Multi-Scale Acoustic Velocity Inversion Based on a Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
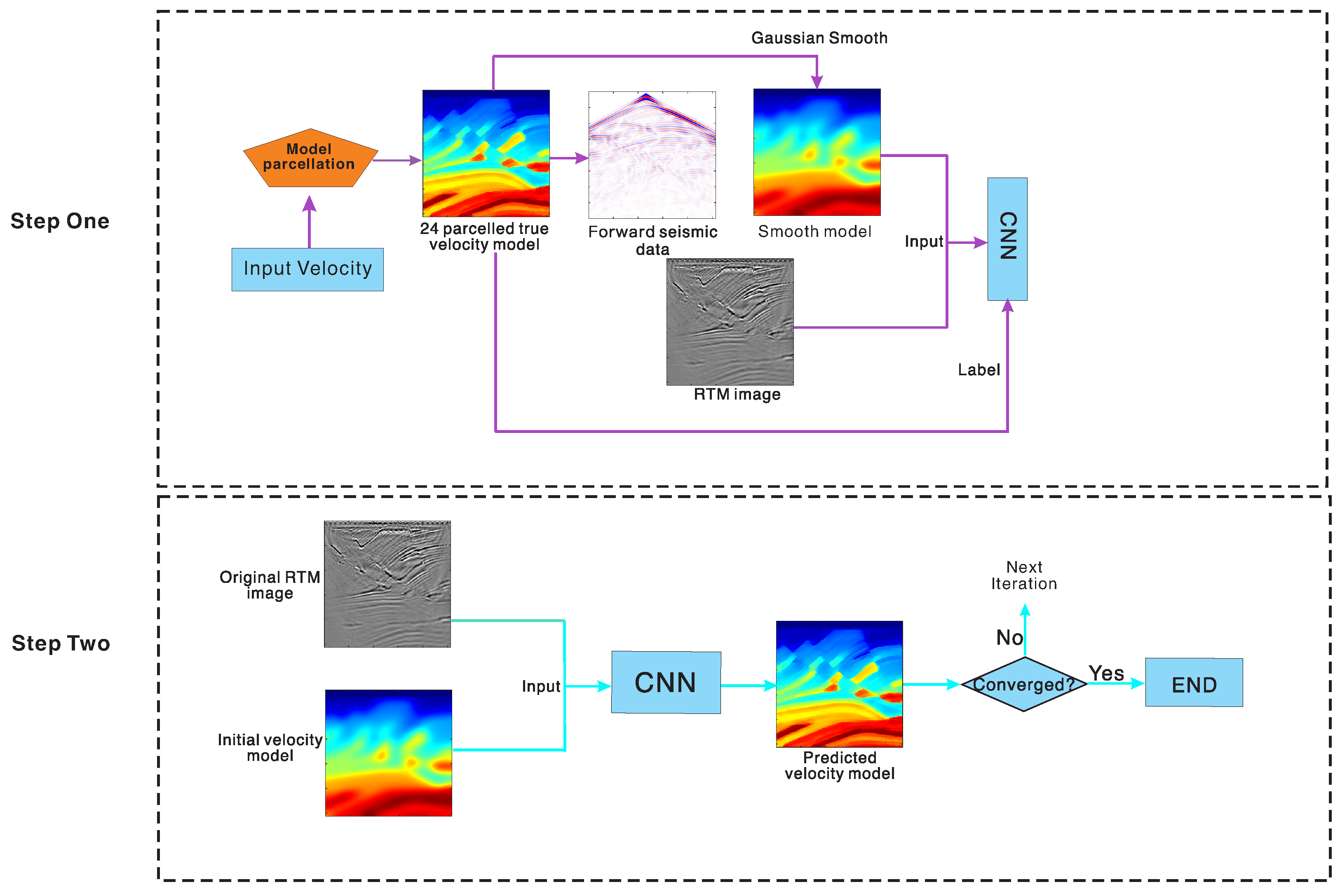
2. Theory and Method
2.1. The Iterative Update Structure
2.1.1. Physical Rationality Analysis
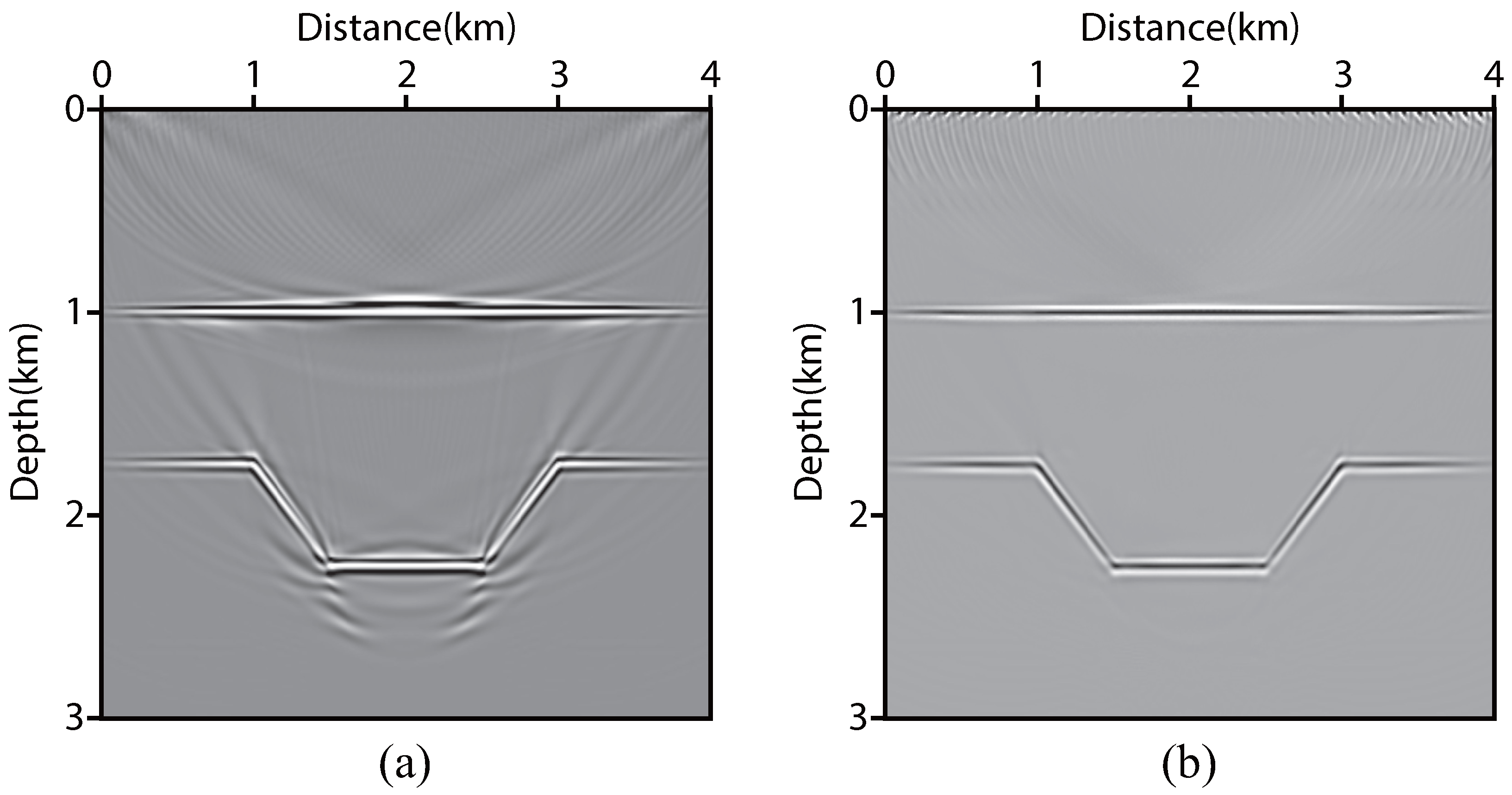
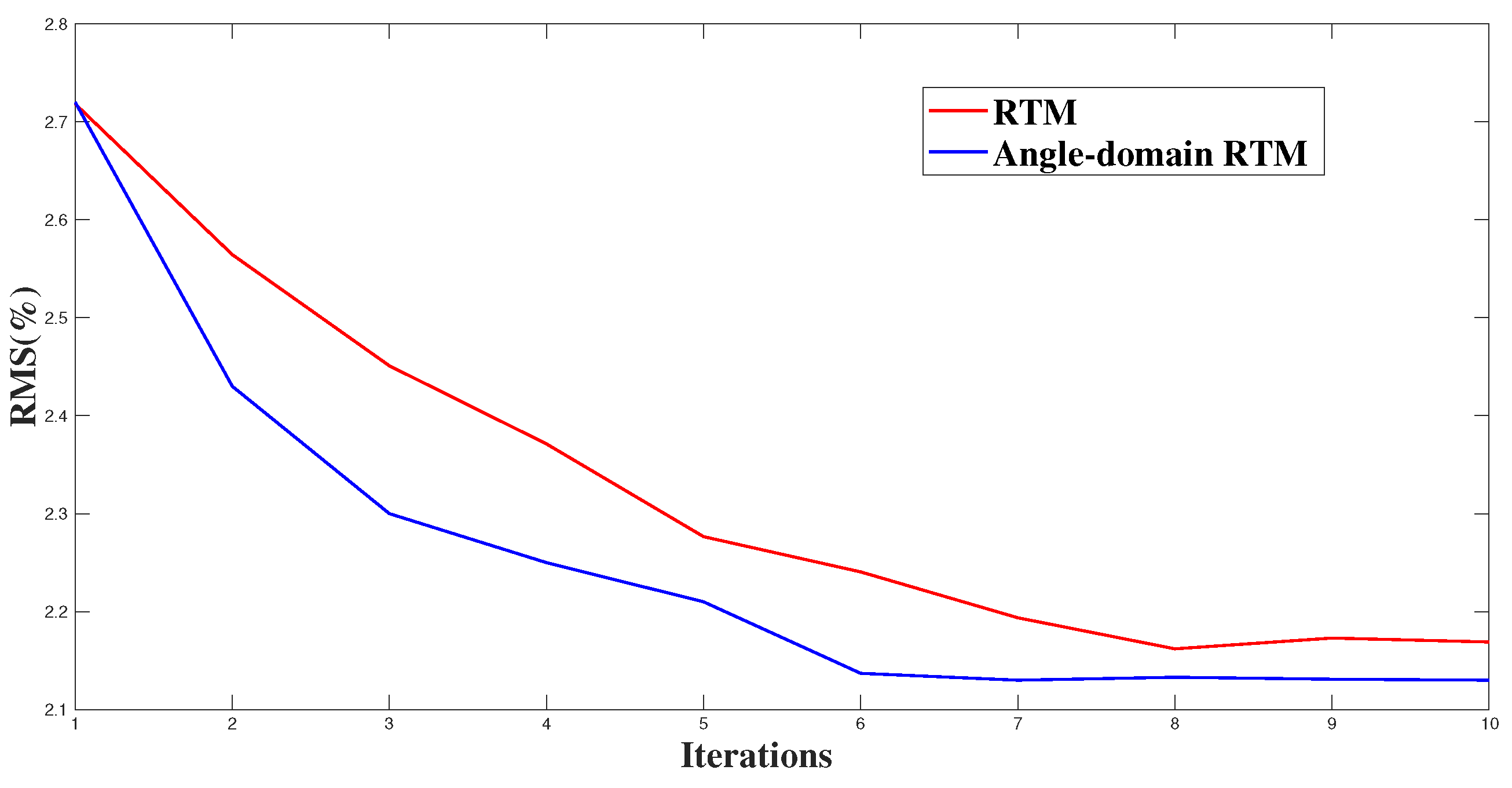
2.1.2. Angle-Domain RTM
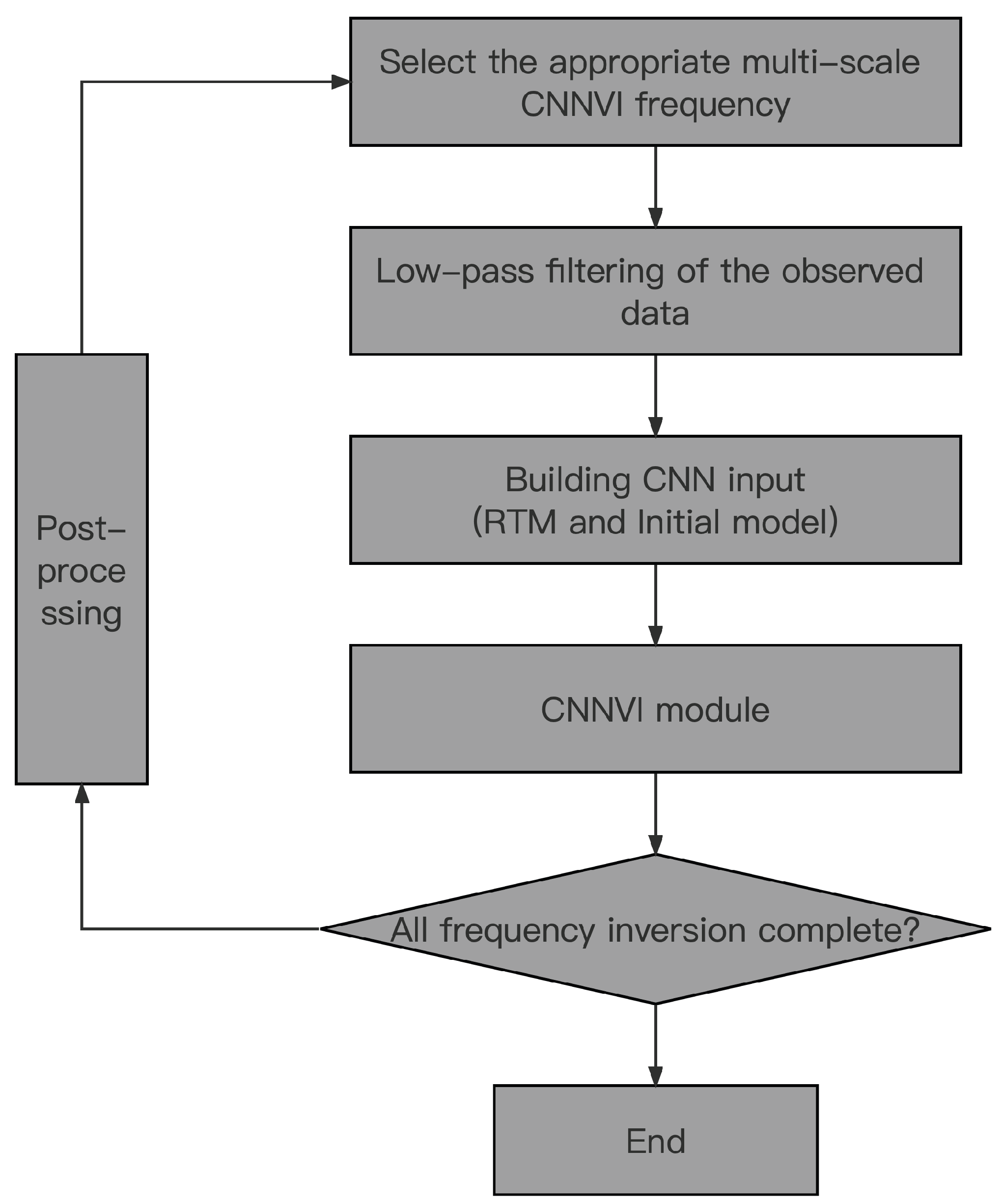
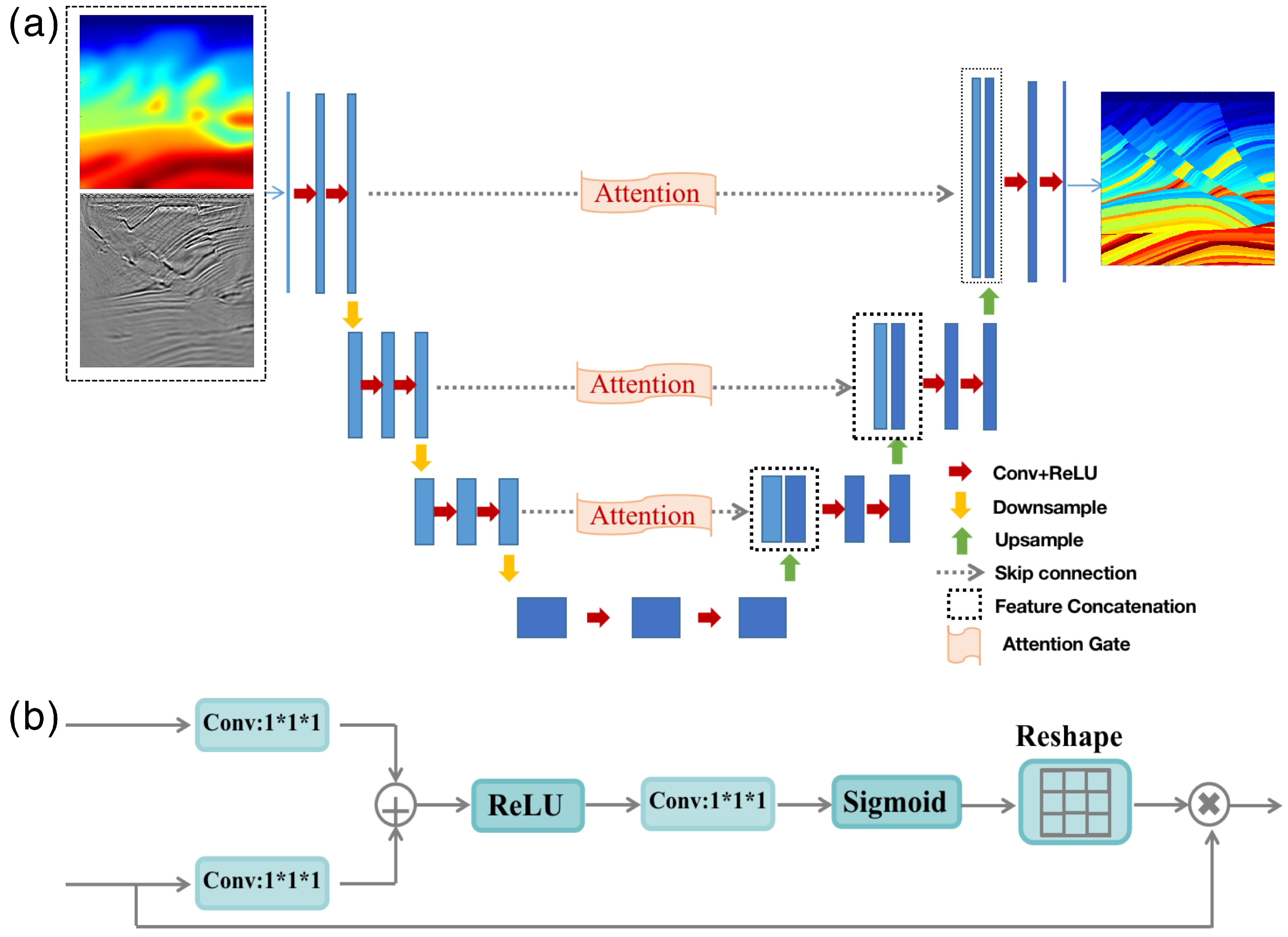
2.2. The Workflow of Multi-Scale CNN Velocity Inversion
- To begin, we carefully choose several inversion frequencies at various scales, taking into account the specific features of the observed seismic data. In a given area, for example, our selection may begin at 5 Hz and progress to 10 Hz, 15 Hz, and 20 Hz in a sequential manner to perform the inversion. Then, at the beginning of the iteration we start with the inversion at low frequencies.
- Once we have chosen the inversion frequency for the current iteration, it is time to apply a low-pass filter to the observations. This step ensures that the data are properly prepared for downstream processing.
- In the construction of the CNN input, both the RTM and the initial velocity model play crucial roles. The RTM component is obtained through the technique of angle-domain RTM imaging, and the initial velocity model can be obtained via tomography imaging or migration velocity analysis (MVA).
