Statistical Analysis of the Occurrence of Ionospheric Scintillations at the Low-Latitude Sanya Station During 2004–2021
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
3. Result and Analysis
3.1. The Distribution of Scintillations of Different Intensities from 2004 to 2021
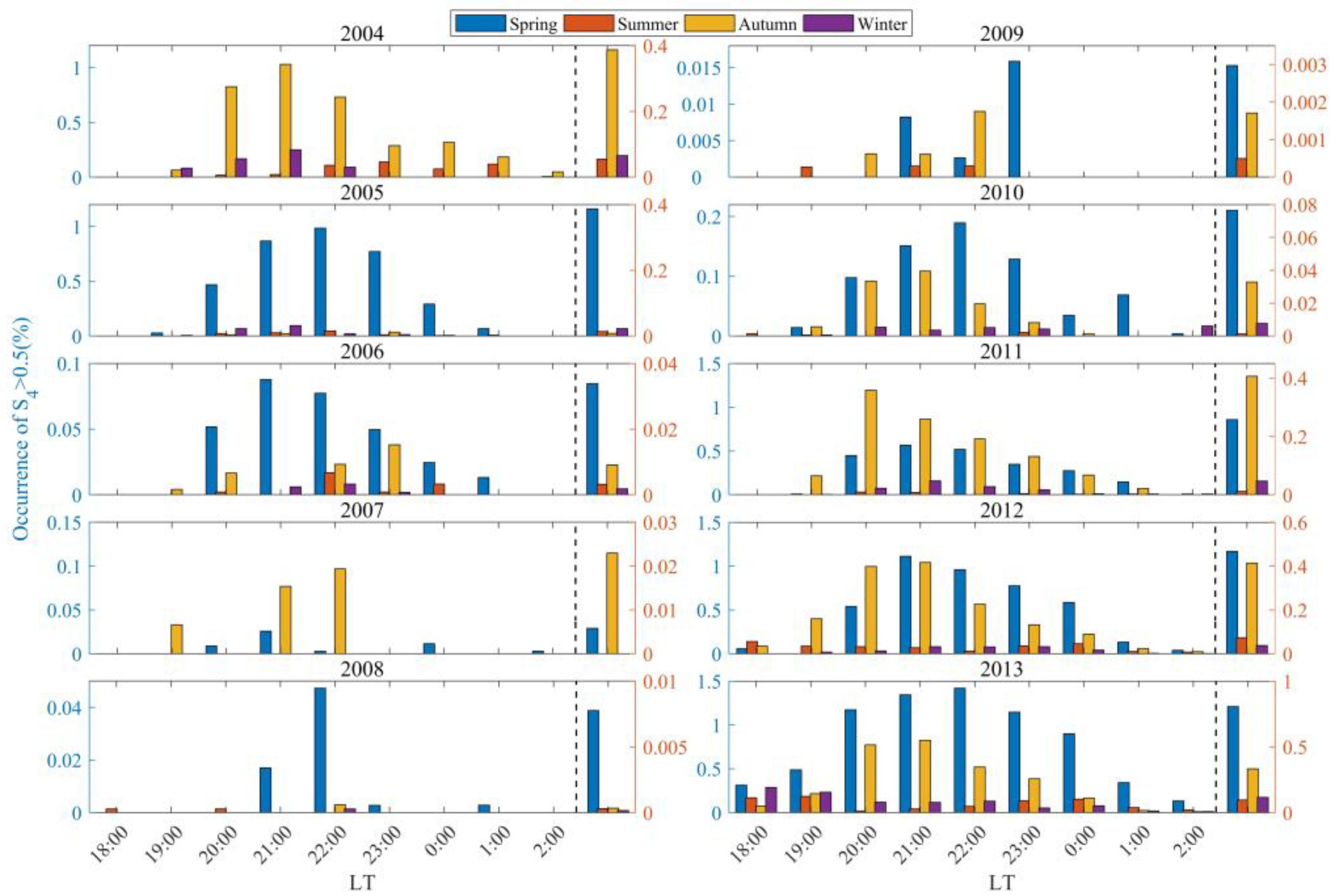
3.2. The Occurrence Rates of Scintillations of Varying Intensities Distributed with Solar Activity
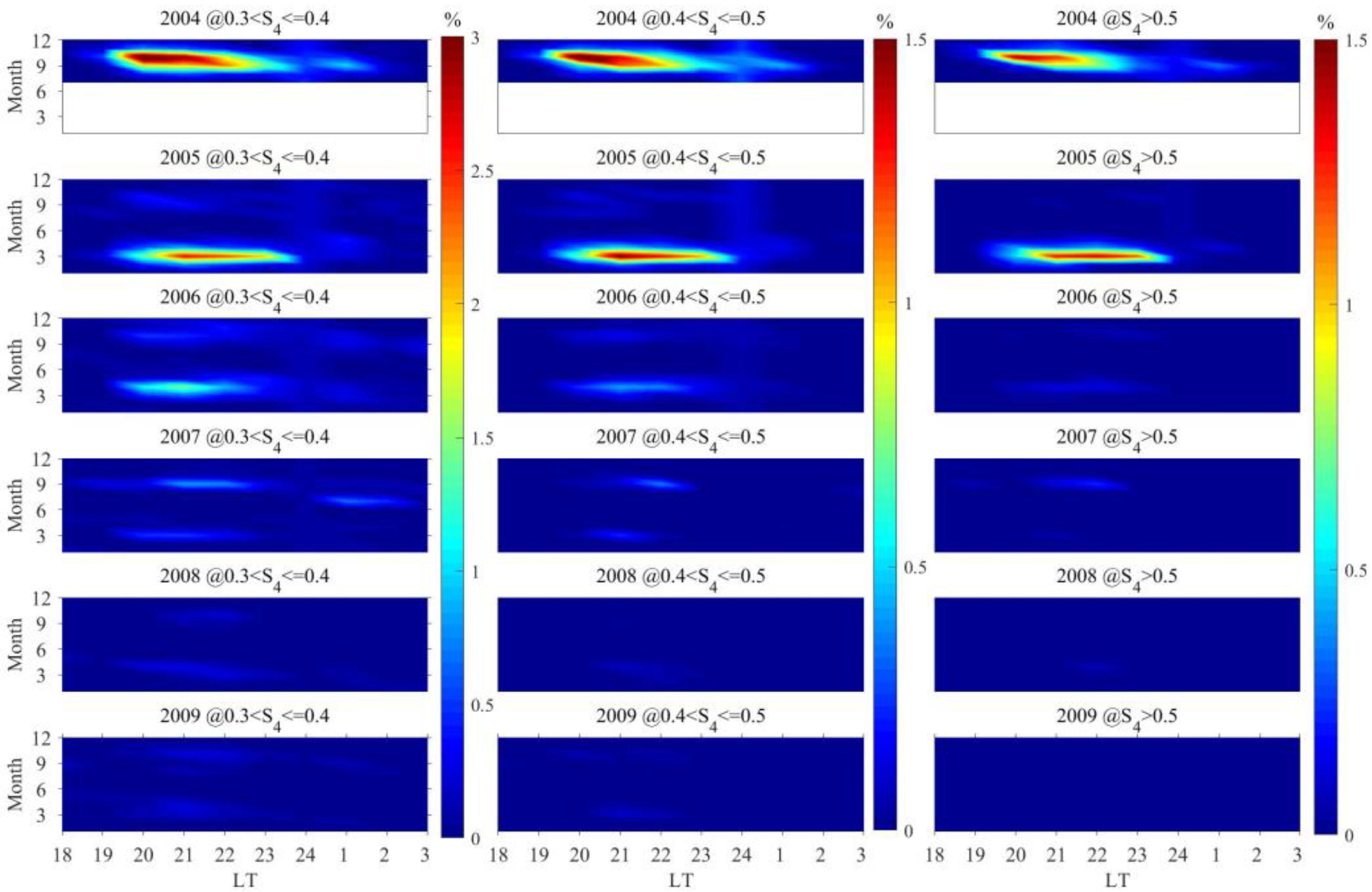
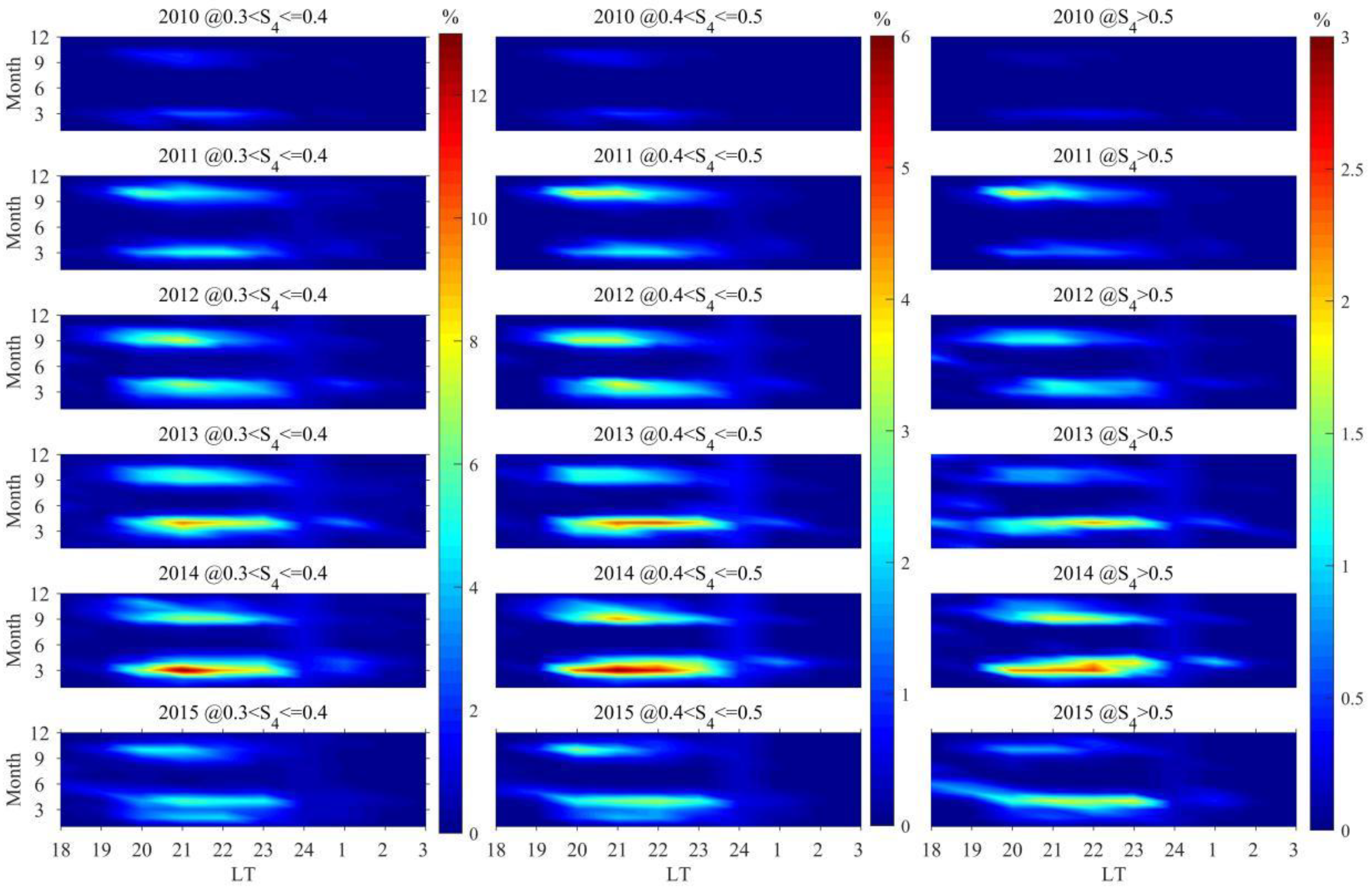
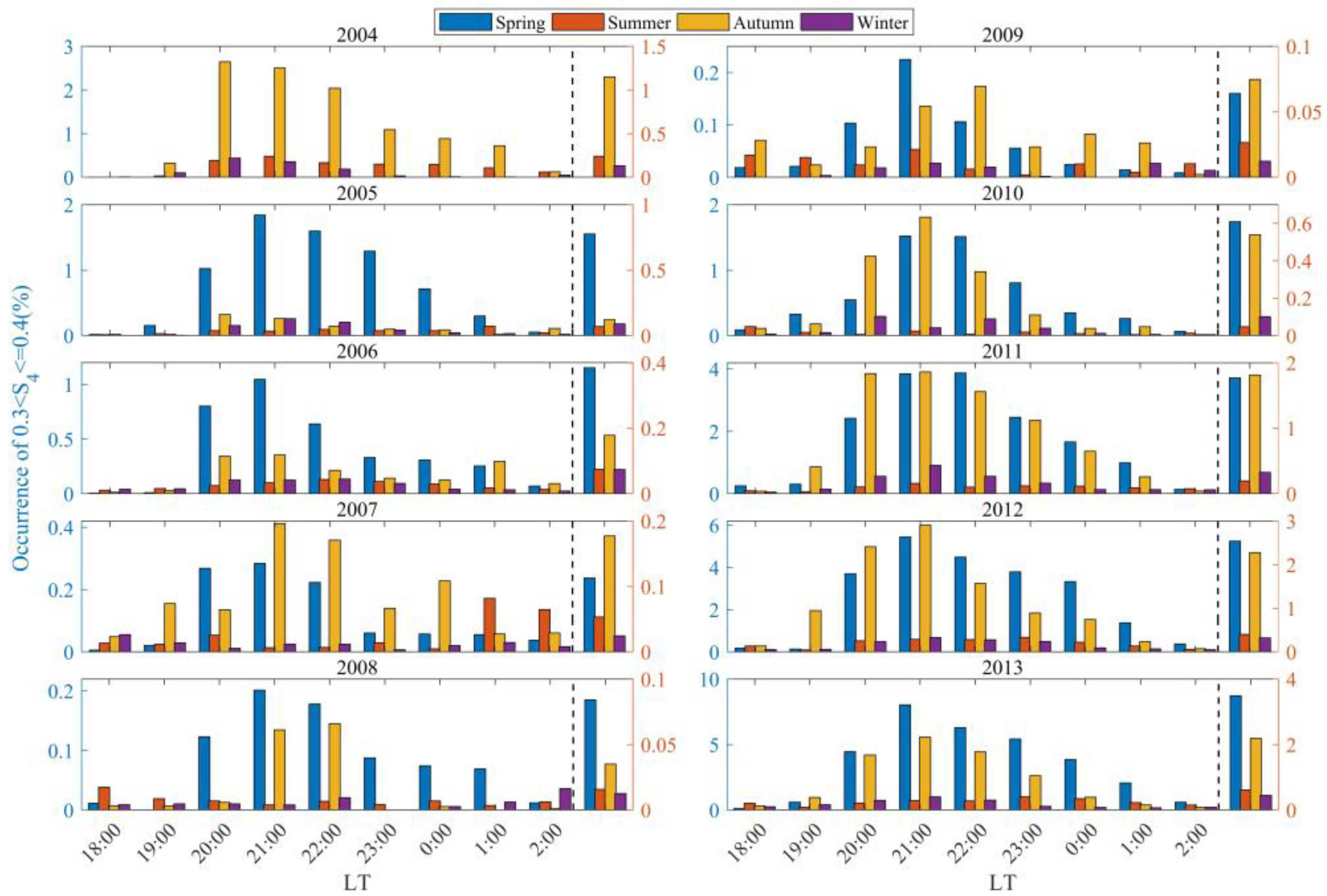
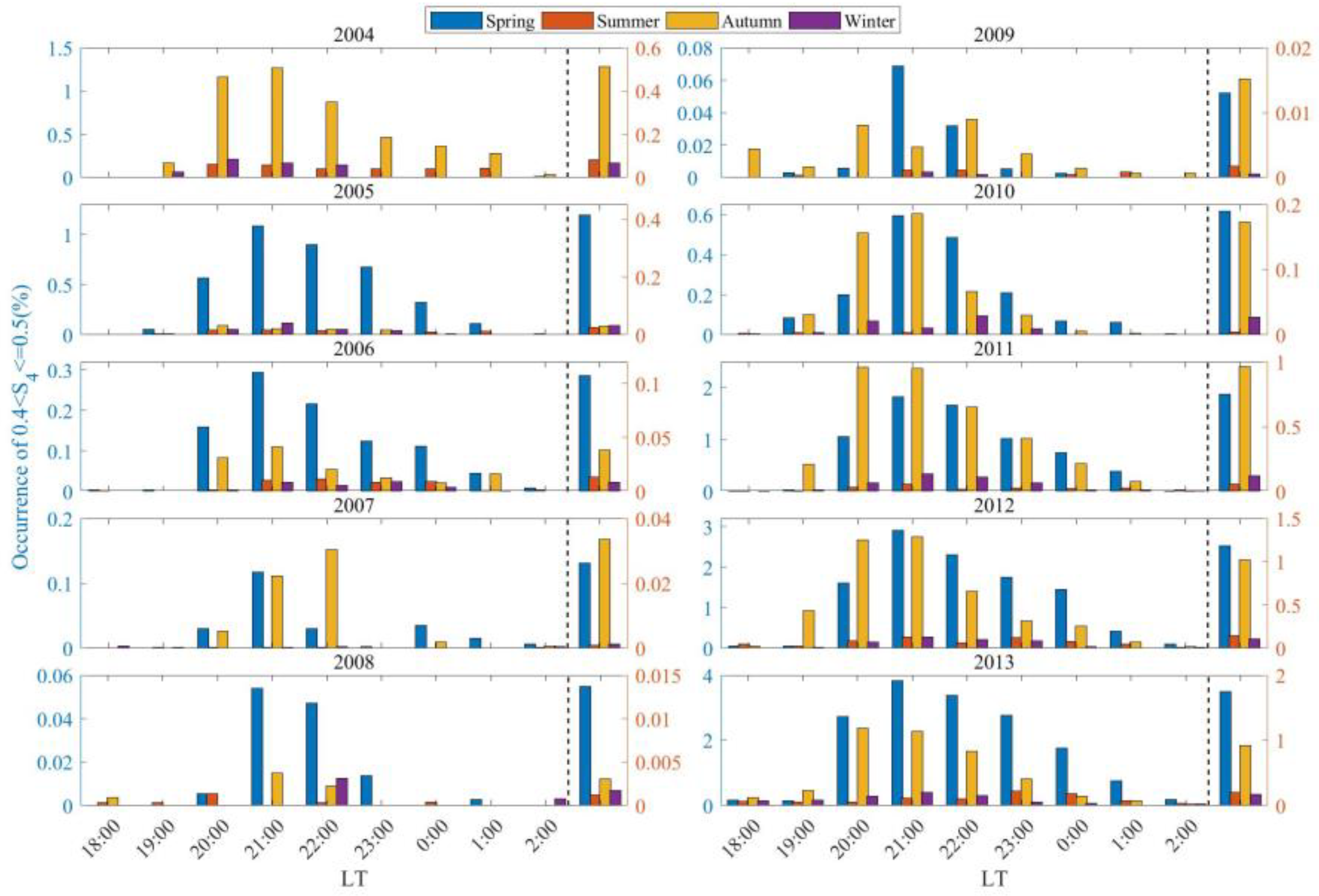
