Abstract
Forest change affects local and global climate by altering the physical properties of the land surface. Accurately assessing urban forest changes in local land surface temperature (LST) is a scientific and crucial strategy for mitigating regional climate change. Despite this, few studies have attempted to accurately characterize the spatial and temporal pattern of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation to optimize their effects on surface temperature. We used the China Land Cover Dataset and knowledge criterion-based spatial analysis model to map urban forestation (e.g., afforestation and reforestation) and deforestation. We then analyzed the impacts of these activities on LST from 2010 to 2020 based on the moving window strategy and the spatial–temporal pattern change analysis method in the urban agglomerations of the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and Pearl River Delta (PRD), China. The results showed that forest areas declined in both regions. Most years, the annual deforestation area is greater than the yearly afforestation areas. Afforestation and reforestation had cooling effects of −0.24 ± 0.19 °C and −0.47 ± 0.15 °C in YRD and −0.46 ± 0.10 °C and −0.86 ± 0.11 °C in PRD. Deforestation and conversion of afforestation to non-forests led to cooling effects in YRD and warming effects of 1.08 ± 0.08 °C and 0.43 ± 0.19 °C in PRD. The cooling effect of forests is more evident in PRD than in YRD, and it is predominantly caused by reforestation. Moreover, forests demonstrated a significant seasonal cooling effect, except for December in YRD. Two deforestation activities exhibited seasonal warming impacts in PRD, mainly induced by deforestation, while there were inconsistent effects in YRD. Overall, this study provides practical data and decision-making support for rational urban forest management and climate benefit maximization, empowering policymakers and urban planners to make informed decisions for the benefit of their communities.
1. Introduction
Global climate change has garnered significant attention and research as a pressing environmental issue with implications for all humanity’s joint development and destiny [,,]. Forest cover change is critical to climate change [,,,]. For example, forestation and deforestation control the exchange of heat, water, and momentum between the surface and the atmosphere by altering the physical properties of the surface, such as radiative (such as albedo) and non-radiative processes (such as evapotranspiration and surface roughness) [,]. These biophysical processes further influence the energy redistribution at the surface, which impacts regional and global climate []. Therefore, studying urban forest changes has critical implications for the global climate and environment [,]. Land surface temperature (LST) is a vital parameter that can monitor environmental changes through biophysical and biogeochemical processes, such as forest change [,,,,].
When monitoring urban forest changes, it is essential to consider various concepts related to forest changes [,]. Different countries and communities have definitions of forest, forestation (e.g., afforestation and reforestation), and deforestation, which can impact the results of measured areas [,]. For example, they usually do not distinguish between afforestation and reforestation and consider afforestation to be the conversion of other non-forest to forest [,]. Some believe that afforestation is a human-driven process of seeding or planting new forests on land that has not been forested for at least 50 years [,]. These activities are closely related to land use, land use change, and forestry (LULUCF)’s carbon accounting, and they affect the assessment of climate change [,]. Despite the international consensus on the importance of forest ecosystems and the increasing amount of research on forest thematic information, there remains a lack of quantitative research on forest changes like forestation and deforestation due to data deficiencies and a limited understanding of the role of these forest activities in temperature regulation [,,].
Forest cover change data can be derived from direct site observations and remote sensing observations [,,,]. However, site observations’ limited spatial and temporal coverage made their widespread use impossible. Predominantly, time series satellite observations like forest cover products are needed because they can hold the potential to identify the spatial distribution of afforestation [,,]. Thus, combining land cover-based definitions and satellite remote sensing data can characterize the spatiotemporal distribution of these forest activities [,,]. Moreover, coarse-resolution satellite remote sensing data often do not reveal spatial details about forest change, which can compromise the accuracy of quantifying the impact of forests on temperature [,,,]. Medium–high-resolution time series remote sensing observations (e.g., Landsat-based land cover data) have become a vital supervisory tool for monitoring afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation due to their extensive spatiotemporal coverage, diverse data sources, strong continuity, and widespread applicability [,,,,].
There are usually three methods to study the effects of forest change on temperature: (1) numerical simulation experiments based on climate models; (2) in situ observations; and (3) satellite observations [,,,,]. The regional climate models demonstrate drawbacks, such as the parameterization scheme of land cover change by numerous climate models vary, and there is significant uncertainty in expressing forest vegetation dynamics [,,]. The spatial resolution of global climate model simulations is coarse and brutal to reflect spatial heterogeneity []. In situ observations are limited by time and space, making their results challenging to realize large-scale observation []. The spatial analysis methods based on satellite observations, including space-for-time and space-and-time, the latter of which is also called the spatial–temporal pattern change analysis method, were popularized [,,,]. The space-for-time method evaluates forests’ impacts on temperature by calculating the surface temperature difference between forest and open lands in the same latitude and similar climate feedback, which mainly focuses on the climate signals of forest changes caused by hypothetical or potential afforestation or deforestation [,]. However, the space-for-time method may change the background state due to changes in large-scale radiative forcing and climatic feedback [,]. In response to this issue, studies have used the satellite observation-based spatial–temporal pattern change analysis method to analyze urban forests’ impact on climate by fully considering the background climate perturbations [,,].
The Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and the Pearl River Delta (PRD) urban agglomerations are two of China’s most economically active areas, and they face the need for ecological protection []. The Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect is becoming more prominent as urbanization speeds up [,,]. Meanwhile, the environmental engineering construction makes the forest green, increasing carbon sink and climate feedback [,,,]. In addition, the Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta belong to different climatic zones (tropical and subtropical regions) and latitude regions (low and middle latitudes), respectively, and the difference in temperature response of forestation and deforestation is worth comparing and exploring and analyzing []. A more profound comprehension of the relationship between forests and ecosystem services can be attained by examining the impact of forest changes on LST in the YRD and PRD regions. This will offer scientific support for the preservation and management of forest resources as well as the advancement of sustainable urban development.
To address the above issues, the objectives of this study were to (1) build a medium–high-resolution accurate dataset of the historical distribution of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation (2010–2020) of urban agglomerations in China’s Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and Pearl River Delta (PRD) based on the 30 m yearly land cover dataset and the knowledge criterion-based spatial analysis model; (2) explore the cooling or warming impacts of afforestation, reforestation, and both types of deforestation on land surface temperature based on the above datasets, moving window searching strategy, and spatial–temporal pattern change analysis method. This research framework was designed to ensure the ability to monitor the subtle urban forest changes and enhance the accuracy of evaluating the effects of regional surface temperature, providing reliable support for driving the regional temperature response model of urban forest change.
2. Materials and Data
2.1. Study Area
The Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region (29°20′–32°34′N, 115°46′–123°25′E) and the Pearl River Delta (PRD) urban agglomerations (21°31′–23°10′N, 112°45′–113°50′E) are located in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China and the south-central part of Guangdong Province in China (Figure 1). The YRD is in the subtropical monsoon climate zone, with low overall forest cover and vegetation types dominated by subtropical evergreen broad-leaved woodlands, as well as deciduous broad-leaved, evergreen coniferous, deciduous coniferous, and shrubs. The PRD is situated in the southern subtropics and has a southern subtropical maritime monsoon climate, with a high forest cover and a variety of vegetation types, including southern subtropical evergreen broad-leaved woodlands, central subtropical evergreen broad-leaved woodlands, and other zonal vegetation types.
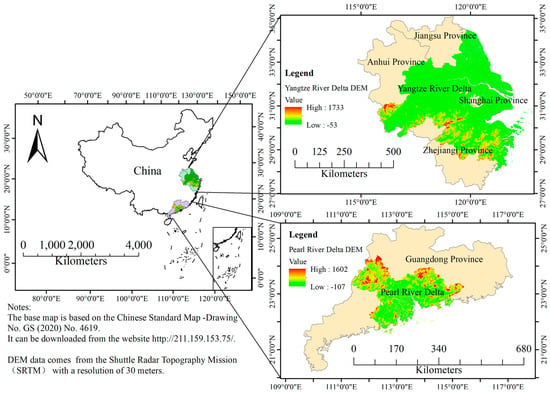
Figure 1.
