A New Method for Top-Down Inversion Estimation of Carbon Dioxide Flux Based on Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Processing
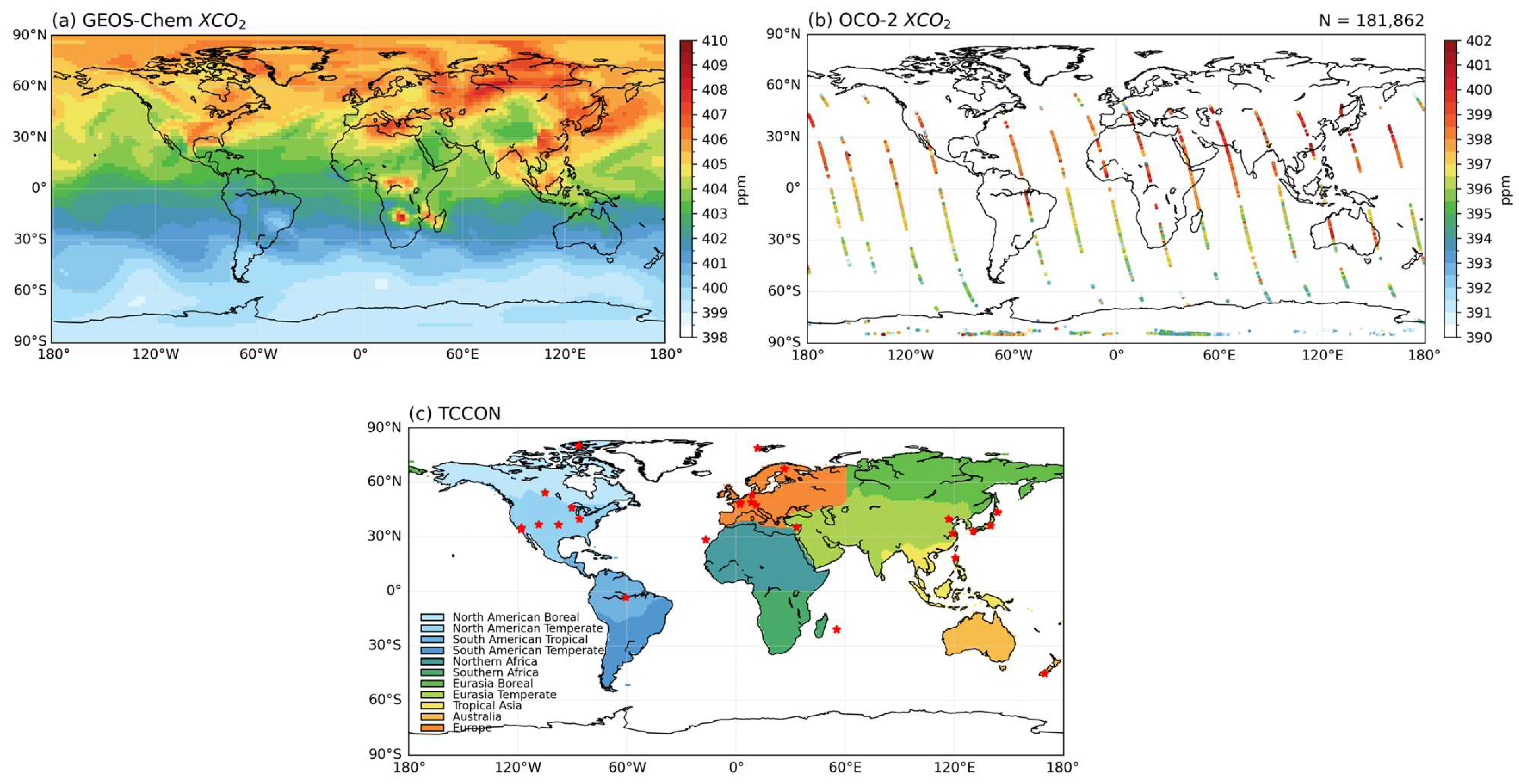
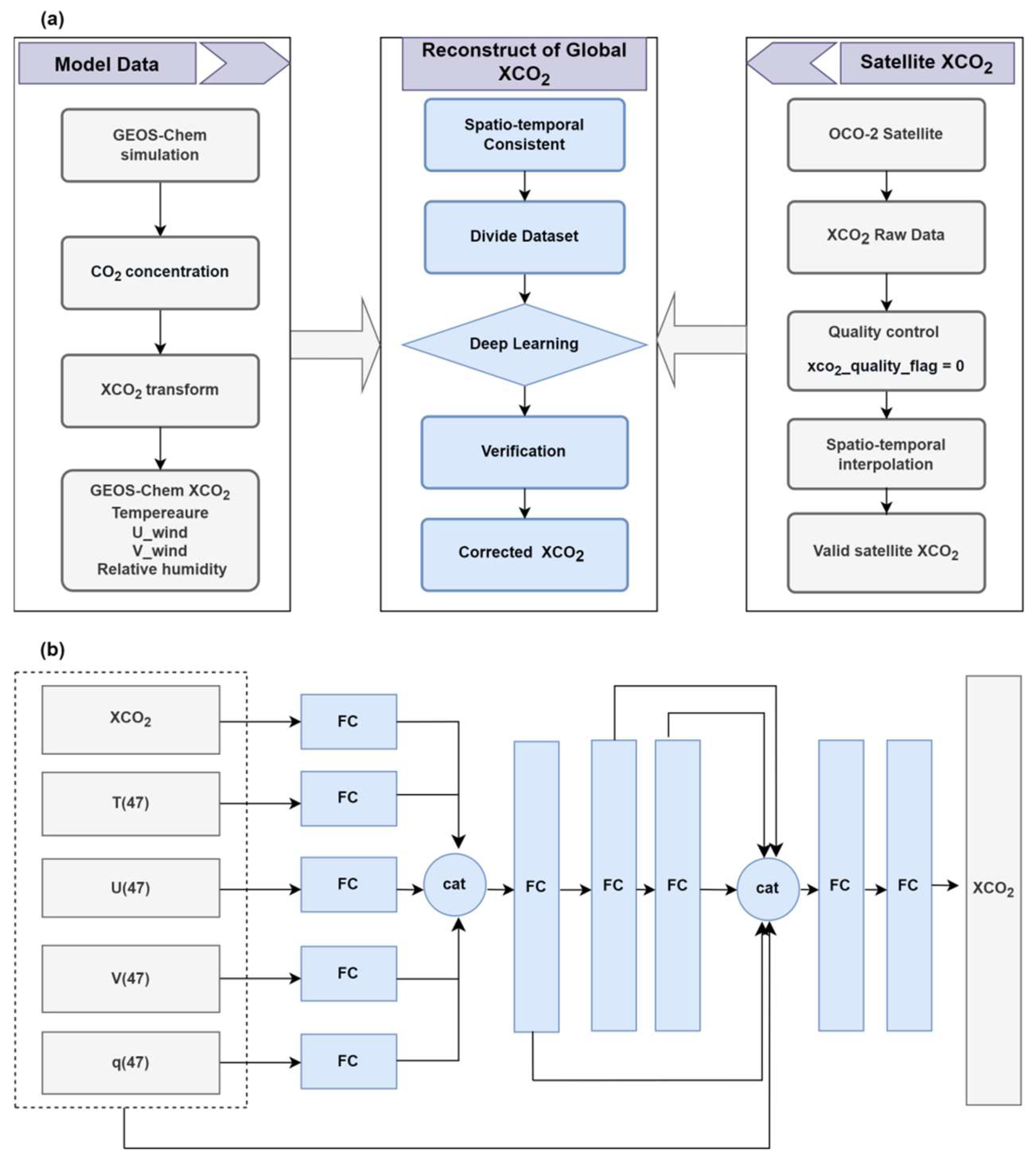
2.1.1. Chemical Transport Model Simulation Data
2.1.2. Satellite Data
2.1.3. Ground-Based CO2 Measurements
2.1.4. Carbon Inversion Productions
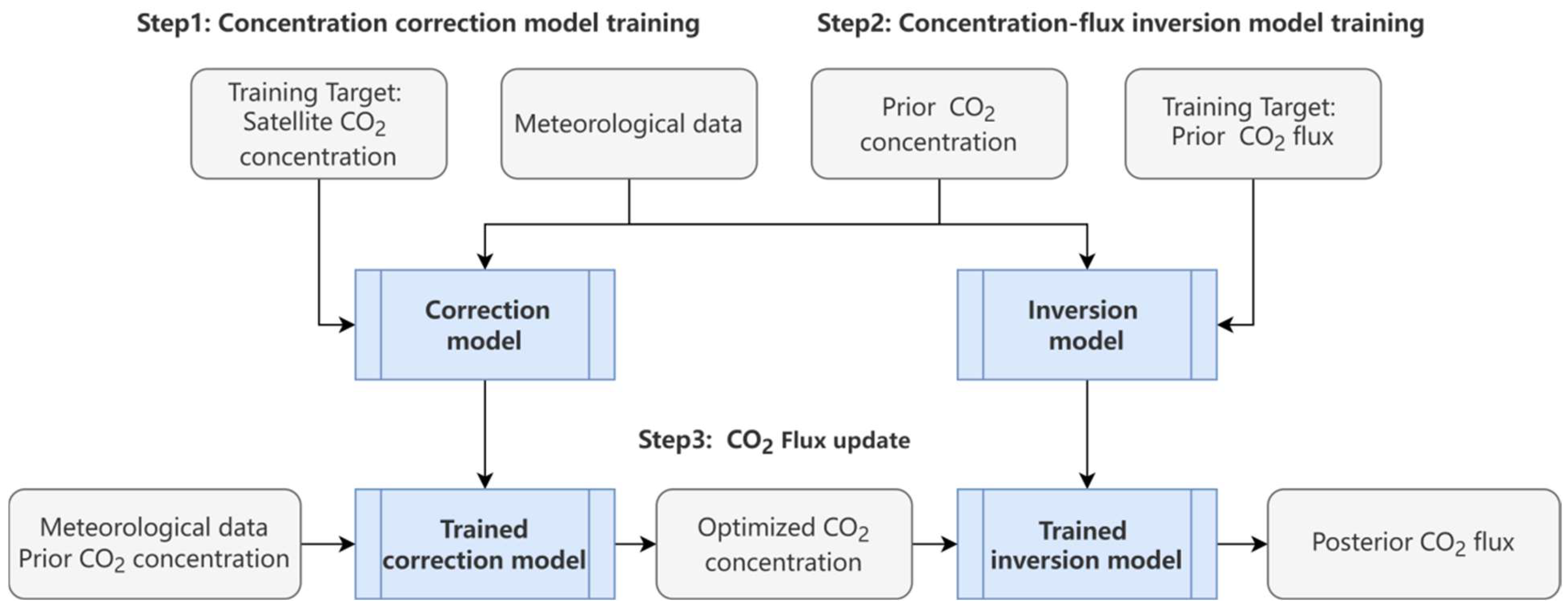
2.2. Deep Learning Model
2.2.1. Main Framework
2.2.2. Concentration Correction Model
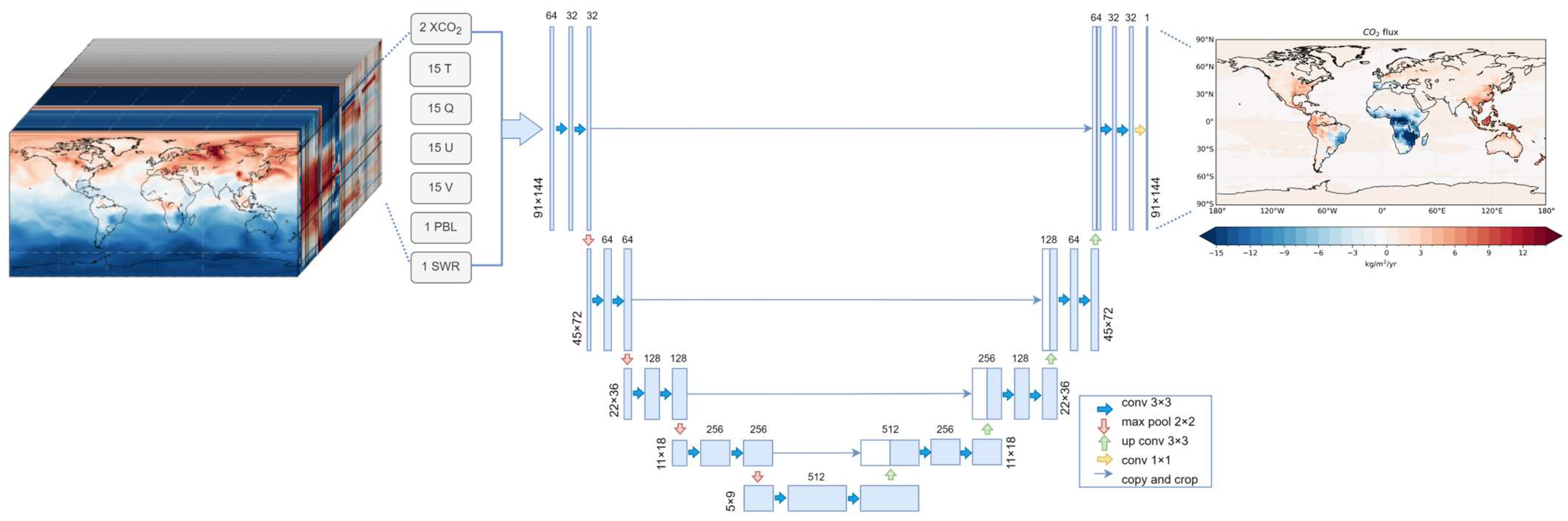
2.2.3. Concentration–Flux Inversion Model
3. Results
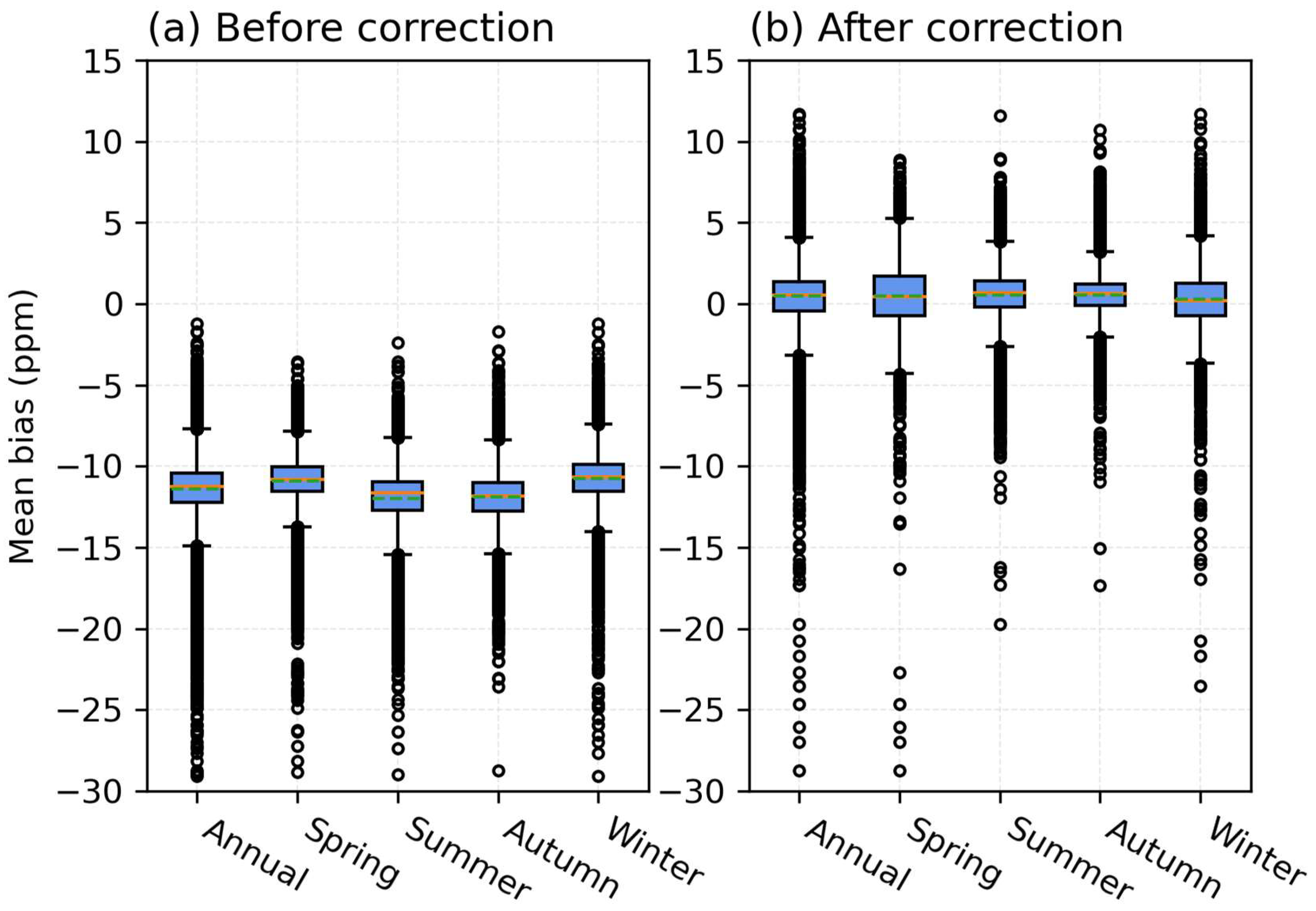
3.1. Performance of Concentration Correction Model
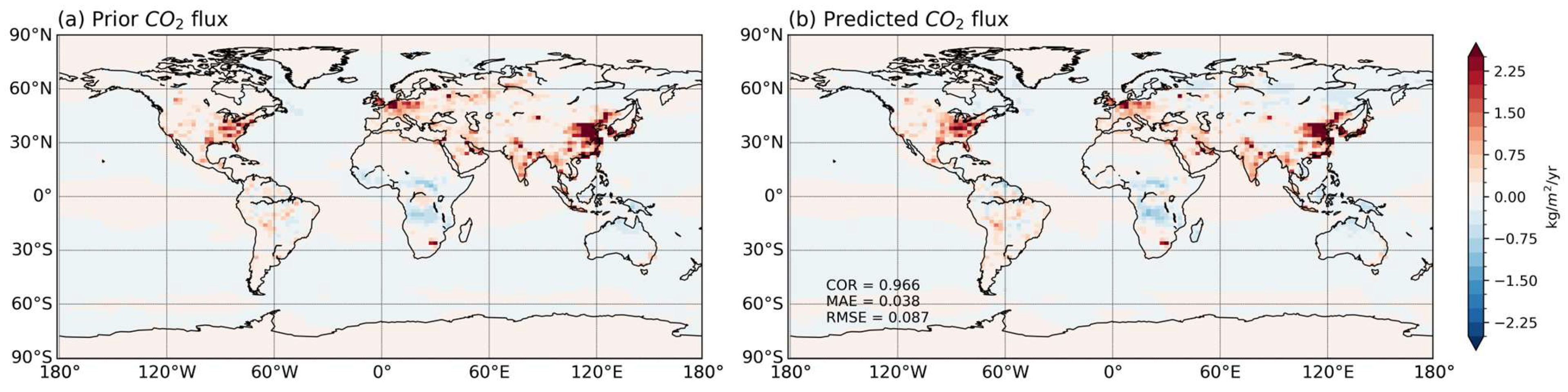
3.2. Performance of the Concentration–Flux Inversion Model
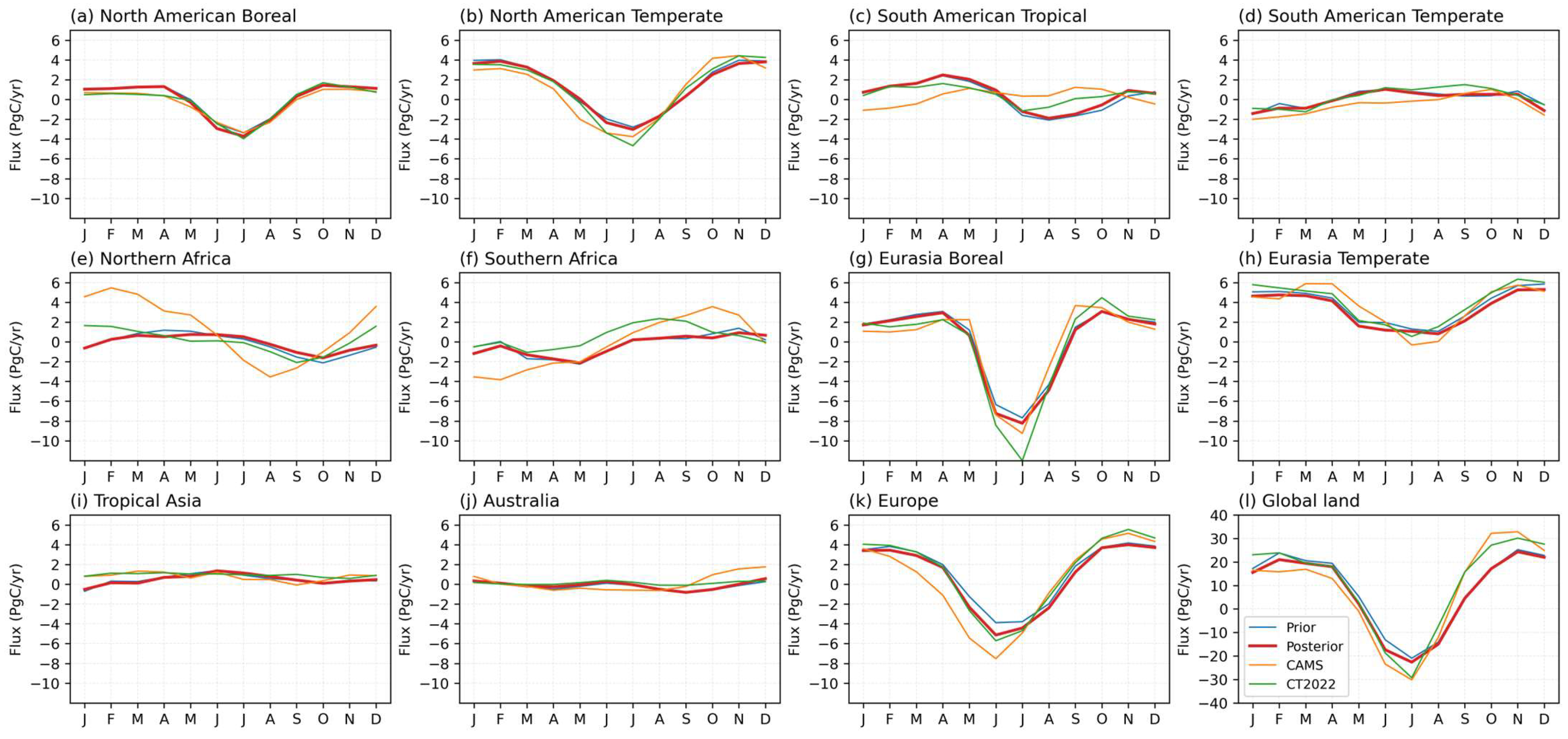
3.3. Surface CO2 Flux Updating and Analysis
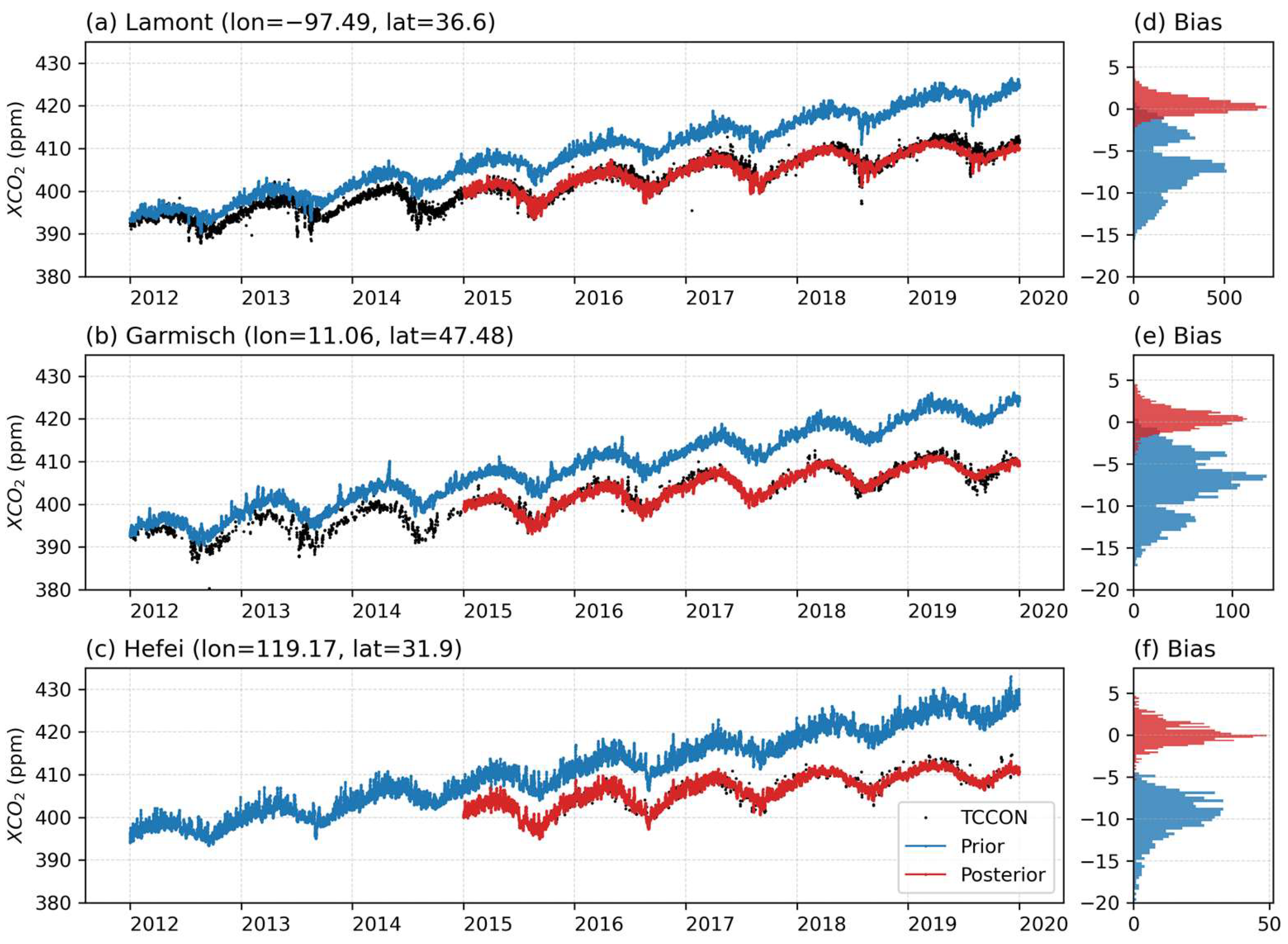
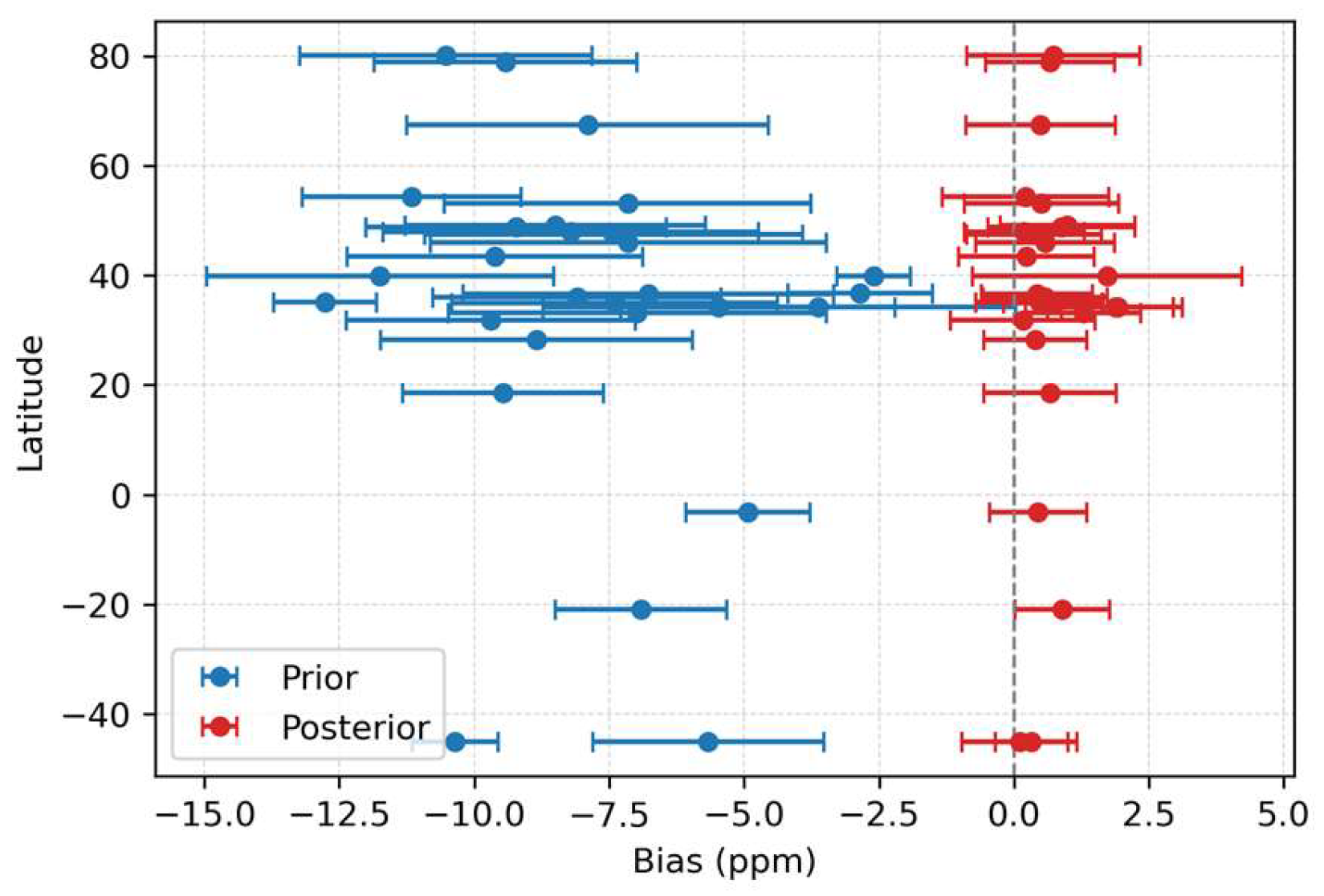
3.3.1. CO2 Concentration Updating
3.3.2. Surface Total CO2 Flux Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UNFCCC. Adoption of the Paris Agreement; United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change; UN: Paris, France, 2015; Available online: https://unfccc.int/resource/docs/2015/cop21/eng/l09r01.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2023).