Newly Discovered NE-Striking Dextral Strike-Slip Holocene Active Caimashui Fault in the Central Part of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block and Its Tectonic Significance
Abstract
1. Introduction
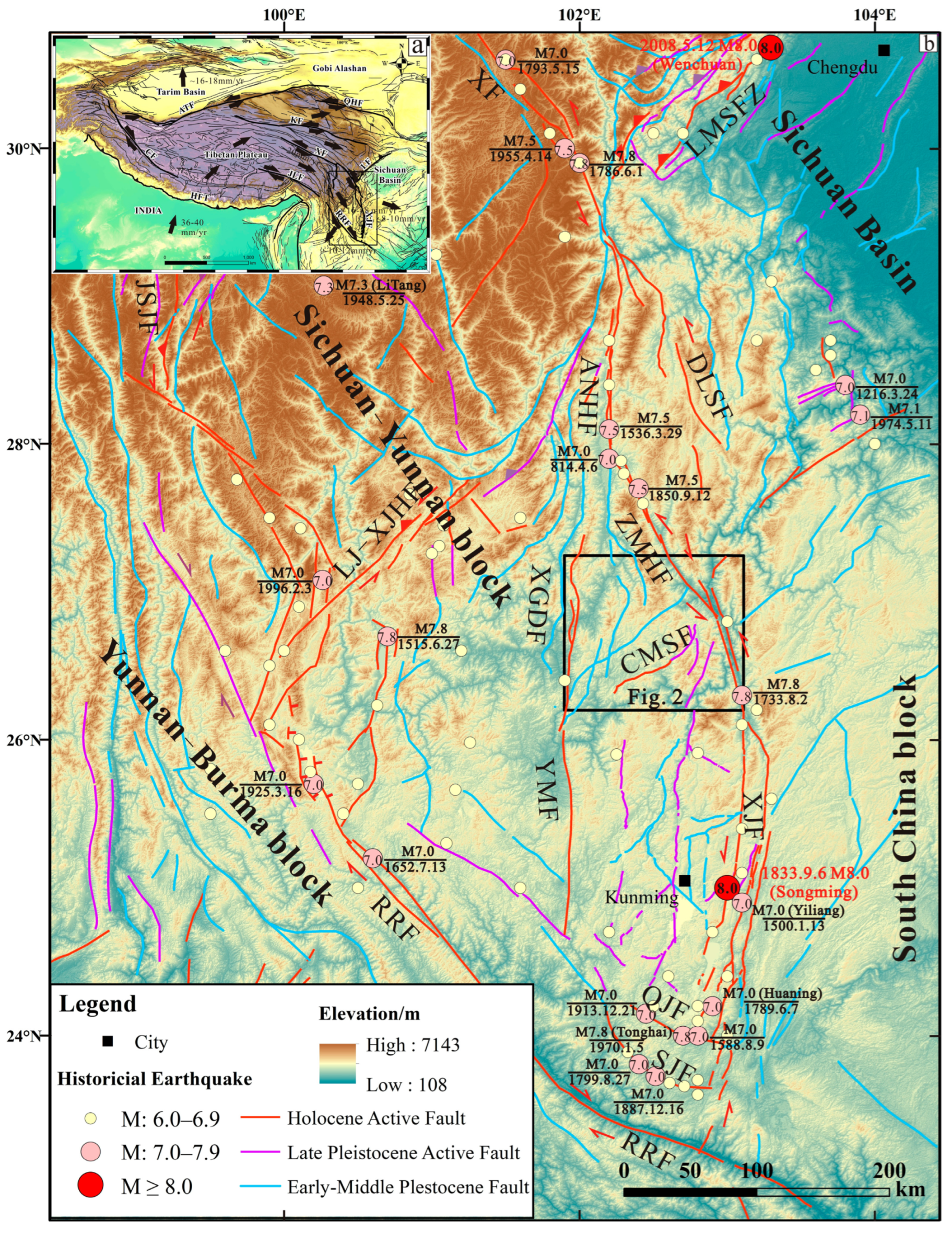
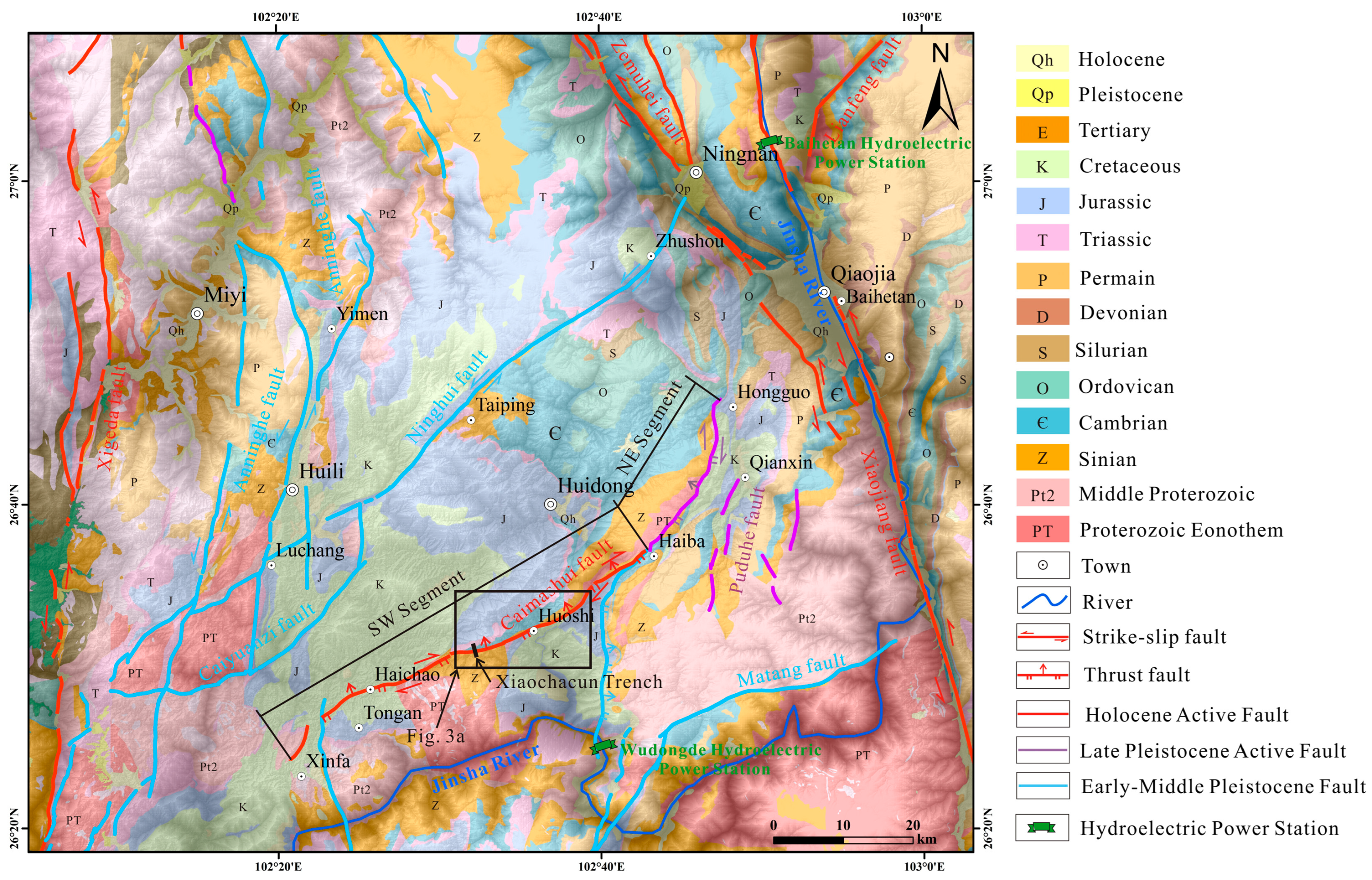
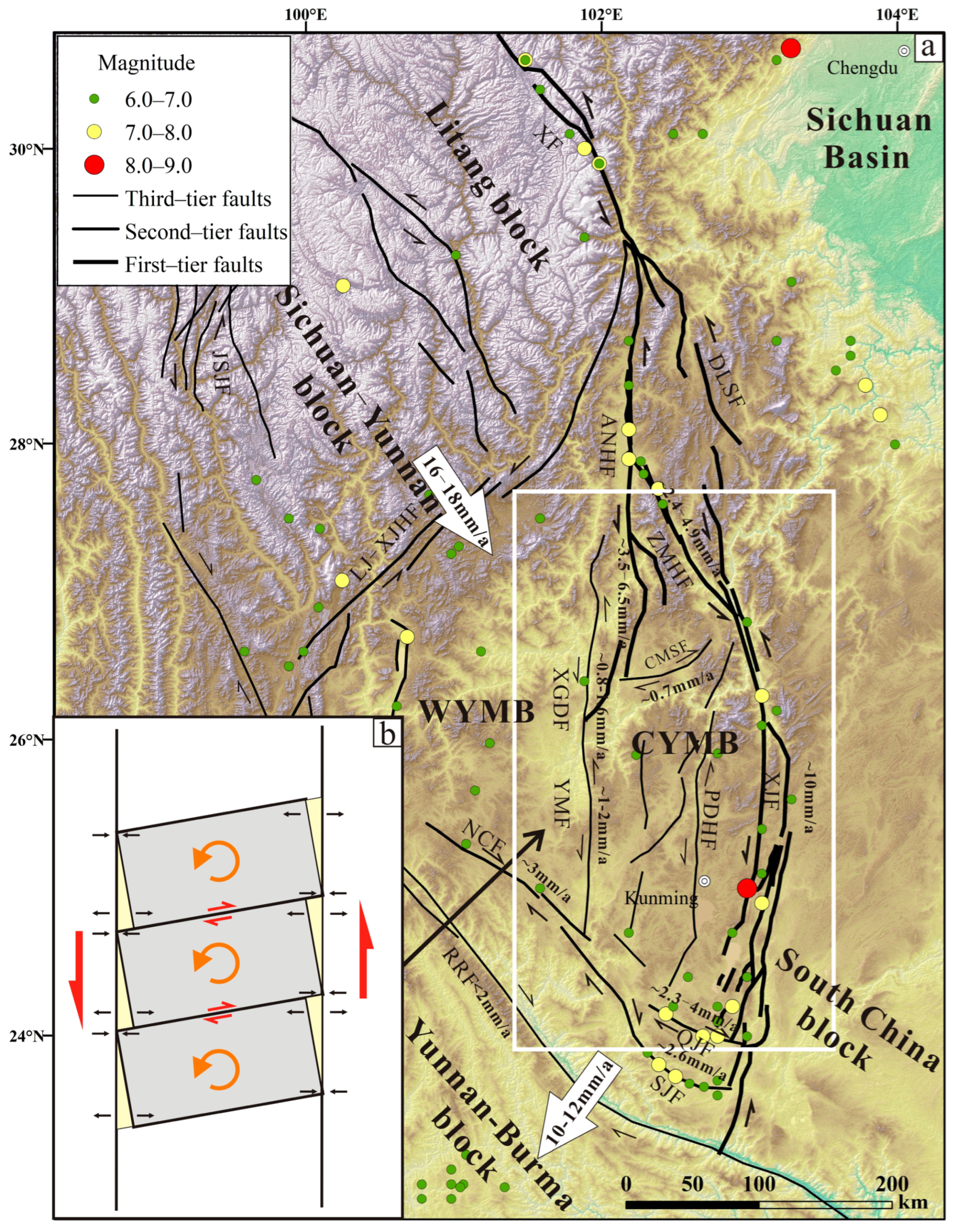
2. Regional Tectonic Setting
3. Methods
3.1. Remote Sensing Interpretation
3.2. UAV Measurement
3.3. Trench
3.4. Quaternary Dating
4. Results
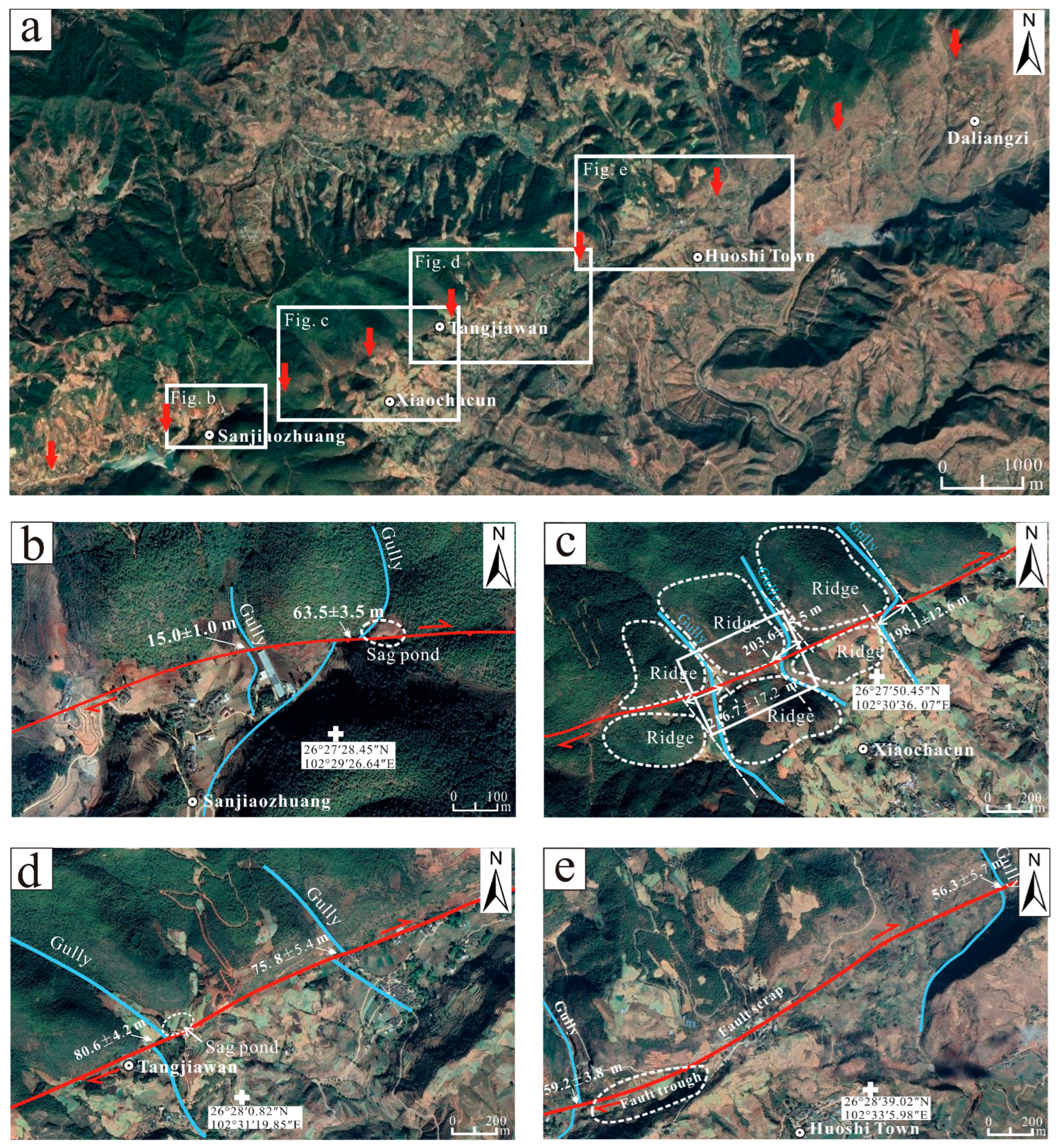
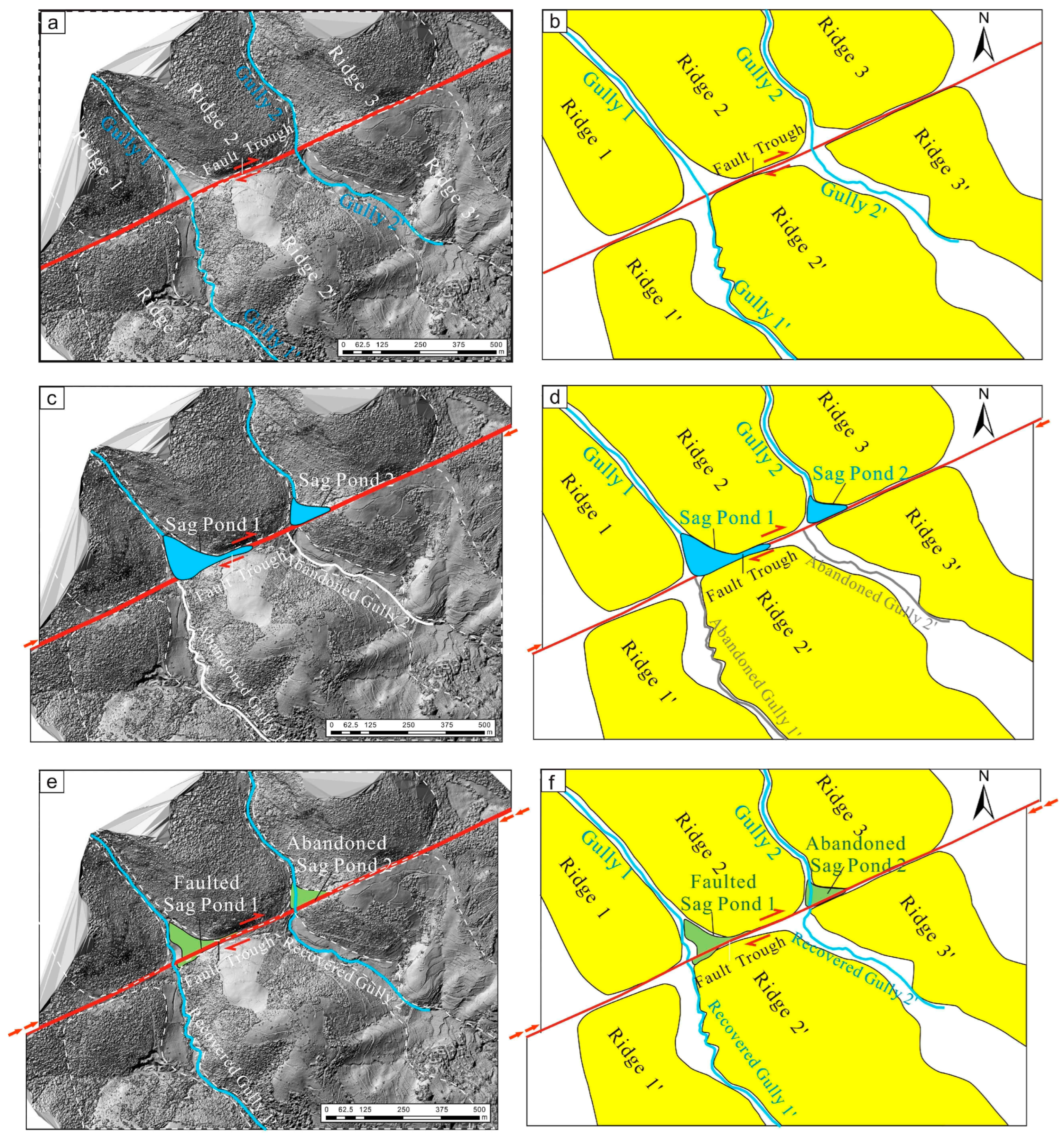
4.1. Google Earth Image Interpretation
4.2. The Activity of the Caimashui Fault
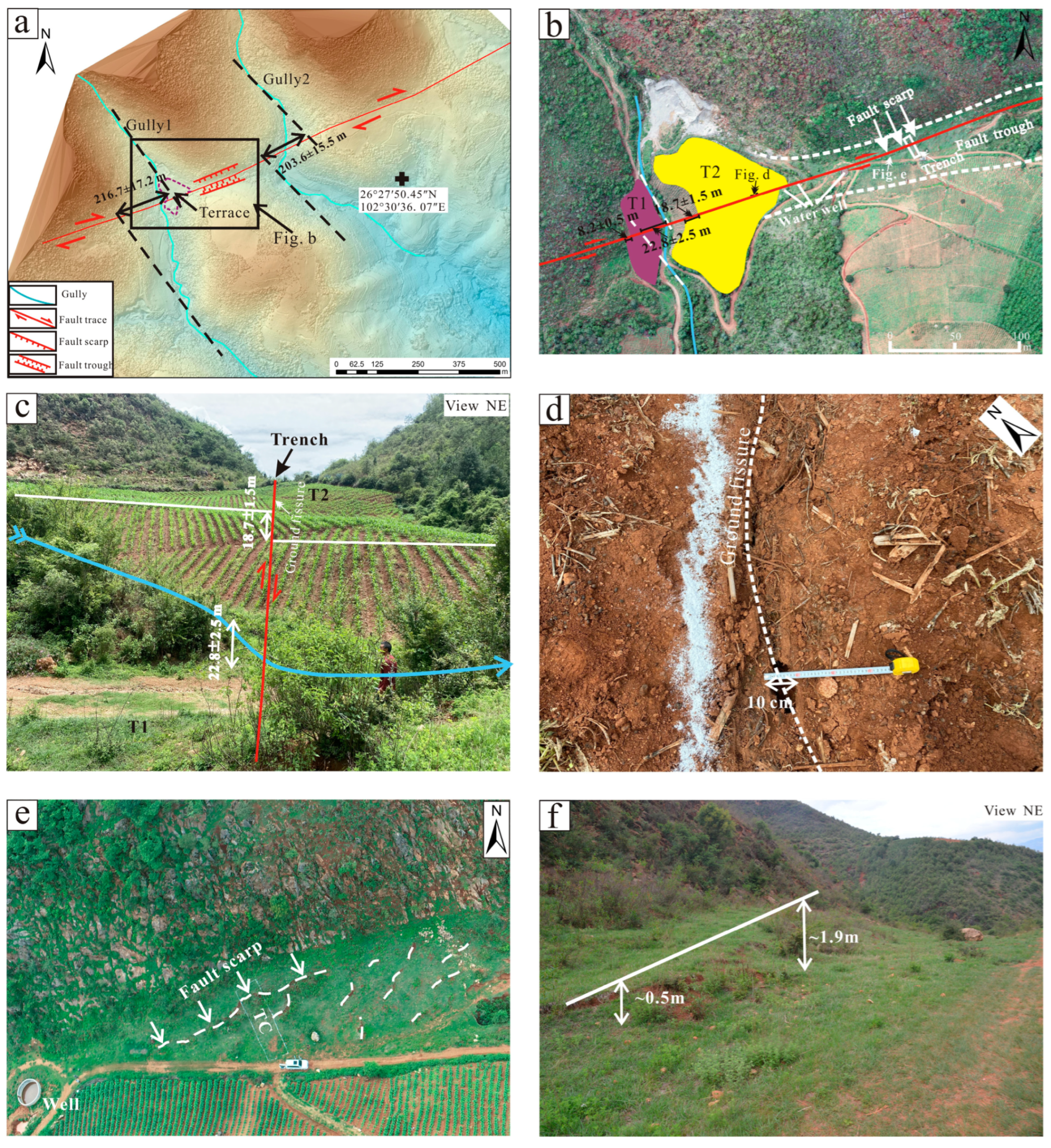
4.2.1. Trench Location and Landforms
4.2.2. Stratigraphy
4.2.3. Description of the Trench
5. Discussion
5.1. Slip Rate of the Caimashui Fault
5.2. Potential Seismic Hazard for the Caimashui Fault
5.3. Faulting Pattern and Deformation Features
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tapponnier, P.E.; Peltzer, G.; Dain, A.; Armijo, R.; Cobbold, P.R. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology 1982, 10, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.E.; Xu, Z.Q.; Roger, F.; Meyer, B.; Arnaud, N.; Wittlinger, G.R.; Yang, J.S. Oblique Stepwise Rise and Growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science 2001, 294, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.Z.; Huang, S.M.; Jiang, Z.X. Neotectonic features of the Ganzi-Yushu fault zone and assessment of its earthquake risk. Seismol. Geol. 1985, 7, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.L.; Li, P.; Fang, Z.J. Analysis of seismogenic conditions in the wedge tectonic region of southeast Yunnan Province. Seismol. Geol. 1992, 14, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, P.H.; England, P.C.; Martinod, J. Mantle dynamics, uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the Indian Monsoon. Rev. Geophys. 