Assessment and Dynamic Prediction of Green Space Ecological Service Value in Guangzhou City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
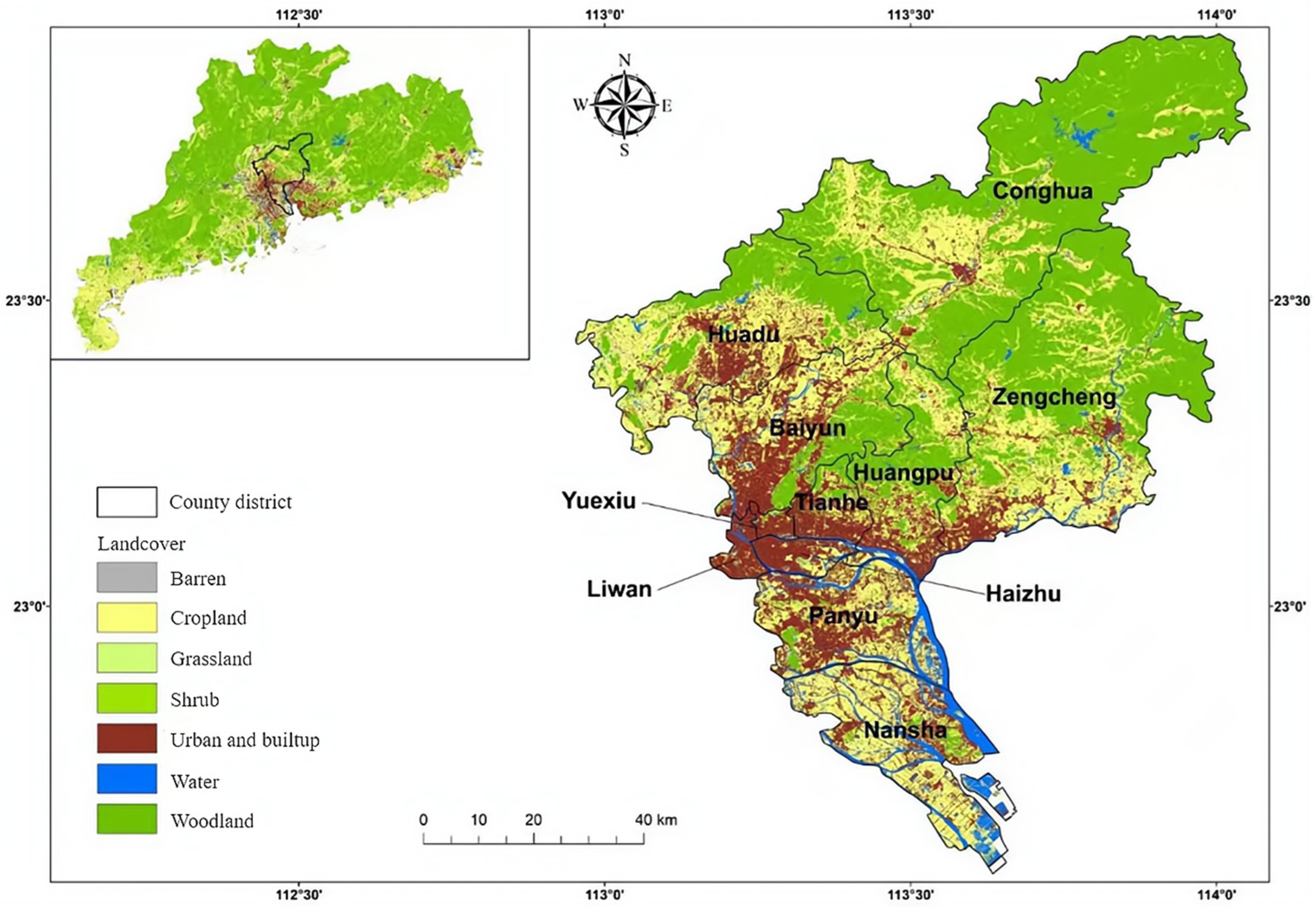
2.1. Study Site
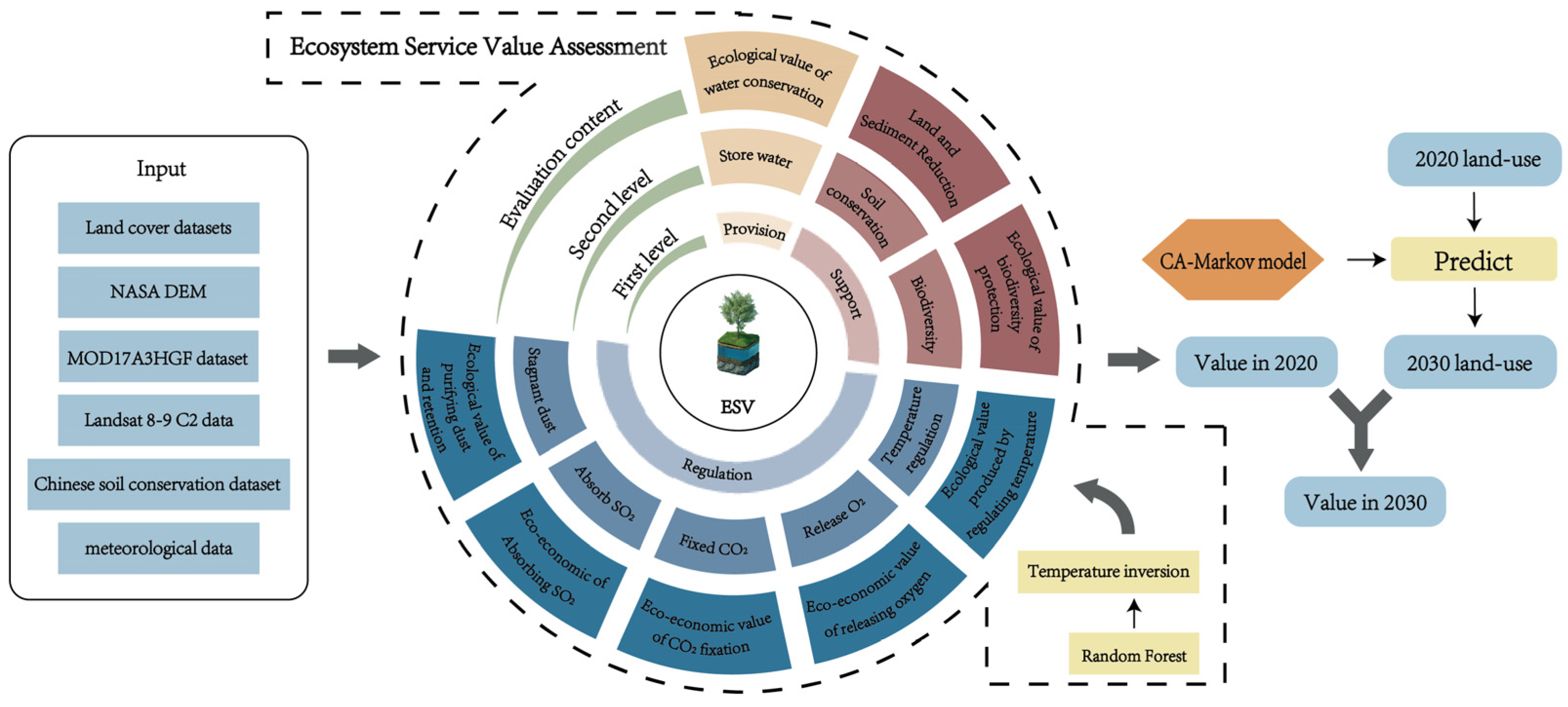
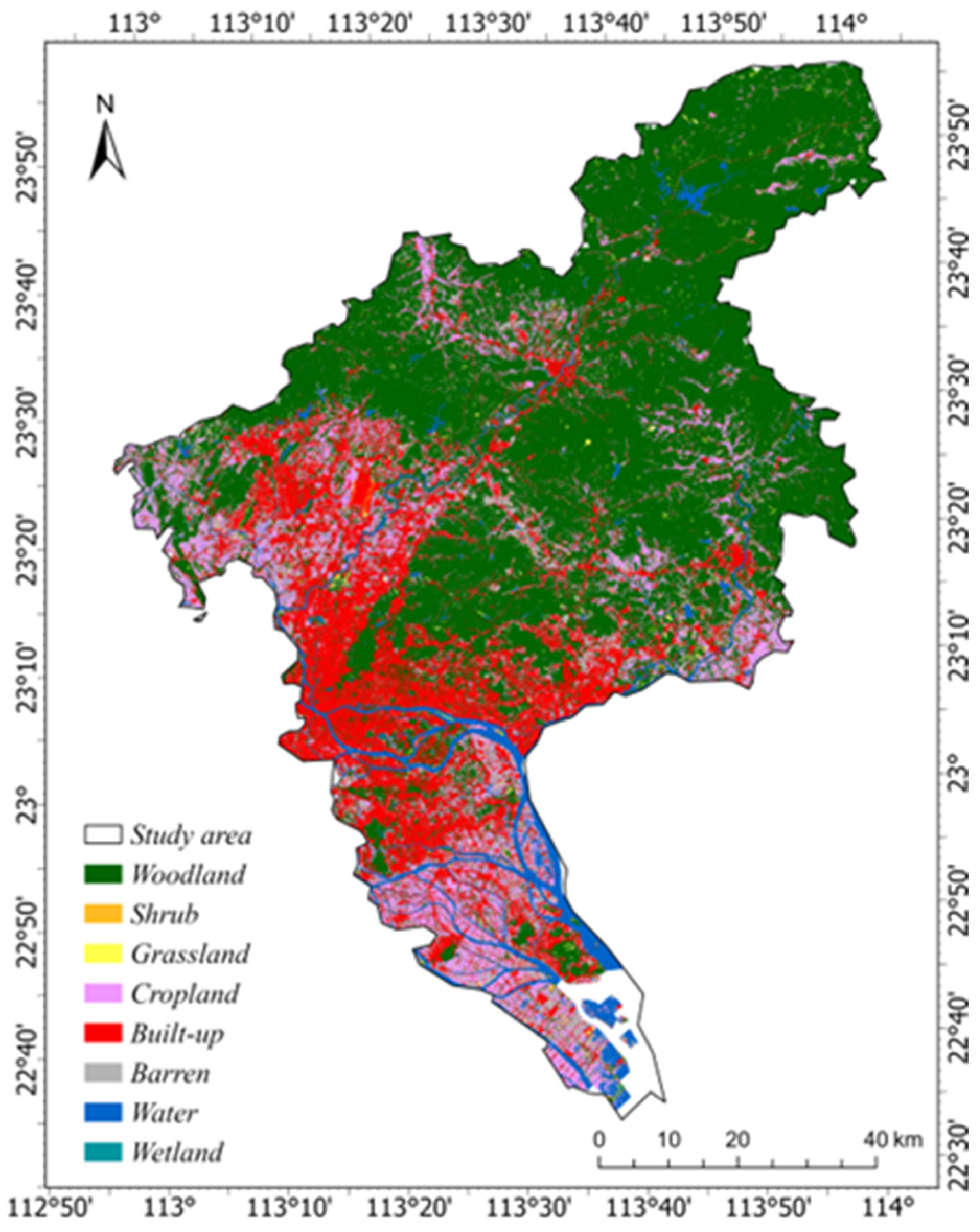
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Ecosystem Service Value Calculation
Estimation of the Value of Conserved Water
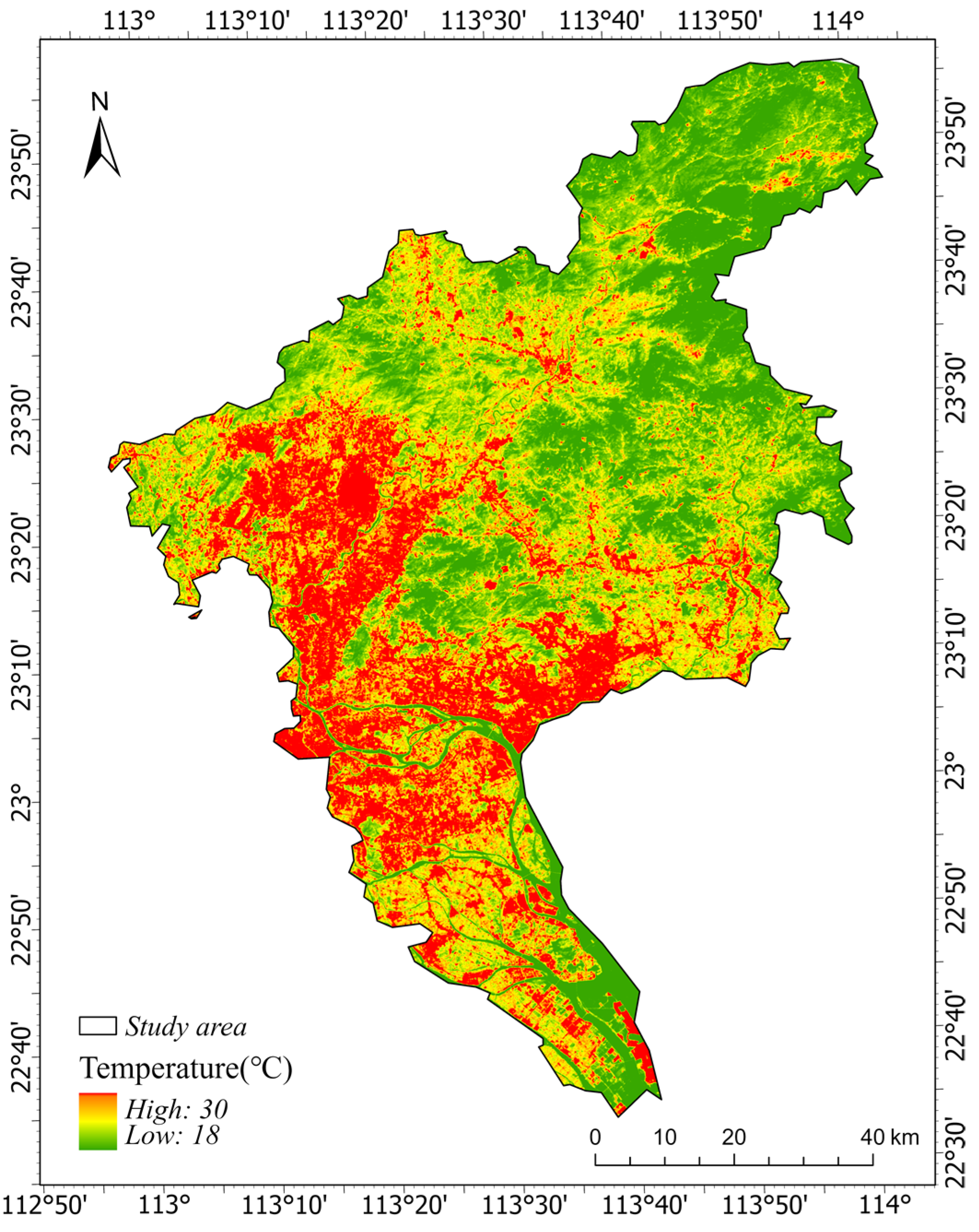
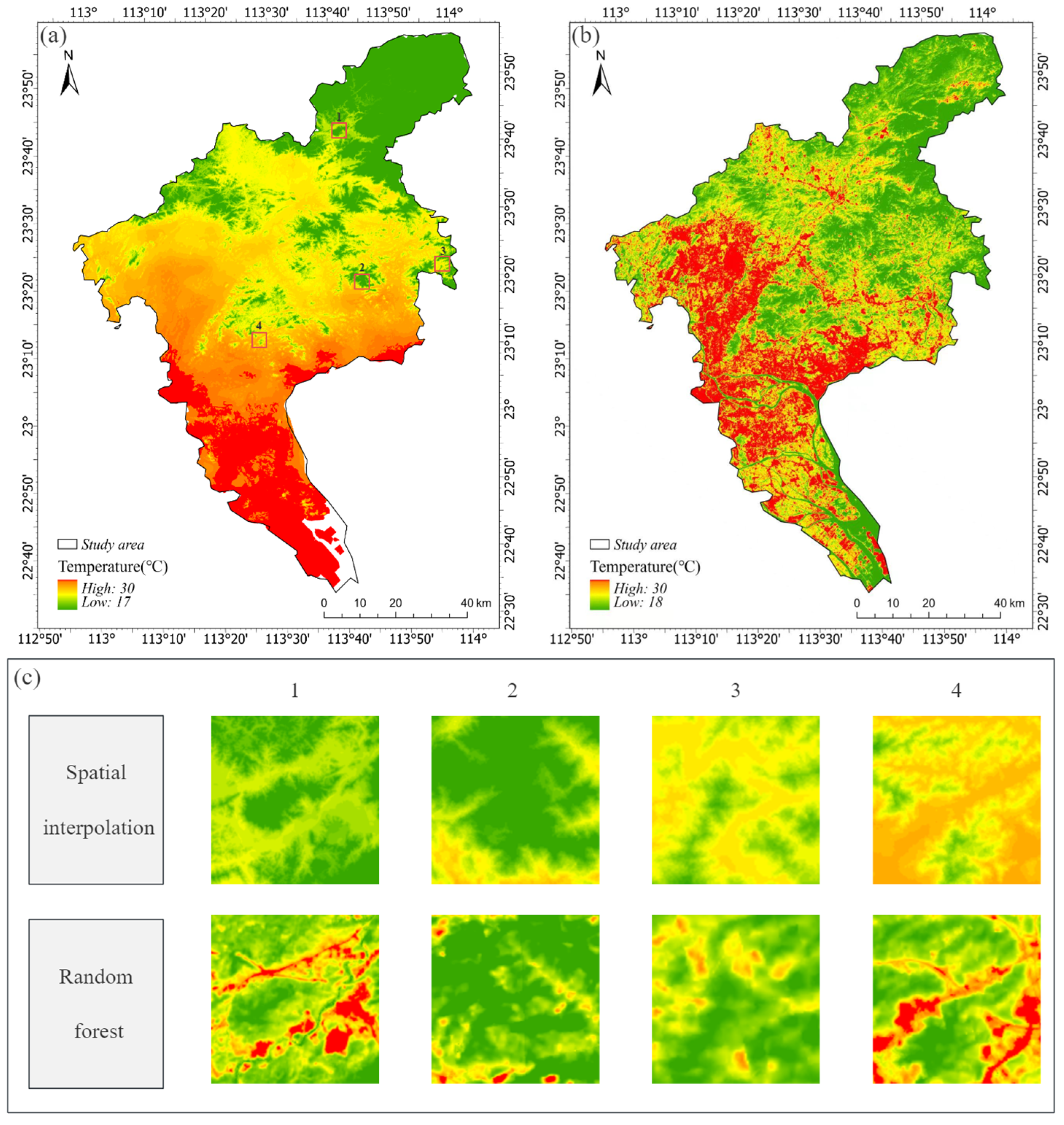
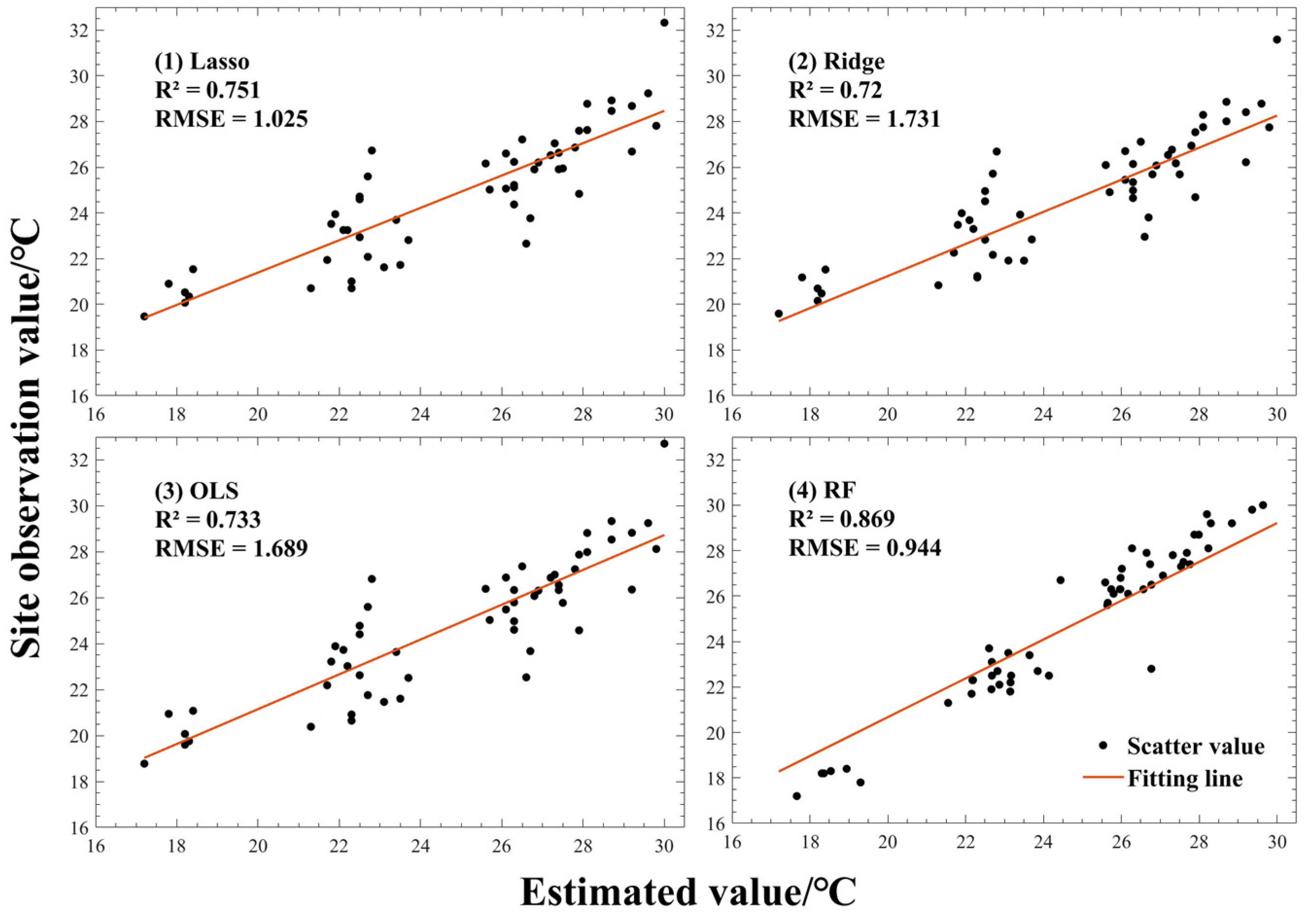
Estimation of the Value of Temperature Regulation
Estimation of Carbon Sequestration and Oxygen Release Value
Estimation of SO2 Absorption Value
Estimation of the Value of Trapped Dust
Soil Conservation Value Estimation
Estimation of Biodiversity Conservation Value
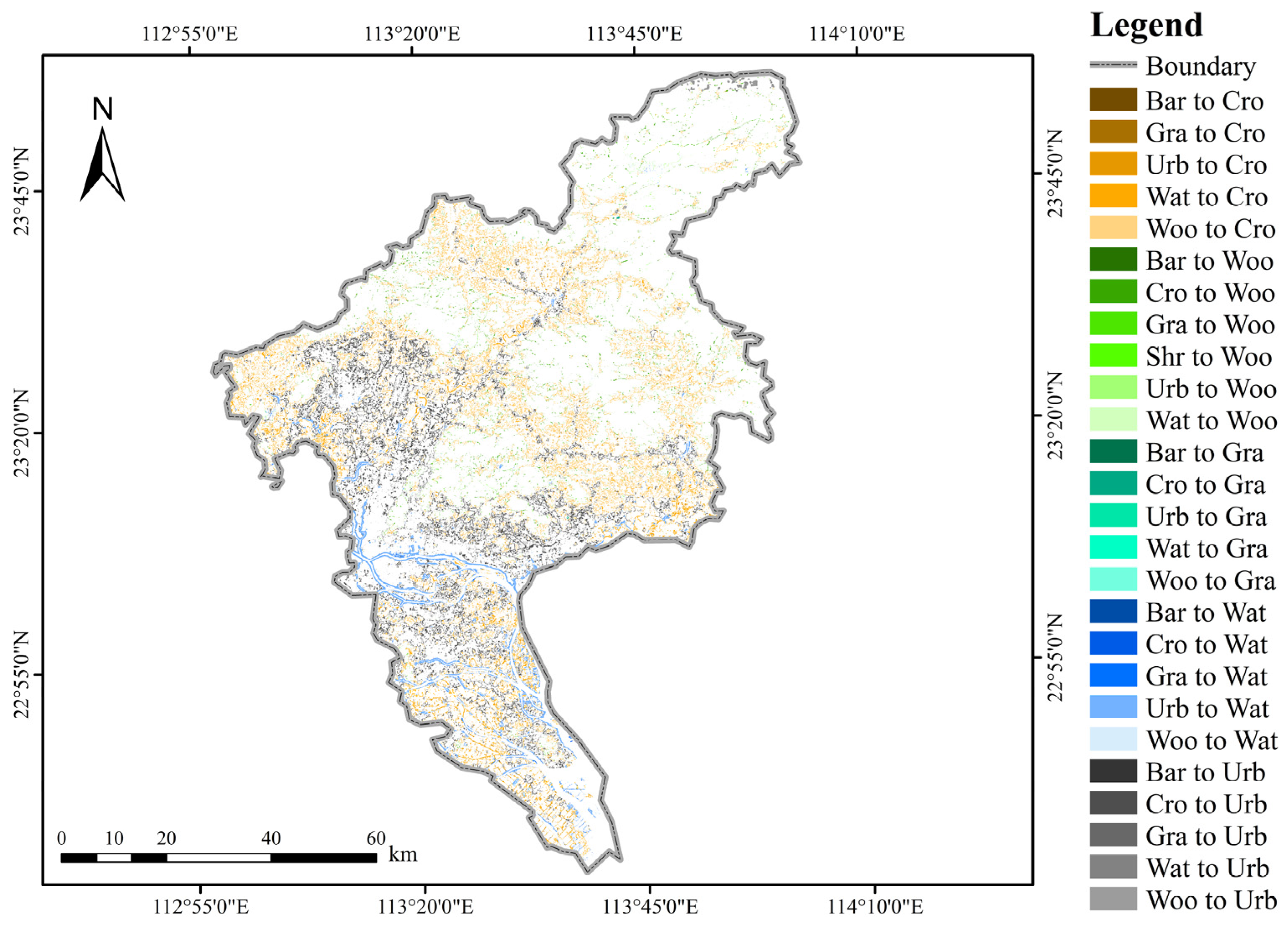
2.3.2. LULC Change Prediction Using the CA-Markov Model
3. Results
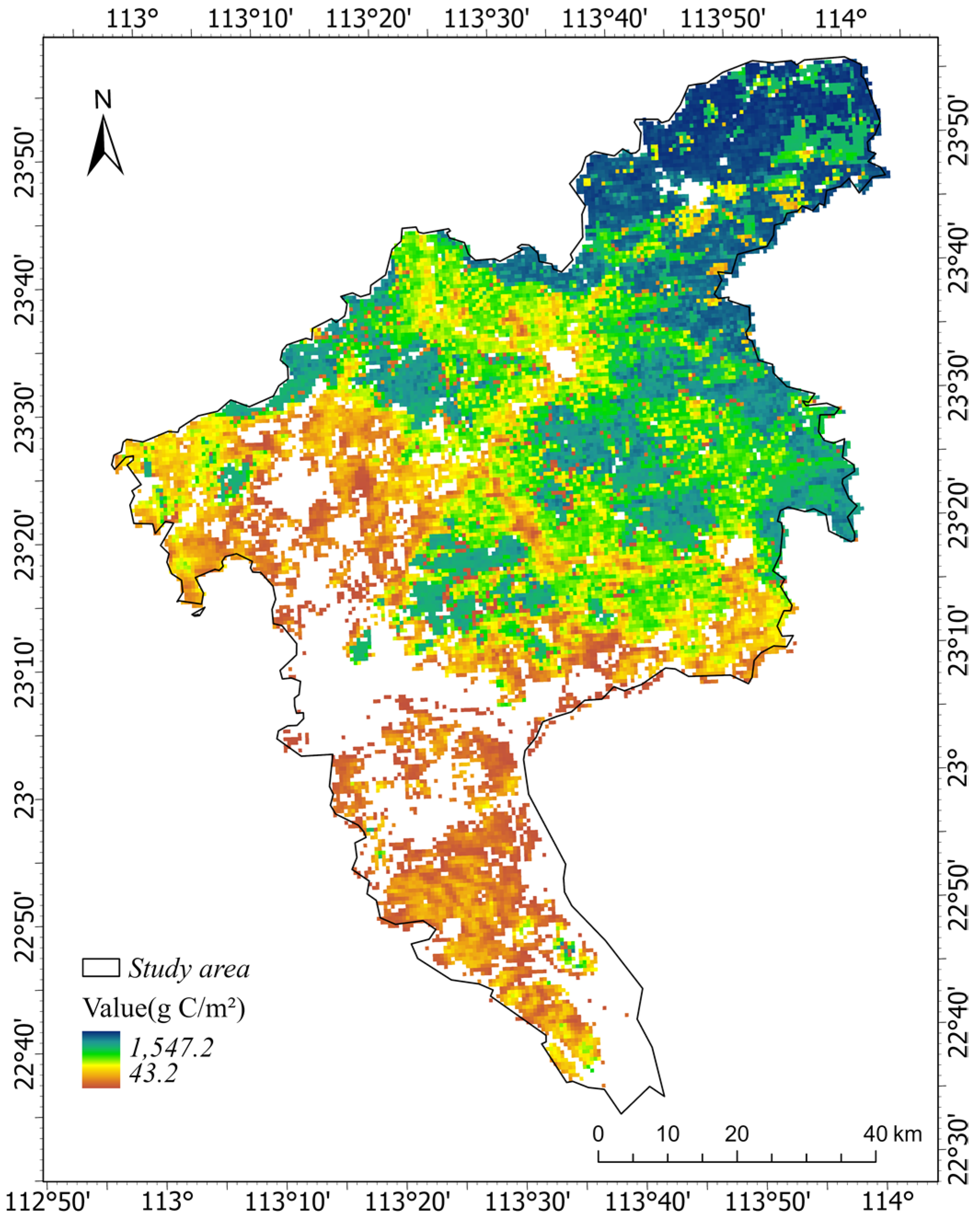
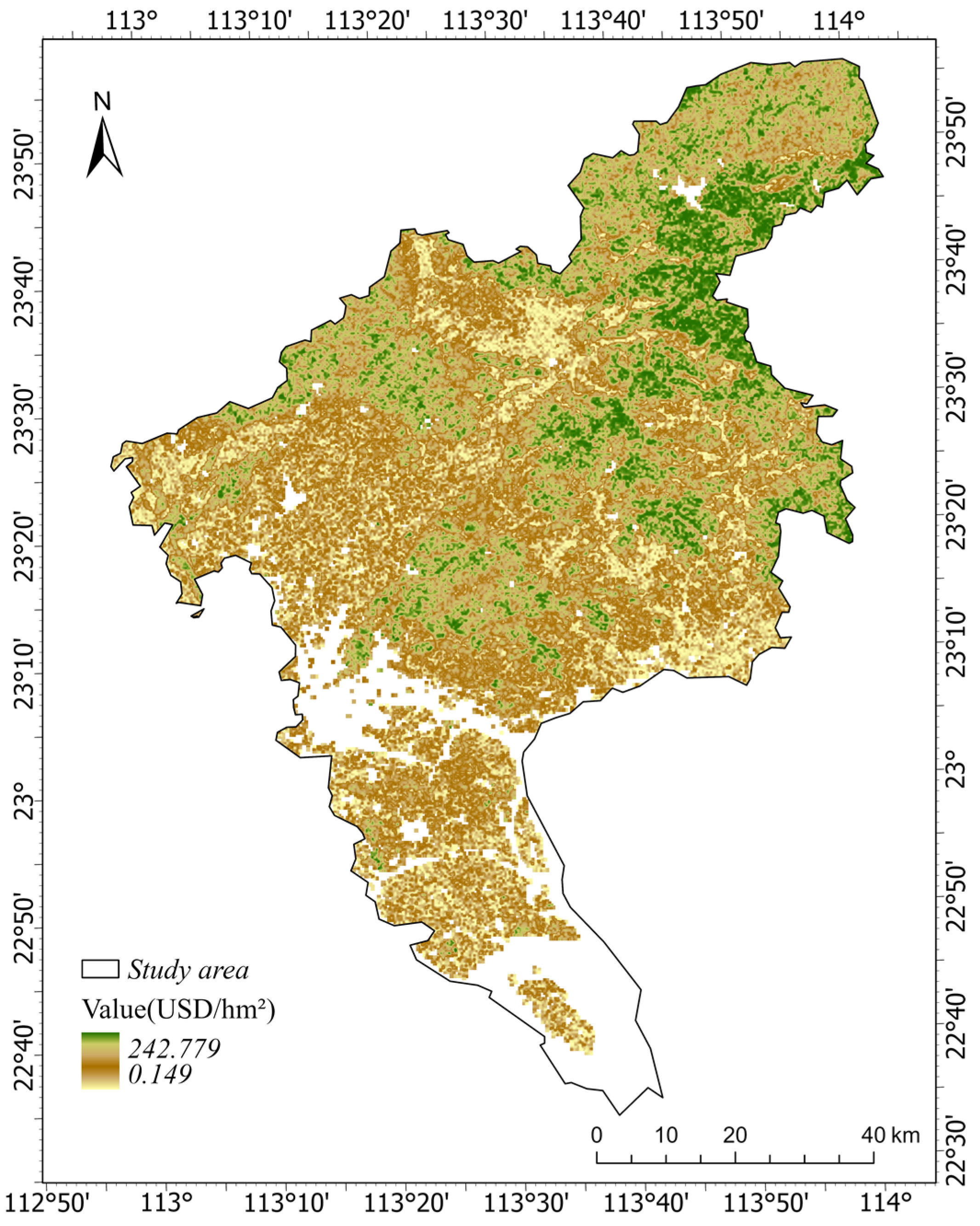
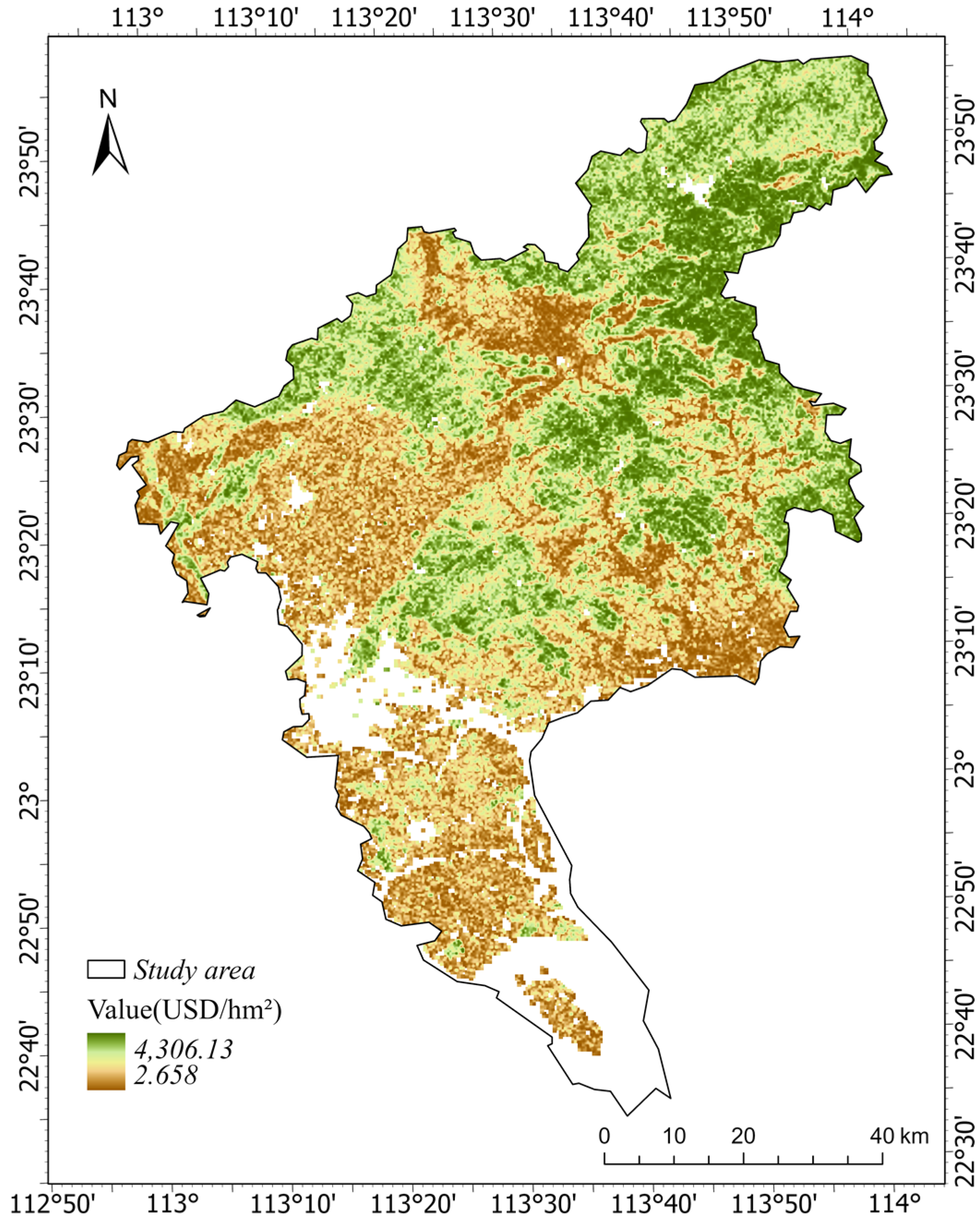
3.1. The Value of Various Functional Ecological Services of Urban Green Space
3.1.1. Provision Service Value
3.1.2. Regulation Service Value
3.1.3. Support Service Value
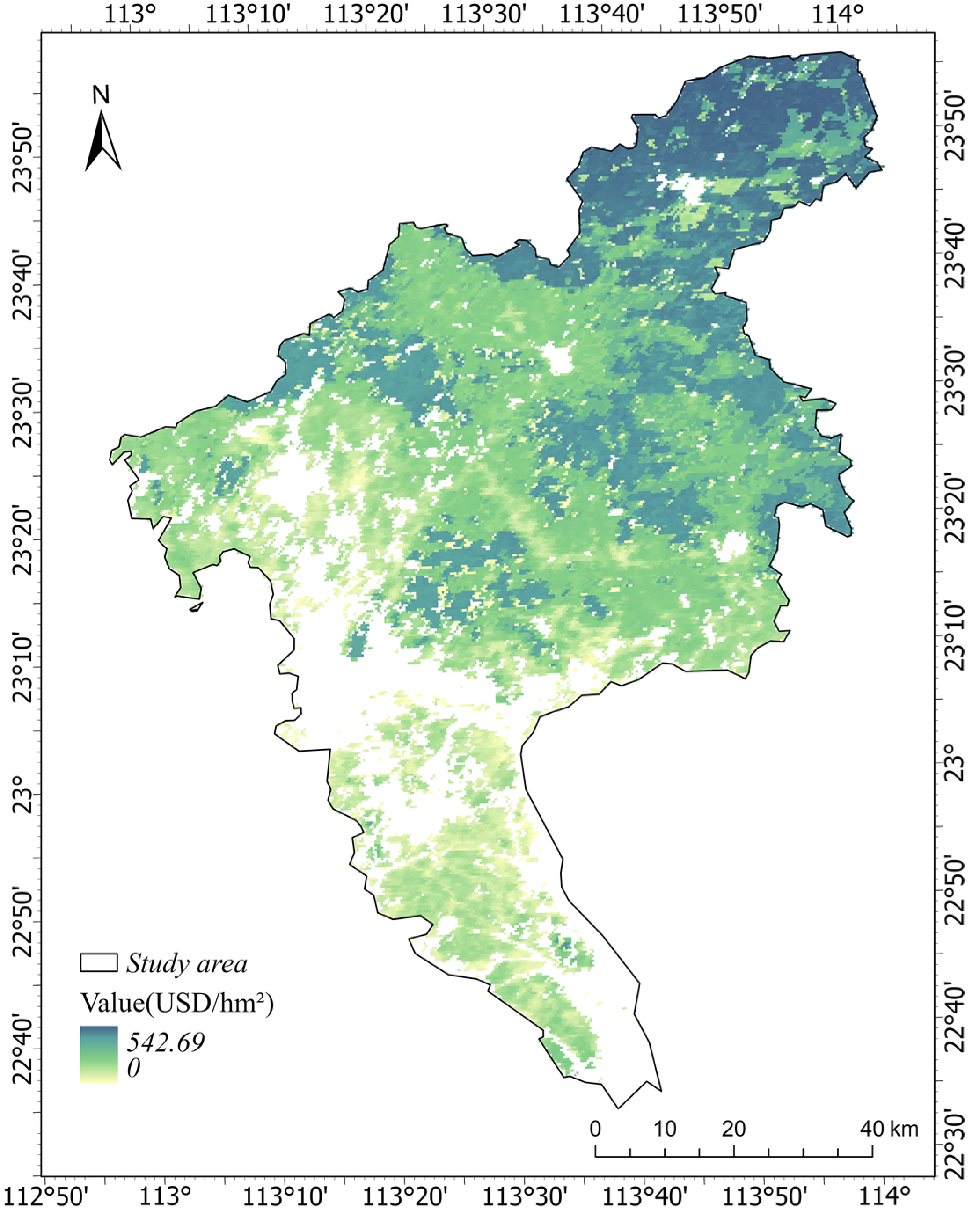
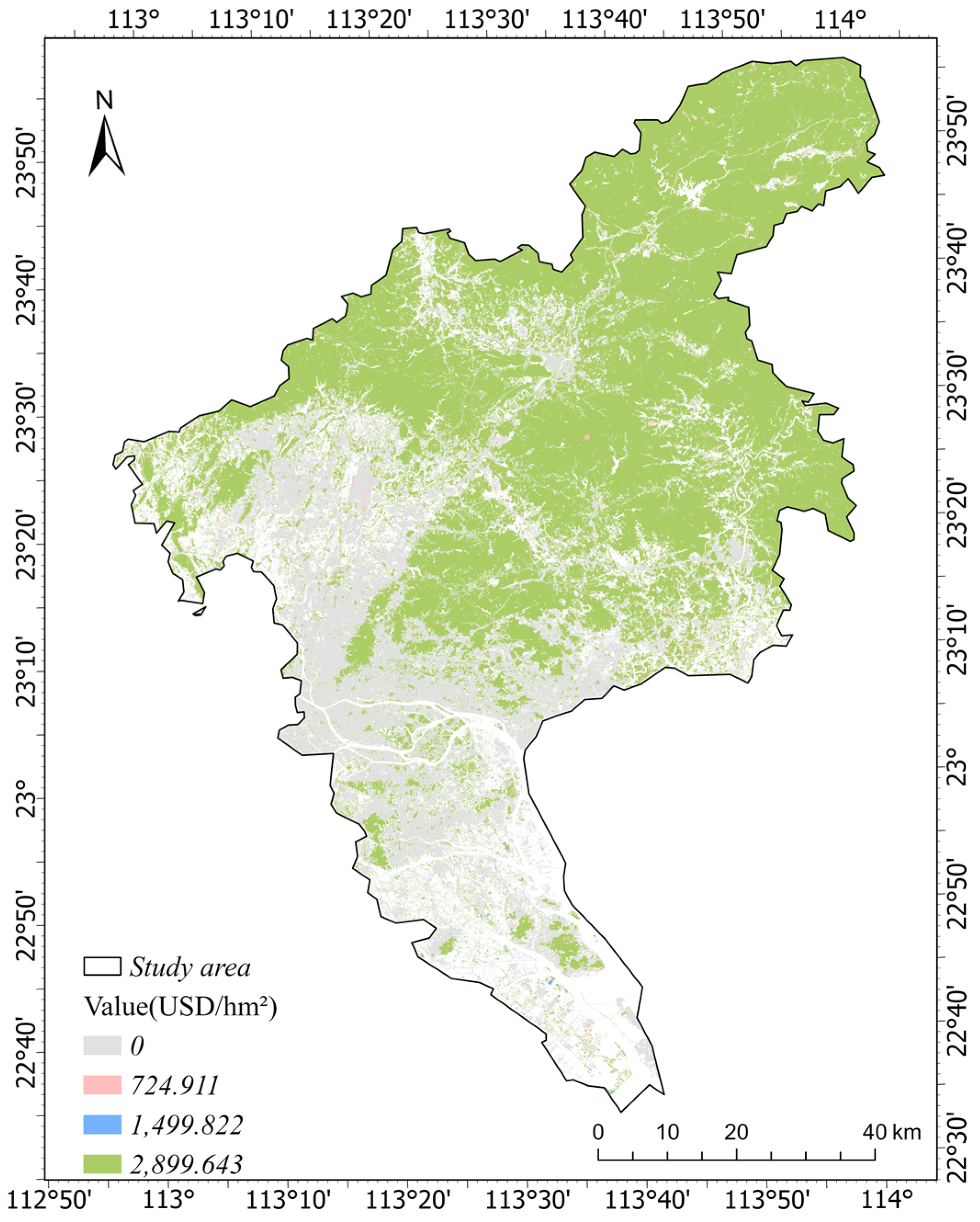
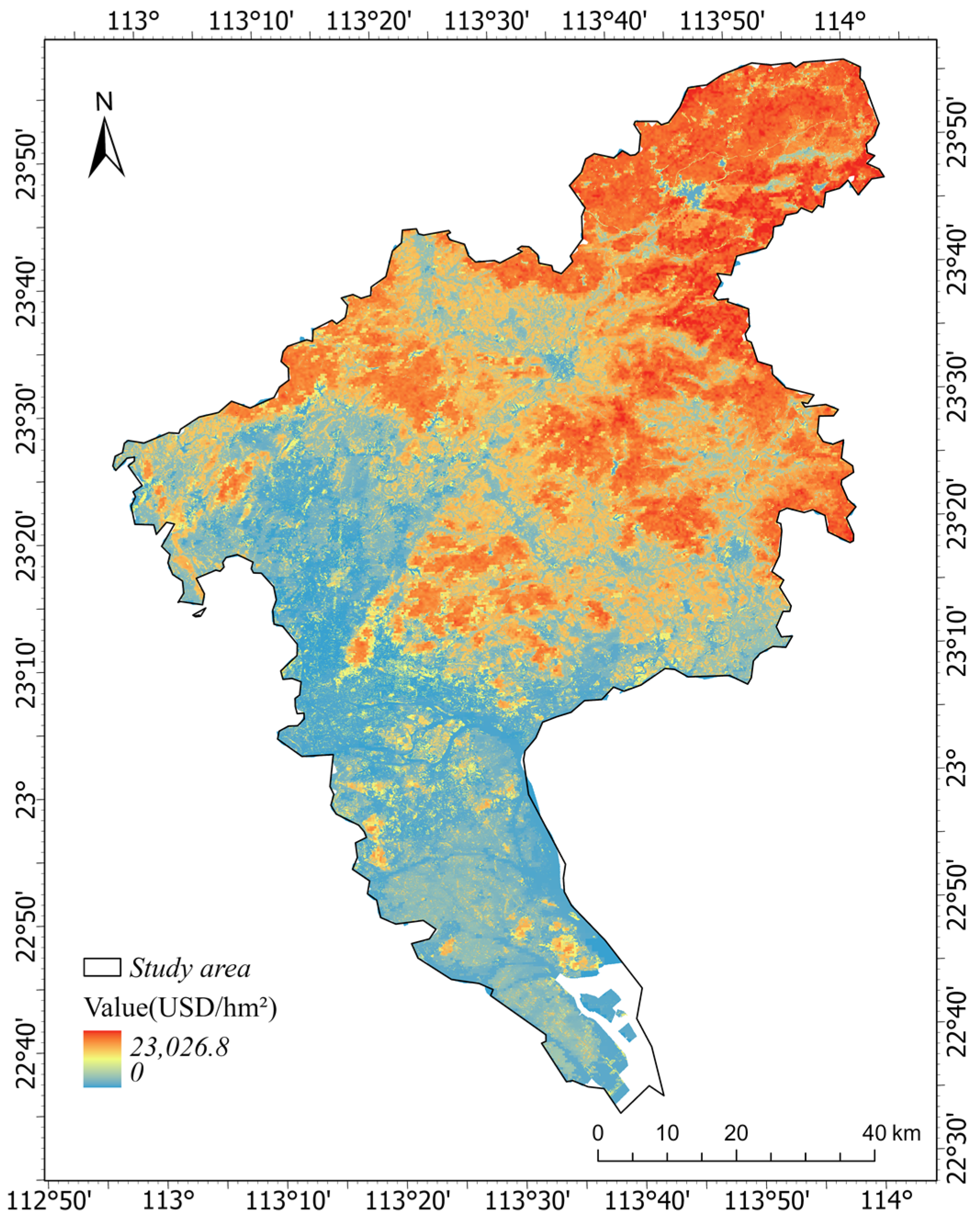
3.2. The Total Ecological Service Value of Urban Green Space
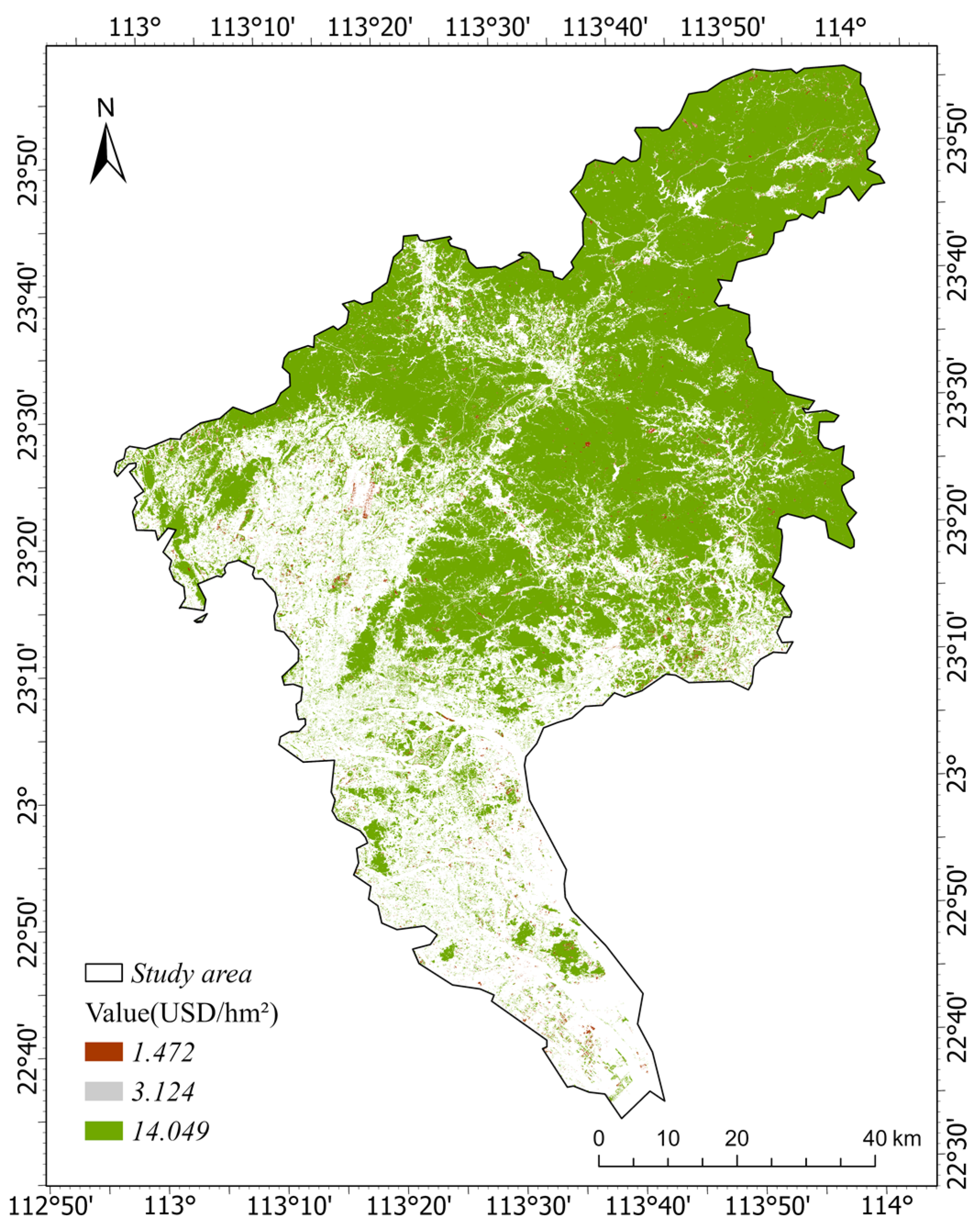
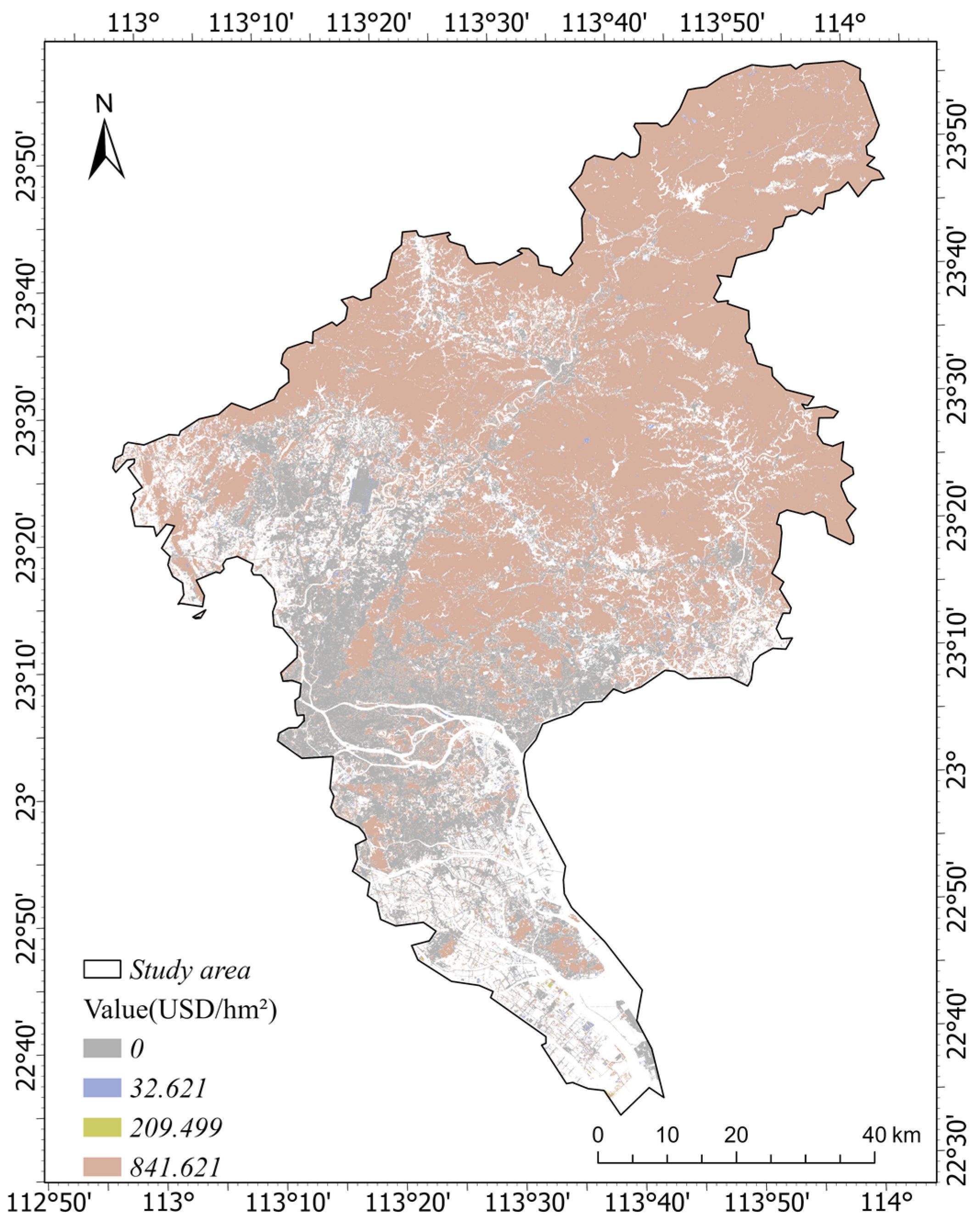
3.3. Ecosystem Service Value Prediction Based on CA_Markov
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Similar Studies
4.2. Prospects for Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westman, W.E. How Much Are Nature’s Services Worth? Science 1977, 197, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Rao, E. Improvements in Ecosystem Services from Investments in Natural Capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya-Romero, M.; Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Ibáñez, B.; Marañón, T. Evaluation of