Evaluation of Urban Microscopic Nighttime Light Environment Based on the Coupling Observation of Remote Sensing and UAV Observation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Time
2.2. Research Data and Methods
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. Ground–Measured Data
2.2.3. UAV Measurement Data
3. Result and Analysis
3.1. Data Analysis
3.1.1. Ground–Measured Data and Remote Sensing Data
3.1.2. Ground–Measured Data and UAV Aerial Photography Data
3.1.3. UAV Aerial Photography Data and Remote Sensing Data
3.2. Data Comparative Analysis
3.2.1. Ground–Measured Data and UAV Aerial Photography Data Comparative Analysis
3.2.2. Ground–Measured Data and Remote Sensing Data Comparative Analysis
3.3. Inversion Map
3.4. Analysis of Campus Nighttime Light Environment and Verification of Inversion Results
3.4.1. Verification of Campus Nighttime Environmental Illumination and Inversion Results
3.4.2. Uniformity of Campus Night Environment Illumination
3.4.3. Influence Factors of Environmental Illuminance and Illuminance Uniformity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyce, P.R. The benefits of light at night. Build. Environ. 2019, 151, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska–Dabkowska, K.M.; Xavia, K. Looking up to the stars. A call for action to save New Zealand’s dark skies for future generations to come. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegel, K.W. Light Pollution: Outdoor lighting is a growing threat to astronomy. Science 1973, 179, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Cruse, D.; Gaston, K.J. Ecological effects of artificial light at night on wild plants. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Sorte, F.A.; Fink, D.; Buler, J.J.; Farnsworth, A.; Cabrera Cruz, S.A. Seasonal associations with urban light pollution for nocturnally migrating bird populations. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 4609–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, C.; Fournari Konstantinidou, I.; Sourbès, L.; Koutsoubas, D.; Mazaris, A.D. Reduction of sea turtle population recruitment caused by nightlight: Evidence from the Mediterranean region. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 153, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybnikova, N.; Stevens, R.G.; Gregorio, D.I.; Samociuk, H.; Portnov, B.A. Kernel density analysis reveals a halo pattern of breast cancer incidence in Connecticut. Spat. Spatio–Temporal Epidemiol. 2018, 26, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, Y.; Reinberg, A.; Touitou, D. Association between light at night, melatonin secretion, sleep deprivation, and the internal clock: Health impacts and mechanisms of circadian disruption. Life Sci. 2017, 173, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancredi, S.; Urbano, T.; Vinceti, M.; Filippini, T. Artificial light at night and risk of mental disorders: A systematic review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerem, A. Assessing the electricity energy efficiency of university campus exterior lighting system and proposing energy–saving strategies for carbon emission reduction. Microsyst. Technol. 