An overview map of the study area.
2.2. Land Cover Dataset
This study used 30 m of land cover data based on Landsat to detect more accurate forest cover changes. Land cover data originated from the yearly China Land Cover Dataset (CLCD) (link to the CLCD dataset: https://zenodo.org/record/8176941 (accessed on 5 January 2021)). The CLCD, a good consistency with existing time series land cover datasets, was released in August 2022 by Prof. Jie Yang and Prof. Xin Huang from Wuhan University. The dataset is derived from 335,709 images of Landsat data on Google Earth Engine and contains year-by-year land cover information on China from 1985 to 2020 []. CLCD is one of the few publicly available 30 m resolution long time-series year-by-year land cover data. The overall accuracy of CLCD is 80%, with accuracy in the order of 79% for water bodies, 85% for forests, 83% for snow and ice, 81% for bare ground, and 72% for the remaining categories (Figure 2). CLCD contains nine land cover types (cropland, forest, shrub, grassland, water, barren land, impervious surface, and wetland). To obtain the historical distribution dataset of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation, we combined the attributes of forest and non-forested land types to obtain the historical forest and non-forest cover map.
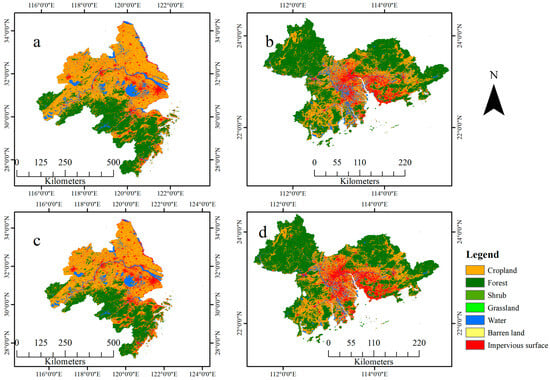
Figure 2.
CLCD-based land cover data of YRD and PRD in 2010 (a,b) and 2020 (c,d).
2.3. Remote Sensing Data
We gathered monthly Landsat 5 TM and 8 OLI/TIRS satellite digital products after filtering cloud cover (<20%) in 2010 and 2020, respectively (Table A1 and Table A2). The atmospheric correction for Landsat 5 images has been processed by the USGS EROS data center using the Landsat Ecosystem Disturbance Adaptive Processing System (LEDAPS), while that for Landsat 8 images has been processed by the Landsat 8 Surface Reflectance Code (LaSRC) []. These processing methods can maintain the highest data radiation consistency among Landsat 5 and Landsat 8 []. The study area’s frequent cloudy and rainy weather often resulted in high cloudiness in individual months of the image data, leading to missing parts. To address this and maintain radiometric consistency, we selected the image data in March, June, September, and December as the representative data of a single quarter in the target year. When the data from the target month were missing or contaminated, we used data from the same or neighboring month in the adjacent years as a replacement. Cloud masking was also applied to all image data to reduce the impact of cloud cover on the precision of the surface temperature inversion. YRD and PRD regions were covered by 20 and 8 paths/rows, respectively. The total number of images used in the two regions was more than 200 (Table A1 and Table A2). All of the data were processed to 30 m resolution.
3. Methodology
The CLCD dataset combined with a knowledge criterion and spatial analysis methods to construct a medium–high-resolution accurate dataset of the historical distribution of afforestation (i.e., AFF), reforestation (i.e., REF), and deforestation (i.e., DEF) in the Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta regions of China. The Landsat-based LST was inverted using the atmospheric correction approach. Based on these datasets and the moving window strategy and spatial–temporal patterns change analysis methods, the medium–high-resolution distribution of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation data were used to quantify the impacts of afforestation, reforestation, deforestation, and conversion of afforestation to non-forests (i.e., AFF to DEF or AFF to NF) on LST in the decade of 2010–2020 (Figure 3).
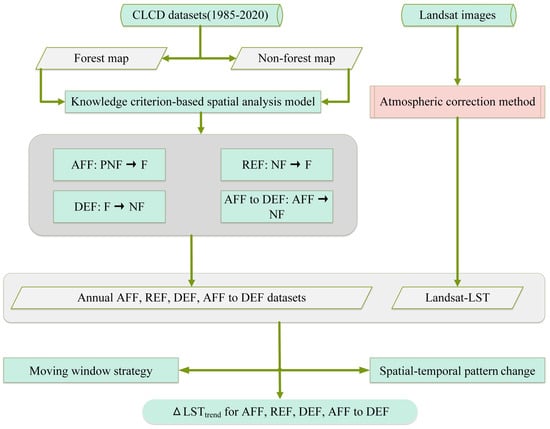
Figure 3.
Workflow diagram.
3.1. Knowledge Criteria-Based Spatial Analysis Model Construction
Our research presents a unique and innovative approach to constructing a knowledge criterion-based spatial analysis model (Figure 4). This model is built upon a comprehensive understanding of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation [,,,,,] but also introduces a novel perspective to these concepts. Afforestation, for instance, transforms persisting non-forested areas into forested land.
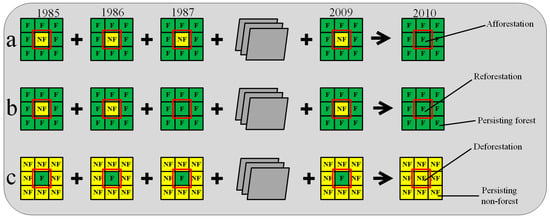
Figure 4.
Conceptual flowchart of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation dataset construction algorithm.
Our approach involved a meticulous process of historical annual afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation dataset construction in the YRD and PRD regions during 2010–2020, which combined the knowledge criterion and the definition of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation with the spatial analysis method (Figure 4). We characterized the distribution of these forest activities from 2010 to 2020 based on the dense time series CLCD dataset (1985–2020). The dataset construction process included identifying the intersection between persisting non-forests (i.e., PNF) of previous years (e.g., 1985–2009) and forests (i.e., F) of the current year (e.g., 2010) to determine the afforestation area (e.g., 2010). The intersection between the non-forests (i.e., NF) of the previous year (e.g., 2009) and the forests of the current year (e.g., 2010) determined the reforestation area, that is, once forest areas (e.g., 1985–2008) are deforested (e.g., 2009) and replanted (e.g., 2010). The deforestation area was identified as the intersection between forests of the previous year (e.g., 2009) and non-forests of the current year (e.g., 2010). As one of the deforestation activities, the conversion of afforestation to non-forests (i.e., AFF to NF) from 2010 to 2020 was mapped based on the intersection between afforestation areas in 2010 and non-forests in 2020. Since deforestation in the second year after afforestation does not generally occur, no annual mapping and analysis of deforestation after afforestation has been conducted.
3.2. Atmospheric Correction Method
The atmospheric correction method, also known as the radiative transfer equation method, was a key component of our work. This method was used to invert the surface temperature [,,,]. The basic steps of the atmospheric correction method are as follows: first, estimate the effect of the atmosphere on the surface thermal radiation. Then, subtract this portion of the error from the total amount of thermal radiation observed by the satellite sensor to obtain the surface thermal radiation intensity. Finally, this intensity of thermal radiation is converted into the corresponding surface temperature. The thermal infrared radiance value Lλ that the satellite sensor receives is composed of upward atmospheric radiation L↑, the energy of actual radiation on the ground that reaches the satellite sensor after passing through the atmosphere, and the energy of downward atmospheric radiation that reaches the ground and is reflected. The satellite sensor’s received thermal infrared radiance value Lλ was computed using the following equation:
where ε is the surface-specific emissivity calculated by the NDVI threshold method based on Sobrino et al. [,] and Qin et al. (2004) []; the land surface is divided into water, natural surface, and urban area, and the specific surface emissivity is calculated for three types of land surface, respectively, as in Equations (2)–(4); TS is the actual surface temperature (K); B(TS) is the blackbody thermal radiation; τ is the transmittance of the atmosphere in the thermal infrared band; L↓ is the downward radiation.
