Dynamic Changes and Driving Factors in the Surface Area of Ebinur Lake over the Past Three Decades
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
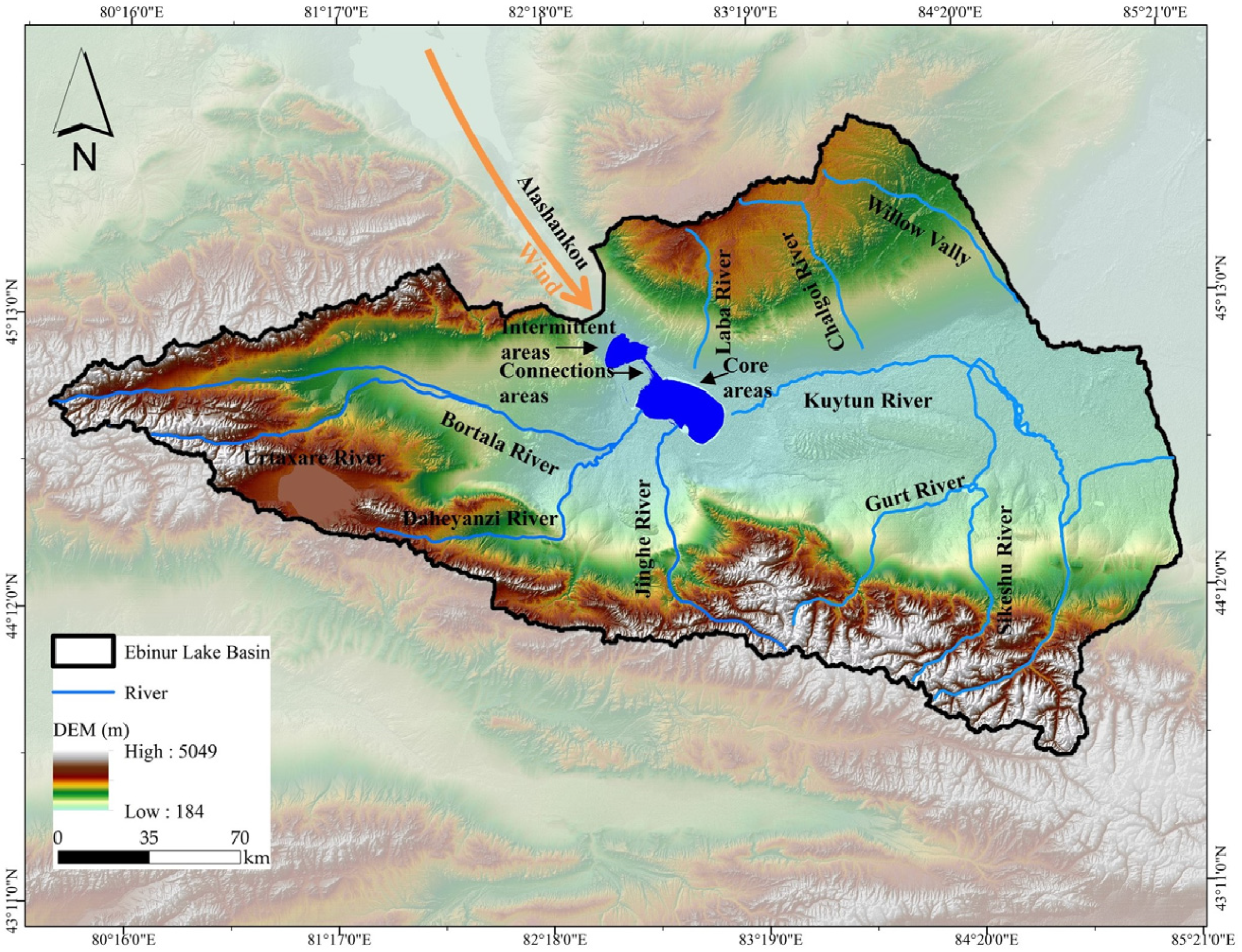
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Landsat Data and Preprocessing
2.3. Water Extraction Algorithm
2.3.1. Construction of the Algorithm
2.3.2. Validation of the Algorithm
2.3.3. Spatio-Temporal Statistics
2.4. Analysis of Driving Forces
2.4.1. Source of Data
2.4.2. Analysis of Driving Factors
3. Results
3.1. Ebinur Lake Water Body Extraction Algorithm
3.1.1. Comparison of Different Water Indices
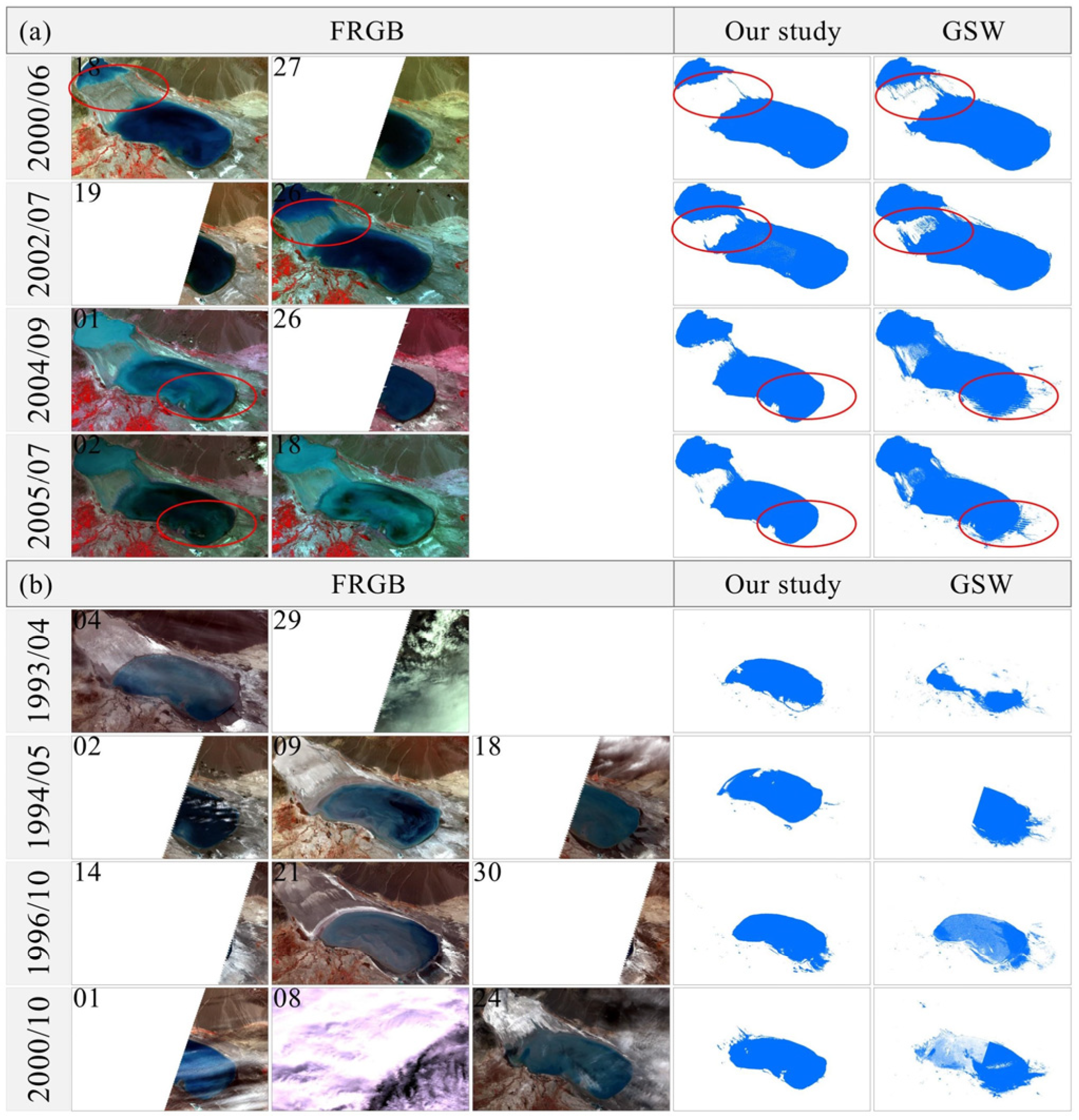
3.1.2. Validation
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Distribution
3.2.1. Spatial Variations
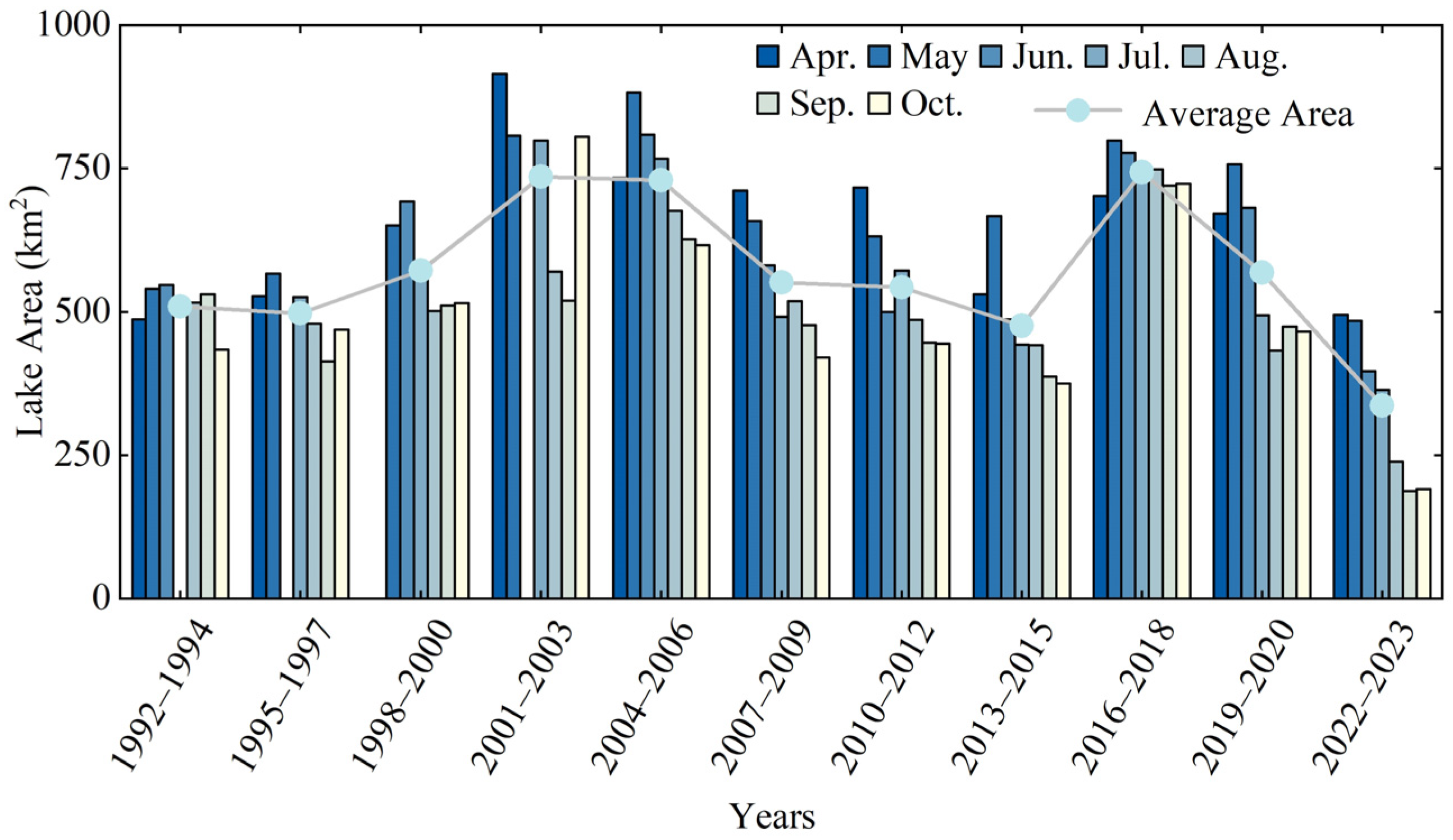
3.2.2. Inter-Annual Variations
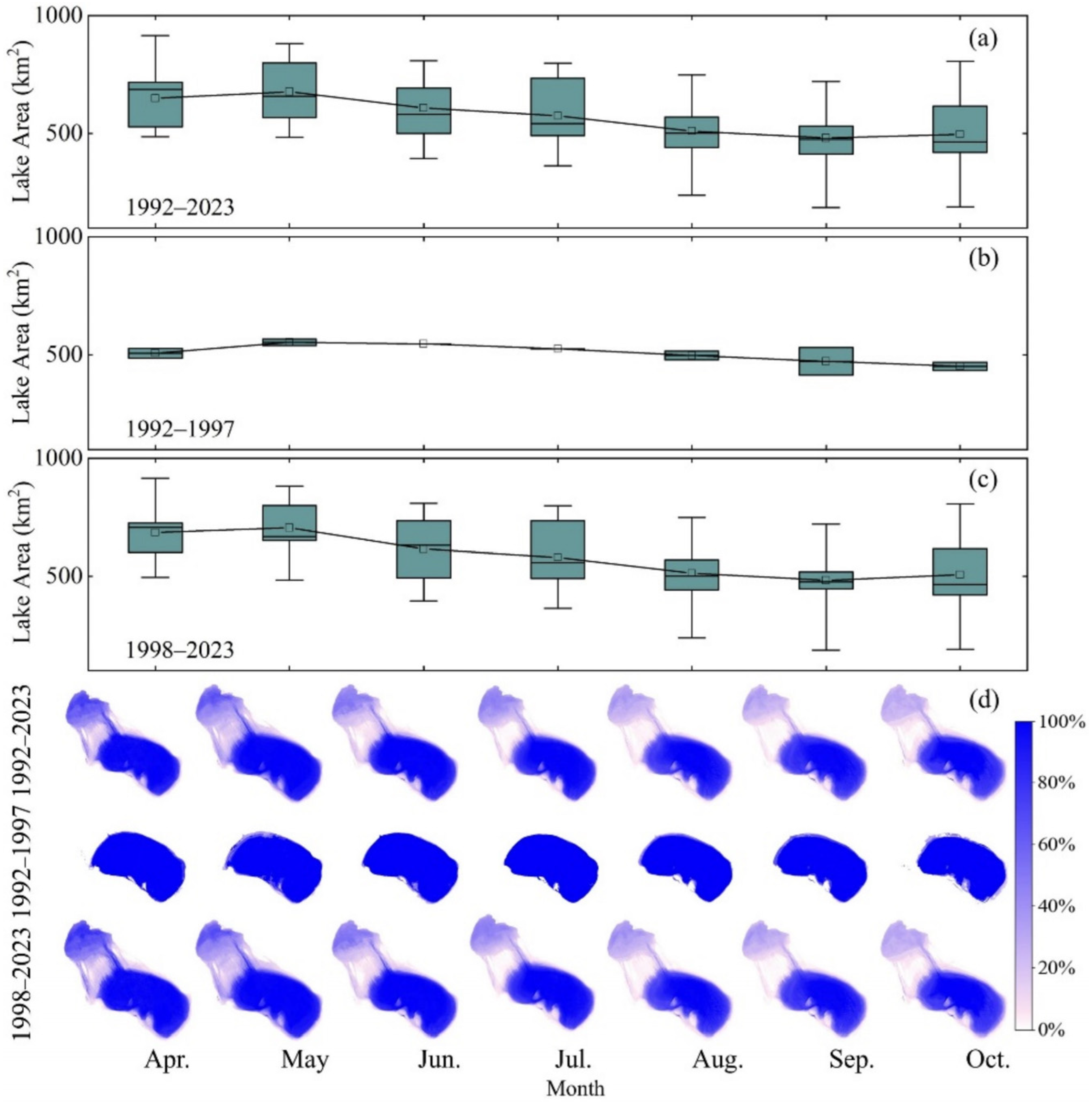
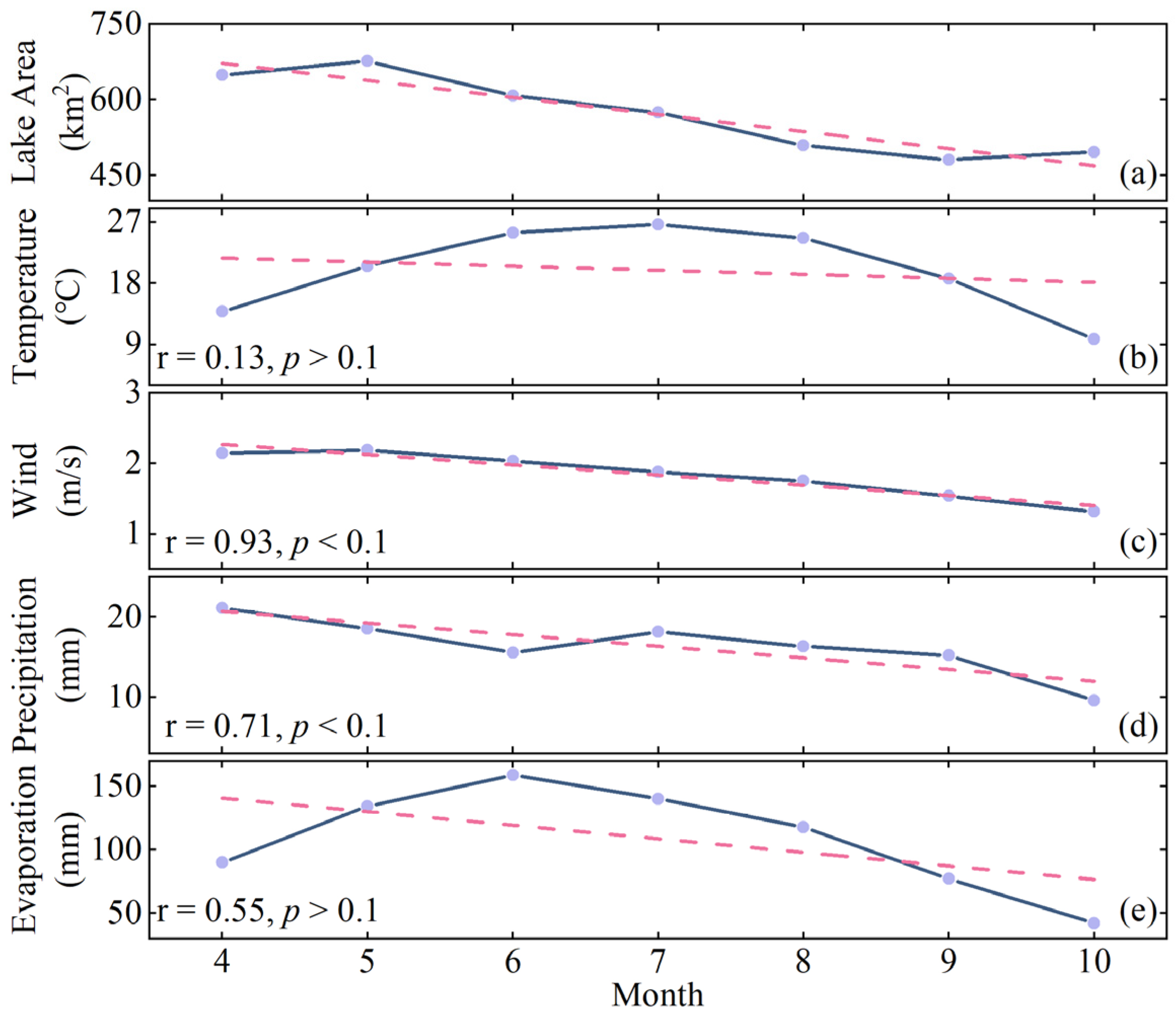
3.2.3. Inner-Annual Variations
3.3. Driving Factors
3.3.1. Drivers of Inter-Annual Variations
3.3.2. Drivers of Inner-Annual Variations
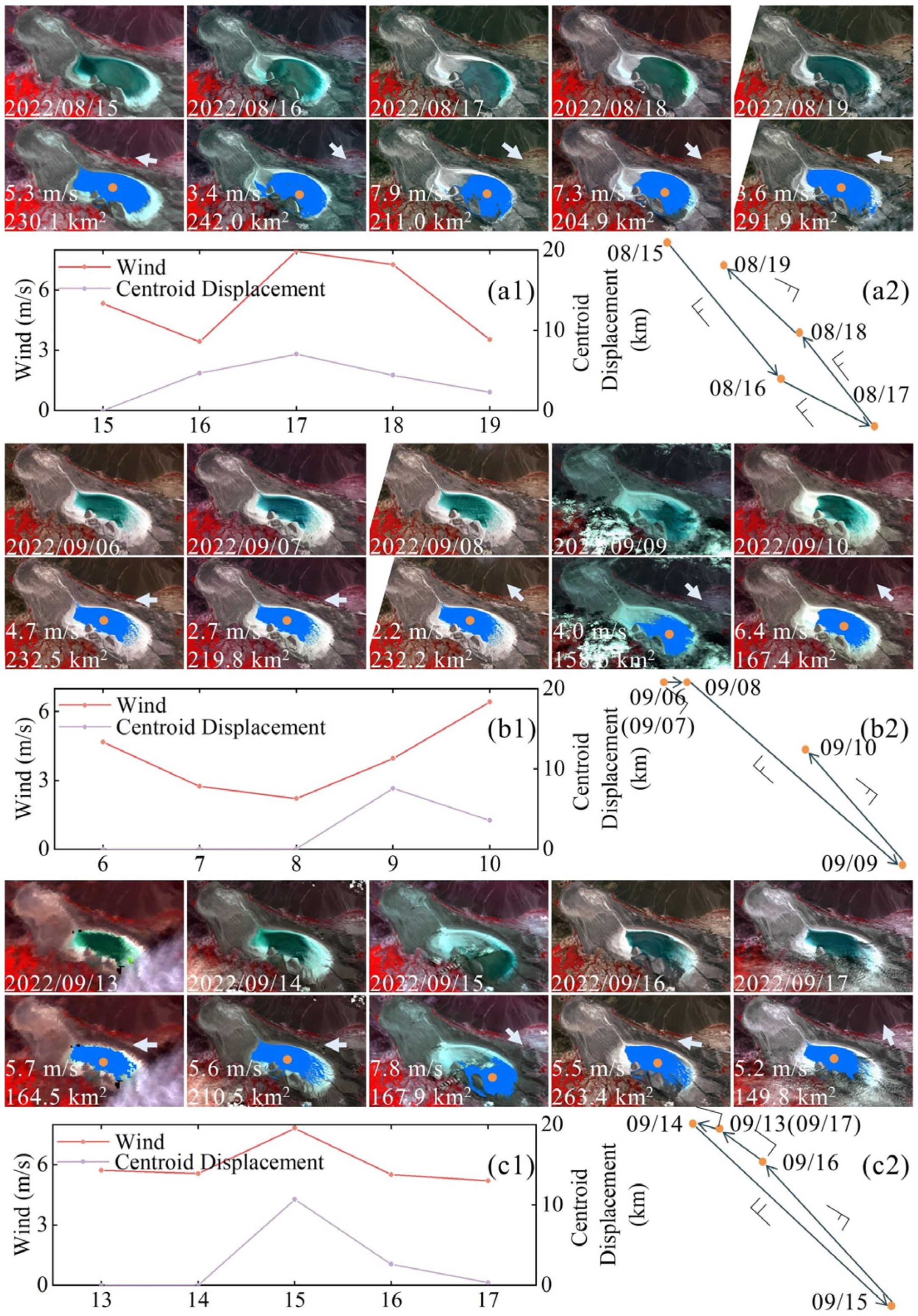
3.3.3. Drivers of Diurnal Variations
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Water Index and Limitations of Otsu Method
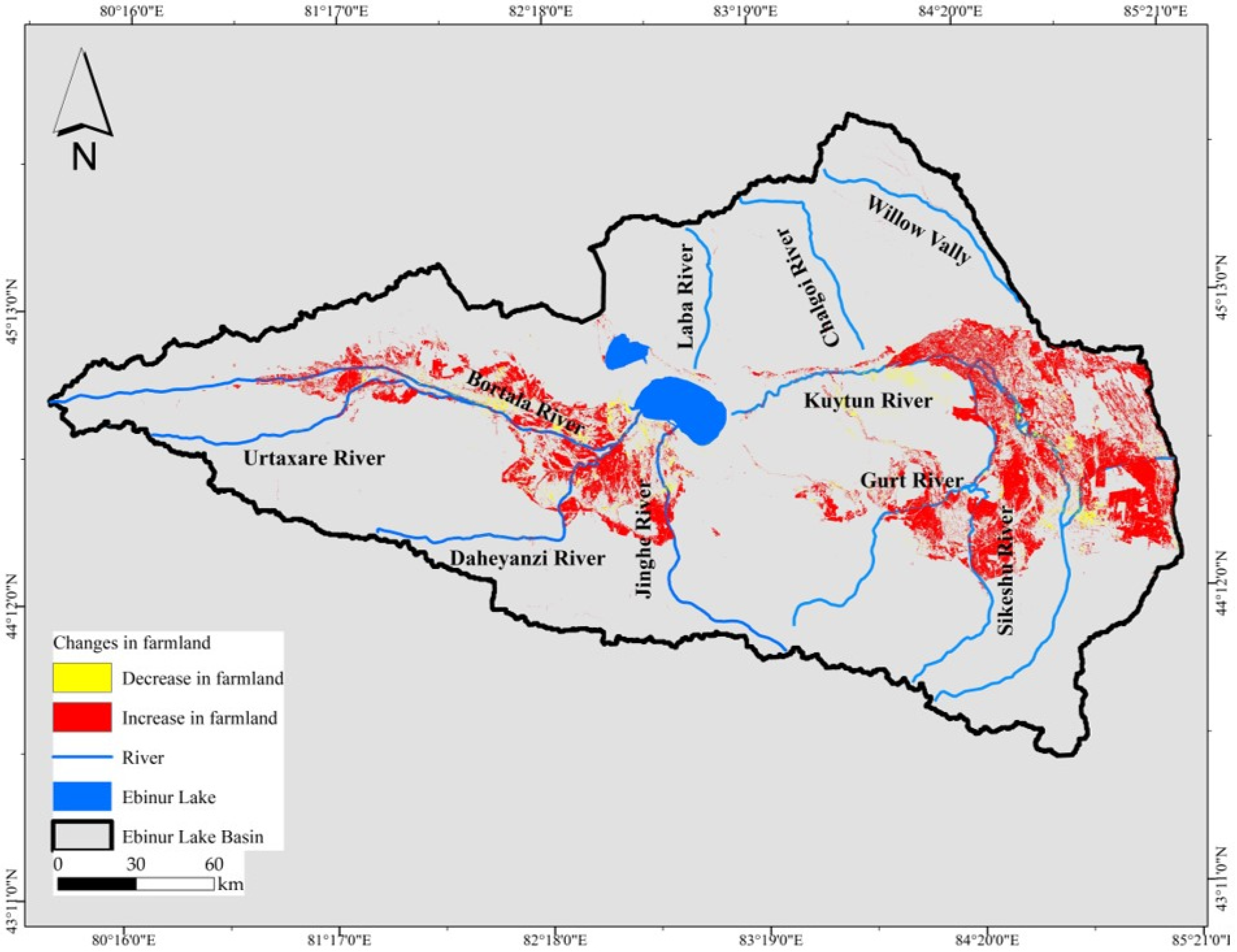
4.2. Runoff Changes Affected by Natural Factors and Policy
4.3. Climate Dominates Seasonal Changes
4.4. Wind Dominates the Daily Dynamic Changes of the Water Body in Ebinur Lake
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, J.B.; Melton, F.; Middleton, E.; Hain, C.; Anderson, M.; Allen, R.; McCabe, M.F.; Hook, S.; Baldocchi, D.; Townsend, P.A. The future of evapotranspiration: Global requirements for ecosystem functioning, carbon and climate feedbacks, agricultural management, and water resources. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 2618–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water management: Current and future challenges and research directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, L.; Huang, B.; Michishita, R.; Xu, B. Dynamic monitoring of the Poyang Lake wetland by integrating Landsat and MODIS observations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Dynamics of the wetland