Abstract
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) ship detection and classification has gained unprecedented attention due to its important role in maritime transportation. Many deep learning-based detectors and classifiers have been successfully applied and achieved great progress. However, ships in SAR images present discrete and multi-centric features, and their scattering characteristics and edge information are sensitive to variations in target attitude angles (TAAs). These factors pose challenges for existing methods to obtain satisfactory results. To address these challenges, a novel target attitude angle-guided network (TAG-Net) is proposed in this article. The core idea of TAG-Net is to leverage TAA information as guidance and use an adaptive feature-level fusion strategy to dynamically learn more representative features that can handle the target imaging diversity caused by TAA. This is achieved through a TAA-aware feature modulation (TAFM) module. It uses the TAA information and foreground information as prior knowledge and establishes the relationship between the ship scattering characteristics and TAA information. This enables a reduction in the intra-class variability and highlights ship targets. Additionally, considering the different requirements of the detection and classification tasks for the scattering information, we propose a layer-wise attention-based task decoupling detection head (LATD). Unlike general deep learning methods that use shared features for both detection and classification tasks, LATD extracts multi-level features and uses layer attention to achieve feature decoupling and select the most suitable features for each task. Finally, we introduce a novel salient-enhanced feature balance module (SFB) to provide richer semantic information and capture the global context to highlight ships in complex scenes, effectively reducing the impact of background noise. A large-scale ship detection dataset (LSSDD+) is used to verify the effectiveness of TAG-Net, and our method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
1. Introduction
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is a remote sensing image sensor that can operate in various weather conditions and at any time of the day. Its widespread application has led to exceptional performance in various domains, including target detection [1,2], disaster monitoring [3,4], and resource exploration [5,6]. The rapid advancements of SAR satellite technology have enabled easy access to a vast amount of high-resolution large-scale SAR image data. It provides richer and more detailed information, which facilitates the fine interpretation of SAR images. One of the most important applications of SAR image interpretation is ship detection and classification [7,8], which is essential for maritime traffic control and fishery management.
Several traditional methods for ship detection [9,10,11,12] and classification [13,14,15] in SAR images have been proposed. The detection methods aim to locate the ship targets in SAR images. A common and representative detection method is the constant false alarm rate (CFAR) [16], which models the background clutter statistically to obtain a threshold and compares it with the pixel values to extract the targets. As for classification, they mainly use features extracted from slices to determine the target category. Template matching [17] is one of the most effective classification methods, which compares the target samples with the pre-defined templates and assigns the target to the most similar category. These traditional methods rely on prior knowledge and manual data analysis to locate and identify the targets, and they can perform well in simple scenes. However, large-scale SAR images often contain complex inshore scenes, where ships are affected by strong scattering interference from artificial structures and many irrelevant targets that look like ships. Therefore, it is challenging to manually design features that distinguish them from the clutter and false targets. Moreover, the traditional methods are time-consuming, which limits their efficiency for large-scale SAR images.
CNN-based methods can automatically extract representative features without manual data analysis, which makes them widely used in SAR ship detection and classification. For the SAR ship detection task, Zhu et al. [18] design an ICM that fuses the spatial information from multi-level features to enhance the model’s sensitivity to size information. Tang et al. [19] use a pooling structure and an adaptive weight feature fusion strategy to improve the difference between a ship and its surroundings. Sun et al. [20] redesign the positive sample regions and introduce a blurry area to enhance the semantic information for regression. Due to its powerful feature extraction and generalization capabilities, deep learning has also been utilized for the task of SAR ship classification. Shang et al. [21] present an MHSA to capture the relevance of features over long distances for the extraction of global information, effectively avoiding class confusion. Guan et al. [22] utilize a PCSA module to assign weights to multi-level features, emphasizing information that is more valuable and informative for the ship target. This module can overcome the challenge of small inter-class differences and improve the accuracy of small-scale ship classification.
Although the above methods have achieved some effects in SAR ship detection or slice classification tasks, they also face some challenges that limit their performance. First, due to the unique imaging mechanism of SAR, ships present various scattering characteristics at different target attitude angles (TAAs), as depicted in Figure 1. This causes high intra-class variance and limited inter-class discrimination, which can easily lead to category confusion and hinders the accurate classification of SAR ships. Second, ships in SAR images exhibit discrete and multi-centric characteristics, which lead to discontinuous edge information. The edge information is also sensitive to the variation in TAA, posing difficulties in accurately regressing ship locations. Third, the presence of various background noise and diverse ship target scales makes the task more complicated. This makes it difficult for conventional feature fusion networks and detection heads, which are designed for natural scenes, to perform well in the complex near-shore SAR ship detection and classification task.
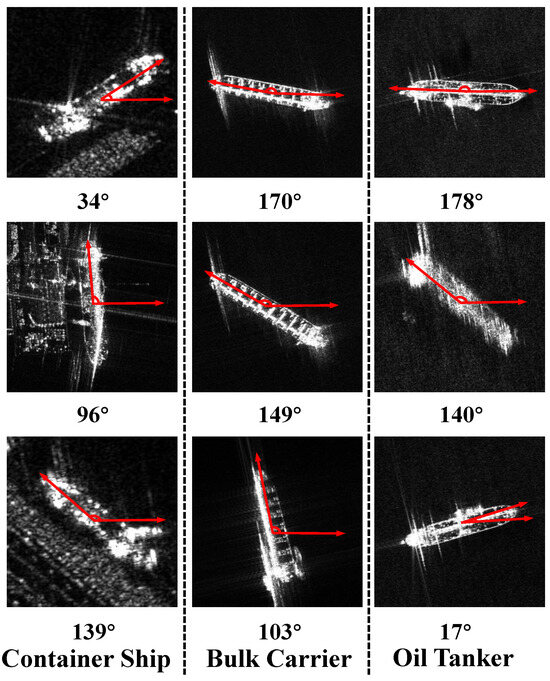
Figure 1.
The imaging results of three different types of ships in SAR images and their corresponding target attitude angles. From left to right, they are a container ship, bulk carrier, and oil tanker. The target attitude angle is defined as the deflection angle of the target relative to the horizontal direction, where the horizontal direction is 0° and the counterclockwise rotation ranges from 0° to 180°.
To address the above issues, a novel target attitude angle-guided network (TAG-Net) is designed to achieve arbitrarily oriented SAR ship detection and classification in complex scenes. TAG-Net’s core idea is to add TAA information and foreground information as prior knowledge and employ an adaptive feature-level fusion strategy to guide the learning of ship foreground information at different TAAs, reducing the intra-class differences while highlighting the ship’s edge information. In addition, TAG-Net fuses multi-scale features in a dynamic fashion to balance spatial and semantic information, and it introduces a scattering information selection mechanism in the detection head to select the most suitable features for each task, making the model more robust to complex scenes.
The design modules of TAG-Net consist of a TAA-aware feature modulation module (TAFM) that guides the detector to learn foreground information at different TAAs, a layer-wise attention-based task decoupling detection head (LATD) that adaptively selects suitable scattering information for different tasks, and a salient-enhanced feature balance module (SFB) that performs multi-feature fusion and enhances the ship saliency. First, we propose a TAFM that uses TAA information as guidance and establishes the relationship between the ship scattering characteristics and TAA information, effectively reducing the intra-class variance and improving the inter-class separability. It also guides the detector to further learn the ship foreground information, which can improve the accuracy in locating ships under various imaging conditions. Second, considering the different requirements of classification and regression tasks for scattering information, we design an LATD that extracts multi-level features and uses layer attention to obtain the suitable scattering information for different tasks. Finally, to improve the performance for multi-scale ships and highlight ships in complex scenes, we propose an SFB module. It adopts a multi-scale feature fusion strategy to adaptively select the spatial and semantic information that matches different scale ships. Moreover, it explores the inter-channel connections to extract the global context, enhancing the model’s anti-interference ability in complex scenes.