- CNNVI is performed using the input data obtained in step c, and more accurate inversion results are obtained. The specific principles of the CNNVI module were introduced in the previous subsection.
- The inversion process is complete for all selected frequencies. If complete, the entire Ms-CNNVI process is ended; if not complete, the post-processing of the data continues.
| Algorithm 1 Multi-scale CNNVI. |
| Given Inversion frequency Observed seismic data Initial velocity model Initialize , Select the max inversion frequency
|
2.3. Method Details
2.3.1. The Structure of the Network in CNNVI
2.3.2. The Data Processing and Training Details
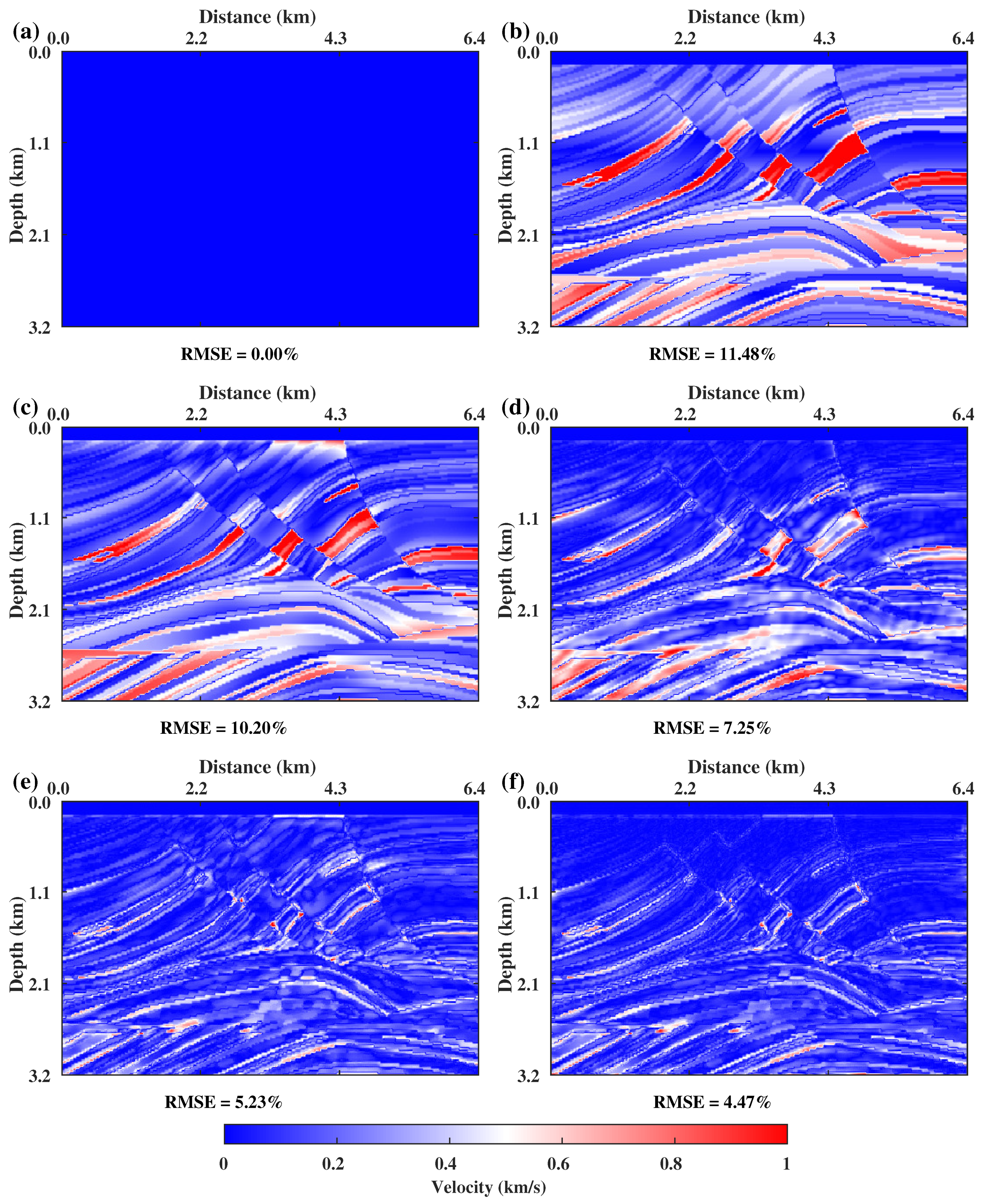
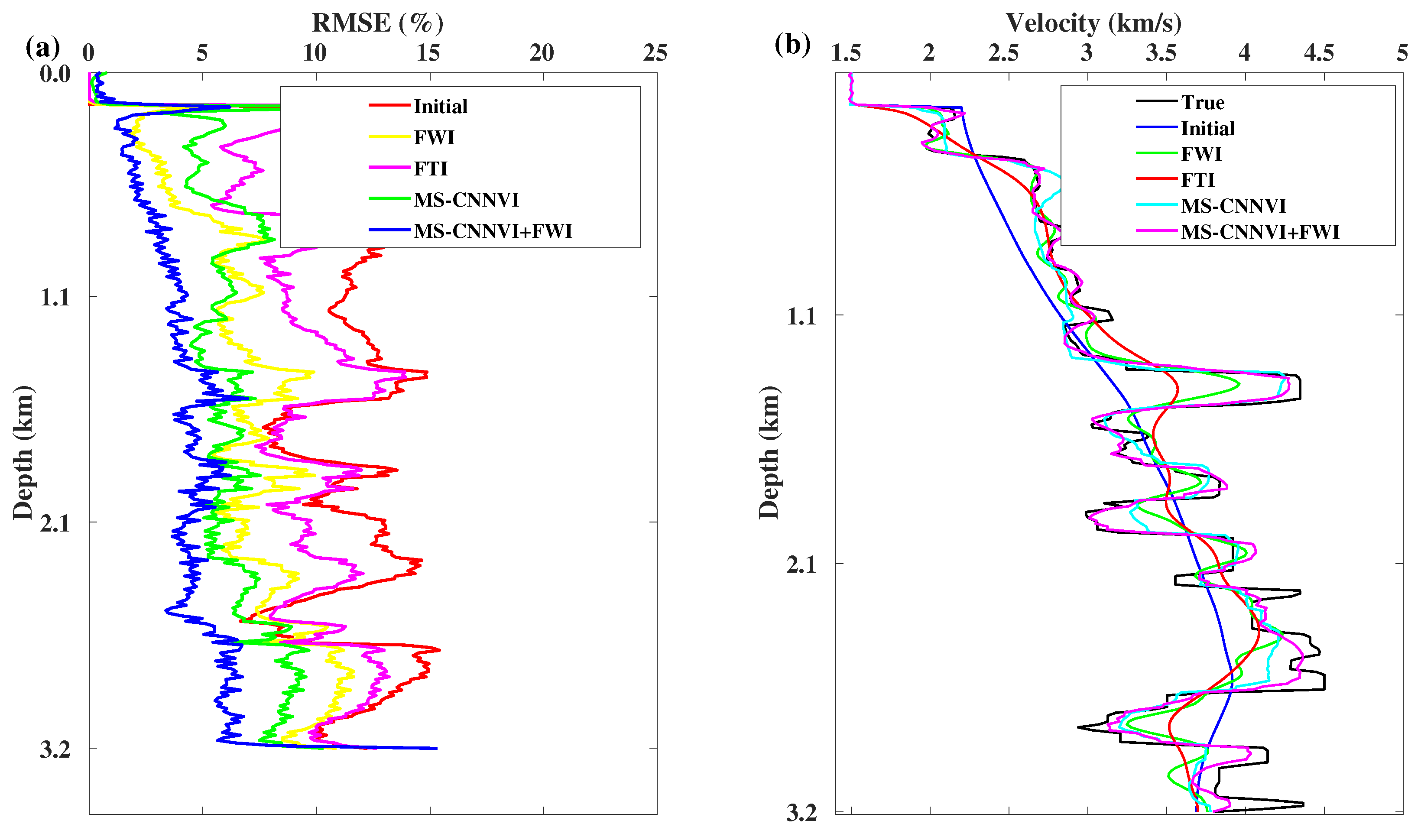
3. Numerical Results
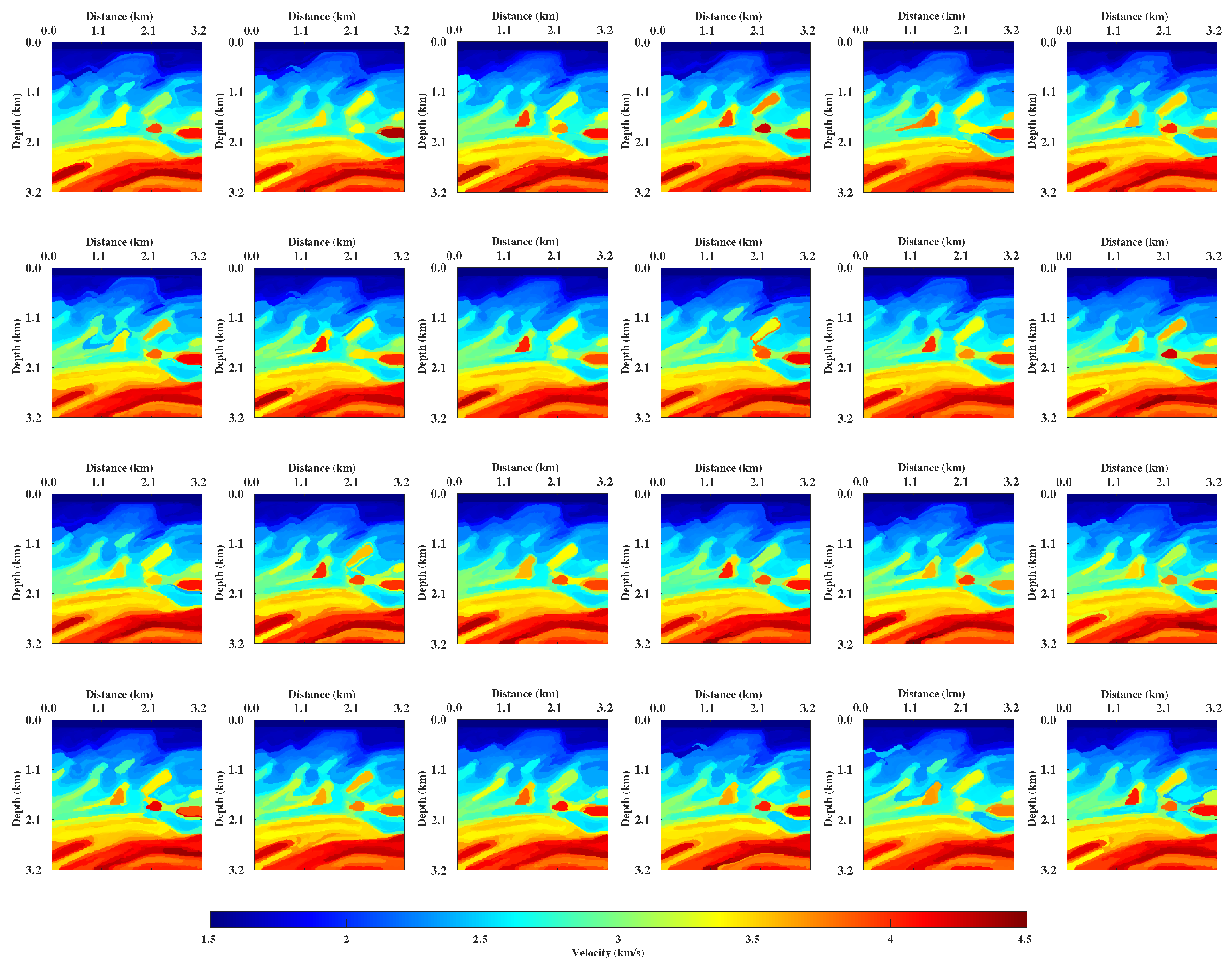
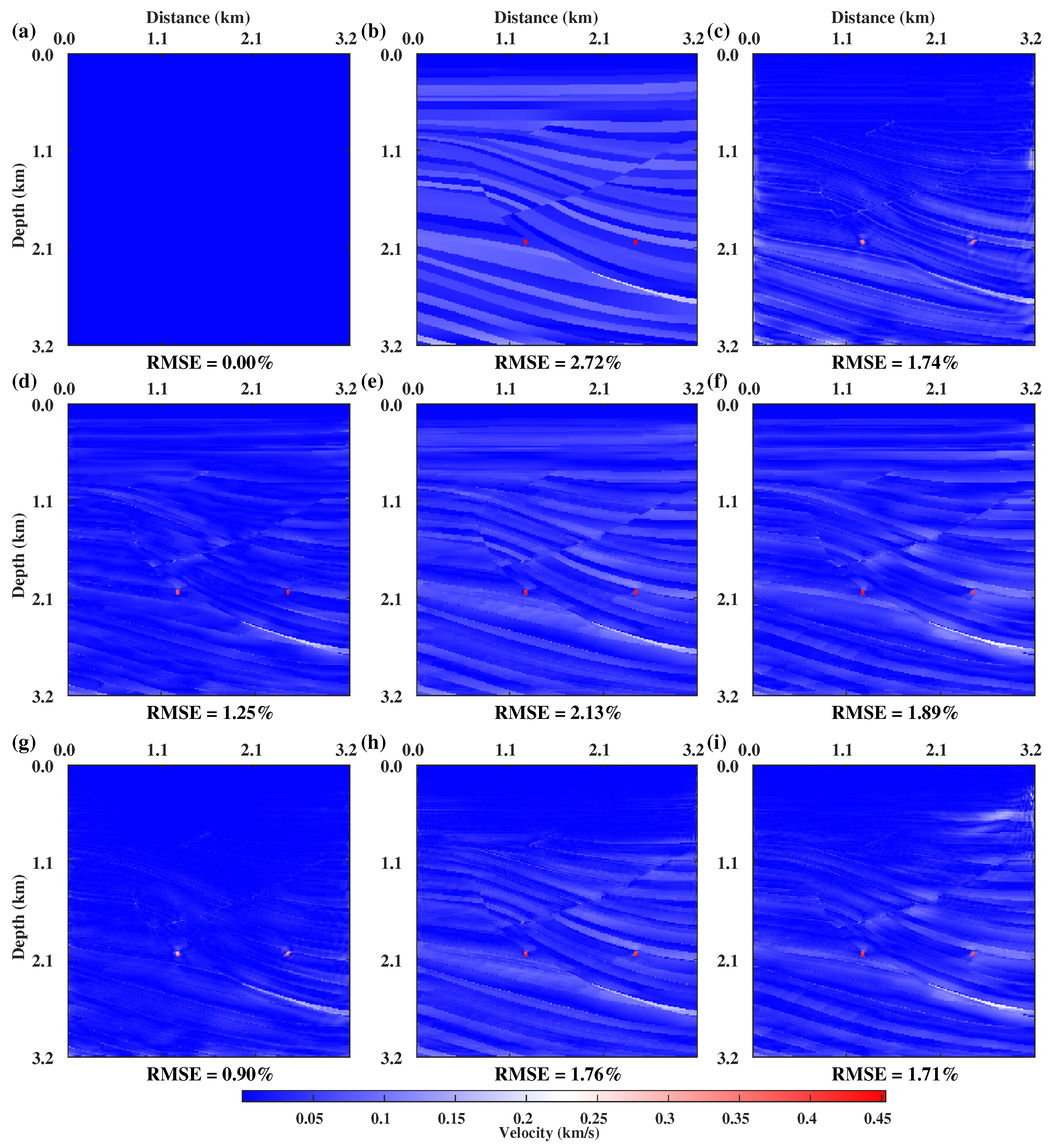
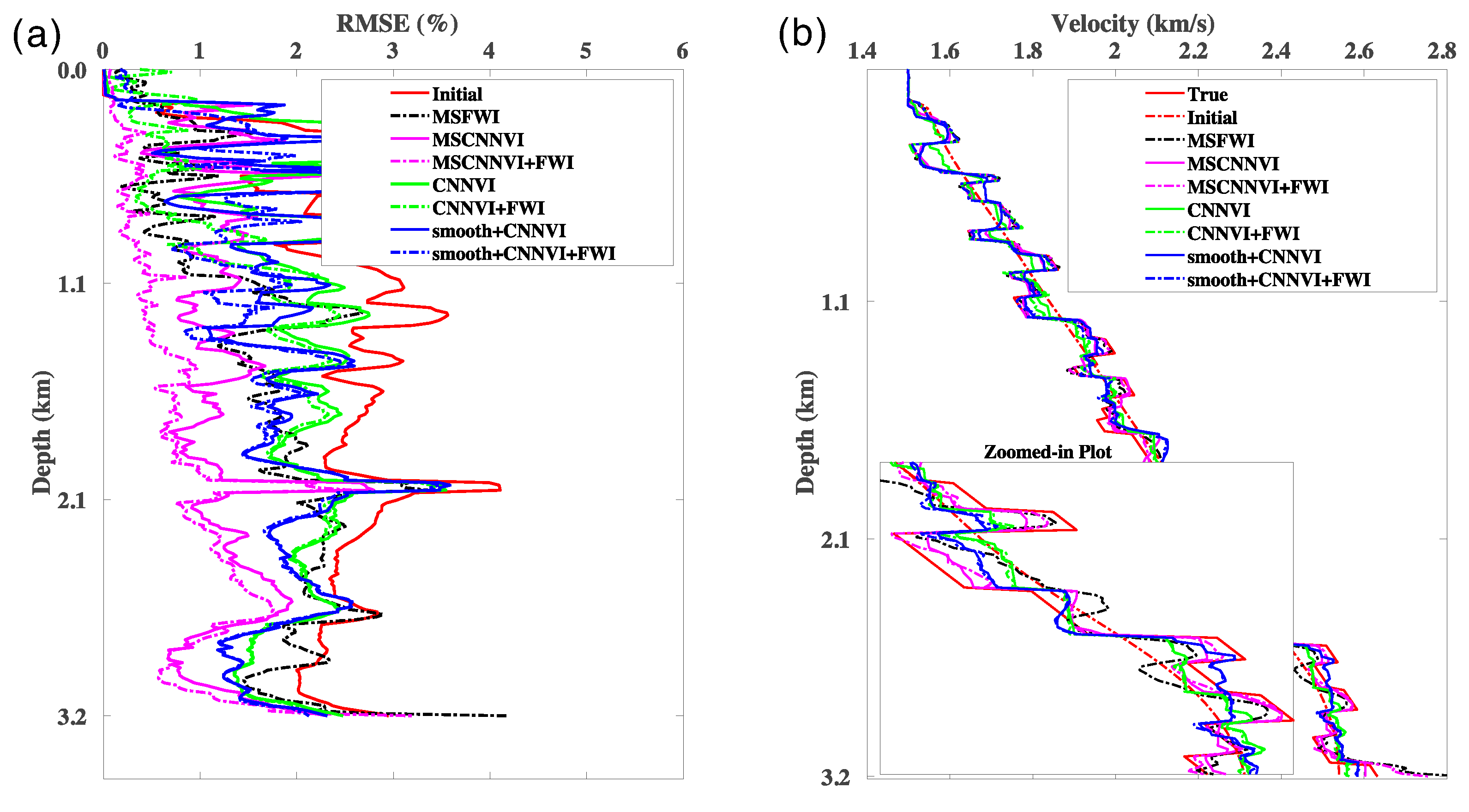
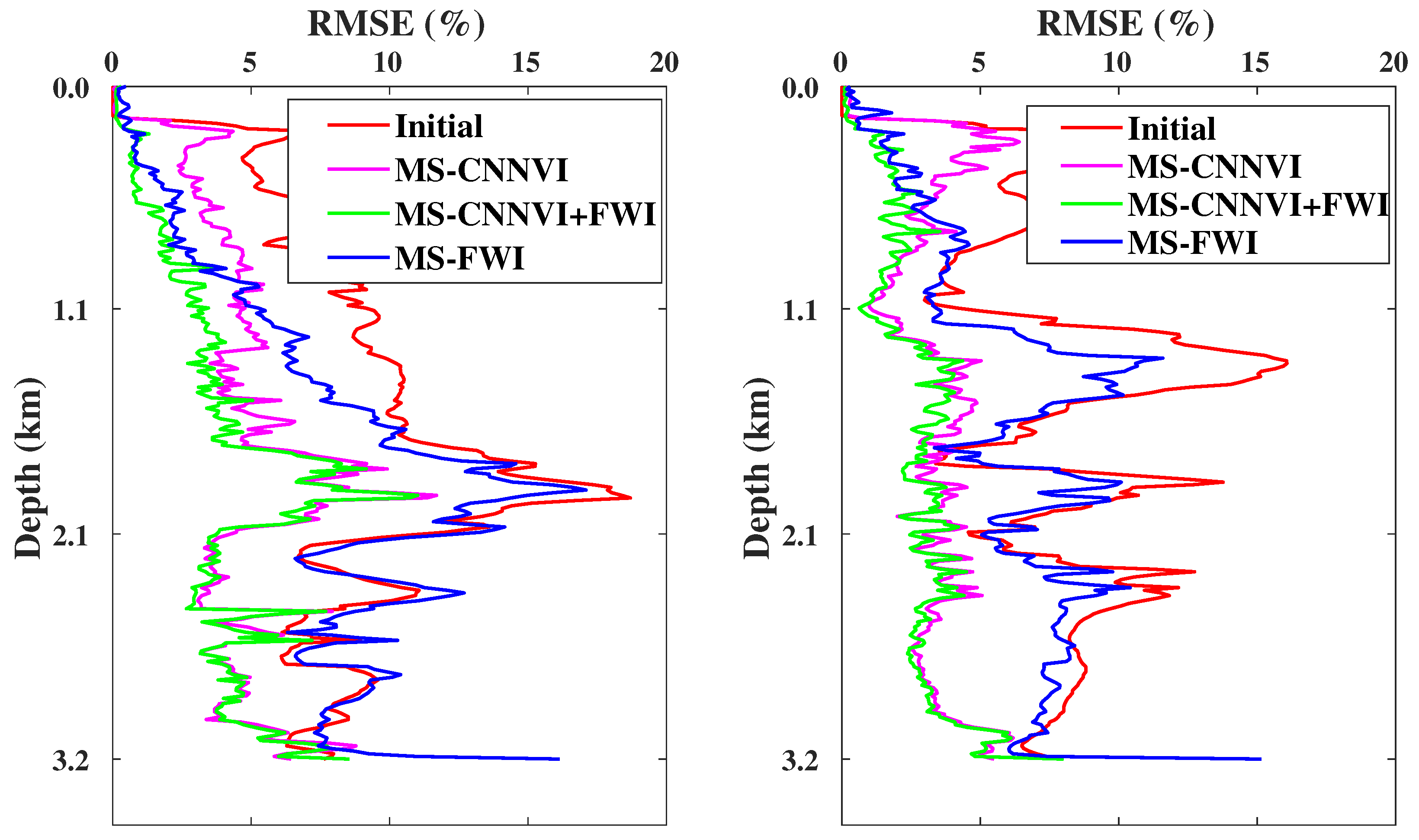
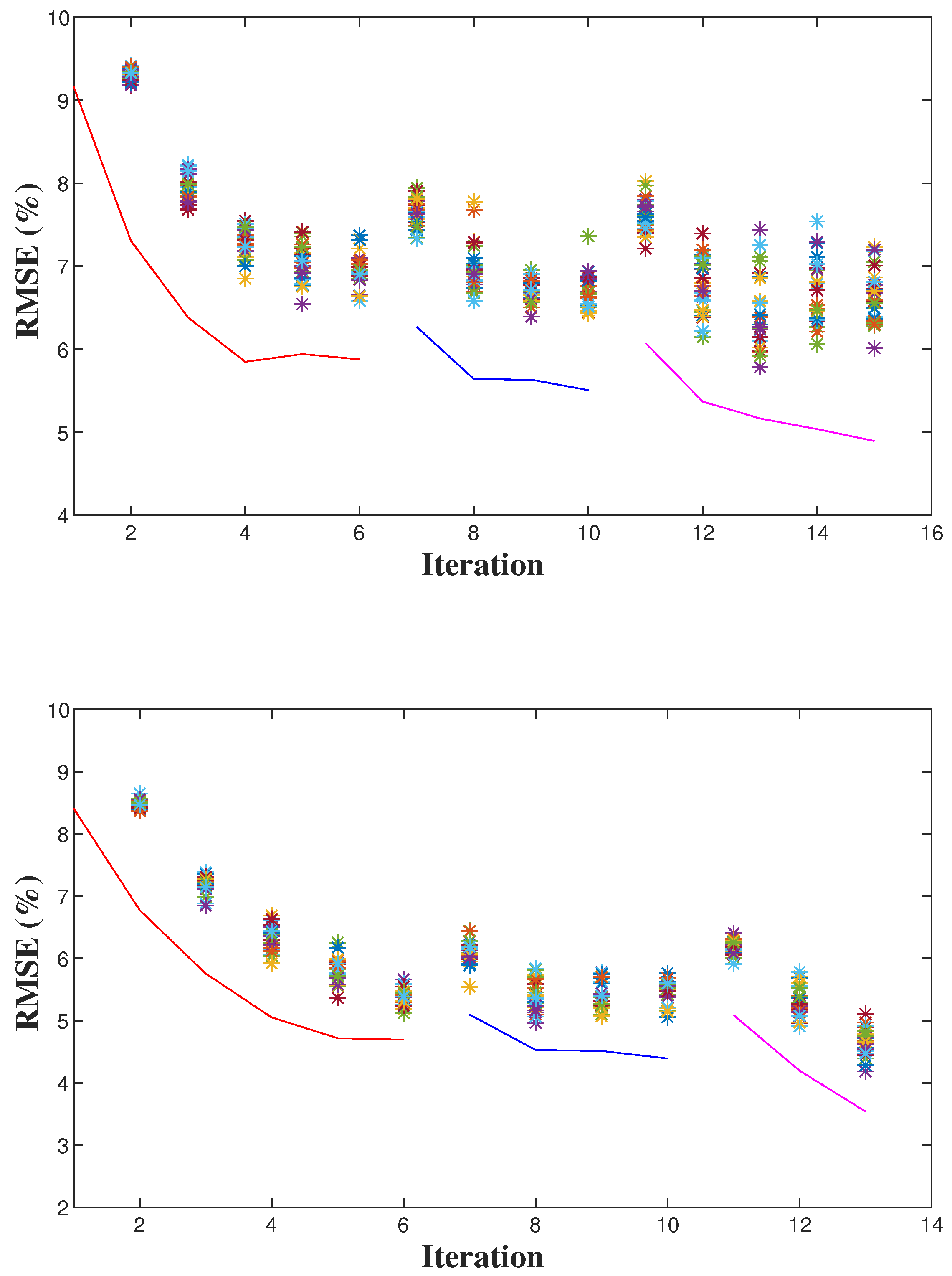
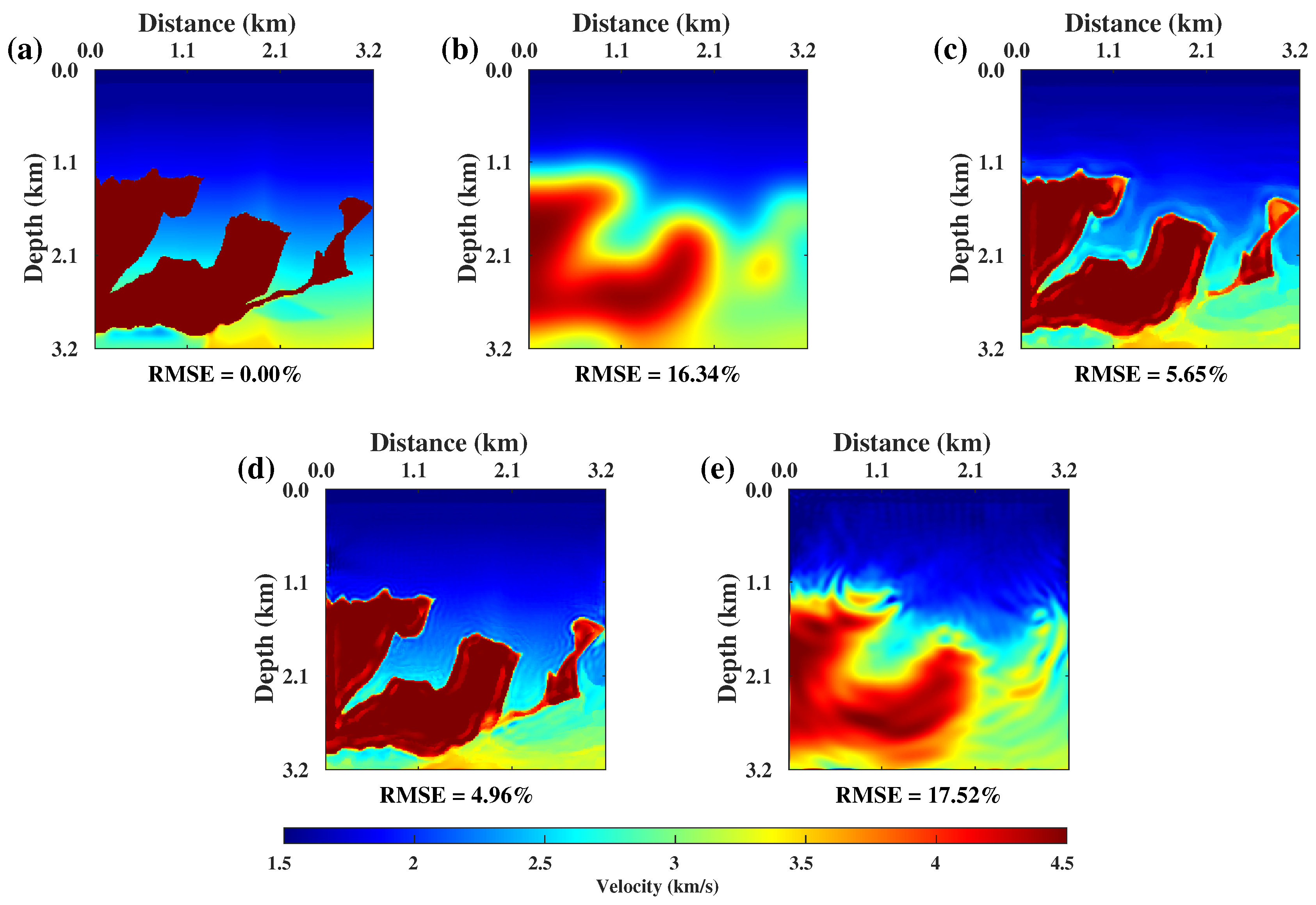
3.1. Ablation Experiments with Ms-CNNVI Method
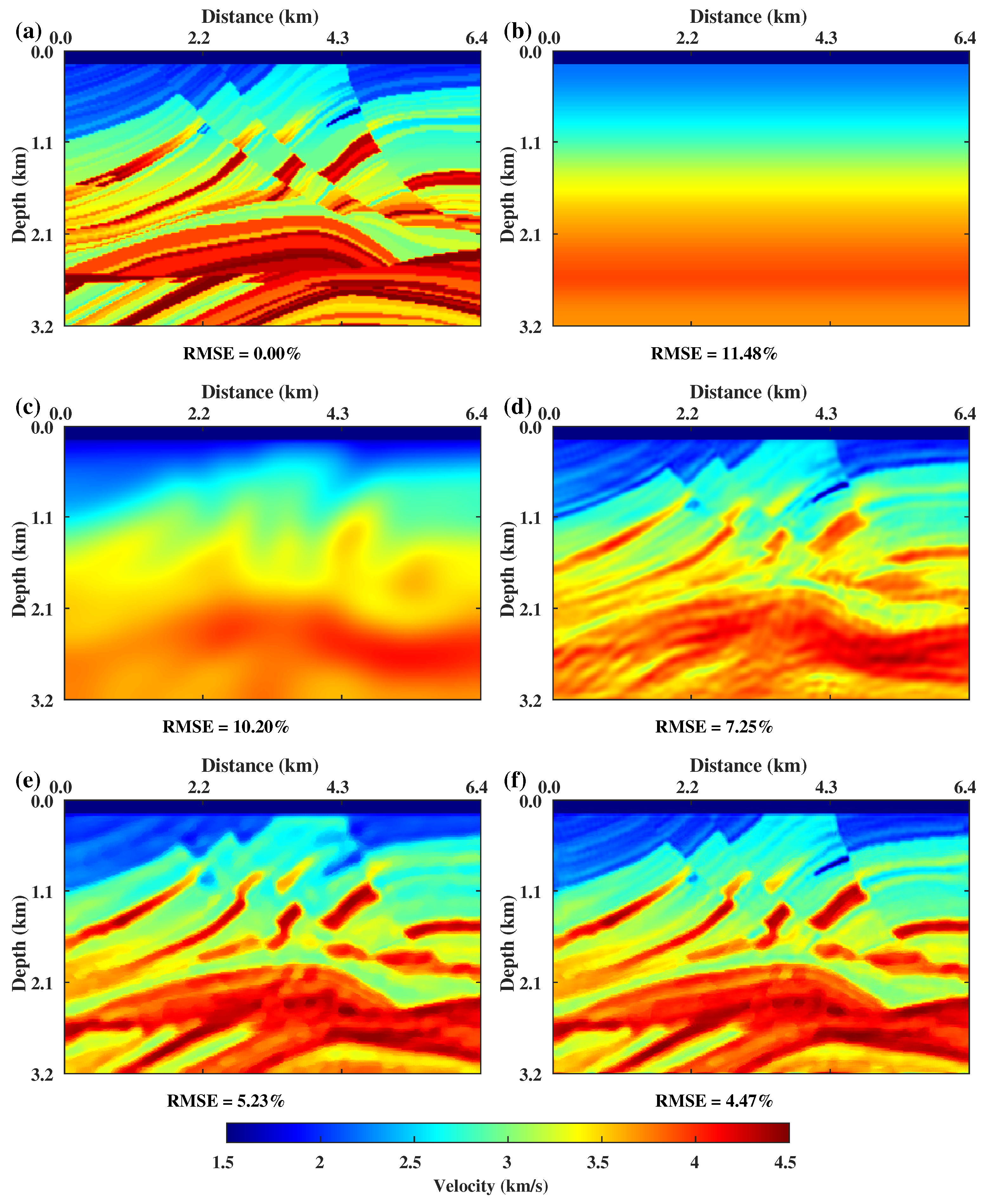
3.2. Complex Velocity Model Testing
3.3. Ms-CNNVI from a Bad Initial Velocity Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Symes, W.W. Migration velocity analysis and waveform inversion. Geophys. Prospect. 