1. Introduction
A strong geomagnetic storm occurred on 1 December 2023, with a Disturbance Storm-Time (Dst) Index of −108 nT. This increase in geomagnetic activity was triggered primarily by a coronal mass ejection (CME) associated with a moderate solar flare on 28 November 2023. This CME joined several other smaller ones heading toward Earth. Although this event ranks eleventh among the thirteen strong geomagnetic storms observed during Solar Cycle 25 (Dst ≤ −100 nT, from December 2019 to August 2024), amazing red auroras were photographed in the Huairou area of Beijing (39°N, 116°E) during this geomagnetic storm (
https://www.globaltimes.cn/page/202312/1302891.shtml, accessed on 12 December 2023). This indicates that the aurora might have extended to northern low latitudes during this storm [
1]. Aside from the superstorm on 10–11 May 2024, when the Dst Index dropped below −400 nT and auroras were also observed in Beijing, no auroras were seen in Beijing during other strong geomagnetic storms of Solar Cycle 25. This makes the December storm particularly notable in Solar Cycle 25.
Understanding storm-time phenomena such as FACs is crucial because of their significant role in the energy coupling process between the magnetosphere and ionosphere. FACs, which flow along magnetic field lines, are essential for transferring energy and momentum among these regions. Observations from ground-based magnetometers, rockets, and satellites, along with model simulations, reveal distinct variations in FACs in response to changes in the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. These phenomena exhibit clear dependencies on local time, season, and hemisphere. However, their behavior during strong geomagnetic storms remains inadequately understood despite comprehensive statistical distributions being well-established.
Meng (1984) [
10] documented shifts in the latitudinal distribution of the auroral oval during intense storms, highlighting asymmetries between noon and midnight sectors and the expansion of the nightside auroral oval equatorward during extreme events [
11]. Other studies, such as Fujii et al. (1992) [
12] and Feldstein et al. (1997) [
13], analyzed dynamic variations in FACs across different storm phases, revealing complex spatial distributions and varying strengths of equivalent currents. Recent studies using satellite data have identified dawn–dusk asymmetries in FACs during storm periods, suggesting influences from the IMF and asymmetric ring currents [
14,
15,
16]. Further research has correlated FAC intensities with geomagnetic parameters and storm onset characteristics [
17,
18,
19], emphasizing seasonal differences and the role of IMF conditions in driving auroral current variability [
20,
21]. These studies illuminate the variability and evolution of auroral current systems during disturbed periods. However, since storm-time FACs exhibit diverse characteristics from one storm to another, and the sequencing variability of storm-time substorms complicates the understanding of auroral current systems, continuing investigations into FACs during strong geomagnetic storms, such as the one in December 2023, is still important for improving space weather forecasting.
This study aims to investigate local time, seasonal and hemispheric asymmetries in the temporal variations in the strengths and MLat of the FACs during the December 2023 storm. The positioning of Swarms A/C and Swarm B satellites across special local time sectors, i.e., pre-noon and pre-midnight, post-noon and post-midnight, presents an excellent opportunity to compare the local time asymmetries in response to strong storm events. Additionally, the characteristics of FACs in various seasons and hemispheres during the December 2023 storm are analyzed.
The following sections describe the instrumentation used and the methods for processing the data. An event analysis based on observations is presented in
Section 3, followed by a discussion of the results in the context of previous research in
Section 4. Finally,
Section 5 summarizes the conclusions drawn from the observations.
2. Materials and Methods
In November 2013, the European Space Agency (ESA) launched the Swarm satellites into a near-polar orbit at an inclination of 87.5° and an altitude of about 500 km. By 17 April 2014, the final orbital configuration for the initial mission phase was achieved. The Swarm constellation consists of Swarms A and C, positioned approximately 1.4° apart in longitude at an altitude of around 450 km, and Swarm B, which orbits at about 510 km with a slightly higher inclination. The orbital period is approximately 93 min, and there exists a 30 min difference in auroral oval crossing times between Swarms A/C and Swarm B during the December storm period.