Lλ = [ε × B(TS) + (1 − ε)L↓]τ + L↑
Here, εwater, εsurface, and εbuilding represent the specific emissivity of the water body, natural surface, and urban area, respectively. The fraction vegetation cover (FVC) is the vegetation coverage calculated using the dimidiate pixel model in Equation (5).
FVC = [(NDVI − NDVISoil)/(NDVIVeg − NDVISoil)]
Among them, NDVI is the normalized vegetation index; NDVISoil is the NDVI value of the utterly bare soil or non-vegetated area, and NDVIVeg represents the NDVI value of the pixel entirely covered by vegetation, that is, the NDVI value of the pure vegetation pixel. The empirical values NDVIVeg = 0.70 and NDVISoil = 0.05 are taken; when the NDVI of a pixel is greater than 0.70, the FVC value is 1. When NDVI is less than 0.05, FVC is 0. B(TS) is calculated by Equation (6):
B(TS) = [Lλ − L↑ − τ(1 − ε)L↓]/(τ × ε)
TS can be obtained as a function of Planck’s formula:
TS = K2/ln (K1/B(TS) + 1)
For TM, K1 = 607.76 W/(m2 µm sr), and K2 = 1260.56 K; for TIRS Band10, K1 = 774.89 W/(m2 µm sr), and K2 = 1321.08 K.
It is evident from the preceding that two parameters are needed for such an algorithm: surface-specific radiance and atmospheric profile parameters. The atmospheric profile parameter can be accessed by inputting the imaging time and the center’s latitude and longitude on the NASA website (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 14 July 2023)). This technique only applies to data in a single thermal infrared band, such as Landsat TM/TIRS data [].
3.3. Moving Window Searching Strategy and Spatial–Temporal Pattern Changes Analysis Method
We used the spatial–temporal pattern variation analysis method [,] to calculate the mean values of the LST change trend in selected 5 km × 5 km grids for each actual conversion type like afforestation (PNF to F), reforestation (NF to F), deforestation (F to NF), and conversion of afforestation to non-forests (AFF to NF) from 2010 to 2020. When forests become non-forests or non-forests are converted to forests, they affect the climate system by altering biogeophysical and biogeochemical processes [,], impacting temperature regulation []. The effects of such changes in the forests on temperature are called actual impacts. The actual impacts can be quantified regarding the difference in LST trends for afforested/reforested and deforested pixels minus nearby unchanged non-forests and forests, respectively []. When the background environment is heterogeneous, non-local factors may impact the difference in LST trends, so these residual effects can be reduced mainly by averaging ΔLST (difference in LST trends) over multiple pixels and comparing samples [].
Specifically, we used a moving window searching strategy to find all available valid forest change grids. This ensures that forested and non-forested areas are close together and have similar climate backgrounds [,]. We first created 5 km × 5 km grids covering the study area. The 5 km × 5 km grids represented a “local” scale for LST. Previous studies have proved that similar trends could be obtained when different grid sizes and thresholds evaluated the impacts on surface temperature [,,]. We then adopted a moving window searching method to filter the valid grids based on afforestation, reforestation, deforestation, and deforestation in afforested areas distribution data as well as the following rules: (i) Effective afforestation (or reforestation) and deforestation grids (5 km × 5 km) must have at least 5% afforestation and deforestation pixels, respectively; (ii) effective unchanged non-forest and unchanged forest pixels must have at least 80% in each valid grid, respectively. Since the afforestation distribution area covers a small proportion of the land area, less deforestation is distributed in afforested areas. So, to satisfy the valid grids of conversion of afforestation to non-forests (AFF to NF), we modified the threshold as at least 5% to 1% and 0.5% deforestation pixels in the Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta region, respectively. The threshold for unchanged forest pixels stayed the same.
Next, the impact of actual afforestation (ΔLSTafforestation_trend) and reforestation (ΔLSTreforestation_trend) on LST can be quantified by subtracting the difference in mean LST trends of nearby unchanged non-forests (LSTunchanged non-forest) from the afforestation pixels (LSTafforestation) and reforestation pixels (LSTreforestation), respectively (Equations (8) and (9)) [,,]. Here, the LSTafforestation is expressed as ‘LST2 (LSTmean of afforestation in 2020) − LST1 (LSTmean of persisting non-forests in 2010)’, and the LSTunchanged non-forest is described as ‘LST2 (LSTmean of unchanged non-forest in 2020) − LST1 (LSTmean of unchanged non-forest in 2010)’. The actual impact of deforestation on LST (ΔLSTdeforestation_trend) can be quantified by subtracting the difference in LST trends of nearby unchanged forests (LSTunchanged forest) from the deforestation pixels (LSTdeforestation) (Equation (10)). The impacts of conversion of afforestation to non-forests (AFF to NF) on LST also can be calculated using Equation (10). The positive or negative values of ΔLSTafforestation_trend, ΔLSTreforestation_trend, and ΔLSTdeforestation_trend mean a warming or cooling effect, respectively. Zero values mean no change. The equations for quantifying the actual impact of forestation (e.g., afforestation and reforestation) and deforestation on LST, respectively, are given below:
Afforestation: ΔLSTafforestation_trend = LSTafforestation − LSTunchanged non-forest
Reforestation: ΔLSTreforestation_trend = LSTreforestation − LSTunchanged non-forest
Deforestation: ΔLSTdeforestation_trend = LSTdeforestation − LSTunchanged forest
4. Results
4.1. Accuracy Assessment of the Spatiotemporal Pattern of Afforestation, Reforestation, and Deforestation Maps
According to the National Forestry Yearbook of China, from 2010 to 2020, the forest area in the YRD region decreased by 1,884,200 hm2, and in the PRD region by 930,000 hm2. Meanwhile, the results of the current study found that from 2010 to 2020, the forest area in the YRD and PRD regions showed a decreasing trend. The forest area in the YRD region decreased by 262,692 hm2 (0.73% of the area), and the forest area in the PRD region decreased by 56,101.68 hm2 (1.00% of the area) in the decade. It indicated a more significant decrease in net forest area in the YRD and a faster decrease in forest area in the PRD. The difference between them is mainly due to the inconsistent definition of forest, but both believe that the forest area of the Yangtze River Delta has declined more seriously. Valuing the afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation maps was difficult. So, the accuracy of the forest cover datasets mentioned in Section 2.2 has been taken as one of the validation results for these maps.
4.2. Historical Distribution of Afforestation, Reforestation, and Deforestation
Figure 5 illustrates that the activities of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation in the Yangtze River Delta from 2010 to 2020 were primarily concentrated in the southwestern part of the region. In the PRD region, afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation activities were mainly observed in the western, northern, and eastern hilly and mountainous areas, with less distribution in other places. Except for individual years, the annual deforestation area in the two regions was more significant than the annual afforestation area.
