Abstract
Black soil is a precious soil resource, yet it is severely affected by gully erosion, which is one of the most serious manifestations of land degradation. The determination of the location and shape of gullies is crucial for the work of gully erosion control. Traditional field measurement methods consume a large amount of human resources, so it is of great significance to use artificial intelligence techniques to automatically extract gullies from satellite remote sensing images. This study obtained the gully distribution map of the southwestern region of the Dahe Bay Farm in Inner Mongolia through field investigation and measurement and created a gully remote sensing dataset. We designed a multi-scale content structure feature extraction network to analyze remote sensing images and achieve automatic gully extraction. The multi-layer information obtained through the resnet34 network is input into the multi-scale structure extraction module and the multi-scale content extraction module designed by us, respectively, obtained richer intrinsic information about the image. We designed a structure content fusion network to further fuse structural features and content features and improve the depth of the model’s understanding of the image. Finally, we designed a muti-scale feature fusion module to further fuse low-level and high-level information, enhance the comprehensive understanding of the model, and improve the ability to extract gullies. The experimental results show that the multi-scale content structure feature extraction network can effectively avoid the interference of complex backgrounds in satellite remote sensing images. Compared with the classic semantic segmentation models, DeepLabV3+, PSPNet, and UNet, our model achieved the best results in several evaluation metrics, the F1 score, recall rate, and intersection over union (IoU), with an F1 score of 0.745, a recall of 0.777, and an IoU of 0.586. These results proved that our method is a highly automated and reliable method for extracting gullies from satellite remote sensing images, which simplifies the process of gully extraction and provides us with an accurate guide to locate the location of gullies, analyze the shape of gullies, and then provide accurate guidance for gully management.
1. Introduction
Land is a kind of fundamental resource for meeting the needs of human survival. Black soil is a kind of precious soil resource on Earth, referring to soil with a black or dark black humus topsoil layer, which is a kind of high-quality land with good traits, high fertility, and suitability for farming. However, under the influence of over-exploitation and natural factors, the phenomenon of soil quality degradation in black soil resources is very serious. Northeast China, one of the world’s major black soil belts, is facing a very serious soil erosion phenomenon, a typical form of which is gully erosion. Gully erosion is defined as the formation of deep gully terrain by soil loss due to local water accumulation and scour [1,2], and it causes significant damage to agricultural production and ecological sustainability [3,4,5,6], such as soil and water erosion [7], land desertification [8], reduced crop yields [9], and increased risk of landslides [10]. Therefore, accurate monitoring of the location and shape of gully erosion is important for soil and water conservation and also provides an important reference for environmental protection in gully areas.
The monitoring methods for gullies are continuously being updated both domestically and internationally. Traditional methods for gully extraction are mainly based on various field surveys and remote sensing techniques. Field surveys are the traditional and straightforward methods for discovering gullies, collecting erosion information, and assessing the severity of erosion levels, involving the use of tools such as erosion pins or Global Positioning Systems (GPSs). However, for large-scale gully erosion research, they can be time consuming, labor intensive, and full of danger. [11,12]. In contrast, remote sensing technologies, like high-resolution optical remote sensing, have been widely applied in monitoring and disaster early warning due to their advantage of long-distance detection [13,14]. However, the visual interpretation of remote sensing relies too much on experts’ interpretation experience and domain knowledge, requiring a significant amount of human resources, and its speed is too slow to be suitable for large-scale dynamic monitoring [15].
Currently, the work on gully extraction can be divided into three categories: (1) detection of gullies using digital elevation models; (2) object-based image analysis (OBIA); and (3) employing computer vision and deep learning methods to segment out gullies from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or satellite remote sensing imagery.
The method for extracting gullies based on DEM utilizes information that includes representational features such as DEM data, gully morphology, depth, and width to detect gullies. Castillo et al. proposed the normalized terrain method (NorToM) based on the processing of DEM data, which uses a variety of topographic factors (e.g., elevation, slope, and slope direction) to map gully-affected areas [16]. Methods for obtaining DEM include photogrammetry with UAVs [9] and utilizing satellite imagery data [17]. In addition, Chen et al. experimented with DEM and GEI (Google Earth Image) data of different accuracies to reconstruct the terrain of several scenes in the Loess Plateau of China [18]. Lu et al. integrated interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) and relative elevation algorithms (REAs) to develop a method for rapidly mapping gullies, which simplified the workflow of erosion gully extraction [19]. Zeng et al. used Random Forest (RF), Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), and Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM) to simulate landslide susceptibility. The contribution of land use land cover (LULC) and distance from the road to landslide susceptibility was also explored [20]. Wang et al. collected topographic data, geological data, and rain-related data, established corresponding databases, and used several machine learning methods including logistic regression (LR) and support vector machine (SVM) to identify landslide terrain [21].
OBIA-based methods, such as Shahabi et al., conducted gully extraction in the Queensland region of Australia using Sentinel 2A imagery and ALOS 12 m DEM [22]. The results indicated that the use of optimal scale object definition and the application of the ensemble stacking of machine learning (ML) models led to higher accuracy in the detection of the gully network. D’Oleire-Oltmanns et al. developed a full-area mapping method for extracting gully-affected areas using only optical satellite imagery, employing a cyclic object-based image analysis method by means of High-Resolution Remote Imagery (HRI) to map gully erosion [23]. Eustace et al. used airborne Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) to collect 20 LiDAR sample strips (5000 × 275 m) to map gullies using topographic attributes and backscattered intensities of LiDAR echoes, as well as to model the relationship between gully volume and auxiliary variables [24]. Wang et al. used open-source optical imagery (Google Earth images) to identify gully erosion through OBIA-based image feature modeling, employing the Light Gradient Boosting Machine (Light GBM) and the dual-end squeezing method of eCognition software for automatic regional extraction of gullies in the Northeast black soil area [15]. Shruthi et al. obtained topographic, spectral, shape, and contextual information from IKONOS and GEOEYE-1 data, using Object-Oriented Image Analysis (OOA) to extract gully erosion features from satellite imagery, conducting gully mapping in semi-arid to semi-humid regions of Morocco [13].
