Underlying Topography Estimation over Forest Using Maximum a Posteriori Inversion with Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Scattering Model
3.1. PolInSAR Data Description
3.2. The Random Volume over Ground (RVoG) Model
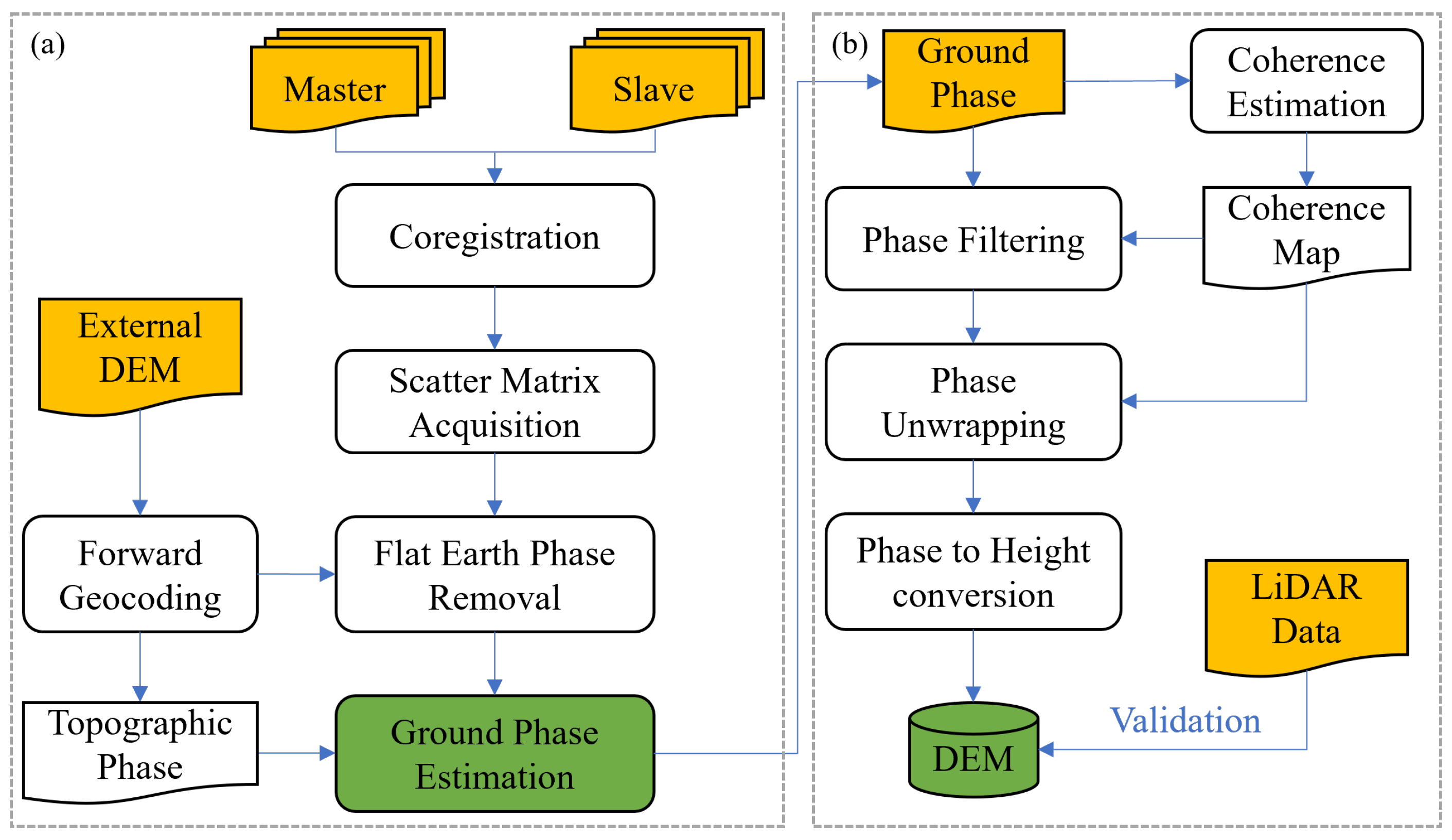