vegetation in large lakes of the Yangtze Plain in response to both fertilizer consumption and climatic changes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 141, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Wang, H. Water body mapping method with HJ-1A/B satellite imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Han, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, L. Monitoring and driving force analysis of spatial and temporal change of water area of Hongjiannao Lake from 1973 to 2019. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 61, 101230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Detecting, extracting, and monitoring surface water from space using optical sensors: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronova, I. Object-based image analysis in wetland research: A review. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6380–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhong, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, A.; Tan, X.; Zhang, L. Large-scale deep learning based binary and semantic change detection in ultra high resolution remote sensing imagery: From benchmark datasets to urban application. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 193, 164–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Roy, D.P.; Crawford, C.J.; Masek, J.G.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B. Current status of Landsat program, science, and applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valman, S.J.; Boyd, D.S.; Carbonneau, P.E.; Johnson, M.F.; Dugdale, S.J. An AI approach to operationalise global daily PlanetScope satellite imagery for river water masking. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 301, 113932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Dong, J.; Menarguez, M.A.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Hooker, K.V.; Hambright, K.D. Continued decrease of open surface water body area in Oklahoma during 1984–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longfei, S.; Zhenxuan, L.; Fei, G.; Min, Y. A review of remote sensing image water extraction. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2021, 33, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jupp, D.L.; Mayo, K.; Kucher, D.; Heggen, S.; Kendall, S.; Radke, B.; Ayling, T. Landsat Based Interpretation of the Cairns Section of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park; CSIRO Division of Water & Land Resources: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Wang, S.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yin, H. Comparison and Analysis of Several Common Water Extraction Methods Based on TM Image. Remote Sens. Inf. 2012, 27, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Baig, M.H.A.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, H.; Tian, J. A Simple Enhanced Water Index (EWI) for Percent Surface Water Estimation Using Landsat Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickens, A.H.; Hansen, M.C.; Hancher, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Potapov, P.; Marroquin, B.; Sherani, Z. Mapping and sampling to characterize global inland water dynamics from 1999 to 2018 with full Landsat time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 243, 111792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.X.; Li, P.; Hu, Y.F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.J.; Li, Z.H. A new algorithm for mapping large inland water bodies using CYGNSS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 45, 1522–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, W.; Deng, Y.; Ling, Z.; Deng, Y. Long Time Series Water Extent Analysis for SDG 6.6.1 Based on the GEE Platform: A Case Study of Dongting Lake. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yushanjiang, A.; Jing, Y. Assessing and predicting changes of the ecosystem service values based on land use/cover change in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Li, G.; Liang, J.; Yu, D.; Aishan, T.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Abulimiti, A.; Liu, J. Dynamic Detection of Water Surface Area of Ebinur Lake using Multi-source Satellite Data (Landsat and Sentinel-1A) and Its Responses to Changing Environment. Catena 2019, 177, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Duan, P.; Jim, C.Y.; Johnson, V.C.; Liu, C.; Chan, N.W.; Tan, M.L.; Kung, H.