Methods based on computer vision and deep learning, such as Boyang Liu et al., compared the results and accuracy assessment of U-Net, R2U-Net, and SegNet image semantic segmentation models for the recognition of ephemeral gullies in the Loess Plateau of China, establishing a rapid and accurate method for the identification of ephemeral gullies in the hilly and gully areas of the Loess Plateau [25]. Zhu et al. developed a small-sample segmentation model, LinkNet, which analyzes high-resolution aerial imagery by integrating global contextual information through asymmetric non-local operations, exploring the extraction of gullies that are narrow and irregular in shape as well as similar in color to the surrounding farmland [26]. M. Gafurov et al. designed a method for automatic gully detection using a UNet model-based approach on publicly available ultra-high-resolution satellite RGB composite images of a test area in the eastern Russian plain with intense basin erosion [27].
The characteristics of gullies are influenced by environmental factors, such as topography and climate [28], and we have found that previous studies have rarely taken full account of the content features and structural features of gullies in remote sensing images. To address this, we propose a multi-scale content feature fusion network for gully extraction to fully utilize the information in satellite remote sensing images. We use the ResNet34 network [29] as a baseline and propose a structural feature extraction module, which takes into account the information on gullies and other geomorphic features in remote sensing images. Through residual connections, multiple scales can be extracted from the feature map and processed separately. We designed a content feature extraction module that uses a multi-scale contextual attention mechanism to perform multi-scale semantic segmentation on graphical information and extract the geometric information of gullies. By integrating the two types of information through a content structure fusion network, the model’s ability to understand the intrinsic characteristics of gullies is enriched. Finally, a multi-scale feature fusion module is designed to fuse the feature map containing high-level semantic information with the low-level feature map to deepen the comprehensive understanding of the image, enhance the ability of gully extraction, and obtain the final prediction results.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
Our study area is located in the Dahe Bay Farm (Figure 1) of Zalantun City, Inner Mongolia, China. Dahe Bay Farm is located in the southeast of Zalantun City, with a total area of 112.56 square kilometers. The region has a temperate continental semi-humid monsoon climate with an average annual temperature of 2.4 °C, an average spring temperature of 5.8–9.1 °C, an annual effective cumulative temperature of 2442.5 °C, and an annual average precipitation of 350–450 mm, mostly concentrated in June–August, with a frost-free period of 100–132 days. Cultivated land in the region is mostly sloping, with a slope of 2°–6°. Currently, there are a total of 468,000 gullies caused by water erosion across the entire Northeast Black Earth region. Within the 112.06 square kilometers of the Dahe Bay demonstration area alone, there are 342 gullies, which have encroached upon an area of 0.197 square kilometers of cultivated land. The cultivated land affected by these gullies amounts to 34.75 square kilometers, accounting for 31% of the total cultivated land area of the Dahe Bay Farm. We have selected the southwestern part of Dahe Bay Farm as our study area, which encompasses 63.31 square kilometers. The natural environment of this area is typical of the Northeastern black soil region, with over 90% being gently rolling terrain. Drought is common in the spring and it is rainy in the summer, and the annual rainfall is between 400 and 500 mm, most of which is concentrated in the summer months. The region suffers from severe wind and water erosion. As a key area for gully erosion prevention, the region has a large number of gullies that are widely distributed, providing a rich source of research samples for our study.
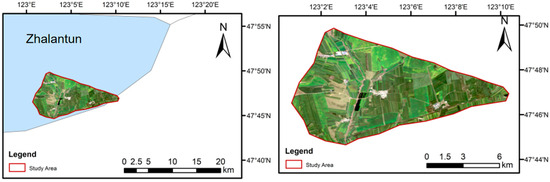
Figure 1.
The geographic location of our study area in the Dahe Bay Farm of Inner Mongolia.
2.2. Data Preparation
We obtained satellite remote sensing image data of the Dahe Bay region of Inner Mongolia with a resolution of 0.5 m from Google Earth images. Subsequently, we conducted a field survey (Figure 2), combining the remote sensing image data with the field survey verification, so as to determine the specific location of the gullies in the Inner Mongolia Dahe Bay region. Through our comparison, we identified different types of gullies, including ephemeral gullies and classical gullies. This study pays more attention to the extraction of classical gullies in remote sensing images because classical gullies have a deeper degree of soil and water loss compared to ephemeral gullies and present greater challenges in management, and more urgent attention is needed. In contrast, ephemeral gullies are relatively more convenient to manage [2].

Figure 2.
We conducted a field investigation in the Dahe Bay Farm to determine the specific location of the gullies.
We use the Labelme annotation tool to tag the gullies in the dataset (Figure 3) and build a dataset of gullies in Dahe Bay, Inner Mongolia, as shown in Figure 3. Then, the remote sensing images are cut into training images and test images according to the ratio of 8:2. The training images were cut using a sliding window of 150 pixels to obtain 412 images of 224 × 224 pixels for the training set, while the testing images were directly cropped to produce 103 images for the test set. In order to further improve the prediction performance of the model, for the training set, we only retained the images with more than 3% of labeled pixels, and for the test set, we kept all the images. During the training process, we performed data augmentation, which included operations such as random horizontal flipping, random vertical flipping, and random rotation. This expanded the training dataset and increased data diversity to improve the generalization ability and robustness of the model.
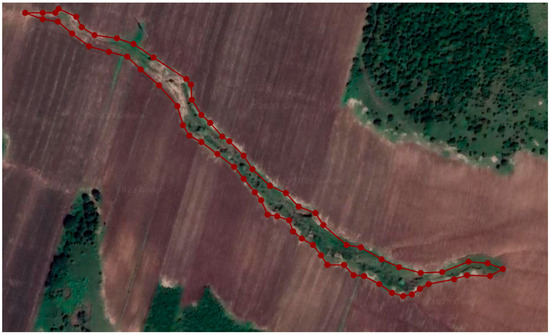
Figure 3.
