The Remote Effects of Typhoons on the Cold Filaments in the Southwestern South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
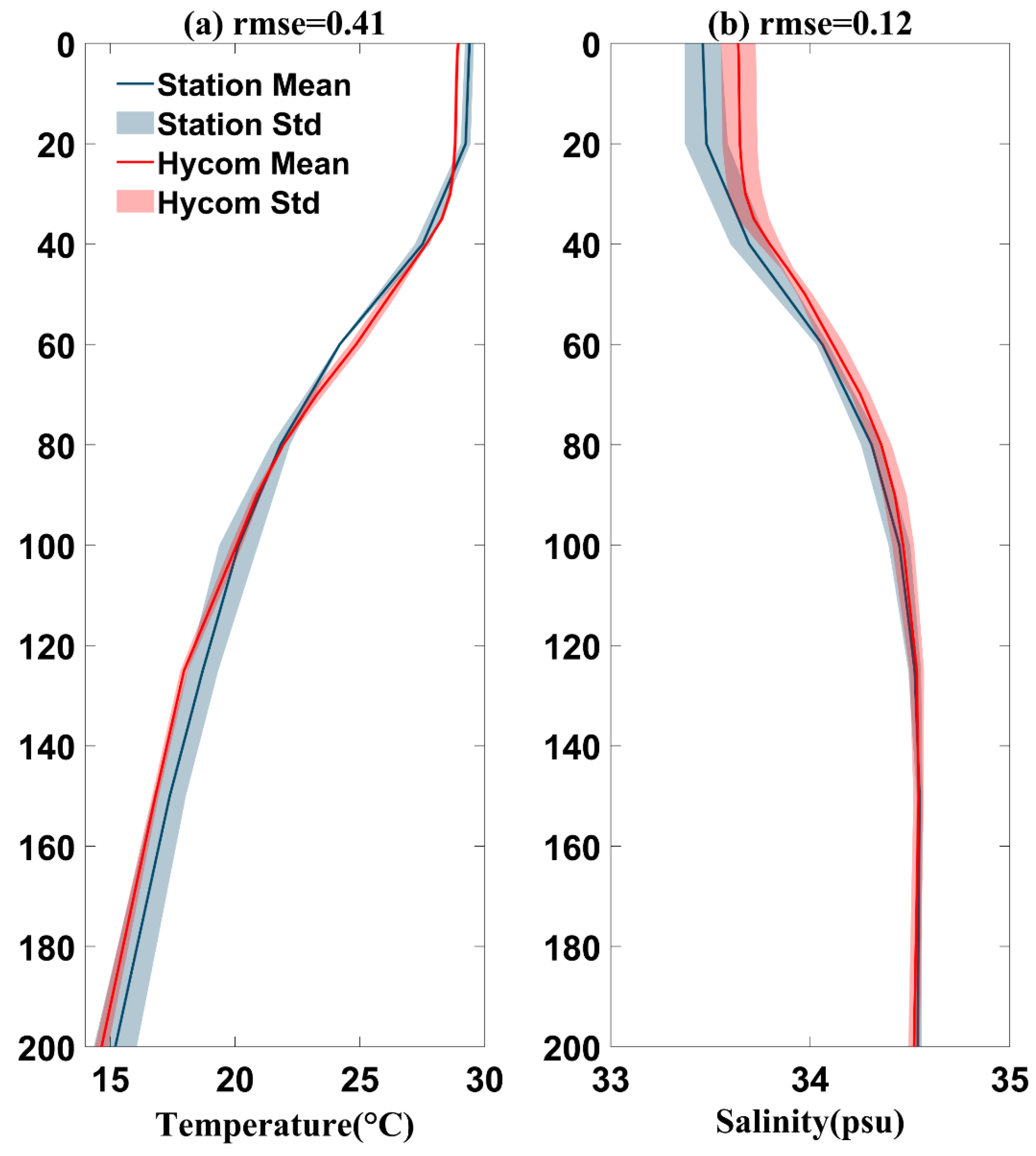
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Sea Surface Temperature
2.2. Sea Surface Height Anomalies and Surface Geostrophic Velocity
2.3. Wind Vectors
2.4. Reanalysis Data
2.5. Calculation of Ekman Pumping
2.6. Cold Filament Identification
3. Results
3.1. Statistics of Typhoons Passing Northern SCS Affecting SWCFs
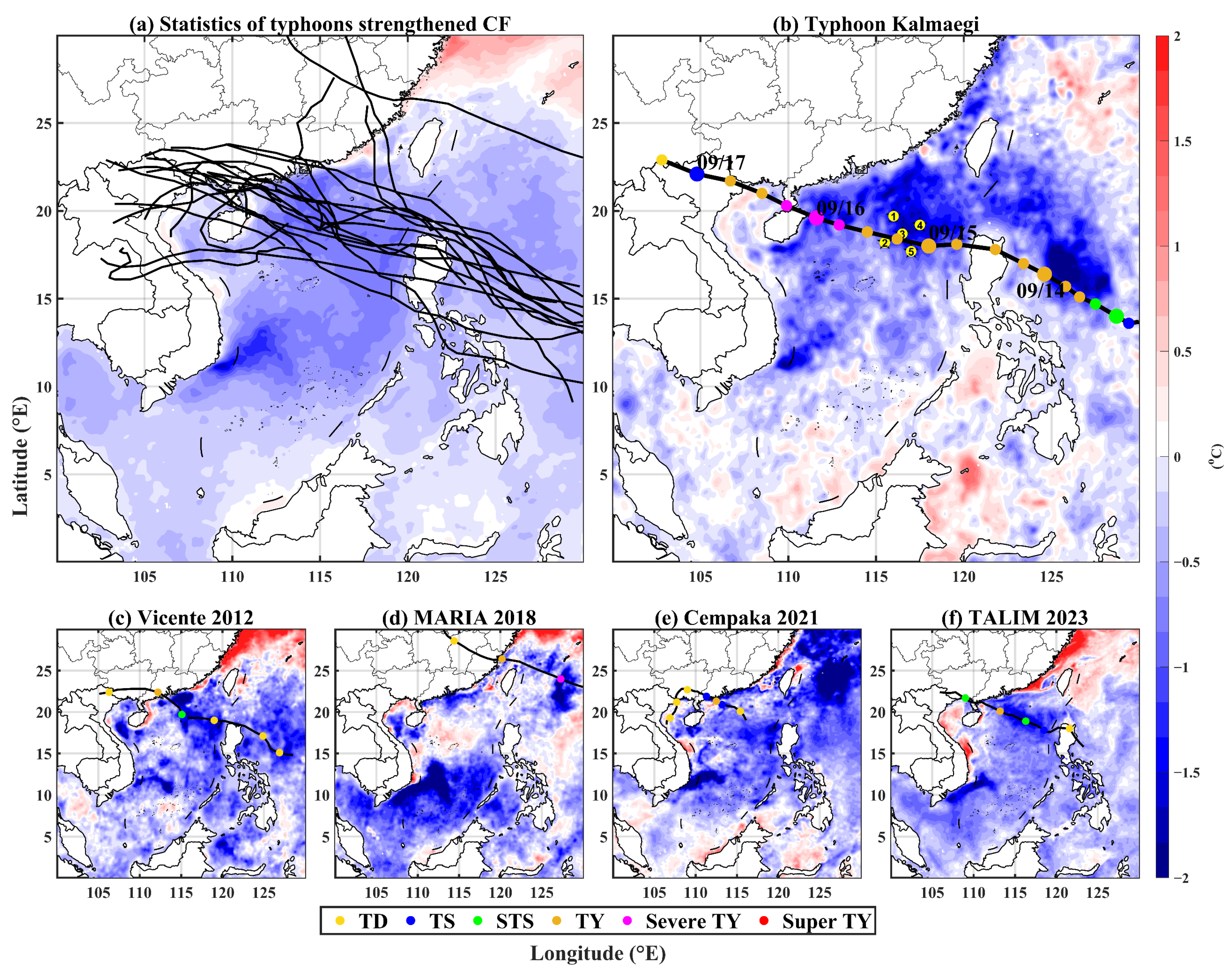
3.2. Case of Typhoon Kalmaegi
3.3. CF Response to Typhoon Kalmaegi
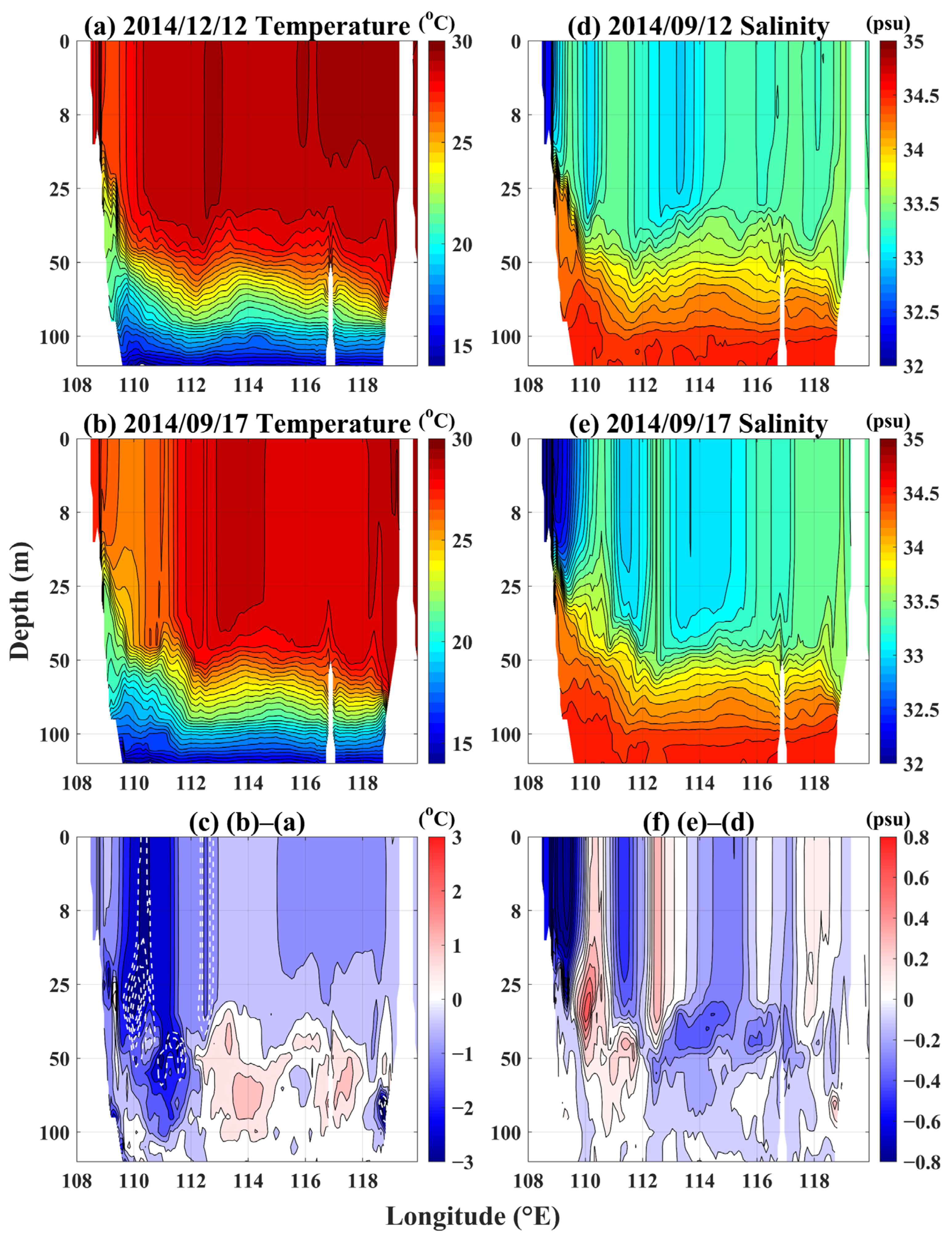
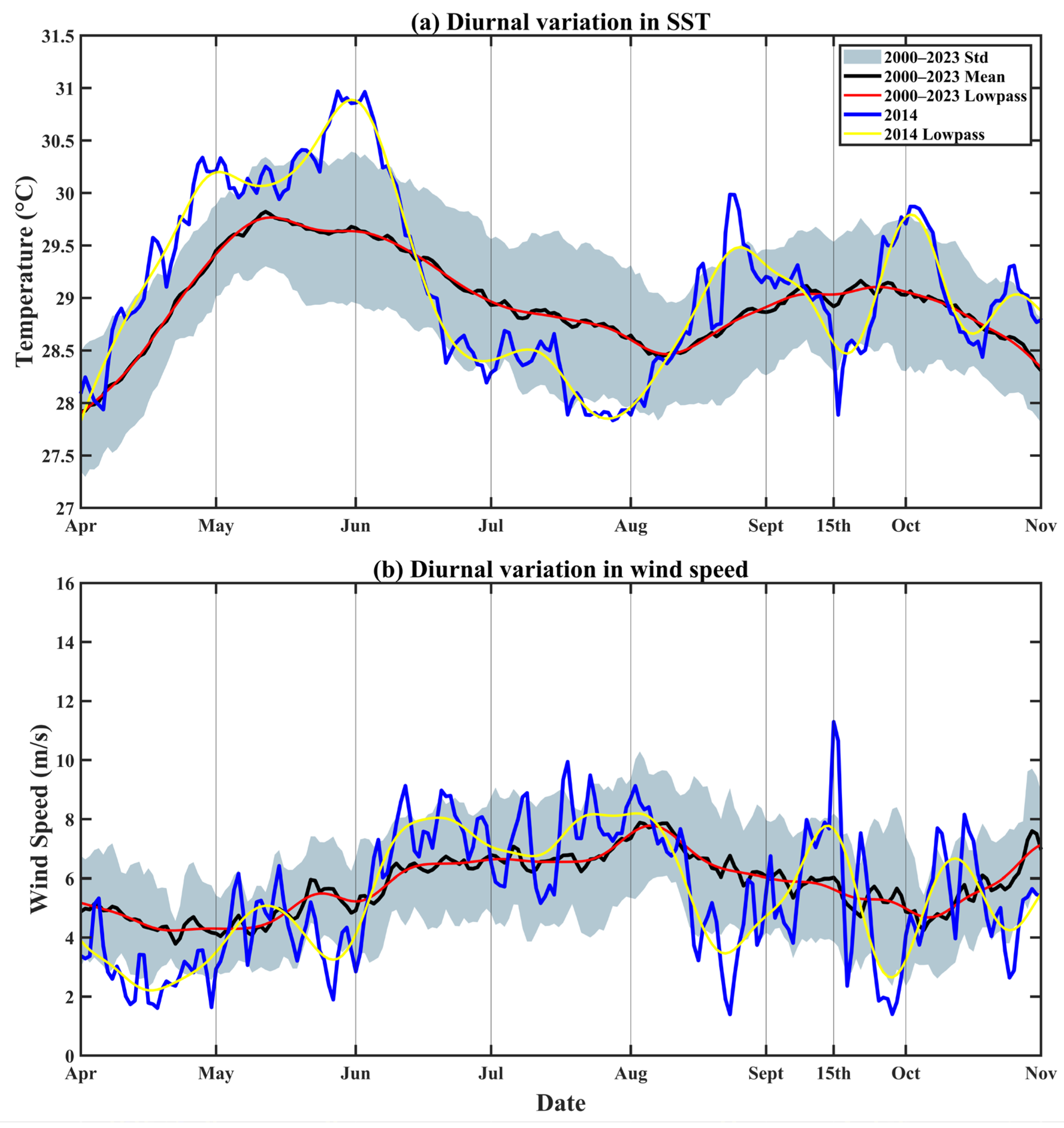
3.3.1. SST Variation during the Passage of Typhoon Kalmaegi in the Southwestern SCS
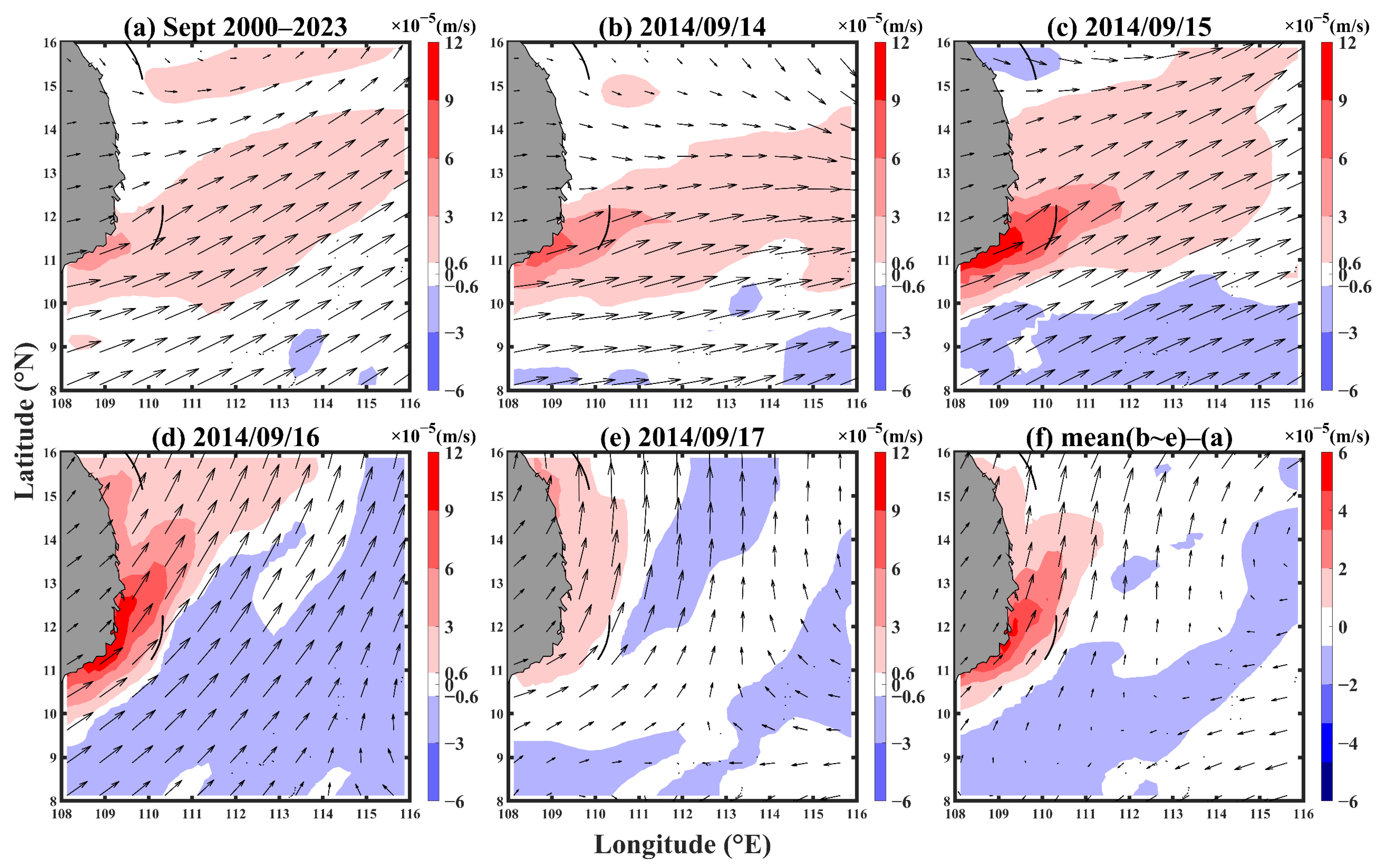
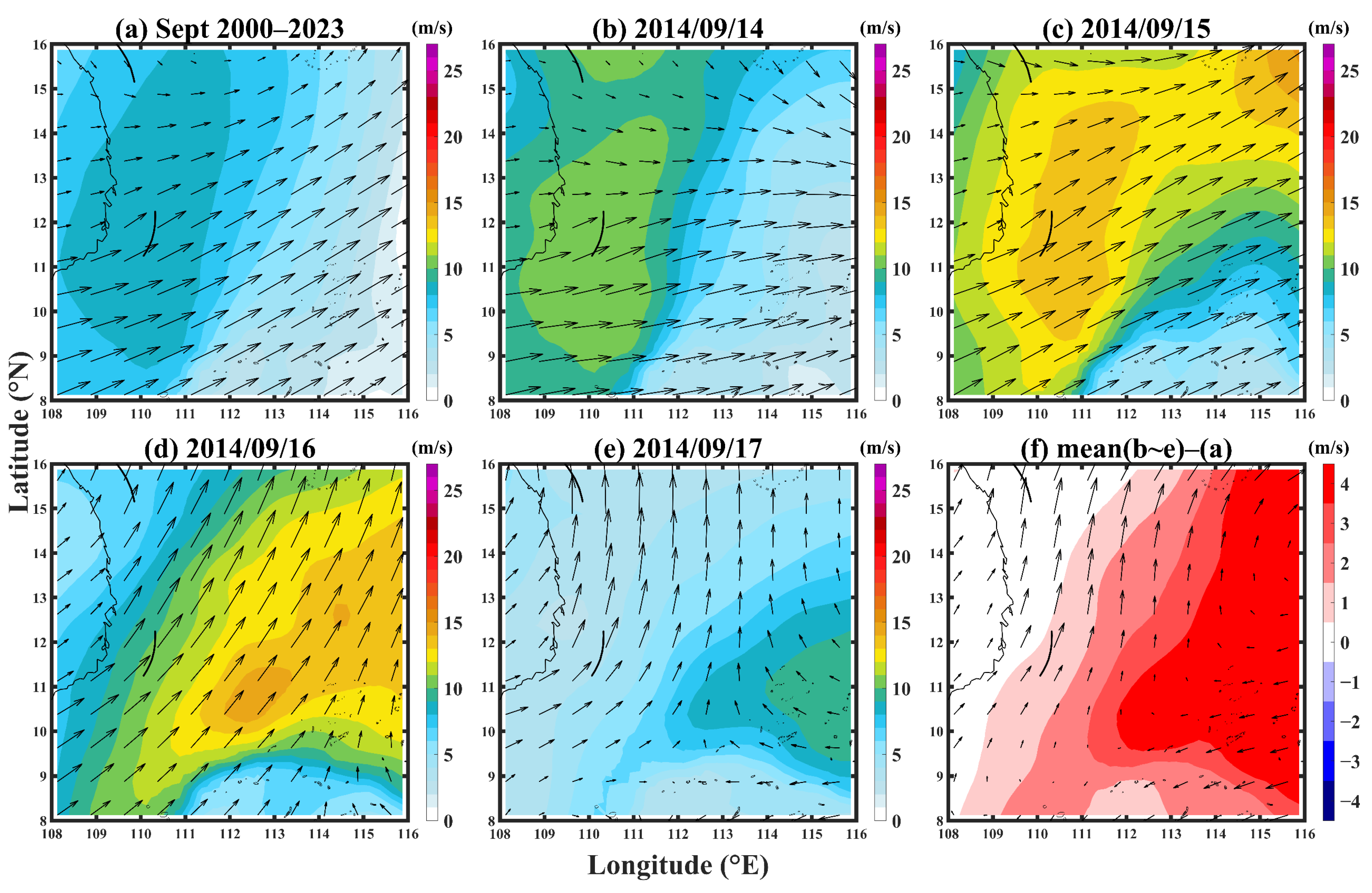
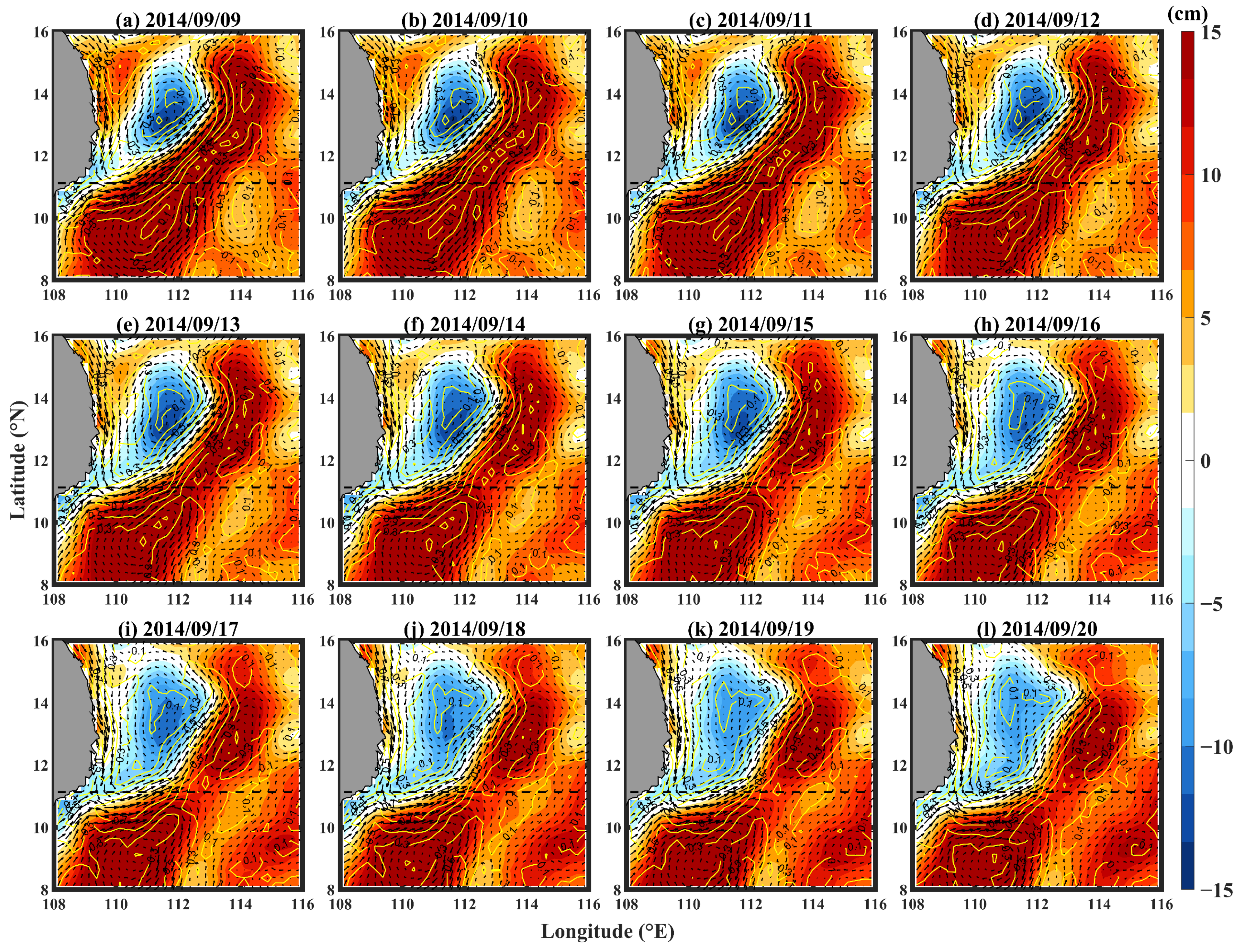
3.3.2. Wind Stress Curl and the Upwelling Response of the Southern SCS
3.3.3. SLA and Sea Surface Current Response of SWCF Area
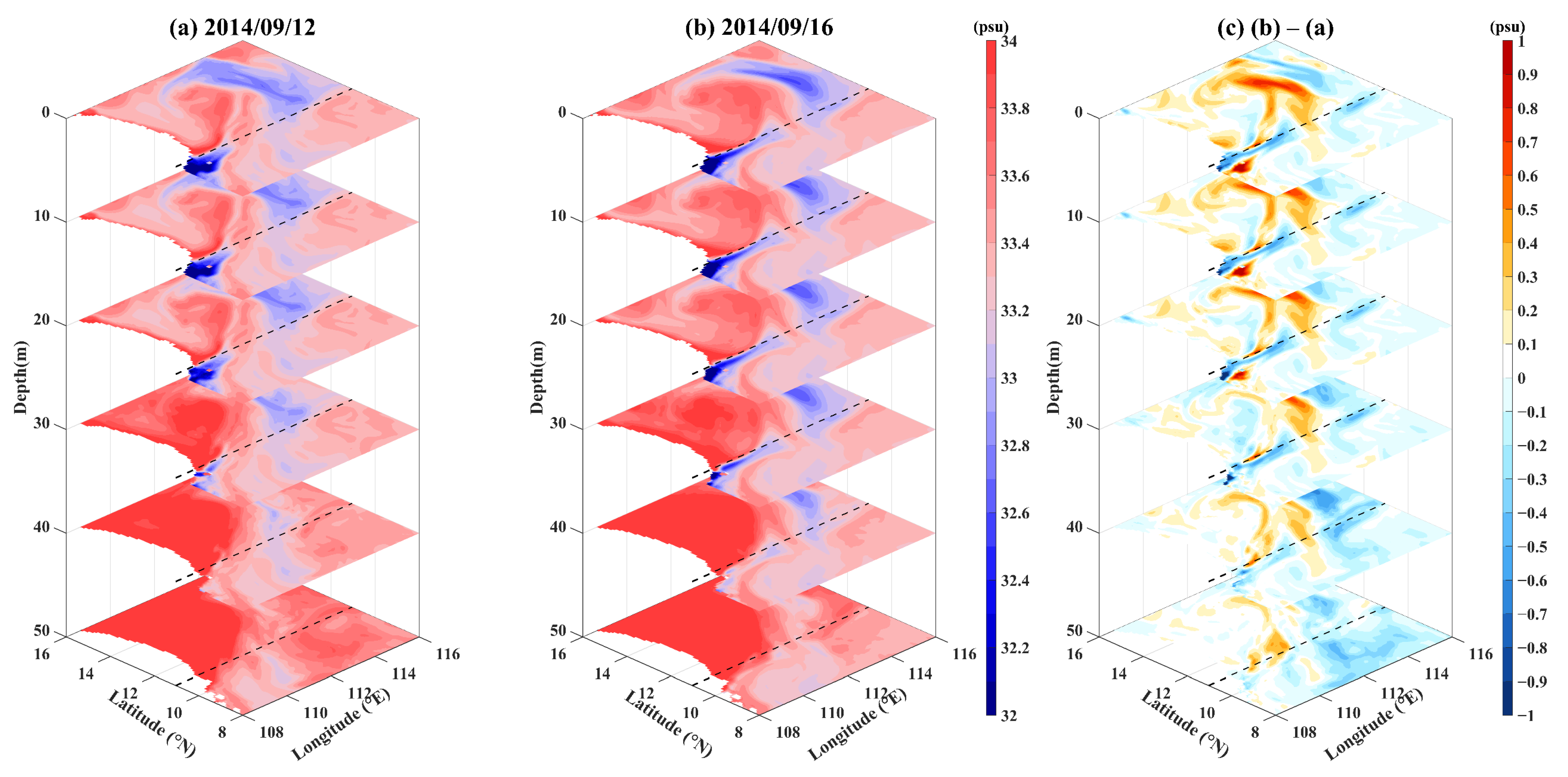
3.3.4. Three-Dimensional Temperature and Salinity Variation of the SWCF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Zhai, X. Observed Cold Filaments Associated with Mesoscale Eddies in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flament, P.; Armi, L.; Washburn, L. The Evolving Structure of an Upwelling Filament. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1985, 90, 11765–11778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, L.; Swenson, M.S.; Largier, J.L.; Kosro, P.M.; Ramp, S.R. Cross-Shelf Sediment Transport by an Anticyclonic Eddy off Northern California. Science 1993, 261, 1560–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooers, C.N.K.; Robinson, A.R. Turbulent Jets and Eddies in the California Current and Inferred Cross-Shore Transports. Science 1984, 223, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strub, P.T.; Kosro, P.M.; Huyer, A. The Nature of the Cold Filaments in the California Current System. