Precise City-Scale Urban Water Body Semantic Segmentation and Open-Source Sampleset Construction Based on Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing: A Case Study in Chengdu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Production of CDUWD
- (1)
- Water bodies smaller than 50 pixels in the image are not annotated.
- (2)
- Dry riverbeds, waterless ditches, and ditches where the presence of water is difficult to determine by the naked eye are not annotated.
- (3)
- Ponds, artificial reservoirs, water-filled ditches, lakes, rivers, clearly water-logged paddy fields, and wetlands are annotated. To ensure the extracted water bodies maintain accurate shapes, shadowed areas cast by buildings onto the water bodies are also labeled as water bodies.
2.3.2. Data Augmentation
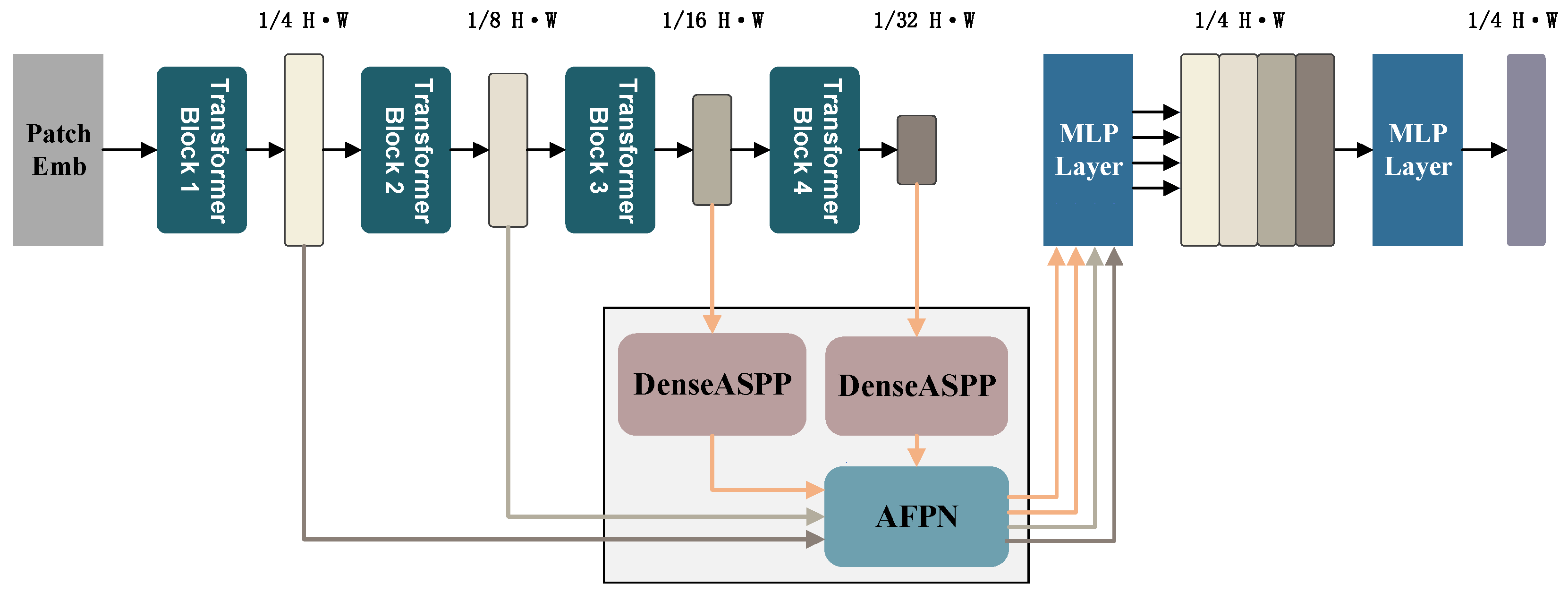
2.3.3. Ad-SegFormer Structure
- (1)
- 3 × 3 atrous convolution layers with different dilation rates (3, 6, 12, 18, 24), which expand the receptive field for multi-scale and long-distance spatial information fusion and feature extraction.