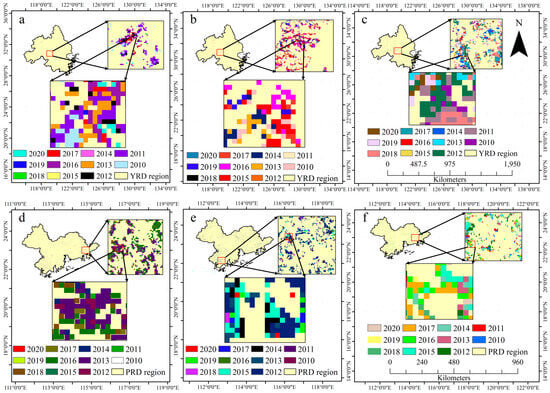
Figure 5.
Historical yearly distribution of afforestation (a,d), reforestation (b,e), and deforestation (c,f) in the YRD and PRD from 2010 to 2020, respectively.
Figure 6a shows that the changing trend of afforested and reforested areas in the Yangtze River Delta region is the same, and the sum of ten years’ deforested area (508,468.32 hm2) is higher than the sum of reforested area (256,341.06 hm2). The ratio of afforested areas fluctuates from year to year. Still, it is relatively stable on the whole, with an annual average of 9588.54 hm2 of the afforested area in the period from 2010 to 2020 (0.05%); the most afforested year was 2010, with an afforested area of 13,839.03 hm2, and the least afforested year was 2019, with an afforested area of 3948.66 hm2. The annual average reforested area for 2010–2020 was 23,303.73 hm2 (0.11%). The most reforested year was 2015, with a reforested area of 39,467.88 hm2, and the year with the least reforestation was 2020, with a reforestation area of 9088.74 hm2. The annual average deforestation area from 2010 to 2020 was 46,224.39 hm2 (0.22%); the year with the most deforestation was 2012, with an area of 112,049.73 hm2, and the year with the least deforestation was 2020, with an area of 13,538.16 hm2.
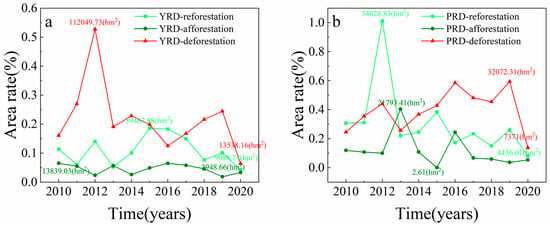
Figure 6.
Annual change in the area rate of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation in the YRD (a) and PRD (b) regions from 2010 to 2020.
Figure 6b shows that the trend of the afforested and reforested areas in the PRD region over the ten years is the same, with the sum of the ten-year deforestation area (234,528.03 hm2) being higher than the sum of the reforested area (182,170.62 hm2). The average annual afforested area from 2010 to 2020 was 4870.87 hm2 (0.09%); the year with the most afforested area was 2013, with an afforested area of 21,793.41 hm2, and the year with the least afforested area was 2015, with an afforested area of 2.61 hm2. The average annual reforested area was 16,560.97 hm2 (0.31%); the most reforested year was 2012, with 54,628.83 hm2, and the most petite reforestation year was 2020, with 4436.01 hm2. The average annual deforestation area was 21,320.73 hm2 (0.40%); the most deforestation year was 2019, with 32,072.31 hm2 of deforestation, and the least deforestation year was 2020, with an area of 7371 hm2.
4.3. Quantifying the Impact of Actual Afforestation, Reforestation, and Deforestation on LST
Based on the filtering criteria of effective grids for afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation, we obtained several effective grids for afforestation, reforestation, deforestation, and conversion of afforestation to non-forests as comparison samples through the moving window strategy, which provided data for subsequent quantification of the impacts of actual afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation on surface temperature (Figure 7). Figure 7 shows that the effective grids of afforestation, reforestation, deforestation, and conversion of afforestation to non-forests in the YRD region are mainly distributed in the southwest region, with fewer effective grids distributed in the northeast. Those of afforestation, reforestation, deforestation, and conversion of afforestation to non-forests in the PRD region are predominantly concentrated in the southwest, northeast, and northwest, with fewer in the central area. In terms of quantity, the number of effective grids for deforestation and conversion of afforestation to non-forested forests was higher than that for forestation in YRD. The opposite condition can be found in PRD.
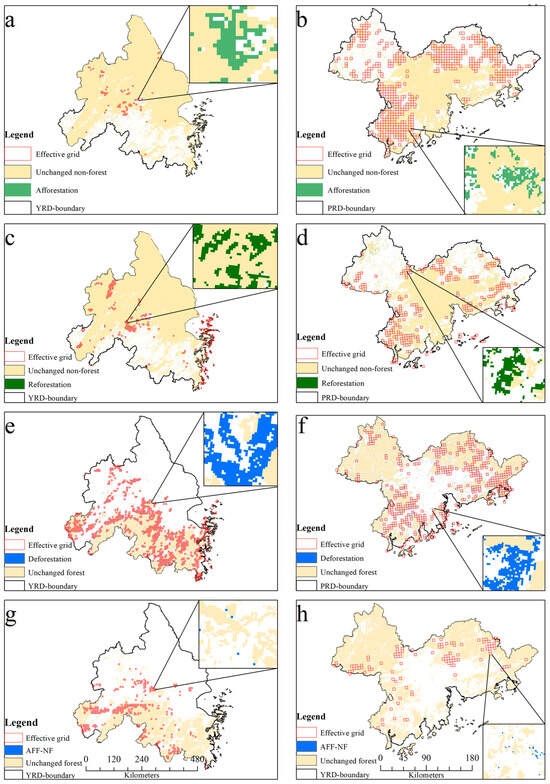
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of effective grids for afforestation (a,b), reforestation (c,d), deforestation (e,f), and conversion of afforestation to non-forests (g,h) in the YRD and PRD regions from 2010 to 2020.
In Figure 8a, afforestation showed a cooling effect in March, June, and September, except for December. The mean value of ΔLSTtrend in each season was −0.24 ± 0.19 °C in YRD. The cooling effect of −1.65 ± 0.32 °C was most pronounced in March; the least pronounced cooling of −0.35 ± 0.32 °C was detected in June, while the warming effect of 1.44 ± 0.36 °C was observed in December. In the PRD region, afforestation showed a cooling impact on all four seasons, and the mean value of ΔLSTtrend in each season was −0.46 ± 0.10 °C. The most considerable cooling effect was −1.29 ± 0.27 °C in June, and the smallest one was −0.06 ± 0.08 °C in March.
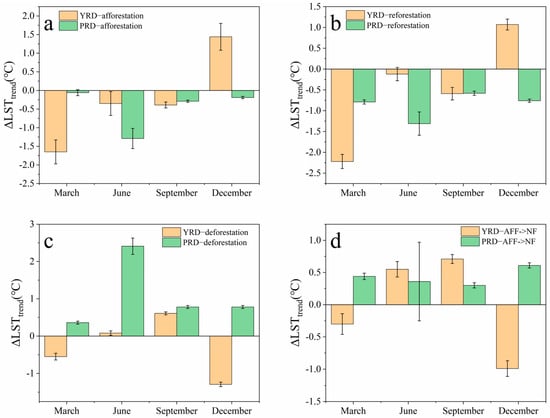
Figure 8.
Seasonal impacts of afforestation (a), reforestation (b), deforestation (c), and conversion of afforestation to non-forests (d) on LST change trend in the YRD and PRD regions from 2010 to 2020, respectively.
In Figure 8b, reforestation showed a cooling effect in March, June, and September, except for December. It indicated that the surface temperature regulation caused by afforestation in the YRD region showed seasonal variations. The mean value of ΔLSTtrend in each season was −0.47 ± 0.15 °C, with the most significant cooling of −2.22 ± 0.17 °C in March; the most negligible impact of −0.12 ± 0.16 °C was found in June, and December had an opposite warming of 1.07 ± 0.13 °C. The cooling effect was reflected in all seasons in the PRD region, with the mean value of ΔLSTtrend in all seasons being −0.86 ± 0.11 °C. The most considerable cooling of −1.31 ± 0.28 °C was in June, and the most negligible impact of −0.58 ± 0.05 °C was found in September.