We used the Labelme annotation tool to label the gullies in the dataset and build the dataset of Dahe Bay gullies in Inner Mongolia. The red lines in the figure represent the boundary of the gully, and the red points represent the anchor point of the gully boundary.
3. Methods
3.1. Overall Structure
The workflow of our model (Figure 4) is as follows. (1) We input the training data from the dataset of Dahe Bay gullies in Inner Mongolia into the ResNet34 network to obtain low-layer and high-layer information. (2) The multi-layer information is separately processed through a structural feature extraction module and a content feature extraction module to achieve richer intrinsic information about the images. (3) The feature fusion network further integrates the structural features and content features. The content features and structural features of the image serve as different perspectives for understanding the image. By independently extracting and then fusing them, the accuracy of feature extraction is improved, and the depth of the model’s understanding of the image is enhanced, allowing the network to comprehend the content within the image more accurately, such as the shape, location of the gullies, and the interrelationships with other elements in the image. (4) The multi-scale feature fusion network further integrates the high-layer and low-layer information to provide a comprehensive understanding of the image and enhance the ability to extract gullies. The final prediction result is obtained. We will describe these steps in further detail below.
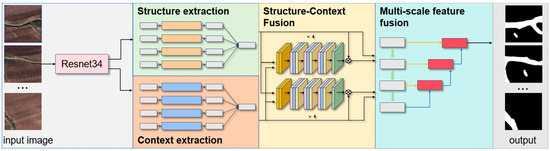
Figure 4.
Overview of the research method.
3.2. Multi-Scale Structure Extraction Module
Our feature extractor utilizes the ResNet34 network (Figure 5) [29], which is a deep residual network proposed by the Microsoft team in 2015 for the task of image recognition in deep learning architectures. It is a member of the residual network family, which solves the problem of gradient vanishing and gradient explosion during deep neural network training by introducing residual connections [30,31,32]. The challenge in training deep neural networks lies in the fact that as the number of layers increases, the gradients become smaller during the backpropagation process, which can prevent deep networks from learning effectively. These residual blocks enable the network to learn a residual function, which is the difference between the input and the desired output, rather than learning the original function directly, which makes it easier to train deep networks.
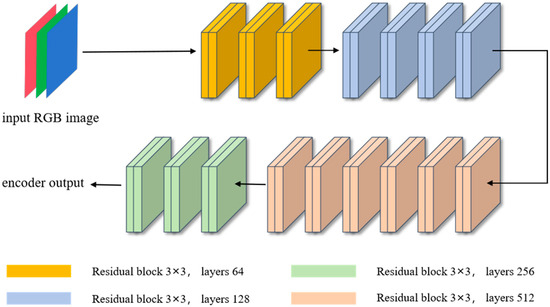
Figure 5.
The architecture of the ResNet34 network adopted by this study.
The ResNet34 network consists of 34 layers, including 33 convolutional layers and 1 fully connected layer. In this study, we adopt the ResNet34 network as an encoder, which employs convolutional kernels based on 3 × 3 stacks multiple residual blocks and ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) activation functions. It also uses maximum pooling operations with a stride of 2 to gradually reduce the size of the feature maps while increasing the depth and level of abstraction of the features, which helps the network to learn features at different scales [33,34,35,36]. Within each residual block, there are primarily two 3 × 3 convolutional layers, along with an identity mapping and a downsampling layer (such as a convolutional layer with a stride of 2) to match the dimensions of the input and output. The structure of ResNet34 is simple yet effective, with high parameter and computational efficiency, making it one of the most commonly used models for image recognition tasks. It has been extensively trained and evaluated on large-scale image datasets, achieving excellent performance. Moreover, due to its relatively shallow network architecture, it has a relatively fast training speed and is easier to deploy on devices with limited resources. Consequently, ResNet34 is widely used in practical applications for tasks, such as image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation, and has made significant contributions to the development of deep learning in the field of computer vision [37,38,39,40,41].
The traditional ResNet34 network maps the classified objects through the fully connected layer at the end. In this study, to enable our model to better determine gullies and non-gully areas, we further process the output results of the ResNet34 by further inputting the four-channel (64, 128, 256, 512) results of the original ResNet34 output into our designed multi-scale structural feature extraction module (Figure 6) and multi-scale content feature extraction module (Figure 7) and further improved the model’s understanding of the image by fusing the content features and structural features with each other through the feature fusion network, thus improving the model prediction accuracy. Specifically, we designed a structural feature extraction module (Figure 8). This module contains three convolutional layers using residual linkage. A ReLU activation function and batch normalization are added between each layer. The ReLU activation function provides non-linear transformation, enhancing the network representation. The batch normalization layer accelerates model training, improves stability, and mitigates overfitting. All the convolutional layers use the same parameters: a 3 × 3 convolutional kernel, a stride of 1, and a padding of 1. The input image goes through the coding layer to obtain 4 layers of features containing low-layer information and high-layer information. This information is fed into the structural feature extraction module, respectively, and the extraction results are aggregated to obtain the structure extraction output so that more intrinsic information about images can be used in our model.
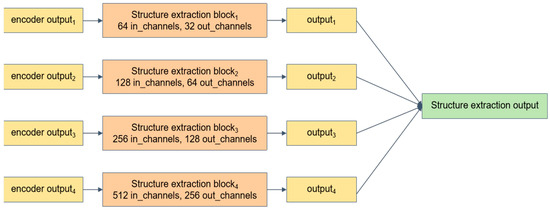
Figure 6.
Multi-scale structure feature extraction module.