1993, 31, 357–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Burchfiel, B.C.; Liu, Y.; King, R.; Royden, L.H.; Tang, W.H.; Wang, E.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X. Global Positioning System measurements from eastern Tibet and their implications for India/Eurasia intercontinental deformation. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 16215–16227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.D.; Zhang, P.Z.; Ran, Y.K.; Yang, X.; Min, W.; Chu, Q.Z. Basic characteristics of active tectonics of China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2003, 46, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Deng, D.Q.; Zhang, G.M.; Ma, J.; Gan, W.J.; Min, W.; Mao, F.Y.; Wang, Q. Active tectonics blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2003, 33, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Replumaz, A.; Tapponnier, P.E. Reconstruction of the deformed collision zone Between India and Asia by backward motion of lithospheric blocks. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.Y.; Ge, W.P.; Chen, Z.W.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhang, P.Z.; Zheng, D.W.; Zheng, W.J.; Craddock, W.H.; et al. The growth of northeastern Tibet and its relevance to large-scale continental geodynamics: A review of recent studies. Tectonics 2013, 32, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Xu, X.W.; Gan, W.J.; Ma, W.T.; Chen, W.T.; Zhang, Y. Block model and dynamic implication from the earthquake activity and crustal motion in the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau. Chin. J. Geophys. 