Forest Ecosystem Services in Mediterranean Areas. A Regional Case Study in South Spain. Ecosyst. Serv. 2016, 20, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, W.; Peng, H. Urban Land Use Change Simulation and Spatial Responses of Ecosystem Service Value Under Multiple Scenarios: A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Q.; Peng, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, B.; Zhou, W. Estimation of Ecosystem Service Value and Function Assessment of Urban Green Space: A Case Study of Nanjing. Ecol. Sci. 2019, 38, 142–149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jie, M.; Sun, J.; Liu, T. Assessment of Ecosystem Service Value of Resource-Based Cities in China: Based on the Perspective of Meta Model. Arid Land Geogr. 2022, 45, 1949–1957. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chu, Y. A Seamless Economical Feature Extraction Method Using Landsat Time Series Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102379. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yang, G.; Chen, W. Ecosystem Service Function Supply–Demand Evaluation of Urban Functional Green Space Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xue, W.; Kang, D.; Peng, Z. Assessment of Ecosystem Service Values of Urban Wetland: Taking East Lake Scenic Area in Wuhan as an Example. Land 2024, 13, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, N.; Zare, F.; Dehghani, R. Assessing Ecosystem Services of Urban Green Spaces: A Remote Sensing Approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3855. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, G.; Giannetti, B.F.; Agostinho, F.; Almeida, C.M.V.B.; Casazza, M. Emergy-Based Ecosystem Services Valuation and Classification Management Applied to China’s Grasslands. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 42, 101073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Huang, H.; She, K.; Xie, L.; Li, D. Assessment of Ecological Service Value of Important Reservoir Water Sources: A Case Study of Zhushuqiao Reservoir. Pearl River 2020, 41, 111–116. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yang, G.; Xu, C.; Li, M. Assessment of Ecosystem Service Value of Green Space in Mountainous Cities: A Case Study of Zunyi City Center. Environ. Protect. Sci. 2023, 49, 112–119. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Sun, F.; Wang, S. Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors Analysis of Ecosystem Services Value: A Case Study in Sunan Canal Basin of Jiangsu Province, Eastern China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman-ul-Haq, M.; Kanwal, A.; Gardezi, A.A.; Fatima, H.; Saqib, Z.; Bokhari, S.A.; Nasr, E.A.; Ahmad, S.; Shafiq, M. Assessing Spatial-Temporal Changes in Monetary Values of Urban Ecosystem Services through Remotely Sensed Data. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Z.; Yang, D.; Mei, C.; Ban, Y.; Yang, X. Assessment of Ecosystem Service Function and Value of Urban Green Space: A Case Study of Futian District, Shenzhen. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 52, 424–431. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, D.; Shukla, A.K.; Devi, N.R. Decadal Changes in Land Use and Land Cover: Impacts and Their Influence on Urban Ecosystem Services. AQUA Water Infrastruct. Ecosyst. Soc. 2024, 73, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.S.; Pan, H.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Tang, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.F.; Ma, H.J. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Force of Ecosystem Service Value in Leshan City Based on Dynamic Equivalent. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 76–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Xie, F.