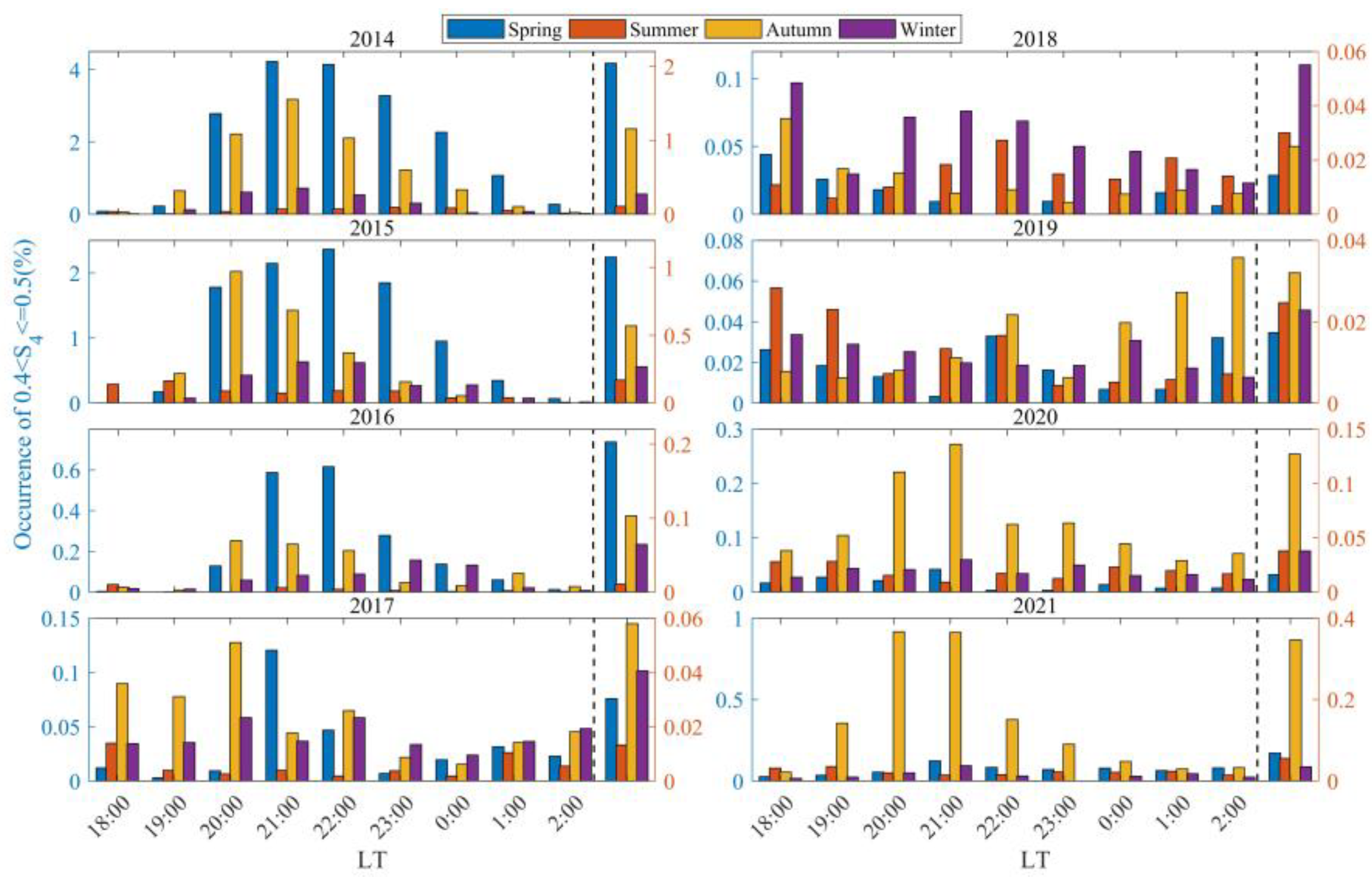
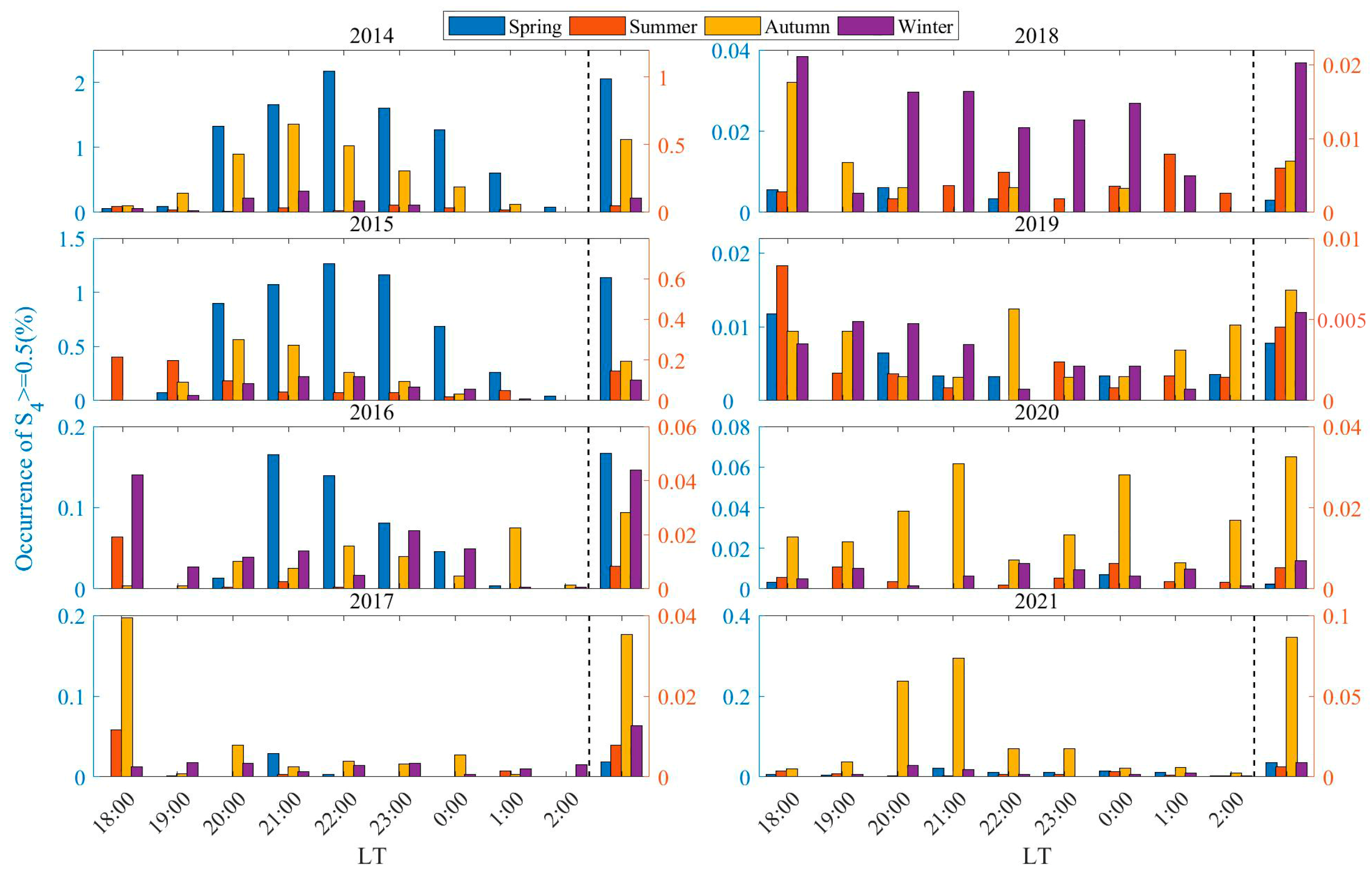
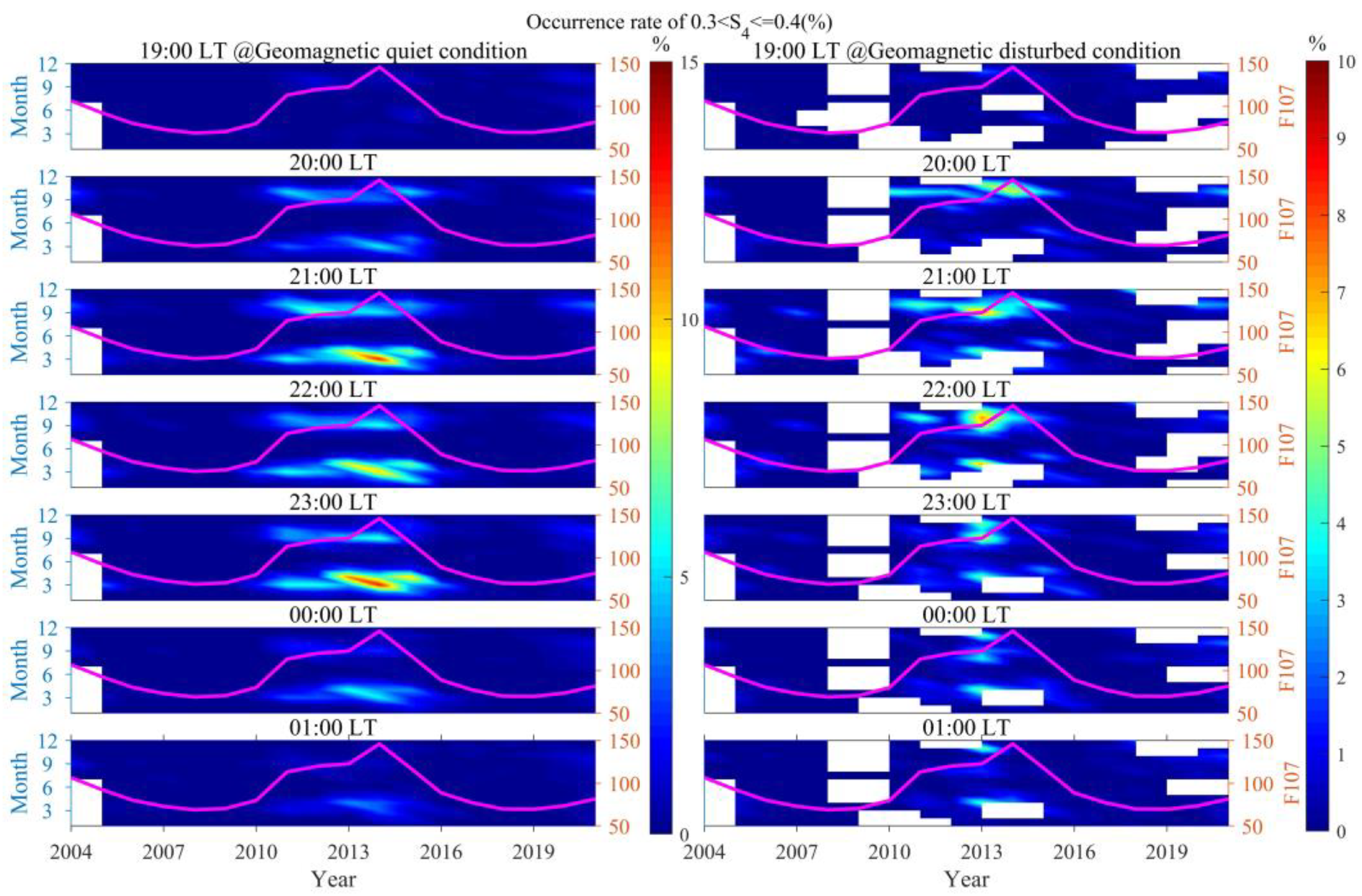
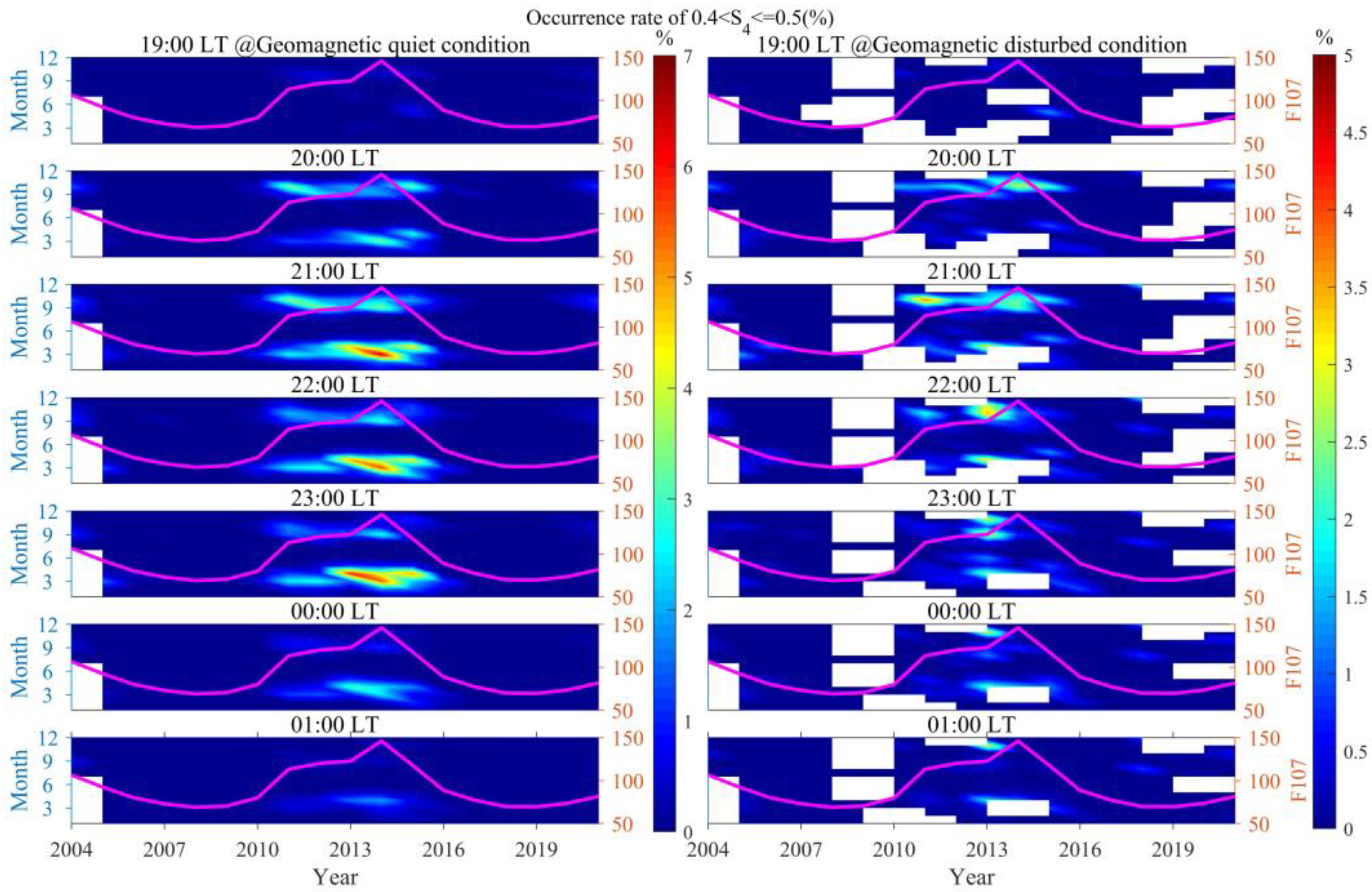
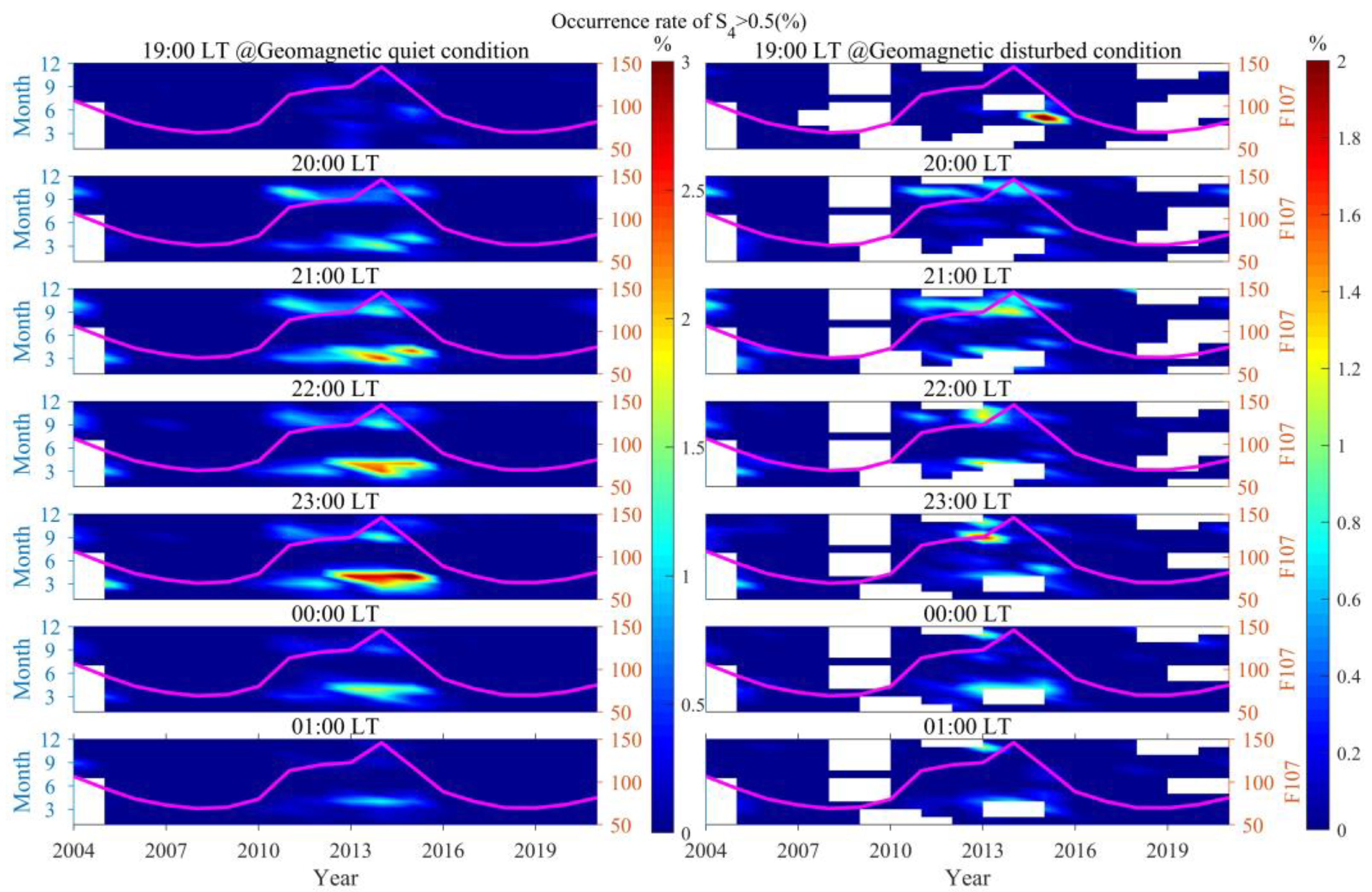
3.3. The Occurrence Rates of Scintillations of Varying Intensities