- (2)
- Dense connections between different feature layers to promote feature reuse, improving target edge accuracy and clarity during segmentation.
2.3.4. Evaluation Index
3. Results
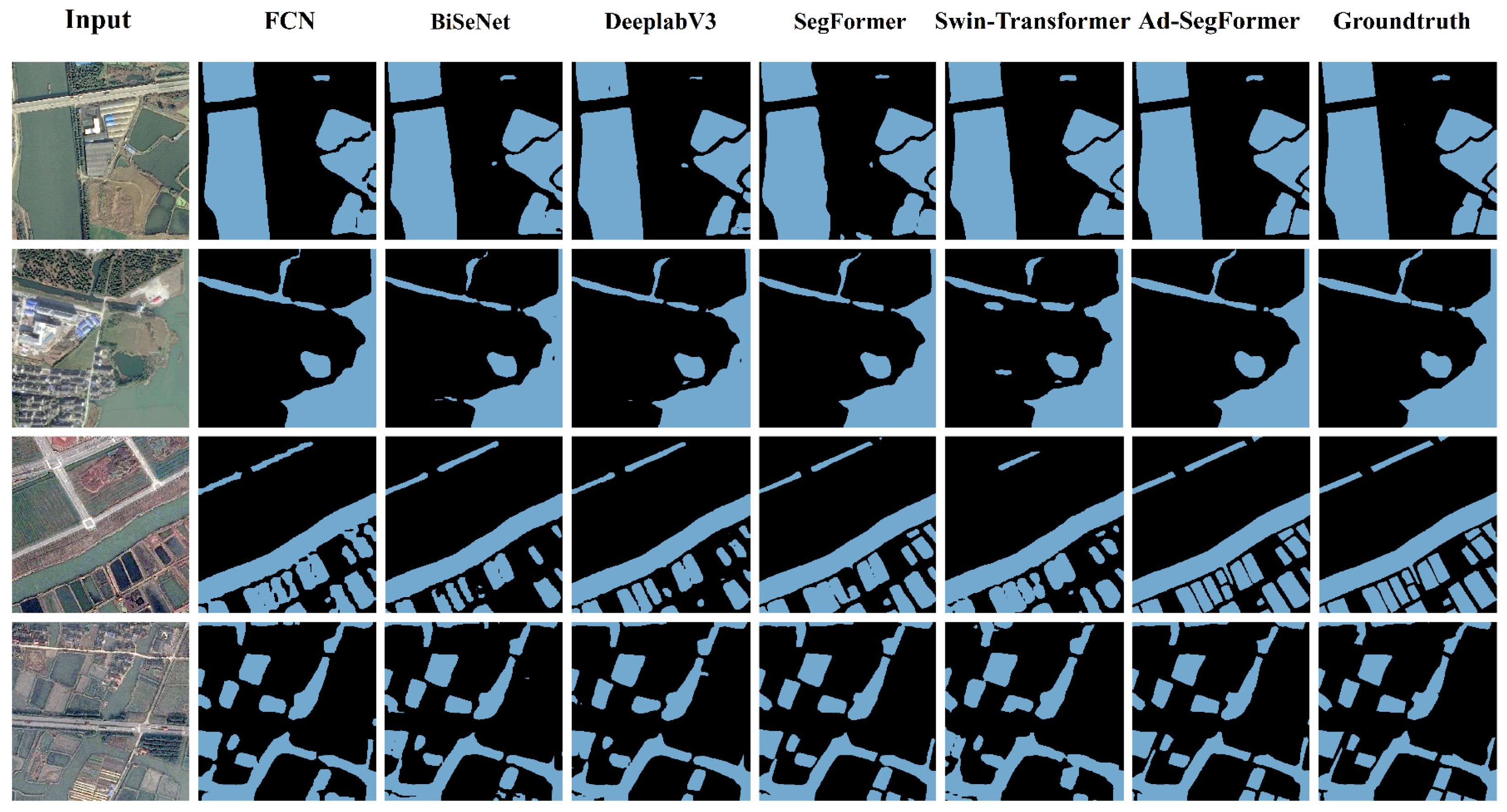
3.1. Comparison of Extraction Results of Different Methods
3.2. Key Parameter Analysis of the Models
3.3. Evaluation of Extraction Performance in CDUWD
3.4. Evaluation of Extraction Performance in on Public Dataset
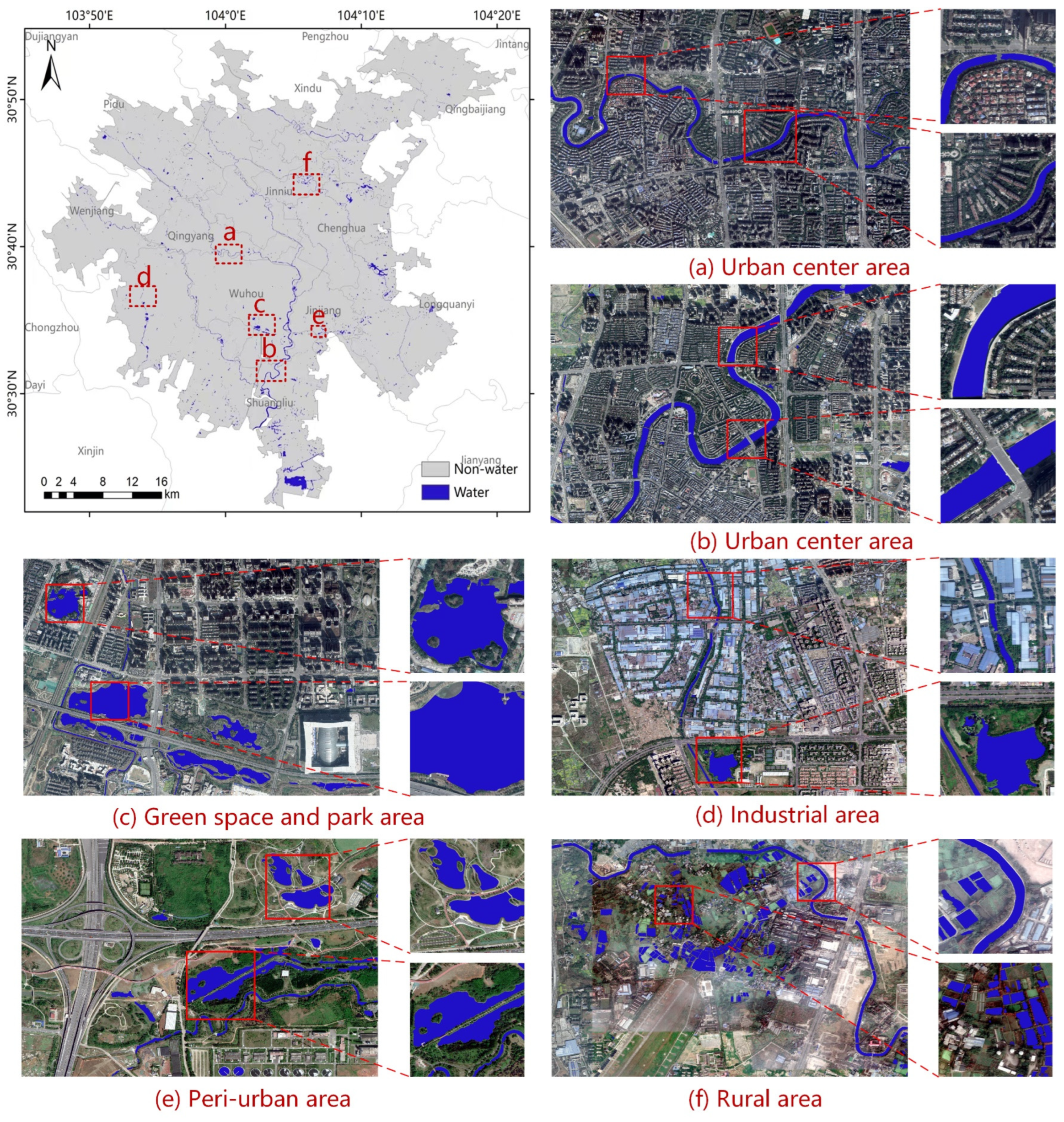
3.5. Mapping of Urban Water Bodies in Chengdu
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages of Transformer Models and Dataset Impact
4.2. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fletcher, T.D.; Andrieu, H.; Hamel, P. Understanding, Management and Modelling of Urban Hydrology and Its Consequences for Receiving Waters: A State of the Art. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, X.; Van De Voorde, T.; Roberts, D.; Jiang, H.; Xu, W. Open Water Detection in Urban Environments Using High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, C.; Fang, X.; Zhang, L. Combining Pixel- and Object-Based Machine Learning for Identification of Water-Body Types from Urban High-Resolution Remote-Sensing Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2097–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Guo, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, H. Investigating Water Variation of Lakes in Tibetan Plateau Using Remote Sensed Data over the Past 20 Years. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2557–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, J.; Shen, Z.; Hu, X.; Yang, H. Multiscale Water Body Extraction in Urban Environments from Satellite Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4301–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, U. Object-Based Water Body Extraction Model Using Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 50, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Cheng, L.; Huang, C.; Qin, S.; Fu, C.; Li, S. Extracting Urban Water Bodies from Landsat Imagery Based on mNDWI and HSV Transformation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tang, Z.; Li, J.; Lv, J.; Chen, Z.; Jia, K. Spatio-Temporal Change of Lake Water Extent in Wuhan Urban Agglomeration Based on Landsat Images from 1987 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The Use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the Delineation of Open Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. NDWI—A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolund, P.; Hunhammar, S. Ecosystem Services in Urban Areas. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, J. Green Infrastructure for Cities: The Spatial Dimension. In Cities of the Future: Towards Integrated Sustainable Water and Landscape Management; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nassauer, J.I. Messy Ecosystems, Orderly Frames. Landsc. J. 1995, 14, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S. The Restorative Benefits of Nature: Toward an Integrative Framework. J. Environ. Psychol. 1995, 15, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.S.; Simons, R.F.; Losito, B.D.; Fiorito, E.; Miles, M.A.; Zelson, M. Stress Recovery during Exposure to Natural and Urban Environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 1991, 11, 201–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senaras, C.; Gedik, E.; Yardimci, Y. A Novel Dynamic Thresholding and Categorizing Approach to Extract Water Objects from VHR Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 4934–4937. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B. Urban Surface Water Mapping from VHR Images Based on Superpixel Segmentation and Target Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 5339–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1411.4038. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. BiSeNet: Bilateral Segmentation Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.00897. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. ISBN 978-3-319-24573-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yan, Z.; Shen, Q.; Cheng, G.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B. Water Body Extraction from Very High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Data Based on Fully Convolutional Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J.; Shi, C.; Hu, W. Urban Water Extraction with UAV High-Resolution Remote Sensing Data Based on an Improved U-Net Model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Hu, F.; Meng, L. Multiscale Features Supported DeepLabV3+ Optimization Scheme for Accurate Water Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 155787–155804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. Aerial-BiSeNet: A Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Network for High Resolution Aerial Imagery. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, L.; Niu, J.; Liu, X.; Wei, L.; Tian, Q. Visformer: The Vision-Friendly Transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.12533. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.14030. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Yu, C.; Huang, H.; Yue, X.; Zhou, B.; Ni, M. WaterSegformer: A Lightweight Model for Water Body Information Extraction from Remote Sensing Images. IET Image Process. 2023, 17, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, G.; Xie, T.; Wu, Z. MST-UNet: A Modified Swin Transformer for Water Bodies’ Mapping Using Sentinel-2 Images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2023, 17, 026507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ning, X.; Shao, Z.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal Pattern Analysis of China’s Cities Based on High-Resolution Imagery from 2000 to 2015. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lei, J.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Feng, Z.; Liang, R. AFPN: Asymptotic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Honolulu, Oahu, HI, USA, 1–4 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1608.06993. [Google Scholar]



| Dataset | CDUWD-1 | CDUWD-2 | CDUWD-3 | CDUWD-4 | CDUWD-5 | CDUWD-6 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Mask |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Count (1024 × 1024) | 192 | 162 | 288 | 78 | 57 | 173 | |||||
| Percentage (%) | 20.2 | 17.1 | 30.3 | 8.2 | 6.0 | 18.2 | |||||
| Precision | Recall | IoU | F1-Score | Backbone | Flops (GFLOPs) | Parameter (M) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | 87.22 | 90.88 | 80.20 | 89.01 | Resnet50 | 791.90 | 49.48 |
| BiSeNet | 86.99 | 94.04 | 82.44 | 90.37 | Resnet50 | 396.31 | 59.24 |
| DeepLabV3 | 89.72 | 93.96 | 84.83 | 91.79 | Resnet50 | 1079.74 | 68.10 |
| SegFormer | 96.02 | 95.44 | 94.77 | 95.73 | mit-b3 | 286.30 | 47.24 |
| Swin Transformer | 97.92 | 98.40 | 96.39 | 98.16 | tiny | 798.73 | 59.83 |
| Ad-SegFormer | 96.25 | 96.60 | 95.59 | 96.42 | mit-b3 | 303.99 | 52.48 |
| Factors | Choices | Explanations |
|---|---|---|
| Data size | ds1 | 1024 × 1024 pixels (including 760 training samples and 190 validation samples) |
| ds2 | 512 × 512 pixels (including 3040 training samples and 760 validation samples) | |
| Data augmentation | da1 | None |
| da2 | Random horizontal flip of 0.2–2.0 ration, random crop (1024 × 1024/512 × 512), fill (1024 × 1024/512 × 512) |
