Modeling of Solar Radiation Pressure for BDS-3 MEO Satellites with Inter-Satellite Link Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. SRP Model
2.1.1. ABW Model
2.1.2. ECOM1 Model
2.2. Satellite Structures and Self-Shadow Impact
2.3. Observation Model
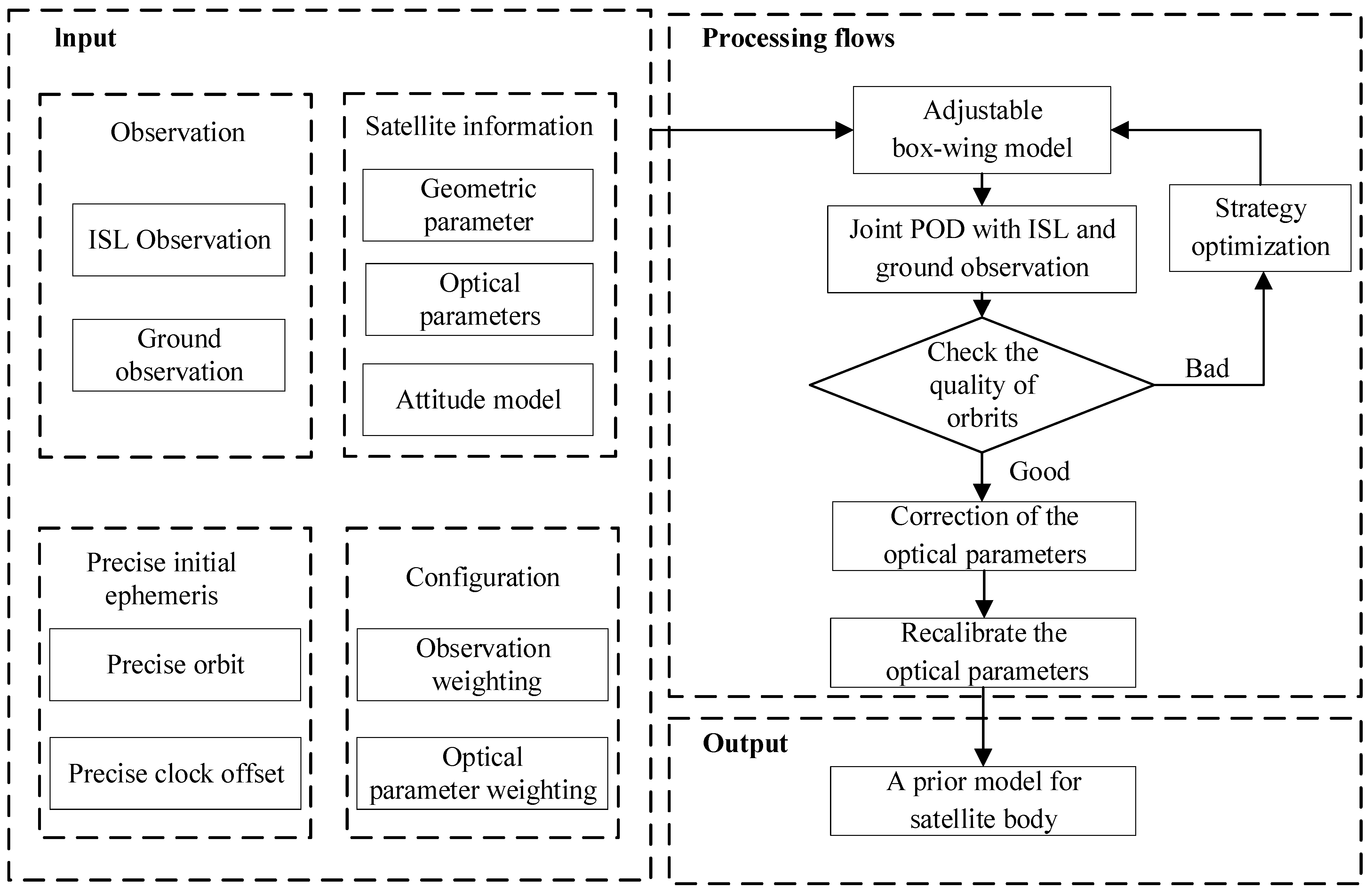
2.4. Strategy of SRP Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Optical Parameters
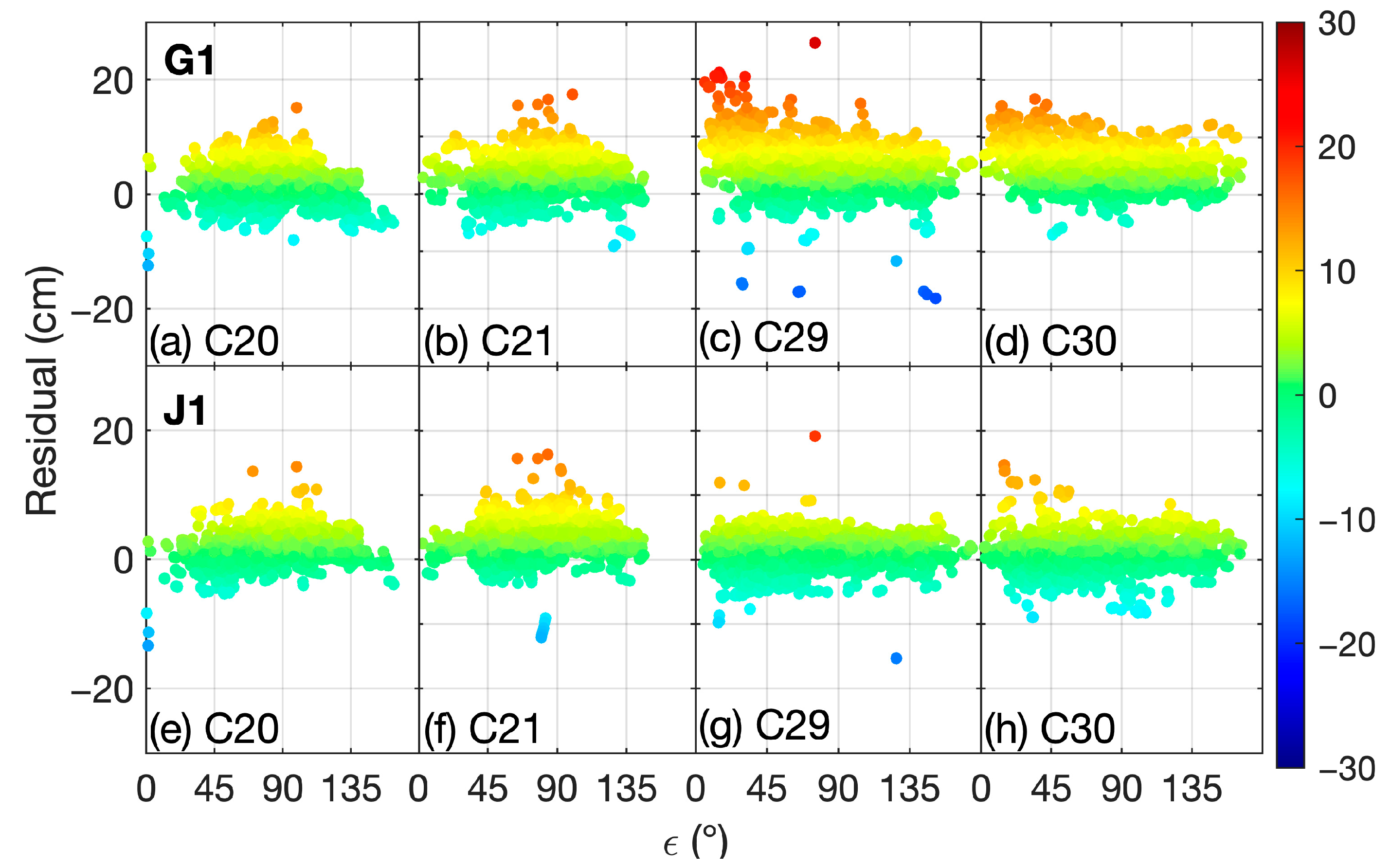
