Development and Comparison of InSAR-Based Land Subsidence Prediction Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
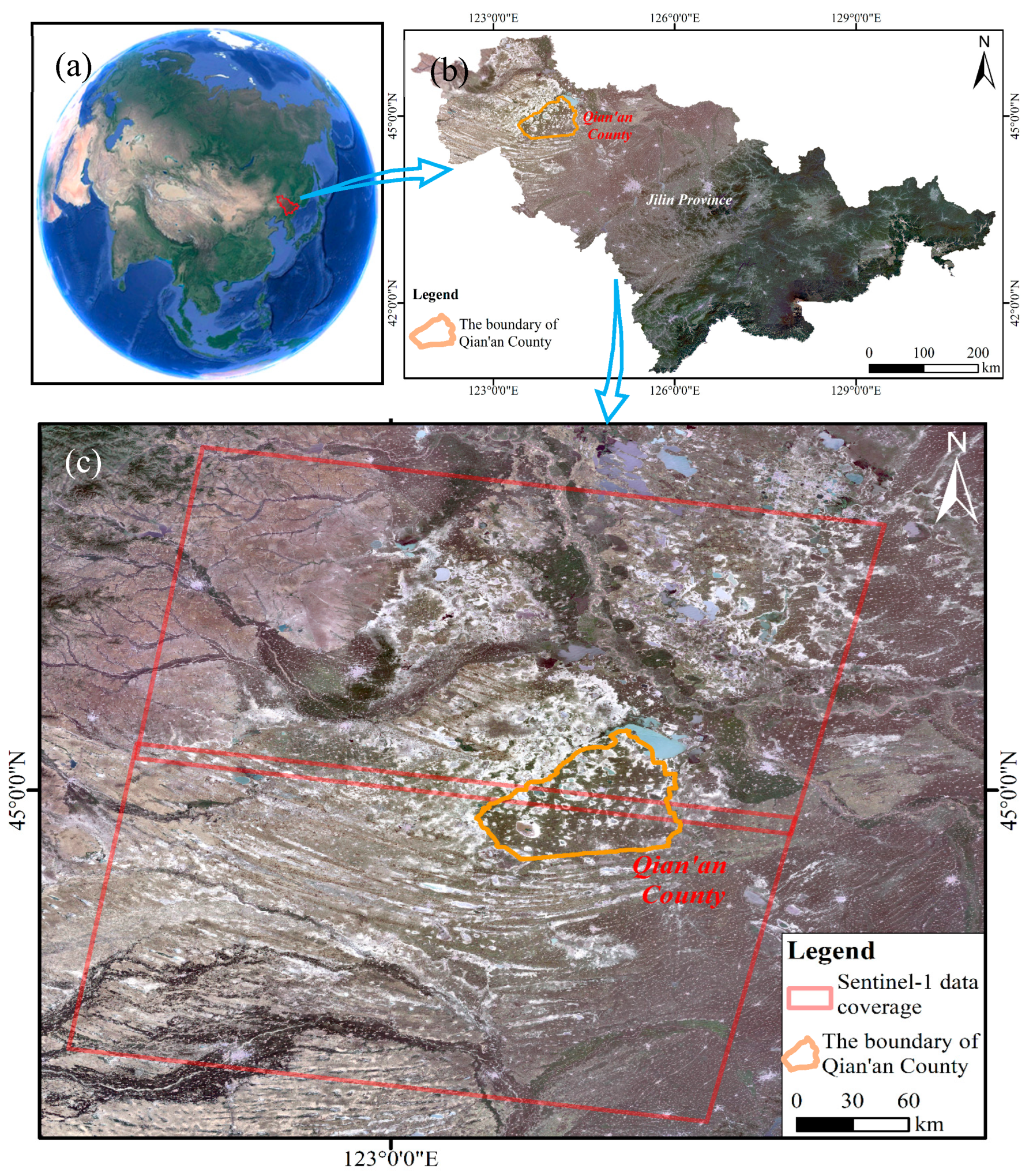
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Data Preprocessing
- (1)
- Abnormal Data Elimination
- (2)
- Gaussian interpolation processing of the time series data
3.2.2. Prediction Model
