Coarse-to-Fine Structure and Semantic Learning for Single-Sample SAR Image Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The proposal of a multi-level hierarchical architecture for SAR image generation. It comprises three distinct GANs that independently model the structural, semantic, and texture patterns, thereby facilitating the generation of highly realistic images with enhanced details.
- (2)
- By integrating a series of prior constraints, learning to generate SAR imagery with a single sample is achieved. Several advanced regularization techniques are employed, including prior-regularized noise sampling, perceptual loss optimization, and the self-attention mechanisms. This enables extensive exploitation of the intrinsic distribution patterns inherent to the sample images. The resultant approach ensures stability and robustness in the image generation process.
- (3)
- The achievement of state-of-the-art (SOTA) method performance in single-sample SAR image generation. Through comprehensive experimental comparisons, the proposed method demonstrates significant improvements in a variety of evaluation metrics, including SIFID, SSIM, diversity, and perceptual quality. Human assessment is also introduced to rigorously assess the authenticity of the generated samples. The results indicate that the proposed technique is capable of synthesizing high-quality and realistic samples with plausible semantic diversity.
2. Related Work
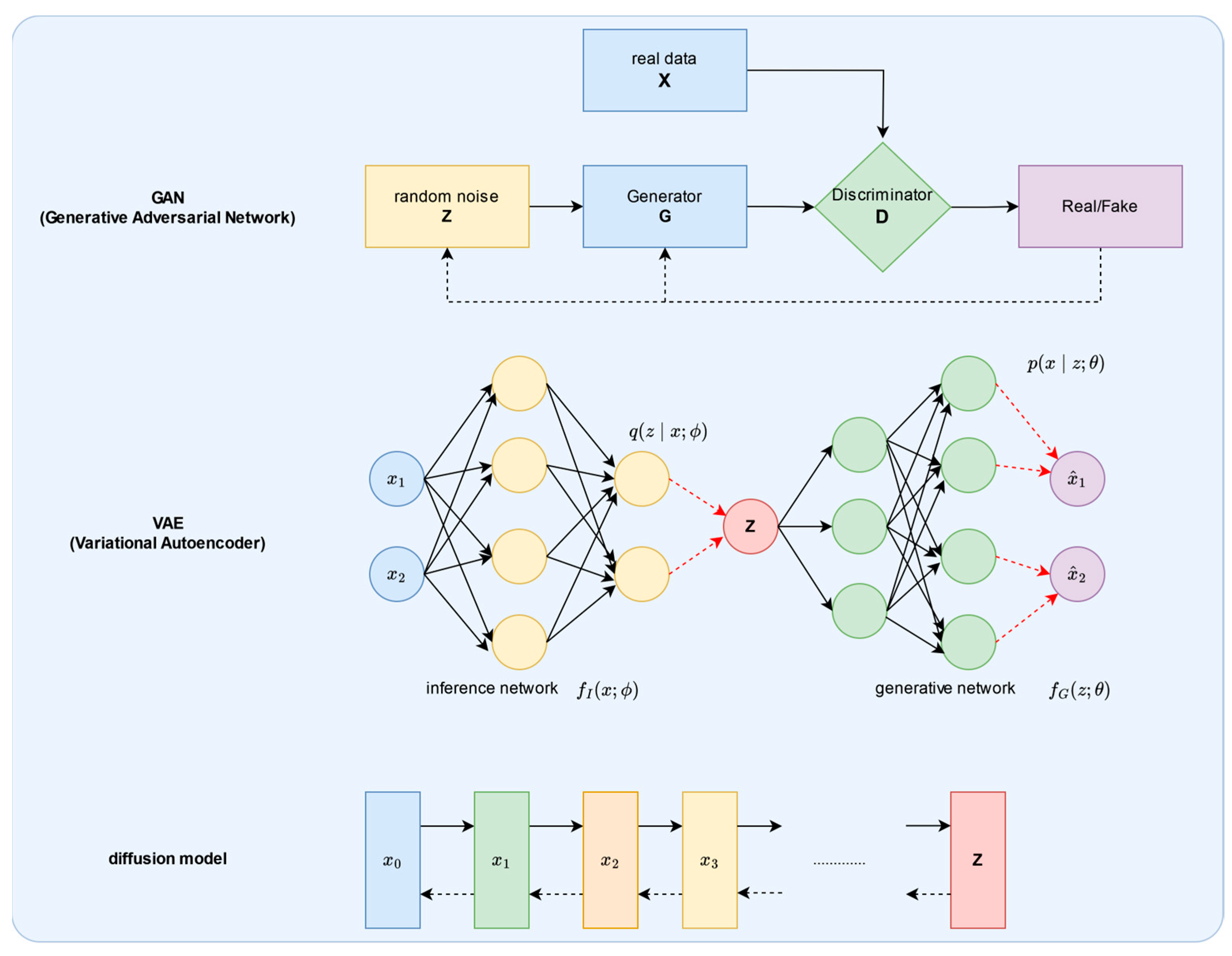
2.1. Generative Models
2.2. Single-Sample Image Generation
2.3. Augmentation of SAR Data with Deep Generative Models
3. Proposed One-Shot SAR Image Generation GAN
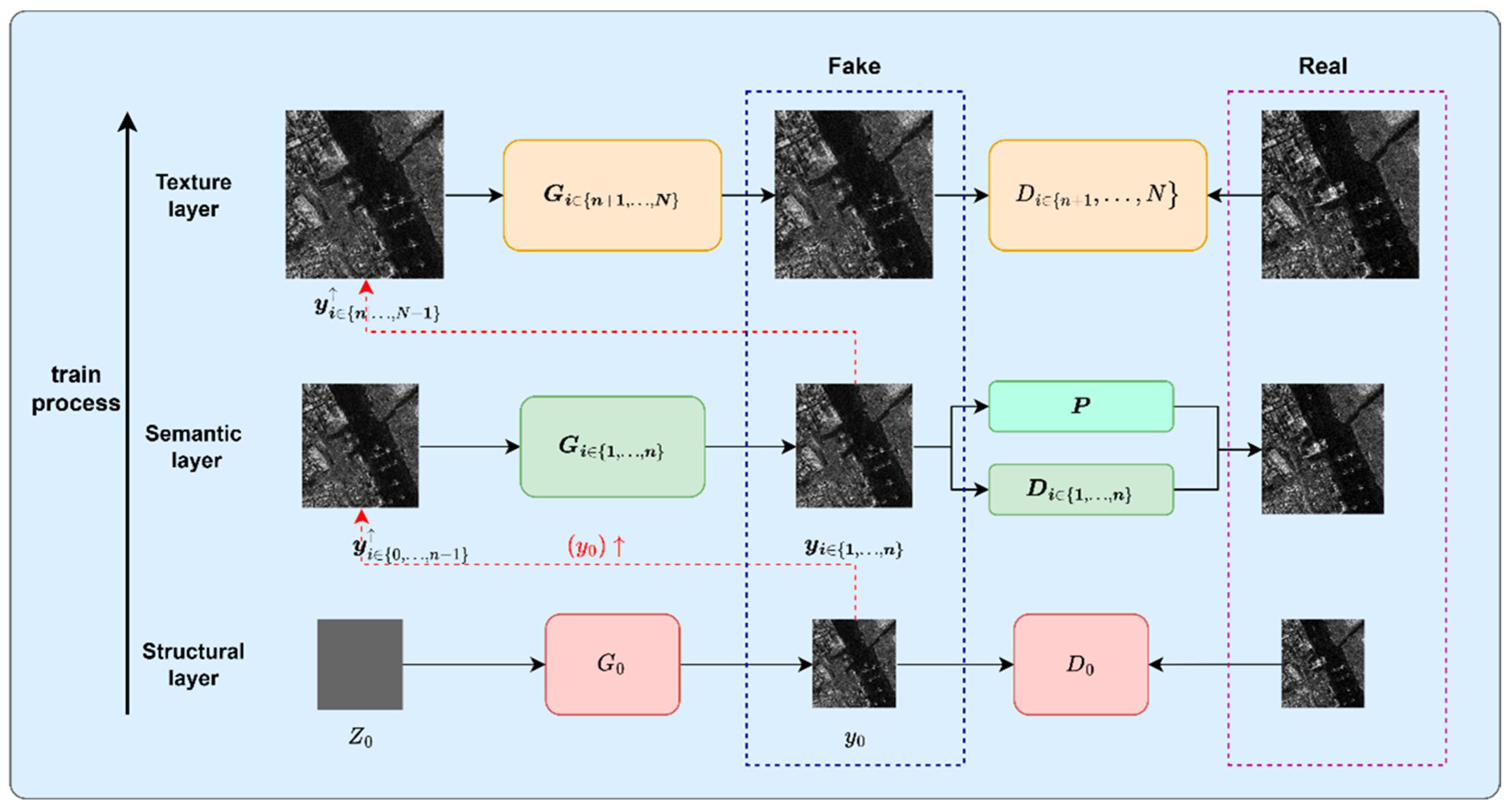
3.1. Motivation and Overall Framwork
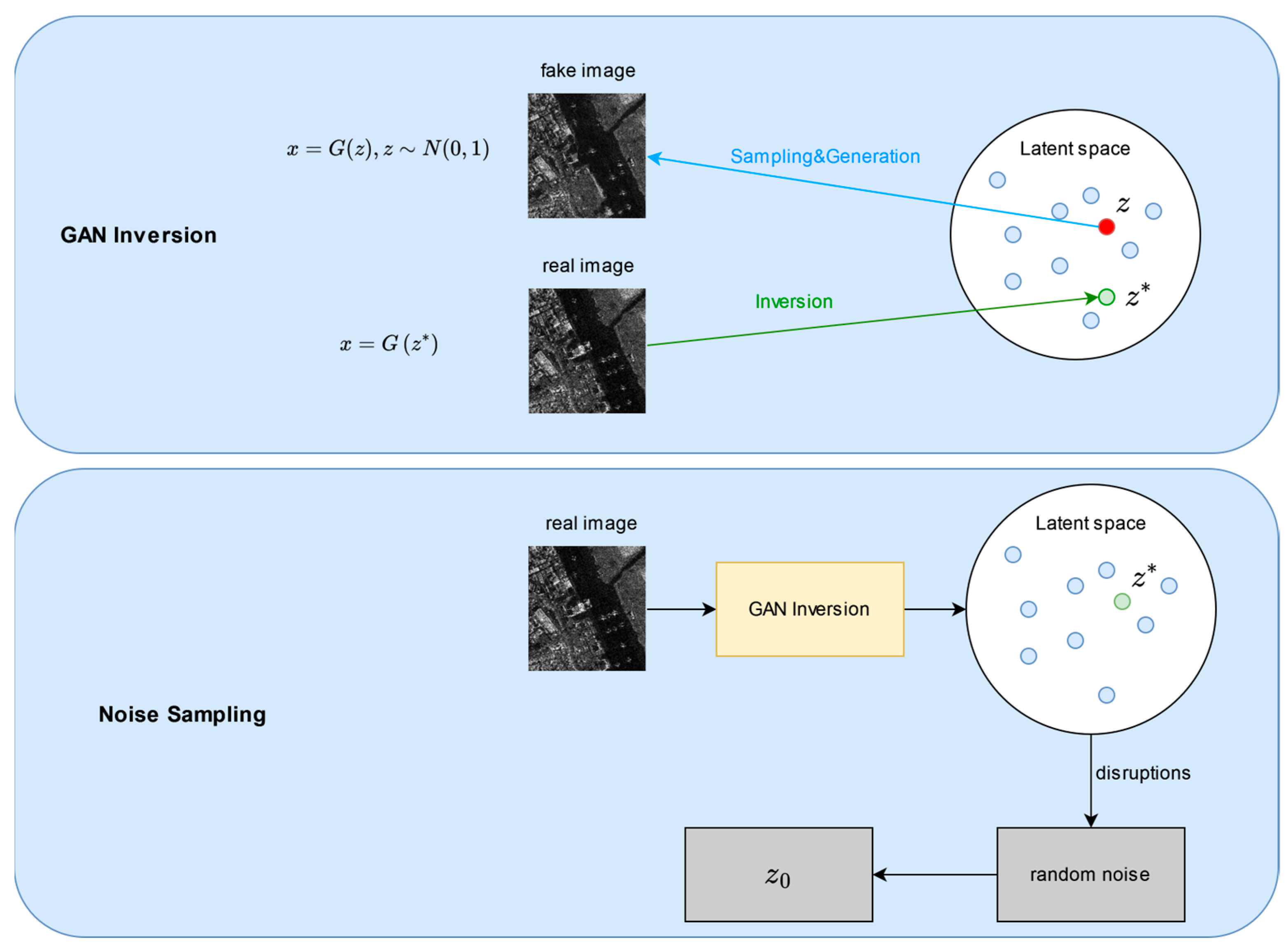
3.1.1. Prior-Regularized Noise Sampling
3.1.2. Hierarchical Coarse-to-Fine Image Generation
3.2. Network Architecture
3.2.1. Structural GAN
3.2.2. Semantic GAN
3.2.3. Texture GAN
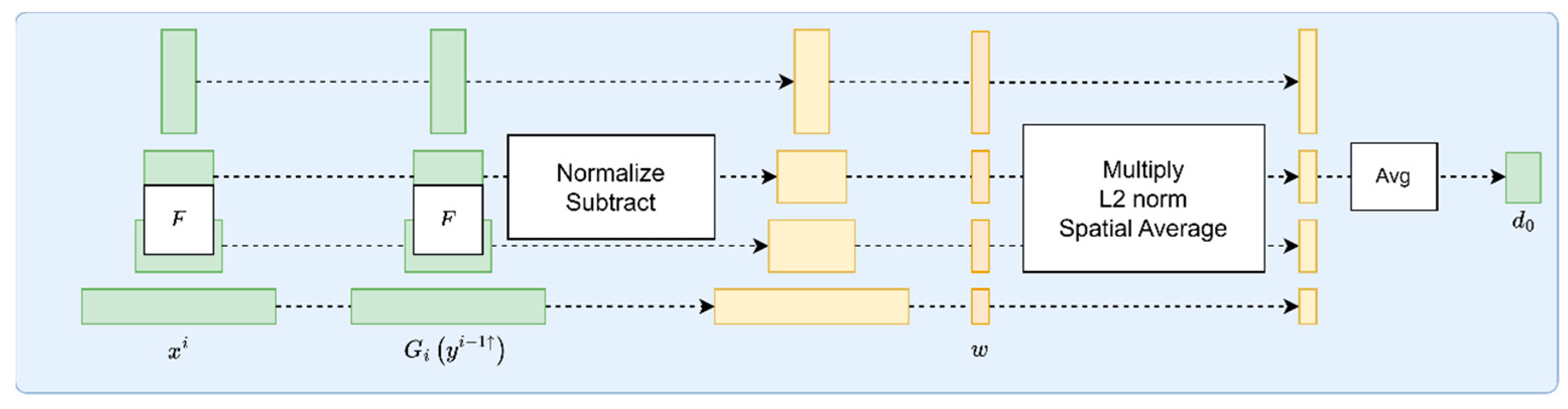
3.2.4. Self-Attention Mechanism Module
3.3. Implementation Details
4. Experimental Analysis and Discussions
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1. SIFID