3.2. Orbit and Clock Accuracy of SRP Modeling
3.3. Verification of the a Priori Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
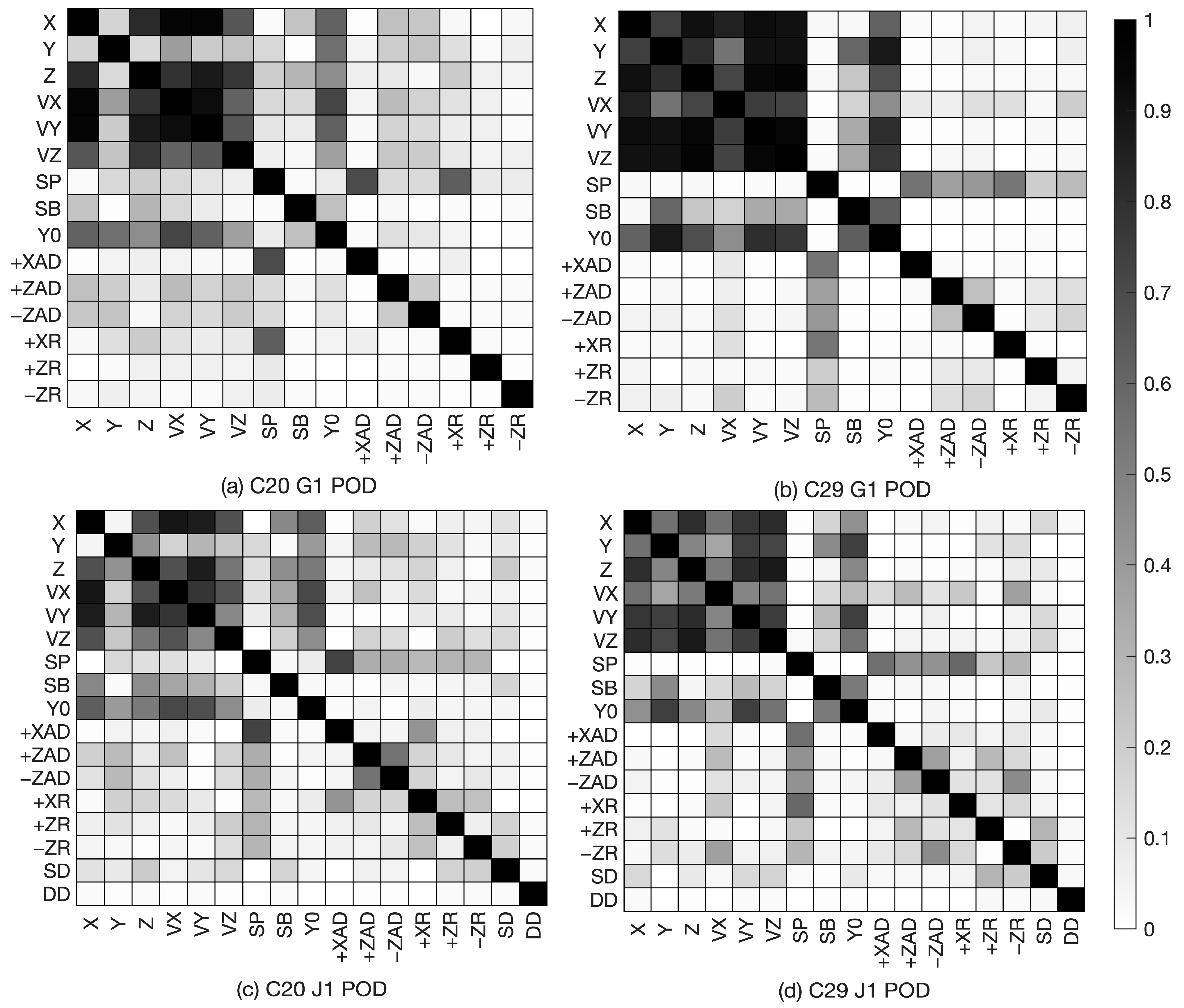
- The correlation between the optical parameters of the +X/±Z panels cannot be significantly decreased even with the ISL observation, due to the parameter settings of the ABW model. Nonetheless, the ISL can still decrease the correlation between orbit parameters, thereby improving the orbit accuracy.
