Stepwise Construction and Integration of Ecological Network in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study on Liaoning Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Source
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Extraction and Classification of Ecological Sources
2.4. Construction and Modification of Resistance Surfaces
2.5. Construction and Optimization of the Ecological Network
2.5.1. Construction of Ecological Networks Based on the MCR Model
2.5.2. Stepwise Construction and Integration of Ecological Network
2.6. Structural Evaluation of the Ecological Network
3. Results
3.1. Ecological Sources
3.2. Construction of Modified Resistance Surface
3.3. Spatial Distribution of the Ecological Network
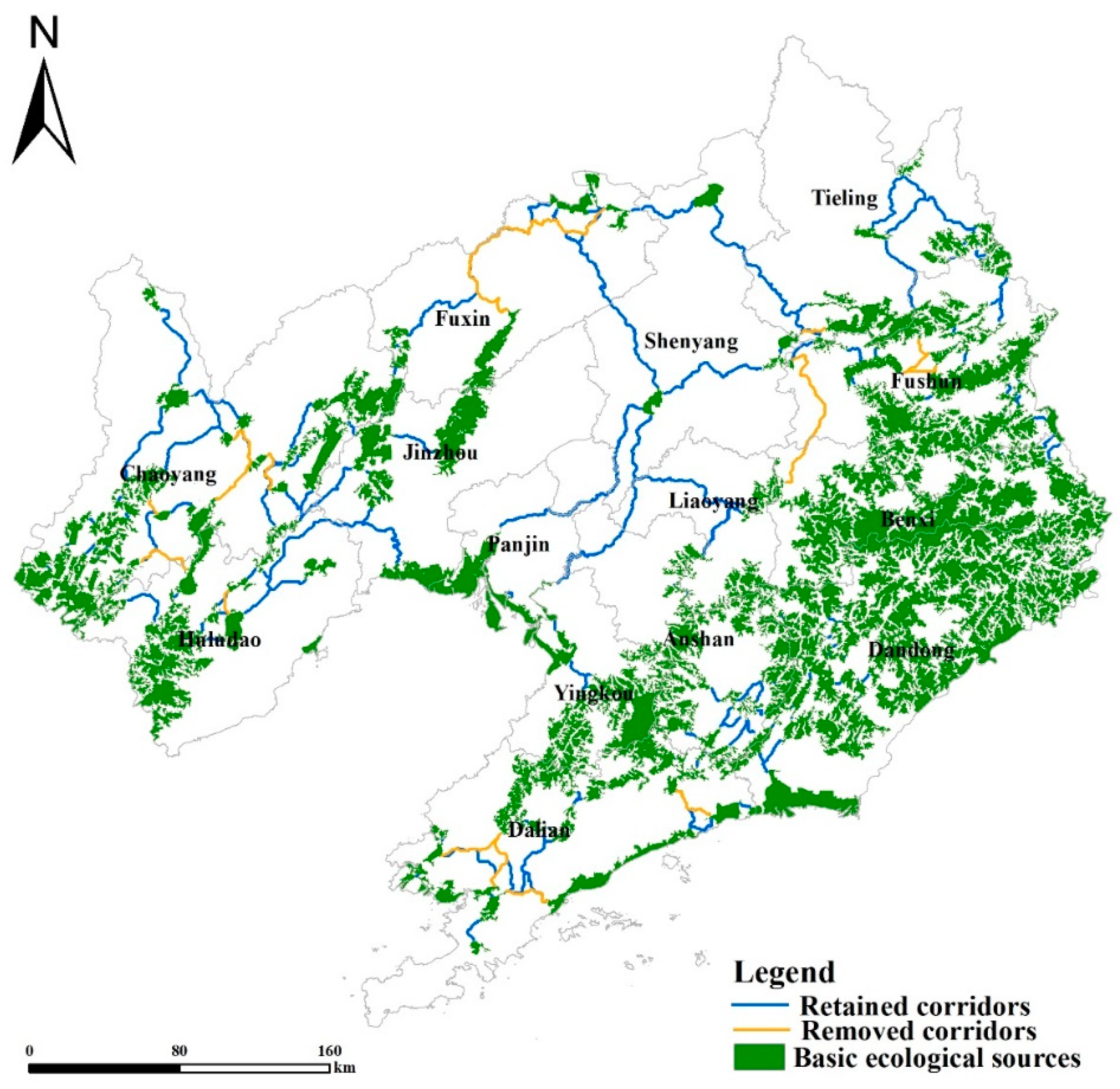
3.3.1. Basic Ecological Network
3.3.2. Supplementary Ecological Network in Each Step
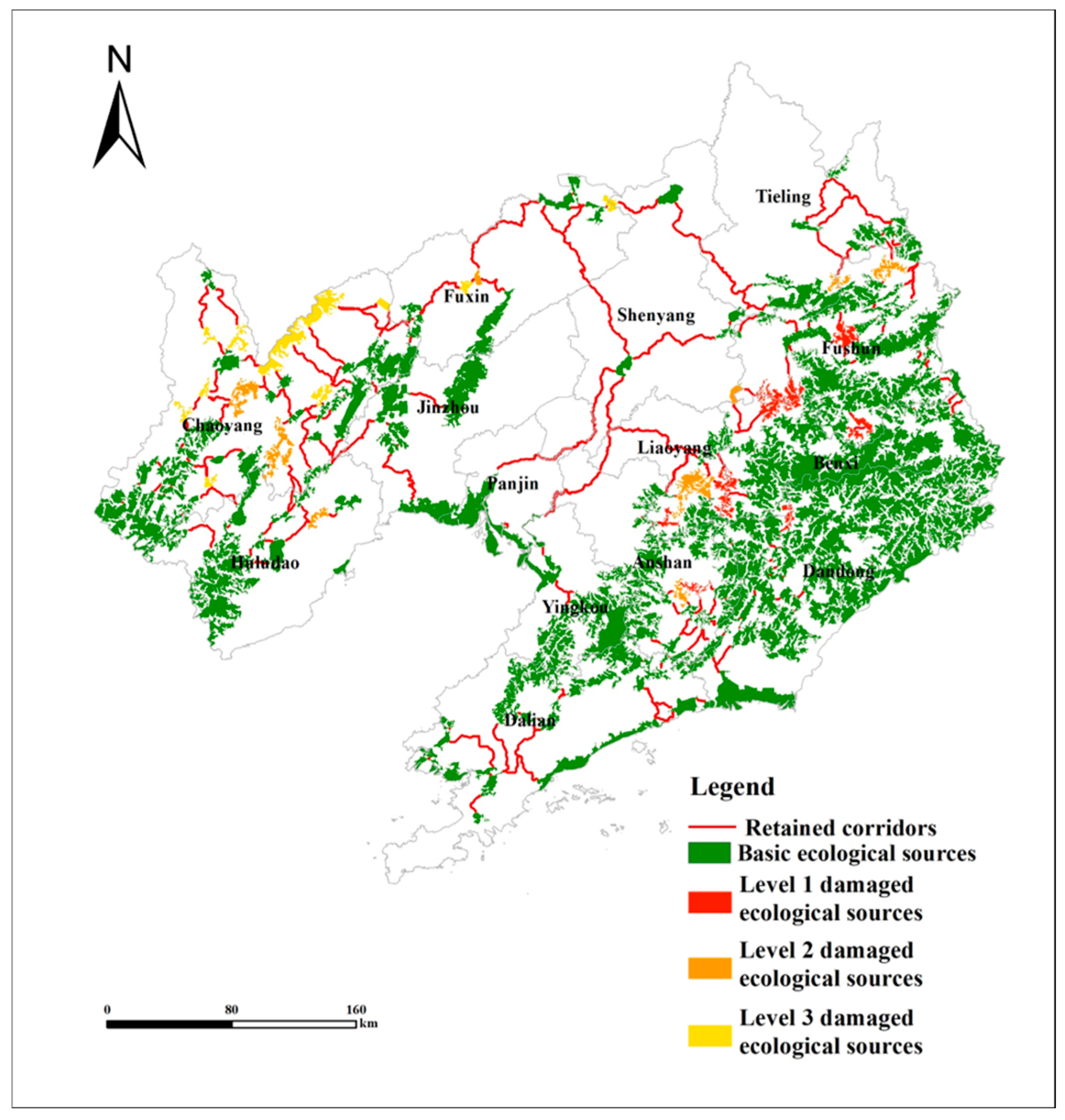
3.3.3. Integration of Ecological Network
3.3.4. Structural Performance Characteristics of Ecological Network
4. Discussion
4.1. Regulation Strategies
4.2. Importance of Supplementary Ecological Network
4.3. Optimization of the Ecological Network
4.3.1. Optimization of Ecological Sources Based on Topological Indicators
4.3.2. Optimization of Ecological Corridors
4.4. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Xu, E.; Zhang, H. Bidirectional Coupling between Land-Use Change and Desertification in Arid Areas: A Study Contrasting Intracoupling and Telecoupling. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, X. Incorporating Ecological Risk Index in the Multi-Process MCRE Model to Optimize the Ecological Security Pattern in a Semi-Arid Area with Intensive Coal Mining: A Case Study in Northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Chen, H. Estimating Soil Erosion Response to Land Use/Cover Change in a Catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhu, H.; Bing, H.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Yu, D.; Wu, Y. Predicting Soil Cadmium Uptake by Plants in a Tailings Reservoir during 48-Year Vegetation Restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, K.; Zhao, Y.; Lechner, A.M.