2008, 56, 765–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, P. Inversion= migration+ tomography. Geophysics 1989, 54, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lailly, P. The Seismic Inverse Problem as a Sequence of Before Stack Migrations; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Tarantola, A. Inversion of seismic reflection data in the acoustic approximation. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virieux, J.; Operto, S. An overview of full-waveform inversion in exploration geophysics. Geophysics 2009, 74, WCC1–WCC26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Qu, Y.M. Research progress on seismic imaging technology. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Z. Wave-field transformations of vertical seismic profiles. Geophysics 1987, 52, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chauris, H.; Donno, D.; Calandra, H. Taking advantage of wave field decomposition in full waveform inversion. In Proceedings of the 75th EAGE Conference & Exhibition Incorporating SPE EUROPEC 2013, London, UK, 10–13 June 2013; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–348. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, S.; Yuan, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S. Enhancing low-wavenumber components of full-waveform inversion using an improved wavefield decomposition method in the time-space domain. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 157, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Alkhalifah, T. Efficient scattering-angle enrichment for a nonlinear inversion of the background and perturbations components of a velocity model. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 210, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Wu, D. Reflection full waveform inversion. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yao, G.; da Silva, N.V.; Warner, M.; Kalinicheva, T. Separation of migration and tomography modes of full-waveform inversion in the plane wave domain. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Wu, D.; Wang, S.X. A review on reflection-waveform inversion. Pet. Sci. 2020, 17, 334–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Guo, Q.; Alkhalifah, T.; Wang, S. Frequency-domain reflection waveform inversion with generalized internal multiple imaging. Geophysics 2021, 86, R701–R710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Z. InversionNet: Accurate and efficient seismic waveform inversion with convolutional neural networks. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2018; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2018; pp. 2096–2100. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Ma, J. Deep-learning inversion: A next-generation seismic velocity model building method. Geophysics 2019, 84, R583–R599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, J. Velocity model building in a crosswell acquisition geometry with image-trained artificial neural networks. Geophysics 2020, 85, U31–U46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, S.; Ren, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, P.; Chen, Y. Deep-learning seismic full-waveform inversion for realistic structural models. Geophysics 2021, 86, R31–R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, J. Deep-learning full-waveform inversion using seismic migration images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5901818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Gao, Z.; Chen, H. Adjoint-driven deep-learning seismic full-waveform inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 8913–8932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; McMechan, G.A.; Wang, Y. CNN-based gradient-free multiparameter reflection full-waveform inversion. In Proceedings of the First International Meeting for Applied Geoscience & Energy, Denver, CO, USA, 26 September–1 October 2021; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2021; pp. 1369–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; McMechan, G.A.; Wang, Y. Adaptive Feedback Convolutional-Neural-Network-Based High-Resolution Reflection-Waveform Inversion. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2022JB024138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.P.; Bom, C.R.; Costa, J.C.; Klatt, M.; Faria, E.L.; Silva, B.d.S.; de Albuquerque, M.P.; de Albuquerque, M.P. Deep-Tomography: Iterative velocity model building with deep learning. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 232, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, U.b.; Alkhalifah, T.; Haghighat, E.; Song, C.; Virieux, J. PINNtomo: Seismic tomography using physics-informed neural networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.01588. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Alkhalifah, T. Wavefield reconstruction inversion via physics-informed neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2021, 60, 5908012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunks, C.; Saleck, F.M.; Zaleski, S.; Chavent, G. Multiscale seismic waveform inversion. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Guo, B.; Schuster, G.T. Multiscale phase inversion of seismic data. Geophysics 2018, 83, R159–R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Alkhalifah, T. Source-independent time-domain waveform inversion using convolved wavefields: Application to the encoded multisource waveform inversion. Geophysics 2011, 76, R125–R134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, J. Multi-scale full waveform inversion for areas with irregular surface topography in an auxiliary coordinate system. Explor. Geophys. 