2012, 55, 1198–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Long, C.X.; Fan, T.Y.; Zhou, C.J.; Feng, H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Tong, Y.B. The arc rotational-shear active tectonic system on the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau and its dynamic characteristics and mechanism. Geol. Bull. China 2015, 34, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.W.; Wen, X.Z.; Zheng, R.Z.; Ma, W.T.; Song, F.M.; Yu, G.H. The structural styles and dynamic source of Sichuan-Yunnan rhombic block. Sci. China Ser. D 2003, 33, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.J.; Guo, S.M.; Xiang, H.F.; Zhang, J.S.; Ran, Y.K. Seismotectonic environment of occurring the February 3, 1996 Lijiang M = 7.0 earthquake, Yunnan Province. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2004, 26, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hou, J.J.; Xu, X.W. Structure and tectonic geomorphology of the Qujiang fault at the intersection of the Ailao Shan–Red River fault and the Xianshuihe–Xiaojiang fault system, China. Tectonophysics 2014, 634, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.F.; Sun, H.Y.; He, Y.L.; Ma, C.; Liu, S.; Yang, D.B. Holocene activity of the Xigeda fault and its implications for the crustal deformation pattern in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics 2021, 40, e2021TC007056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.P.; Chen, L.C.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, H.; Han, M.M.; Feng, J.H.; Lu, L.L.; Peng, S.X.; Jin, C.; Liu, L.T. Rupture behavior of the Litang Fault within the Sichuan-Yunnan active block, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Lithosphere 2021, 8773676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.J.; Zeng, H.Y.; Shi, Q.B.; Liu, J.H.; Luo, H.; Hu, W.