- (1)
- Support Vector Regression (SVR)
- (2)
- Holt’s Exponential Smoothing Model
- (3)
- Multi-layer perceptron (MLP) model
4. Results and Discussion
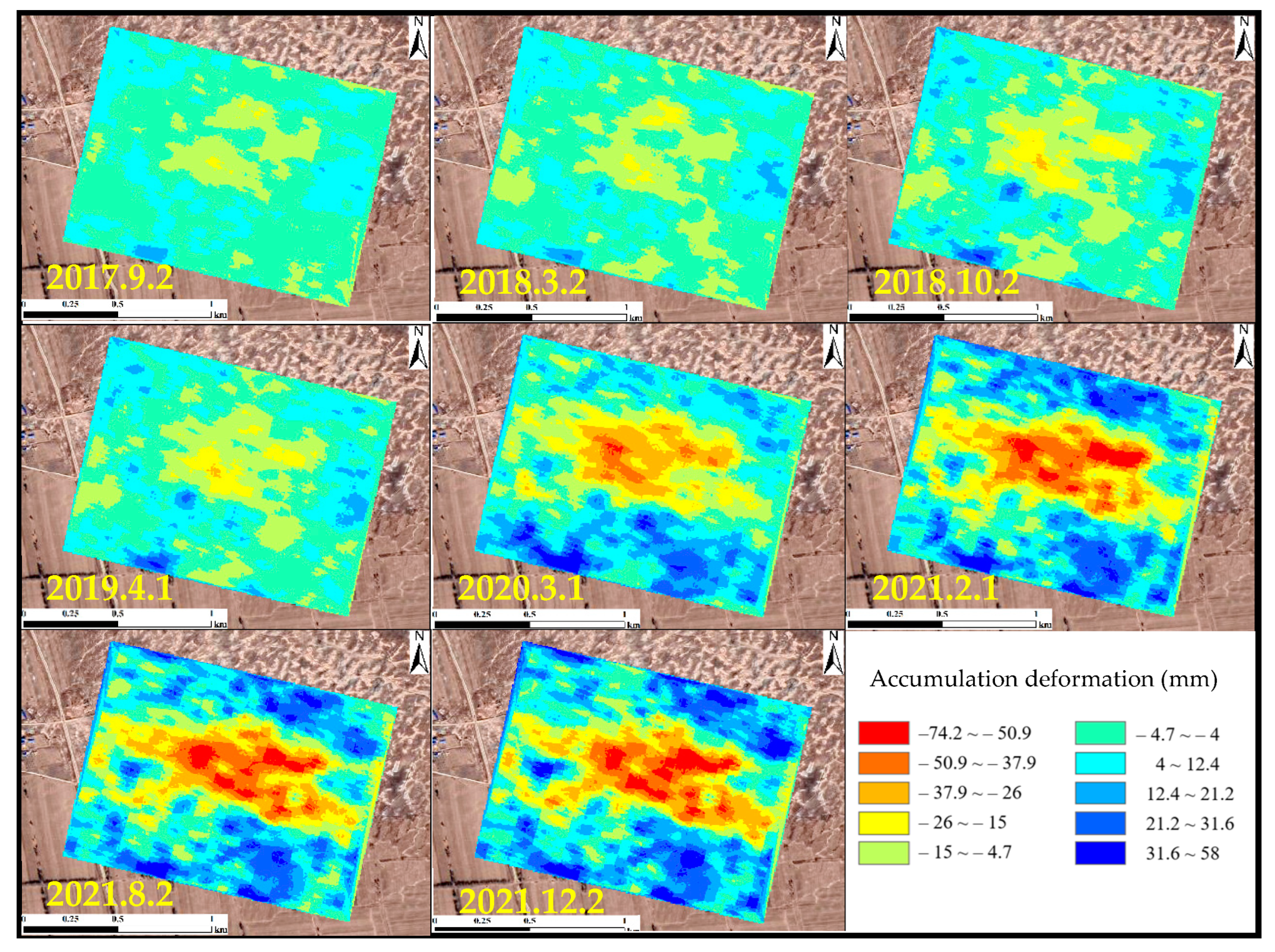
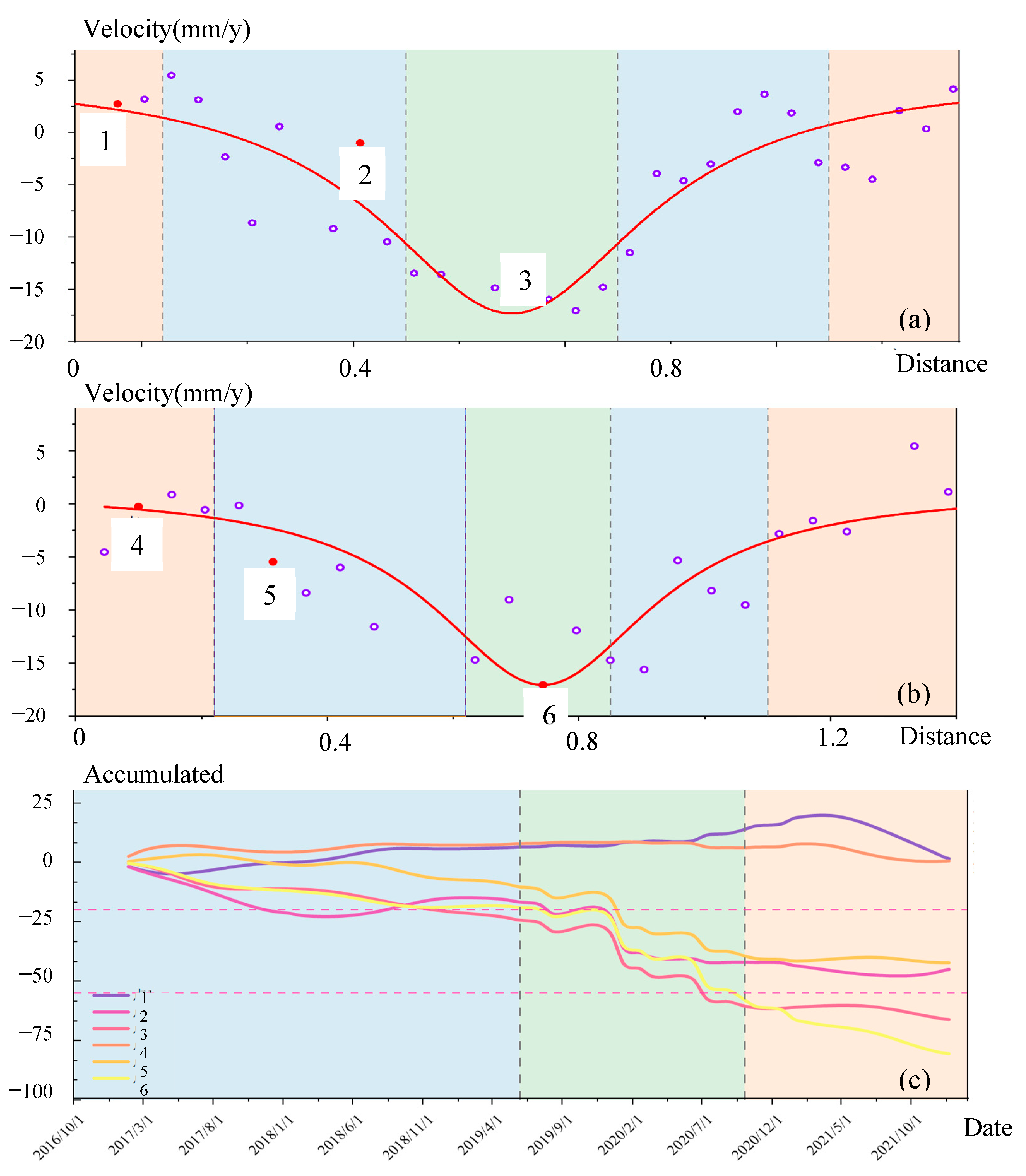
4.1. Deformation of Typical Subsidence
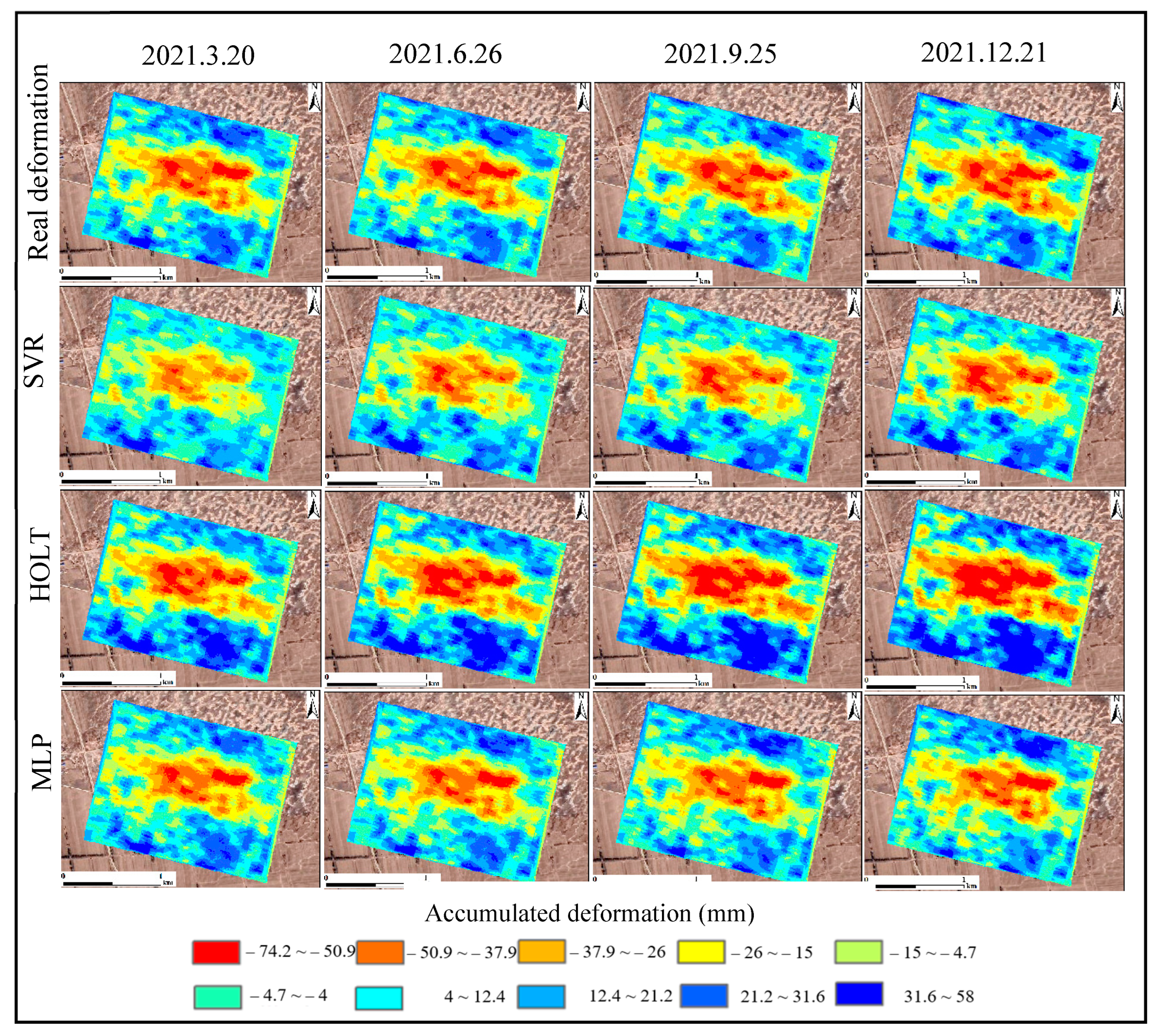
4.2. Time Series Deformation Prediction of the Overall Settlement Funnel Area
4.3. Temporal Deformation Prediction of the Coherent Points
4.4. Discussion
4.5. Limitations and Future Work—Variations in External Factors
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- This paper introduces three time-series surface deformation prediction models—SVR, Holt, and MLP—offering an alternative to traditional physical and mathematical models. These models can directly predict without the need for complex physical modeling or manual feature extraction. By comparing these models, we addressed the limitations of each, improving their accuracy in predicting time-series deformation data. This approach provides a new method for handling such prediction challenges.