Our main contributions are as follows.
- To address the challenges of detecting and classifying targets with diverse imaging variations at different TAAs, we propose a TAFM module. It uses TAA information and foreground information as guidance and applies an adaptive feature-level fusion strategy to dynamically learn more representative features. This module effectively reduces intra-class variations, increases inter-class distinctions, and improves the accuracy in locating ships under various imaging conditions.
- Considering the different requirements of detection and classification tasks for scattering information, an LATD is designed, which extracts multi-level features through stacked convolutional layers and uses layer attention to adaptively select the most suitable features for each task, thereby improving the overall accuracy.
- The SFB module is introduced to adopt an adaptive dynamic fusion method to balance the multi-size features, providing high-resolution and semantically rich features for multi-scale ships. Moreover, it highlights the ship targets by extracting the global context through exploring inter-channel connections, effectively mitigating the impact of background interference.
To demonstrate the effectiveness of TAG-Net, we conduct extensive experiments and our method achieves satisfactory results compared to current competitive methods. This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews related work, Section 3 describes our proposed method in detail, Section 4 introduces the LSSDD+ dataset and presents the results and analysis of our experiments on it, and Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Ship Detection and Classification Method in SAR Images
In the 1980s, the Lincoln Laboratory pioneered research on SAR automatic target recognition (ATR) [17]. They divided the SAR ATR process into three stages: detection, discrimination, and classification. This three-stage processing flow, initially developed for ground target detection and identification, made significant progress and became the standard workflow for SAR ATR systems. Later, researchers extended this framework to SAR ship detection and classification.
However, SAR ship ATR faces some challenges in dealing with background noise and interference, especially in inland areas. Therefore, it is common to employ preprocessing steps, including coherent speckle suppression and land–sea segmentation, to enhance the performance of the subsequent three stages.
Land–sea segmentation plays a vital role in the preprocessing stage as it generates a land mask, which allows the detector to concentrate solely on the sea surface. Various scholars have proposed different methods to perform land–sea segmentation before applying the three-stage processing flow. To adapt to diverse imaging conditions, Mariví et al. [23] propose a wavelet-based edge detection algorithm for automated coastline extraction. Similarly, Baselice et al. [24] introduce a threshold segmentation method, which utilizes the correlations among neighboring pixels to extract coastlines. These methods effectively reduce the interference from inland regions and improve the efficiency of subsequent detection and classification processes. However, they are susceptible to interference from complex background noise, which hinders their effectiveness in highly turbulent or challenging sea conditions.
Ship detection is a crucial aspect of the SAR ATR system. Traditional methods for SAR ship detection involve detecting regions from the image that potentially contain ship targets and then discriminating these targets from the candidate regions to reduce false alarms effectively. The constant false alarm rate (CFAR) [16] is the most commonly used and representative method. It applies a sliding window approach to classify pixels into target and background pixels. It primarily models and analyzes the statistical characteristics of sea clutter to obtain a discriminant threshold, and then compares the threshold with the pixel values to extract targets. Several improvement methods have been proposed based on CFAR. GO-CFAR [25] utilizes two independent windows to estimate the noise power, effectively reducing false alarms in clutter transition regions. Ao et al. [26] propose a multi-scale CFAR method that filters pixels in three different scales, leveraging both global and local information to improve the recall rate while maintaining high detection efficiency. Furthermore, Leng et al. [27] use a 2-D Ostu method to extract ARI feature groups to compensate for the CFAR loss, improving the detection capability for densely distributed ships in inshore scenes.
The traditional SAR ship classification stage consists of extracting features from detected ship slices and using a classifier to determine the category. Template matching is a representative method that compares the ship samples with the template library samples for each category to determine the category. Wang et al. [14] use the auto-correlation repeat cycle and scattering intensity to evaluate the geometric characteristics of ships, thereby obtaining ship categories. To better capture the scattering features of ships and address the issue of feature redundancy, Chen et al. [28] introduce an RCS intensity encoding and two-stage feature selection method. This method encodes the scattering intensity of ships in segments and analyzes the stability, discriminability, and correlation of features to eliminate redundant features and enhance the ship classification performance. Since template-based methods have poor generalization abilities, some model-based methods have been proposed. Knapskog et al. [13] first construct a comprehensive 3D model of a ship using ship photos captured from various viewpoints. Then, they apply threshold and morphological operations to extract the reference contour data of the target from the input image slices. Finally, they compare the similarity between the reference contour data and the corresponding data obtained from the 3D model to identify the target category. However, this method heavily relies on ship sample photos captured from various angles, which poses significant modeling challenges and reduces the stability.
Although traditional SAR target detection and classification methods have demonstrated satisfactory performance in simple scenes, they heavily rely on manual data analysis, which restricts their adaptability and generalizability when applied to large-scale and complex scenes. Additionally, the multi-stage processing pipeline is time-consuming and struggles to meet the efficiency requirements of practical applications.
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Ship Detection and Classification Methods in SAR Images
Due to their remarkable feature extraction capabilities, CNN-based methods have been extensively applied in the field of object detection and classification, leading to significant breakthroughs [29,30,31]. The current CNN-based methods can be divided into two categories: two-stage detectors and single-stage detectors. Two-stage detectors, such as Faster R-CNN [32], R-FCN [33], and Cascade R-CNN [34], first extract candidate regions from the original image and subsequently utilize the network to refine the bounding boxes and obtain category information. Unlike two-stage detectors, single-stage detectors eliminate the step of generating candidate regions. This makes them computationally efficient and has caused them to attract a lot of attention. For instance, FCOS [35] directly performs regression on each position of the feature map to obtain the position and category of the object. CornerNet [36] abandons the concept of anchor boxes and detects the keypoints of the target, which are then paired to form the bounding boxes. Currently, single-stage methods have achieved comparable accuracy with remarkable speed compared to two-stage methods.
The traditional SAR ATR process heavily relies on manually designed features, which often leads to poor feature stability. In contrast, deep learning methods can effectively achieve automatic feature extraction, which allows for the better handling of complex scenes. However, directly applying mainstream CNN methods to SAR images leads to challenges in achieving the desired performance due to the significant differences in the imaging mechanisms between SAR images and natural scenes. Therefore, a large number of scholars have refined and developed the mainstream CNN-based methods specifically for SAR ship detection and classification tasks.
In recent years, SAR ship detection methods have made significant advancements, transitioning from CFAR algorithms to CNN-based methods [37]. To overcome the challenges posed by strong winds and waves, Wang et al. [38] utilize a dual backbone network based on the Haar wavelet transform, which effectively extracts comprehensive and detailed texture information from ship targets. Additionally, they introduce a feature fusion block that emphasizes spatial information, which helps to highlight ship targets in complex scenes. However, detecting multi-scale ships, particularly small-scale ships, remains a challenging task in SAR ship detection. To address this, Fu et al. [39] develop an ABP module that enhances the semantic information of small-scale ships and boosts the overall performance. In addition, the scene imbalance limits the performance of the detector. Zhang et al. [40] propose an unsupervised BSLM module for scene feature learning and sample augmentation, which can effectively avoid overfitting caused by excessive attention to offshore scenes.