2022, 28, 2623–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyba, C.C.; Kuester, T.; Sánchez De Miguel, A.; Baugh, K.; Jechow, A.; Hölker, F.; Bennie, J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Gaston, K.J.; Guanter, L. Artificially lit surface of Earth at night increasing in radiance and extent. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Xinshuo, Z.; Li, Q.; Rouyi, M.; Yong, C.; Jingfeng, X.; Zhen, T. Influence of colored light projected from night–time excessive luminance outdoor LED display screens on vehicle driving safety along urban roads. Build. Environ. 2021, 188, 107448. [Google Scholar]
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Duriscoe, D.; Kyba, C.C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Portnov, B.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Furgoni, R. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.; Zhang, Q.; de Miguel, A.S.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Zhao, N.; Yang, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Hu, K.; Yue, W.; Qi, J.; Li, Z. Improved population mapping for China using remotely sensed and points–of–interest data within a random forests model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, X.; Xu, K. Analysis of Urban Expansion Characteristics of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration Based on Dmsp/ols Nighttime Light Data. Isprs Ann.Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 3, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Qiu, B.; Yu, B. The potential of nighttime light remote sensing data to evaluate the development of digital economy: A case study of China at the city level. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 92, 101749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Ma, Z.; Mi, Z.; Kelsey, J.; Zheng, J.; Yin, W.; Yan, M. Spatio–temporal simulation of energy consumption in China’s provinces based on satellite night–time light data. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Construction and Application of Urban Nighttime Light Environment Inversion Method Based on Remote Sensing and Field Measurement. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tahar, M.R. Spatial Model of Sky Brightness Magnitude in Langkawi Island, Malaysia. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 17, 037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Xu, W.; Yao, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, S.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. Spectral–level assessment of light pollution from urban façade lighting. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, J.; Zamorano, J.; Pascual, S.; Sánchez De Miguel, A.; Gallego, J.; Gaston, K.J. Evolution of brightness and color of the night sky in Madrid. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.; Anderson, S.J.; Pipkin, A.; Fristrup, K. Changes in night sky brightness after a countywide LED retrofit. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, Y.; Levin, N. Quantifying urban light pollution—A comparison between field measurements and EROS–B imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Cui, W.E.A. Monitoring of nighttime light pollution in Nanjing City based on Luojia 1—01 remote sensing data. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources 2022, 34, 289. [Google Scholar]