4. Maximum a Posteriori Estimation of the Ground Phase
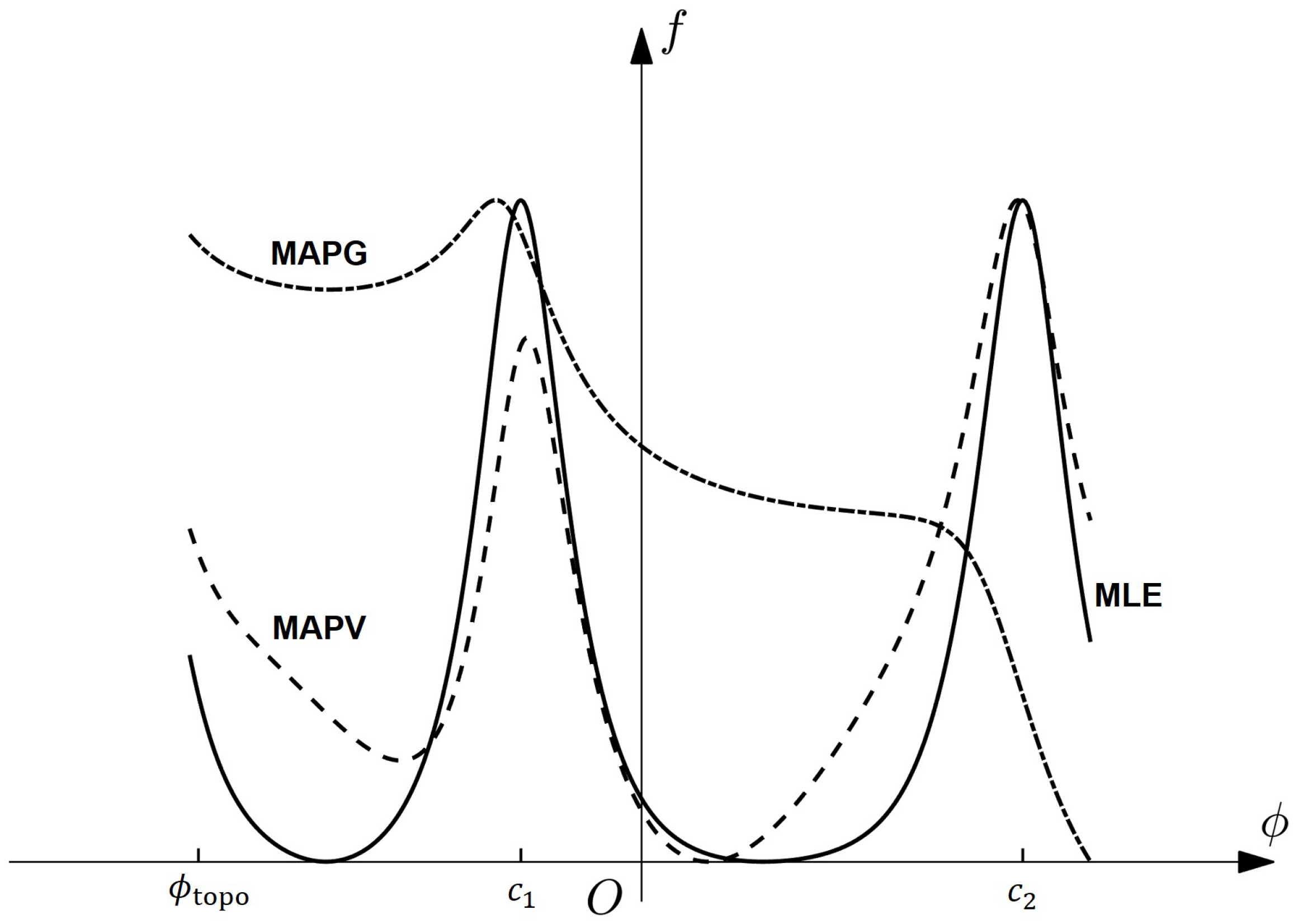
4.1. A Prior Probability Model of the Ground Phase
4.2. MAP with Von Mises Distribution as Prior
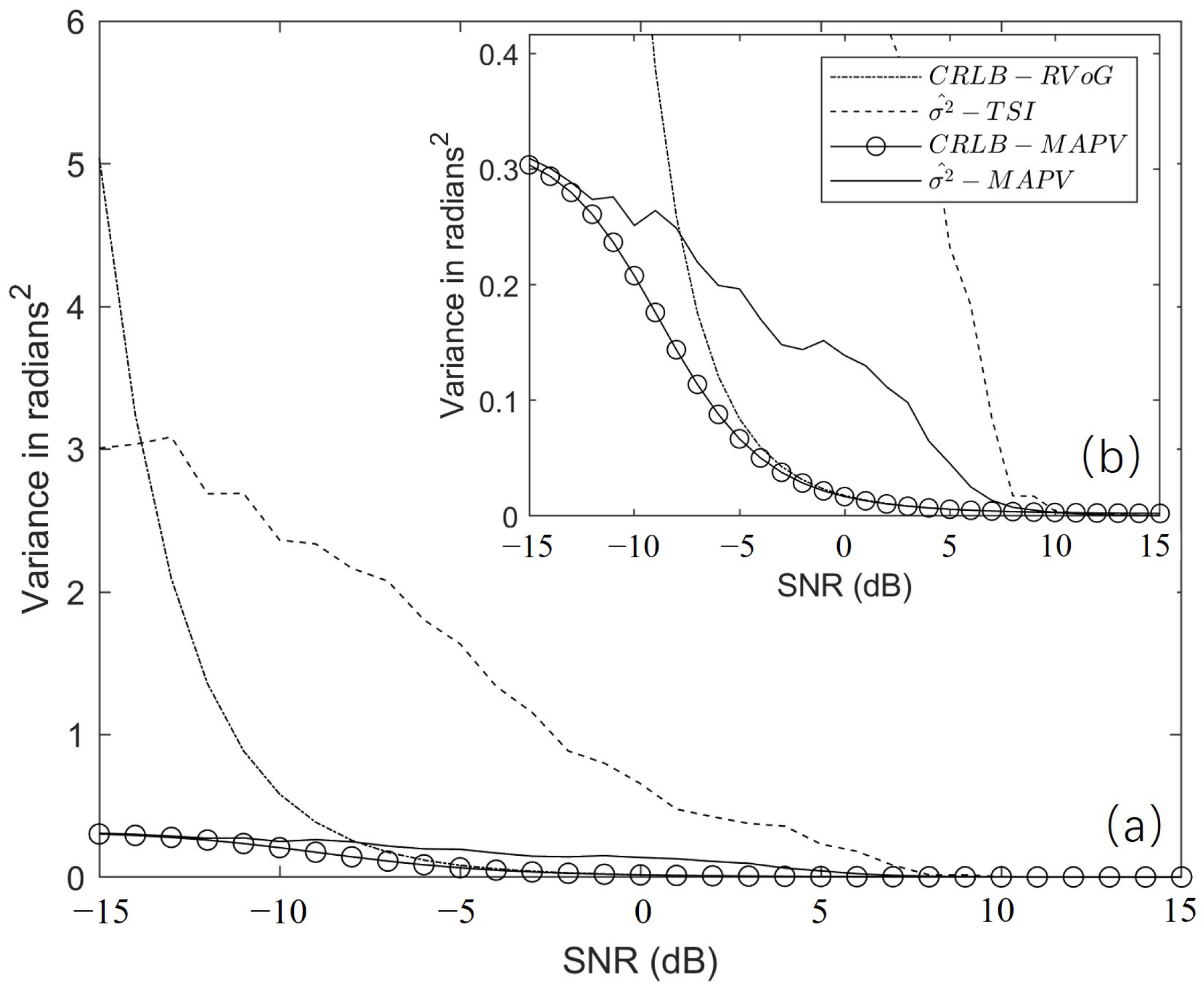
4.3. The Cramer–Rao Lower Bound Analysis
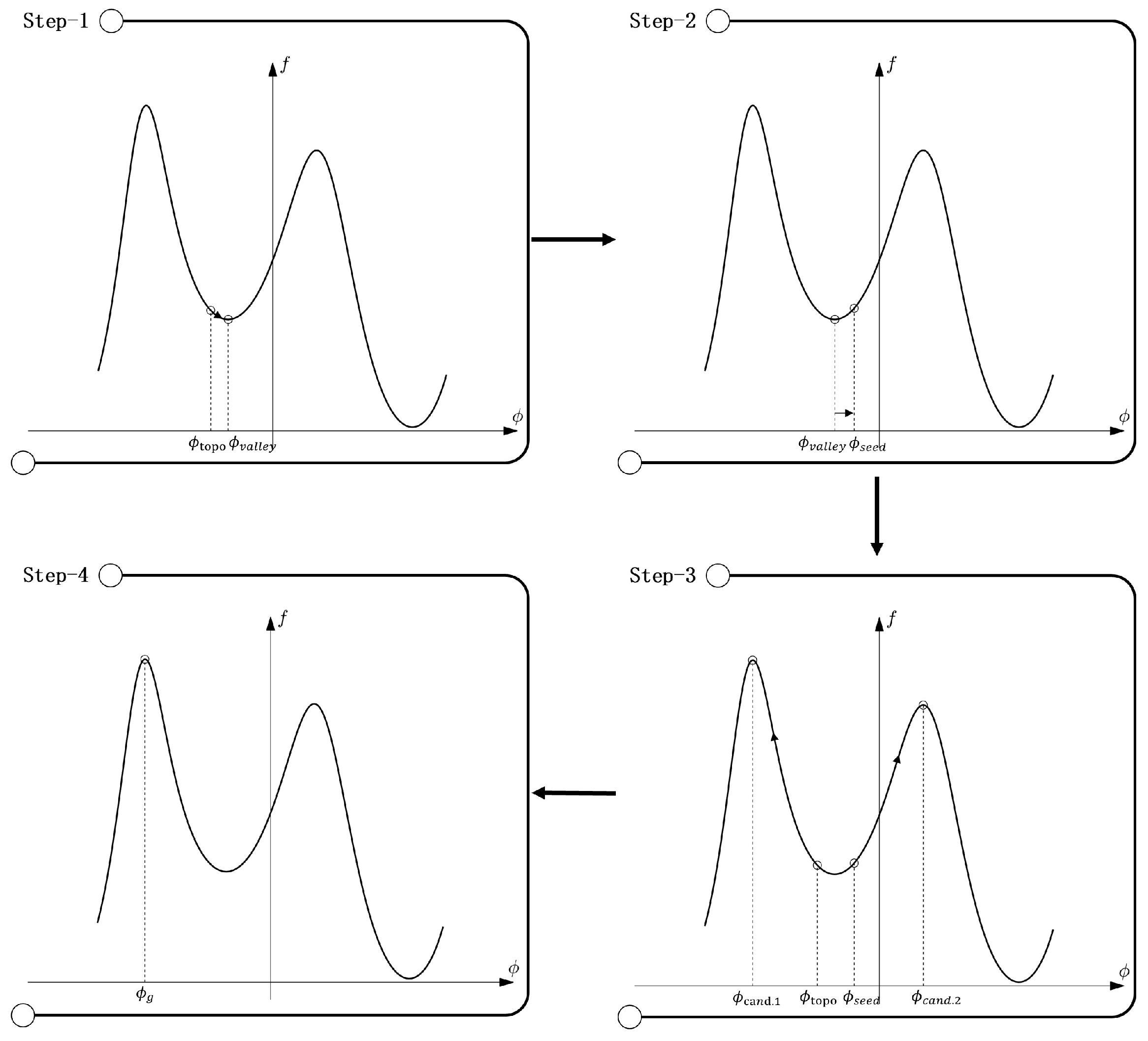
4.4. Four-Step Optimized Solution for MAPV
- Initial phase: Due to the presence of two peaks in the objective function, a single initial point is prone to fall into the local maximum. Therefore, it is necessary to choose an appropriate strategy to ensure that the results converge to the global maximum.