Benefitting from its powerful feature extraction and representation capabilities, deep learning has also been introduced into the SAR ship classification task, gaining widespread attention [41]. Hu et al. [42] employ triplet CNNs to extract more distinctive features, with the aim of reducing the similarity between ships of the same class for enhanced classification accuracy at medium resolutions. Wang et al. [43] explore the relationships among principal features to generate adaptive weights, enhancing the salient features and enlarging the feature differences between different categories, thereby improving the separability of scale-similar targets. To mitigate the impact of cross-range sidelobes on the classification performance, Zhu et al. [44] leverage visual saliency models to extract ship body information, effectively eliminating sidelobe interference and resulting in improved classification performance.
The above methods have shown good performance in SAR ship detection and classification. However, these methods do not consider that the scattering characteristics of ships are sensitive to the variations in TAAs. Therefore, they have difficulty in capturing the representative features under different imaging conditions, which poses challenges for the detection and classification tasks.
3. Proposed Method
To address the above issues, a novel target attitude angle-guided network (TAG-Net) is designed to mitigate the impact of the diversity of SAR ship target imaging on the detection and classification tasks. Specifically, TAG-Net utilizes a feature-level learning strategy to add TAA information as prior knowledge, guide the detection network to learn the ship foreground features at different TAAs, and obtain more discriminative features. Moreover, it employs an adaptive task decoupling strategy and the dynamic fusion of multi-scale features to improve its robustness to complex scenes.
3.1. Overall Scheme of the Proposed Method
TAG-Net is designed based on the CenterNet [45] detection framework and its overall architecture is illustrated in Figure 2. It has four main components: the backbone for feature extraction, the improved FPN equipped with an SFB module for multi-feature fusion and ship saliency enhancement, the TAFM to guide the detector to learn the foreground information at different TAAs, and the LATD to adaptively select the suitable scattering information for each task.
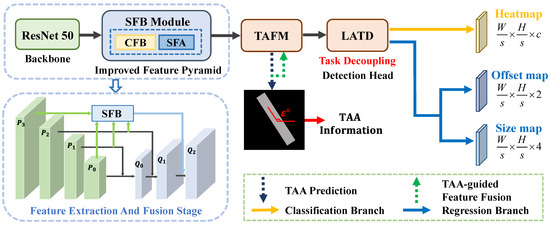
Figure 2.
The overview of TAG-Net.
In the feature extraction and fusion stage, we adopt ResNet50 [46] and FPN [47] to build an encoder–decoder structure. Specifically, we feed the input image into ResNet50 and use the outputs of the last four stacked downsampling convolution modules as the inputs of FPN. Since the accuracy of ship center point prediction is very important for methods based on the CenterNet framework, we choose the largest feature map produced by FPN, which has rich spatial information, for the subsequent detection and classification tasks. However, the low-level feature map lacks adequate semantic information, leading to insufficient saliency for smaller ships in complex scenes and increased susceptibility to interference from background noise. To balance the semantic and spatial information of features at different scales, we design an SFB module, which employs an adaptive dynamic fusion method to generate high-resolution and semantically rich features suitable for diverse ship scales. Moreover, the SFB module is used to explore the inter-channel relationships to highlight ships and mitigate the impact of imaging noise.
Between the feature extraction stage and the detection head, we design a TAFM to mitigate the adverse effects caused by the scattering information and edge information of ships, which are sensitive to the variations in TAAs. It adopts a feature-level information fusion strategy that uses TAA and foreground information as guidance, to dynamically learn more representative features while enhancing the ship saliency. This effectively avoids category confusion and improves the localization accuracy.
To meet the different requirements of the detection and classification tasks for the scattering information, we design an LATD. It uses multi-level convolutional layers to generate features with different scales of effective receptive fields, and it adopts a layer attention mechanism that selects the most suitable scattering information for each task, thereby enhancing the model’s overall performance.
The detection head of TAG-Net consists of three parallel branches, each with a convolutional layer and a convolutional layer. The three branches generate a heatmap, an offset map, and a size map. The heatmap indicates the ship classes and the center point positions of each ship category. The offset map is used to refine the center point positions. The size map represents the size information, which is expressed by two mutually perpendicular vectors . Specifically, the heatmap H and offset map O are used to determine the class and center point location C of the ship target, and the two vectors at the corresponding location on the size map S are used to determine the boundaries of the oriented bounding boxes, as shown in Figure 3.
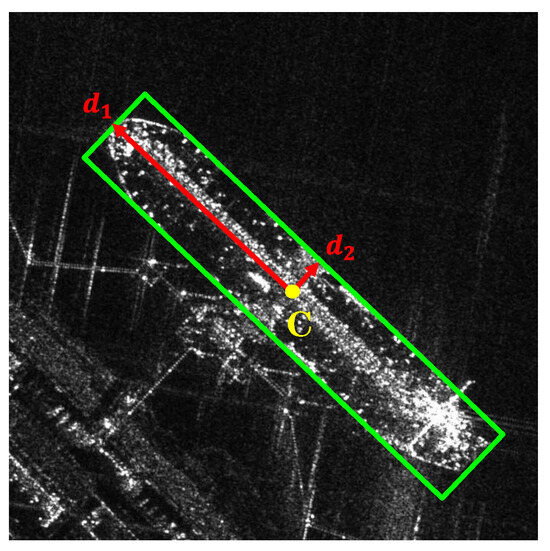
Figure 3.
Representation of the oriented bounding box.
3.2. TAA-Aware Feature Modulation Module (TAFM)
Compared with natural scenes, ships of the same type in SAR images show greater intra-class diversity, mainly because the scattering characteristics of ships are sensitive to the variations in TAAs, as shown in Figure 1. This can easily cause class confusion and reduce the accuracy of SAR ship classification. Moreover, ships in SAR images exhibit discrete and multi-centric features, and their edge information is also sensitive to the TAA, which poses a challenge for the precise localization of ships. To tackle these challenges, we propose a TAFM module. It uses TAA information as guidance and adopts a feature-level information fusion strategy to establish the relationship between the TAA information and ship scattering characteristics. This effectively reduces the intra-class variance and enhances the inter-class separability, improving the classification performance. At the same time, it highlights the edge information of ships through a pixel-level classification task, improving the model’s localization accuracy in complex scenes. The structure of the TAFM consists of two components: the TAA prediction branch and the TAA-guided feature fusion block (TAGF).
(1) TAA Prediction Branch
The TAA prediction branch introduces a pixel-level classification task, which uses the beneficial TAA information and foreground information to direct the model to learn the scattering characteristics of ships at different TAAs. This can highlight the more discriminative and representative information within features for the ship and enhance the ship saliency in complex scenes to overcome the challenges brought by the target imaging diversity.
Figure 4 illustrates the architecture of the TAA prediction branch, which aims to learn the ship discriminative information at different TAAs. The input feature is denoted as . To obtain more refined features from F, we apply three consecutive convolutional layers to produce . Then, a convolutional layer is used to predict the TAA map from . We adopt a novel strategy to construct the ground truth of the TAA map, as shown in Figure 5, which fuses the TAA information with the foreground information. Specifically, the pixel values outside the ship region are set to 0, indicating the background. Conversely, within the ship region, the pixel values are assigned the corresponding TAA values. The TAA is denoted as the angle between the ship and the horizontal axis, ranging from 0° to 180° in a counterclockwise direction. The expert-annotated ship-oriented bounding box information is used to automatically generate both the TAA information and the corresponding foreground information for the TAA map. This process eliminates the necessity for additional annotations, enabling end-to-end training. This supervised classification task of the TAA prediction branch enables the detector to learn the scattering information of ships at different TAAs, which is crucial for the subsequent classification tasks. Moreover, the foreground information in the TAA map enhances the ability of the convolutional layers to accurately capture the ship contours, enabling high-precision localization in complex scenes.