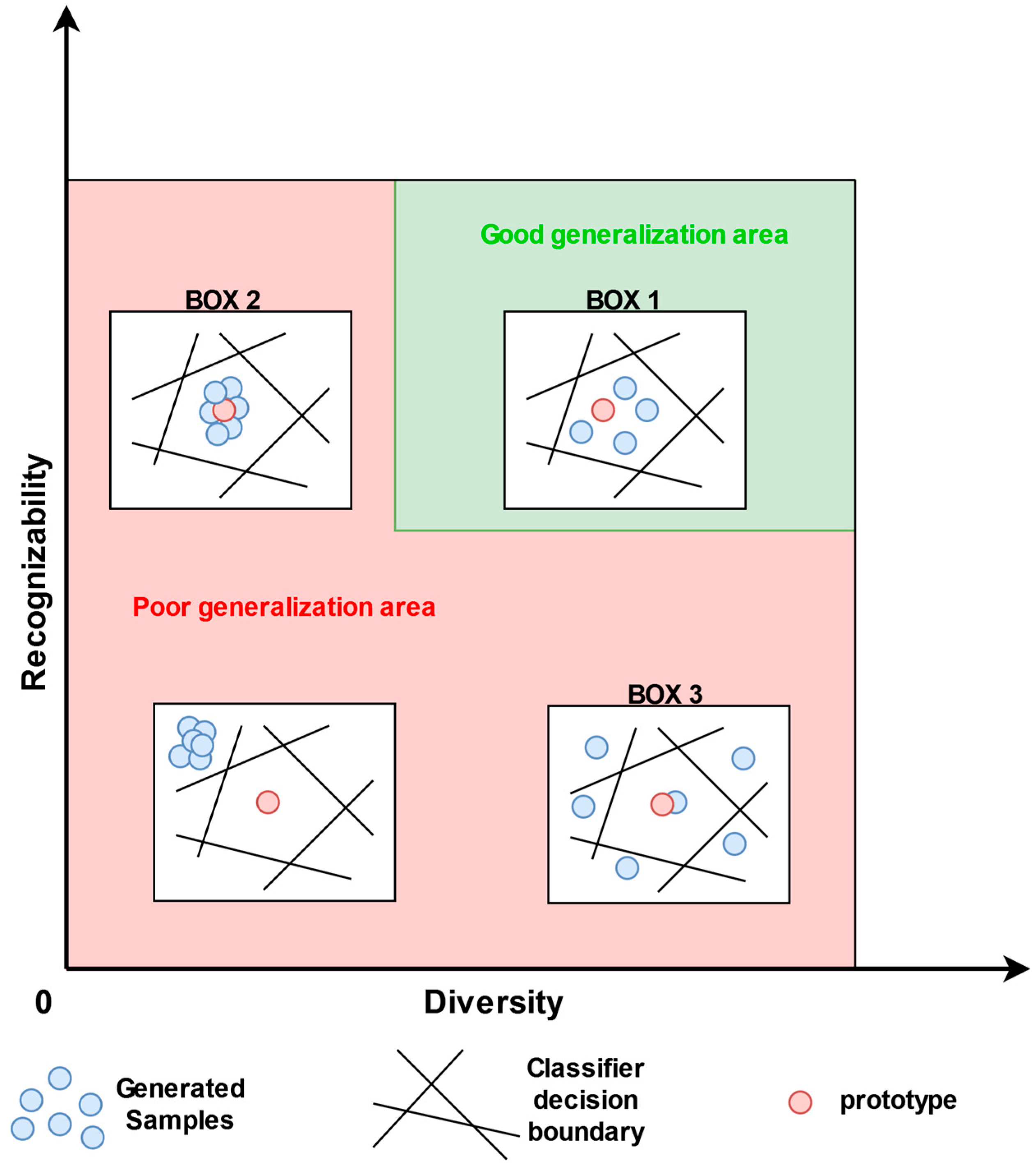
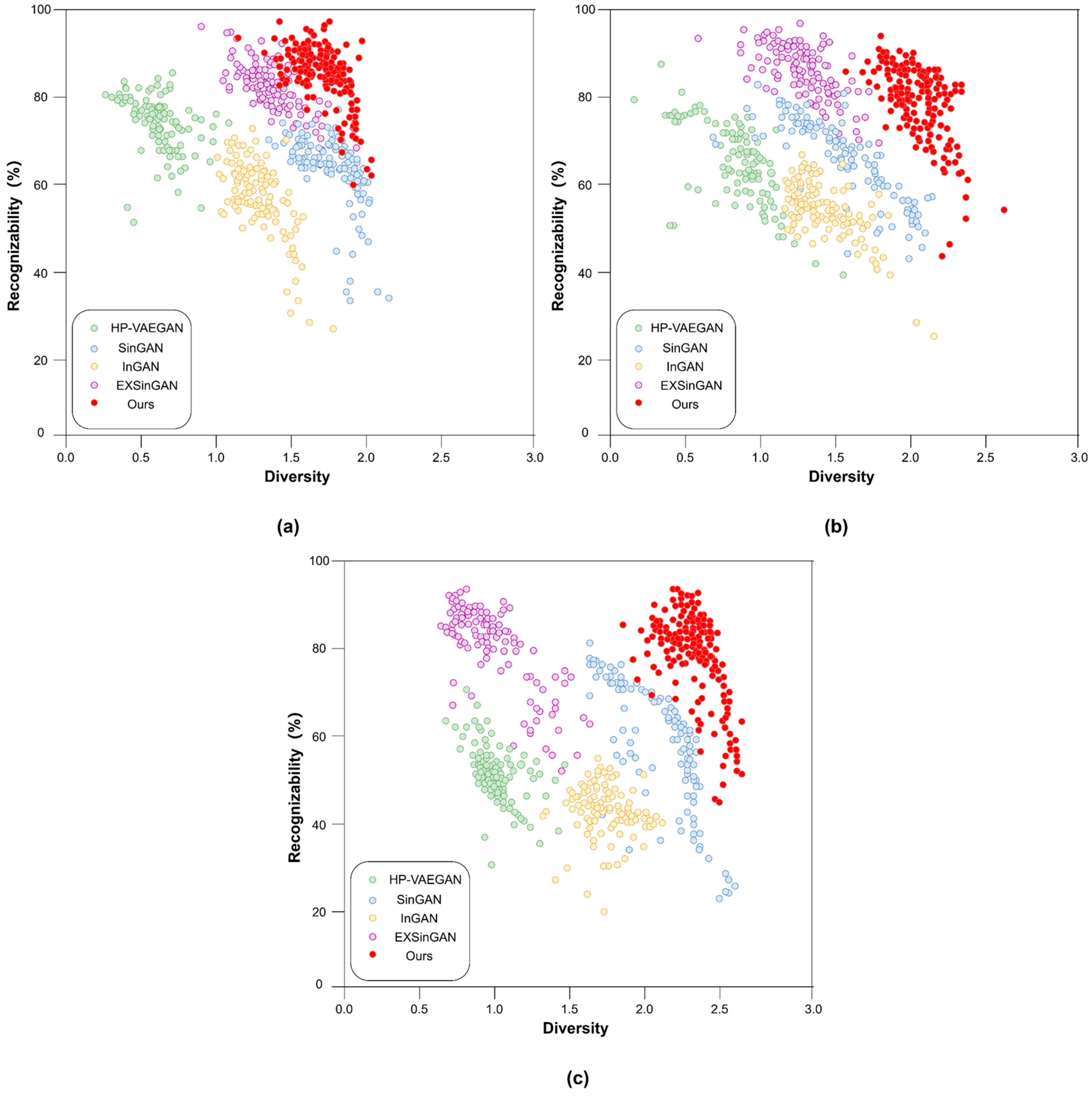
4.1.2. Recognizability vs. Diversity Evaluation Framework
4.2. Ablation Study
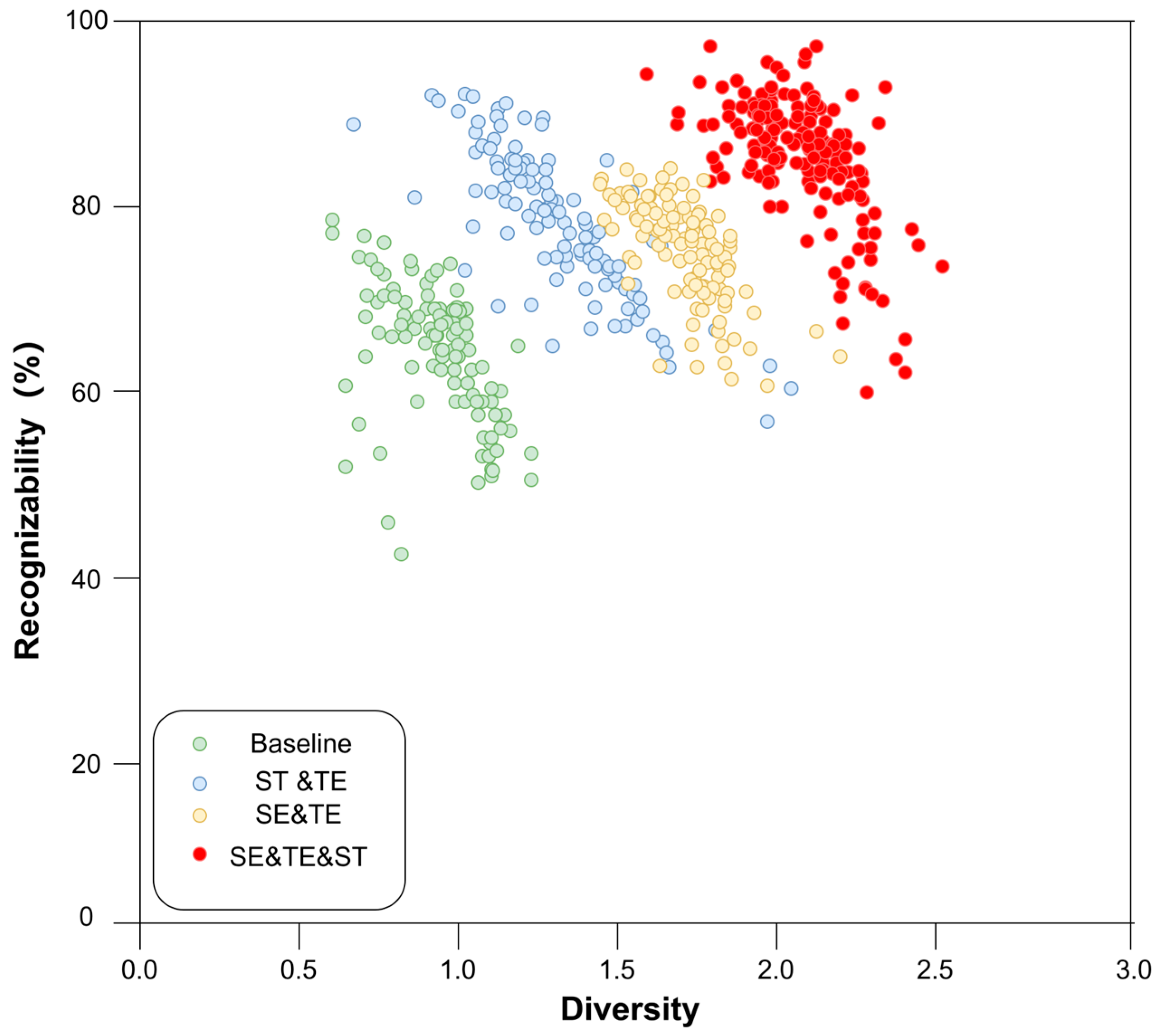
4.2.1. Ablation Study of the Modularized GANs
4.2.2. Ablation Study of the MSDA Modules
4.2.3. Sensitivity Analysis of the Weighting Parameters
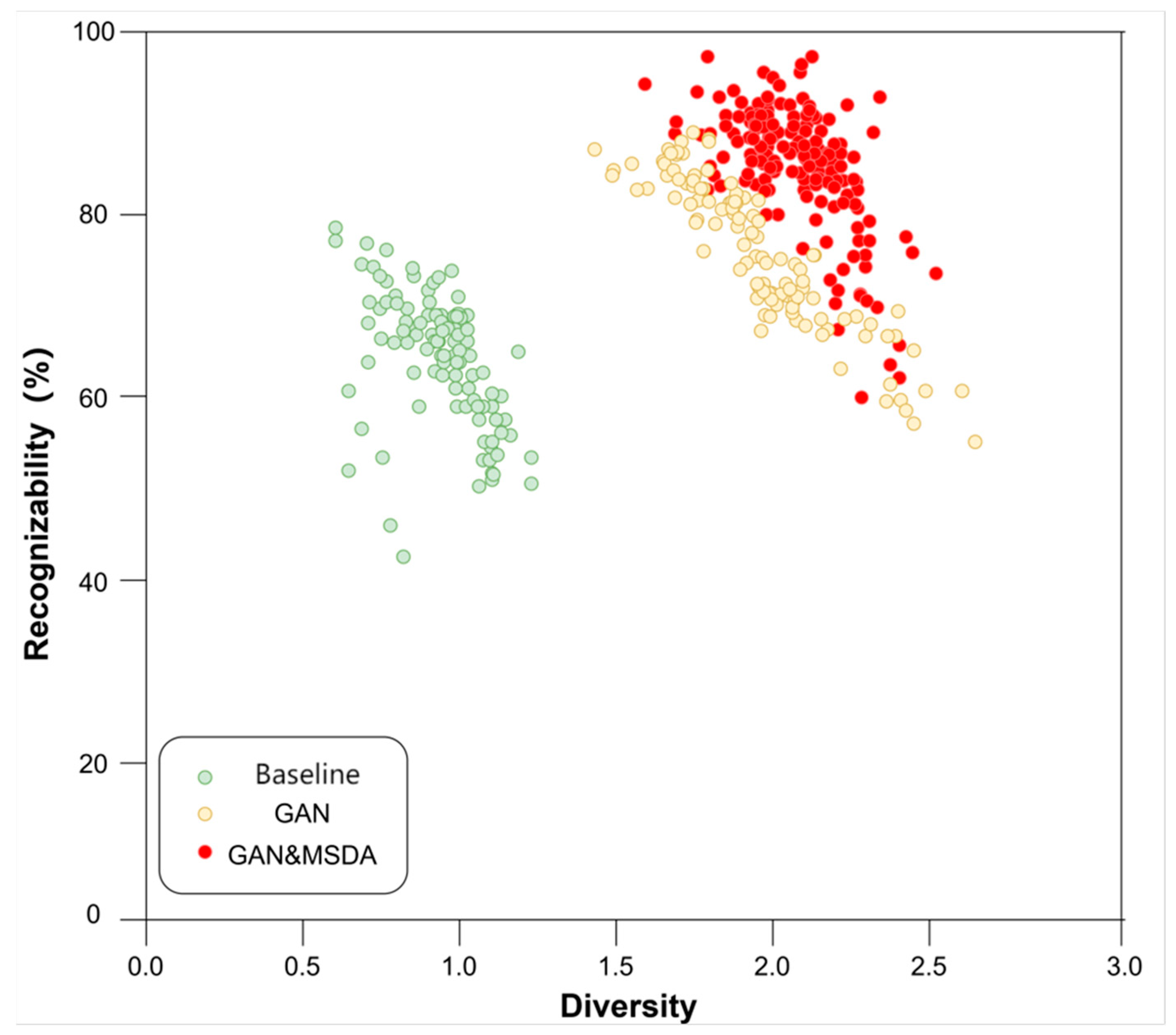
4.3. Comparative Experiments
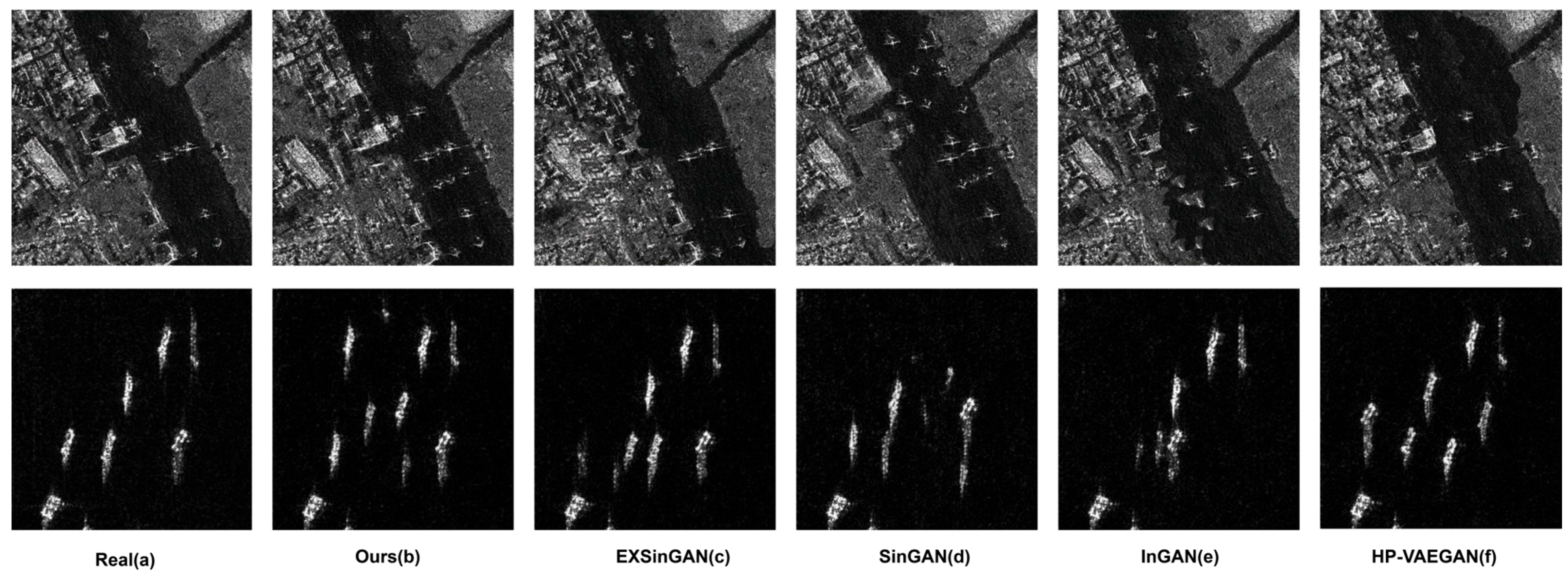
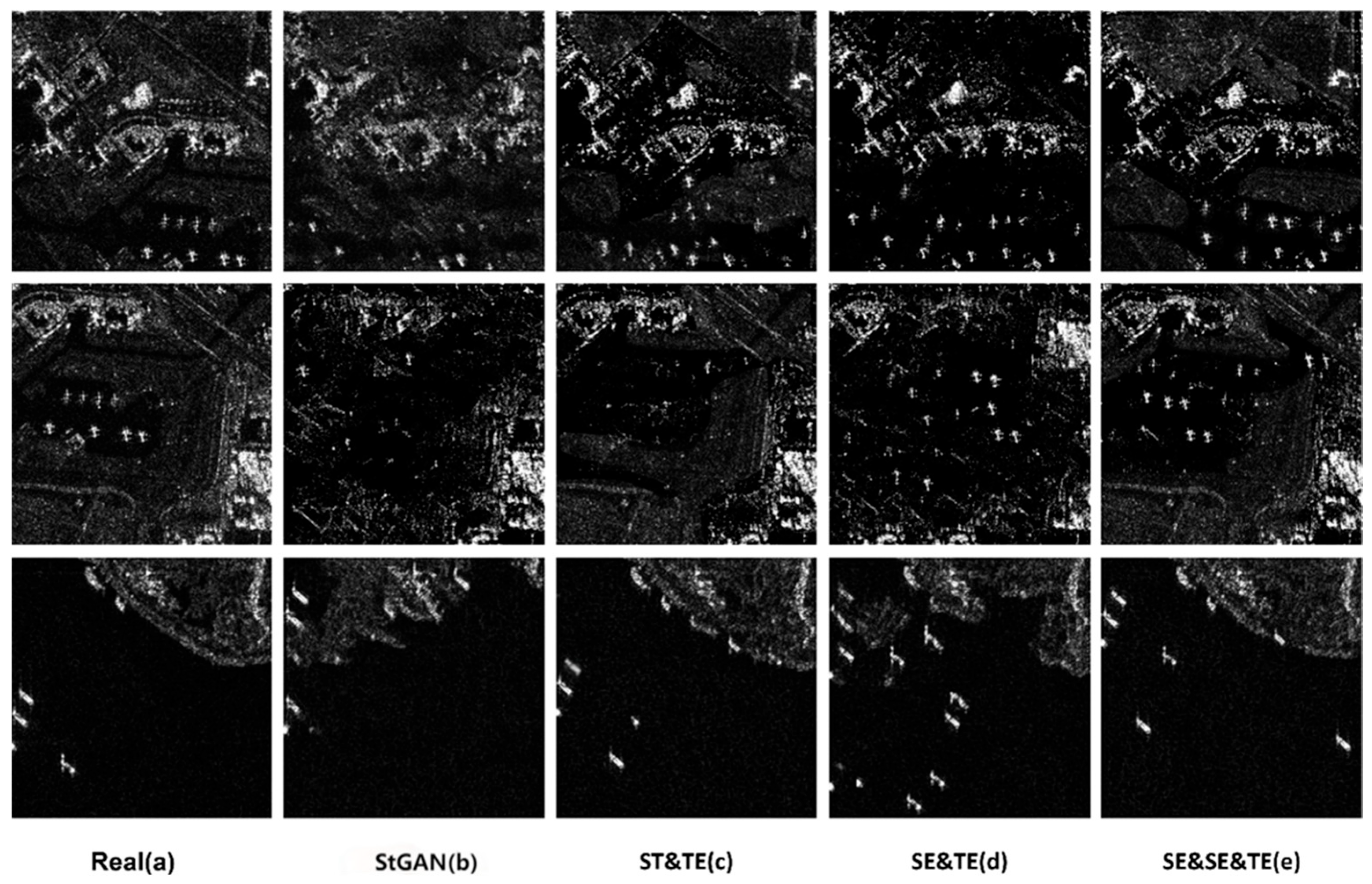
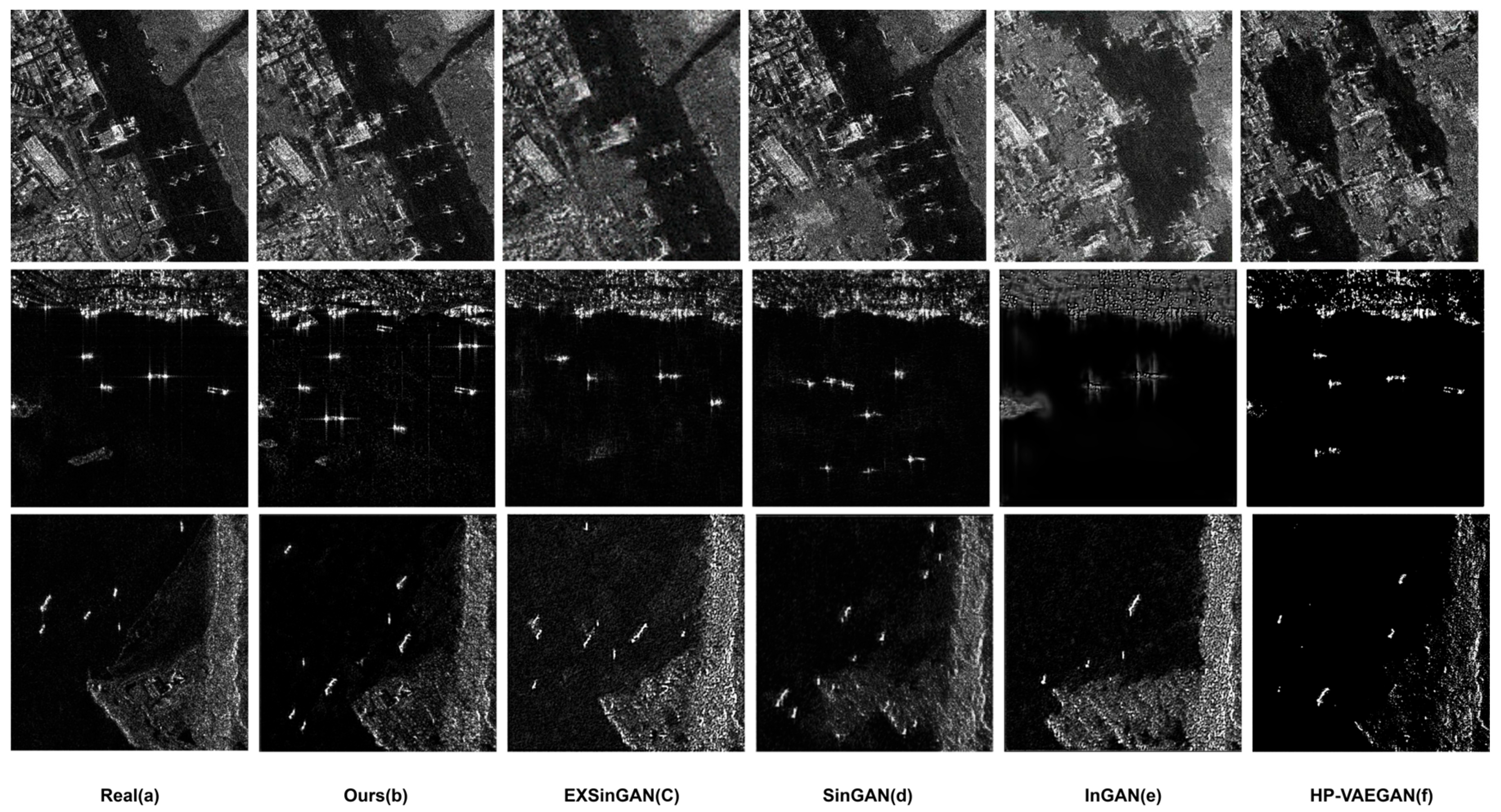
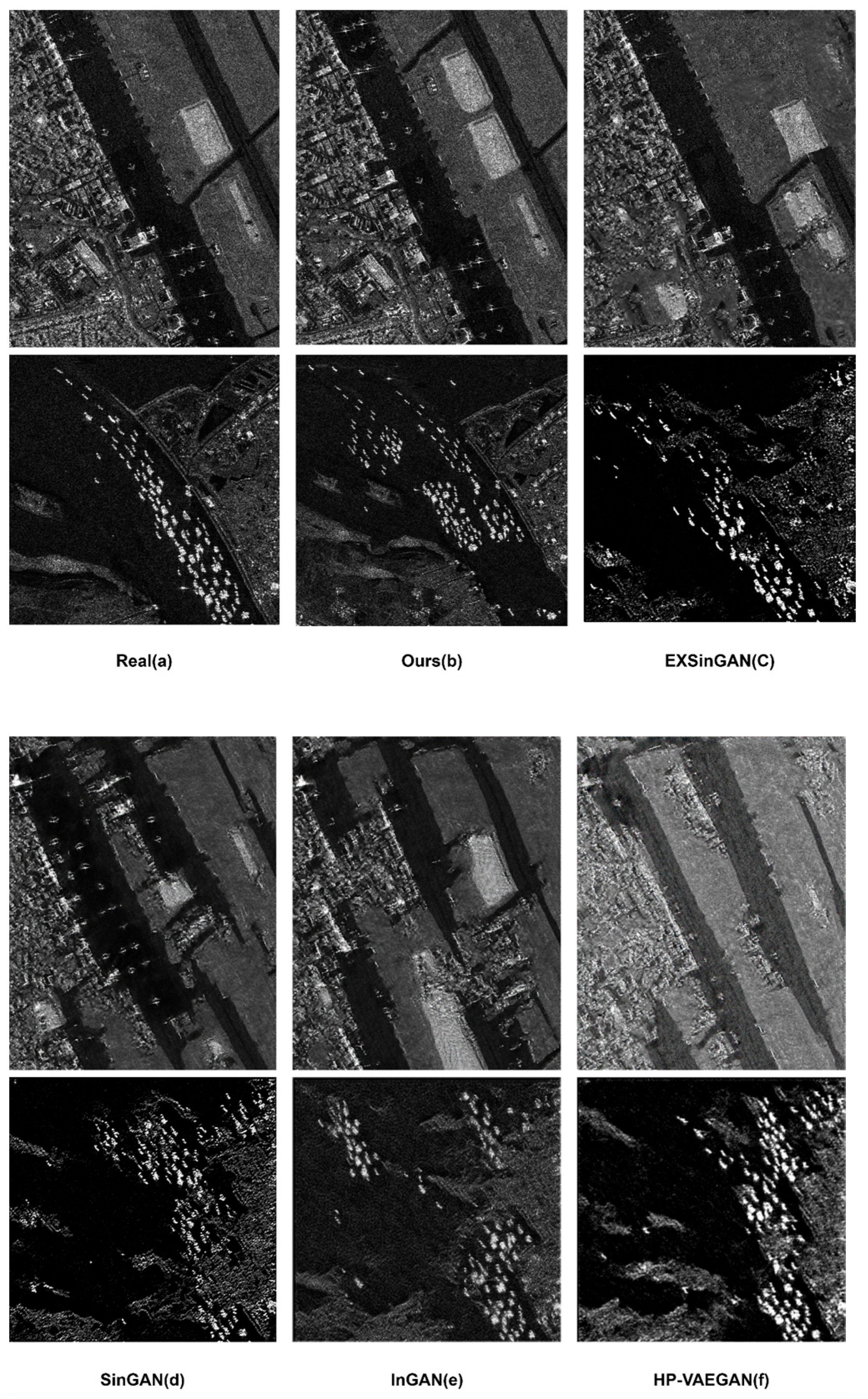
4.3.1. Qualitative Evaluation of Generated Images
4.3.2. Quantitative Evaluation of Generated Images
4.3.3. Human Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Shanmugam, P.; Das, S. A Deep-Learning-Based Lightweight Model for Ship Localizations in SAR Images. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 94415–94427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, W. An initial assessment of the performance achieved by the Seasat-1 radar altimeter. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1980, 5, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, H.; Fu, S.; Lin, H.; Xu, F. Reinforcement Learning for SAR Target Orientation Inference with the Differentiable SAR Renderer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2024, 62, 5216913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stofan, E.R.; Evans, D.L.; Schmullius, C.; Holt, B.; Plaut, J.J.; van Zyl, J.; Wall, S.D.; Way, J. Overview of results of Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C, X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1995, 33, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhan, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. LMSD-YOLO: A Lightweight YOLO Algorithm for Multi-Scale SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gao, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Hussain, A.; Zhou, H. Novel Category Discovery Without Forgetting for Automatic Target Recognition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 4408–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Kong, L.; Lang, R.