The FACs are computed using vector magnetic field data collected by Swarms A and C, applying Ampere’s integral law, as follows:
. The integral is computed along a closed path encircling the measurement quadrilateral; encompassing the intertrack connections between the orbits of Swarms A and C (refer to Figure 6.2 in [
22]). The horizontal-plane disturbance magnetic field
B is derived by subtracting the background magnetic field provided by the CHAOS-6 model. Here,
dl represents the line element along the integration path,
A denotes the area of the closed quadrilateral formed by the four observation points,
i is the magnetic field inclination angle, and
μ0 represents vacuum permeability. For the single satellite Swarm B, the FACs are determined through
, where
By denotes the disturbance magnetic eastward component parallel to the current sheet, and
vx represents the velocity perpendicular to the current sheet in the mean-field-aligned system [
3]. The magnetic field data underwent low-pass filtering with a cutoff period of 20 s to attenuate small-scale FAC structures smaller than 150 km [
3,
22,
23]. Regarding the current direction, positive values indicate FACs flowing outward from the ionosphere, while negative values indicate FACs flowing inward the ionosphere. To mitigate outliers, only the FACs with absolute values less than 50 µA/m
2 are included in the analysis.
The PEJ are derived from scalar magnetic field data obtained by Swarms A and B using the spherical elementary current system method [
24]. The zonal component of curl-free horizontal sheet current density vector represents PEJ, where positive values indicate eastward currents and negative values indicate westward electrojets. To mitigate false detections, the peaks’ absolute values must fall within the range of 0.03 A/m to 3 A/m. Apex latitudes are employed for the FACs, mapping observation points along field lines into the E region and dipole latitudes are used for PEJ [
4,
25]. In the following text, the ‘latitude’ corresponds to MLat. For characterizing interplanetary conditions, 1 min IMF and solar wind velocity data, adjusted to the bow shock, were obtained from the OMNI website.
3. Results
The event under investigation occurred from 1 November to 3 December 2023, driven by a CME observed in the solar wind. During this period, Swarms A/C satellites were positioned around the pre-noon and pre-midnight meridians (~10 and ~22 magnetic local times, MLT sectors), while Swarm B was positioned around the post-noon and post-midnight meridians (~13 and ~01 MLT sectors). This configuration allowed us to study the dependence of large-scale FACs on solar wind parameters and storm effects around local noon and midnight sectors. Interhemispheric comparisons were conducted to explore hemispheric and seasonal differences in the FACs.
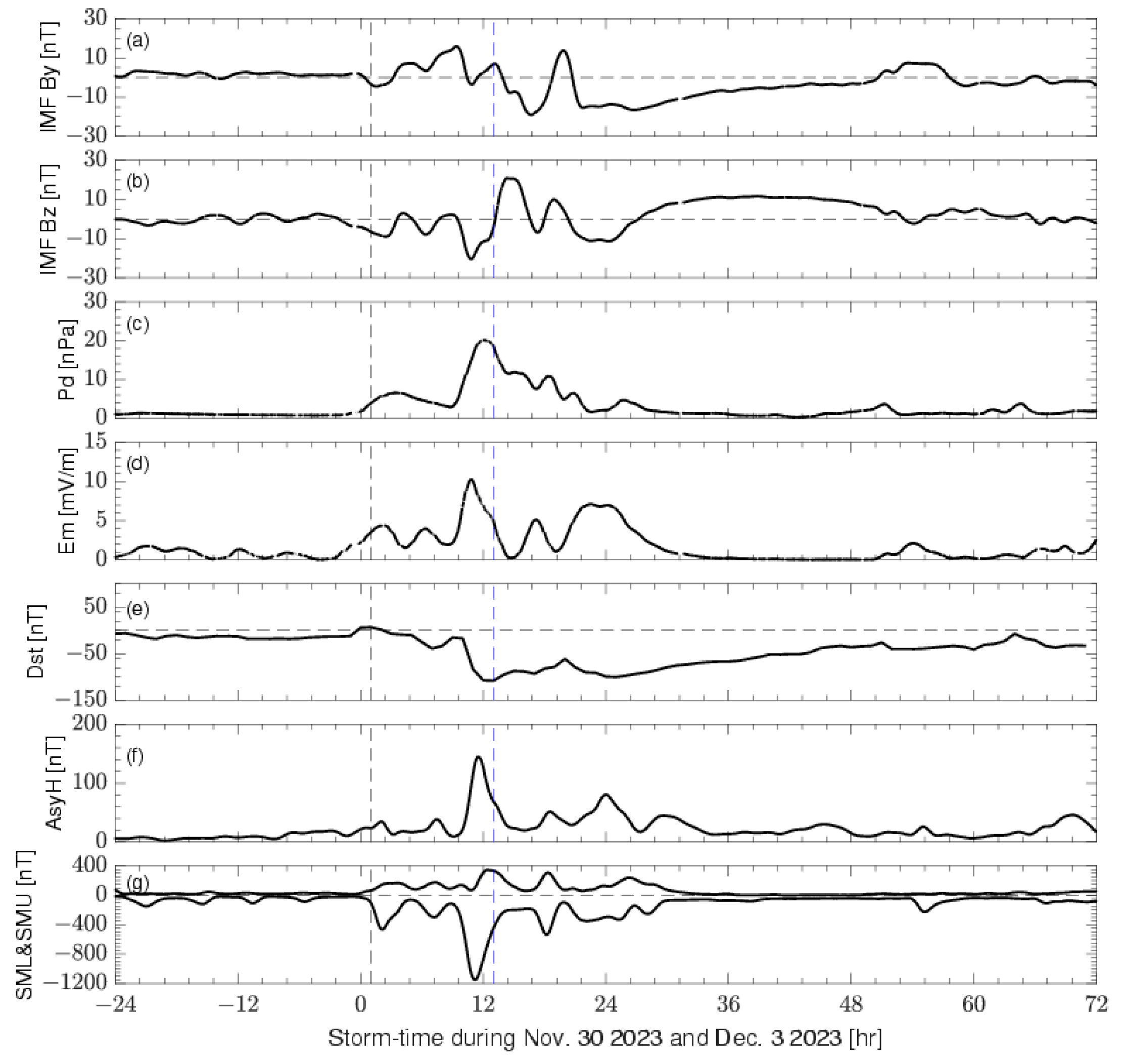