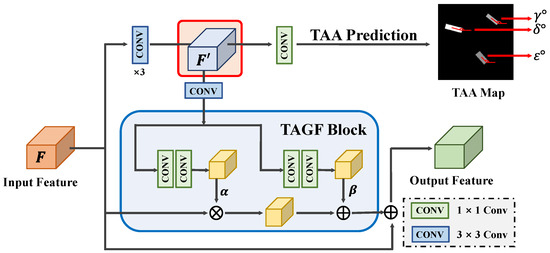
Figure 4.
Structure of the TAFM.
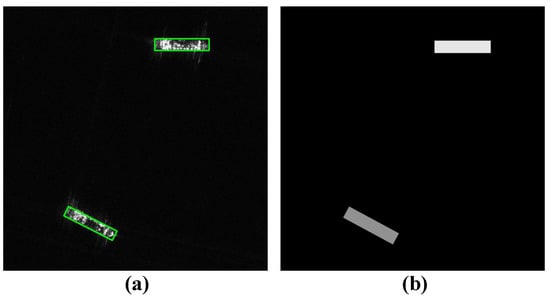
Figure 5.
(a) Ground truth bounding box. (b) Ground truth of TAA map.
(2) TAA-Guided Feature Fusion Block (TAGF)
To enhance the original features with the valuable TAA information and foreground information from the TAA-enhanced feature , inspired by [48], we design the TAGF block. The TAGF block uses to generate modulation parameters and applies spatial affine transformation to adaptively modulate the input feature to achieve feature-level fusion.
Specifically, we take as the input of the TAGF block, which generates modulation parameters for affine transformations through two branches. Each branch consists of two convolutional layers that facilitate information exchange across different channels. The generation of the modulation parameters is denoted as . is the mapping function, is the scale parameter for modulation, and is the shift parameter for smoothing, which can be calculated as follows:
where is a convolution.
After obtaining the modulation parameters, the feature modulation process is as follows:
where ⊗ denotes element-wise matrix multiplication, and F represents the input feature. By modulating the original features through this affine transformation, the TAGF block adaptively integrates TAA information and foreground information as semantic guidance, enabling detectors to better identify the scattering characteristics of ships.
The TAFM module performs an extra pixel-level classification task and uses an adaptive feature-level fusion strategy to incorporate TAA information and corresponding foreground information into the original features. This reduces intra-class variations and makes the ships more salient. As a result, the model can adapt to different imaging conditions and improve the detection and classification accuracy.
3.3. Layer-Wise Attention-Based Task Decoupling Detection Head (LATD)
Presently, mainstream deep learning-based joint detection and classification methods commonly employ shared features for both tasks. However, these methods ignore the different needs for scattering characteristics required by each task, leading to feature conflicts that negatively impact the accuracy of both tasks. Specifically, the ship regression task relies on edge scattering features, which can offer useful information about the ship’s position, scale, and orientation. Therefore, the feature fed to the regression branch should have high spatial location sensitivity to achieve precise positioning. In contrast, the classification task requires features that are stable against spatial variations and can capture scattering characteristics that reflect the structures of ships. The features fed to the classification branch should highlight the distribution of the dihedral and trihedral angles on ships, revealing details about the ship’s superstructure to aid in identifying the ship’s type. Consequently, when using a shared feature for these two tasks, feature conflicts often occur during parameter optimization, making it difficult to obtain optimal performance for both tasks. To obtain task-specific scattering information and avoid feature conflicts, we propose a novel detection head called the LATD. The LATD is designed to dynamically select appropriate scattering information from multi-level features for each specific task. The overall structure of the LATD, illustrated in Figure 6, consists of two stages: the multi-level feature extraction stage and the layer-wise attention-based feature selection stage.
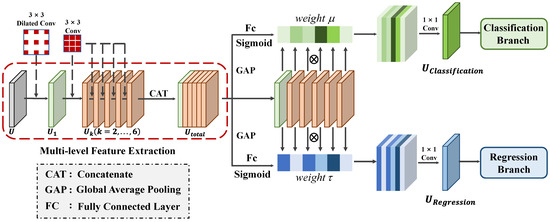
Figure 6.
Structure of the LATD.
(1) Multi-Level Feature Extraction stage: In this stage, we use stacked convolutional layers to extract multi-level features with different scales of effective receptive fields, which provide selectable ship scattering characteristics for each task. The multi-level feature extraction stage consists of a contextual extractor and a multi-level feature extractor. The contextual extractor uses a dilated convolution with a stride of 3, offering a broader receptive field. This enables the model to acquire more semantic information and better comprehend the original features. Given the input feature , the output produced by the contextual extractor is denoted as . Then, the multi-level feature extractor uses a series of convolutional layers on to produce features with different scales of effective receptive fields, which are denoted as (). Each convolutional layer helps to capture various spatial information and different ship scattering characteristics, thus satisfying the specific needs of different tasks. The whole process of the multi-level feature extraction stage can be expressed as follows:
where represents the contextual extractor composed of a dilated convolutional layer, while represents the multi-scale feature extractor consisting of stacked convolutional layers, and represents the ReLU operation.
(2) Layer-Wise Attention-Based Feature Selection Stage: Since detection and classification tasks have different focuses on the scattering information of ships, they usually require different levels of spatial or semantic information. Therefore, we design a layer-wise attention-based feature selection stage, which aims to dynamically and adaptively select the most relevant features for each task, improving the performance of ship detection and classification. Inspired by the selection kernel mechanism [49], we employ a layer attention mechanism to achieve task decoupling and enhance the overall performance. In this stage, the extracted multi-level features are first concatenated to form a fused feature, . To capture global information from , we utilize spatial-wise global average pooling, leading to the generation of a global information feature, .
The global information feature is then used to generate two sets of layer attention weights: for the classification branch and for the regression branch. These weights serve as adaptive feature-level selection weights, allowing the model to focus on different-level features that are relevant to each task. This task-driven feature selection method effectively combines features of varying levels based on their relevance to each task, ensuring that the extracted scattering information aligns with the requirements of each task. Specifically, we use a layer-wise attention mechanism, guided by a variant of a multi-layer perceptron, to compute the feature selection weight for each task. The calculation of is defined as follows:
where and represent two fully connected layers. The first one performs feature dimension reduction, while the second one is responsible for generating the corresponding feature selection weights. denotes the sigmoid operation.
Once the feature selection weights are obtained, we can generate task-specific features for classification and regression tasks as follows:
where denotes the task-specific features generated for each task, and ⊗ represents the element-wise multiplication.
This task decoupling method utilizes the layer-wise attention mechanism to selectively extract features that are highly relevant for ship detection and classification tasks. Hence, the LATD effectively enhances the accuracy of ship detection and classification in complex scenes.
3.4. Salient-Enhanced Feature Balance Module (SFB)
Ships exhibit a diverse range of sizes, and different scales of ships require different levels of spatial and semantic information. We use ResNet to extract multi-scale features in the feature extraction stage. High-level feature maps have a larger receptive field and provide more rich semantic information, making them more suitable for detecting large-scale ships. However, due to the lack of sufficient spatial information, they fail to locate the edges of ships precisely. Conversely, low-level feature maps offer more detailed spatial information, enabling more accurate localization for small-scale ships. However, these maps may lack sufficient semantic information, resulting in ships being less prominent in complex scenes and susceptible to interference from background noise and strong scattering from surrounding structures. Therefore, the imbalance of semantic and spatial information of features poses great difficulties in both detecting and classifying ships.