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Sha, W.; Wang, Y. Modelling Regional Ecological Security Pattern and Restoration Priorities after Long-Term Intensive Open-Pit Coal Mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lei, S.; Lu, Q.; Bian, Z. Impacts of Large-Scale Open-Pit Coal Base on the Landscape Ecological Health of Semi-Arid Grasslands. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zong, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Assessing Landscape Ecological Risk in a Mining City: A Case Study in Liaoyuan City, China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8312–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Qiao, N.; Wang, Z.; Sha, W.; Luo, K.; Wang, H.; Feng, Z. Ecological Risk Assessment of Coal Mine Area Based on “Source-Sink” Landscape Theory–A Case Study of Pingshuo Mining Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, S. Construction of Landscape Ecological Network Based on Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment in a Large-Scale Opencast Coal Mine Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, C.P.; Commander, L.E.; Merino-Martin, L.; Golos, P.J.; Stevens, J.; Miller, B.P. An Approach to Defining and Achieving Restoration Targets for a Threatened Plant Community. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, e2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, B.; Xu, F.; Wei, Z. Hyperspectral Characterization and Chlorophyll Content Inversion of Reclaimed Vegetation in Rare Earth Mines. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 36839–36853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B. Identifying Priority Areas for Conservation in the Lower Yellow River Basin from an Ecological Network Perspective. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2022, 8, 2105751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhai, T.; Cheng, H. An Integrated Approach towards Spatial Identification of Restored and Conserved Priority Areas of Ecological Network for Implementation Planning in Metropolitan Region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H. Optimization of Ecological Security Patterns Considering Both Natural and Social Disturbances in China’s Largest Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 180, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Gao, G.; Xi, H.