- (2)
- The proposed time-series data prediction models can also provide high-precision predicted shape variables based on historical surface deformation monitoring data without considering external factors, which is more practical and convenient than other prediction models that need to consider external factors.
- (3)
- The three time-series data prediction models developed in this study can effectively capture the time-series correlation characteristics of surface deformation in the study area. The SVR and Holt models are suitable for analyzing fewer external interference factors and shorter periods, while the MLP model has higher accuracy and universality, making it more suitable for predicting short- and long-term time-series surface deformation.
- (4)
- This study verifies the feasibility of three time-series data prediction models for the surface deformation prediction of the settlement funnel in Zhouzi Village, Qian’an County. The results show that the MLP model achieved the best prediction results for the entire region and individual coherent points among the three models, making it better suited for studying land subsidence in this region.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagheri-Gavkosh, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Sohani, Y.; Ebrahimian, H.; Morovat, F.; Ashrafi, S. Land Subsidence: A Global Challenge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Yang, T.; Xu, Y.; Tosi, L.; Stouthamer, E.; Andreas, H.; Minderhoud, P.; Ladawadee, A.; Hanssen, R.; Erkens, G. Advances and Practices on the Research, Prevention and Control of Land Subsidence in Coastal Cities. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. Ed. 2020, 94, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljammaz, A.; Sultan, M.; Izadi, M.; Abotalib, A.Z.; Elhebiry, M.S.; Emil, M.K.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Saleh, M.; Becker, R. Land Subsidence Induced by Rapid Urbanization in Arid Environments: A Remote Sensing-Based Investigation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, G.; Bao, Y.; Su, G.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Preventing Subsidence Reoccurrence in Tianjin: New Preconsolidation Head and Safe Pumping Buffer. Groundwater 2024, 5, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, O. Monitoring of Land Subsidence Due to Excessive Groundwater Extraction Using Small Baseline Subset Technique in Konya, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Bi, J. Coupling Model of Groundwater and Land Subsidence and Simulation of Emergency Water Supply in Ningbo Urban Area, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shinawi, A.; Kuriqi, A.; Zelenakova, M.; Vranayova, Z.; Abd-Elaty, I. Land Subsidence and Environmental Threats in Coastal Aquifers under Sea Level Rise and Over-Pumping Stress. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Loc, H.H.; Van Binh, D.; Kantoush, S. The Worst 2020 Saline Water Intrusion Disaster of the Past Century in the Mekong Delta: Impacts, Causes, and Management Implications. Ambio 2022, 51, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.T. Extended Fully Coupled Analysis of Consolidation Using the Finite Element Method. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.-W.; Wang, X.-Y.; Liu, C.-L.; Li, B.-Y. Finite-Diference Model of Land Subsidence Caused by Cluster Loads in Zhengzhou, China. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. Vol 2020, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Janbaz Fotamy, M.; Kholghi, M.; Abdeh Kolahchi, A.; Roostaei, M. Land Subsidence Assessment Due to Groundwater Exploration by Using Differential Radar Interferometry Technique, Case Study: Qazvin Province. Iran-Water Resour. Res. 2020, 16, 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Wei, X. Probabilistic Analysis of Land Subsidence Due to Pumping by Biot Poroelasticity and Random Field Theory. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Xu, J. Parallel Finite Layer Method for Land Subsidence and Its Homotopy Parameter Inversion. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 176, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ding, L.; Cui, X.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bai, Z. Calculation Model for Progressive Residual Surface Subsidence above Mined-out Areas Based on Logistic Time Function. Energies 2022, 15, 5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhu, J. Prediction of Mining-Induced Kinematic 3-D Displacements from Insar Using a Weibull Model and a Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4500912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Hong, S.H. Nonlinear Modeling of Subsidence from a Decade of Insar Time Series. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.