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Hussain, A.; Zhou, H. SAR target incremental recognition based on features with strong separability. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5202813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Pu, X.; Xu, F. Conditional Diffusion for SAR to Optical Image Translation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 4000605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y. Target Classification Using the Deep Convolutional Networks for SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Tao, M.; Wei, J. A Two-Stage SAR Image Generation Algorithm Based on GAN with Reinforced Constraint Filtering and Compensation Techniques. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, X.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, T. SPA-GAN: SAR Parametric Autofocusing Method with Generative Adversarial Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Hong, J.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Y. A high-quality multicategory SAR images generation method with multiconstraint GAN for ATR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4011005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, X.; Xiang, D.; Hu, C. SAR vehicle image generation with integrated deep imaging geometric information. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Ma, F.; Li, F.; Liu, F.; Zhang, F. Semantic-Layout-Guided Image Synthesis for High-Quality Synthetic-Aperature Radar Detection Sample Generation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.Q.; Tian, X. K-Means clustering guided generative adversarial networks for SAR-optical image matching. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 217554–217572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.W. Continuous restricted Boltzmann machines. Wirel. Netw. 2022, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, L. Research on Medical Image Enhancement Method Based on Conditional Entropy Generative Adversarial Networks. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Su, J.; Li, X. Application of SAR Ship Data Augmentation Based on Generative Adversarial Network in Improved SSD. Acta Armamentarii 2019, 40, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar]