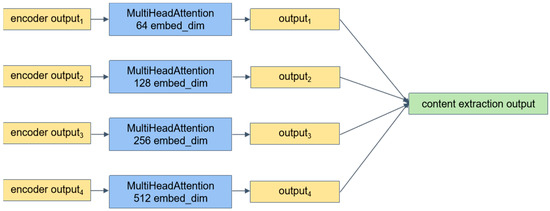
Figure 7.
Multi-scale content feature extraction module.
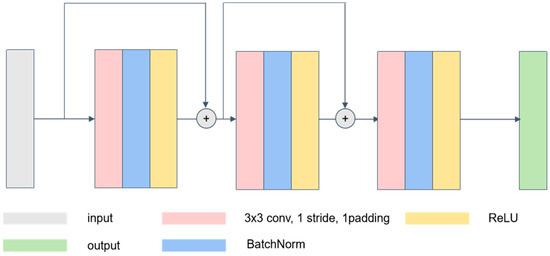
Figure 8.
Structure feature extraction block.
3.3. Multi-Scale Content Extraction Module
We employ the multi-head attention mechanism [42] as the multi-scale content extraction module (Figure 7) of our model. Multi-head attention is primarily used for processing sequential data, such as sentences in natural language processing and regions in image processing. The mechanism of multiple attention heads enhances the model’s ability to model input data by capturing important information from different parts of the sequence in parallel [43,44]. In traditional attention mechanisms, a single attention head is used to calculate the attention weights, which determines the importance of each element within the sequence. In contrast, the multi-head attention mechanism introduces multiple parallel attention heads, each learning different attention representations. These representations are then merged or concatenated in subsequent operations, resulting in a more enriched and complex feature representation [45,46,47,48].
The core idea of the multi-attention mechanism is to map the input sequence into different attention subspaces, where each subspace can focus on extracting different aspects of information. Through this parallel processing, the model is better able to capture both local and global relationships within the sequence, thereby enhancing its representational and expressive capabilities regarding the sequence [49,50,51,52,53,54]. In practice, the multi-head attention mechanism is often combined with the self-attention mechanism, a technique that generates attention weights by calculating the relationships between various elements within the sequence. The self-attention mechanism allows the model to create long-distance dependencies between different positions. The multi-head mechanism, in turn, enables the model to make better use of these dependencies, thus improving the overall performance of the model.
We employ a multi-head self-attention module to extract features from the feature maps. Specifically, we perform multi-head attention calculations separately on the low-layer and high-layer information output by the encoding layers and then aggregate the results to capture global contextual information. Compared to convolutional networks, this approach provides a larger receptive field, enabling the extraction of richer and more accurate semantic information.
3.4. Structure-Content Fusion Network
We designed a structure-content feature fusion network (Figure 9) for synthesizing the extraction results of features from two different perspectives. Initially, we concatenate the two tensors, structure extraction output and context extraction output, on the channel dimension. Then, we use a convolutional layer to perform preliminary fusion on the concatenated results. The convolution layer reduces the fused vector by half on the channel dimension, matching the size of the input vector, followed by a softmax transformation into weight probabilities. The convolutional layer leverages the additional context extraction features to make a selection regarding the importance of the structure extraction features, which are then multiplied to obtain the final output. To reflect the mutual influence between structure and content, we have added two feature fusion networks, representing the re-extraction of structure based on content and the re-extraction of content based on structure.
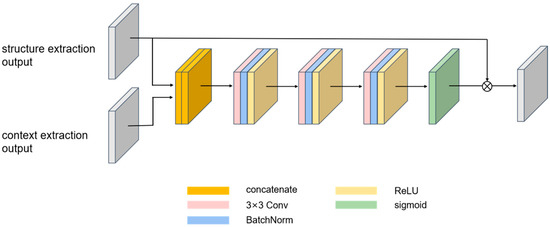
Figure 9.
Structure-content feature fusion network.
3.5. Muti-Scale Feature Fusion Module
We designed a multi-scale feature fusion module (Figure 10) that achieves the upsampling of feature maps through deconvolution (transposed convolution) and convolution operations. This module is capable of upsampling the feature maps to the same resolution as the input image, thereby providing accurate probabilistic predictions for the classification of each pixel in the original image. The decoder initially uses a deconvolution layer to upsample the feature maps from a resolution of H/16 × W/16 to H/8 × W/8. Subsequently, it employs a batch normalization layer to normalize the features and adds them to the feature maps at the same layer, followed by further upsampling. This process is progressively carried out in a similar manner, with different combinations of deconvolution and batch normalization layers, to achieve upsampling from H/16 × W/16 to H/8 × W/8, from H/8 × W/8 to H/4 × W/4, and ultimately from H/4 × W/4 to H/2 × W/2 in feature map resolution.
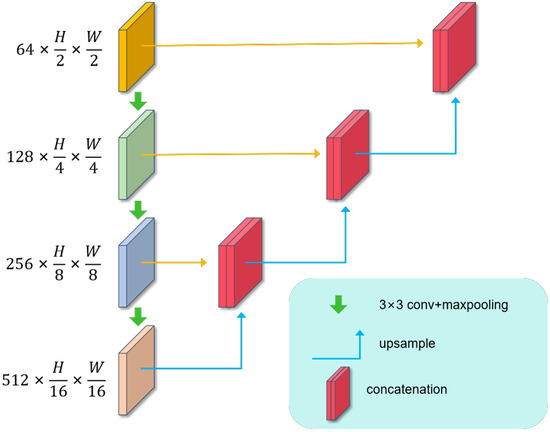
Figure 10.
Muti-scale feature fusion module.
Each stage in ResNet34 focuses on different scales of information in the image. In the early stages of the network, the output feature maps are larger, which can capture more detailed information about the image. As the network deepens, the size of the output feature maps decreases, which can include more contextual information and higher-level semantic information [55]. To enable the network output to have different spatial resolutions and feature expression capabilities, we fuse the feature maps after each upsampling step with the corresponding resolution feature maps from a shallower layer. This fusion is achieved by concatenating the two feature maps along the channel dimension, followed by a 1 × 1 convolution. Through this layer-by-layer fusion strategy, the model can effectively combine feature information at different layers, thereby restoring more details in the decoding process and improving the quality and accuracy of the final output [56,57,58,59,60,61].