Distributed with Different Seasons and LTs
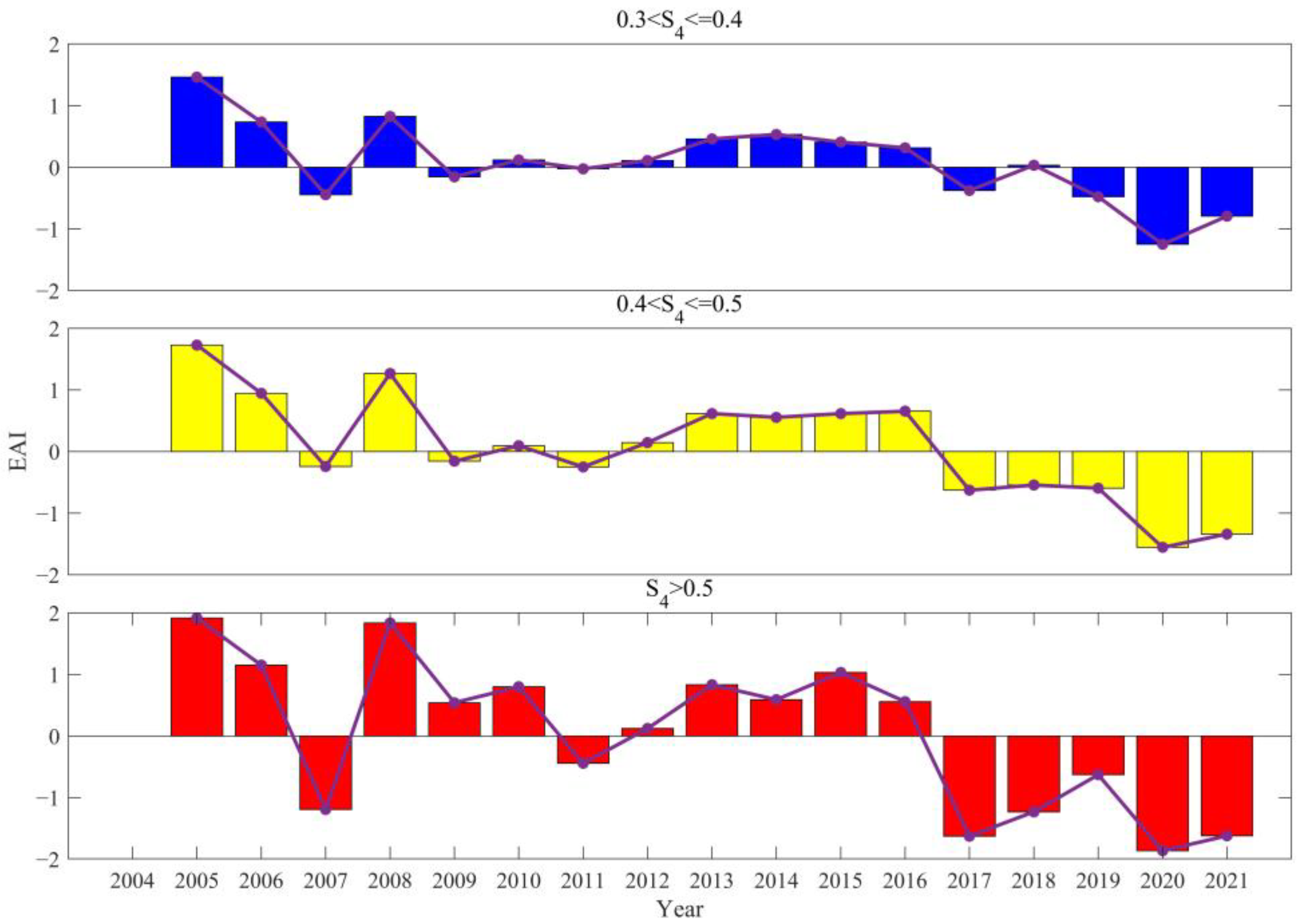
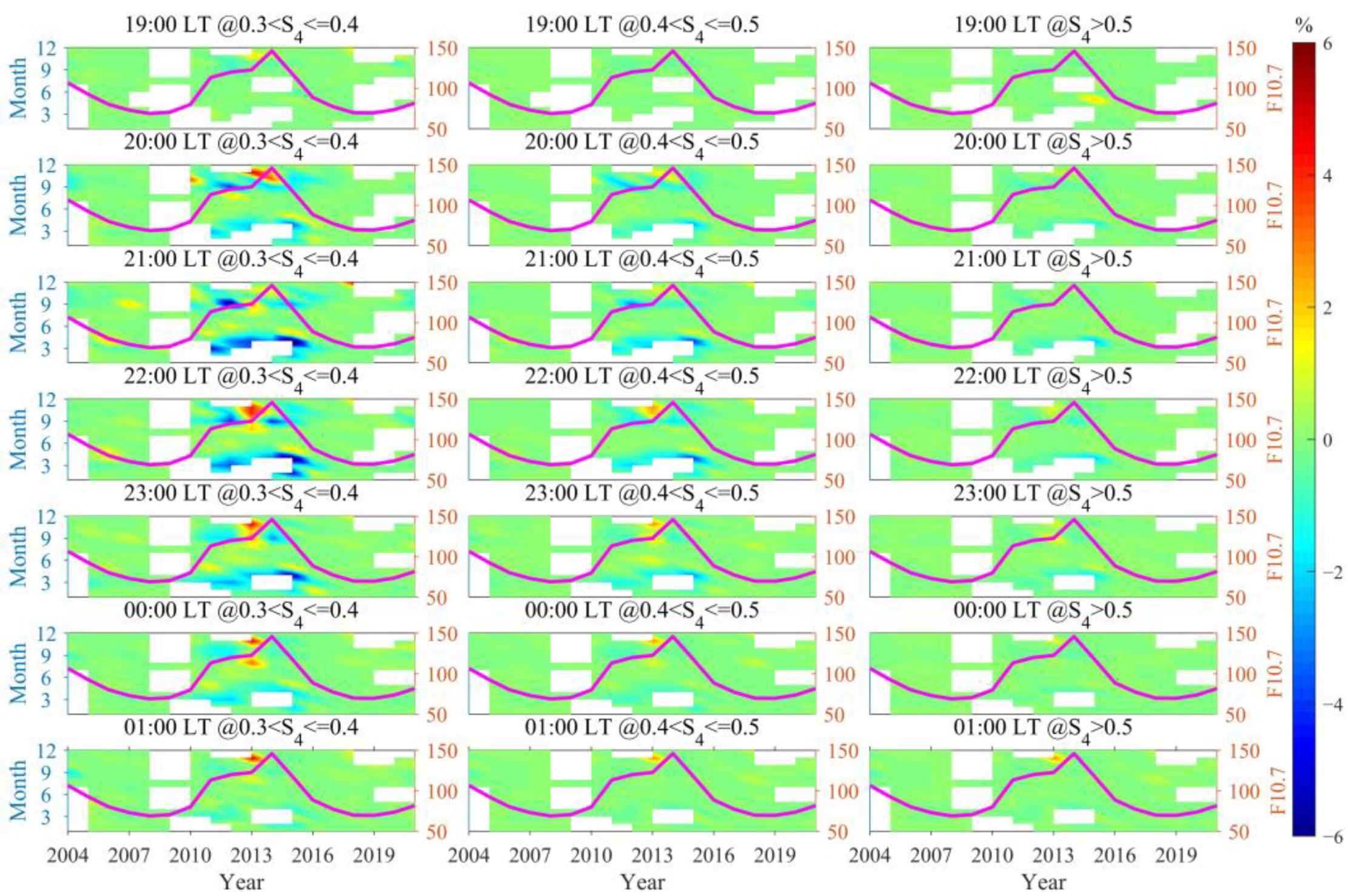
3.4. The Impact of Geomagnetic Activity on the Occurrence Rates of Scintillations of Different Intensities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- From 2005 to 2016, scintillations in Sanya mainly occurred during the equinoxes, exhibiting a spring–autumn equinox asymmetry with a higher occurrence rate in spring than in autumn. This result can be associated with the geomagnetic meridian near the equinoxes in Sanya being almost at a 0° angle with the sun’s terminator, as well as the asymmetry caused by neutral winds. During the period of low solar activity from 2017 to 2021, the peak of scintillation occurrence in 2018 was observed in winter, while in other years, the peaks were predominantly in autumn.