-T.; Shi, J.; Wang, W. An Advanced Spatiotemporal Fusion Model for Suspended Particulate Matter Monitoring in an Intermontane Lake. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, L.X.; Zhao, L.; Kong, Z.C. Preliminary study on pollen, charcoal records and environmental evolution of Alahake Saline Lake in Xinjiang since 4700 cal yr BP. Quat. Int. 2019, 513, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.J.; Liu, D.W.; Cheng, G.S.; Zhang, G.C.; Wang, L.X. Spatial distribution and genesis of salt on the saline playa at Qehan Lake, Inner Mongolia, China. Catena 2019, 177, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Yu, M.; Lan, T. Research on water information extraction based on MAWEI index. J. Earth Environ. 2019, 10, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, G.; Li, X.; Wu, B.; Wang, X.; Xie, H. An automatic method for delineating lake surfaces in Qaidam Basin using Landsat images. Arid Zone Res. 2022, 39, 774–786. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Luo, X.; Xu, X.; Pan, H.; Tong, X. Evaluation of Landsat 8 OLI imagery for unsupervised inland water extraction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1826–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Li, W.; Zhou, D.; Tian, L.; Ling, F.; Wang, H.; Gui, Y.; Sun, B. Analysis of Landsat-8 OLI imagery for land surface water mapping. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D. Analysis of Different Turbid Inland Water Mapping Using Landsat Images. Master’s Thesis, Northwest University, Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.F.; Liu, X.D.; Wang, Z.H.; Huang, G.H.; Shu, R. Classification of Laser Footprint Based on Random Forest in Mountainous Area Using GLAS Full-Waveform Features. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2284–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Busker, T.; de Roo, A.; Gelati, E.; Schwatke, C.; Adamovic, M.; Bisselink, B.; Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A. A global lake and reservoir volume analysis using a surface water dataset and satellite altimetry. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 669–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.J.; Patel, P.L.; Jothiprakash, V. Impact of rainfall variability and anthropogenic activities on streamflow changes and water stress conditions across Tapi Basin in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-f.; Qin, B.