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; He, X.; Chu, Y. Estimation of the Value of Regional Ecosystem Services of an Archipelago Using Satellite Remote Sensing Technology: A Case Study of Zhoushan Archipelago, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, C.; Ou, S.; Feng, Q.; Guo, K.; Xie, J.; Wei, X. Evolutionary Characteristics and Driving Forces of Green Space in Guangzhou from a Zoning Perspective. Forests 2024, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; Niu, L. Scale Differences and Gradient Effects of Local Climate Zone Spatial Pattern on Urban Heat Island Impact—A Case in Guangzhou’s Core Area. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m Annual Land Cover Datasets and Its Dynamics in China from 1985 to 2022. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, H.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, L.; Sun, R. Dataset of Soil Conservation Capacity Preventing Water Erosion in China (1992–2019). Sci. Data Bank 2023, 16, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Changes in the Value of China’s Ecosystem Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaiti, B.; Chen, S.; Kasimu, A.; Mamat, A.; Aierken, N.; Chen, Q. Coupling and Coordination Relationships between Urban Expansion and Ecosystem Service Value in Kashgar City. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.Y.; Zi, X.H.; Li, Z. Resource and Environment Common Data Sheets; China Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1992. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.Q.; Lan, T.X. Progress of Increasing-Block Electricity Pricing Policy Implementation in China’s First-Tier Cities and the Impact of Resident Policy Perception. Energy Policy 2023, 117, 113544. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Gao, W. NCEP/NCAR Hourly Analysis and Comparative Analysis of Measured Land Surface Temperature and Surface Air Temperature in China. Meteorol. Mon. 2008, 35, 83–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.N.; Wu, J.B.; Zhu, J.P.; Xie, B.C. A Review of Technologies on Random Forests. Stat. Inf. Forum 2011, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, S.R.; Sun, P.S.; Wang, T. The Basic Principle of Random Forest and Its Applications in Ecology: A Case Study of Pinus yunnanensis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 650–659. [Google Scholar]