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, R.; Hu, L.; Hu, X.; Fang, X. Knowledge gaps are making it harder to formulate national climate policies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2218563120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Guan, D.; Wei, W.; Davis, S.; Ciais, P.; Bai, J.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Klaus, H.; Marland, G.; et al. Reduced carbon emission estimates from fossil fuel combustion and cement production in China. Nature 2015, 524, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsbakken, J.I.; Peters, G.P.; Andrew, R.M. Uncertainties around reductions in China’s coal use and CO2 emissions. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. Estimation of China’s terrestrial ecosystem carbon sink: Methods, progress and prospects. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, L.; Palmer, P.I.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.; Tang, X.; Yang, D.; Liu, L.; Xia, C. Large Chinese land carbon sink estimated from atmospheric carbon dioxide data. Nature 2020, 586, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, X.; Chen, J.M.; Chen, Z.; Dan, B.; Yi, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, G. A global carbon assimilation system using a modified ensemble Kalman filter. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.M.; Ju, W.; Tian, X.; Feng, S.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; et al. Regional CO2 fluxes from 2010 to 2015 inferred from GOSAT XCO2 retrievals using a new version of the Global Carbon Assimilation System. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 1963–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Xie, Z.; Cai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, H. The Chinese carbon cycle data-assimilation system (Tan-Tracker). Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürmann, G.J.; Kaminski, T.; Köstler, C.; Carvalhais, N.; Voßbeck, M.; Kattge, J.; Giering, R.; Rödenbeck, C.; Heimann, M.; Zaehle, S. Constraining a land-surface model with multiple observations by application of the MPI-Carbon Cycle Data Assimilation System V1.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 2999–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Chen, B.Z.; van der Laan-Luijkx, I.T.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Yan, J.W.; Zhou, L.X.; Fukuyama, Y.; Tans, P.P.; Peters, W. Net terrestrial CO2 exchange over China during 2001–2010 estimated with an ensemble data assimilation system for atmospheric CO2. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3500–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijkx, I.; Velde, I.; Veen, E.; Tsuruta, A.; Stanisławska, K.; Babenhauserheide, A.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Chen, H.; et al. The CarbonTracker Data Assimilation Shell (CTDAS) v1.0: Implementation and global carbon balance 2001–2015. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 2785–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.; Krol, M.; Werf, G.; Houweling, S.; Jones, C.; Hughes, J.; Schaefer, K.; Masarie, K.; Jacobson, A.; Miller, J.; et al. Seven years of recent European net terrestrial carbon dioxide exchange constrained by atmospheric observations. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1317–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.; Jacobson, A.; Sweeney, C.; Andrews, A.; Conway, T.; Masarie, K.; Miller, J.; Bruhwiler, L.; Petron, G.; Hirsch, A.; et al. An atmospheric perspective on North American carbon dioxide exchange: CarbonTracker. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18925–18930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, W.; Miller, J.B.; Whitaker, J.; Denning, A.S.; Hirsch, A.; Krol, M.C.; Zupanski, D.; Bruhwiler, L.; Tans, P.P. An ensemble data assimilation system to estimate CO2 surface fluxes from atmospheric trace gas observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D24304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Maki, T.; Patra, P.; Nakazawa, T. Assessing the impact of satellite, aircraft, and surface observations on CO2 flux estimation using an ensemble-based 4-D data assimilation system. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D16306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. Global and regional carbon budget for 2015–2020 inferred from OCO-2 based on an ensemble Kalman filter coupled with GEOS-Chem. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 10769–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, H.; Shen, F.; Ahmad, S.; Li, Z. Carbon Emissions Estimation and Spatiotemporal Analysis of China at City Level Based on Multi-Dimensional Data and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Q.; Zhu, L. Calculation of CO2 Emissions from China at Regional Scales Using Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, G. Mapping contiguous XCO2 by machine learning and analyzing the spatio-temporal variation in China from 2003 to 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Wu, J. Deriving gapless CO2 concentrations using a geographically weighted neural network: China, 2014–2020. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, W.; Sun, Q. Satellite-Based Reconstruction of Atmospheric CO2 Concentration over China Using a Hybrid CNN and Spatiotemporal Kriging Model. Remote Sensing 2024, 16, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, Z.; Xing, J.; Zhang, J.; Bian, J.; Li, S.; Sahu, S.K.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.Y. Exploring deep learning for air pollutant emission estimation. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 4641–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Fu, T.