-q.; Zhu, G.-w.; Zhu, M.-y.; Wei, L.; Luan, C.-m. Modeling of turbidity dynamics caused by wind-induced waves and current in the Taihu Lake. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2013, 28, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadzadeh, H.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Hosseini, S.M.; Simmons, C.T. Interaction of lake-groundwater levels using cross-correlation analysis: A case study of Lake Urmia Basin, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Yao, J.; Xia, B. Meteorological driving factors effecting the surface area of Ebinur Lake and determining associated trends and shifts. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 994260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, F.; Gambelli, S.; Viviano, G.; Thakuri, S.; Guyennon, N.; D’Agata, C.; Diolaiuti, G.; Smiraglia, C.; Stefani, F.; Bocchiola, D. High alpine ponds shift upwards as average temperatures increase: A case study of the Ortles–Cevedale mountain group (Southern Alps, Italy) over the last 50 years. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 120, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Chen, W.; Zheng, G.; Shum, C.; Yang, K.; Piao, S.; Sheng, Y.; Yi, S.; Li, J. Regional differences of lake evolution across China during 1960s–2015 and its natural and anthropogenic causes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Kummu, M.; Porkka, M.; Döll, P.; Ramankutty, N.; Scanlon, B.R. A global data set of the extent of irrigated land from 1900 to 2005. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1521–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Huang, X.; Mu, H.; Yin, W. Impacts of land-use changes on the lakes across the Yangtze floodplain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3669–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Detection of terminal lake wetland and its landscape dynamics in arid regions: A case study from Ebinur Lake Wetland. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2021, 50, 562. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Tiyip, T.; Johnson, V.C.; Kung, H.T.; Ding, J.L.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, M.; Kelimu, A.; Nurmuhammat, I.; Chan, N.W. The influence of natural and human factors in the shrinking of the Ebinur Lake, Xinjiang, China, during the 1972–2013 period. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Liu, Z.; Wei, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Change of Ebinur Lake Area and Its Response Characteristics of the Runoff Change. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 23, 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Chahan, B.; Pang, C.; Ji, J. Change in Ebinur Lake Area and Its Impact on Eco-environment. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2006, 28, 941–949. [Google Scholar]
- Kilibarda, M.; Tadić, M.P.; Hengl, T.; Luković, J.; Bajat, B. Global geographic and feature space coverage of temperature data in the context of spatio-temporal interpolation. Spat. Stat. 2015, 14, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Potential Evapotranspiration Dataset for China (1901–2023). 2024. Available online: http://loess.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=34595274939620&docid=74 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Luo, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhai, J.; Cao, Z.; Ma, J.; Qi, T.; Shen, M.; Gu, X.; Duan, H. Coordinated dynamics of aquaculture ponds and water eutrophication owing to policy: A case of Jiangsu province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tiyip, T.; Ding, J.; Kung, H.; Johnson, V.C.; Sawut, M.; Tashpolat, N.; Gui, D. Studies on the reflectance spectral features of saline soil along the middle reaches of Tarim River: A case study in Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2743–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y. Segment anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X. Monitoring dynamics and driving forces of lake changes in different seasons in Xinjiang using multi-source remote sensing. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 51, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Recent Lake Area Changes in Central Asia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P.; De Jong, S.; Bierkens, M. Large-scale monitoring of snow cover and runoff simulation in Himalayan river basins using remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Tang, J.; Song, X.-P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, Y. Anthropogenic transformation of Yangtze Plain freshwater lakes: Patterns, drivers and impacts. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wu, B.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, N. A trade-off method between environment restoration and human water consumption: A case study in Ebinur Lake. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Gun, Z. What Drive Regional Changes in the Number and Surface Area of Lakes Across the Yangtze River Basin During 2000–2019: Human or Climatic Factors? Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Jia, Q.; Mamat, A.; Guan, H. Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data for Lake Change Detection in Xinjiang, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G.; Li, Z. Changes in Central Asia’s water tower: Past, present and future. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuduwaili, J.; Gabchenko, M.V.; Junrong, X. Eolian transport of salts—A case study in the area of Lake Ebinur (Xinjiang, Northwest China). J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Water | Non-Water | |
|---|---|---|
| Predicted water | True Positive (TP) | False Negative (FN) |
| Predicted non-water | False Positive (FP) | True Negative (TN) |
| Water Index | OA (%) | Kappa | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDWI | 98.42 | 0.94 | 98.82 | 90.83 | 0.95 |
| MNDWI | 92.33 | 0.75 | 67.48 | 97.86 | 0.8 |
| AWEIsh | 83.83 | 0.58 | 50.92 | 97.86 | 0.67 |
| AWEInsh | 84.67 | 0.59 | 51.32 | 98.39 | 0.68 |
| MAWEI | 39.17 | 0.09 | 19.47 | 91.95 | 0.32 |
| LWDM | 94.17 | 0.81 | 73.53 | 97.86 | 0.84 |
| Satellites | Date | OA (%) | Kappa | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score | Category | Confusion Matrix | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Non-water | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | OA (%) | Kappa | F1 Score | ||||||||