To fully leverage the benefits of both low- and high-level features, we introduce the SFB module. It adopts an adaptive dynamic fusion strategy to balance multi-scale features, providing suitable spatial and semantic information for different scales of ships. Moreover, it strengthens the connections between different channels to capture the global context, thereby enhancing the saliency of ships and effectively suppressing background noise. The SFB module comprises two stages: the contextual feature balance stage (CFB) and the saliency feature attention stage (SFA).
(1) Contextual Feature Balance Stage (CFB): The CFB stage aims to fuse multi-level features to balance the spatial and semantic information, which enhances the overall performance for ships of various sizes. As shown in Figure 7, the multi-scale features extracted from the last four convolutional blocks of ResNet (denoted as , , , and ) are used as the inputs for the CFB stage. To preserve the high spatial resolution, , , and are first upsampled to the same size as . Then, convolutional layers are applied to refine each feature map, and a residual connection is added to retain the original feature information. The refined features are denoted as , , , and .
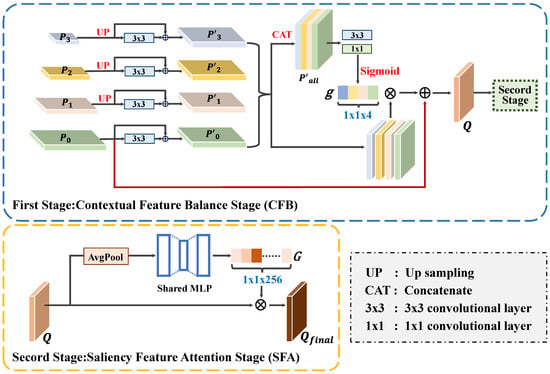
Figure 7.
Structure of the SFB.
Next, we adopt a dynamic selection mechanism that chooses features from different scales to match the varying semantic and spatial information needs of ship targets with different sizes. The scale feature highlighting weights for each level are denoted as . These weights are obtained by concatenating as the input and applying and convolutional layers to generate the corresponding weights.
Then, a sigmoid function is used to normalize the to the range of . After obtaining the scale feature highlighting weights, we multiply them with to balance the spatial and semantic information of the multi-scale features. Finally, the generated features are added to to preserve the spatial information. The final features are generated as follows:
where is the generated fused feature, which can provide rich semantic information and high-resolution detail information for ships at different scales.
(2) Saliency Feature Attention Balance Stage (SFA): In the SFA stage, SE blocks [50] are used to capture the inter-channel correlations and obtain the global context, which improves the saliency of ships and reduces the impact of the background noise. The fused feature Q generated by the CFB stage is taken as the input of this stage, and an average pooling operation is performed along the channel dimension to obtain the global context . Next, a two-layer fully connected network and a sigmoid function are used to obtain the global context map , which highlights ships and reduces the impact of imaging noise.
where denotes the average pooling operation, and and are the weights of the fully connected layers.
Finally, the generated global context map G is utilized to modulate the channel weights:
where denotes the output feature of the SFA stage and ⊗ represents the element-wise multiplication.
The SFB module adaptively selects features from different scales to meet the diverse semantic and spatial information requirements of various sizes of ships. It also enhances the global perception capability in the feature fusion process, which extracts rich contextual information and explores the inter-channel connections to highlight the ships and reduce the impact of imaging noise. This can significantly enhance the accuracy of the following detection and classification tasks. Moreover, we maintain the original structure of FPN to guarantee the information flow across different levels and preserve more original feature details.
3.5. Loss Function
The loss function of TAG-Net can be divided into four parts:
where , , , and represent the heatmap loss, the offset loss, the size loss, and the TAA loss, respectively. is a balance parameter that controls the contribution of the TAA loss.
To mitigate the effect of the imbalance between positive and negative samples on the performance, we employ the focal loss [51] to optimize :
where denotes the heatmap generated by the center position of class c ships. Assuming that the center point coordinates of a ship of class c in the original image are , its position after downsampling on the feature map is . Following CenterNet [45], a two-dimensional non-normalized Gaussian function, , is used to assign the target values of each pixel of the ship on the heatmap, where represents a scale-adaptive radius and N is the number of ships.
To overcome the precision error of ship localization caused by the downsampling process, we use the smooth L1 loss to optimize :
where denotes the offset for ship i—specifically, —and is the predicted offset.
We utilize the smooth L1 loss to optimize the size parameter :
where denotes the size information for ship i, and is the predicted size information.
Additionally, we employ the smooth L1 loss to guide the generation of the TAA map, and is formulated as follows:
where is the ground truth value and is the predicted value at the location on the TAA map.
4. Experiments and Results
In this section, we present comprehensive experiments on the LSSDD+ dataset to demonstrate the effectiveness of TAG-Net. We start by introducing the dataset, the experimental settings, and the evaluation metrics. Then, we measure the overall performance and present a detailed analysis of each module that we designed. Finally, we compare TAG-Net with selected CNN-based methods based on the accuracy and model parameters, and we investigate its practical applicability on large-scale images.
The LSSDD+ dataset consists of 116 single-polarization large-scale SAR images acquired by the Gaofen-3 satellite, with a resolution of 1 m. The dataset covers 16 port scenes captured at different times and includes a total of 4683 ship samples spanning 11 categories. Figure 8 shows the distribution of instances for each category. The dataset includes 5 types of civil ships, namely a bulk carrier (BC), container ship (CS), oil tanker (OT), work boat (WB), and research vessel (RV), and 6 types of other ships, which are labeled as “T0” to “T5”. The slices of civil ships are shown in Figure 9. For training and validation, a subset of 94 images is randomly selected, while the remaining 22 are considered as the test set. For the training set, each large image is randomly cropped into three different sizes. Subsequently, slices containing ship targets are resized to pixels, resulting in a total of 12,061 slices. For the test set, a sliding window approach is employed to crop the original images into pixels with a 512-pixel overlap.
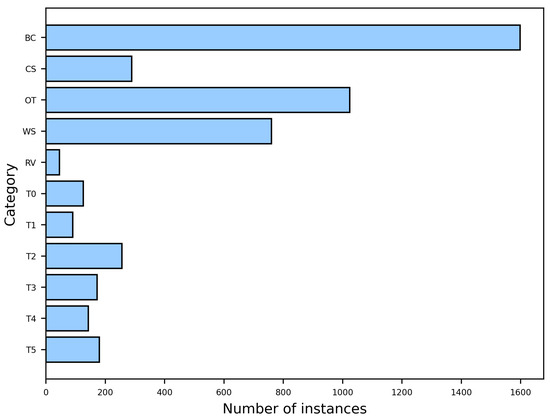
Figure 8.
Number of instances per category in LSSDD+.
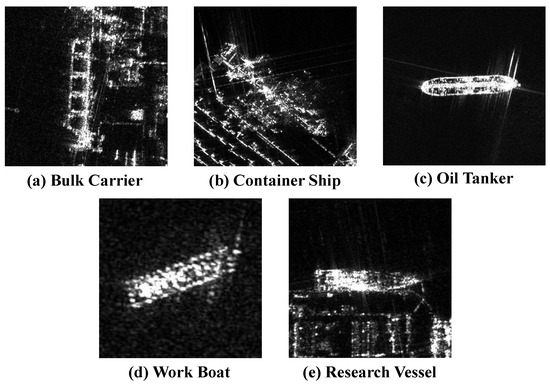
Figure 9.
Example images of civil ships in LSSDD+.
4.1. Dataset and Settings
The LSSDD+ provides rich fine-grained categories and different sizes of ships, and it includes ship targets under various imaging conditions. This makes it similar to the real-world application scenario and thus provides a reliable way to evaluate the performance of the detector in practical applications.