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X.; Ou, W.; Tao, Y. An Integrated Evaluation Framework for Multiscale Ecological Protection and Restoration Based on Multi-Scenario Trade-Offs of Ecosystem Services: Case Study of Nanjing City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 108962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segnon, A.C.; Totin, E.; Zougmore, R.B.; Lokossou, J.C.; Thompson-Hall, M.; Ofori, B.O.; Achigan-Dako, E.G.; Gordon, C. Differential Household Vulnerability to Climatic and Non-Climatic Stressors in Semi-Arid Areas of Mali, West Africa. Clim. Dev. 2021, 13, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Pan, J.; Liu, X. Landscape Ecological Safety Assessment and Landscape Pattern Optimization in Arid Inland River Basin: Take Ganzhou District as an Example. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020, 26, 782–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; An, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. Ecological Network Construction of the Heterogeneous Agro-Pastoral Areas in the Upper Yellow River Basin. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Lv, C. Construction and Optimization of Green Space Ecological Networks in Urban Fringe Areas: A Case Study with the Urban Fringe Area of Tongzhou District in Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Yue, W.; Wu, T. Optimizing Ecological Security Pattern in the Coal Resource-Based City: A Case Study in Shuozhou City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yu, Q.; Niu, T.; Fang, M.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. Restoration and Renewal of Ecological Spatial Network in Mining Cities for the Purpose of Enhancing Carbon Sinks: The Case of Xuzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Shi, F.; Beazley, R. Construction and Optimization of an Ecological Network Based on Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis and Circuit Theory. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2059–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Cao, X.-S.; Zhang, Q.-Q. Establishing and Optimizing the Ecological Security Pattern in Shaanxi Province (China) for Ecological Restoration of Land Space. Forests 2022, 13, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Guo, C.-X.; Zhao, M.-Y.; Yang, Z.-G.; Guo, M.-Y.; Wu, B.-Y.; Chen, Q.