SST Forecast Skills Based on Hybrid Deep Learning Models: With Applications to the South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
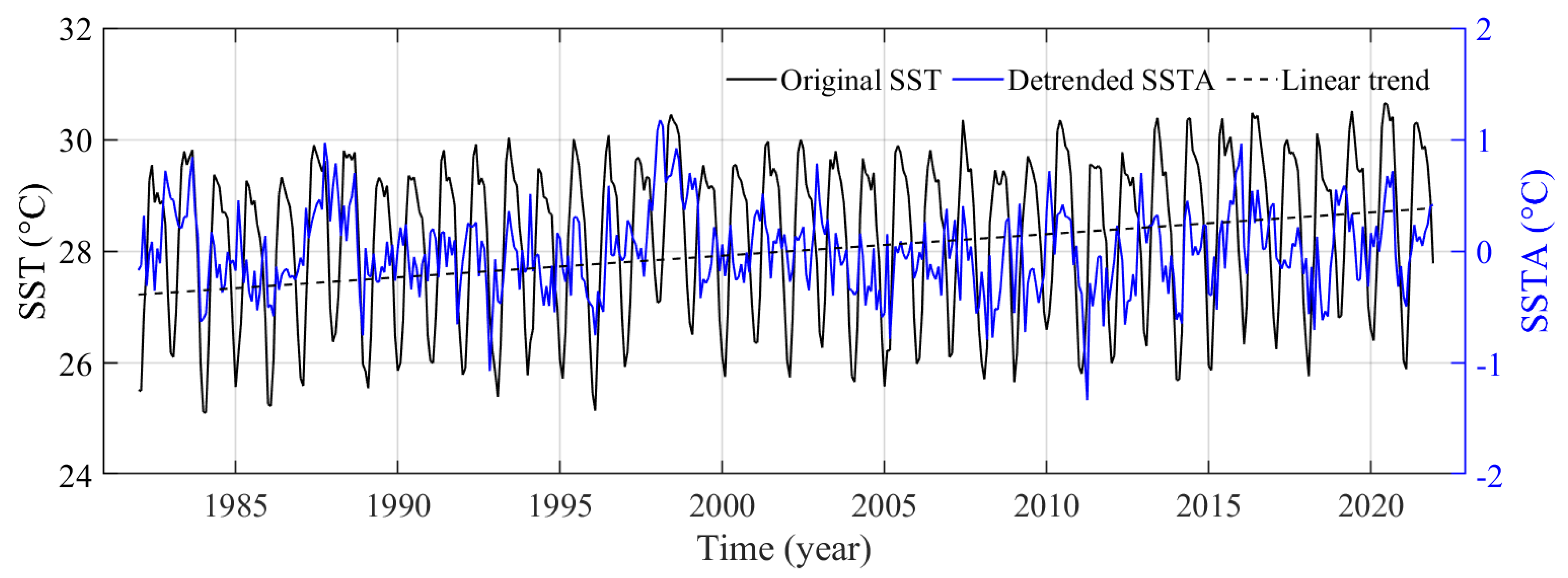
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
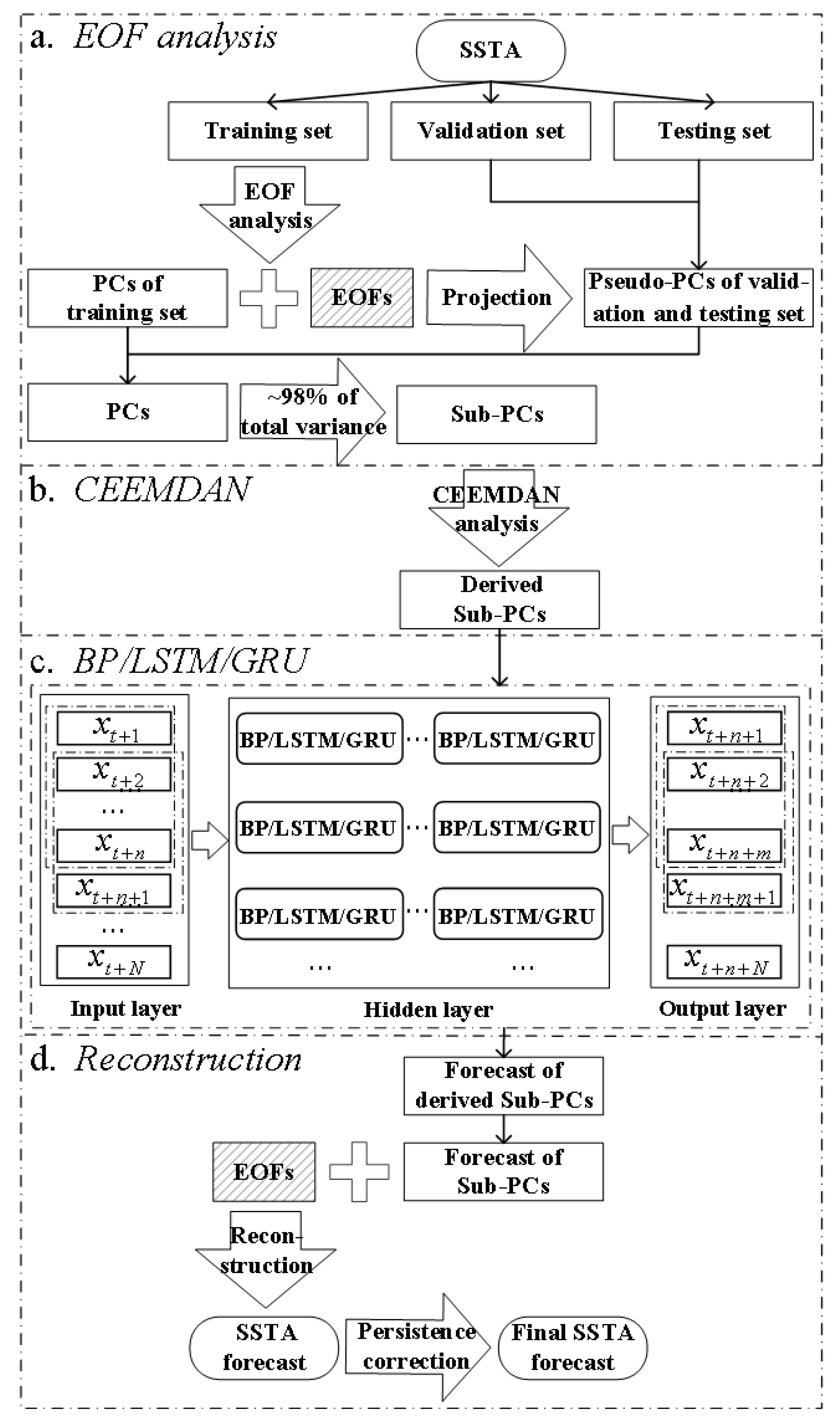
2.2.1. Hybrid Model
2.2.2. EOF Analysis
2.2.3. CEEMDAN Method
2.2.4. Neural Network
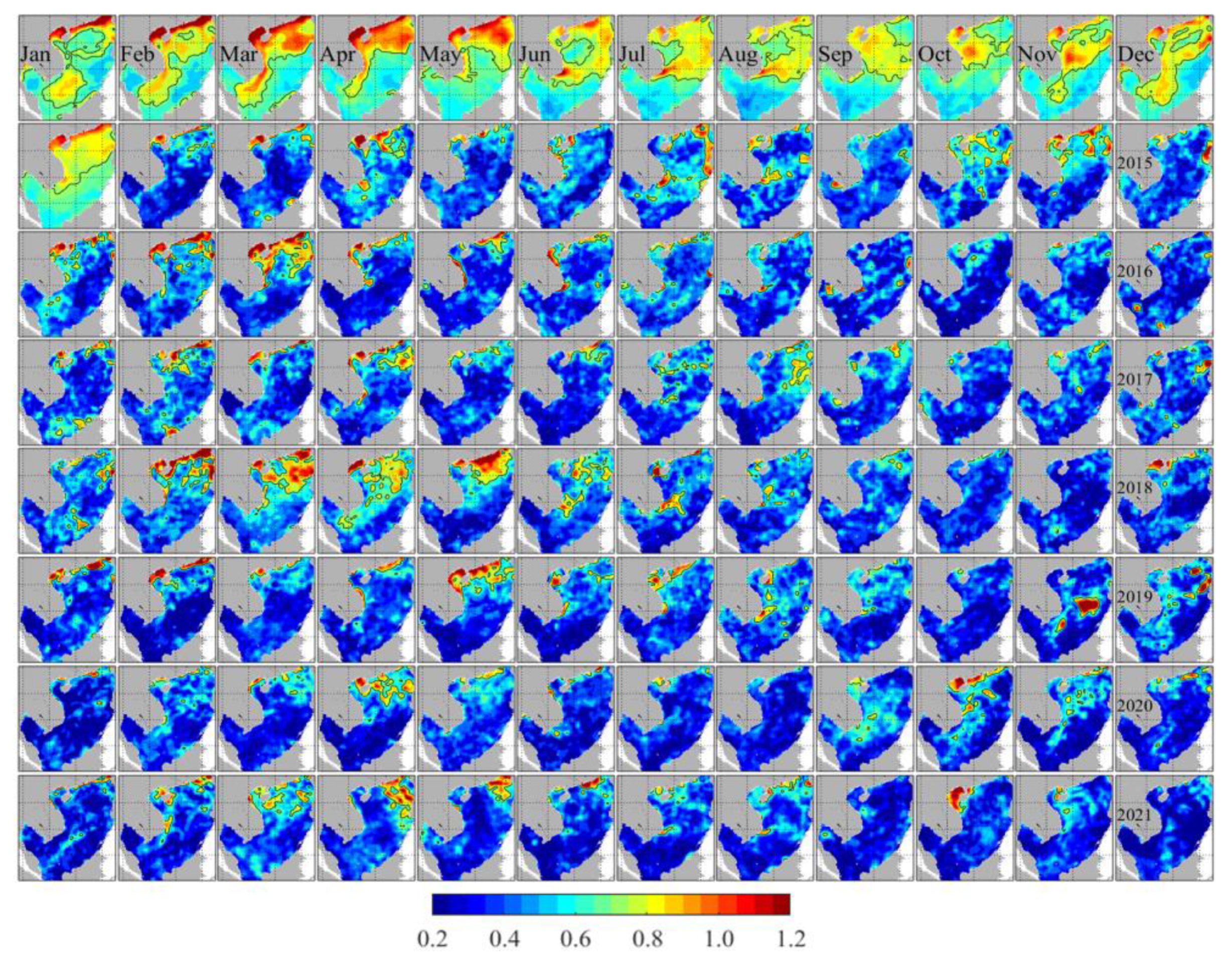
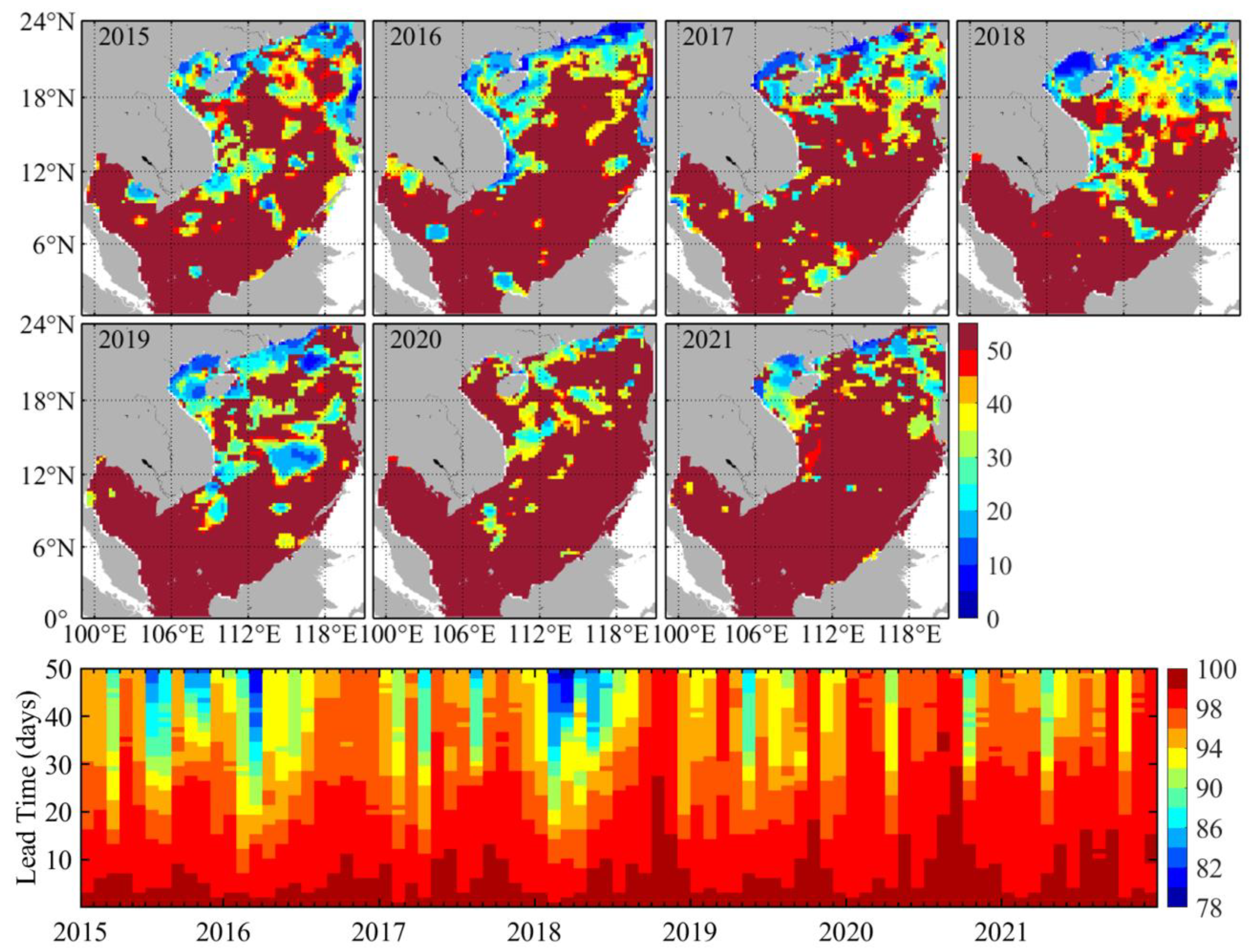
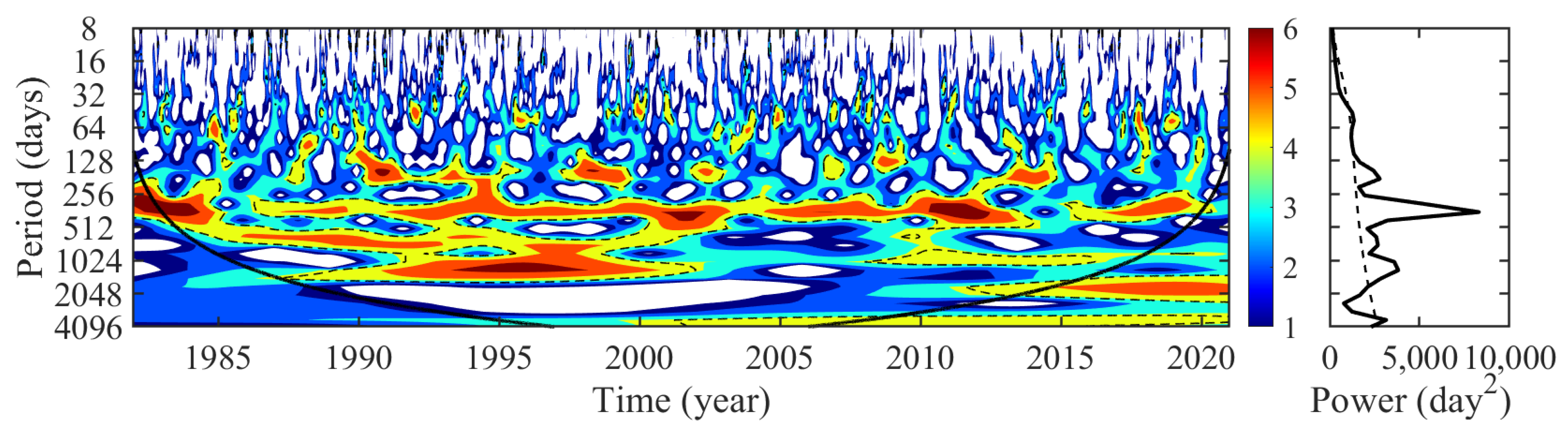
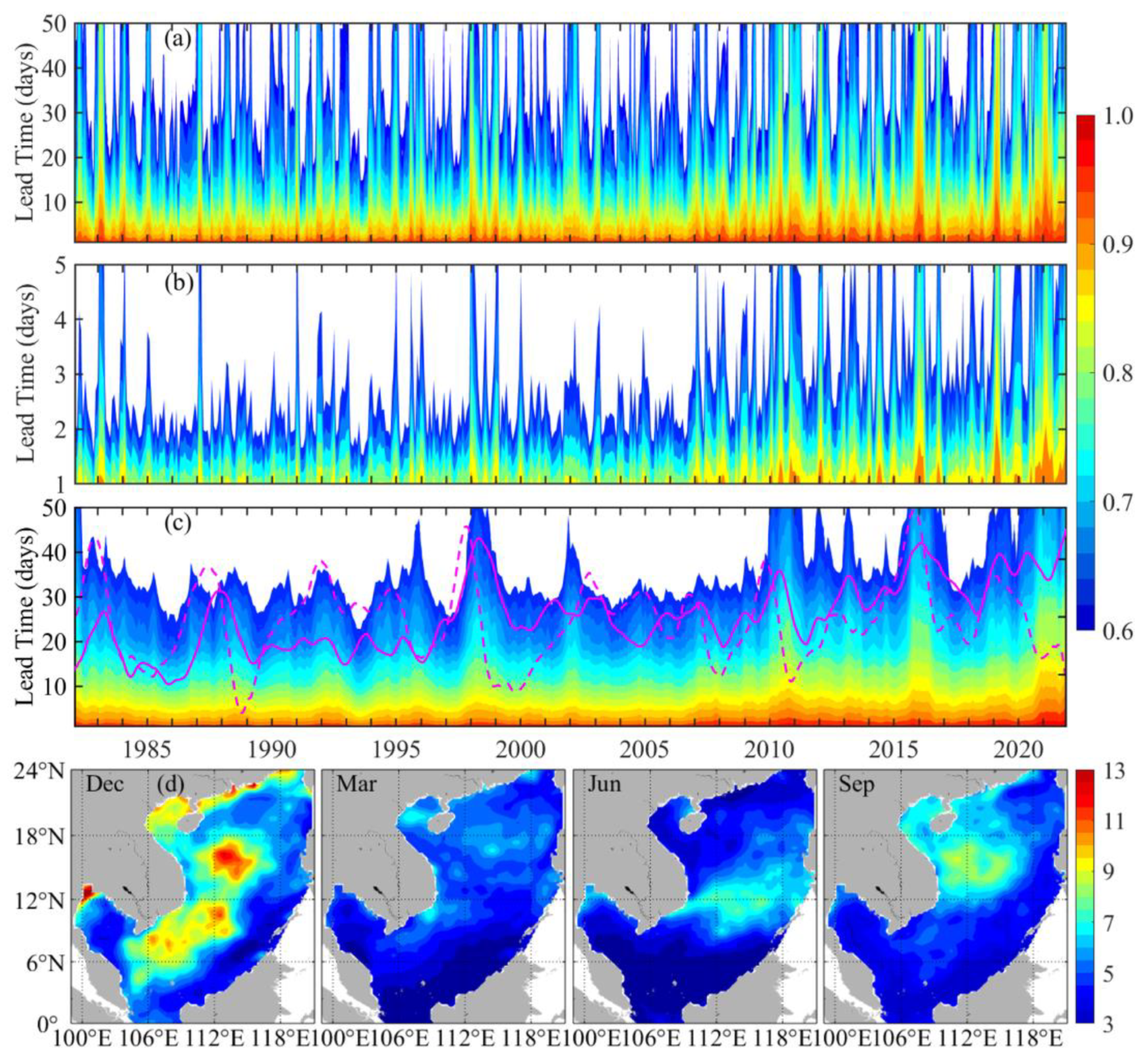
3. Results
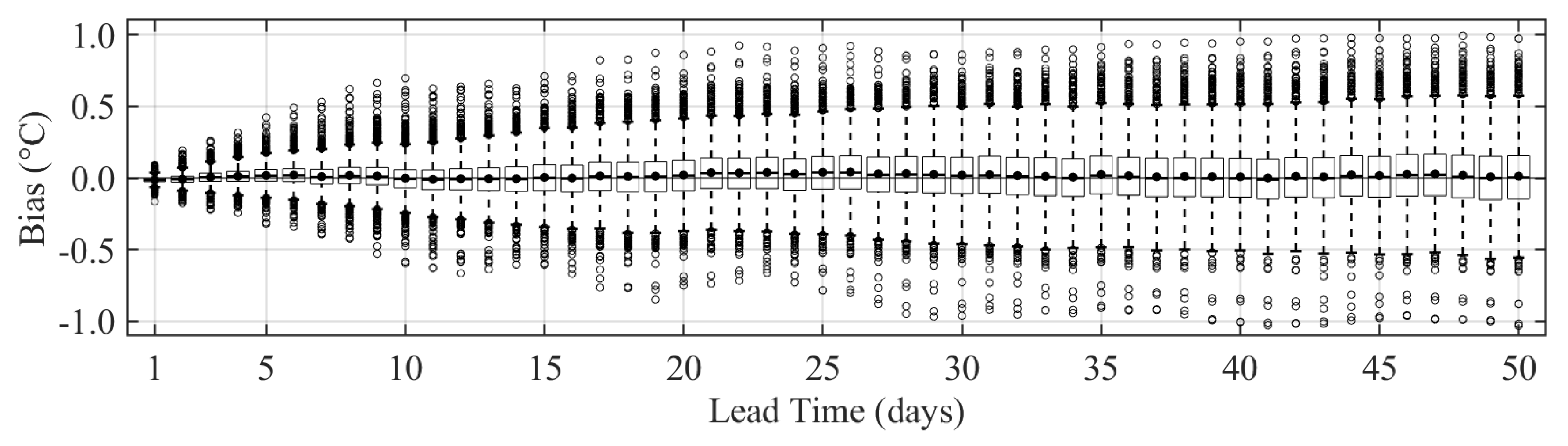
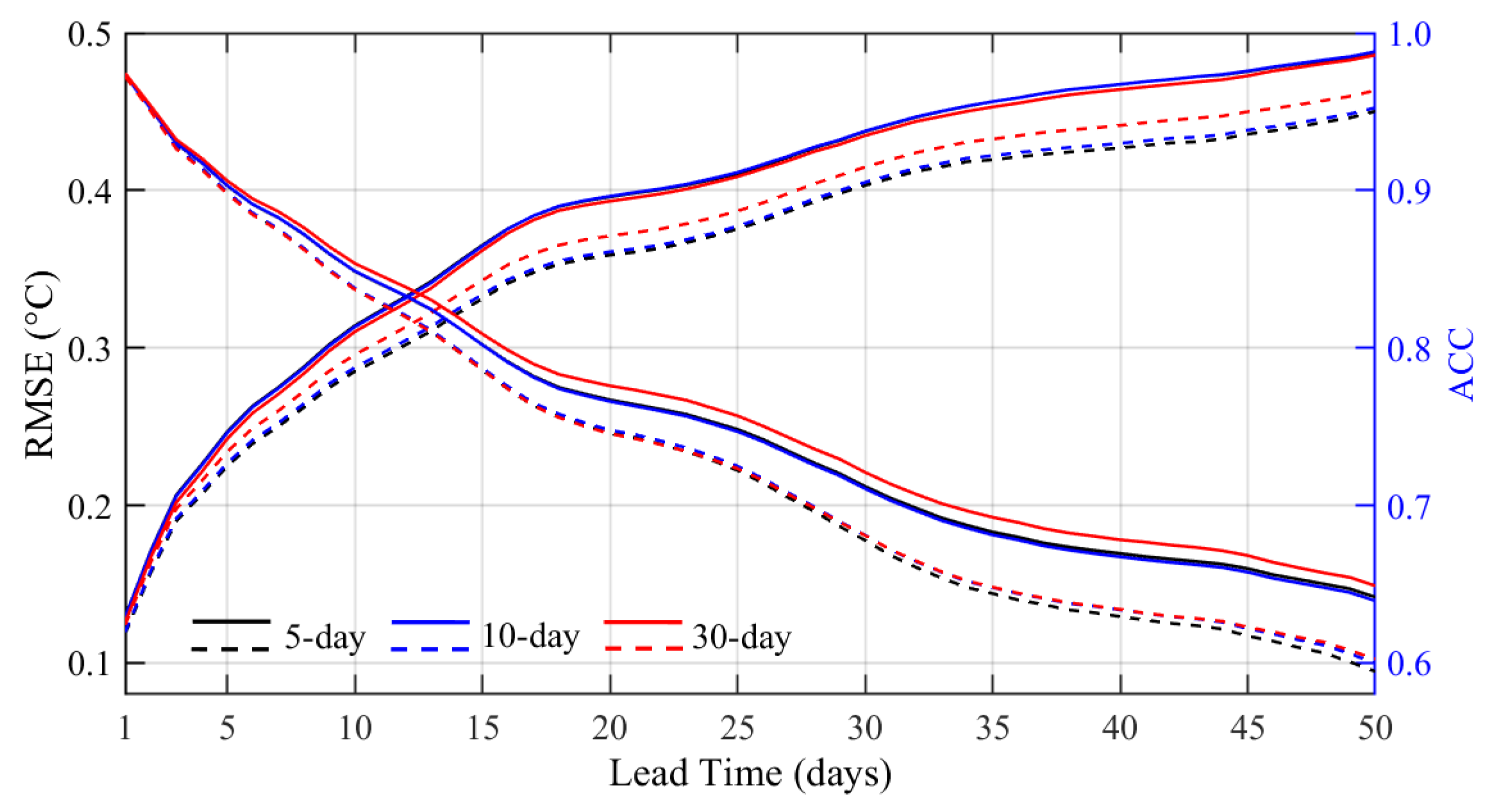
3.1. Forecasts Verification
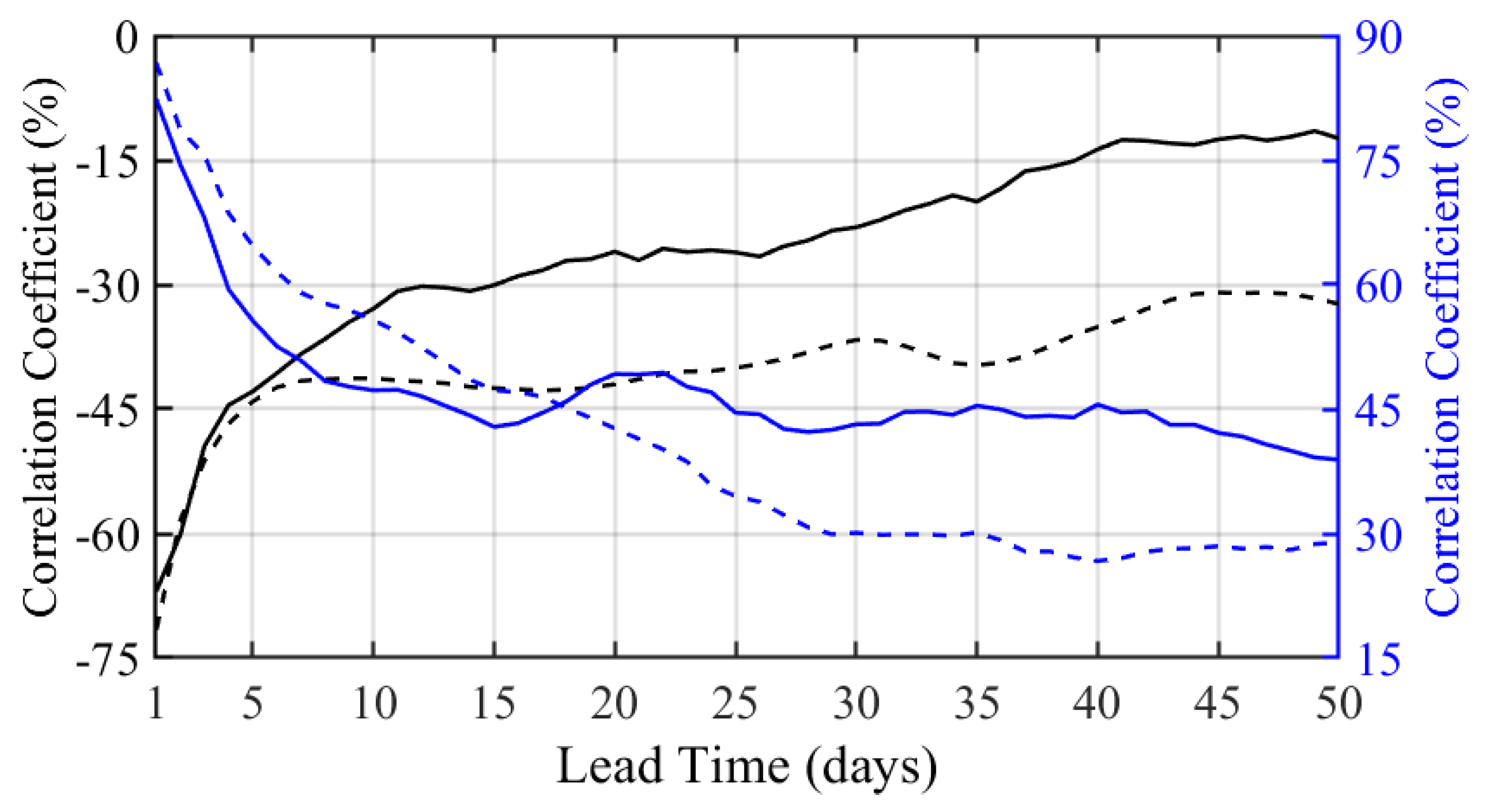
3.2. Time Scales of Forecast Skill Horizon
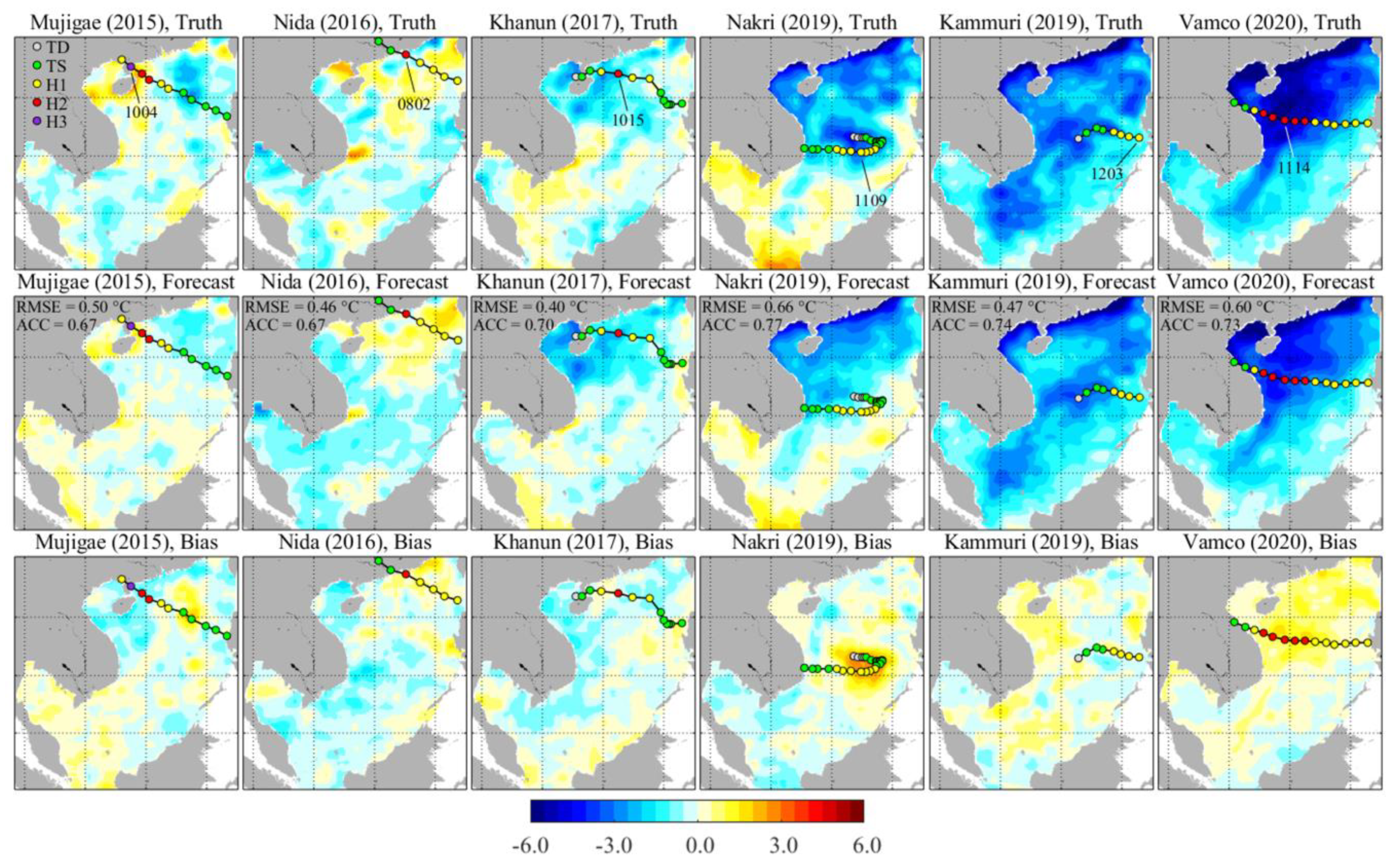
3.3. Impact of Tropical Cyclones
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N.; Prabhat. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.-H.; Liu, B. Purely satellite data-driven deep learning forecast of complicated tropical instability waves. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparna, S.G.; D’souza, S.; Arjun, N.B. Prediction of daily sea surface temperature using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4214–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Chen, N.; Hu, C.; Wang, K.; Gong, J.; Chen, Z. Short and mid-term sea surface temperature prediction using time-series satellite data and LSTM-AdaBoost combination approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Hou, G.; Li, W.; Han, G.; Liang, K.; Bai, Y. Ocean reanalysis data-driven deep learning forecast for sea surface multivariate in the South China Sea. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Li, W.; Hou, G.; Han, G.; Wu, X. Mid-term simultaneous spatiotemporal prediction of sea surface height anomaly and sea surface temperature using satellite data in the South China Sea. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N.; Metzger, E.J.; Reynolds, C.A.; Ruston, B.; Rowley, C.; Smedstad, O.M.; Ridout, J.A.; Wallcraft, A.; Frolov, S.; Hogan, P.; et al. The Navy’s Earth System Prediction Capability: A new global coupled atmosphere-ocean-sea ice prediction system designed for daily to subseasonal forecasting. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.; Tkalich, P.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P. Regime shift of the South China Sea SST in the Late 1990s. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.W.; Smith, T.M.; Liu, C.; Chelton, D.B.; Casey, K.S.; Schlax, M.G. Daily high-resolution-blended analyses for sea surface temperature. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5473–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.E.; Emery, W.J. Chapter 4-The spatial analyses of data fields. In Data Analysis Methods in Physical Oceanography, 3rd. ed.; Thomson, R.E., Emery, W.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 313–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Chen, H.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, C. Trends and interannual variability of the South China Sea Surface winds, surface height, and surface temperature in the recent decade. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111, C11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.-R.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y. Trends of sea surface temperature and sea surface temperature fronts in the South China Sea during 2003–2017. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, N.E. Empirical orthogonal functions and statistical weather prediction. In Statistical Forecasting Project Report; Department of Meteorology; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1956; Volume 1, pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 4144–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.; Sun, Z.; Hughes, T.W.; Park, T.; Bartlett, B.; Williamson, I.A.D.; Minkov, M.; Milanizadeh, M.; Abebe, N.; Morichetti, F.; et al. Experimentally realized in situ backpropagation for deep learning in photonic neural networks. Science 2023, 380, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, S. Assessment of the spatiotemporal prediction capabilities of machine learning algorithms on sea surface temperature data: A comprehensive study. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 118, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Li, W.; Han, G.; Hou, G.; Liu, S.; Gong, Y.; Qu, P. A deep learning model for forecasting sea surface height anomalies and temperatures in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendlebury, S.F.; Adams, N.D.; Hart, T.L.; Turner, J. Numerical weather prediction model performance over high southern latitudes. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2003, 131, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoppil, P.G.; Frolov, S.; Rowley, C.D.; Reynolds, C.A.; Jacobs, G.A.; Joseph Metzger, E.; Hogan, P.J.; Barton, N.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Smedstad, O.M.; et al. Ensemble forecasting greatly expands the prediction horizon for ocean mesoscale variability. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C. Carbon Price Forecasting Based on CEEMDAN and LSTM. Appl. Energy 2022, 311, 118601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Yao, W.; Ma, X.; Yao, Y.; Liu, L. Short-Term Rainfall Forecast Model Based on the Improved BP–NN Algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zor, K.; Buluş, K. A Benchmark of GRU and LSTM Networks for Short-Term Electric Load Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Innovation and Intelligence for Informatics, Computing, and Technologies (3ICT), Online, 29–30 September 2021; pp. 598–602. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, A.C.; Buluş, K.; Zor, K. Medium- to Long-Term Nickel Price Forecasting Using LSTM and GRU Networks. Resour. Policy 2022, 78, 