- Global learning rate: Because of the large differences between the objective functions of different pixels, it is very important to choose the global learning rate so that the method can adapt to all objective functions.
4.4.1. Initial Phase
- Step 1: Gradient descent using as initial phase. Get the between the two peaks.
- Step 2: Give the a in the opposite direction to as a .
- Step 3: Perform gradient ascent separately using this and to obtain the two peak values and their respective phases.
- Step 4: Compare the magnitudes of these two peak values and select the phase corresponding to the larger peak value as the final result.
4.4.2. Global Learning Rate
| Algorithm 1: Framework of improved RMSprop algorithm. |
| Require: Global learning rate , Decay rate , Initial phase |
| Initialize: , , , , , |
 |
5. Results
5.1. Evaluation Indicator
5.2. Efficiency of FSO for MAPV
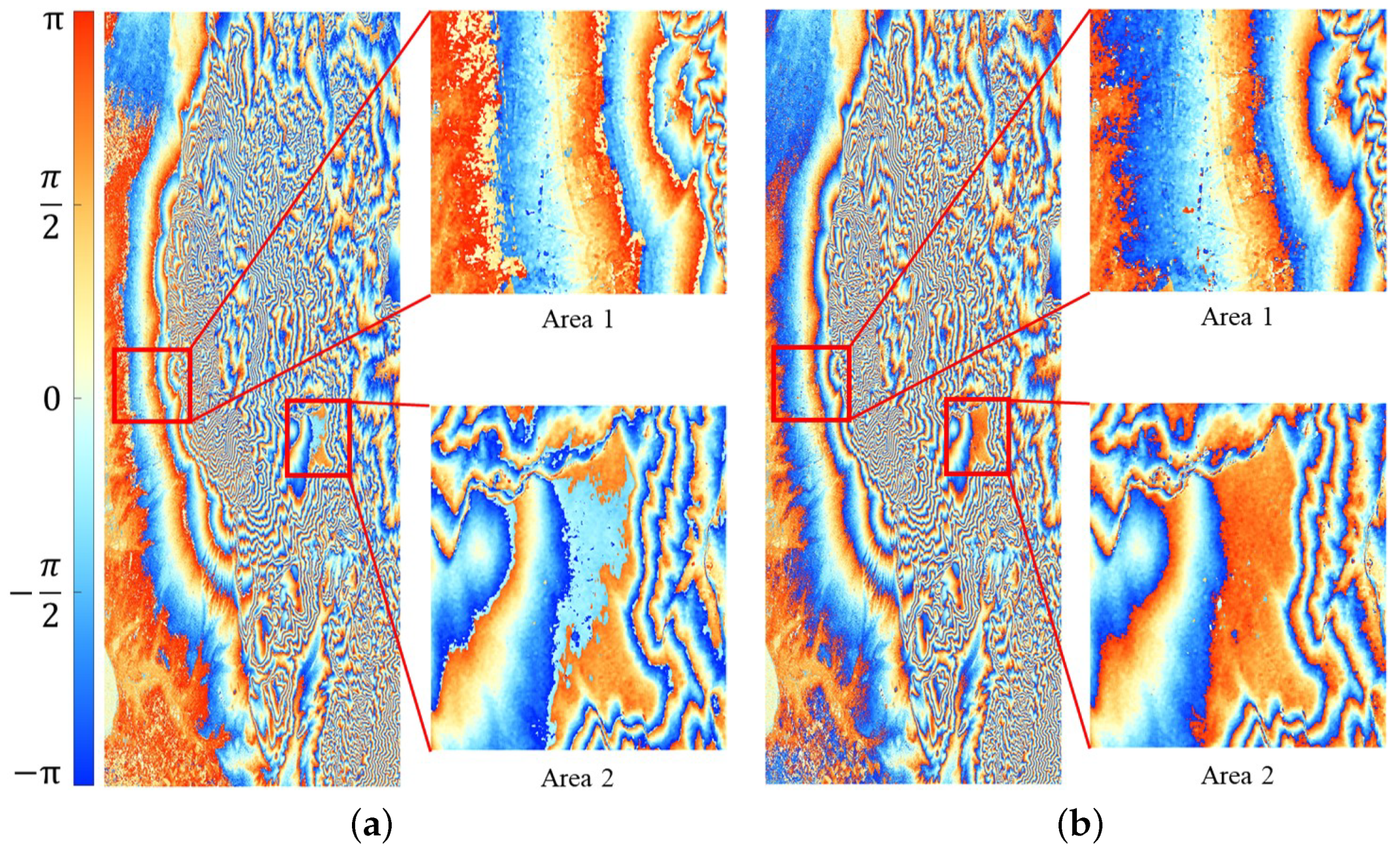
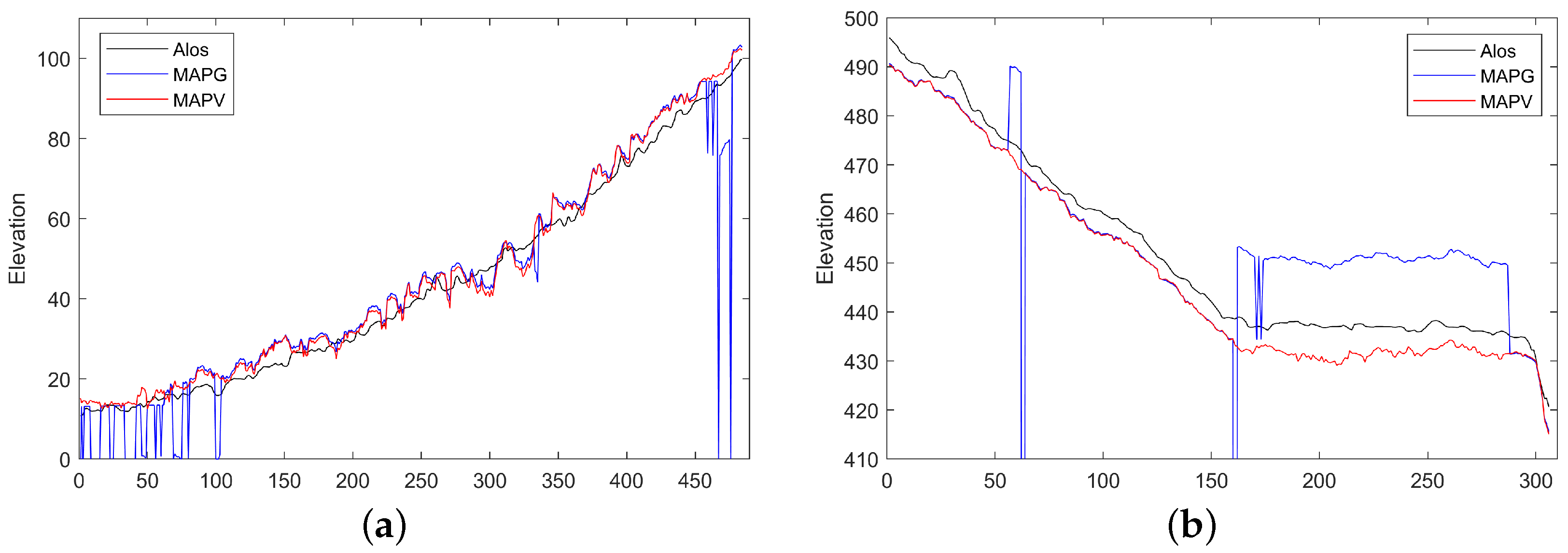
5.3. Results of DEM Inversion in the Test Area
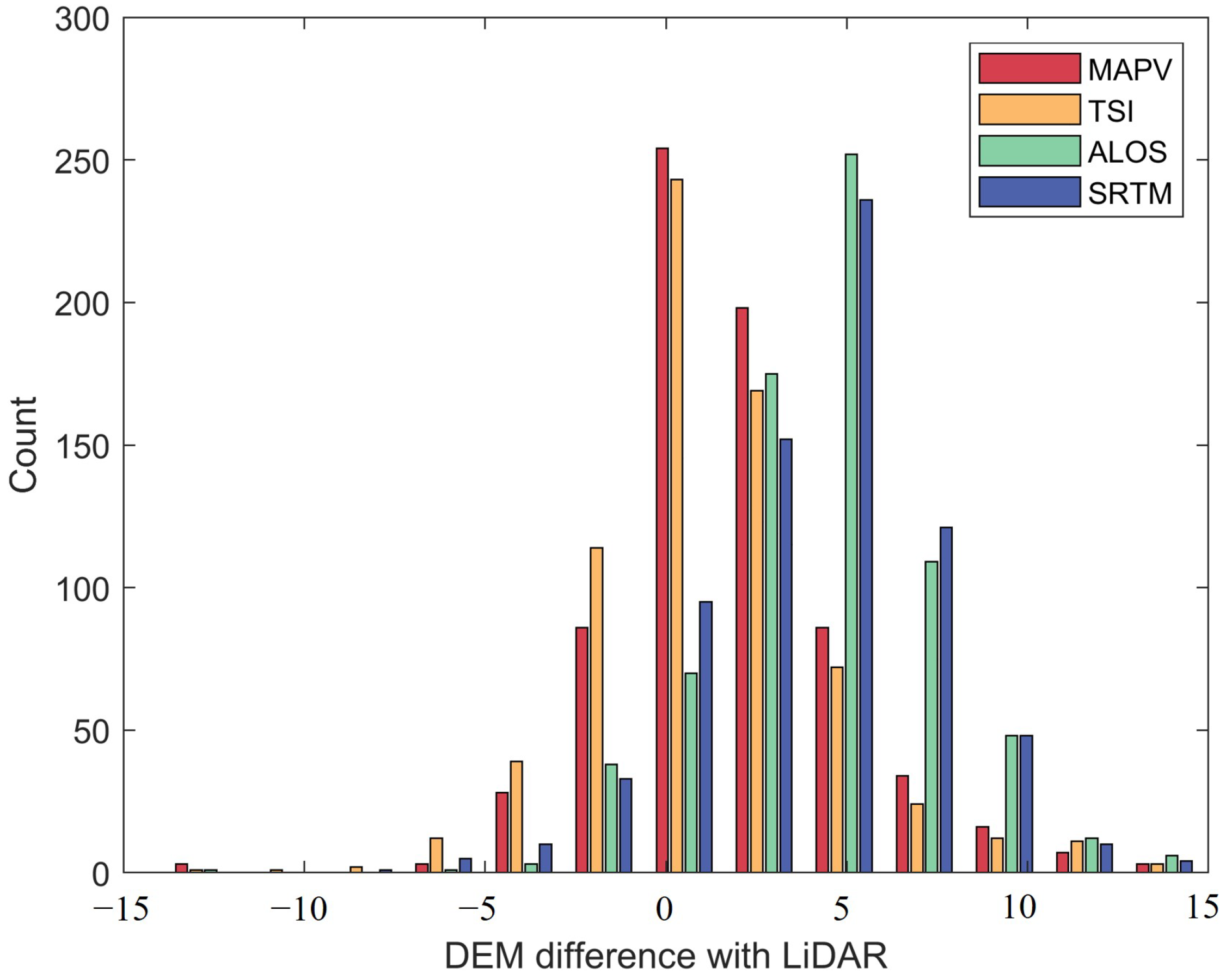
5.4. Performance Assessment of the Proposed Method
6. Conclusions
- Compared to the traditional exhaustive search method, FSO significantly improves computational efficiency without compromising accuracy.
- The MAPV method effectively addresses the issue of elevation jumps in DEM caused by the discontinuity in ground phase solutions by MAPG.
- Using IceSat-2 data as a benchmark, the DEM of the test forest area is compared with the DEMs of Alos, SRTM, and TSI. The results show that MAPV has better estimation performance, with improvements in both mean error (ME) and root mean square error (RMSE).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| PolInSAR | Polarimetric Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| Lidar | Light Detection and Ranging |
| RVoG | Random Volume over Ground |
| TSI | Three-Stage Inversion |
| MAP | Maximum a Posteriori |
| MAPG | Maximum a Posteriori with Gaussian distribution as prior |
| MAPV | Maximum a Posteriori with Von Mises distribution as prior |
| CRLB | Cramer–Rao Lower Bound |
| FSO | Four-Step Optimization |
| ME | Mean Error |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
Appendix A. The Fisher Information of MAPV
Appendix B. Gradient of the MAPV Objective Function
References
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, Y. Development of a GIS-based decision-support system of forest resource management. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2006, 49, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, H.C.; Hölbling, D.; Dias, V.C.; Grohmann, C.H. Application of Object-Based Image Analysis for Detecting and Differentiating between Shallow Landslides and Debris Flows. GI_Forum 2023 2023, 11, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, A.E.; Oğuz, H.; Karas, I.R.; Aruga, K. Using LiDAR Technology in Forestry Activities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 151, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Ma, H.