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.T.; Ma, Z.F.; Liu, J.; et al. Simultaneous rupture propagation through fault bifurcation of the 2021 Mw7.4 Maduo earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.W.; Li, H.B.; Chevalier, M.L.; Tapponnier, P.E.; Bai, M.K.; Li, C.; Liu, F.C.; Liu, D.L.; Wu, K.G.; Wang, P.; et al. Co-seismic rupture of the 2021, M7.4 Maduo earthquake (northern Tibet): Short-cutting of the Kunlun fault big bend. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 2022, 117703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, G.H.; Liu, J.R.; Ren, Z.K.; Zhu, X.X.; Bao, G.D.; Wu, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.L. The interpretation of seismogenic fault of the Maduo Mw 7.3 Earthquake, Qinghai based on remote sensing images—A branch of the East Kunlun Fault System. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 33, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Liu, B.H. Seismic geological characteristics of Tonghai earthquake in 1970. Sci. Geol. Sin. 1978, 4, 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.N. Qujiang Fault geometry and its relation to seismicity. J. Seismol. Res. 1984, 7, 525–532. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.K.; Chai, T.J.; Li, Z.X. Morphotectonic features of the Tonghai earthquake region, Yunnan province. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1983, 38, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Huang, P.G.; Jin, Z.L. 1970 Tonghai Earthquake; Seismological Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.Z.; Du, F.; Long, F.; Fan, J.; Zhu, H. Tectonic