3.6. Data Augmentation
Data augmentation is crucial for achieving better performance [62,63], especially when the experimental dataset in this paper is relatively small. Since the dataset cannot generalize to all cases, to enhance the robustness of the model, we have introduced the means of data augmentation [64,65,66,67,68,69]. We employ simple data augmentation techniques, such as random rotation, mirror flipping, translation, and scaling. By artificially introducing inductive bias into the model, we guide the model to learn the invariance of the image. Data augmentation implies assumptions about the data distribution and helps the model learn the underlying structure of the data.
3.7. Evaluation Metrics
We used the F1 score, recall, and intersection over union (IoU) as the evaluation metrics for this experiment. In the calculation process, the number of true positives, false positives, and false negatives were first counted, and then the precision and recall were calculated using these numbers. Finally, the F1 score was calculated based on precision and recall. We also calculated the IoU using the degree of overlap between the pixels predicted by the model to be gullies and the pixels that were actually gullies.
Precision is a metric that measures the accuracy of positive predictions made by a model, that is, the proportion of instances that are correctly identified as positive among all instances predicted as positive. In this study, it refers to the probability that the model’s predictions of gullies are indeed gullies (Equation (1)).
Recall is a metric that measures a model’s ability to identify all the positive instances, that is, the proportion of actual positive instances that are correctly identified by the model. In this study, it means the proportion of pixels that are both predicted by the model as gullies and have the true label as gullies among all pixels that have the true label as gullies (Equation (2)).
The F1 score is a statistical measure used to evaluate the accuracy of a model in binary classification tasks. It takes into account both the precision and recall of the classification model, thus effectively addressing the issue of data imbalance. In this study, this data imbalance is reflected in the fact that the proportion of pixels covered by gullies is significantly smaller than that of the background pixels in the entire image (Equation (3)). The F1 score ranges from 0 to 1, and a higher value means the more accurate the model prediction results.
Intersection over union (IoU) is a metric that measures the degree of overlap between the model’s segmentation results and the ground truth labels (Equation (4)), and it is commonly used to evaluate the performance of segmentation models [70,71,72,73,74].
4. Results
4.1. Implementation Details
In order to verify that the proposed algorithm has better performance, we compared the prediction effect of classical semantic segmentation algorithms such as DeepLabV3+ [75], FCN [76], PSPNet [77], UNet [78] and our model on the gully dataset of Dahe Bay Farm in Inner Mongolia. In our experiment, the deep learning framework used was PyTorch 1.10.0, and the specific parameter settings for both our experiment and the comparative experiments were as follows: the batch size was set to 4; the learning rate was set to 1E-4; and the number of epochs was 100.
4.2. Analysis and Discussion of the Experimental Results
It can be observed that under the same training conditions, UNet and PSPNet have the lowest F1 scores for gully extraction (Table 1). The UNet network has a simple structure with fewer feature extraction layers, which results in a poorer ability to learn complex terrain features, leading to the lowest F1 value. It can also be seen in Figure 11 that the F1 value of UNet fluctuates significantly as the number of training epochs increases. On the other hand, PSPNet, due to the incorporation of a pooling pyramid structure, can more fully combine contextual information compared to UNet and thus has a better ability to extract gullies. Our model, by utilizing a feature fusion network to combine the results extracted by multi-head attention and residual convolutional layers, is able to better preserve the content and structural information in remote sensing images. It also performs multi-scale feature fusion and reduces the loss of information caused by downsampling operations, thereby achieving optimal results in the task of gully extraction.

Table 1.
The performance of the four models on the gully dataset of Dahe Bay Farm in Inner Mongolia.
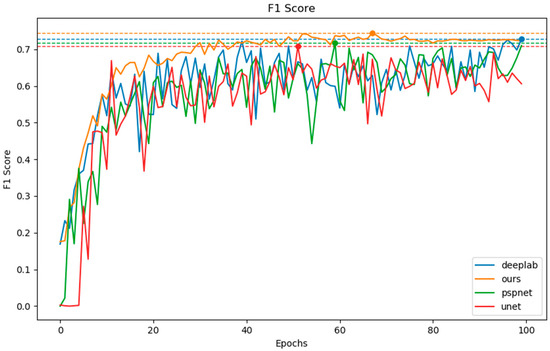
Figure 11.
Gully extraction F1 score by four models. The blue, green, red, and orange lines represent DeepLabV3+, PSPNet, UNet, and our model, respectively.
In Table 1 and Figure 12, it can be seen that our model consistently outperforms the other three models, and higher recall scores mean that our model can have better control over missed detections. Similarly, in Figure 13, it can be observed that our model achieves the highest IoU score. In terms of IoU, the performance ranking of the models from best to worst is ours > DeepLabV3+ > PSPNet > UNet. It can be seen that for gully extraction, the content structure extraction network we designed is superior to DeepLabV3+ and PSPNet, which use spatial pyramid pooling structures, as well as UNet, which employs a symmetric encoder–decoder architecture.
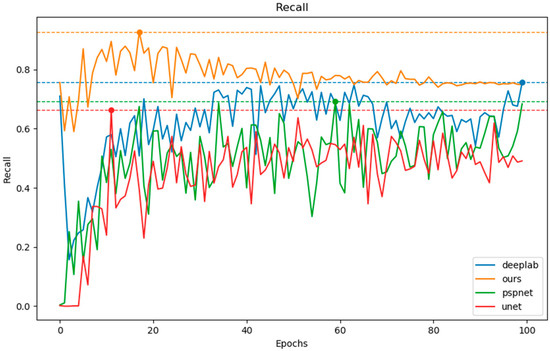
Figure 12.