2018, 49, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, J.; Cui, C.; Li, Z.; Fu, L.; Li, Q. Multi-source multi-scale source-independent full waveform inversion. J. Geophys. Eng. 2019, 16, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.J.; Huang, J.P.; Wang, Z.Y. Convolution-based multi-scale envelope inversion. Pet. Sci. 2020, 17, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, C.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, B. Multi-scale Fusion Network with SR-attention for seismic velocity model building. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5923011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, H.; Wu, T.; Huo, S. A High Resolution Velocity Inversion Method Based on Attention Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5918314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, P. Nonlinear two-dimensional elastic inversion of multioffset seismic data. Geophysics 1987, 52, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; McMechan, G.A. Direct vector-field method to obtain angle-domain common-image gathers from isotropic acoustic and elastic reverse time migration. Geophysics 2011, 76, WB135–WB149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, T.; Liu, H. Structure-Preserving Random Noise Attenuation Method for Seismic Data Based on a Flexible Attention CNN. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Guo, B.; Han, S.; Luo, Y. Near-surface velocity estimation using source-domain full traveltime inversion and early-arrival waveform inversion. Geophysics 2018, 83, R335–R344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qu, Y. Q-compensated full waveform inversion for velocity and density. Explor. Geophys. 2022, 53, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Wu, T.; Liu, H. Multi-Scale Acoustic Velocity Inversion Based on a Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050772
Li W, Wu T, Liu H. Multi-Scale Acoustic Velocity Inversion Based on a Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(5):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050772
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenda, Tianqi Wu, and Hong Liu. 2024. "Multi-Scale Acoustic Velocity Inversion Based on a Convolutional Neural Network" Remote Sensing 16, no. 5: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050772
APA StyleLi, W., Wu, T., & Liu, H. (2024). Multi-Scale Acoustic Velocity Inversion Based on a Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sensing, 16(5), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16050772