dynamics and correlation of major earthquake sequences of the Xiaojiang and Qujiang-Shiping fault systems, Yunnan, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.J.; Xu, X.W.; Yeats, R.S.; Zhang, S.M. Latest Quaternary paleoseismology and slip rates of the Longriba fault zone, eastern Tibet: Implications for fault behavior and strain partitioning. Tectonics 2013, 32, 216–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; He, H.L.; Wei, Z.Y.; Shi, F.; Gao, W. Late Quaternary paleoearthquakes along the northern segment of the Nantinghe fault on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 138, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, L.M. Exploration of the seismic geological features of the Yunnan-west Sichuan region. Chin. J. Geol. 1975, 4, 308–326. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, R.J.; Zhang, S.C.; Yan, F.T.; Yu, L.S. Present tectonic stress field and its relation to the characteristics of recent tectonic activity in southeastern China. Acta Geophys. Sin. 1977, 20, 96–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P. Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang Fault Zone; Earthquake Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.Z. Rupture segmentation and probabilistic estimation of seismic potential in the Xiaojiang fault zone. J. Earthq. Sci. 1993, 15, 322–330. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.L.; Fang, Z.J.; Li, P. A preliminary approach to the fault activity of southern segment on Xiaojiang West Branch Fault. J. Seismol. Res. 1993, 16, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- China Earthquake Administration. The Catalogue of Chinese Historical Strong Earthquakes; Seismological Press: Beijing, China, 1995.