-M.; Cao, H.; Tian, H.; Fan, Q.; Chen, X. Neural network predictions of pollutant emissions from open burning of crop residues: Application to air quality forecasts in southern China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 204, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fung, J.C.H.; Yuan, D.; Chen, W.; Fung, T.; Lu, X. Development of an integrated machine-learning and data assimilation framework for NOx emission inversion. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bey, I.; Jacob, D.; Yantosca, R.; Logan, J.; Field, B.; Fiore, A.; Li, Q.-B.; Liu, H.; Mickley, L.; Schultz, M. Global Modeling of Tropospheric Chemistry with Assimilated Meteorology: Model Description and Evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 23073–23095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.; Jones, D.; Kulawik, S.; Worden, J.; Bowman, K.; Andres, R.; Suntharalingam, P.; Chen, J.; Brenninkmeijer, C.; Schuck, T.; et al. Inverse modeling of CO2 sources and sinks using satellite observations of CO2 from TES and surface flask measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6029–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A very high-resolution (1 km×1 km) global fossil fuel CO2 emission inventory derived using a point source database and satellite observations of nighttime lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S.; Andres, R.J. The Open-source Data Inventory for Anthropogenic CO2, version 2016 (ODIAC2016): A global monthly fossil fuel CO2 gridded emissions data product for tracer transport simulations and surface flux inversions. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.; Napier-Linton, L.; Gurney, K.R.; Andres, R.J.; Oda, T.; Vogel, F.R.; Deng, F. Improving the temporal and spatial distribution of CO2 emissions from global fossil fuel emission data sets. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; van Leeuwen, T.T.; Chen, Y.; Rogers, B.M.; Mu, M.; van Marle, M.J.E.; Morton, D.C.; Collatz, G.J.; et al. Global fire emissions estimates during 1997–2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Ichoku, C.; Chin, M.; Bian, H.; Darmenov, A.; Colarco, P.; Ellison, L.; Kucsera, T.; da Silva, A.; Wang, J.; et al. Six global biomass burning emission datasets: Intercomparison and application in one global aerosol model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 969–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, Y.; Takatani, Y.; Kojima, A.; Ishii, M. Global trends of ocean CO2 sink and ocean acidification: An observation-based reconstruction of surface ocean inorganic carbon variables. J. Oceanogr. 2021, 77, 323–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, L. GEOS-Carb CASA-GFED 3-Hourly Ecosystem Exchange Fluxes 0.5 Degree x 0.625 Degree V3; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2022.