Figure 1 illustrates the one-hour mean solar wind parameters, as well as the magnetic indices, as follows: Dst, longitudinal asymmetric disturbances for the geomagnetic H component (AsyH), SMU, and SML variations from 30 November to 3 December 2023. The standard indices SMU and SML are used to describe the maximum current strength of the westward and eastward electrojets based on hundreds of SuperMAG magnetometers. An abrupt geomagnetic disturbance, starting at 01 UT on 1 December (marked by a black vertical dashed line), was triggered by increased solar wind dynamic pressure (Pd) (
Figure 1c). The Dst Index reached its minimum value of −108 nT at 13:00 UT (13 h storm time, ST) on 1 December, indicated by the blue vertical dashed line, and gradually recovered to −50 nT by the end of 3 December (
Figure 1e). Throughout the storm’s main phase, the IMF Bz predominantly remained southward with intermittent northward deviations, reaching a minimum of −20 nT at around 11 ST on 1 December (
Figure 1b). Concurrently, the IMF By changed polarity during the IMF Bz minima, aligning with the passage of the CME-related flux rope (
Figure 1a). The solar wind dynamic pressure exhibited two peaks, approximately 6.5 nPa and 21 nPa at around 03 h ST and 12 h ST, respectively, during the storm’s main phase (
Figure 1c). The merging electric field, Em, which represents the solar wind–magnetosphere energy input (following [
26]), displayed peaks generally corresponding to the IMF Bz minima (
Figure 1d). AsyH exhibited multiple peaks, with a maximum of 145 nT at around 11:30 ST. The SMU peaked later than the SML, with the SMU reaching approximately 344 nT at around 12:24 ST and the SML reaching approximately −1148 nT at around 11:12 ST.
Figure 2 illustrates the color-coded distribution of the FACs density as a function of MLat and storm time, as observed by Swarms A/C (
Figure 2a–d) and Swarm B (
Figure 2e–h) satellites, where the FACs with a density lower than 0.5 µA/m
2 are not shown. The Dst index is shown as a black curve. The left panel represents the NH, and the right panel represents the SH. From top to bottom, the panels depict the local time sectors of pre-noon, pre-midnight, post-noon, and post-midnight. It can be seen that the temporal variation in the MLat of the equatorward boundary of the intense FACs is well correlated with storm periods, whereas the most poleward FACs are not as well correlated. Consequently, the total latitudinal range of the FACs is broader than normal periods.
The equatorward boundary of the nightside FACs at 22 MLT and 01 MLT are situated at lower latitudes compared to their dayside counterparts at 10 MLT and 13 MLT. The nightside FACs can extend at most to 52° MLat (
Figure 2c,g), the whereas dayside FACs reach a minimum of 58° MLat (
Figure 2e), indicating a 6° MLat equatorward shift during nighttime compared to daytime. Furthermore, in both daytime (
Figure 2a vs.