- Jaskie, K.; Dezember, M.; Majumder, U.K. VAE for SAR active learning. In Proceedings of the Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXX, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 April–4 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Yang, L. SAR-to-Optical Image Translation via an Interpretable Network. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, S.; Sharma, R. A Note on the Inception Score. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.01973. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, S. Facies conditional simulation based on VAE-GAN model and image quilting algorithm. J. Appl. Geophys. 2023, 219, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Stability, and Variation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10196. [Google Scholar]
- Dalva, Y.; Yesiltepe, H.; Yanardag, P. GANTASTIC: GAN-based Transfer of Interpretable Directions for Disentangled Image Editing in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.19645. [Google Scholar]
- Shocher, A.; Cohen, N.; Irani, M. Zero-Shot Super-Resolution Using Deep Internal Learning(Conference Paper). In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3118–3126. [Google Scholar]
- Shabtay, N.; Schwartz, E.; Giryes, R. Deep Phase Coded Image Prior. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.03906. [Google Scholar]
- Shocher, A.; Bagon, S.; Isola, P.J.; Irani, M. InGAN: Capturing and Retargeting the “DNA” of a Natural Image. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shaham, T.R.; Dekel, T.; Michaeli, T. SinGAN: Learning a Generative Model from a Single Natural Image. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.01164. [Google Scholar]