Gully extraction recall by four models. The blue, green, red, and orange lines represent DeepLabV3+, PSPNet, UNet, and our model, respectively.
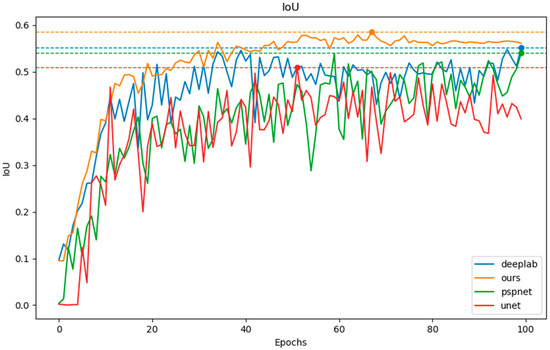
Figure 13.
Gully extraction IoU by four models. The blue, green, red, and orange lines represent DeepLabV3+, PSPNet, UNet, and our model, respectively.
We randomly selected some experimental comparison images to demonstrate the gully extraction capabilities of different models more intuitively. The images include the original gully image, the ground truth, the results from DeepLabV3+, PSPNet, UNet, and our model, where the white pixels represent the gullies identified by the models and the black pixels represent the rest of the background excluding the gullies.
In Figure 14, it can be observed that UNet provides the least complete extraction of gullies in remote sensing images, especially for the slender and shallow gullies in parts (a), (b), and (i), which UNet fails to extract completely, and the extracted gully shapes are not intact. Both PSPNet and DeepLabV3+ have issues with misidentification. As can be seen in (f) and (j), these two models incorrectly identify areas without gullies as having gullies. Compared to DeepLabV3+, the results from PSPNet are rougher. Although both models can identify most gullies well, PSPNet tends to produce broader identification results. It can be seen in the images that our model performs the best in gully extraction. As shown in (b) and (c), only our model can identify fine gullies effectively. In (h) and (j), it can be seen that the gully boundaries extracted by our model can fit the ground truth most accurately.
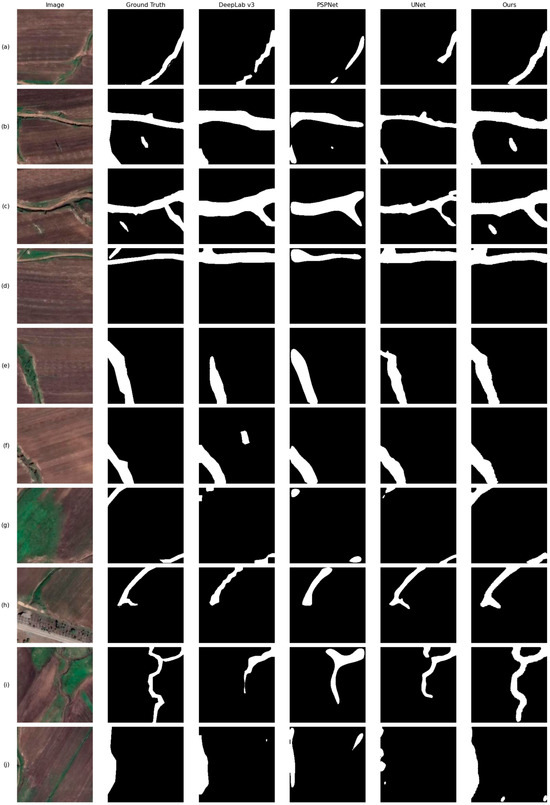

Figure 14.
Intuitive comparison of the prediction results of the four models on the gully dataset of Dahe Bay Farm in Inner Mongolia with the original image on the far left followed by the ground truth and the prediction results of the four models. (a–j) represent images we randomly selected from the databset.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a multi-scale content structure fusion network for gully extraction from satellite remote sensing images to address the serious problem of gully erosion in black soil. Firstly, we obtained multi-layer semantic information about gullies by feature extraction of remote sensing images with the ResNet34 network as a backbone. Secondly, we designed a content feature fusion network that separately extracted content features and structural features from the multi-layer information and then fused the two types of information to enhance the model’s understanding of the intrinsic characteristics of gullies. Finally, we designed a multi-scale feature fusion network that integrates feature information at different scales to obtain a more complete gully prediction map. We collected and created a gully remote sensing dataset for the Dahe Bay basin in Inner Mongolia, trained and tested our model on this dataset, and compared it with the classic models, DeepLabV3+, PSPNet, and UNet. Our model impacts 0.745, 0.777, and 0.586 on the three evaluation indicators of the F1 value, recall, and IoU, respectively. The results indicate that our model performed the best and was capable of effectively extracting gullies from remote sensing images.