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1991, 96, 14743–14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, E.D.; Inall, M.E.; Sherwin, T.J.; Torres, R. Vertical Structure, Turbulent Mixing and Fluxes during Lagrangian Observations of an Upwelling Filament System off Northwest Iberia. Prog. Oceanogr. 2001, 51, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peliz, Á.; Santos, A.M.P.; Oliveira, P.B.; Dubert, J. Extreme Cross-Shelf Transport Induced by Eddy Interactions Southwest of Iberia in Winter 2001. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 2004GL019618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, T.; Barton, E.D.; Barreiro, B.; Torres, R. Upwelling Filaments off Cap Blanc: Interaction of the NW African Upwelling Current and the Cape Verde Frontal Zone Eddy Field? J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, 2012JC007905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, N.G.F.; Nolasco, R.; Cordeiro-Pires, A.; Barton, E.D.; Dubert, J. Filaments on the Western Iberian Margin: A Modeling Study. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 5400–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutjeharms, J.R.E.; Shillington, F.A.; Duncombe Rae, C.M. Observations of Extreme Upwelling Filaments in the Southeast Atlantic Ocean. Science 1991, 253, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.-T.; Johnson, R.; Keenan, T.; Cifelli, R.; Gerlach, J.; Thiele, O.; Rickenbach, T.; Tsay, S.-C.; et al. A Report of the Field Operations and Early Results of the South China Sea Monsoon Experiment (SCSMEX). Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Meng, X.; Jing, Z.; Yang, X. High-Resolution Simulation of Upper-Ocean Submesoscale Variability in the South China Sea: Spatial and Seasonal Dynamical Regimes. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Jing, Z. Submesoscale-Enhanced Filaments and Frontogenetic Mechanism within Mesoscale Eddies of the South China Sea. Acta Oceanolog. Sin. 2022, 41, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jing, Z.; Zheng, R.; Cao, H. Dynamical Analysis of Submesoscale Fronts Associated with Wind-Forced Offshore Jet in the Western South China Sea. Acta Oceanolog. Sin. 2020, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Menemenlis, D.; Huang, Y. Characterizing Meso- to Submesoscale Features in the South China Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 188, 102420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.-R.; Chai, F. Distribution and Variability of Sea Surface Temperature Fronts in the South China Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 240, 106793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Xie, Q.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.T. Summer Upwelling in the South China Sea and Its Role in Regional Climate Variations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2003, 108, 2003JC001867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tang, D.L. Effect of 1998 El Niño on the Distribution of Phytoplankton in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, 2006JC003536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrtki, K. Physical Oceanography of the Southeast Asian Waters by Klaus Wyrtki NAGA Report Volume 2. Scientific Results of Marine Investigations of the South China Sea and the Gulf of Thailand, 1959–1961. S.I.O., La Jolla, Calif., 1961. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 1962, 42, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Wang, G.; Fang, Y.; Fang, W. A Review on the South China Sea Western Boundary Current. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wu, R. Seasonality of Interannual Atmosphere–Ocean Interaction in the South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2013, 69, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, L. Trends of Upper-layer Circulation in the South China Sea during 1959–2008. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, 2012JC008068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Belkin, I.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. Thermal Fronts of the Southern South China Sea from Satellite and in Situ Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 7458–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, D.; Su, J. Generation and Life Cycle of the Dipole in the South China Sea Summer Circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111, 2005JC003314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Chang, C.; Xie, Q.; Wang, D. Intraseasonal Variability in the Summer South China Sea: Wind Jet, Cold Filament, and Recirculations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, 2007JC004238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Tang, R.; Chai, F. The Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction over a Summer Upwelling System in the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sys. 2020, 208, 103360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, G.; Xu, C.; Gao, G.; Sun, R. The Influence of Cold Filaments on the Evolution of Dipole Structures. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1113993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Yang, Z.; Feng, M.; Yang, J.; Rippeth, T.P.; Shang, X.; Sun, Z.; Jing, C.; Wang, D. Observational Energy Transfers of a Spiral Cold Filament within an Anticyclonic Eddy. Prog. Oceanogr. 2024, 220, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xie, S.-P.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, D. Orographic Effects on South China Sea Summer Climate. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2008, 100, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, G.; Tang, D.; Huang, P.; Yan, H.; Gao, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; et al. Basin-Wide Responses of the South China Sea Environment to Super Typhoon Mangkhut (2018). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, D.; Liao, S. Strengthening Effect of Super Typhoon Rammasun (2014) on Upwelling and Cold Eddies in the South China Sea. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J. The Emissivity of the Ocean Surface Between 6 and 90 GHz Over a Large Range of Wind Speeds and Earth Incidence Angles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3004–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilburn, K.A.; Wentz, F.J. Intercalibrated Passive Microwave Rain Products from the Unified Microwave Ocean Re-trieval Algorithm (UMORA). J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 778–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiser, P.W.; St Germain, K.M.; Twarog, E.M.; Poe, G.A.; Purdy, W.; Richardson, D.; Grossman, W.; Jones, W.L.; Spencer, D.; Golba, G.; et al. The WindSat Spaceborne Polarimetric Microwave Radiometer: Sensor Description and Early Orbit Performance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2347–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, D.W.; Newell, D.A.; Wentz, F.J.; Krimchansky, S.; Skofronick-Jackson, G.M. The Global Precipitation Meas-urement (GPM) Microwave Imager (GMI): Instrument Overview and Early On-Orbit Performance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3452–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J.; Gentemann, C.; Smith, D.; Chelton, D. Satellite Measurements of Sea Surface Temperature through Clouds. Science 2000, 288, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, T.; Zhou, B. Upper Ocean Response to Typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 6520–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F. Upper Ocean Response to a Hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes, B.; Shay, L.K. Enhanced Wind-Driven Downwelling Flow in Warm Oceanic Eddy Features during the Intensification of Tropical Cyclone Isaac (2012): Observations and Theory. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 1667–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.D.; Vickery, P.J.; Reinhold, T.A. Reduced Drag Coefficient for High Wind Speeds in Tropical Cyclones. Nature 2003, 422, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, P.G.; D’Asaro, E.A.; Drennan, W.M.; French, J.R.; Niiler, P.P.; Sanford, T.B.; Terrill, E.J.; Walsh, E.J.; Zhang, J.A. Air–Sea Exchange in Hurricanes: Synthesis of Observations from the Coupled Boundary Layer Air–Sea Transfer Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelan, M.A.; Haus, B.K.; Reul, N.; Plant, W.J.; Stiassnie, M.; Graber, H.C.; Brown, O.B.; Saltzman, E.S. On the Limiting Aerodynamic Roughness of the Ocean in Very Strong Winds. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 2004GL019460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, P.J.; Wadhera, D.; Powell, M.D.; Chen, Y. A Hurricane Boundary Layer and Wind Field Model for Use in Engineering Applications. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2009, 48, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, W.; Wilkin, J.L.; Zhang, W.G.; Arango, H.; Zavala-Garay, J.; Levin, J.; Castruccio, F.S. Interannual Variability of the Surface Summertime Eastward Jet in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 7205–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, R.; Chen, D.; Zhang, D.; Shang, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Jin, W.; Yu, L.; et al. Sea Surface Current Response Patterns to Tropical Cyclones. J. Mar. Sys. 2020, 208, 103345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Impact of Typhoon Kalmaegi (2014) on the South China Sea: Simulations Using a Fully Coupled Atmosphere-Ocean-Wave Model. Ocean Model. 2018, 131, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D. Effect of Typhoon Kalmaegi (2014) on Northern South China Sea Explored Using Muti-Platform Satellite and Buoy Observations Data. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 180, 102218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Song, J.; Leng, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, C. The Abnormal Track of Super Typhoon Hinnamnor (2022) and Its Interaction with the Upper Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part I 2023, 201, 104160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, J.; Zhao, C.; Yang, X.; Leng, H.; Zhou, N. Validation of the Multi-Satellite Merged Sea Surface Salin-ity in the South China Sea. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 41, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Song, J.; Leng, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Ke, D.; Zhao, C. Ocean Response Offshore of Taiwan to Su-per Typhoon Nepartak (2016) Based on Multiple Satellite and Buoy Observations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1132714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; He, Y.; Liu, G. Atmospheric and Oceanic Responses to Super Typhoon Mangkhut in the South China Sea: A Coupled CROCO-WRF Simulation. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2023, 41, 1369–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Tang, D.; Yan, H.; Ning, G. Association between the Biophysical Environment in Coastal South China Sea and Large-Scale Synoptic Circulation Patterns: The Role of the Northwest Pacific Subtropical High and Typhoons. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, Q. Extratropical Transition and Re-Intensification of Typhoon Toraji (2001): Large-Scale Circulations, Structural Characteristics, and Mechanism Analysis. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2018, 17, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Ahn, Y.; Kim, C. Impact of Ocean Roughness and Bogus Typhoons on Summertime Circulation in a Wave-Atmosphere Coupled Regional Climate Model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, 2003JD003781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | Year | Start Date | End Date | Sea Surface Cooling (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Utor | 2001 | 1 July | 7 July | −1.26 |