- Hinz, T.; Fisher, M.; Wang, O.; Wermter, S. Improved Techniques for Training Single-Image GANs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2021; pp. 1300–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Horry, M.J.; Chakraborty, S.; Paul, M.; Ulhaq, A.; Pradhan, B.; Saha, M.; Shukla, N. COVID-19 Detection Through Transfer Learning Using Multimodal Imaging Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 149808–149824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur, S.; Benaim, S.; Wolf, L. Hierarchical Patch VAE-GAN: Generating Diverse Videos from a Single Sample. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.12226. [Google Scholar]
- Eryilmaz-Eren, E.; Senbayrak, S.; Karlidag, G.E.; Mert, D.; Urkmez, F.Y.; Peña-López, Y.; Rello, J.; Alp, E. Ventilator-associated event (VAE) epidemiology and prognosis: Preliminary results of VAE-Türkiye. J. Crit. Care 2024, 81, 154671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Q.; Kang, Q.; Zhou, M. MOGAN: Morphologic-Structure-Aware Generative Learning From a Single Image. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2103.02997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, C.; Guo, T. ExSinGAN: Learning an Explainable Generative Model from a Single Image. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2105.07350. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.G.J.; Lei, B.L.B.; Ding, C.D.C.; Zhang, Y.Z.Y. Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Synthesis by Using Generative Adversarial Nets. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, E.; Zhou, H. A Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks (DCGANs)-Based Semi-Supervised Method for Object Recognition in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghim, S.; Kim, Y.; Bang, H.; Lim, D.; Ko, J. SAR Image Generation Method Using DH-GAN for Automatic Target Recognition. Sensors 2024, 24, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Wei, S. A SAR Dataset of Ship Detection for Deep Learning under Complex Backgrounds. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Ban, Y.; Rahnemoonfar, M. GAN-based SAR and optical image translation for wildfire impact assessment using multi-source remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 289, 113522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Menouar, H.; Hamila, R. Multimodal Crowd Counting with Pix2Pix GANs. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, Rome, Italy, 27–29 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Men, Z.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Yang, W. Advanced high-order nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high-resolution wide-swath spaceborne SAR. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zeng, X.; Qu, Q.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Shi, J. HRSID: A High-Resolution SAR Images Dataset for Ship Detection and Instance Segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 120234–120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golhar, M.V.; Bobrow, T.L.; Ngamruengphong, S.; Durr, N.J. GAN Inversion for Data Augmentation to Improve Colonoscopy Lesion Classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cao, X.; Ding, E.; Han, S. MAFormer: A transformer network with multi-scale attention fusion for visual recognition. Neurocomputing 2024, 595, 127828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y. Target Recognition for SAR Images Enhanced by Polarimetric Information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5204516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazanfari, S.; Garg, S.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Khorrami, F.; Araujo, A. R-LPIPS: An Adversarially Robust Perceptual Similarity Metric. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.15157. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J. Lightweight Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network for SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.; Pinto, M.F.; Melo, A.G.; Ramos, G.S.; Marcato, A.L.M. A novel sEMG data augmentation based on WGAN-GP. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 26, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixe, S.; Leite, J.; Fonseca, J.C.; Borges, J. BigGAN evaluation for the generation of vehicle interior images. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 204, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deijn, R.; Batra, A.; Koch, B.; Mansoor, N.; Makkena, H. Reviewing FID and SID Metrics on Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.03654. [Google Scholar]