In our experiment, we initialize ResNet50 with pre-trained weights from ImageNet. The Adam optimizer is used with an initial learning rate of 0.000125, decreased by a factor of 10 at 70 epochs. The experiment is run on a P100 GPU for 100 epochs with a batch size of 8. During testing, each slice is fed into the model and NMS [52] is used to merge the results for large-scale images. All metrics are computed based on these merged results.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
To measure the model’s performance on the ship detection and classification task, we use the mAP to reflect the model’s overall performance on all categories of ships. For each category of ship targets, we calculate the precision, using different confidence scores, for each recall value . The AP is the mean of the precision values under different recall rates.
where , , are the total numbers of true positives, false positives, and false negatives, respectively.
After obtaining the AP for each category, the mAP can be obtained as follows:
where is the number of categories, and represents the AP of the i-th category.
4.3. Ablation Studies
To evaluate the impact of each component and the overall performance of TAG-Net, we conduct a series of ablation studies on the LSSDD+. For a fair comparison, we keep the same settings in all experiments. We use CenterNet as the baseline, and then gradually add the three modules that we designed to the baseline network. Table 1 shows that each module improves the performance, and the final model achieves a 5.99% increase in mAP. This indicates that our method enhances the model’s ability to detect and classify ships, resulting in more accurate ship localization and category predictions.

Table 1.
Impact of each component of TAG-Net.
(1) Effect of TAA-Aware Feature Modulation module (TAFM): The TAFM module utilizes ship TAA information and foreground information as guidance and employs an adaptive feature-level information fusion strategy to guide the model to learn the scattering and edge information of the ship at different TAAs. Table 2 shows that the TAFM module increases the mAP by 3.87% and improves nine categories. Notably, the improvement of five ship categories exceeds 2%. This indicates that the TAFM effectively improves the detection and classification performance by integrating the TAA information and foreground information into the features.

Table 2.
Effectiveness of TAFM.
To investigate the impact of the prior knowledge (TAA information and foreground information) introduced in the TAFM module on the performance, we remove the relevant supervision information while maintaining the same network structure for an ablation experiment. Table 3 shows that this additional supervision information is quite beneficial for the detection and classification task, and it improves the mAP by 2.87%. This indicates that by adding prior knowledge to the TAA prediction branch, the model can learn the ship’s scattering information at different TAAs, which enhances the detector’s performance in complex scenes.

Table 3.
Ablation studies of prior knowledge (TAA information and foreground information).
To investigate how different modulation fusion strategies affect the performance of the TAA-guided feature fusion block, we conduct comparative experiments on four different combinations of shift and scale modulation, ⊕ and ⊗, which represent shift and scale modulation, respectively. Table 4 shows that the mAP of all four fusion strategies is enhanced after incorporating prior knowledge (TAA information and foreground information), which also implies that the modulation strategy influences the information fusion. The first two rows of Table 4 show that using only scale modulation or shift modulation is not enough to fully leverage the prior knowledge. The joint effect of the two modulation methods can fuse the valuable information with the original features more effectively. The best result is obtained by performing scale modulation followed by shift modulation. This might be because scale modulation enables shift modulation to refine the details and use the TAA information and foreground information more efficiently. Therefore, we adopt scale modulation followed by shift modulation in this block.

Table 4.
Ablation studies of different modulation fusion strategies.
In the TAFM module, we use the TAA loss to guide the generation of the TAA map. We examine how different loss functions and the parameter affect the results through ablation experiments. From Table 5 and Table 6, we can see that the optimal detection performance is achieved when using the smooth L1 loss and is set to 0.5.

Table 5.
Ablation studies of different loss functions.

Table 6.
Ablation studies of parameter .
(2) Effect of Layer-Wise Attention-Based Task Decoupling Detection Head (LATD): The LATD generates multi-scale feature information by stacking convolutional layers. Then, it adaptively selects features suitable for each task based on the layer attention mechanism. Table 7 demonstrates that the LATD enhances the mAP by 4.1% and boosts the performance in nine categories. Notably, six of these categories exhibit an improvement of over 2%. This shows that adopting the LATD improves the overall performance, which may be attributed to its ability to select the most suitable scattering information for different tasks.

Table 7.
Effectiveness of LATD.
Figure 10 presents some visualized detection results that further demonstrate the effectiveness of the LATD. As shown in Figure 10b, the baseline methods fail to capture the edge information of ships in complex scenes accurately, and they suffer from missed detection or incorrect category classification. This may be because the baseline method directly uses the same features to generate detection and classification results, without considering the different scattering information required for the two tasks, resulting in poor performance in both the classification and regression tasks. As shown in Figure 10c, the LATD uses a layer attention mechanism to dynamically select the scattering information that is suitable for different tasks, effectively improving the overall performance of both tasks and better adapting to complex scenes.
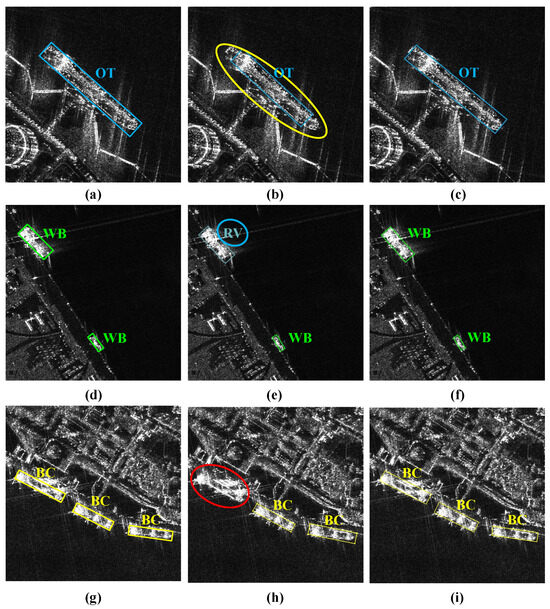
Figure 10.
Visual comparison of detection results without and with LATD. The bounding boxes show the detected objects, with different colors indicating different categories: the yellow circles, blue circles, and red circles denote the objects with inaccurate localization, category errors, and missing ships, respectively. (a,d,g) Ground truth, (b,e,h) baseline without LATD, (c,f,i) baseline with LATD.
In the LATD, stacked convolutional layers are utilized to extract multi-level features with different receptive fields, where the first layer is a dilated convolutional layer, followed by stacked regular convolutional layers. Table 8 shows that the detection head with dilated convolution achieves higher mAP, which demonstrates the improved performance in detection and classification. The dilated convolution enables the stacked convolutional layers to provide larger effective receptive fields and capture more rich semantic information, which enhances the performance in locating and classifying ships.

Table 8.
Ablation studies of the dilated convolutional layer of the LATD.
(3) Effect of Salient-Enhanced Feature Balance Module (SFB): The SFB module dynamically balances the features of different levels to adapt to different scales of targets, while extracting global context information to highlight ships in complex scenes. The SFB module consists of a CFB stage that fuses multi-level features and an SFA stage that captures the global context. As shown in Table 9 and Table 10, the CFB stage and the SFA stage improve the mAP by 2.37% and 1.28%, respectively, and the performance achieves a greater improvement when the two stages work together.

Table 9.
Effectiveness of SFB.

Table 10.
Ablation studies of SFB module.