- Oukawa, G.Y.; Krecl, P.; Targino, A.C. Fine-Scale Modeling of the Urban Heat Island: A Comparison of Multiple Linear Regression and Random Forest Approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D. Research on Remote Sensing Water Extraction Method Based on SWIR Band. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2013, 28, 682–686. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dairma, D.; Bao, Y. Comparative Analysis of Surface Albedo Retrieval Methods Based on TM Data. J. Inner Mongolia Normal Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2010, 39, 186–190. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.L.; Wu, H.; Wang, N.; Qiu, S.; Sobrino, J.A.; Wan, Z.; Tang, B.H.; Yan, G. Land Surface Emissivity Retrieval from Satellite Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 3084–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valor, E.; Caselles, V. Mapping Land Surface Emissivity from NDVI: Application to European, African and South American Areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 57, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhao, Z. Progress in the Study of Estimation Methods for Vegetation Cover Based on Remote Sensing. Green Sci. Technol. 2015, 3, 10–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, W.C.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.-Z. Classification-Based Emissivity for Land Surface Temperature Measurement from Space. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 2753–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, Q.; Ren, P. Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Mechanisms of Vegetation Net Primary Productivity in Xinjiang, China from 2001 to 2022. Land 2024, 13, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, L. Evaluation and Management of Ecosystem Service Value in Tibet Gongbu Nature Reserve. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 29, 217–224. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, D.; Wang, L. The Value of Environmental Purification Services for Urban Green Space Ecosystems in Qingdao. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 2576–2584. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Ou, S.; Yang, T.; Yi, C.X. Quantitative Assessment of Ecological Value of Urban Green Space Based on GIS/RS. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 38–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Ren, X.; Hu, W. Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Services Value in China. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2011, 47, 145–153. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lin, A.; Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Cen, L.Y.; Liu, H. Refined Simulation of Urban Land Use Change Considering Spatial Scale Effects Environ. Protect. Sci. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 2738–2756. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Xu, Y.; He, M.; Li, N. Research on Remote Sensing Inversion of Near-Surface Air Temperature Based on Random Forest Algorithm. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2017, 19, 390–397. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Estimation and Distribution of R in Weibei Area. J. Northwest For. Univ. 1993, 8, 21–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, G. Assessment of the Value of Urban Green Space Ecological Service Function: A Case Study of Beijing Forestry University. Ningxia J. Agric. For. Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 48–51. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Guan, Y.; Cai, D.; Zhang, C.; Yao, W.; Liao, Z.; Deng, R.; Qian, J.; Xia, Y.; Guo, S. An Assessment Method of Ecosystem Service Value Based on Improved Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2024, 26, 1763–1778. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, M.; Peng, B.; Yuan, S.; Li, H.; Liao, Y. A Preliminary Study on Remote Sensing Estimation of Daily Minimum Temperature in Guizhou Province Based on Polar-Orbiting Satellites Environ. Protect. Sci. Mid-Low Lat. Mt. Meteorol. 2023, 47, 69–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]