- Song, F.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Yu, W.X.; Cao, Z.Q.; Shen, X.H.; Shen, J. Xiaojiang Active Fault; Seismological Publishing Press: Beijing China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- China Earthquake Administration. Recent Earthquake Catalog of China (1912–1990, Ms ≥ 4.7); Chinese Sciences and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Lu, H.F.; Ji, Z.J. Activity characteristics on the Xigeda fault in the Late Quaternary and recrudescing interval of the strong earthquake. Geoscience 2011, 25, 440–446. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.F. Neotectonic significance of the Yuanmou-Xigeda fault in the Late Cenozoic. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 2877–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B. Studies on the late Quaternary tectonic deformation of the Xigeda Fault. Master’s Thesis, Institute of Earthquake Forcasting, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.S.; Lu, H.F. Late Cenozoic tectonic stress field of Xigeda fault. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2017, 27, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.D.; Ran, Y.K.; Yang, X. Active Tectonics Map of China (1:4000000); Seismological Press: Beijing China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- China Earthquake Networks Center. Seismological Data Search System. 2021. Available online: http://www.ceic.ac.cn/history (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Zhang, P.Z.; Deng, Q.D.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, H.B. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China. Sci. China. Earth Sci. 2013, 43, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.W. Late Quaternary displacement and slip rate of Zemuhe Fault in Sichuan, China. Seismol. Geol. 1994, 16, 146. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.L.; Song, F.M.; Li, C.Y. Topographic survey of micro faulted landform and estimation of strike slip rate for the Zemuhe Fault, Sichuan Province. Seismol. Geol. 1999, 21, 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Ran, Y.K.; Li, Y.B. Growth of a small pull-apart basin and slip rate of strike-slip fault: With the example of Zemuhe Fault on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Seismol. Geol. 2011, 33, 818–827. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, G.X.; Wen, X.Z.; Fan, J.; Wang, S.W. Assessing current faulting behaviors and seismic risk of the Anninghe-Zemuhe fault zone from seismicity parameters. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2004, 26, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.B.; Jiang, G.F. Study on seismicity of Daliangshan and Anninghe-Zemuhe fault zones. J. Seismol. Res. 2005, 28, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.J.; Ren, Z.K.; Zhang, J.L. Study of paleoearthquakes by combined trench on Zemuhe fault around Daqingliangzi, Xichang, Sichuan. Seismol. Geol. 2008, 30, 400–411. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.L.; Xu, X.W.; Gan, W.J.; Chen, G.H. The possible asperities on the Xianshuihe-Anninghe-Zemuhe Fault Zone: Evidence from background seismicity. Earth Sci. Front. 2009, 16, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.K.; Lin, A.; Rao, G. Late Pleistocene–Holocene activity of the Zemuhe Fault on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonophysics 2010, 495, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.J.; Dong, S.P.; Mao, Z.B.; Hu, N.; Tan, X.B.; Yuan, R.M.; Guo, P. The Holocene activity and strike-slip rate of the southern segment of Xiaojiang Fault in the southeastern Yunnan region, China. Seismol. Geol. 2017, 39, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.K.; Lü, J.N.; Wang, M.; Bürgmann, R. Contemporary crustal deformation around the Southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Ear. 2005, 110, B11409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, E.N.; Shen, Z.K.; Wang, M.; Gan, W.J.; Qiao, X.J.; Meng, G.J.; Li, T.M.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.L.; et al. GPS-constrained inversion of present-day slip rates along major faults of the Sichuan-Yunnan region, China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.M.; Wu, Z.H.; Li, J.C.; Huang, X.L. The Late Quaternary strike-slip rate of the Qiaojia segment of the Xiaojiang fault zone. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 16–29. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Liu, Z.F.; Ye, J.Q.; Li, Z.H. Analysis on strong earthquake risk of Xiaojiang Fault Zone. J. Seismol. Res. 2016, 39, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.; Liang, K.; Ma, B.Q. A review of research progress on the late quaternary activities of the Xiaojiang Fault Zone. Technol. Earthq. Disasters Prevent 2023, 18, 757–772. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.W.; Sun, X.M.; Liao, Z.W.; Qu, W.J.; Yang, B.; Jiang, X.F.; Li, C.; Li, Y.C. Platinum group elements and Re-Os isotope geochemistry of harzburgites from Caiziyuan nickel deposit in Huili County of Sichuan Province and its geological significance. Miner. Depos. 2013, 32, 515–532. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.L. Some problems of aerial photo interpretation in active fault mapping. Seismol. Geol. 2011, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Jiang, W.L.; Tian, T.; Wang, X. High resolution remote sensing application research in active fault surveying. Acta Seismol. Sinca 2016, 38, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.L.; Zhang, J.F.; Shen, X.H.; Jiao, Q.S.; Tian, T.; Wang, X. Geometric and geomorphic features of active fault structures interpreted from high-resolution remote sensing data. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 22, 192–211. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.T.; Ma, B.Q. Holocene paleoearthquakes of the Daqingshan fault detected from knickpoint identification and alluvial soil profile. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 98, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Ren, J.J.; Zhang, X.L. Application of high-precision UAV aerial survey in the detailed study of surface rupture of Maduo MS7.4 earthquake in 2021. Technol. Earthq. Disasters Prevent 2021, 16, 437–447. [Google Scholar]
- Bemis, S.P.; Micklethwaite, S.; Turner, D.; James, M.R.; Akciz, S.; Thiele, S.T.; Bangash, H.A. Ground-based and UAV-based photogrammetry: A multi-scale, high-resolution mapping tool for structural geology and paleoseismology. J. Struct. Geol. 2014, 69, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.X.; Xu, X.W.; Klinger, Y.; Woerd, J.; Tapponnier, P.E. High-resolution mapping based on an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) to capture paleoseismic offsets along the Altyn-Tagh fault, China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 7, 8281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.E. Active faults, paleoseismology, and earthquake hazards in the western United States. In Earthquake Prediction–An International Review; Simpson, D.W., Richards, P.G., Eds.; Maurice Ewing Series; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; pp. 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Crone, A.J. Introduction to Directions in Paleoseismology; US Geological Survey Open File Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1987; pp. 87–683.