- Tiedemann, H.; Morgenstern, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Fleming, R.W. One-shot generalization in humans revealed through a drawing task. eLife 2022, 11, e75485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, P.; Xiang, S.; Zhao, Y. Texturize a GAN Using a Single Image. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.10600. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, R.; Boukerche, A.; Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Yan, B.; Zhou, X. Data augmentation method for insulators based on Cycle GAN. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, V.; Singhal, L.; Thomas, X.; Serre, T. Diversity vs. Recognizability: Human-like generalization in one-shot generative models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.10370. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; McClelland, J.L. Information Processing in Dynamical Systems: Foundations of Harmony Theory; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 194–281. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzan, M.; Abid, A.; Bilal, M.; Aamir, K.M.; Memon, S.A.; Chung, T.-S. Effectiveness of Pre-Trained CNN Networks for Detecting Abnormal Activities in Online Exams. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 21503–21519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubičić, R.; Dal Sasso, S.F.; Zindović, B. SSIMS-Flow: Image velocimetry workbench for open-channel flow rate estimation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 173, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Evaluation Metrics | Baseline | StGAN & TeGAN | TeGAN & SeGAN | StGAN & TeGAN & SeGAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIFID | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.09 |
| SSIM | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.41 |
| Evaluation Metrics | Baseline | GANs w./o. MSDA | GANs w. MSDA |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIFID | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.09 |
| SSIM | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.41 |