102906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgin, C.E.; Merchant, C.J.; Ferreira, D. Tendencies, variability and persistence of sea surface temperature anomalies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Li, J. Decadal and seasonal dependence of North Pacific sea surface temperature persistence. J. Geophys. Res. (Atmos.) 2009, 114, D01105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, D.; Xie, Q. Harmonic analysis of sea surface temperature and wind stress in the vicinity of the maritime continent. J. Meteorol. Res. 2003, 17, 226–237. Available online: http://jmr.cmsjournal.net/article/id/1549 (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Yan, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, C.; Ling, Z. Annual and semiannual cycles of diurnal warming of sea surface temperature in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 5797–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Cao, X.; Chen, S. Covariations of SST and surface heat flux on 10–20 day and 30–60 day time scales over the South China Sea and western North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12486–12499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Yasunari, T.; Wang, B. Decadal change in intraseasonal variability over the South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, GL037174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yu, H.; Ying, M.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Lin, L.; Bai, L.; Wan, R. Western North Pacific tropical cyclone database created by the China Meteorological Administration. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dare, R.A.; McBride, J.L. Sea surface temperature response to tropical cyclones. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2011, 139, 3798–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Lien, C.-C.; Lin, I.-I.; Xie, S.-P. Tropical cyclone–induced ocean response: A comparative study of the South China Sea and tropical Northwest Pacific. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 5952–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klie, H. A Tale of Two Approaches: Physics-Based vs. Data-Driven Models. The Way Ahead. 2021. Available online: https://jpt.spe.org/twa/a-tale-of-two-approaches-physics-based-vs-data-driven-models (accessed on 9 March 2024).


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Han, G.; Wu, X.; Li, C.; Shao, Q.; Li, W.; Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, W.; Ji, Z. SST Forecast Skills Based on Hybrid Deep Learning Models: With Applications to the South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061034
Zhang M, Han G, Wu X, Li C, Shao Q, Li W, Cao L, Wang X, Dong W, Ji Z. SST Forecast Skills Based on Hybrid Deep Learning Models: With Applications to the South China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(6):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061034
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mengmeng, Guijun Han, Xiaobo Wu, Chaoliang Li, Qi Shao, Wei Li, Lige Cao, Xuan Wang, Wanqiu Dong, and Zenghua Ji. 2024. "SST Forecast Skills Based on Hybrid Deep Learning Models: With Applications to the South China Sea" Remote Sensing 16, no. 6: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061034
APA StyleZhang, M., Han, G., Wu, X., Li, C., Shao, Q., Li, W., Cao, L., Wang, X., Dong, W., & Ji, Z. (2024). SST Forecast Skills Based on Hybrid Deep Learning Models: With Applications to the South China Sea. Remote Sensing, 16(6), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16061034