Figure 2b,e vs.
Figure 2f) and nighttime (
Figure 2c vs.
Figure 2d,g vs.
Figure 2h), the equatorward boundary of the NH FACs are positioned more equatorward than their SH counterparts. Such hemispheric displacement is more pronounced during the daytime (i.e., 10 MLT and 13 MLT). Specifically, the NH pre-noon FACs can reach at most 60° MLat (
Figure 2a), whereas in the SH pre-noon, the FACs extend to −66° MLat (
Figure 2b). Similarly, the NH post-noon FACs could reach 58° MLat (
Figure 2e), compared to −60° MLat in the SH (
Figure 2f).
Additionally, the pre-noon FACs are located at higher latitudes compared to the post-noon FACs, as evident in
Figure 2a vs.
Figure 2b,e vs.
Figure 2f, which is more pronounced in the SH than in the NH. The equatorward boundary of the SH pre-noon FACs can extend to −66° MLat, while the SH post-noon FACs reach approximately −60° MLat, indicating a 6° MLat equatorward shift from pre-noon to post-noon in the SH. In contrast, there is a 2° MLat equatorward shift from pre-noon to post-noon in the NH. The IMF By component is unlikely to be the primary factor driving the pre-noon and post-noon asymmetry, as its effects should be opposite in the NH and SH. However, both the pre-midnight and post-midnight FACs are located at quite comparable latitudes (
Figure 2c vs.
Figure 2g and
Figure 2d vs.
Figure 2h).
These findings highlight significant variations in the latitudinal distribution of FACs during geomagnetic storms across different local times. The FACs on the nightside extend to the lowest latitudes, followed by those in the post-noon and pre-noon sectors. The pre-noon FACs are located at relatively higher latitudes compared to the post-noon FACs, while the FACs in the pre-midnight and post-midnight sectors are at comparable latitudes. Additionally, a distinct hemispheric asymmetry is apparent between the NH and SH in the day–night sectors, where the FACs in the northern regions occur at lower latitudes than their southern counterparts. Such hemispheric differences in the FACs’ latitudes might be related to summer vs. winter differences in the ionospheric conductivity, as discussed in
Section 4.2.
Table 1 lists the peak current densities encountered during the storm, revealing significant differences between day and night sectors and between hemispheres. Based on the data in the table, we found that the peak FAC densities on the dayside and nightside appear to be independent of each other (i.e., the peak time of the FACs differs on the dayside and nightside). Moreover, within the same local time sector, peak current densities in opposite hemispheres are rarely observed during the same orbit. It can be seen that the peak density of the FACs during the storm was approximately 7.8 times higher than the nominal values of ~1 µA/m
2 at most. In terms of the peak density, with the exception of the pre-midnight FACs, the current densities were generally stronger in the SH compared to the NH in most local time sectors. Such hemispheric differences in the FACs’ densities might be related to the summer vs. winter differences in the ionospheric conductivity, as discussed in
Section 4.1. In the SH, the daytime (i.e., pre-noon and post-noon) FACs were stronger than the nighttime (i.e., pre-midnight and post-midnight) FACs. However, in the NH, the post-noon FACs were stronger than the post-midnight FACs, whereas the pre-noon FACs were weaker than the pre-midnight FACs.
To highlight variations in storm-time FAC density in different local times, we examine the peak densities of the upward and downward FACs during each satellite polar pass from 00-30 ST, covering the intense FACs interval (indicated by the grey vertical dashed line in
Figure 2). FACs typically form a multisheet current system around noon and midnight during storm periods. Therefore, our analysis focuses on comparing the relative magnitudes of peak upward and downward currents in these local time sectors.