- Bettanini, C.; Bartolomei, M.; Aboudan, A.; Colombatti, G.; Olivieri, L. Flight test of an autonomous payload for measuring sky brightness and ground light pollution using a stratospheric sounding balloon. Acta Astronaut. 2022, 191, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmeseiry, N.; Alshaer, N.; Ismail, T. A detailed survey and future directions of unmanned aerial vehicles (uavs) with potential applications. Aerospace 2021, 8, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, M.F.; Durdu, A.; Sabanci, K.; Ropelewska, E.; Gültekin, S.S. A comprehensive survey of the recent studies with UAV for precision agriculture in open fields and greenhouses. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Tian, T.; Yin, J. A review of unmanned aerial vehicle low–altitude remote sensing (UAV–LARS) use in agricultural monitoring in China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitijiang, M.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Hartling, S.; Esposito, F.; Fritschi, F.B. Soybean yield prediction from UAV using multimodal data fusion and deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, P.B.; Hockridge, E.G.; Singh, J.; Davies, A.B. Flying high: Sampling savanna vegetation with UAV-lidar. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2023, 14, 1668–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, D.; Bonifazi, A.; Gravina, M.F.; Belluscio, A.; Ardizzone, G. Mapping and classification of ecologically sensitive marine habitats using unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery and object–based image analysis (OBIA). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R. Application of UAV–low altitude remote sensing system in sea area supervision. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2021, 25, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, D.; Alicandro, M.; Massimi, V. UAV photogrammetry in the post–earthquake scenario: Case studies in L’Aquila. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. UAV–based forest fire detection and tracking using image processing techniques. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Denver, CO, USA, 9–12 June 2015; pp. 639–643. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Peng, Z.; Lu, Q.; Wang, D.; Hu, X.; Wang, D.; Li, B.; Fu, Q.; Xiu, G.; He, H. Evaluation of unmanned aerial system in measuring lower tropospheric ozone and fine aerosol particles using portable monitors. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Minner, J. UAVs and 3D City Modeling to Aid Urban Planning and Historic Preservation: A Systematic Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X. Observations of Winter Physical Activities in Urban Parks Using UAVs: A Case Study of Four City Parks in Harbin. Chin. Landsc. Archit. 