Figure 8c shows that deforestation generally has a warming effect. In the warm season, including June and September, deforestation manifested a warming impact in YRD. The cold season, including March and December, showed a cooling effect in YRD, showing apparent seasonal variations. The mean value of ΔLSTtrend for each season in YRD caused by deforestation was −0.29 ± 0.06 °C, with a more significant cooling impact of −1.29 ± 0.06 °C in December and a minor cooling of −0.55 ± 0.09 °C in March, a more substantial warming of 0.61 ± 0.04 °C in September, and a minor warming of 0.08 ± 0.06 °C in June. Deforestation caused a warming effect in PRD during all seasons. The mean value of ΔLSTtrend for all seasons in the PRD was 1.08 ± 0.08 °C, with the most significant warming of 2.42 ± 0.22 °C in June and the slightest warming of 0.36 ± 0.04 °C in March.
Figure 8d shows that the conversion of afforestation to non-forests (AFF to NF) generally has a warming effect. It caused a warming effect in the YRD region in June and September. A cooling effect in the YRD region was detected in March and December. Those showed noticeable seasonal variations. The mean value of ΔLSTtrend for each season due to deforestation in afforested areas in the YRD was −0.01 ± 0.12 °C, with a larger warming amplitude of 0.71 ± 0.07 °C in September and a smaller warming amplitude most of all of 0.55 ± 0.12 °C in June. The most considerable cooling of −0.99 ± 0.12 °C was found in December, and the most minor cooling was in March at −0.30 ± 0.16 °C. The conversion of afforestation to non-forests had a warming effect in all seasons in the PRD region. The mean value of ΔLSTtrend for all seasons in PRD was 0.43 ± 0.19 °C, with the most significant warming in December at 0.61 ± 0.04 °C and the smallest in September at 0.30 ± 0.04 °C.
The cooling impacts caused by different conversion types were detected in YRD, especially reforestation. In contrast, the warming impacts caused by deforestation and conversion of afforestation to non-forests offset the cooling caused by afforestation and reforestation in PRD. The values showed a cooling of −1.01 ± 0.13 °C in YRD and a warming of 0.19 ± 0.12 °C in PRD. Among them, reforestation dominated the cooling, especially in the PRD region. Moreover, the cooling effect of forestation and the warming effect of two kinds of deforestation in the PRD is higher than that in YRD, especially for reforestation and deforestation. In detail, afforestation and reforestation led to seasonal cooling impacts, especially in summer in the PRD, while consistent cooling was found in YRD, except for December. Deforestation and afforestation converting to non-forests increased the LST in the PRD region, mainly induced by deforestation. In contrast, those in the YRD region caused inconsistent impacts like warming in March and December and cooling in June and September.
5. Discussion
5.1. Spatial–Temporal Patterns of Afforestation, Reforestation, and Deforestation in Two Regions
This study presents reliable spatial distribution data on afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and Pearl River Delta (PRD) regions from 2010 to 2020. Our findings indicate that afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation activities were concentrated in the southwestern region of the YRD. In contrast, these activities were mainly distributed in the PRD’s western, northern, and eastern hilly and mountainous areas. According to the China Forestry Statistical Yearbook, the cities in YRD witnessed the largest afforestation areas in the southwest (cities in Anhui province: 48,711 hm2 in 2010 and 51,264 hm2 in 2020) and the northeast (cities in Jiangsu province: 86,256 hm2 in 2010 and 32,370 hm2 in 2020). In PRD, the regions with the most afforestation in 2010 were located in the northwest (Zhaoqing City: 8606 hm2), the east (Huizhou City: 5871 hm2), and the southwest (Jiangmen City: 6952 hm2). In 2020, the largest afforestation areas were located in the east (Huizhou City: 1340 hm2) and the southwest (Jiangmen City: 6952 hm2). Primarily, our findings about the spatial–temporal distribution characteristics of afforestation data were consistent with the characteristics reflected by these field measurement data, indicating the data’s reliability and the knowledge criteria-based spatial analysis model.
Moreover, our results indicate that, with few exceptions, the annual deforestation area exceeded the afforestation area in both regions each year. A previous study that reported a gradual decline in forest cover in the Yangtze River Delta region from 2001 to 2015 can support this condition []. Figure 6 reveals notable deforestation in the YRD region and substantial reforestation in the PRD region in 2012. Based on CLCD-based land cover change analysis, the transition between forest and cropland is predominant in these two areas. Specifically, 12,686 hm2 of forest were converted to cropland in the YRD region in 2012. This conversion may be attributed to various factors, including economic development and urbanization, policy pressures related to cultivated land protection, and the impacts of natural disasters and ecological stress. These factors are corroborated by national government documents (https://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2010-05/24/content_1612730.htm (accessed on 24 March 2024), https://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2011-06/08/content_1879180.htm (accessed on 24 March 2024)). Concurrently, 58,979.88 hm2 of cropland were converted into forest in the PRD region in 2012. This shift may be driven by the promotion of ecological and environmental protection policies, the need for ecological restoration and security, economic restructuring, and the implementation of policies by national and local governments (https://www.gdlinye.cn/news/665.html (accessed on 24 March 2024), https://ghzyj.gz.gov.cn/ywpd/tdgl/tdghjh/content/post_2747682.html (accessed on 24 March 2024)).
5.2. Effect of Forest on Surface Temperature in Different Regions
Forestation has a cooling effect, while deforestation leads to localized temperature increases in two regions [,,]. Transpiration is the main driving force behind the cooling effect of forests despite the reduced surface albedo, especially in low-latitude areas []. Furthermore, the forest plants’ comparatively high specific heat absorbs heat radiation and prevents heat conduction to produce the cooling effect. The tree canopy also serves as a shield to lessen the radiant heat that reaches the ground. When the forest was lost, a decrease in evapotranspiration and roughness would lead to a warming effect [,]. It has been suggested that there has been controversy at different latitudes; for example, deforestation may also bring cooling at higher latitudes [,,].
Afforestation and reforestation maintained similar temperature effect trends in this study. Reforestation has more excellent climatic benefits than afforestation in the two regions. It is suggested that forests be replanted or restored on once forested land can better mitigate climate impacts. Because reforested areas were once forested, reforestation can increase biodiversity and prevent additional effects of land cover change on the local climate []. The cooling effect of forests in the PRD region is more pronounced than in the YRD region. Past studies have found that compared with other climate zones, the south subtropical and tropical humid zone has the most significant increase in carbon storage and sinks and a substantial increase in latent heat fluxes; afforestation in this climate zone, therefore, showed the most apparent cooling effect [,,]. The PRD region belongs to this zone, with stronger evapotranspiration and more extensive forest carbon stocks and sinks. In contrast, the YRD region belongs to the central and northern subtropical humid zones and the mid-latitude zone, so the cooling effect of forests is not as strong as that of the PRD region. Deforestation and conversion of afforestation to non-forests almost had an overall warming effect, respectively. However, two deforestation activities led to some cooling impact in the YRD region. The Pearl River Delta has a lower latitude than the Yangtze River Delta. When forests decrease, the temperature changes across latitudes, with warming at lower latitudes and reduced warming or cooling at higher latitudes because the high albedo effects may exceed the effect of evapotranspiration [,,].