| L5 TM | 1994/05/09 | 95.83 | 0.85 | 80.90 | 95.69 | 0.87 | Water | 395 | 43 | 88.20 | 88.40 | 95.17 | 0.86 | 0.89 |
| 1996/10/21 | 96.17 | 0.88 | 84.56 | 98.29 | 0.90 | |||||||||
| 2009/05/02 | 96.83 | 0.89 | 94.28 | 88.39 | 0.91 | Non-water | 53 | 1909 | 88.16 | 90.18 | ||||
| 2010/06/06 | 95.17 | 0.83 | 94.84 | 79.31 | 0.86 | |||||||||
| L7 ETM+ | 2000/06/18 | 98.83 | 0.96 | 98.65 | 96.71 | 0.97 | Water | 548 | 45 | 94.30 | 92.40 | 96.75 | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| 2001/05/20 | 96.17 | 0.89 | 95.56 | 88.35 | 0.91 | |||||||||
| 2008/04/21 | 96.67 | 0.92 | 96.31 | 93.36 | 0.94 | Non-water | 33 | 1774 | 94.32 | 92.41 | ||||
| 2015/08/15 | 95.33 | 0.83 | 83.17 | 89.89 | 0.86 | |||||||||
| L8 OLI | 2015/09/24 | 95.83 | 0.85 | 82.24 | 93.61 | 0.87 | Water | 469 | 27 | 88.5 | 94.6 | 96.36 | 0.89 | 0.91 |
| 2016/08/09 | 95.49 | 0.87 | 99.20 | 92.90 | 0.90 | |||||||||
| 2018/08/31 | 97.50 | 0.92 | 93.22 | 94.1 | 0.93 | Non-water | 61 | 1843 | 88.49 | 94.56 | ||||
| 2019/07/01 | 96.50 | 0.90 | 89.17 | 97.22 | 0.93 | |||||||||
| Overall | 90.57 | 92.46 | 96.36 | 0.89 | 91.51 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Si, Y.; Qi, T.; Duan, H.; Shen, M. Dynamic Changes and Driving Factors in the Surface Area of Ebinur Lake over the Past Three Decades. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203876
Liu Y, Wang Q, Wang D, Si Y, Qi T, Duan H, Shen M. Dynamic Changes and Driving Factors in the Surface Area of Ebinur Lake over the Past Three Decades. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(20):3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203876
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuan, Qingyu Wang, Dian Wang, Yunrui Si, Tianci Qi, Hongtao Duan, and Ming Shen. 2024. "Dynamic Changes and Driving Factors in the Surface Area of Ebinur Lake over the Past Three Decades" Remote Sensing 16, no. 20: 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203876
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, D., Si, Y., Qi, T., Duan, H., & Shen, M. (2024). Dynamic Changes and Driving Factors in the Surface Area of Ebinur Lake over the Past Three Decades. Remote Sensing, 16(20), 3876. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203876