However, the model also has some limitations. On one hand, there is still room for improvement in the precision of gully extraction from remote sensing images by the model. On the other hand, for very fine and shallow gullies in remote sensing images, our model is not yet able to extract them completely. We hope to overcome these challenges in future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.D., J.J., L.L., H.L. and Y.Z.; methodology, F.D., J.J., L.L., H.L. and Y.Z.; software, J.J., F.D., L.L., H.L. and Y.Z.; validation, J.J., F.D., L.L., H.L. and Y.Z.; formal Analysis, F.D., J.J., L.L., H.L. and Y.Z.; resources, Y.Z., L.L., H.L., F.D. and J.J; data curation, F.D., J.J., L.L., H.L. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, F.D., J.J. and L.L.; writing—review and editing, F.D., J.J., L.L. and Y.Z.; visualization, F.D., J.J., L.L. and H.L.; supervision, L.L. and Y.Z.; project administration, Y.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Innovation Funding of the Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, under Grant No. E261030.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request due to restrictions (project data privacy). The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the staff at Dahe Bay Farms for providing guidance and assistance with our field trips.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| OBIA | Object-Based Image Analysis |
| NorToM | Normalized Terrain Method |
| InSAR | Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| REA | Relative Elevation Algorithm |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| HRI | High-Resolution Remote Imagery |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| OOA | Object-Oriented Image Analysis |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| GEI | Google Earth Image |
References
- Luo, L.; Ma, J.; Li, F.; Jiao, H.; Strobl, J.; Zhu, A.; Dai, Z.; Liu, S. Simulation of loess gully evolution based on geographic cellular automata. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 47, 756–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environmental change: Importance and research needs. CATENA 2002, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, C.; Poesen, J.; Li, Y. Gully erosion: Impacts, factors and control. CATENA 2005, 63, 132–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimes, G.N.; Schultz, R.C. Assessing riparian conservation land management practice impacts on gully erosion in Iowa. Environ. Manag. 2012, 49, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakerinejad, R.; Maerker, M. An integrated assessment of soil erosion dynamics with special emphasis on gully erosion in the Mazayjan basin, southwestern Iran. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garosi, Y.; Sheklabadi, M.; Conoscenti, C.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Van Oost, K. Assessing the performance of GIS- based machine learning models with different accuracy measures for determining susceptibility to gully erosion. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 664, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, F. Towards accurate mapping of loess waterworn gully by integrating google earth imagery and DEM using deep learning. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Vanmaercke, M.; Ballabio, C.; Hervás, J.; Maerker, M.; Scarpa, S.; Panagos, P. Monitoring gully erosion in the European Union: A novel approach based on the Land Use/Cover Area frame survey (LUCAS). Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 10, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.; Xiong, L.; Tang, G.; Qiu, F.; Strobl, J. Optimized segmentation based on the weighted aggregation method for loess bank gully mapping. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, I.; Fullen, M.A.; Zgłobicki, W.; Poesen, J. Gully erosion as a natural and human-induced hazard. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J.; Van Mele, B.; Demuzere, M.; Bruynseels, A.; Golosov, V.; Bezerra, J.F.R.; Bolysov, S.; Dvinskih, A.; Frankl, A.; et al. How fast do gully headcuts retreat? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 154, 336–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, H. Monitoring of gully erosion on the Loess Plateau of China using a global positioning system. CATENA 2005, 63, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, R.B.; Kerle, N.; Jetten, V. Object-based gully feature extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Geomorphology 2011, 134, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ding, H.; Tang, G.; Zhu, A.-X.; Yang, X.; Jiang, S.; Cao, J. An object-based approach for two-level gully feature mapping using high-resolution DEM and imagery: A case study on hilly loess plateau region, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Yi, L.; Hu, S. Object-based mapping of gullies using optical images: A case study in the black soil region, Northeast of China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, C.; Taguas, E.V.; Zarco-Tejada, P.; James, M.R.; Gómez, J.A. The normalized topographic method: An automated procedure for gully mapping using GIS. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2014, 39, 2002–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.; Spencer, J.; Brooks, A.; Phinn, S.R. Large-area, high-resolution remote sensing based mapping of alluvial gully erosion in Australia’s tropical rivers. In Proceedings of the 5th Australian Stream Management Conference, Albury, NSW, Australia, 12 January 2007; pp. 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, C.; Lu, M.; Dai, W.; Fan, J.; Li, M.; Lei, S. Integrating Topographic Skeleton into Deep Learning for Terrain Reconstruction from GDEM and Google Earth Image. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, B.; Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. Erosion Gully Networks Extraction Based on InSAR Refined Digital Elevation Model and Relative Elevation Algorithm—A Case Study in Huangfuchuan Basin, Northern Loess Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Jin, B.; Wu, F.; Guo, R. Tempo-spatial landslide susceptibility assessment from the perspective of human engineering activity. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yin, K.; Luo, H.; Li, J. Landslide identification using machine learning. Geosci. Front. 2020, 12, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, H.; Jarihani, B.; Piralilou, S.T.; Chittleborough, D.; Avand, M.; Ghorbanzadeh, O. A Semi-automated object-based gully networks detection using different machine learning models: A case study of bowen catchment, Queensland, Australia. Sensors 2019, 19, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Oleire-Oltmanns, S.; Marzolff, I.; Tiede, D.; Blaschke, T. Detection of gully-affected areas by applying object-based image analysis (OBIA) in the region of Taroudannt, Morocco. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8287–8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustace, A.; Pringle, M.; Witte, C. Give me the dirt: Detection of gully extent and volume using high-resolution lida. In Innovations in Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 255–269. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Feng, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, J.; Zou, Y.; Siddique, K.H. Ephemeral gully recognition and accuracy evaluation using deep learning in the hilly and gully region of the Loess Plateau in China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Xu, H.; Zhou, L.; Yu, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S. Automatic mapping of gully from satellite images using asymmetric non-local LinkNet: A case study in Northeast China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 12, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafurov, A.M.; Yermolayev, O.P. Automatic gully detection: Neural networks and computer vision. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.N.; Kinsey-Henderson, A.E.; Hawdon, A.A.; Hairsine, P.B.; Bartley, R.; Baker, B. Grazing impacts on gully dynamics indicate approaches for gully erosion control in northeast Australia. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 1711–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 43, 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Philipp, G.; Song, D.; Carbonell, J.G. The exploding gradient problem demystified-definition, prevalence, impact, origin, tradeoffs, and solutions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.05577. [Google Scholar]
- Balduzzi, D.; Frean, M.; Leary, L.; Lewis, J.P.; Ma, K.W.-D.; McWilliams, B. The shattered gradients problem: If resnets are the answer, then what is the question? In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 28 February 2017; pp. 342–350. [Google Scholar]
- Taki, M. Deep residual networks and weight initialization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.02956. [Google Scholar]