| Combination | Precision | Recall | IoU | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g1 | ds1-da1 | 96.24 | 96.60 | 95.59 | 96.42 |
| g2 | ds1-da2 | 97.45 | 96.27 | 96.18 | 96.86 |
| g3 | ds2-da1 | 96.93 | 96.88 | 96.16 | 96.90 |
| g4 | ds2-da2 | 97.30 | 97.11 | 94.57 | 97.21 |
| Subset of the Dataset | Type of Water Body | Overall Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| CDUWD-1 | main rivers | 98.09% |
| CDUWD-2 | small rivers | 97.61% |
| CDUWD-3 | lakes | 98.98% |
| CDUWD-4 | small water | 98.12% |
| CDUWD-5 | others water | 99.16% |
| CDUWD-6 | non-water | 99.86% |
| Precision | Recall | IoU | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | 94.13 | 87.39 | 82.9 | 90.28 |
| BiSeNet | 94.85 | 92.3 | 88.09 | 93.51 |
| DeepLabV3 | 94.33 | 85.85 | 81.46 | 89.33 |
| SegFormer | 93.64 | 92.63 | 87.36 | 93.12 |
| Swin Transformer | 95.35 | 92.53 | 88.68 | 93.86 |
| Ad-SegFormer | 95.22 | 93.42 | 89.41 | 94.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, X.; Zhu, Q.; Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhao, B.; Shen, Z. Precise City-Scale Urban Water Body Semantic Segmentation and Open-Source Sampleset Construction Based on Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing: A Case Study in Chengdu. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203873
Cheng X, Zhu Q, Song Y, Yang J, Wang T, Zhao B, Shen Z. Precise City-Scale Urban Water Body Semantic Segmentation and Open-Source Sampleset Construction Based on Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing: A Case Study in Chengdu. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(20):3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203873
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Xi, Qian Zhu, Yujian Song, Jieyu Yang, Tingting Wang, Bin Zhao, and Zhanfeng Shen. 2024. "Precise City-Scale Urban Water Body Semantic Segmentation and Open-Source Sampleset Construction Based on Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing: A Case Study in Chengdu" Remote Sensing 16, no. 20: 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203873
APA StyleCheng, X., Zhu, Q., Song, Y., Yang, J., Wang, T., Zhao, B., & Shen, Z. (2024). Precise City-Scale Urban Water Body Semantic Segmentation and Open-Source Sampleset Construction Based on Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing: A Case Study in Chengdu. Remote Sensing, 16(20), 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16203873