-L. Integrating Morphological Spatial Pattern Analysis and the Minimal Cumulative Resistance Model to Optimize Urban Ecological Networks: A Case Study in Shenzhen City, China. Ecol. Process. 2021, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, W. Green Infrastructure Network Identification at a Regional Scale: The Case of Nanjing Metropolitan Area, China. Forests 2022, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Hu, M.; Xia, B. Integrating Ecosystem Services and Landscape Connectivity into the Optimization of Ecological Security Pattern: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76051–76065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, W.; Liu, S.; Bai, Z. Ecological Restoration of a Loess Open-Cast Mining Area in China: Perspective from an Ecological Security Pattern. Forests 2022, 13, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Identification of Green Infrastructure Networks Based on Ecosystem Services in a Rapidly Urbanizing Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 300, 126945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Shi, Y.; Siaw, M.J.; Yang, F.; Wu, R.; Wu, X.; Zheng, X.; Bao, Z. Constructing and Optimizing Ecological Network at County and Town Scale: The Case of Anji County, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Shan, L.; Xiao, F. Constructing and Optimizing Urban Ecological Network in the Context of Rapid Urbanization for Improving Landscape Connectivity. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Li, H.; Lin, W. Integrating Ecosystems and Socioeconomic Systems to Identify Ecological Security Pattern and Restoration Strategy in a Rapidly Urbanizing Landscape. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 862310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, P.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Rong, T.; Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Lou, Y. Construction of GI Network Based on MSPA and PLUS Model in the Main Urban Area of Zhengzhou: A Case Study. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 878656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, W. Twenty Years before and Hence; Ecological Risk Assessment at Multiple Scales with Multiple Stressors and Multiple Endpoints. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2003, 9, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, D.; He, C. Ecological Security Assessment and Ecological Pattern Optimization for Lhasa City (Tibet) Based on the Minimum Cumulative Resistance Model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 83437–83451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, S. An Integrated Approach to Constructing Ecological Security Patterns and Identifying Ecological Restoration and Protection Areas: A Case Study of Jingmen, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, M. Integrating Ecosystem Services and Landscape Connectivity to Construct and Optimize Ecological Security Patterns: A Case Study in the Central Urban Area Chongqing Municipality, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43138–43154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Cui, S.; Yan, X.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Zhong, J.; Wang, X. Guiding Sustainable Urban Development via a Multi-Level Ecological Framework Integrating Natural and Social Indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mao, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Jia, M.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Xiang, H. Understanding the Contrasting Effects of Policy-Driven Ecosystem Conservation Projects in Northeastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, Y. Identification of Ecological Risk “Source-Sink” Landscape Functions of Resource-Based Region: A Case Study in Liaoning Province, China. Land 2023, 12, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Hu, M.; Fan, C.; Wang, T.; Xia, B. Promoting Landscape Connectivity of Highly Urbanized Area: An Ecological Network Approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Tian, P.; Pu, R.; Cao, L. Construction of Ecological Security Patterns and Ecological Restoration Zones in the City of Ningbo, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, Z.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Luo, P. Urban Green Space Planning Based on Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Dong, T. Watershed Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment and Landscape Pattern Optimization: Take Fujiang River Basin as an Example. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2021, 27, 2254–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Pei, Y.; Qiao, W.; Wu, Y. Classification of the Type of Eco-Geological Environment of a Coal Mine District: A Case Study of an Ecologically Fragile Region in Western China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, R.-C.; Wang, Q.-W. Connecting Urban Area with Rural Hinterland: A Stepwise Ecological Security Network Construction Approach in the Urban-Rural Fringe. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Du, F.; Zuo, L.; Jiang, Y. Integrating Ecosystem Services and Rocky Desertification into Identification of Karst Ecological Security Pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2113–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, F. Research on Recognition and Protection of Ecological Security Patterns Based on Circuit Theory: A Case Study of Jinan City. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12414–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Lin, Z.; Ma, S.; Qi, J.; Yan, T. Assessing an Ecological Security Network for a Rapid Urbanization Region in Eastern China. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2642–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gu, X.; Liu, G.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Q. Construction of Regional Ecological Security Patterns Based on Multi-Criteria Decision Making and Circuit Theory. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Huan, Y.; Wang, L.; Lan, Y.; Liang, T.; Shi, B.; Zhang, Q. Linking Ecosystem Services and Circuit Theory to Identify Priority Conservation and Restoration Areas from an Ecological Network Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guo, S.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Xie, S. A Multi-Criteria Spatial Approach for Mapping Urban Ecosystem Services Demand. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, W.; Ma, X. Vegetation Changes in Coal Mining Areas: Naturally or Anthropogenically Driven? Catena 2022, 208, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, D. Impacts of Road Network Expansion on Landscape Ecological Risk in a Megacity, China: A Case Study of Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Zhu, B.; Wu, Y.; Wei, G.; Liao, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ren, L.; Han, Q. Dynamic Projection of Ecological Risk in the Manas River Basin Based on Terrain Gradients. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Sun, R.; Cheng, X. Impacts of Landscape Multifunctionality Change on Landscape Ecological Risk in a Megacity, China: A Case Study of Beijing. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Integrating the MCR and DOI Models to Construct an Ecological Security Network for the Urban Agglomeration around Poyang Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, C.; Cheng, Y. Spatial Influence of Ecological Networks on Land Use Intensity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Yin, H.; Nakagoshi, N.; Zong, Y. Urban Green Space Network Development for Biodiversity Conservation: Identification Based on Graph Theory and Gravity Modeling. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 95, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Pan, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, P.; Yan, C.; Liu, L. Research on Urban Ecological Network Under the Threat of Road Networks-A Case Study of Wuhan. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H. Spatiotemporal Changes in Ecological Network Resilience in the Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Z.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Li, Y.-Y.; Yang, Z.-G.; Wang, X.-H.; Li, X.-B. Construction and Optimization of an Urban Ecological Security Pattern Based on Habitat Quality Assessment and the Minimum Cumulative Resistance Model in Shenzhen City, China. Forests 2021, 12, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Niu, T.; Yu, Q.; Yang, L.; Ma, J.; Qiu, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.; Li, J. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Relationship between the Topological Structure of Eco-Spatial Network and Biodiversity Maintenance Function in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y. Evolution Analysis of Ecological Networks Based on Spatial Distribution Data of Land Use Types Monitored by Remote Sensing in Wuhan Urban Agglomeration, China, from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y. Can Policy Maintain Habitat Connectivity under Landscape Fragmentation? A Case Study of Shenzhen, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