- Deng, Q.D.; Wen, X.Z. A review on the research of active tectonics-History, progress and suggestions. Seismol. Geol. 2008, 30, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Y.K.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.B.; Chen, L.C. Key techniques and several cases analysis in paleoseismic studies in mainland China(1): Trenching sites, layouts and paleoseismic indicators on active strike-slip faults. Seismol. Geol. 2012, 34, 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.D.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.F.; Shao, Y.X.; Li, Z.G.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Yao, W.Q. Tecto-geomorphic analysis of paleoseismic trenching sites on active strike-slip faults. Geol. Bull. China 2016, 35, 1807–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.D.; Chen, L.C.; Ran, Y.K. Quantitative studies and applications of active tectonics. Earth Sci. Front. 2004, 11, 383–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Y.K.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.L.; Xu, L.X. Key techniques and several cases analysis in paleoseismic studies in mainland China(4)—Sampling and event analysis of paleoseismic dating methods. Seismol. Geol. 2014, 36, 939–955. [Google Scholar]
- Lienkaemper, J.J.; Ramsey, C.B. OxCal: Versatile tool for developing paleoearthquake chronologies—A primer. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2009, 80, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, C.B. Bayesian analysis of radiocarbon dates. Radiocarbon 2009, 51, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Austin, W.E.; Bard, E. The IntCal20 Northern hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55 cal kBP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 725–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitman, N.G.; Bennett, S.E.K.; Gold, R.D.; Briggs, R.W.; DuRoss, C.B. High-resolution trench photomosaics from image-based modeling: Workflow and error analysis. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2015, 105, 2354–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, D.L.; Coppersmith, K.J. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1994, 84, 974–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.D.; Yu, G.H.; Ye, W.H. Research on the relationship between earthquake surface rupture parameters and magnitude. In Research on Active Fault; Earthquake Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 247–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, H.L. Empirical relations between earthquake magnitude and parameters of strike-slip seismogenic active faults associated with historical earthquakes in western China. Seismol. Geol. 2011, 33, 577–585. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.Y. Research on the Method for Evaluating the Earthquake Surface Rupture. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration, Harbin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.M.; Chen, L.C.; Li, Y.B.; Gao, S.P.; Feng, J.H. Paleoearthquakes of the Yangda-Yaxu fault across the Nujiang suture and Lancang river suture zone, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 990187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, P.; Molnar, P. Right-lateral shear and rotation as the explanation for strike-slip faulting in eastern Tibet. Nature 1990, 344, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Shen, Z.K.; Wang, M.; Gan, W.J.; Bürgmann, R.; Molnar, P. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data. Geology 2004, 32, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Z.; Wang, W.T.; Gan, W.J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.P.; Zheng, D.W.; Zheng, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, B.B.; et al. Present-day deformation and geodynamics processes of the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geol. Sin. 2022, 96, 3297–3313. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, W.J.; Zhang, P.Z.; Shen, Z.K.; Niu, Z.J.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhou, D.M.; Cheng, J. Present-day crustal motion within the Tibetan Plateau inferred from GPS measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B08416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.J.; Molnar, P.; Zhang, P.Z.; Xiao, G.R.; Liang, S.M.; Zhang, K.L.; Li, Z.J.; Xu, K.K.; Zhang, L. Initiation of clockwise rotation and eastward transport of Southeastern Tibet inferred from deflected fault trace sand GPS observations. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2021, 134, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z.K. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, e2019JB018774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.M.; Ren, Z.K.; Liu, J.R. Review of structural deformation in the upper crust of the Southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau since the Late Cenozoic. Earth Sci. 2023, 49, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.F.; Wang, E. Structural interpretation of extensional deformation along the Dali Fault system, southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Inter. Geol. Rev. 2006, 48, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozos, J.C.; Oglesby, D.D.; Duan, B. The effects of double fault bends on rupture propagation: A geometrical parameter study. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2011, 101, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tian, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P. Contemporary deformation of the North China Plain from global positioning system data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liang, K.; Ma, B.; He, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, J. A catastrophic, buried fault-generating earthquake: The 1937 M7.0 Heze earthquake in the south-central North China Plain. J. Struct. Geol. 2023, 177, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