| Name | Spatial Resolution | Time Resolution | Time Frame | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1985 to 2022 | 30 m | Annual | 2010, 2015, 2020, 2022 | Jie Yang and Xin Huang (2023) [23] The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1985 to 2022 [Data set]. In Earth System Science Data (1.0.2, Vol. 13, Number 1, pp. 3907–3925). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8176941 (accessed on 8 November 2023) |
| Vector data of three administrative divisions of provinces, cities and counties in China | Vector | Annual | 2024 | https://cloudcenter.tianditu.gov.cn/administrativeDivision (accessed on 8 November 2023) |
| NASA DEM 30 m | 30 m | Annual | 2020 | https://earthdata.nasa.gov/esds/competitive-programs/measures/nasadem (accessed on 8 November 2023) |
| MOD17A3HGF V061 dataset | 500 m | Annual | 2001 to 2022 | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 8 November 2023) |
| Landsat 8-9 C2 L2SP product data | 30 m | Diurnal | 2021 to 2024 | https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 8 November 2023) |
| Dataset of Soil Conservation Capacity Preventing Water Erosion in China (1992–2019) | 500 m | Annual | 1992 to 2019 | Jialei Li, Hongbin He, Qinghua Zeng, et al. [24] Dataset of Soil Conservation Capacity Preventing Water Erosion in China (1992–2019) [DS/OL]. V1. Science Data Bank, 2023. https://cstr.cn/31253.11.sciencedb.07135 (accessed on 8 November 2023). |
| The meteorological data in Guangzhou | Panel data | Annual | 2020 to 2023 | http://data.cma.cn (accessed on 8 November 2023) |
| Types of Ecosystem Service 1st Service | 2nd Level | Assessment Content |
|---|---|---|
| Provision service | Store water | Ecological value of water conservation |
| Regulation service | Temperature regulation | Ecological value produced by regulating temperature |