To perform a visual comparison, we visualize the output feature maps of the FPN with and without the SFB module. As Figure 11b shows, the detector struggles to locate the ship targets due to imaging noise and irrelevant facilities with similar visual attributes, leading to errors in localization and classification. In contrast, after adding the SFB module, the introduced global context and the selected multi-scale feature information make the ships in Figure 11c more prominent. In addition, the activation values of the near-shore irrelevant objects and the background noise are significantly reduced. This suggests that the SFB module can highlight ships effectively, while improving the model’s anti-interference ability in complex scenes. These improvements may result from the following two factors. First, the SFB offers more suitable semantic and spatial information for ships of various scales, which enhances the separability of the ships and the background. Second, it explores the inter-channel connections and extracts the context information that highlights the ship targets, while effectively reducing the impact of imaging noise.
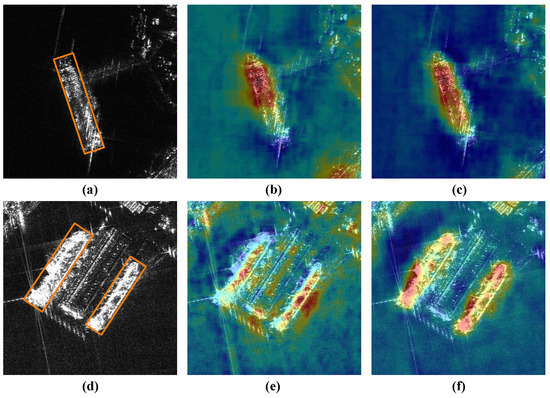
Figure 11.
Visualization of feature maps extracted by different methods. The orange boxes indicate the positions of ships. (a,d) the positions of the ships, (b,e) baseline without SFB, (c,f) baseline with SFB.
4.4. Comparison with CNN-Based Methods
To further verify the effectiveness of TAG-Net, we compare it with some advanced CNN-based methods on the LSSDD+. We choose eight methods, including the Oriented R-CNN [53], ROI Trans [54], Gliding Vertex [55], Rotated Faster RCNN [32], -Net [56], Oriented CenterNet [45], Rotated ATSS [57], and Rotated FCOS [35], which cover the single-stage and two-stage mainstream CNN-based methods that use OBB representation for deep learning applications in object detection and classification. Table 11 illustrates that by leveraging TAA information and selecting features suitable for each task, TAG-Net outperforms other methods in SAR ship detection and classification, achieving mAP of 73.91%. Additionally, we compare the model parameters (Params) of different methods. TAG-Net not only exhibits superior detection and classification capabilities, but also has higher efficiency than the second-best method, the Oriented R-CNN. Compared with the oriented CenterNet, which has the fewest parameters, TAG-Net has slightly more parameters but it performs much better. This means that TAG-Net achieves a better balance between model complexity and performance.

Table 11.
Comparison with different methods on the LSSDD+.
Figure 12 compares the detection results of the Rotated FCOS, Rotated ATSS, ROI Trans, Oriented R-CNN, and TAG-Net. As Figure 12 illustrates, TAG-Net surpasses other methods in both detection and classification tasks in complex near-shore and off-shore multi-target scenes. Other methods struggle to achieve high accuracy in both tasks, possibly because of the use of shared features for multi-task learning. This can result in feature conflicts and lead to category confusion or false alarms. TAG-Net can adaptively select the appropriate scattering information for different tasks and thus enhance the overall performance. Moreover, TAG-Net can better capture the accurate foreground information of ships at different TAAs, which not only enables precise localization but also prevents category confusion.
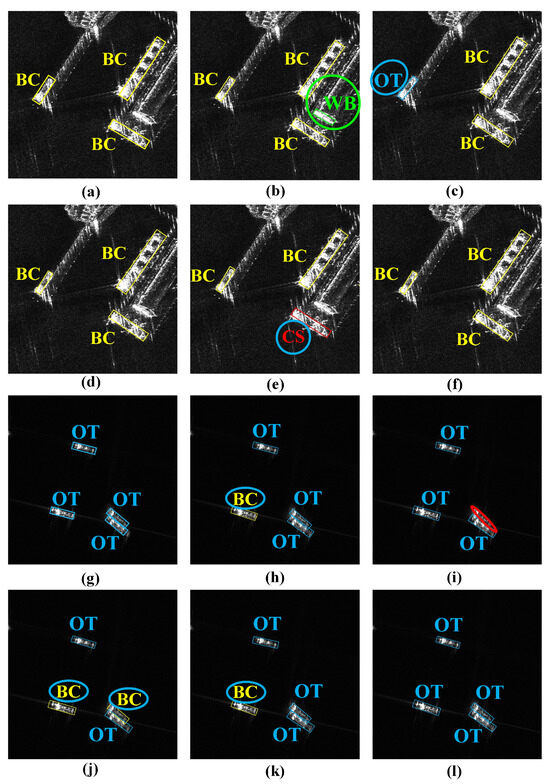
Figure 12.
Detection results of different methods on LSSDD+. The bounding boxes show the detected objects, with different colors indicating different categories: the yellow circles, blue circles, and red circles denote the objects with inaccurate localization, category errors, and missing ships, respectively. (a,g) Ground truth, (b,h) Rotated FCOS, (c,i) Rotated ATSS, (d,j) ROI Trans, (e,k) Oriented R-CNN, (f,l) TAG-Net.
To further validate the practical applicability of TAG-Net, we carried out comparative experiments on large-scale images and analyzed the detection results. Since the Oriented R-CNN exhibited the second-best performance, we selected our proposed method and the Oriented R-CNN for experimentation on large-scale SAR images. As depicted in Figure 13, our method outperformed the Oriented R-CNN with superior performance. TAG-Net can better capture the ship boundaries and make correct category judgments. At the same time, it can successfully differentiate near-shore similar objects from ship targets, indicating that TAG-Net has stronger robustness in complex scenes.
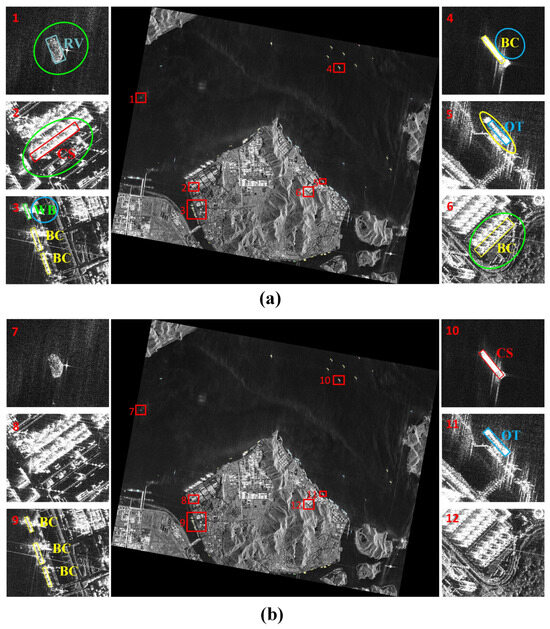
Figure 13.
Detection results in large-scale SAR images. The bounding boxes show the detected objects, with different colors indicating different categories: the yellow circles, blue circles, and red circles denote the objects with inaccurate localization, category errors, and missing ships, respectively. (a) Oriented R-CNN, (b) TAG-Net.
5. Discussion
In the previous section, a series of ablation studies show the effectiveness of the TAFM module, LATD, and SFB module designed in TAG-Net, and their performance is further improved when they work together. We also compare TAG-Net with other CNN-based methods and show that it achieves a value of 73.91% in mAP, outperforming other competitive detectors in terms of performance, while using only 88% of the model parameters of the second-best method, achieving a better balance between model complexity and performance. Additionally, its superior performance on large-scale SAR images further demonstrates its effectiveness in practical applications.