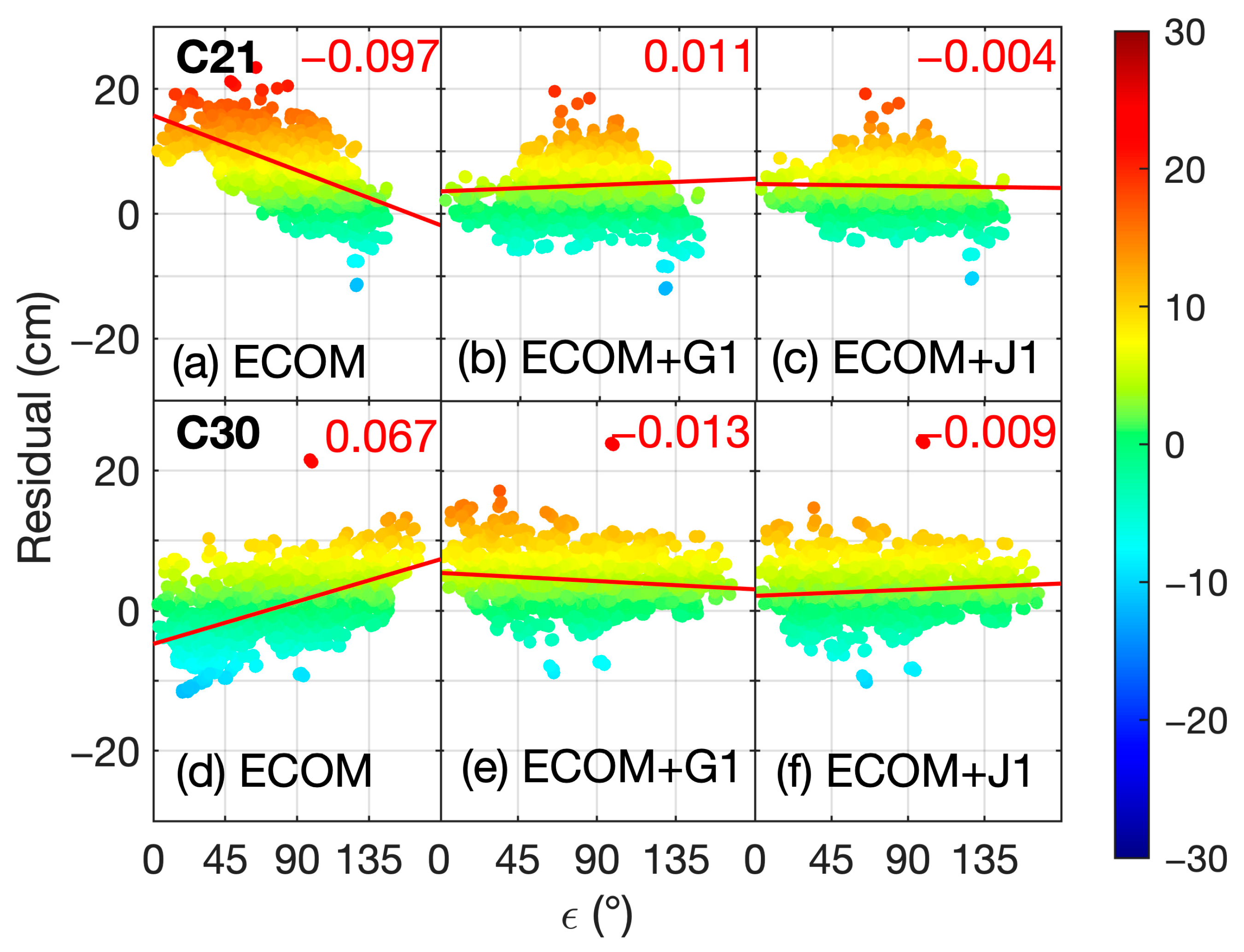
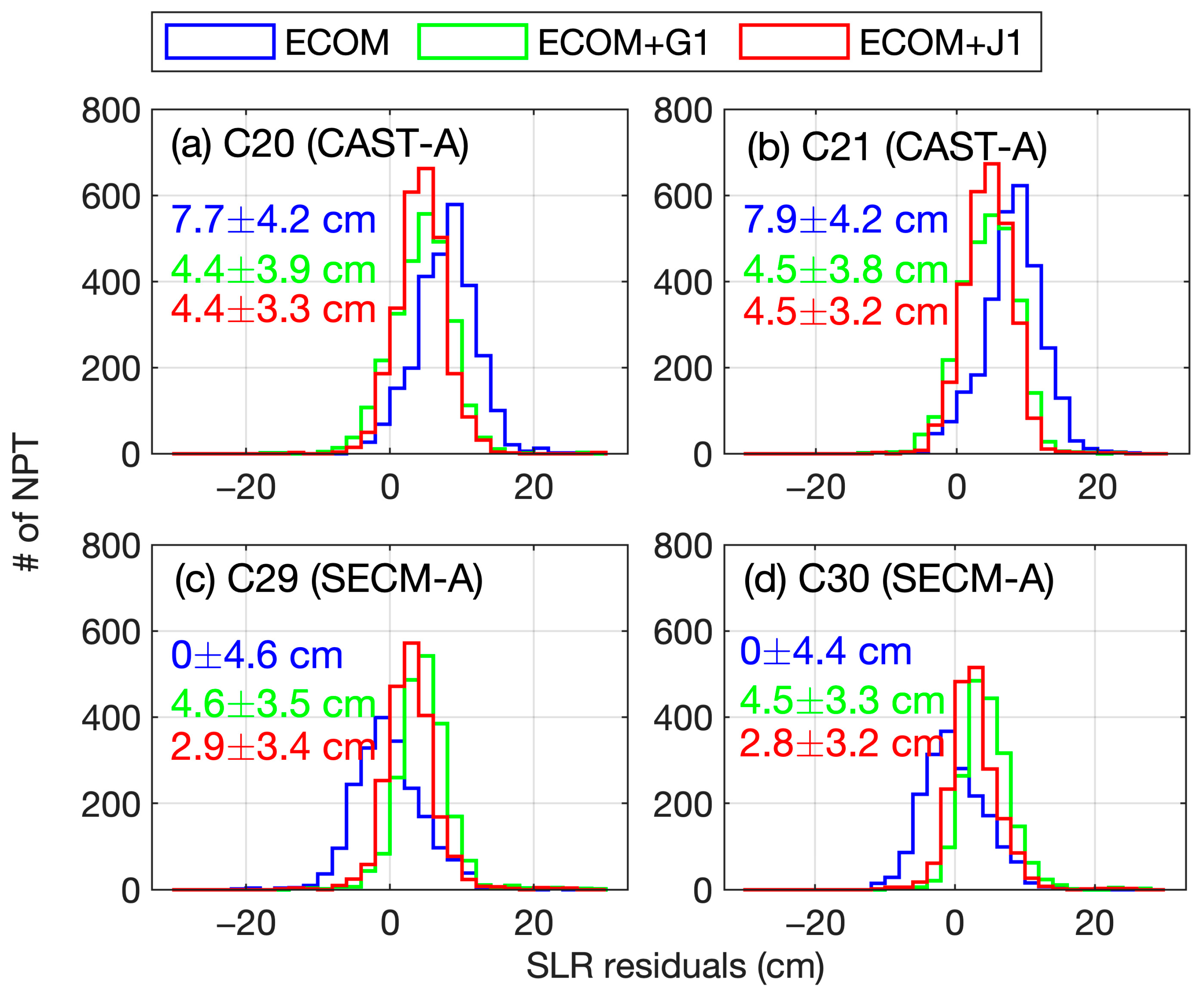
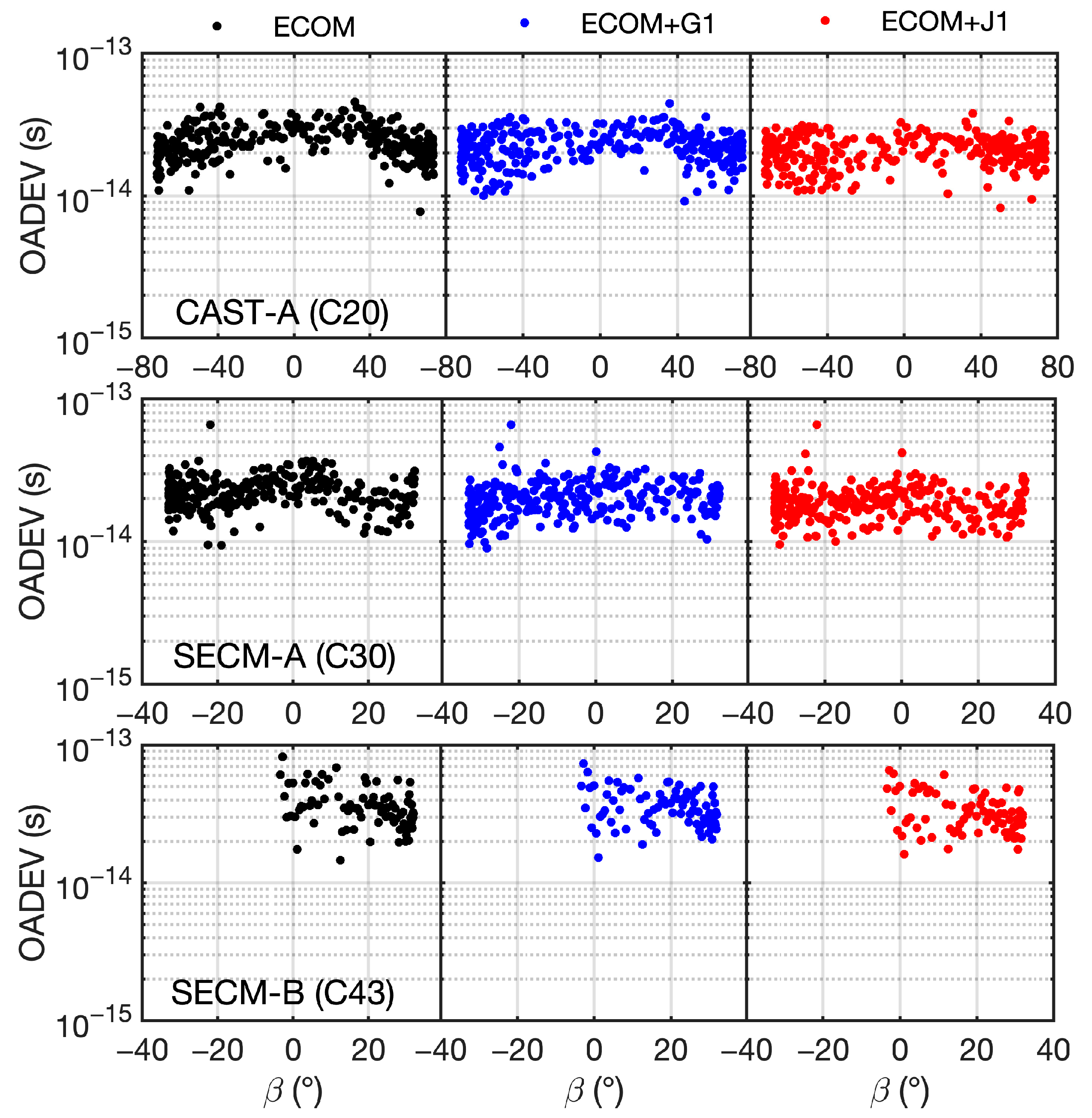
- An a priori model established for the satellite body can reduce the systematic errors in ECOM orbits, and the model established using ISL observation demonstrates superior performance compared to solely using L-band observations. With the enhanced a priori model, the slopes in the SLR residual of CAST and SECM satellites are reduced from −0.097 cm/deg and 0.067 cm/deg to −0.004 cm/deg and −0.009 cm/deg, respectively. The STD values are reduced with an improvement of 21.8% and 26.6%, respectively. Furthermore, a reduced β-dependent variation is observed in the OADEV of the corresponding clock offset. Nevertheless, systematic biases are still present in the SRL residual when using the a priori model. It is suspected that there are other effects that are yet to be properly accounted for.
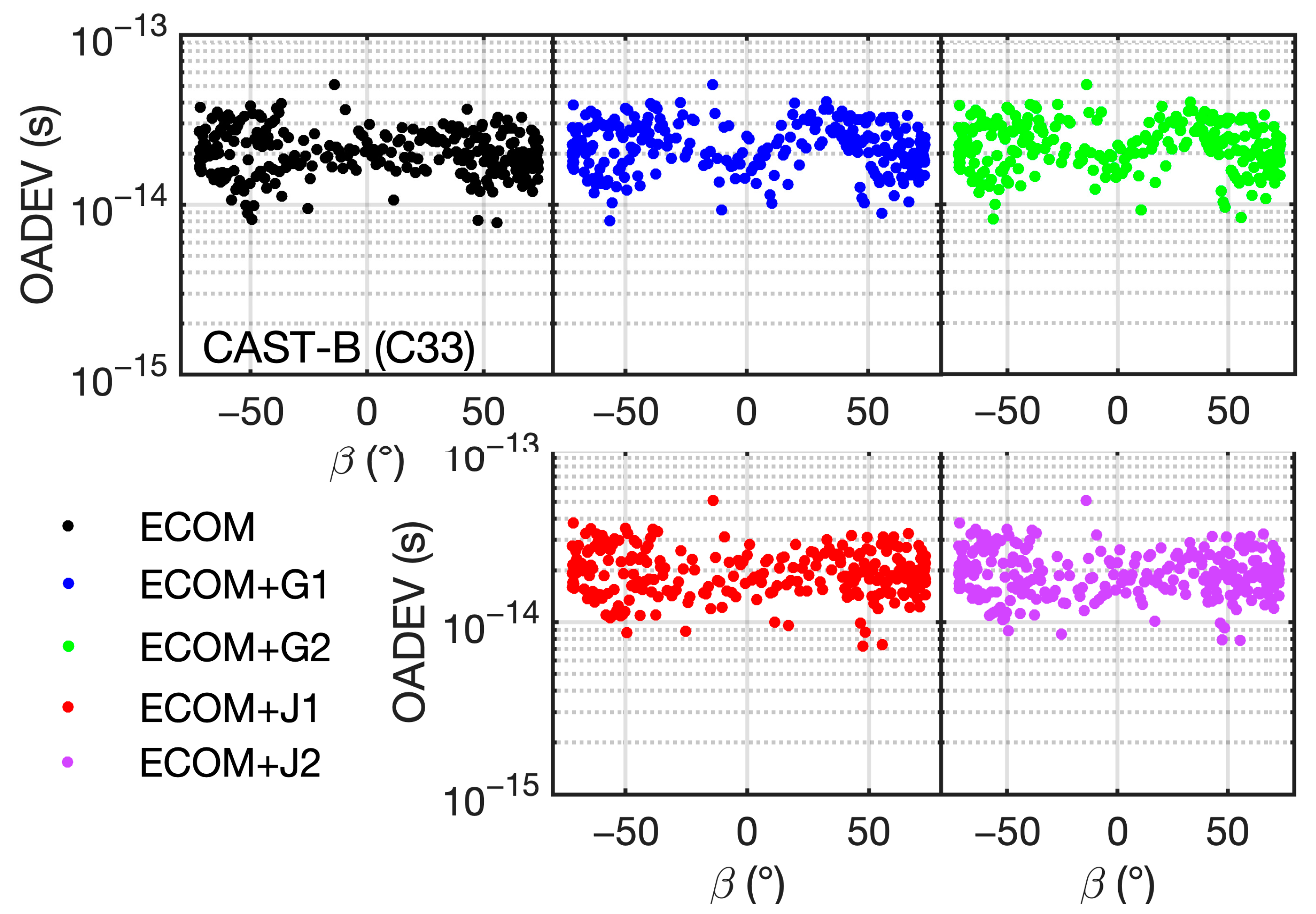
- The impact of self-shadowing from SAR-carrying satellites was considered. The systematic trends within the decreased with the a priori model established by ISL observation. The orbit accuracy as indicated in the DBD and OADEV of clock offset exhibited a litter improvement. Because of the absence of SAR antenna geometric details from BDS authorities, we propose disregarding the SAR antennas’ impact on the satellites in the current modeling phase.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Guo, S.; Mao, Y.; Yang, Y. Introduction to BeiDou-3 Navigation Satellite System. Navigation 2019, 66, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B. Basic Performance and Future Developments of BeiDou Global Navigation Satellite System. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lin, B.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Bai, T. Satellite Geometry and Attitude Mode of BDS-3 MEO Satellites Developed by SECM. In Proceedings of the 31st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2018), Miami, FL, USA, 24–28 September 2018; pp. 1268–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, R.