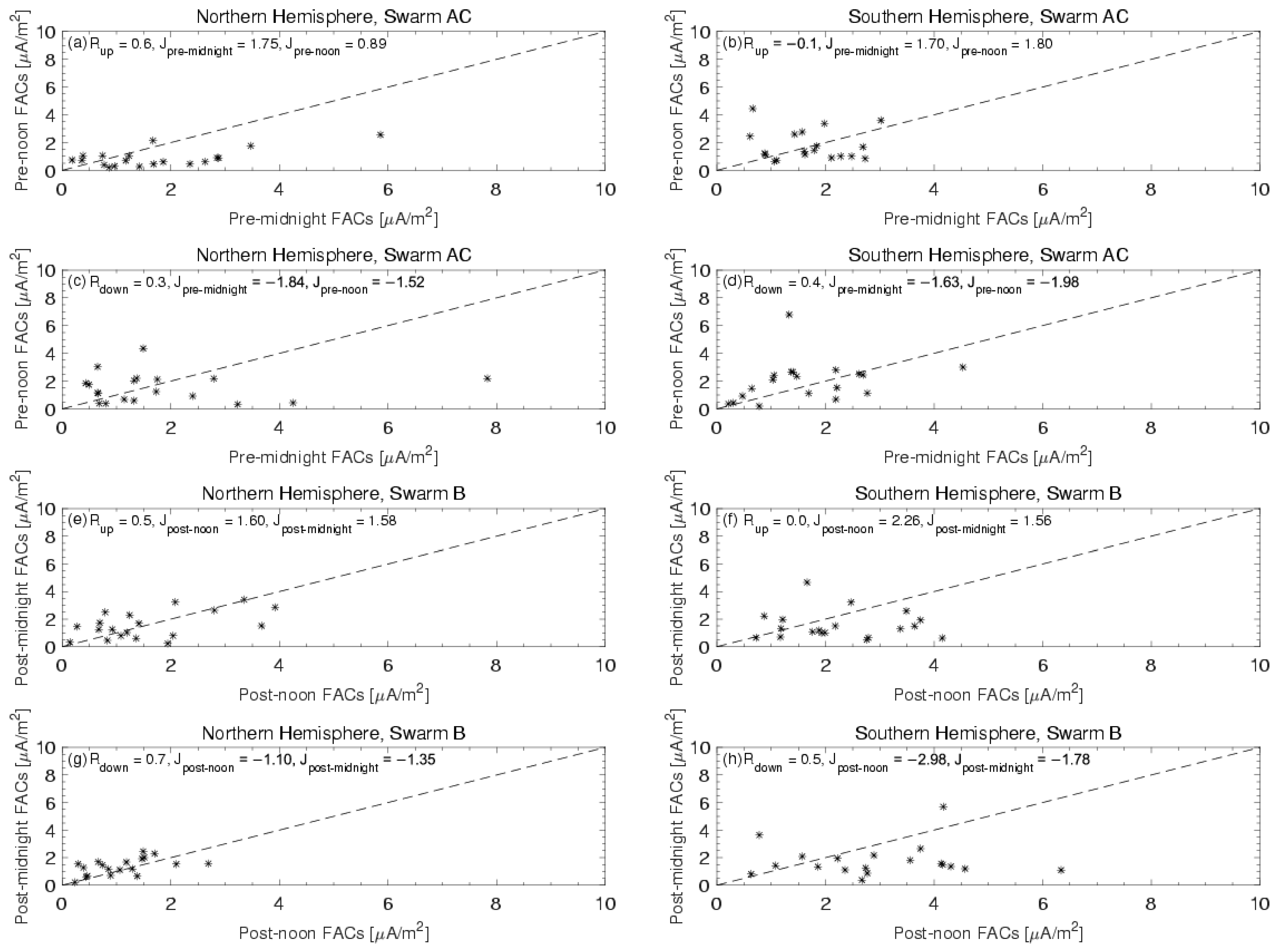
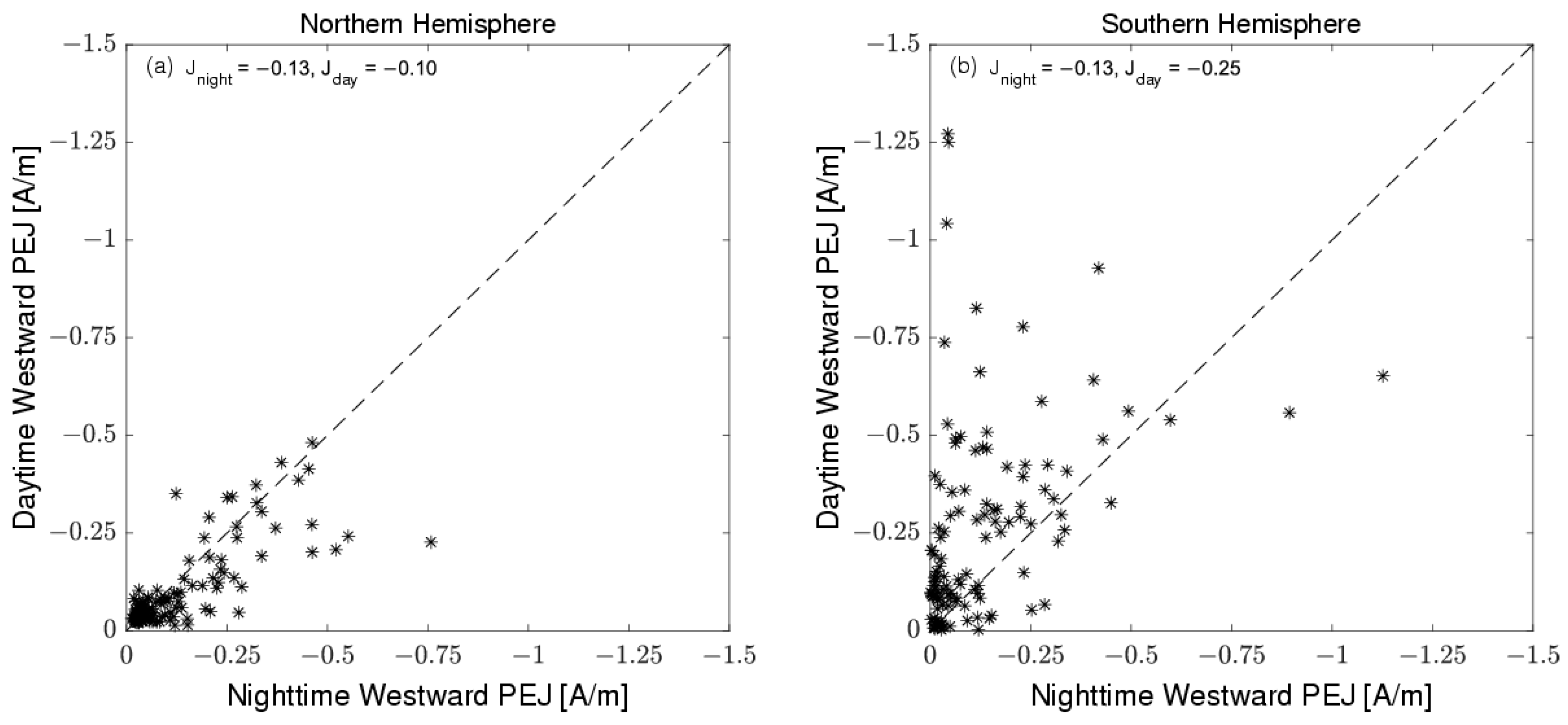
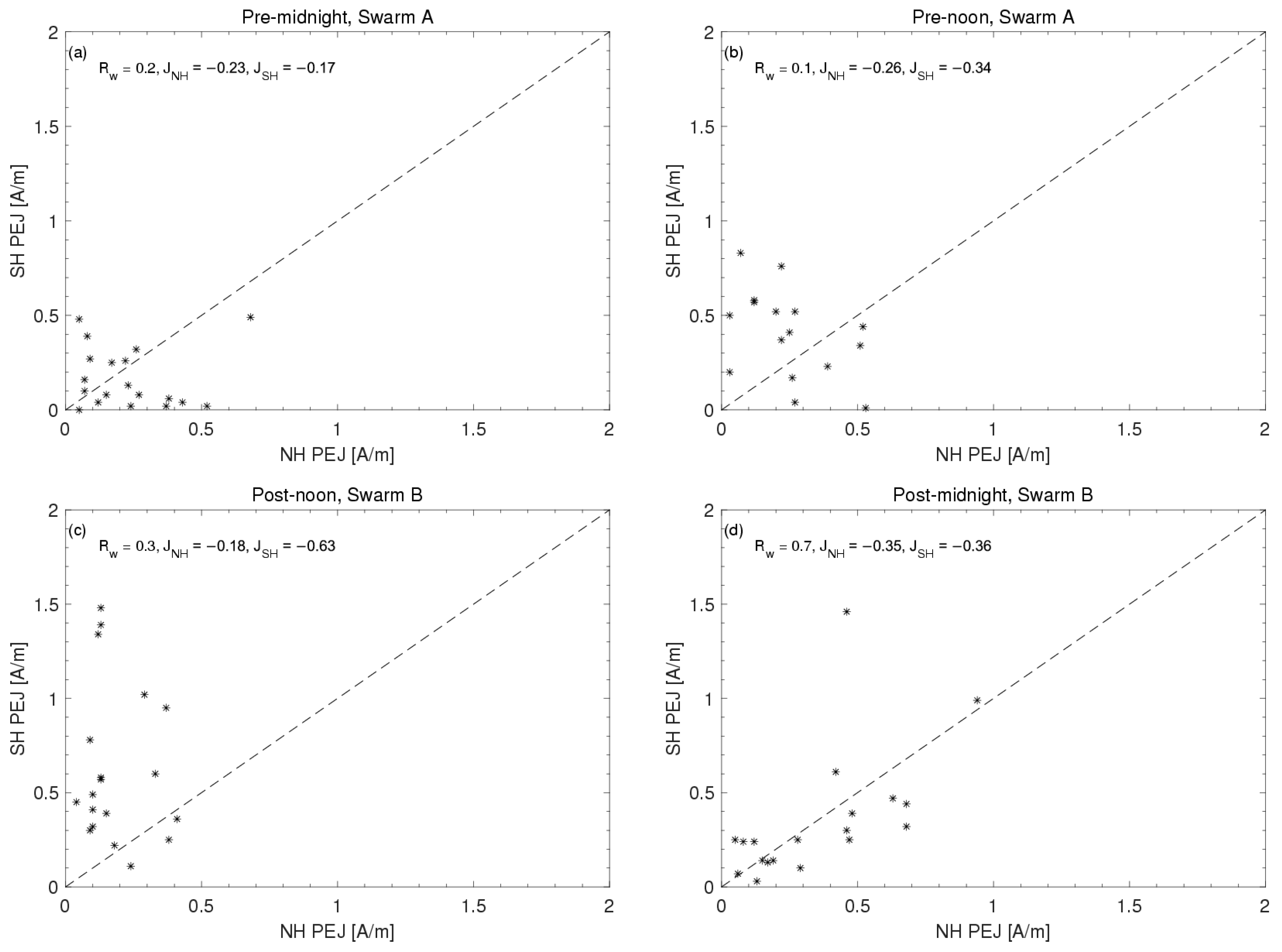
Figure 3 illustrates the correlations of the peak upward and downward FACs between the daytime and nighttime, with local time sector crossings spaced approximately 10 min apart. The left panel presents data from the NH, while the right panel depicts data from the SH. The top two panels display results from Swarms A/C in the pre-noon and pre-midnight sectors, and the bottom two panels show results from Swarm B in the post-noon and post-midnight sectors. Within each subfigure, the black dashed line represents equal FAC densities between different local time sectors. Correlation coefficients and mean values for the peak FAC densities across various local time sectors are provided for each panel.