| Release O2 | Eco-economic value of releasing oxygen | |
| Fixed CO2 | Eco-economic value of CO2 fixation | |
| Absorb SO2 | Eco-economic value of absorbing SO2 | |
| Stagnant dust | Ecological value of purifying dust and retention | |
| Support service | Soil conservation | Reduce the value of land loss |
| Reduce the value of sediment deposition disaster | ||
| Biodiversity | Ecological value of biodiversity protection |
| Types of Ecosystem Service 1st Service | 2nd Level | Value in 2020 (Unit: USD 100 Million) | Value in 2030 (Unit: USD 100 Million) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provision service | Store water | 31.252 | 27.759 |
| Regulation service | Temperature regulation | 12.561 | 11.135 |
| Release O2 | 10.806 | 9.582 | |
| Fixed CO2 | 1.420 | 1.259 | |
| Absorb SO2 | 0.058 | 0.052 | |
| Stagnant dust | 3.496 | 3.106 | |
| Support service | Soil conservation | 3.105 | 2.751 |
| Biodiversity | 12.112 | 10.721 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Si, J.; Ou, J. Assessment and Dynamic Prediction of Green Space Ecological Service Value in Guangzhou City, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224180
Li Z, Zhou Z, Liu Z, Si J, Ou J. Assessment and Dynamic Prediction of Green Space Ecological Service Value in Guangzhou City, China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(22):4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224180
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhefan, Zhaokang Zhou, Zhenhua Liu, Jiahe Si, and Jiaming Ou. 2024. "Assessment and Dynamic Prediction of Green Space Ecological Service Value in Guangzhou City, China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 22: 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224180
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhou, Z., Liu, Z., Si, J., & Ou, J. (2024). Assessment and Dynamic Prediction of Green Space Ecological Service Value in Guangzhou City, China. Remote Sensing, 16(22), 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16224180