- Philip, S.; Johnson, M.S.; Potter, C.; Genovesse, V.; Baker, D.F.; Haynes, K.D.; Henze, D.K.; Liu, J.; Poulter, B. Prior biosphere model impact on global terrestrial CO2 fluxes estimated from OCO-2 retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13267–13287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiro, H.; Crowell, S.; Moore Iii, B. Optimizing 4 years of CO2 biospheric fluxes from OCO-2 and in situ data in TM5: Fire emissions from GFED and inferred from MOPITT CO data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 15817–15849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, B.J.; Boesch, H.; Toon, G.; Sen, B.; Miller, C.; Crisp, D. Orbiting Carbon Observatory: Inverse method and prospective error analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D05305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, D.; Atlas, R.M.; Breon, F.M.; Brown, L.R.; Burrows, J.P.; Ciais, P.; Connor, B.J.; Doney, S.C.; Fung, I.Y.; Jacob, D.J.; et al. The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO) mission. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 34, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, J.; Ialongo, I.; Tamminen, J. Direct space-based observations of anthropogenic CO2 emission areas from OCO-2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 11400–11406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Huang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, F. Comparisons of OCO-2 satellite derived XCO2 with in situ and modeled data over global ocean. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Zhang, P.; Bi, Y.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, T.; et al. Retrieval of Global Carbon Dioxide From TanSat Satellite and Comprehensive Validation With TCCON Measurements and Satellite Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, F.; Fisher, M.; Peylin, P.; Serrar, S.; Bousquet, P.; Breon, F.-M.; Chedin, A.; Ciais, P. Inferring CO2 sources and sinks from satellite observations: Method and application to TOVS data. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D24309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.R.; Schuldt, K.N.; Tans, P.; Arlyn, A.; Miller, J.B.; Oda, T.; Mund, J.; Weir, B.; Ott, L.; Aalto, T.; et al. CarbonTracker CT2022; NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory: Boulder, CO, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Tian, X. Constraint of satellite CO2 retrieval on the global carbon cycle from a Chinese atmospheric inversion system. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, F.; Remaud, M.; O’Dell, C.W.; Baker, D.; Peylin, P.; Cozic, A. Objective evaluation of surface- and satellite-driven carbon dioxide atmospheric inversions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14233–14251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Prior CO2 Fluxes | Sources | References |
|---|---|---|
| terrestrial biospheric flux | CASA-GFED version 3 | Ott et al. [36] |
| ocean flux | JMA Ocean CO2 Map | Iida et al. [35] |
| fossil fuel flux | ODIAC version 2022 | Oda et al. [30] |
| biomass burning flux | GFED4.1s | van der Werf et al. [33] |
| Annual | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COR | 0.920 | 0.920 | 0.906 | 0.921 | 0.931 |
| MAE | 0.226 | 0.209 | 0.331 | 0.194 | 0.167 |
| RMSE | 0.899 | 0.842 | 1.235 | 0.796 | 0.719 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, R.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. A New Method for Top-Down Inversion Estimation of Carbon Dioxide Flux Based on Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193694
Wang H, Li D, Zhou R, Hu X, Wang L, Zhang L. A New Method for Top-Down Inversion Estimation of Carbon Dioxide Flux Based on Deep Learning. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(19):3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193694
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hui, Dan Li, Ruilin Zhou, Xiaoyu Hu, Leyi Wang, and Lang Zhang. 2024. "A New Method for Top-Down Inversion Estimation of Carbon Dioxide Flux Based on Deep Learning" Remote Sensing 16, no. 19: 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193694
APA StyleWang, H., Li, D., Zhou, R., Hu, X., Wang, L., & Zhang, L. (2024). A New Method for Top-Down Inversion Estimation of Carbon Dioxide Flux Based on Deep Learning. Remote Sensing, 16(19), 3694. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16193694