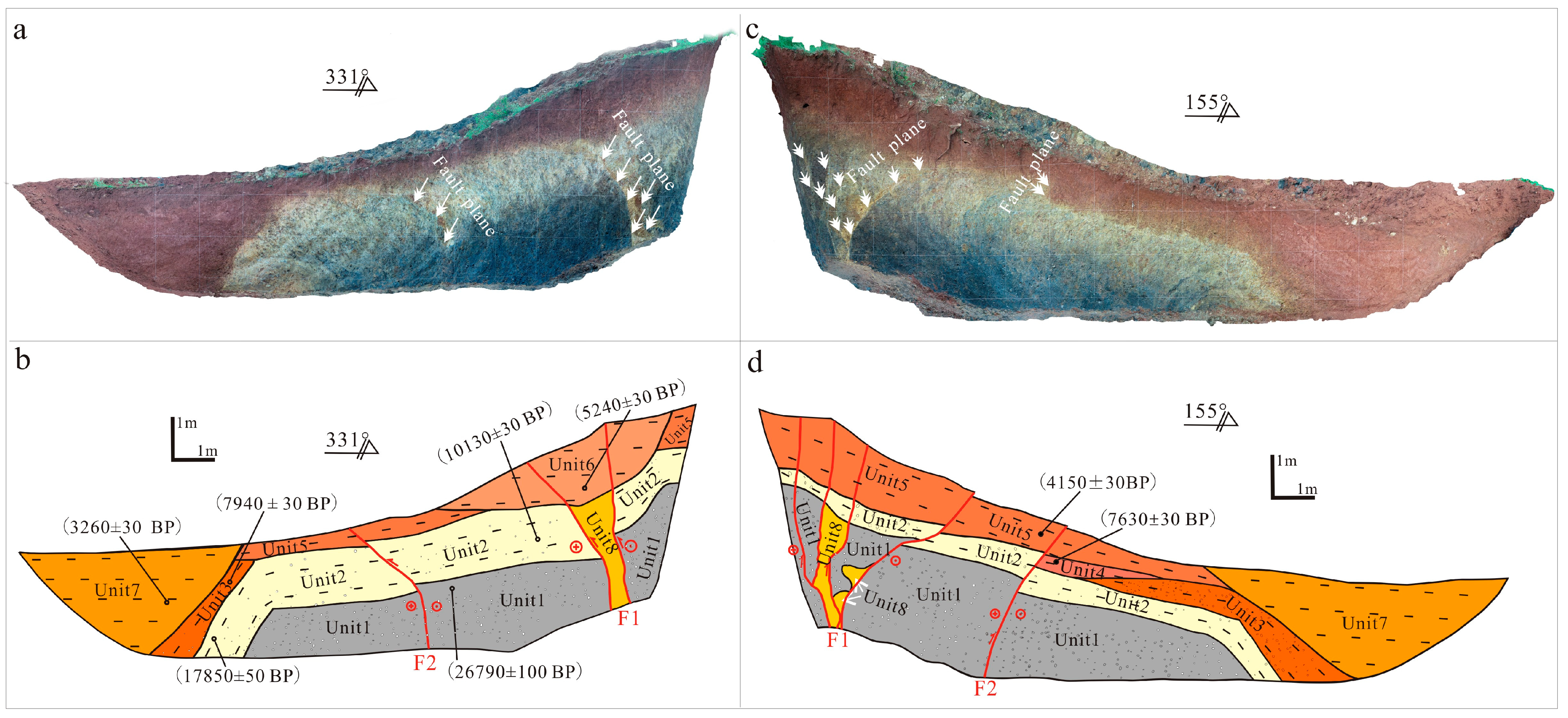
| ID | Lab No. | Radiocarbon Age (a BP) | Correction Age (cal B.P.) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSZXCC-TC1-14C-01 | 598698 | 7940 ± 30 | 8815–8640 | Organic sediment |
| LSZXCC-TC1-14C-02 | 598699 | 3260 ± 30 | 3562–3441 | Organic sediment |
| LSZXCC-TC1-14C-03 | 598700 | 17,850 ± 50 | 21,916–21,428 | Organic sediment |
| LSZXCC-TC1-14C-04 | 598701 | 26,790 ± 100 | 31,155–30,885 | Organic sediment |
| LSZXCC-TC1-14C-05 | 598702 | 5240 ± 30 | 6020–5920 | Organic sediment |
| LSZXCC-TC1-14C-06 | 598703 | 10,130 ± 30 | 11,882–11,611 | Organic sediment |
| LSZXCC-TC1-14C-07 | 612196 | 4150 ± 30 | 4825–4575 | Organic sediment |
| LSZXCC-TC1-14C-08 | 612197 | 7630 ± 30 | 8463–8371 | Organic sediment |
| Unit No. | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit1 | Black peat layer, with a gravel content of approximately 10%, well sorted and poorly rounded. Most gravels are 3–4 cm in diameter. The top of the layer has a vertical drop of approximately 1.7 m on both sides of the fault F1. |
| Unit2 | Light yellow clay layer with a small amount of gravel, approximately 5–7%. The gravel is well sorted and moderately rounded. The layer contains some small pieces of grayish-white clay, approximately 15%. The top of the layer has a vertical drop of approximately 1.5–1.6 m on both sides of the fault F1. |
| Unit3 | Orange-red clay layer with a gravel content of approximately 20–30%. The gravel size is mostly 0.5–1 cm. The gravels are better sorted and poorly rounded. |
| Unit5 | Brown topsoil layer with plant roots. |
| Unit6 | Brick red clay layer with a small amount of gravel. The layer forms a colluvial wedge with pre-scarp deposits. |
| Unit7 | Brick red clay layer, uniform in lithology and color, without gravel and stratification. |
| Unit8 | Orange fault zone with approximately 5 mm wide white faulted mud. The southern boundary is clearer, while the northern boundary is blurred. |
| Unit No. | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit1 | Black peat layer with high carbon content, deposited by a sag pond. Most gravels are 0.5–1 cm in diameter, black in color, well sorted, and poorly rounded. |
| Unit2 | Light yellow and grayish-white clay layer with less than 10% gravel content. The clay has a patterned appearance, with the trench being yellowish on the northern side and whitish on the southern side. |
| Unit3 | Orange gravel layer with orange clay. Most gravels are 0.5–1 cm in diameter, and the gravel content is approximately 40%. The gravels are slightly reddish, well sorted, and poorly rounded, with mostly orange clay as the filler. This layer may be an accumulation in front of the wedge. |
| Unit4 | Purplish-red clay layer, slightly black, accumulated in front of the wedge of F2. |
| Unit5 | Purplish-red clay layer, slightly black and purplish. |
| Unit7 | Brick red clay layer with almost no gravel and stratification, representing recent deposits. |
| Unit8 | Orange clay layer in the deformation zone of F1, affected by fault activity, with a messy accumulation. Both sides of the layer are black peat, while the middle part consists mostly of grayish-yellow clay mud, likely rolled up by fault activity. |
| No. | Formula | Applicable Area | Calculated Seismic Magnitude | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M = 5.16 + 1.12lgL | Worldwide | 7.04 | Wells and Coppersmith [77] |
| 2 | M = 5.92 + 0.88lgL | Tibet Plateau | 7.47 | Deng [78] |
| 3 | M = 5.303 + 1.181lgL | West China | 7.38 | Ran [79] |
| 4 | M = 6.2078 + 0.715lgL | West China | 7.47 | Huang [80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, X.; Liang, K.; Ma, B.; He, Z. Newly Discovered NE-Striking Dextral Strike-Slip Holocene Active Caimashui Fault in the Central Part of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block and Its Tectonic Significance. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173203
Tan X, Liang K, Ma B, He Z. Newly Discovered NE-Striking Dextral Strike-Slip Holocene Active Caimashui Fault in the Central Part of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block and Its Tectonic Significance. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(17):3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173203
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Xin, Kuan Liang, Baoqi Ma, and Zhongtai He. 2024. "Newly Discovered NE-Striking Dextral Strike-Slip Holocene Active Caimashui Fault in the Central Part of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block and Its Tectonic Significance" Remote Sensing 16, no. 17: 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173203
APA StyleTan, X., Liang, K., Ma, B., & He, Z. (2024). Newly Discovered NE-Striking Dextral Strike-Slip Holocene Active Caimashui Fault in the Central Part of the Sichuan-Yunnan Block and Its Tectonic Significance. Remote Sensing, 16(17), 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16173203