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, W. High-Accuracy Filtering of Forest Scenes Based on Full-Waveform LiDAR Data and Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Hao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Li, T.; Wang, T.; Lu, W.; Ding, Y.; Hu, H. Modeling the Global Relationship via the Point Cloud Transformer for the Terrain Filtering of Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshamsi, M.; Xia, J.; Yokoya, N.; Garcia, M.; Lavalle, M.; Pottier, E.; Balzter, H. Tropical Forest Canopy Height Estimation from Combined Polarimetric SAR and LiDAR Using Machine-Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 172, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martinez, C.; Alonso, A.; Fabregas, X.; Papathannassiou, K.P. Ground Topography Estimation over Forests Considering Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3612–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, B. Estimation of Pine Forest Height and Underlying DEM Using Multi-Baseline P-Band PolInSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, R. Underlying Topography Estimation over Forest Areas Using High-Resolution P-Band Single-Baseline PolInSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Z. Underlying Topography Extraction over Forest Areas from Multi-Baseline PolInSAR Data. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Suo, Z.; Guo, R.; Bao, Z. S-RVoG Model for Forest Parameters Inversion over Underlying Topography. Electron. Lett. 2013, 49, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenglong Guo, S.G.; Yurun Tian, Y.T.; Yang Li, Y.L.; Qiang Yin, Q.Y.; Wen Hong, W.H. Estimation of Ground Topography under Forests with Polarimetric SAR Interferometry Data. In Proceedings of the IET International Radar Conference 2015, Hangzhou, China, 14–16 October 2015; p. 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mette, T.; Papathanassiou, K.; Hajnsek, I. Biomass Estimation from Polarimetric SAR Interferometry over Heterogeneous Forest Terrain. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2004—IGARSS ’04: Proceedings, 2004, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; Volume 1, pp. 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Rodriguez, E.; Kim, Y.; Boerner, W. Polarimetric SAR Interferometry for Forest Canopy Analysis by Using the Super-Resolution Method. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2001: Scanning the Present and Resolving the Future: Proceedings: IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (Cat. No.01CH37217), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; Volume 3, pp. 1101–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D. A Modified ESPRIT Algorithm to Estimate Tree Height Using Simulated Dual-Polarization PolInSAR Datasets. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2018; 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 4–7 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Jun, Z.Y.; Gang, W.Z. Joint Phase and Power Estimation for Polarimetric Interferometric SAR Based on TEL-ESPRIT Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 16–19 October 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Sato, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Boerner, W.M. Interferometric Phase and Coherence of Forest Estimated by ESPRIT-based Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; Volume 2, pp. 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Boerner, W. Forest Height Feature Extraction in Polarimetric SAR Interferometry by Using Rotational Invariance Property. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003: 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium: Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 3, pp. 1426–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.P.; Wang, C.; Zou, B.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Le, V.N. Forest Height Extraction from PolInSAR Image Using a Hybrid Method. Int. J. Signal Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 7, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaso, S.; Reigber, A.; Ferro-Famil, L. Evaluation of the ESPRIT Approach in Polarimetric Interferometric SAR. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2005. IGARSS ’05, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 29 July 2005; Volume 1, pp. 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Madsen, S.N.; Moghaddam, M.; Van Zyl, J.J. Vegetation Characteristics and Underlying Topography from Interferometric Radar. Radio Sci. 1996, 31, 1449–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treuhaft, R.N.; Siqueira, P.R. Vertical Structure of Vegetated Land Surfaces from Interferometric and Polarimetric Radar. Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 141–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.; Papathanassiou, K. Three-Stage Inversion Process for Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. IEE Proc.—Radar Sonar Navig. 2003, 150, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabb, M.; Flynn, T.; Carande, R. Full Maximum Likelihood Inversion of Polinsar Scattering Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2004, IGARSS ’04. Proceedings, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1232–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabb, M.; Carande, R. Robust Inversion of Vegetation Structure Parameters from Low-Frequency, Polarimetric Interferometric SAR. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2001: Scanning the Present and Resolving the Future: Proceedings: IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (Cat. No.01CH37217), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; Volume 7, pp. 3188–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, F.; Lee, S.-K.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Forest Height Estimation by Means of Pol-InSAR Data Inversion: The Role of the Vertical Wavenumber. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5294–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lv, X.; Li, X.; Chai, H. Maximum a Posteriori Inversion for Forest Height Estimation Using Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, N.I. Statistical Analysis of Circular Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Letzepis, N. On the von Mises Approximation for the Distribution of the Phase Angle between Two Independent Complex Gaussian Vectors. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 3247–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammalamadaka, S.R.; Sengupta, A. Topics in Circular Statistics; Number v. 5 in Series on Multivariate Analysis; World Scientific: River Edge, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Haji, S.H.; Abdulazeez, A.M. Comparison of optimization techniques based on gradient descent algorithm: A review. PalArch’s J. Archaeol. Egypt/Egyptol. 2021, 18, 2715–2743. [Google Scholar]
- Ruder, S. An Overview of Gradient Descent Optimization Algorithms. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.04747. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalati, W.; Zwally, H.J.; Bindschadler, R.; Csatho, B.; Farrell, S.L.; Fricker, H.A.; Harding, D.; Kwok, R.; Lefsky, M.; Markus, T.; et al. The ICESat-2 Laser Altimetry Mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Shan, J. Comprehensive Evaluation of the ICESat-2 ATL08 Terrain Product. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 8195–8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.; Papathanassiou, K. Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Polarization Coherence Tomography: Polarization coherence tomography. Radio Sci. 2006, 41, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Monti-Guarnieri, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Massonet, D. InSAR Principles—Guidelines for SAR Interferometry Processing and Interpretation. ESA Train. Man. 2007, 19, A17–A19. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A. Circular data. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Ferro-Famil, L.; Reigber, A. Estimation of Forest Structure, Ground, and Canopy Layer Characteristics From Multibaseline Polarimetric Interferometric SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1086–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, F. A PolinSAR Inversion Error Model on Polarimetric System Parameters for Forest Height Mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5669–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roueff, A.; Arnaubec, A.