5.3. Effect of Forest on Surface Temperature in Different Seasons
In the PRD region, forests have the most significant moderating effect on surface temperature in summer, mainly due to the robust photosynthesis and transpiration in summer and stronger evapotranspiration from forests, which has a more intense cooling effect [,,]. The moderating effect of forests on surface temperature in the YRD region showed apparent seasonal variations. In general, forests showed a warming effect in the cold and cooling effects in the warm seasons. The study of Anderson et al. [] pointed out that the interaction between vegetation removal and the atmosphere in temperate forests varied seasonally. They found a cooling effect occurring in winter and spring and a warming effect in summer. It can support the cooling or warming impacts caused by deforestation in the YRD region. Previous studies showed that tropical forests maintain a robust cooling effect throughout the year, whereas apparent seasonal variations can be seen at mid-to-high latitudes []. For instance, during the warmer months, there is a significant net daily cooling impact due to the dominance of the daytime cooling effect. In contrast, daytime warming extends to most mid- and high-latitude forests during the colder months. Moreover, daytime and extensive nocturnal warming lead to the most significant daily warming effect [,]. The YRD region is located in the mid-latitude zones. During the summer, forests have a strong cooling effect due to solid evapotranspiration and absorption of thermal radiation, resulting in a dominant cooling effect during the daytime. In winter, due to solid surface albedo and weaker evapotranspiration, forests have a warming effect both during the day and at night, leading to a general warming effect [,,,]. Ultimately, this condition leads to seasonal variations in the thermoregulatory effect of forests [].
5.4. Deficiencies and Prospects
The temperature data obtained in this study were surface temperature. Air temperature was usually recommended for studying the ability of forest-regulated temperature. Although there is a strong correlation between air temperature and surface temperature, there are still differences. Mutiibwa et al. (2015) studied surface and air temperature relationships in complex terrain []. They found the most robust relations in late summer and autumn and the weakest in winter and early spring. No proven conversion formula between them can be adopted, which is a shortcoming of this study. In addition, this study suffers from data validation deficiencies and lacks site-measured temperature data to validate the accuracy of the surface temperature inversion data because it has been proven that there was an inconsistency between the inversion surface temperature and the actual station temperature data []. The LST inversion results of different Landsat sensors are slightly different due to the inconsistent parameters []. However, although using different sensors’ results to detect LST change may lead to a slight overestimation or underestimation, the overall trend of forest change’s impact on LST is not affected in these cases []. This situation also manifests in validating afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation data due to insufficient historical survey data and inconsistent definitions []. Future work must integrate remote sensing data, in situ measurements, and simulation modeling to develop a robust evaluation model of the climate effect of precision forest change [,].
6. Conclusions
In this study, we constructed the spatial distribution data of afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation in the YRD and PRD urban agglomerations from 1985 to 2020 based on the 30 m year-by-year land cover dataset and knowledge criteria-based spatial analysis models. We also used the surface temperature inversion data, combined with the moving window strategy and the spatial and temporal pattern change analysis method, to analyze the surface temperature effects of afforestation, reforestation, deforestation, and afforestation converting to non-forests in the YRD and the PRD urban agglomerations from 2010 to 2020. Meanwhile, we compared the differences in the regulation of surface temperatures by forests in these two regions and different seasons. Overall, there was a decreasing trend in forest area, as evidenced by the annual deforestation area in the YRD and PRD regions, which was more significant than the yearly afforestation area in most years. Most afforestation, reforestation, and deforestation in the YRD region are in the western and southern hills. In contrast, those in the PRD region are in western, northern, and eastern hills and mountains. In addition, afforestation and reforestation led to a cooling effect. On the contrary, deforestation and afforestation converting to non-forests led to inconsistent impacts. The cooling effect of forests in the PRD region was more evident than in the YRD region. In PRD, the cooling effect of forests was more significant in summer. Forests’ surface temperature regulation in the YRD region showed apparent seasonal variations. Our conclusions contribute to understanding the climate mitigation effects of forestation and reduced deforestation in Southern China.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, Z.T.; writing—review and editing, supervision, conceptualization, W.S.; investigation, X.S. and C.G.; validation, T.W.; writing—review and editing, data curation, J.H.; conceptualization, C.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Our work was jointly funded or supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32371878, 32001251), the Jiangsu Science and Technology Association Youth Science and Technology Talent Lifting Project, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20200781), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Data Availability Statement
The data used are primarily included in this paper. Other relevant data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the China Land Cover Dataset (CLCD) from Wuhan University, China, which provided the Landsat-based land cover data. It is also the appropriate place to thank colleagues, editors, reviewers, and Wenjing Ye.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Summary of Landsat data used for the Yangtze River Delta region.
Table A1.
Summary of Landsat data used for the Yangtze River Delta region.
| Period | Acquisition Date | Satellite | Cloud | Path/Row |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 10 March 2011 29 May 2011 2 September 2011 20 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 1% 17% 2% | 117/039 |
| 17 March 2011 21 June 2011 19 September 2009 5 December 2008 | Landsat 5 TM | 14% 0% 2% 3% | 118/038 | |
| 24 March 2008 20 July 2010 19 September 2009 27 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 6% 12% 7% | 118/039 | |
| 18 April 2011 15 June 2009 21 October 2009 27 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 14% 1% 2% | 118/040 | |
| 10 February 2010 23 July 2011 22 September 2010 27 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 8% 3% 4% 1% | 118/041 | |
| 8 March 2011 2 June 2008 7 September 2008 2 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 9% 12% 12% 0% | 119/037 | |
| 29 March 2007 22 June 2009 31 October 2010 18 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 2% 17% 0%, 5% | 119/038 | |
| 29 March 2007 6 June 2009 10 September 2009 18 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 19% 6% 7% | 119/039 | |
| 29 March 2007 6 June 2009 16 September 2011 12 December 2008 | Landsat 5 TM | 1% 4% 2% 9% | 119/040 | |
| 8 March 2011 6 June 2009 16 September 2011 26 November 2008 | Landsat 5 TM | 8% 0% 3% 3% | 119/041 | |
| 12 March 2010 3 June 2011 13 August 2008 9 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 7% 3% 17% 5% | 120/036 | |
| 28 March 2010 24 June 2007 23 September 2011 25 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 11% 3% 2% 1% | 120/037 | |
| 28 March 2010 13 June 2009 20 September 2010 9 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 2% 2% 15% 1% | 120/038 | |
| 28 March 2010 13 June 2009 12 September 2007 9 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 1% 0% 0% | 120/039 | |
| 28 March 2010 19 June 2011 28 September 2007 9 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 1% 11% 2% 0% | 120/040 | |
| 19 March 2010 28 June 2011 23 September 2011 14 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 2% 12% 11% 1% | 121/037 | |
| 19 March 2010 4 June 2009 14 September 2011 10 December 2008 | Landsat 5 TM | 0%, 5% 17% 0% | 121/038 | |
| 19 March 2010 4 June 2009 14 September 2011 10 December 2008 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 0% 10% 0% | 121/039 | |
| 26 March 2010 1 June 2011 18 September 2010 7 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 20% 2% 0% | 122/038 | |
| 26 March 2010 27 June 2009 18 September 2010 7 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 11% 1% 0% | 122/039 | |
| 2020 | 16 March 2019 1 June 2018 24 September 2019 7 December 2017 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 1% 6.35% 8% 7.14% | 117/039 |
| 28 March 2021 2 June 2018 28 September 2018 22 December 2020 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 5.45% 9.33 16.82% 0.61% | 118/038 | |
| 28 March 2021 16 June 2021 28 September 2018 22 December 2020 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 15.73% 17.06% 18.78% 0.81% | 118/039 | |
| 1 March 2017 5 June 2017 20 September 2021 22 December 2020 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 1.7% 14.55% 9.19% 0.27% | 118/040 | |
| 1 March 2017 16 June 2015 17 September 2020 17 December 2018 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.28% 7.19% 15.54% 2.35% | 118/041 | |
| 27 March 2018 19 May 2020 24 September 2020 11 December 2019 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.47% 1.22% 19.85% 0.71% | 119/037 | |
| 27 March 2018 23 June 2021 8 September 2020 5 December 2017 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 8.95% 3.98% 13.98% 0.68% | 119/038 | |
| 11 March 2018 23 June 2021 27 September 2021 5 December 2017 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 1.36% 8.32% 0.62% 18.86% | 119/039 | |
| 11 March 2018 23 June 2021 27 September 2021 11 December 2019 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.62% 15.86% 0.02% 0.14% | 119/040 | |
| 11 March 2018 4 June 2020 27 September 2021 11 December 2019 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.03% 7.97% 0.09% 2.28% | 119/041 | |
| 23 March 2020 16 June 2016 29 September 2019 4 December 2020 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 4.79% 10.66% 3.27% 5.62% | 120/036 | |
| 7 March 2020 6 June 2018 29 September 2019 20 December 2020 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.04% 0.79% 15.42% 18.06% | 120/037 | |
| 26 March 2021 6 June 2018 18 September 2021 20 December 2020 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.23% 4.8% 1.81% 0.48% | 120/038 | |
| 26 March 2021 27 June 2020 29 September 2019 2 December 2019 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.01% 0.67% 1.12% 3.6% | 120/039 | |
| 26 March 2021 11 June 2020 29 September 2019 7 December 2021 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.01% 9.94% 1.97% 0.6% | 120/040 | |
| 14 March 2020 21 June 2020 14 September 2017 14 December 2021 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 4.45% 7.96% 0.05% 0.12% | 121/037 | |
| 14 March 2020 5 June 2021 14 September 2017 9 December 2019 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 1.24% 2.66% 1.38% 5.39% | 121/038 | |
| 14 March 2020 5 June 2021 6 September 2020 30 December 2021 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 3.27% 4.23% 4.44% 0.13% | 121/039 | |
| 5 March 2020 25 June 2020 27 September 2019 13 December 2018 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 4.98% 4.4% 15.83% 0.99% | 122/038 | |
| 5 March 2020 9 June 2020 16 September 2021 21 December 2021 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 3.88% 4.01% 4.99% 0.22% | 122/039 |

Table A2.