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J. Inter-Satellite Link Enhanced Orbit Determination for BeiDou-3. J. Navig. 2019, 73, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhou, R. Initial Assessment of BDS-3 Preliminary System Signal-in-Space Range Error. GPS Solut. 2019, 24, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Deng, Z.; Guo, J.; Prange, L.; Song, S.; Montenbruck, O. BeiDou-3 Orbit and Clock Quality of the IGS Multi-GNSS Pilot Project. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q. BDS-3 Precise Orbit and Clock Solution at Wuhan University: Status and Improvement. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Qin, Z.; Xie, S. A Priori Solar Radiation Pressure Model for BeiDou-3 MEO Satellites. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliegel, H.; Feess, W.; Layton, W.; Verdun, A. The GPS radiation force model. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Precise Positioning with the Global Positioning System, Rockville, MD, USA, 15–19 April 1985; pp. 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel, H.; Gallini, T. Radiation pressure models for Block II GPS satellites. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Geodetic Symposium on Satellite Positioning, Rockville, MD, USA, 13–17 March 1989; pp. 789–798. [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel, H.; Gallini, T.; Swift, E. Global Positioning System Radiation Force Model for Geodetic Applications. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1992, 97, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliegel, H.; Gallini, T. Solar Force Modeling of Block IIR Global Positioning System Satellites. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 1996, 33, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Luthcke, S. Modeling Radiation Forces Acting on Topex/Poseidon for Precision Orbit Determination. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 1994, 31, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.J.; Hugentobler, U.; Steigenberger, P. Adjustable box-wing model for solar radiation pressure impacting GPS satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, G.; Brockmann, E.; Gurtner, W.; Hugentobler, U.; Mervart, L.; Rothacher, M.; Verdun, A. Extended orbit modeling techniques at the CODE processing center of the international GPS service for geodynamics (IGS): Theory and initial results. Manuscr. Geod. 1994, 19, 367–386. [Google Scholar]