In future research, we will take into account more factors related to SAR imaging to guide the network to extract the distinctive features of the target under different imaging conditions. Furthermore, we will explore the combination of the edge detection method and the TAFM module, to achieve applications in unlabeled data, thus broadening its potential use cases.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a novel and unified framework named TAG-Net to achieve arbitrarily oriented SAR ship detection and classification in large-scale and complex scenes. TAG-Net introduces TAA information and applies an adaptive feature-level fusion strategy to relate ship scattering characteristics to TAA information, improving the ship localization and classification accuracy under different imaging conditions. It consists of three core modules: the TAFM to learn the foreground information at different TAAs, the LATD to select the most suitable scattering information for each task, and the SFB module for multi-feature fusion and ship saliency enhancement. To alleviate the impact of SAR target imaging variability, the TAFM adopts a feature modulation strategy to jointly learn the TAA information and foreground information in a dynamic manner, which reduces the intra-class differences and enhances the inter-class separability. Meanwhile, the pixel-level classification task added by the TAFM guides the detector to learn the contour information of the ships, effectively mitigating the negative effects caused by the discrete and multi-center imaging of SAR targets. In addition, considering the different requirements of detection and classification tasks for scattering information, the LATD is designed to extract multi-level features and uses layer attention to adaptively select the most suitable features for each task, thereby improving the overall performance. Furthermore, the SFB module is introduced to balance multi-scale features to provide more rich semantic information and improve the accuracy of localization and classification. Meanwhile, it explores the inter-channel connections to obtain the global context, enhancing the saliency of ships and reducing the negative effects of imaging noise. Compared with other advanced methods, our proposed method achieves a value of 73.91% in mAP, outperforming other competitive detectors in terms of performance while using only 88% of the model parameters of the second-best method, achieving a better trade-off between model complexity and performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P. and Y.W.; methodology, D.P. and Y.W.; validation, D.P. and X.G.; formal analysis, D.P.; investigation, D.P. and W.D.; resources, D.P.; data curation, D.P. and X.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.P. and Y.W.; writing—review and editing, X.G. and T.M.; visualization, D.P.; supervision, W.Z.; project administration, X.G.; funding acquisition, X.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under Grant (62331027).
Data Availability Statement
All data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ma, X.; Hou, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Multiscale and dense ship detection in SAR images based on key-point estimation and attention mechanism. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5221111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T. GCBANET: A global context boundary-aware network for SAR ship instance segmentation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Yun, S.H.; Kim, D.J.; Lavalle, M. Damage-Mapping Algorithm Based on Coherence Model Using Multitemporal Polarimetric–Interferometric SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, V.; Doulgeris, A.P.; Eltoft, T. Monitoring Glacier Changes Using Multitemporal Multipolarization SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3729–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hua, Y.; Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X. CG-Net: Conditional GIS-Aware Network for Individual Building Segmentation in VHR SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5201215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Chapman, M.A. Semiautomated Segmentation of Sentinel-1 SAR Imagery for Mapping Sea Ice in Labrador Coast. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, N. Dense Attention Pyramid Networks for Multi-Scale Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8983–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. High-speed ship detection in SAR images based on a grid convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.K.; Baumgartner, S.V.; da Silva, A.B.; Krieger, G. Range-Doppler based CFAR ship detection with automatic training data selection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Qi, X.; Yu, W.; Deng, Y.; Liu, F.; Shi, L. A new CFAR ship detection algorithm based on 2-D joint log-normal distribution in SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M. Analysis of some modified cell-averaging CFAR processors in multiple-target situations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1982, 1, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, V.G. Constant false alarm rate processing in search radars. IEEE Radar-Present Future 1973, 20, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Knapskog, A.O. Classification of ships in TerraSAR-X images based on 3D models and silhouette matching. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 7–10 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, B.; Tang, Y. A novel hierarchical ship classifier for COSMO-SkyMed SAR data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Meng, J. Ship classification in SAR image by joint feature and classifier selection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 13, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, G. False-alarm regulation in log-normal and Weibull clutter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1973, 9, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, L.M.; Owirka, G.J.; Brower, W.S.; Weaver, A.L. The automatic target-recognition system in SAIP. Linc. Lab. J. 1997, 10, 187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Hu, G.; Zhou, H.; Wang, S. Multiscale ship detection method in SAR images based on information compensation and feature enhancement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5117913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zhao, H.; Claramunt, C.; Zhu, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y. PPA-Net: Pyramid Pooling Attention Network for Multi-Scale Ship Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Dai, M.; Leng, X.; Lei, Y.; Xiong, B.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. An anchor-free detection method for ship targets in high-resolution SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7799–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Pu, W.; Wu, C.; Liao, D.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; et al. HDSS-Net: A Novel Hierarchically Designed Network With Spherical Space Classifier for Ship Recognition in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5222420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, G.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, C. Fishing Vessel Classification in SAR Images Using a Novel Deep Learning Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5215821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.T.; López-Martínez, C.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Salembier, P. Edge enhancement algorithm based on the wavelet transform for automatic edge detection in SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 49, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselice, F.; Ferraioli, G. Unsupervised coastal line extraction from SAR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xie, J.; Li, G.; Du, Y. Robust CFAR detector with weighted amplitude iteration in nonhomogeneous sea clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Detection and discrimination of ship targets in complex background from spaceborne ALOS-2 SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Ji, K.; Xing, X.; Zhou, S.; Zou, H. Area ratio invariant feature group for ship detection in SAR imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2376–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.t.; Ji, K.f.; Xing, X.w.; Zou, H.x.; Sun, H. Ship recognition in high resolution SAR imagery based on feature selection. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Computer Vision in Remote Sensing (CVRS 2012), Xiamen, China, 16–18 December 2012; pp. 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, D.; Hu, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Adapter is All You Need for Tuning Visual Tasks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.15010. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Zhang, T.; Shao, Z. Scale-aware dimension-wise attention network for small ship instance segmentation in synthetic aperture radar images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2023, 17, 046504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Guo, P.; Wei, H.; Zhao, X.; Wu, X. Disentangled Discriminator for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation on Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 5685–5691. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. R-fcn: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade r-cnn: Delving into high quality object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 9627–9636. [Google Scholar]
- Law, H.; Deng, J. Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 734–750. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Wei, S. Depthwise separable convolution neural network for high-speed SAR ship detection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, Z.; Yuan, J. Automatic SAR Ship Detection Based on Multi-Feature Fusion Network in Spatial and Frequency Domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 4102111. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K. An anchor-free method based on feature balancing and refinement network for multiscale ship detection in SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Ahmad, I.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; et al. Balance learning for ship detection from synthetic aperture radar remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 182, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. A polarization fusion network with geometric feature embedding for SAR ship classification. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 123, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Ship classification in medium-resolution SAR images via densely connected triplet CNNs integrating Fisher discrimination regularized metric learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 3022–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pei, J.; Luo, S.; Huo, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. SAR Ship Target Recognition via Multiscale Feature Attention and Adaptive-Weighed Classifier. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 4003905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Ship classification based on sidelobe elimination of SAR images supervised by visual model. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–14 May 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Krähenbühl, P. Objects as points. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07850. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Dong, C.; Loy, C.C. Recovering realistic texture in image super-resolution by deep spatial feature transform. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 606–615. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective kernel networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Bodla, N.; Singh, B.; Chellappa, R.; Davis, L.S. Soft-NMS–improving object detection with one line of code. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5561–5569. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Oriented R-CNN for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3520–3529. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Long, Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q. Learning RoI Transformer for Oriented Object Detection in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2849–2858. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xia, G.S.; Bai, X. Gliding Vertex on the Horizontal Bounding Box for Multi-Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.S. Align deep features for oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5602511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, C.; Yao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9759–9768. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).