| Parameters | SIFID SSIM | SIFID SSIM | SIFID SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value: 0.05 | Value: 0.1 | Value: 0.3 | |
| = 1) | 0.20 0.37 | 0.21 0.41 | 0.34 0.27 |
| = 1) | 0.18 0.35 | 0.25 0.36 | 0.39 0.14 |
| = 1) | 0.18 0.16 | 0.14 0.19 | 0.22 0.12 |
| = 0.5) | value: 5 | value: 10 | value: 20 |
| 0.19 0.18 | 0.11 0.25 | 0.52 0.19 |
| Methods | 200 × 200 | 400 × 400 | 800 × 800 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIFID SSIM | SIFID SSIM | SIFID SSIM | |
| Ours | 0.09 0.41 | 0.15 0.42 | 0.28 0.47 |
| SinGAN | 0.12 0.36 | 0.25 0.20 | 0.28 0.47 |
| EXSinGAN | 0.10 0.38 | 0.18 0.39 | 0.27 0.52 |
| InGAN | 0.64 0.18 | 0.75 0.13 | 0.93 0.07 |
| HP-VAEGAN | 0.30 0.19 | 0.32 0.15 | 0.61 0.05 |
| Methods | Parameters (m) | FLOPS (Gbps) | Training Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ours | 45.38 | 141.7 | 1.5 h |
| SinGAN | 32.82 | 124.9 | 1 h |
| EXSinGAN | 37.13 | 133.6 | 1 h |
| InGAN | 22.67 | 104.9 | 50 min |
| HP-VAEGAN | 29.31 | 118.1 | 50 min |
| Methods | 400 × 400 Realism Diversity | 800 × 800 Realism Diversity |
|---|---|---|
| The proposed method | 68% 70% | 75% 66% |
| SinGAN | 14% 8% | 15% 8% |
| EXSinGAN | 6% 12% | 10% 16% |
| InGAN | 8% 7% | 3% 7% |
| HP-VAEGAN | 4% 3% | 2% 3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Hui, B.; Guo, P.; Jin, R.; Ding, L. Coarse-to-Fine Structure and Semantic Learning for Single-Sample SAR Image Generation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173326
Wang X, Hui B, Guo P, Jin R, Ding L. Coarse-to-Fine Structure and Semantic Learning for Single-Sample SAR Image Generation. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173326
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xilin, Bingwei Hui, Pengcheng Guo, Rubo Jin, and Lei Ding. 2024. "Coarse-to-Fine Structure and Semantic Learning for Single-Sample SAR Image Generation" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173326
APA StyleWang, X., Hui, B., Guo, P., Jin, R., & Ding, L. (2024). Coarse-to-Fine Structure and Semantic Learning for Single-Sample SAR Image Generation. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3326. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173326