- (2)
- Geomagnetic disturbances were observed to promote weak scintillations at 20:00 LT during the autumn and winter of 2014, and from 20:00 to 01:00 LT the next day in the latter half of 2013. In contrast, during the spring and autumn of most other years with high solar activity, these disturbances were found to inhibit weak scintillations from 20:00 LT to midnight. As scintillation intensity increases, the promoting/inhibiting effect of geomagnetic disturbances on scintillations gradually decreases. The promoting/inhibiting effect of geomagnetic disturbances on ionospheric scintillations is not solely influenced by electric field perturbations; it is to some extent jointly controlled by a variety of factors, including solar activity, season, and LT.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alfonsi, L.; Spogli, L.; Pezzopane, M.; Romano, V.; Zuccheretti, E.; De Franceschi, G.; Cabrera, M.A.; Ezquer, R.G. Comparative analysis of spread-F signature and GPS scintillation occurrences at Tucumán, Argentina. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 4483–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H. Observational Study on the Low-Latitude Ionospheric Field-Aligned Irregularities over Hainan; Wuhan University: Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.K.; Wang, G.J.; Reinisch, B.W.; Shang, S.P.; Wang, X.; Zherebotsov, G.; Potekhin, A. Relationship between strong range spread F and ionospheric scintillations observed in Hainan from 2003 to 2007. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A08306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukao, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsunoda, R.T. First observations of the spatial structure of F region 3-m-scale field-aligned irregularities with the equatorial atmosphere radar in Indonesia. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, A02304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, H.; Nagashima, I.; Sakata, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Akaike, Y.; Takano, T.; Shimakura, S.; Shiokawa, K.; Ogawa, T. Observations of equatorial plasma bubbles using broadcast VHF radio waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, R.; Chakrabarty, D.; Sarkhel, S.; Patra, A.K.; Devasia, C.V.; Kelley, M.C. Identification of active fossil bubbles based on coordinated VHF radar and airglow measurements. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 2099–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A. Equatorial spread F/plasma bubble irregularities under storm time disturbance electric fields. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, A05301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkner, L.V.; Wells, H.W. F-region ionosphere: Investigations at low latitudes. Terr. Magn. Atmos. Electr. 1934, 39, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, C.M.N.; Batista, I.S.; Becker-Guedes, F.; Abdu, M.A.; Sobral, J.H.A.; Takahashi, H. Spread F occurrence over a southern anomaly crest location in Brazil during June solstice of solar minimum activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A06316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.J.; Buchau, J.; Eather, R.H.; Mende, S.B. North-south aligned equatorial airglow depletions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1978, 83, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, Y.; Fagundes, P.R.; Bittencourt, J.A. Transequatorial F-region ionospheric plasma bubbles: Solar cycle effects. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2000, 62, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobral, J.H.A.; Abdu, M.A.; Takahashi, H.; Taylor, M.J.; de Paula, E.R.; Zamlutti, C.J.; de Aquino, M.G.; Borba, G.L. Ionospheric plasma bubble climatology over Brazil based on 22 years (1977–1998) of 630 nm airglow observations. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Yuan, W. Interesting equatorial plasma bubbles observed by all-sky imagers in the equatorial region of China. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, C.; Baumgardner, J.; Wroten, J.; Mendillo, M. All-sky-imaging capabilities for ionospheric space weather research using geomagnetic conjugate point observing sites. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 1636–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.K.; Li, G.Z.; Hu, L.H.; Xie, H.Y.; Sun, W.J.; Li, Y.; Ning, B.Q.; Liu, L.B. Solar and geomagnetic activity and seasonal dependence of global equatorial plasma bubbles based on GNSS observations. Chin. J. Geophys. 2023, 66, 2703–2712. [Google Scholar]
- Akala, A.O.; Amaeshi, L.L.N.; Doherty, P.H.; Groves, K.M.; Carrano, C.S.; Bridgwood, C.T.; Seemala, G.K.; Somoye, E.O. Characterization of GNSS scintillations over Lagos, Nigeria during the minimum and ascending phases (2009–2011) of solar cycle 24. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.K.; Li, G.Z.; Ning, B.Q.; Hu, L.H.; Li, H.K. Statistical characteristics of low-latitude ionospheric scintillation over China. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysell, D.L.; Kelley, M.C.; Swartz, W.E.; Woodman, R.F. Seeding and layering of equatorial spread F by gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1990, 95, 17253–17260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cheng, J.; Xu, J.S. Statistical feature of TEC fluctuations and phase scintillations in the low latitude ionosphere of China. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; MacKenzie, E.; Basu, S. Ionospheric constraints on VHF/UHF communications links during solar maximum and minimum periods. Radio Sci. 1988, 23, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarons, J. The longitudinal morphology of equatorial F-layer irregularities relevant to their occurrence. Space Sci. Rev. 1993, 63, 209–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmanandam, P.S.; Uma, G.; Liu, J.Y.; Chu, Y.H.; Latha Devi, N.S.M.P.; Kakinami, Y. Global S4 index variations observed using FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC GPS RO technique during a solar minimum year. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, A017966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Ning, B.Q.; Otsuka, Y.; Abdu, M.A.; Abadi, P.; Liu, Z.; Spogli, L.; Wan, W.X. Challenges to equatorial plasma bubble and ionospheric scintillation short-term forecasting and future aspects in east and southeast Asia. Surv. Geophys. 2021, 42, 201–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Park, J.; Lühr, H.; Stolle, C.; Ma, S.Y. Comparing plasma bubble occurrence rates at CHAMP and GRACE altitudes during high and low solar activity. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Heelis, R.A. Equatorial plasma bubbles: Variations of occurrence and spatial scale in LT, longitude, season, and solar activity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Ji, S. Effects of solar and geomagnetic activity on the occurrence of equatorial plasma bubbles over Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 9164–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z. Studies on Monitoring, Analysis and Application of Mid- and Low-Latitude Ionospheric Scintillation in China; Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.-Y.; Liu, C.H.; Ho, H.H.; Chao, C.K. Distribution characteristics of topside ionospheric density irregularities: Equatorial versus midlatitude regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111, A06305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.J.; Shi, J.K.; Wang, X.; Shang, S.P.; Zherebtsov, G.; Pirog, O.M. The statistical properties of spread F observed at Hainan station during the declining period of the 23rd solar cycle. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, B. Study on Ionospheric Spread-Fat Low- and Mid-Latitude and Wavelike Structure in Equatorial Ionization Anomaly Crests; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.S.; de La Beaujardiere, O.; Roddy, P.A.; Hunton, D.E.; Pfaff, R.F.; Valladares, C.E.; Ballenthin, J.O. Evolution of equatorial ionospheric plasma bubbles and formation of broad plasma depletions measured by the C/NOFS satellite during deep solar minimum. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A03306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.K.; Xie, H.Y.; Hu, L.H.; Sun, W.J.; Hao, X.Q.; Ning, B.Q.; Hisao, T.; Li, G.Z. Climatology of equatorial and low-latitude F region kilometer-scale irregularities over the meridian circle around 120°E/60°W. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Burke, W.J.; Machuzak, J.S.; Gentile, L.C.; Sultan, P.J. DMSP observations of equatorial plasma bubbles in the topside ionosphere near solar maximum. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 8131–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolle, C.; Lühr, H.; Rother, M.; Balasis, G. Magnetic signatures of equatorial spread F as observed by the CHAMP satellite. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111, A02304. [Google Scholar]