-Z.; Luo, Z.-J.; Wu, X.-H. Sensitivity Analysis of Related Parameters in Simulation of Land Subsidence and Ground Fissures Caused by Groundwater Exploitation. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2016, 75, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, G.; Tao, Q.; Zhai, M. Land Subsidence Prediction Model Based on Its Influencing Factors and Machine Learning Methods. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 3015–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Allechy, F.B.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, R.; Kouadio, K.L. Machine Learning-Based Techniques for Land Subsidence Simulation in an Urban Area. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanmiri, S.; Noorian-Bidgoli, M. Land Subsidence Prediction in Coal Mining Using Machine Learning Models and Optimization Techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 31942–31966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malozyomov, B.V.; Martyushev, N.V.; Sorokova, S.N.; Efremenkov, E.A.; Valuev, D.V.; Qi, M. Analysis of a Predictive Mathematical Model of Weather Changes Based on Neural Networks. Mathematics 2024, 12, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.J.; Maclaren, O.J.; Simpson, M.J. Implementing Measurement Error Models with Mechanistic Mathematical Models in a Likelihood-Based Framework for Estimation, Identifiability Analysis and Prediction in the Life Sciences. J. R. Soc. Interface 2024, 21, 20230402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Jia, C.; Sun, H.; Yang, T.; Yao, Y. Integrating Multi-Source Data to Assess Land Subsidence Sensitivity and Management Policies. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Falah, F.; Naghibi, S.A.; Biggs, T.; Soltani, M.; Deo, R.C.; Cerdà, A.; Mohammadi, F.; Bui, D.T. Land Subsidence Modelling Using Tree-Based Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, O.; Golkarian, A.; Biggs, T.; Keesstra, S.; Mohammadi, F.; Daliakopoulos, I.N. Land Subsidence Hazard Modeling: Machine Learning to Identify Predictors and the Role of Human Activities. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Zuo, X.; Zhao, Z. Constructing A Large-Scale Urban Land Subsidence Prediction Method Based on Neural Network Algorithm from the Perspective of Multiple Factors. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien Bui, D.; Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Chapi, K.; Pradhan, B.; Chen, W.; Khosravi, K.; Panahi, M.; Bin Ahmad, B.; Saro, L. Land Subsidence Susceptibility Mapping in South Korea Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Sensors 2018, 18, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarakhsh, Z.; Azadbakht, M.; Matkan, A. Estimation, Modeling, and Prediction of Land Subsidence Using Sentinel-1 Time Series in Tehran-Shahriar Plain: A Machine Learning-Based Investigation. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2022, 25, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimai, K.; Liu, W.; Maruyama, Y. Prediction and Factor Analysis of Liquefaction Ground Subsidence Based on Machine-Learning Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cui, J.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Guo, J.; Chen, Z. Land Subsidence Prediction in Zhengzhou’s Main Urban Area Using the Gtwr and Lstm Models Combined with the Attention Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Lei, K.; Zhu, L.; Duan, L.; Zhao, X. Land Subsidence and Its Relation with Groundwater Aquifers in Beijing Plain of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, A.M. A Numerical Study on Land Subsidence Due to Extensive Overexploitation of Groundwater in Aliabad Plain, Qom-Iran. Nat. Hazards 2018, 93, 1085–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.Z.; Chu, H.-J.; Burbey, T.J. Mapping and Predicting Subsidence from Spatio-Temporal Regression Models of Groundwater-Drawdown and Subsidence Observations. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2865–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Jia, C.; Di, S.; Wang, L.; Bian, C.; Yang, X. Analysis and Prediction of Land Subsidence along Significant Linear Engineering. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 5125–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.-H.; Wang, Z.-P.; Li, G.; Skibniewski, M.J.; Chen, Z.-S. Prediction of Airport Runway Settlement Using an Integrated Sbas-Insar and Bp-Enkf Approach. Inf. Sci. 2024, 665, 120376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Majd, A.; Rasoulzadeh, A.; Hasanpour Kashani, M.; Kisi, O. Enhancing the Accuracy of Metaheuristic Neural Networks in Predicting Underground Water Levels Using Meteorological Data and Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Ardabil Plain, Iran.