- Springer, T.A.; Beutler, G.; Rothacher, M. A New Solar Radiation Pressure Model for GPS Satellites. GPS Solut. 1999, 2, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.; Meindl, M.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Lutz, S.; Prange, L.; Sośnica, K.; Mervart, L.; Jäggi, A. CODE’s New Solar Radiation Pressure Model for GNSS Orbit Determination. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. Definitions and Descriptions of BDS/GNSS Satellite Parameters for High Precision Application. Available online: https://ilrs.cddis.eosdis.nasa.gov/docs/2019/BeiDou_MetaData_191201.cn.en.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Duan, B.; Hugentobler, U.; Selmke, I.; Marz, S.; Killian, M.; Rott, M. BeiDou Satellite Radiation Force Models for Precise Orbit Determination and Geodetic Applications. IEEE T. Aero. Elec. Syst. 2022, 58, 2823–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, X. General design of the third generation BeiDou navigation satellite system. J. Nanjing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. (Chin.) 2020, 52, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office (CSNO), BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Search and Rescue Service (Version 1.0). 2020. Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202008/P020200803362068698004.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jiao, W.; Bian, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Improving BDS-3 Precise Orbit Determination for Medium Earth Orbit Satellites. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, R.; Jia, X.; Feng, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F. Modeling non-conservative forces for BDS-3 MEO satellites. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. (Chin.) 2022, 51, 1862G1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.; Lou, J.; Li, X. Examination and enhancement of solar radiation pressure model for BDS-3 satellites. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2021, Vienna, Austria, 19–30 April 2021; Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021EGUGA..23.8307L/abstract (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Xie, M.; Zhao, D. A Study of Solar Radiation Pressure Model in BDS-3 Precise Orbit Determination. Chin. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 47, 894–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, C. Contribution of Intersatellite Link Measurements to ECOM Solar Radiation Pressure Estimation on the BDS-3 MEO Satellite. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X. Evaluation of BDS-3 Orbit Determination Strategies Using Ground-Tracking and Inter-Satellite Link Observation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Lv, Y.; Cai, H.; Liu, J. Orbit and Clock Analysis of BDS-3 Satellites Using Inter-Satellite Link Observations. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yang, J.; Li, G.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, C. Globalization Highlight: Orbit Determination Using BeiDou Inter-Satellite Ranging Measurements. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Performance Analysis and Progress of Inter-Satellite-Link of Beidou System. In Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2017), Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 September 2017; pp. 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Tang, C.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, G. Time Synchronization of New-Generation BDS Satellites Using Inter-Satellite Link Measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS conventions (2010) (No. IERS-TN-36); IERS Convention Center: Frankfurt, Germany, 2010; Available online: https://iers-conventions.obspm.fr/content/tn36.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- Pavlis, N.K.; Holmes, S.A.; Kenyon, S.C.; Factor, J.K. The Development and Evaluation of the Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.J. Impact of the Albedo Modeling on GPS Orbits. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität München, München, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Steigenberger, P.; Thoelert, S. Initial BDS-3 transmit power analysis (with BDS-2 gain pattern). 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Geng, T.; Ma, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, J. Estimation and Analysis of BDS-3 Satellite Yaw Attitude Using Inter-Satellite Link Observations. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Q. Yaw Attitudes for BDS-3 IGSO and MEO Satellites: Estimation, Validation and Modeling with Intersatellite Link Observations. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
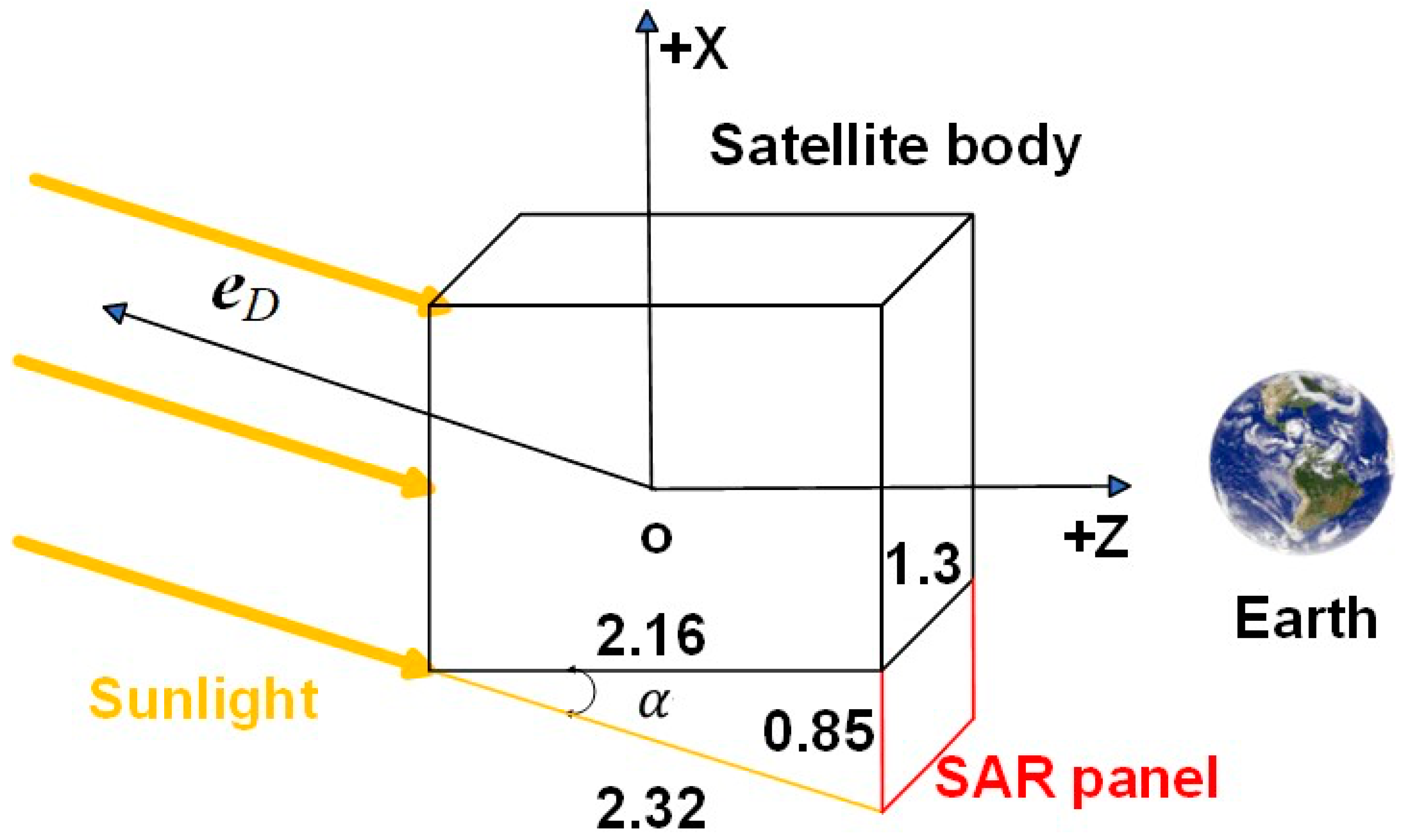



| Sat. Type | Sat. | Panel | ) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAST-A | C19, C20, C21, C22, C23, C24, C36, C37, C41, C42 | +X | 1.25 | 0.350 | 0.650 |
| +Z | 2.59 | 0.920 | 0.080 | ||
| −Z | 2.59 | 0.350 | 0.650 | ||
| CAST-B | C32, C33, C45, C46 | +X | 1.25 | 0.350 | 0.650 |
| +Z | 2.59 | 0.920 | 0.080 | ||
| −Z | 2.59 | 0.350 | 0.650 | ||
| SECM-A | C25, C26, C27, C28, C29, C30, C34, C35 | +X | 1.25 | 0.200 | 0.800 |
| +Z | 2.59 | 0.200 | 0.800 | ||
| −Z | 2.59 | 0.200 | 0.800 | ||
| SECM-B | C43, C44 | +X | 1.24 | 0.200 | 0.800 |
| +Z | 2.57 | 0.200 | 0.800 | ||
| −Z | 2.57 | 0.200 | 0.800 |
| Strategy | Observation | SAR Antenna |
|---|---|---|
| G1 | L-band | Unconsidered |
| J1 | L-band, Ka-band | Unconsidered |
| G2 | L-band | Considered |
| J2 | L-band, Ka-band | Considered |
| Items | Models |
|---|---|
| Tide displacement | Solid Earth tide, pole tide, and ocean tide loading [32] |
| Relativity effect | Schwarzschild and Lense-Thirring |
| Geopotential | EGM2008 up to 12 × 12 degrees and orders [33] |
| N-body gravitation | Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) DE405 ephemeris |
| Earth radiation pressure | Applied [34] |
| Antenna thrust | 310 W for CAST satellite and 280 W for SECM satellite [35] |
| # of Normal Point | G1 | J1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bias | STD | RMS | Bias | STD | RMS | ||
| C20 | 2646 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.9 |