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Refregier, P. Cramer–Rao Lower Bound Analysis of Vegetation Height Estimation With Random Volume Over Ground Model and Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaubec, A.; Roueff, A.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Refregier, P. Vegetation Height Estimation Precision With Compact PolInSAR and Homogeneous Random Volume Over Ground Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refregier, P.; Roueff, A.; Arnaubec, A.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C. Invariant Contrast Parameters of PolInSAR Homogenous RVoG Model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1414–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, M.; Cumming, I. Maximum Likelihood Estimation for SAR Interferometry. In Proceedings of the IGARSS ’94—1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–12 August 1994; Volume 4, pp. 2272–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.B.; Pedersen, M.S. The Matrix Cookbook; Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 2008; Volume 7, pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
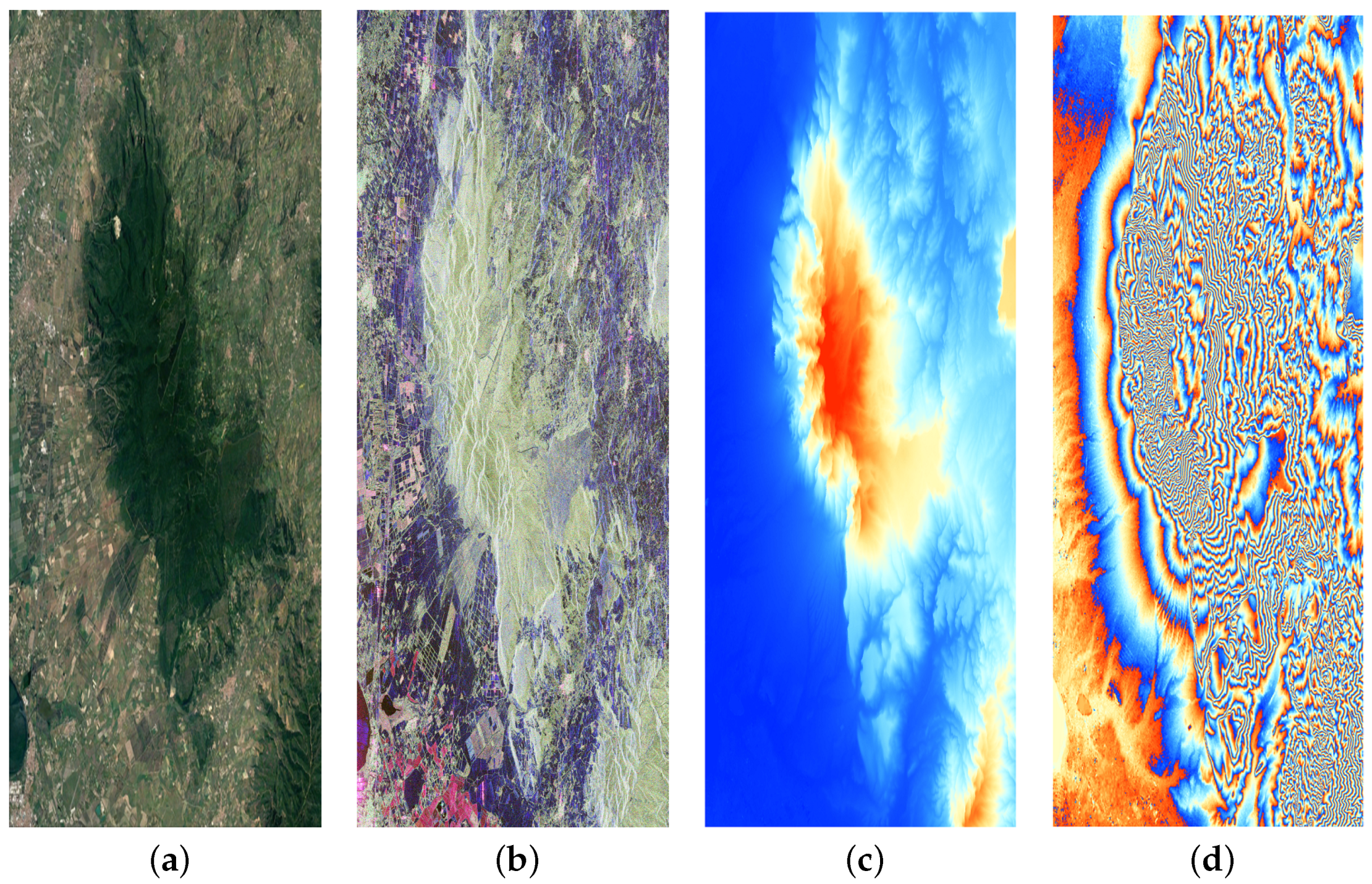




| Size | Time (s) | Iterations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES | FSO | ES | FSO | |||
| 7015 × 2673 | 6880.0 | 1235.1 | 360 | 24.5 | 99.97% | 99.99% |
| ID | ||
|---|---|---|
| MAPG | MAPV | |
| Area 1 | 87.48% | 99.06% |
| Area 2 | 89.13% | 99.14% |
| DEM | ME (m) | RMSE (m) |
|---|---|---|
| TSI | −13.2407 | 73.7140 |
| ALOS | 2.6370 | 7.7956 |
| SRTM | 2.1311 | 7.8972 |
| MAPV | 0.2111 | 5.9944 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Lv, X.; Huang, Z. Underlying Topography Estimation over Forest Using Maximum a Posteriori Inversion with Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16060948
Li X, Lv X, Huang Z. Underlying Topography Estimation over Forest Using Maximum a Posteriori Inversion with Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(6):948. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16060948
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoshuai, Xiaolei Lv, and Zenghui Huang. 2024. "Underlying Topography Estimation over Forest Using Maximum a Posteriori Inversion with Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry" Remote Sensing 16, no. 6: 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16060948
APA StyleLi, X., Lv, X., & Huang, Z. (2024). Underlying Topography Estimation over Forest Using Maximum a Posteriori Inversion with Spaceborne Polarimetric SAR Interferometry. Remote Sensing, 16(6), 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16060948