- Wang, C.J.; Zhang, T.; Luo, J.H.; Ma, C.; Duan, L.C. Utilization of Neural Network Feedback Method to Prediction of Thermal Resistivity of Soils. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2019, 41, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.X.; Zhao, J.F.; Huo, Z.G.; Peng, H.W.; Xie, H.-F. Application of Deep Learning Technology In Monitoring, Forecasting and Risk Assessment of Agricultural Drought. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2023, 44, 943. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D. Land Subsidence Susceptibility Mapping in Urban Settlements Using Time-Series Ps-Insar and Random Forest Model. Gondwana Res. 2024, 125, 406–424. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadeh, E.; Anamaghi, S.; Behboudian, M.; Kalantari, Z. Evaluating Machine Learning-Based Approaches in Land Subsidence Susceptibility Mapping. Land 2024, 13, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudpour, M.; Khamehchiyan, M.; Nikudel, M.R.; Ghassemi, M.R. Numerical Simulation and Prediction of Regional Land Subsidence Caused by Groundwater Exploitation in the Southwest Plain of Tehran, Iran. Eng. Geol. 2016, 201, 6–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhao, J.; Leung, H.; Ma, K.F.; Wang, W. A Review of Deep Learning Models for Time Series Prediction. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 21, 7833–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, G.; Polak, J. Practical Time Series Forecasting with R: A Hands-on Guide; Axelrod Schnall Publishers: Green Cove Springs, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J.; Croux, C. Alternatives to the Median Absolute Deviation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1993, 88, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esseen, C.-G. Fourier Analysis of Distribution Functions. A Mathematical Study of the Laplace-Gaussian Law. Acta Math. 1945, 77, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; Khanna, R. Efficient Learning Machines: Theories, Concepts, and Applications for Engineers and System Designers; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lewins, J. Introducing the Lagrange Multiplier to Engineering Mathematics. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Educ. 1994, 22, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalekar, P.S. Time Series Forecasting Using Holt-Winters Exponential Smoothing. Kanwal Rekhi Sch. Inf. Technol. 2004, 4329008, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, C.C. Forecasting Seasonals and Trends by Exponentially Weighted Moving Averages. J. Econ. Soc. Meas. 2004, 29, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozos, E.; Dimitriadis, P.; Mazi, K.; Koussis, A.D. A Multilayer Perceptron Model for Stochastic Synthesis. Hydrology 2021, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskath, J.; Sivakamasundari, G.; Begum, A.A.S. A Study on Different Deep Learning Algorithms Used in Deep Neural Nets: Mlp Som and Dbn. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2023, 128, 2913–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zou, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Wei, Z. Research of Stock Price Prediction Based on Dmd-Lstm Model. Appl. Res. Comput. 2020, 37, 662. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, H.; Jeon, H.; Yeo, N.; Baek, D. Big Data and Deep Learning for Rna Biology. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 1293–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, N.; Luo, W.; Shi, Z. A Survey of Machine Learning Algorithms for Big Data. PR&AI 2014, 27, 327–336. [Google Scholar]




| Satellite | Sentinel-1 |
|---|---|
| Orbital direction | Descending |
| Product type | SLC |
| Temporal coverage | 28 January 2017–18 December 2021 |
| Band | C band |
| Wavelength | 5.6 cm |
| Resolution | 5 × 20 m |
| Average incident angle | 36.02°, 36.94° |
| Polarization mode | VV |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, C.; Shan, B.; Jin, T.; Zhu, K.; Li, Z. Development and Comparison of InSAR-Based Land Subsidence Prediction Models. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3345. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173345
Zheng L, Wang Q, Cao C, Shan B, Jin T, Zhu K, Li Z. Development and Comparison of InSAR-Based Land Subsidence Prediction Models. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3345. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173345
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Lianjing, Qing Wang, Chen Cao, Bo Shan, Tie Jin, Kuanxing Zhu, and Zongzheng Li. 2024. "Development and Comparison of InSAR-Based Land Subsidence Prediction Models" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3345. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173345
APA StyleZheng, L., Wang, Q., Cao, C., Shan, B., Jin, T., Zhu, K., & Li, Z. (2024). Development and Comparison of InSAR-Based Land Subsidence Prediction Models. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3345. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173345