2019, 35, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bouroussis, C.A.; Topalis, F.V. Assessment of outdoor lighting installations and their impact on light pollution using unmanned aircraft systems–The concept of the drone–gonio–photometer. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 253, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massetti, L.; Paterni, M.; Merlino, S. Monitoring light pollution with an unmanned aerial vehicle: A case study Comparing RGB images and night ground brightness. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaka, P. Pilot measurement of illuminance in the context of light pollution performed with an unmanned aerial vehicle. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Levin, N.; Xie, J.; Li, D. Monitoring hourly night–time light by an unmanned aerial vehicle and its implications to satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahia, R.T.; Estur, M.C.; Blanco, A.C.; Soriano, M. Illuminance Mapping of Nighttime Road Environment Using Unmanned Aerial System. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guk, E.; Levin, N. Analyzing spatial variability in night–time lights using a high spatial resolution color Jilin–1 image–Jerusalem as a case study. Isprs–J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Research on Observation Methods and Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Urban Night Light Pollution. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Comparison and Analysis of the Light Pollution Effect at Night in the Typical Commercial Areas of Milan and Dalian. China Illum. Eng. J. 2020, 31, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Lü, M.; Zhu, T. Integration of DMSP–OLS and NPP–VIIRS nighttime light remote sensing images. Bull. Surv. Mapp. 2023, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Dou, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Fu, B.; Li, X.; Zou, Z.; Liang, D. SDGSAT–1: The world’s first scientific satellite for sustainable development goals. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, B.; Hao, Q.; Li, W. Urban Nighttime Light Pollution Testing Method; Dalian University of Technology: Dalian, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- CIE. Colorimetry—Part 1: CIE Standard Colorimetric Observers; International Commission on Illumination: Vienna, Austria, 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, B.; Luo, T.; Liu, Y.; Portnov, B.A.; Trop, T.; Jiao, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. Evaluating street lighting quality in residential areas by combining remote sensing tools and a survey on pedestrians’ perceptions of safety and visual comfort. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Luo, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q. Research on the Distribution Characteristics of Night Light Environment Security Levelin Old Residential Areas. China Illum. Eng. J. 2022, 33, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Portnov, B.A.; Saad, R.; Trop, T.; Kliger, D.; Svechkina, A. Linking nighttime outdoor lighting attributes to pedestrians’ feeling of safety: An interactive survey approach. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, R.; Portnov, B.A.; Trop, T. Saving energy while maintaining the feeling of safety associated with urban street lighting. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Su, T.; Liu, H.; Sun, H. Calibration of Bus Free–flow Travelling Speed Based on Natural Break Method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Transp. Sci. Eng.) 2023, 47, 982–986. [Google Scholar]