- Aa, E.; Zou, S.; Liu, S. Statistical analysis of equatorial plasma irregularities retrieved from Swarm 2013–2019 observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, W.J.; Gentile, L.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Valladares, C.E.; Su, S.Y. Longitudinal variability of equatorial plasma bubbles observed by DMSP and ROCSAT-1. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, A12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.A.; Cai, Y.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Lei, J.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, M.Y.; Zhang, N.; Ding, F.; Ning, B.Q. Ionospheric Pre-Sunrise Uplift: Comparison of Sanya Incoherent Scatter Radar Observations and Numerical Simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2023, 128, A031119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Ning, B.Q.; Abdu, M.A.; Otsuka, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Liu, L.B. Longitudinal characteristics of spread F backscatter plumes observed with the EAR and Sanya VHF radar in Southeast Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 6544–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Ning, B.Q.; Liu, L.B.; Wan, W.X.; Liu, J.Y. Effect of magnetic activity on plasma bubbles over equatorial and low-latitude regions in East Asia. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripathi, S.; Kakad, B.; Bhattacharyya, A. Study of equinoctial asymmetry in the Equatorial Spread F (ESF) irregularities over Indian region using multi-instrument observations in the descending phase of solar cycle 23. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, A11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yue, X.A.; Zhen, W.M.; Xu, J.X.; Liu, D.; Guo, S. On the occurrence of F region irregularities over Haikou retrieved from COSMIC GPS radio occultation and ground-based ionospheric scintillation monitor observations. Radio Sci. 2017, 52, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; Batista, I.S.; Brum, C.G.M.; MacDougall, J.W.; Santos, A.M.; de Souza, J.R.; Sobral, J.H.A. Solar flux effects on the equatorial evening vertical drift and meridional winds over Brazil: A comparison between observational data and the IRI model and the HWM representations. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejer, B.G.; Farley, D.T.; Woodman, R.F.; Calderon, C. Dependence of equatorial F region vertical drifts on season and solar cycle. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1979, 84, 5792–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejer, B.G.; De Paula, E.R.; Gonzalez, S.A.; Woodman, R.F. Average vertical and zonal F region plasma drifts over Jicamarca. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1991, 96, 13901–13906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejer, B.G.; Scherliess, L.; De Paula, E.R. Effects of the vertical plasma drift velocity on the generation and evolution of equatorial spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1999, 104, 19859–19869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Liu, J.Y.; Reinisch, B.W.; Chen, W.S.; Chu, F.D. The effects of the pre-reversal ExB drift, the EIA asymmetry, and magnetic activity on the equatorial spread F during solar maximum. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.A. Dependence of equatorial bubbles and bottomside spread F on season, magnetic activity, and E×B drift velocity during solar maximum. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, SIA-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, P.J. Linear theory and modeling of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability leading to the occurrence of equatorial spread F. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 26875–26891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.M.; Abdu, M.A.; Sobral, J.H.A.; Mascarenhas, M.; Nogueira, P.A.B. Equatorial evening prereversal vertical drift dependence on solar EUV flux and F10.7 index during quiet and disturbed periods over Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2013, 118, 4662–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.G. The Ionospheric Characteristics of Haikou Region. J. Radio Sci. 1995, 10, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, G.J.; Shi, J.K.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Z.W.; Wang, Z.; Shang, S.P. Response of Low-latitude Hainan Ionospheric Plasma Drifts to Geomagnetic Activities. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2019, 39, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A. Day-to-day and short-term variabilities in the equatorial plasma bubble/spread F irregularity seeding and development. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, R.T. Control of the seasonal and longitudinal occurrence of equatorial scintillations by the longitudinal gradient in integrated E region Pedersen conductivity. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1985, 90, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Matuura, N. Longitudinal variability of annual changes in activity of equatorial spread F and plasma bubbles. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1984, 89, 10903–10912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Saito, S.; Kawamura, M.; Nozaki, K.; Krall, J.; Huba, J.D. Equinoctial asymmetry of a low-latitude ionosphere-thermosphere system and equatorial irregularities: Evidence for meridional wind control. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A. Coherence of geomagnetic DP2 fluctuations with interplanetary magnetic variations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1968, 73, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, M.; Richmond, A.D. The ionospheric disturbance dynamo. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1980, 85, 1669–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Year | Observation Days | Observation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 157 | 42.8962 |
| 2005 | 362 | 99.1781 |
| 2006 | 364 | 99.7260 |
| 2007 | 364 | 99.7260 |
| 2008 | 365 | 99.7268 |
| 2009 | 365 | 100 |
| 2010 | 363 | 99.4521 |
| 2011 | 362 | 99.1781 |
| 2012 | 338 | 92.3497 |
| 2013 | 363 | 99.4521 |
| 2014 | 364 | 99.7260 |
| 2015 | 364 | 99.7260 |
| 2016 | 364 | 99.4536 |
| 2017 | 364 | 99.7260 |
| 2018 | 364 | 99.7260 |
| 2019 | 365 | 100 |
| 2020 | 364 | 99.4536 |
| 2021 | 363 | 99.4521 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, B.; Yu, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, Y. Statistical Analysis of the Occurrence of Ionospheric Scintillations at the Low-Latitude Sanya Station During 2004–2021. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244668
Xiong B, Yu C, Li X, Li Y, Hu L, Wang Y, Du L, Wang Y. Statistical Analysis of the Occurrence of Ionospheric Scintillations at the Low-Latitude Sanya Station During 2004–2021. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(24):4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244668
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Bo, Changhao Yu, Xiaolin Li, Yuxiao Li, Lianhuan Hu, Yuqing Wang, Lingxiao Du, and Yuxin Wang. 2024. "Statistical Analysis of the Occurrence of Ionospheric Scintillations at the Low-Latitude Sanya Station During 2004–2021" Remote Sensing 16, no. 24: 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244668
APA StyleXiong, B., Yu, C., Li, X., Li, Y., Hu, L., Wang, Y., Du, L., & Wang, Y. (2024). Statistical Analysis of the Occurrence of Ionospheric Scintillations at the Low-Latitude Sanya Station During 2004–2021. Remote Sensing, 16(24), 4668. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16244668