- Nagi, J.; Ducatelle, F.; Di Caro, G.A.; Cireşan, D.; Meier, U.; Giusti, A.; Nagi, F.; Schmidhuber, J.; Gambardella, L.M. Max-pooling convolutional neural networks for vision-based hand gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications (ICSIPA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 16–18 November 2011; pp. 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Fan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, S.; Pan, C. Augfpn: Improving multi-scale feature learning for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 12595–12604. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Guizani, M. Deep feature learning for medical image analysis with convolutional autoencoder neural network. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2017, 7, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Lu, H.; Liu, Z.; Vong, C.-M.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zwicker, M.; Han, J.; Chen, C.L.P. 3D2SeqViews: Aggregating sequential views for 3D global feature learning by CNN with hierarchical attention aggregation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 3986–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Qi, D.; Mu, H.; Chen, J. A Transfer residual neural network based on ResNet-34 for detection of wood knot defects. Forests 2021, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Wang, B.; Li, J. The Application of ResNet-34 Model Integrating Transfer Learning in the Recognition and Classification of Overseas Chinese Frescoes. Electronics 2023, 12, 3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; Gan, S.; Zhang, L. Human-computer interaction based health diagnostics using ResNet34 for tongue image classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 226, 107096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. Resnet-based model for autonomous vehicles trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICCECE), Guangzhou, China, 15–17 January 2021; pp. 565–568. [Google Scholar]
- Venerito, V.; Angelini, O.; Cazzato, G.; Lopalco, G.; Maiorano, E.; Cimmino, A.; Iannone, F. A convolutional neural network with transfer learning for automatic discrimination between low and high-grade synovitis: A pilot study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Gangrade, S.; Sharma, P.C.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, Y.P. Modified DeeplabV3+ with multi-level context attention mechanism for colonoscopy polyp segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 108096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, R.; Basile, V.; Bono, V. Local Multi-Head Channel Self-Attention for Facial Expression Recognition. Information 2022, 13, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.K.; Raparthi, M.; Alsaadi, M.; Bhatt, M.W.; Dodda, S.B.; Prashant, G.C.; Sandhu, M.; Patni, J.C. Deep learning-based multi-head self-attention model for human epilepsy identification from EEG signal for biomedical traits. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J. Attention as relation: Learning supervised multi-head self-attention for relation extraction. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Conference on International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, Vienna, Austria, 11–17 July 2020; pp. 3787–3793. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, T.; Jiang, X. Novel hybrid multi-head self-attention and multifractal algorithm for non-stationary time series prediction. Inf. Sci. 2022, 613, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.F.; Younis, M.S. Multi-horizon electricity load and price forecasting using an interpretable multi-head self-attention and EEMD-based framework. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 85918–85932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Huang, G.; Yu, H.; Wu, R.; Tao, J.; Liu, C. Geological information prediction for shield machine using an enhanced multi-head self-attention convolution neural network with two-stage feature extraction. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Tang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Multi-head self-attention-based deep clustering for single-channel speech separation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 100013–100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Y.; Chen, B.; Gu, D.; Tang, B. Multi-head self-attention based gated graph convolutional networks for aspect-based sentiment classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 81, 19051–19070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthi, P.; Mohan, L. Multi-Head-Self-Attention based YOLOv5X-transformer for multi-scale object detection. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 36491–36517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, K. Entity recognition of Chinese medical text based on multi-head self- attention combined with BILSTM-CRF. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 19, 2206–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Cao, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Chen, B.M. Synergizing low rank representation and deep learning for automatic pavement crack detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 10676–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Wu, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, X. A Small-sized object detection oriented multi-scale feature fusion approach with application to defect detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, C.; Yun, J.; Sun, Y.; Tian, J.; Hao, Z.; Yu, H.; Ma, H. Multi-scale feature fusion convolutional neural network for indoor small target detection. Front. Neurorobotics 2022, 16, 881021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Sun, G.; Tian, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Long, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, A. HiFuse: Hierarchical multi-scale feature fusion network for medical image classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 87, 105534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Zhu, J.; Huyan, J.; Ma, T.; Zhang, W. Multi-scale feature fusion network for pixel-level pavement distress detection. Autom. Constr. 2022, 141, 104436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Yu, S.; Li, K. Region-to-boundary deep learning model with multi-scale feature fusion for medical image segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wei, X.; Wei, Z. Traffic sign detection based on multi-scale feature extraction and cascade feature fusion. J. Supercomput. 2022, 79, 2137–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumuni, A.; Mumuni, F. Data augmentation: A comprehensive survey of modern approaches. Array 2022, 16, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcea, F.; Serra, A.; Lamberti, F.; Morra, L. Data augmentation for medical imaging: A systematic literature review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebaili, A.; Lapuyade-Lahorgue, J.; Ruan, S. Deep learning approaches for data augmentation in medical imaging: A review. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlap, P.; Min, H.; Vandenberg, N.; Dowling, J.; Holloway, L.; Haworth, A. A review of medical image data augmentation techniques for deep learning applications. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 65, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.-Y.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning data augmentation strategies for object detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 566–583. [Google Scholar]
- Maharana, K.; Mondal, S.; Nemade, B. A review: Data pre-processing and data augmentation techniques. Glob. Transit. Proc. 2022, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, T.; Yu, F.; Dai, J.; Konukoglu, E.; Van Gool, L. Exploring cross-image pixel contrast for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Beijing, China, 28 January 2021; pp. 7303–7313. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, Z.; Tang, Q.; Chu, X.; Wei, X.; Shen, C.; Liu, Y. Segvit: Semantic segmentation with plain vision transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 4971–4982. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, C.; Duan, C.; Su, J.; Wang, L.; Atkinson, P.M. Multiattention network for semantic segmentation of fine-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; He, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G. Dynamic snake convolution based on topological geometric constraints for tubular structure segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 17 July 2023; pp. 6047–6056. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W.; Yu, X. CMTFNet: CNN and multiscale transformer fusion network for remote-sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loey, M.; Manogaran, G.; Khalifa, N.E.M. A deep transfer learning model with classical data augmentation and CGAN to detect COVID-19 from chest CT radiography digital images. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wng, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).