| Hagupit | 2002 | 9 September | 15 September | −0.68 |
| Imbudo | 2003 | 15 July | 25 July | −0.78 |
| Washi | 2005 | 28 July | 31 July | −0.41 |
| Fengshen | 2008 | 17 June | 27 June | −0.59 |
| Hagupit | 2008 | 17 September | 25 September | −0.80 |
| Molave | 2009 | 15 July | 19 July | −0.77 |
| Goni | 2009 | 31 July | 9 August | −0.50 |
| Haima | 2011 | 16 June | 25 June | −1.40 |
| Vicente | 2012 | 18 July | 25 July | −0.85 |
| Cimaron | 2013 | 14 July | 19 July | −0.96 |
| Rammasun | 2014 | 10 July | 19 July | −0.48 |
| Kalmaegi | 2014 | 10 September | 17 September | −0.64 |
| Sonca | 2017 | 21 July | 29 July | −0.45 |
| Maria | 2018 | 3 July | 13 July | −1.50 |
| Wipha | 2019 | 30 July | 3 August | −0.83 |
| Podul | 2019 | 25 August | 30 August | −0.46 |
| Cempaka | 2021 | 17 July | 24 July | −1.22 |
| Talim | 2023 | 13 July | 18 July | −0.78 |
| Doksuri | 2023 | 20 July | 31 July | −0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Yuan, T.; Ren, K. The Remote Effects of Typhoons on the Cold Filaments in the Southwestern South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173293
Zhao Z, Yang S, Wang H, Yuan T, Ren K. The Remote Effects of Typhoons on the Cold Filaments in the Southwestern South China Sea. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173293
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zezheng, Shengmu Yang, Huipeng Wang, Taikang Yuan, and Kaijun Ren. 2024. "The Remote Effects of Typhoons on the Cold Filaments in the Southwestern South China Sea" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173293
APA StyleZhao, Z., Yang, S., Wang, H., Yuan, T., & Ren, K. (2024). The Remote Effects of Typhoons on the Cold Filaments in the Southwestern South China Sea. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173293