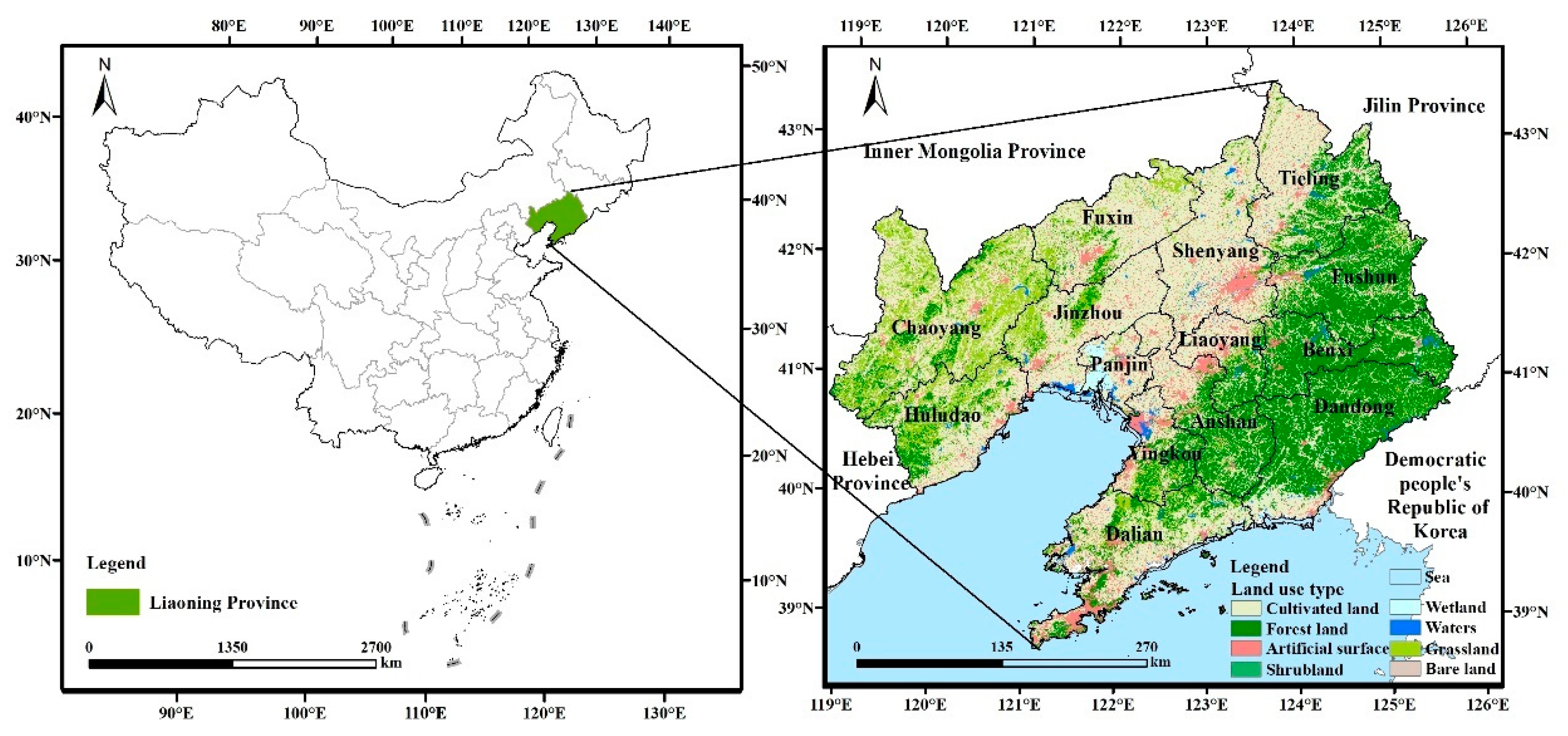
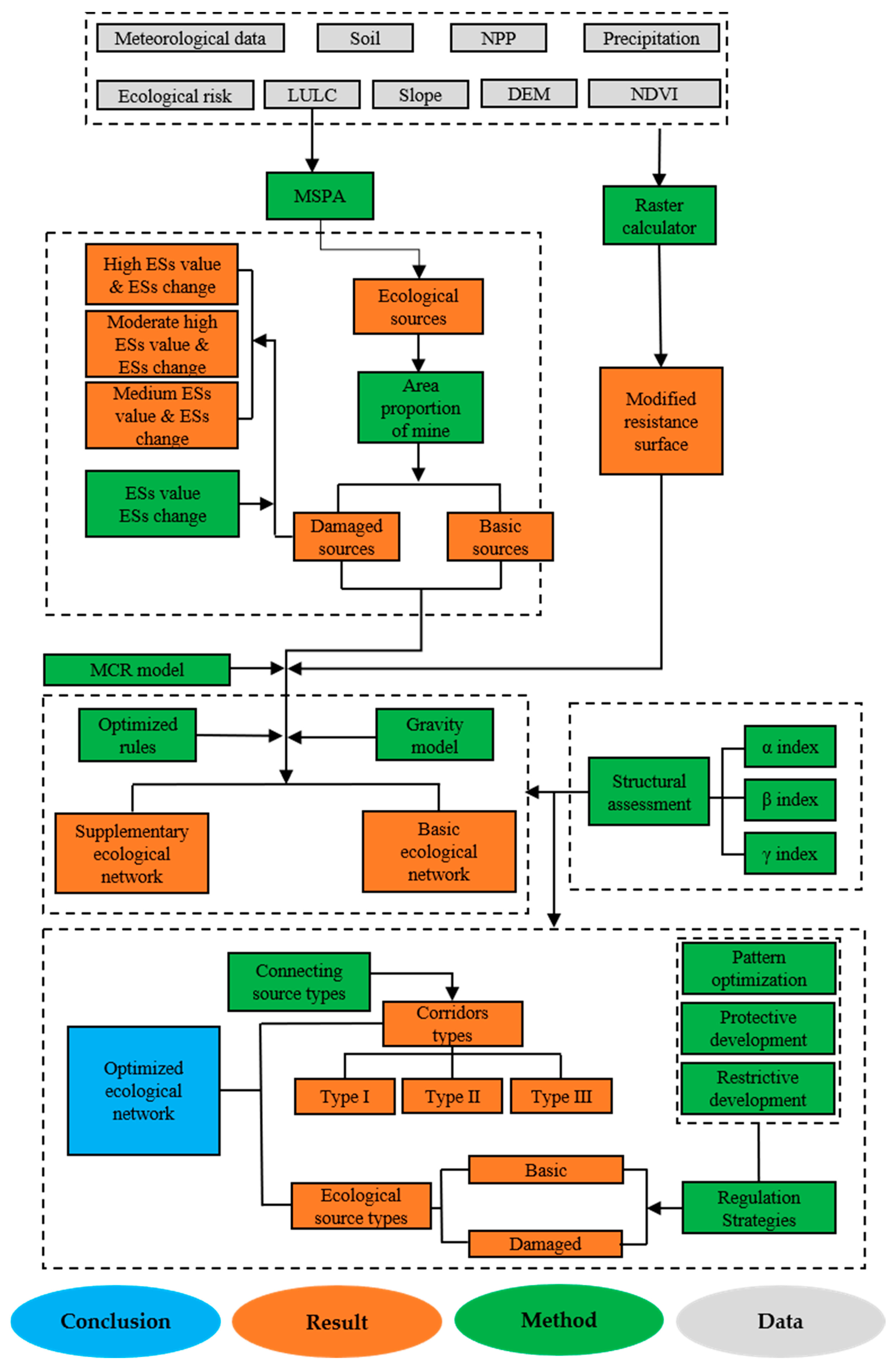
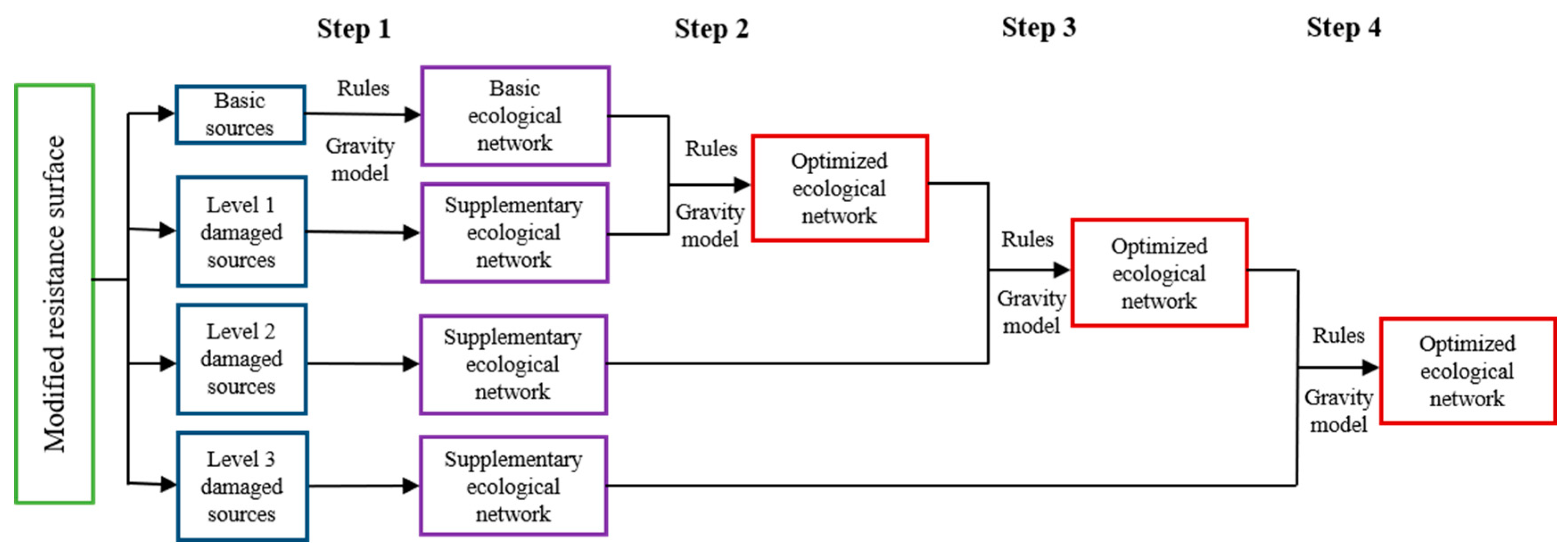
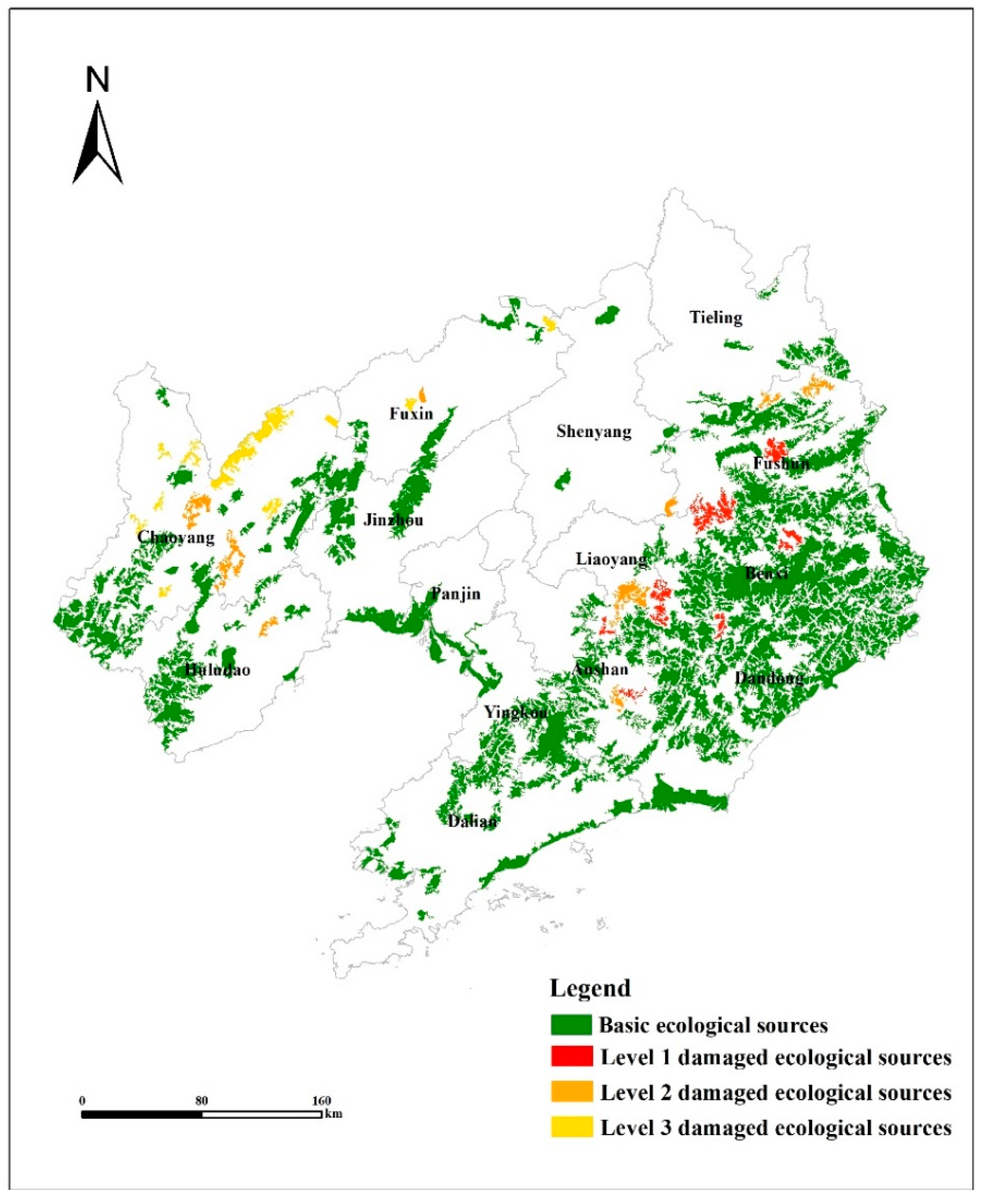
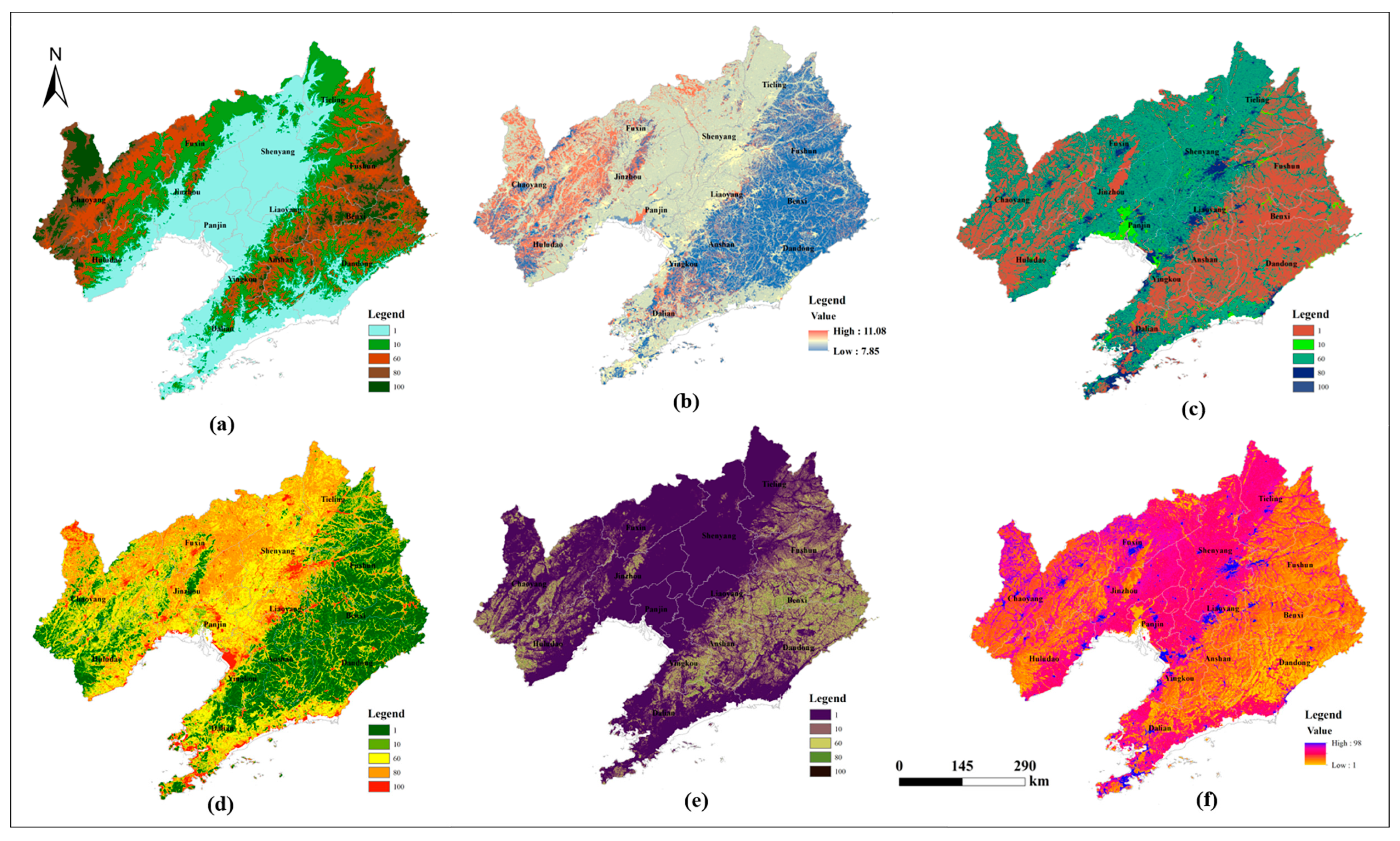


| Factor | Grade | Resistance Value | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land cover and land use type | Cultivated land | 60 | 0.25 |
| Forest, Grassland, Shrubland | 1 | ||
| Wetland, Waterbody | 10 | ||
| Artificial land | 100 | ||
| Bare land | 80 | ||
| Slope | <8° | 1 | 0.25 |
| 8~15° | 10 | ||
| 15~25° | 60 | ||
| 25~35° | 80 | ||
| >35° | 100 | ||
| DEM | −274~108 | 1 | 0.25 |
| 109~251 | 10 | ||
| 252~417 | 60 | ||
| 418~615 | 80 | ||
| 616~1330 | 100 | ||
| Vegetation coverage | ≤0.2 | 100 | 0.25 |
| 0.2~0.4 | 80 | ||
| 0.4~0.6 | 60 | ||
| 0.6~0.8 | 10 | ||
| >0.8 | 1 |
| Matrix Type | Basic Source | Damaged Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | |
| Forest | 22,528.8079 | 76.48 | 1777 | 67.45 |
| Grassland | 5622 | 19.14 | 780 | 29.61 |
| Shrubland | 111.2 | 0.33 | 3.12 | 0.13 |
| Wetland | 198.1 | 0.68 | 35.78 | 1.36 |
| Waterbody | 992.6 | 3.37 | 38.20 | 1.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhu, S. Stepwise Construction and Integration of Ecological Network in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study on Liaoning Province, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173228
Wang S, Zhao Y, Ren H, Zhu S. Stepwise Construction and Integration of Ecological Network in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study on Liaoning Province, China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173228
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shaoqing, Yanling Zhao, He Ren, and Shichao Zhu. 2024. "Stepwise Construction and Integration of Ecological Network in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study on Liaoning Province, China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173228
APA StyleWang, S., Zhao, Y., Ren, H., & Zhu, S. (2024). Stepwise Construction and Integration of Ecological Network in Resource-Based Regions: A Case Study on Liaoning Province, China. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3228. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173228