| C21 | 2746 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 4.1 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 3.8 |
| C29 | 2032 | 4.9 | 4.2 | 6.4 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 2.5 |
| C30 | 1848 | 4.9 | 3.4 | 6.0 | 0.7 | 2.6 | 2.7 |
| Sat. Type | Strategy | Along (cm) | Cross (cm) | Radial (cm) | 3D (cm) | OADEV (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAST-A | ECOM | 20.5 | 7.3 | 5.4 | 22.5 | 2.47 × 10−14 |
| ECOM+G1 | 21.8 | 9.1 | 6.7 | 24.5 | 2.67 × 10−14 | |
| ECOM+J1 | 21.8 | 8.2 | 6.0 | 24.0 | 2.36 × 10−14 | |
| CAST-B | ECOM | 27.2 | 8.8 | 8.5 | 29.9 | 2.75 × 10−14 |
| ECOM+G1 | 28.5 | 10.3 | 9.6 | 31.8 | 3.43 × 10−14 | |
| ECOM+G2 | 28.3 | 10.2 | 9.5 | 31.6 | 3.40 × 10−14 | |
| ECOM+J1 | 27.5 | 8.9 | 8.6 | 30.2 | 2.81 × 10−14 | |
| ECOM+J2 | 27.4 | 8.8 | 8.5 | 30.1 | 2.75 × 10−14 | |
| SECM-A | ECOM | 30.2 | 6.3 | 5.3 | 31.3 | 2.36 × 10−14 |
| ECOM+G1 | 29.6 | 7.1 | 5.2 | 30.9 | 2.12 × 10−14 | |
| ECOM+J1 | 29.0 | 6.4 | 5.2 | 30.2 | 1.95 × 10−14 | |
| SECM-B | ECOM | 34.5 | 10.3 | 9.4 | 37.2 | 3.53 × 10−14 |
| ECOM+G1 | 33.8 | 10.8 | 9.1 | 36.6 | 3.41 × 10−14 | |
| ECOM+J1 | 33.2 | 10.1 | 9.1 | 35.8 | 3.18 × 10−14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, R.; Xie, X. Modeling of Solar Radiation Pressure for BDS-3 MEO Satellites with Inter-Satellite Link Measurements. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203900
Lv Y, Liu Z, Jiang R, Xie X. Modeling of Solar Radiation Pressure for BDS-3 MEO Satellites with Inter-Satellite Link Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(20):3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203900
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Yifei, Zihao Liu, Rui Jiang, and Xin Xie. 2024. "Modeling of Solar Radiation Pressure for BDS-3 MEO Satellites with Inter-Satellite Link Measurements" Remote Sensing 16, no. 20: 3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203900
APA StyleLv, Y., Liu, Z., Jiang, R., & Xie, X. (2024). Modeling of Solar Radiation Pressure for BDS-3 MEO Satellites with Inter-Satellite Link Measurements. Remote Sensing, 16(20), 3900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203900