Summary of Landsat data used for the Pearl River Delta region.
Table A2.
Summary of Landsat data used for the Pearl River Delta region.
| Period | Acquisition Date | Satellite | Cloud | Path/Row |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 16 March 2009 16 May 2008 8 September 2009 10 December 2008 | Landsat 5 TM | 5% 10% 15% 0% | 121/044 |
| 19 March 2010 4 June 2009 19 September 2009 13 December 2009 | Landsat 5 TM | 10% 0% 2% 14% | 121/045 | |
| 26 March 2010 1 June 2011 18 September 2010 4 December 2009 | Landsat 5 TM | 0% 13% 11% 1% | 122/043 | |
| 26 March 2010 11 June 2011 18 September 2010 4 December 2009 | Landsat 5 TM | 6% 0% 19% 3% | 122/044 | |
| 26 March 2010 1 June 2011 18 September 2020 15 December 2009 | Landsat 5 TM | 3% 0% 10% 4% | 122/045 | |
| 14 March 2009 21 June 2010 28 September 2011 8 December 2008 11 October 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 2% 4% 14% 10% | 123/043 | |
| 14 March 2009 29 June 2007 6 September 2009 30 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 1% 4% 16% 1% | 123/044 | |
| 11 March 2009 1 May 2009 22 September 2009 30 December 2010 | Landsat 5 TM | 18% 1% 8% 0% | 123/045 | |
| 2020 | 9 March 2018 16 June 2019 9 September 2021 14 December 2021 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.77% 15.89% 18.76% 6.07% | 121/044 |
| 1 March 2021 10 June 2017 4 September 2019 9 December 2019 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 6.11% 11.64% 18.64% 13.77% | 121/045 | |
| 20 April 2019 28 August 2020 27 September 2021 5 December 2021 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 3.65% 5.89% 5.99% 0.02% | 122/043 | |
| 26 March 2016 17 June 2017 27 September 2019 2 December 2020 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 10.93% 17.34% 4.73% 16.53% | 122/044 | |
| 19 March 2019 7 June 2019 27 September 2019 2 December 2020 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 4.02% 19% 15.53% 6.16% | 122/045 | |
| 7 March 2018 16 June 2020 25 September 2016 7 December 2019 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 5.37% 16.54% 16.89% 0.02% | 123/043 | |
| 23 March 2018 14 June 2019 18 September 2019 12 December 2021 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.03% 7.15% 15.63% 1.51% | 123/044 | |
| 23 March 2018 19 June 2020 15 September 2018 12 December 2021 | Landsat 8 OLI/TIRS | 0.51% 18.87% 10.96% 2.69% | 123/045 |
References
- Brockhaus, M.; Di Gregorio, M.; Djoudi, H.; Moeliono, M.; Pham, T.T.; Wong, G.Y. The forest frontier in the Global South: Climate change policies and the promise of development and equity. AMBIO 2021, 50, 2238–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, H.; Bastos, A.; Das, A.J.; Esquivel-Muelbert, A.; Hammond, W.M.; Martinez-Vilalta, J.; McDowell, N.G.; Powers, J.S.; Pugh, T.A.M.; Ruthrof, K.X.; et al. Climate Change Risks to Global Forest Health: Emergence of Unexpected Events of Elevated Tree Mortality Worldwide. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 673–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadka, D.; Babel, M.S.; Tingsanchali, T.; Penny, J.; Djordjevic, S.; Abatan, A.A.; Giardino, A. Evaluating the impacts of climate change and land-use change on future droughts in northeast Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvjetković, B.; Mataruga, M. Afforestation and Its Climate Change Impact. In Life on Land; Leal Filho, W., Azul, A.M., Brandli, L., Lange Salvia, A., Wall, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; He, J.; Huang, C.; Li, M. Quantifying the Actual Impacts of Forest Cover Change on Surface Temperature in Guangdong, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yue, C.; Luyssaert, S. Reconciling different approaches to quantifying land surface temperature impacts of afforestation using satellite observations. Biogeosciences 2023, 20, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Tang, W.; Zuo, T.; Li, E.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Impacts of afforestation on land surface temperature in different regions of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 318, 108901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shen, W.; Wang, T.; He, J.; Cao, P.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, W.; Huang, C. Impacts of forest cover change on local temperature in Yangtze River Delta and Pearl River Delta urban agglomerations of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 357, 110205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; He, J.; He, T.; Hu, X.; Huang, C. Biophysical Effects of Afforestation on Land Surface Temperature in Guangdong Province, Southern China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2022, 127, e2022JG006913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, R.M.; Davin, E.; O’Halloran, T.; Pongratz, J.; Zhao, K.; Cescatti, A. Local temperature response to land cover and management change driven by non-radiative processes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lim, C.H.; Chung, H.I.; Kim, Y.; Cho, H.J.; Hwang, J.; Kraxner, F.; Biging, G.S.; Lee, W.K.; Chon, J.; et al. Forest management can mitigate negative impacts of climate and land-use change on plant biodiversity: Insights from the Republic of Korea. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuyper, M.; Chávez, R.O.; Lohbeck, M.; Lastra, J.A.; Tsendbazar, N.; Hackländer, J.; Herold, M.; Vågen, T.-G. Continuous monitoring of forest change dynamics with satellite time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Li, M.; Huang, C.; He, T.; Tao, X.; Wei, A. Local land surface temperature change induced by afforestation based on satellite observations in Guangdong plantation forests in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 276–277, 107641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Soria, G.; Romaguera, M.; Guanter, L.; Moreno, J.; Plaza, A.; Martinez, P. Land Surface Emissivity Retrieval From Different VNIR and TIR Sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, W.; Yu, W.; Wu, T. Combined effects of urban forests on land surface temperature and PM2.5 pollution in the winter and summer. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 104, 105309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Liu, Q.; Ji, M.; He, J.; He, T.; Huang, C. Impacts of urban forests and landscape characteristics on land surface temperature in two urban agglomeration areas of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, A.; Mohan, M.; Galgamuwa, G.A.P.; Watt, M.S.; Montenegro, J.F.; Mills, F.; Carlsen, S.C.H.; Valasquez-Camacho, L.; Bomfim, B.; Pons, J.; et al. The status of forest carbon markets in Latin America. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevedello, J.A.; Winck, G.R.; Weber, M.M.; Nichols, E.; Sinervo, B. Impacts of forestation and deforestation on local temperature across the globe. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Xiao, L. Is Forest Restoration in the Southwest China Karst Promoted Mainly by Climate Change or Human-Induced Factors? Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9895–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch, M.G.; Davin, E.L.; Seneviratne, S.I. Prioritizing forestation based on biogeochemical and local biogeophysical impacts. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Lugo, A.E.; Chapman, J. Biomass of tropical tree plantations and its implications for the global carbon budget. Can. J. For. Res. 1986, 16, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavani, B.F.; Sousa Junior, W.C.; Inouye, C.E.N.; Vieira, S.A.; Mello, A.Y.I. Estimating and valuing the carbon release in scenarios of land-use and climate changes in a Brazilian coastal area. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 226, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yin, L.; Feng, X. Quantifying the policy-driven large scale vegetation restoration effects on evapotranspiration over drylands in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Liu, X.; Burakowski, E.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Li, D. Sensitivities and Responses of Land Surface Temperature to Deforestation-Induced Biophysical Changes in Two Global Earth System Models. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 8381–8399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.; Goetz, S.; Loveland, T.; et al. High-Resolution Global Maps of 21st-Century Forest Cover Change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Motesharrei, S.; Mu, Q.; Kalnay, E.; Li, S. Local cooling and warming effects of forests based on satellite observations. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frate, L.; Saura, S.; Minotti, M.; Di Martino, P.; Giancola, C.; Carranza, M.L. Quantifying Forest Spatial Pattern Trends at Multiple Extents: An Approach to Detect Significant Changes at Different Scales. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9298–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Li, M.; Huang, C.; Tao, X.; Li, S.; Wei, A. Mapping Annual Forest Change Due to Afforestation in Guangdong Province of China Using Active and Passive Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.; Goulden, M.L.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Barr, A.; Black, T.A.; Bohrer, G.; Bracho, R.; Drake, B.; Goldstein, A.; Gu, L.; et al. Observed increase in local cooling effect of deforestation at higher latitudes. Nature 2011, 479, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyssaert, S.; Jammet, M.; Stoy, P.C.; Estel, S.; Pongratz, J.; Ceschia, E.; Churkina, G.; Don, A.; Erb, K.; Ferlicoq, M.; et al. Land management and land-cover change have impacts of similar magnitude on surface temperature. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Mildrexler, D.J.; Motesharrei, S.; Mu, Q.; Kalnay, E.; Zhao, F.; Li, S.; Wang, K. Potential and Actual impacts of deforestation and afforestation on land surface temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 14372–14386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugini, L.; Caporaso, L.; Marconi, S.; Cescatti, A.; Quesada, B.; de Noblet-Ducoudré, N.; House, J.I.; Arneth, A. Biophysical effects on temperature and precipitation due to land cover change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ge, Q.; Dong, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Han, S. Characterizing spatial, diurnal, and seasonal patterns of agricultural irrigation expansion-induced cooling in Northwest China from 2000 to 2020. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 330, 109304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Singh, V.P.; Liu, C. Impacts of Spatial Configuration of Land Surface Features on Land Surface Temperature across Urban Agglomerations, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, L.A.; Jung, J.; Masuda, Y.J.; Vargas Zeppetello, L.R.; Wolff, N.H.; Kroeger, T.; Battisti, D.S.; Spector, J.T. Tropical deforestation accelerates local warming and loss of safe outdoor working hours. One Earth 2021, 4, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, T.; Bu, K.; Yan, F.; Yang, C.; Yang, J.J.T.; Climatology, A. The effect of deforestation on the regional temperature in Northeastern China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 120, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Shao, Q.; Cao, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, L. Satellite-Observed Energy Budget Change of Deforestation in Northeastern China and its Climate Implications. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11586–11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ji, F.; Feng, G.; Ma, Q. Analysis of Land Surface Temperature Sensitivity to Vegetation in China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Jackson, R. Biophysical forcings of land-use changes from potential forestry activities in North America. Ecol. Monogr. 2014, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yan, S.; Chen, G. Effects of Urban Redevelopment on Surface Urban Heat Island. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Mirzaei, P.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z. Urban heat island effect of a typical valley city in China: Responds to the global warming and rapid urbanization. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Tariq, A.; Arshad, A.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Bashir, B.; Zhang, H.; Gu, C.; et al. Impacts of Green Fraction Changes on Surface Temperature and Carbon Emissions: Comparison under Forestation and Urbanization Reshaping Scenarios. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Xia, B. Spatial deconstruction and differentiation analysis of early warning for ecological security in the Pearl River Delta, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jin, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, W. Spatiotemporal variation and evolutionary analysis of the coupling coordination between urban social-economic development and ecological environments in the Yangtze River Delta cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 111, 105561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Chen, S.; Wu, M.; Jia, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, D. Increased Ecosystem Carbon Storage between 2001 and 2019 in the Northeastern Margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Li, M.; Huang, C.J. Review of remote sensing algorithms for monitoring forest disturbance from time series and multi-source data fusion. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 22, 1005–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary analysis of the performance of the Landsat 8/OLI land surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.P.; Hansen, M.C.; Stehman, S.V.; Potapov, P.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Vermote, E.F.; Townshend, J.R. Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 2018, 560, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, Z.; Wang, C.; Feng, M.; Pang, Y.; Yu, T.; Li, X. Forest Change Dataset during the 1986–2018 in the Natural Forest Conversion Program, Northeast China; A Big Earth Data Platform for Three Poles: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Paolini, L. Land surface temperature retrieval from LANDSAT TM 5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Qiu, J.; Wang, N.; Ye, J.; Li, M. Predicting Land Surface Temperature and Land Cover Changes Based on Multisource Remote Sensing Spatio-Temporal Fusion in Hefei, Eastern China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 8764–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.H.; Li, W.; Xu, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J. The estimation of land surface emissivity for Landsat TM6. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2004, 16, 28–32,36,41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, R.A. Afforestation cools more or less. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 504–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.; Narisma, G.; Barford, C.; Kucharik, C.; Foley, J. An alternative approach for quantifying climate regulation by ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, D. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation coverage and its associated influence factor analysis in the Yangtze River Delta, eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 32866–32879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Cescatti, A.; Shang, J.; Chen, J.M.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.-P.; Yuan, W.; et al. Asymmetric influence of forest cover gain and loss on land surface temperature. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Teixeira, K.J.; Snyder, P.K.; Twine, T.E.; Cuadra, S.V.; Costa, M.H.; DeLucia, E.H. Climate-regulation services of natural and agricultural ecoregions of the Americas. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutiibwa, D.; Strachan, S.; Albright, T. Land Surface Temperature and Surface Air Temperature in Complex Terrain. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4762–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekertekin, A.; Bonafoni, S. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from Landsat 5, 7, and 8 over Rural Areas: Assessment of Different Retrieval Algorithms and Emissivity Models and Toolbox Implementation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Meng, X.; Dong, S.; Liang, S. Generating the 30-m land surface temperature product over continental China and USA from landsat 5/7/8 data. Sci. Remote Sens. 2021, 4, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).