Parameter Identification for MIMO Systems in the Presence of Non-Gaussian Interference" Remote Sensing 16, no. 7: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071243
APA StyleZhang, J., Shi, Z., Chen, Y., & Liu, M. (2024). Spatial Parameter Identification for MIMO Systems in the Presence of Non-Gaussian Interference. Remote Sensing, 16(7), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16071243