- China Academy of Building Research. Lighting Measurement Methods; China Standard Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M. Measurement, Experiment and Evaluation on Main Light Pollutions from Urban Lighting; Tianjin University: Tianjin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]

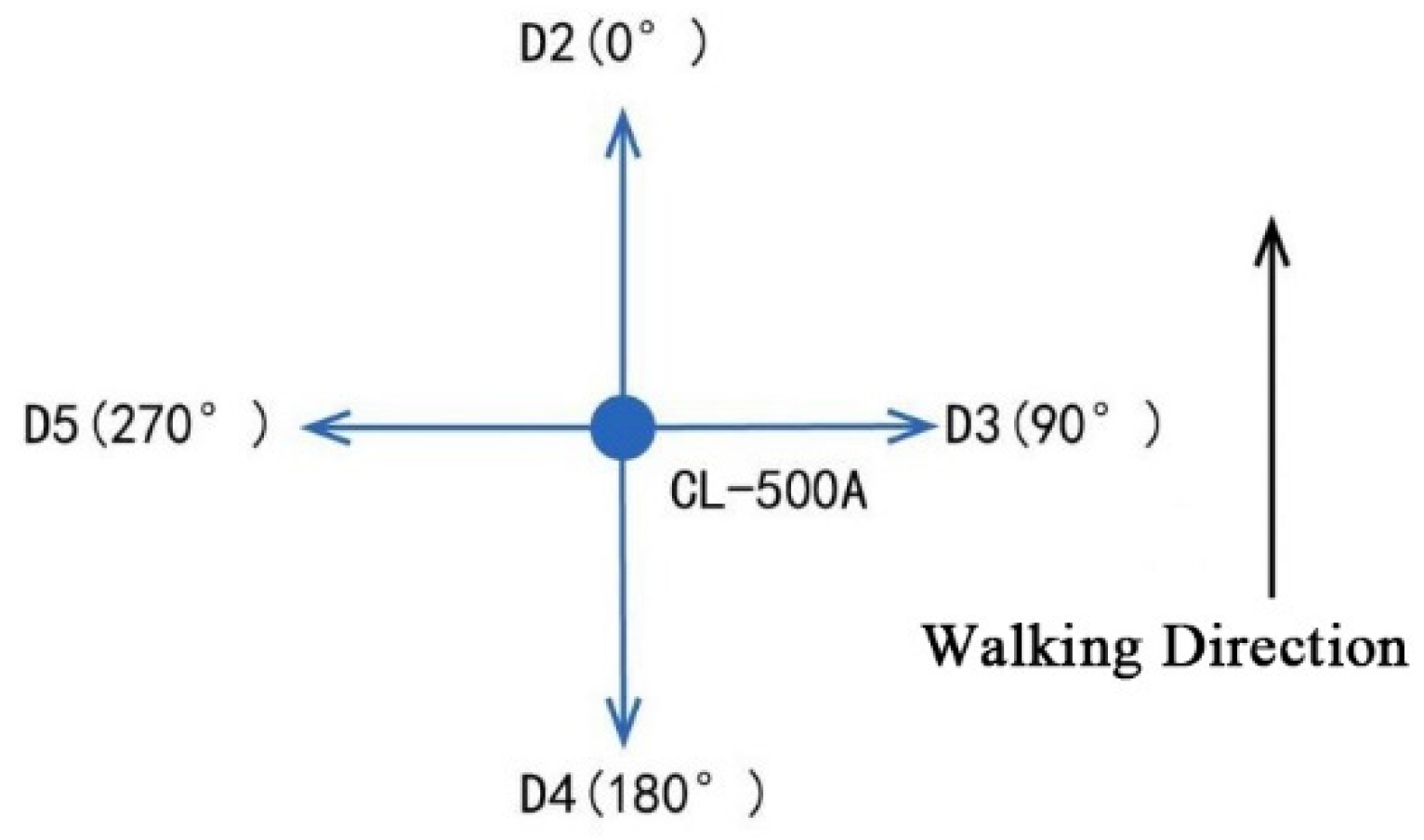
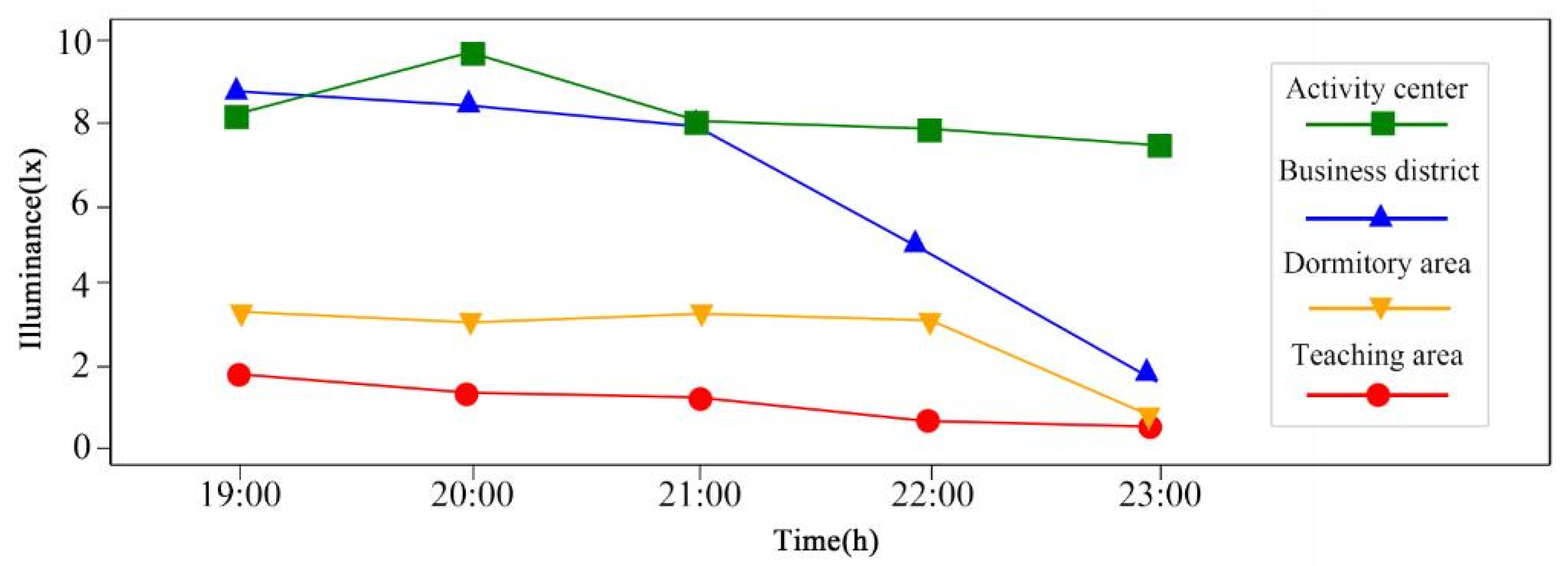

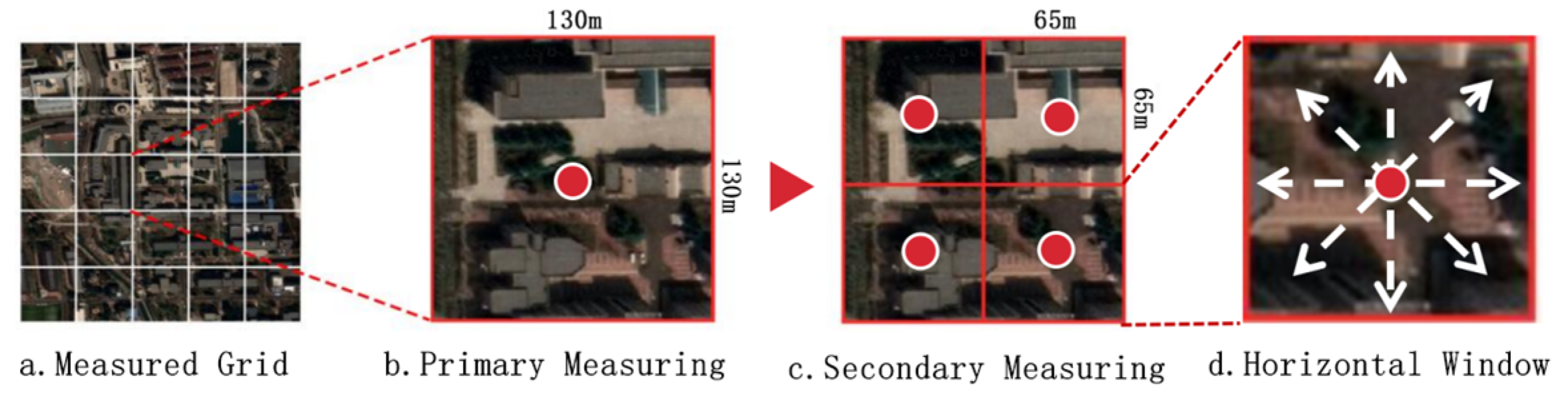





















| Items | Date | Time | Weather | Sunset Time | Average Temperature (°C) | AQI | Cloud Cover |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground measurement | 7 April 2023 | 19:00–22:00 | clear | 18:17 | 8 | 51 | cloudless |
| Ground measurement | 8April 2023 | 19:00–22:00 | clear | 18:18 | 11.5 | 90 | cloudless |
| Ground measurement | 12 April 2023 | 19:00–22:00 | clear | 18:23 | 13.5 | 44 | cloudless |
| Ground measurement | 16 April 2023 | 19:00–22:00 | clear | 18:27 | 12 | 44 | cloudless |
| UAV aerial photography | 9 May 2023 | 19:30–22:00 | clear | 18:52 | 19.5 | 57 | cloudless |
| UAV aerial photography | 10 May 2023 | 19:30–22:00 | clear | 18:53 | 19 | 48 | cloudless |
| UAV aerial photography | 11 May 2023 | 19:30–22:00 | clear | 18:54 | 19 | 52 | cloudless |
| Bands | Gain | Bias | Detection Spectral Bands |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0.00001354 | 0.0000136754 | 600~894 nm |
| G | 0.00000507 | 0.000006084 | 506~612 nm |
| B | 0.0000099253 | 0.0000099253 | 424~526 nm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Liu, M.; Li, R.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, W.; Lang, L. Evaluation of Urban Microscopic Nighttime Light Environment Based on the Coupling Observation of Remote Sensing and UAV Observation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173288
Zhang B, Liu M, Li R, Liu J, Feng L, Zhang H, Jiao W, Lang L. Evaluation of Urban Microscopic Nighttime Light Environment Based on the Coupling Observation of Remote Sensing and UAV Observation. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173288
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Baogang, Ming Liu, Ruicong Li, Jie Liu, Lie Feng, Han Zhang, Weili Jiao, and Liang Lang. 2024. "Evaluation of Urban Microscopic Nighttime Light Environment Based on the Coupling Observation of Remote Sensing and UAV Observation" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173288
APA StyleZhang, B., Liu, M., Li, R., Liu, J., Feng, L., Zhang, H., Jiao, W., & Lang, L. (2024). Evaluation of Urban Microscopic Nighttime Light Environment Based on the Coupling Observation of Remote Sensing and UAV Observation. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173288