For instance, for each ascending orbital segment in the NH (i.e., from 40° MLat toward the north pole), we identified the peak upward and downward FACs. Similarly, for the corresponding descending orbital segment (i.e., from the north pole to 40° MLat), we also identified the peak upward and downward FACs. The time difference between the detection of the peak FACs on the ascending and descending segments is approximately 10 min. Therefore, in
Figure 3a, the
x-axis of each asterisk represents the peak upward FACs during one ascending orbital segment in the NH (at 22 MLT), while the
y-axis represents the peak upward FACs during the corresponding descending orbital segment (at 10 MLT). The peak downward FACs for the ascending (at 22 MLT) and descending (at 10 MLT) orbital segments are shown in
Figure 3c.
In the NH, both the upward and downward averaged FACs exhibit greater strength in the pre-midnight sector compared to the pre-noon sector, as indicated by more asterisks below the dashed line (
Figure 3a,c). However, in the SH, the average pre-noon FACs (1.8 µA/m
2 and −1.98 µA/m
2) are larger than those observed in the pre-midnight sector (1.70 µA/m
2 and −1.63 µA/m
2) ((
Figure 3b,d)). For Swarm B, in the NH, the mean upward FACs during post-noon (1.6 µA/m
2) are slightly stronger than those during post-midnight (1.58 µA/m
2), while the mean downward FACs during post-noon (−1.1 µA/m
2) are weaker than those during post-midnight (−1.35 µA/m
2) (
Figure 3e,g). In the SH, both the averaged upward and downward FACs during post-noon are stronger compared to those during post-midnight, as indicated by more asterisks below the dashed line (
Figure 3f,h). In summary, in the NH, the post-noon upward FACs are stronger than post-midnight, while the pre-noon FACs are weaker than pre-midnight. In contrast, in the SH, the daytime FACs are stronger than the nighttime FACs.
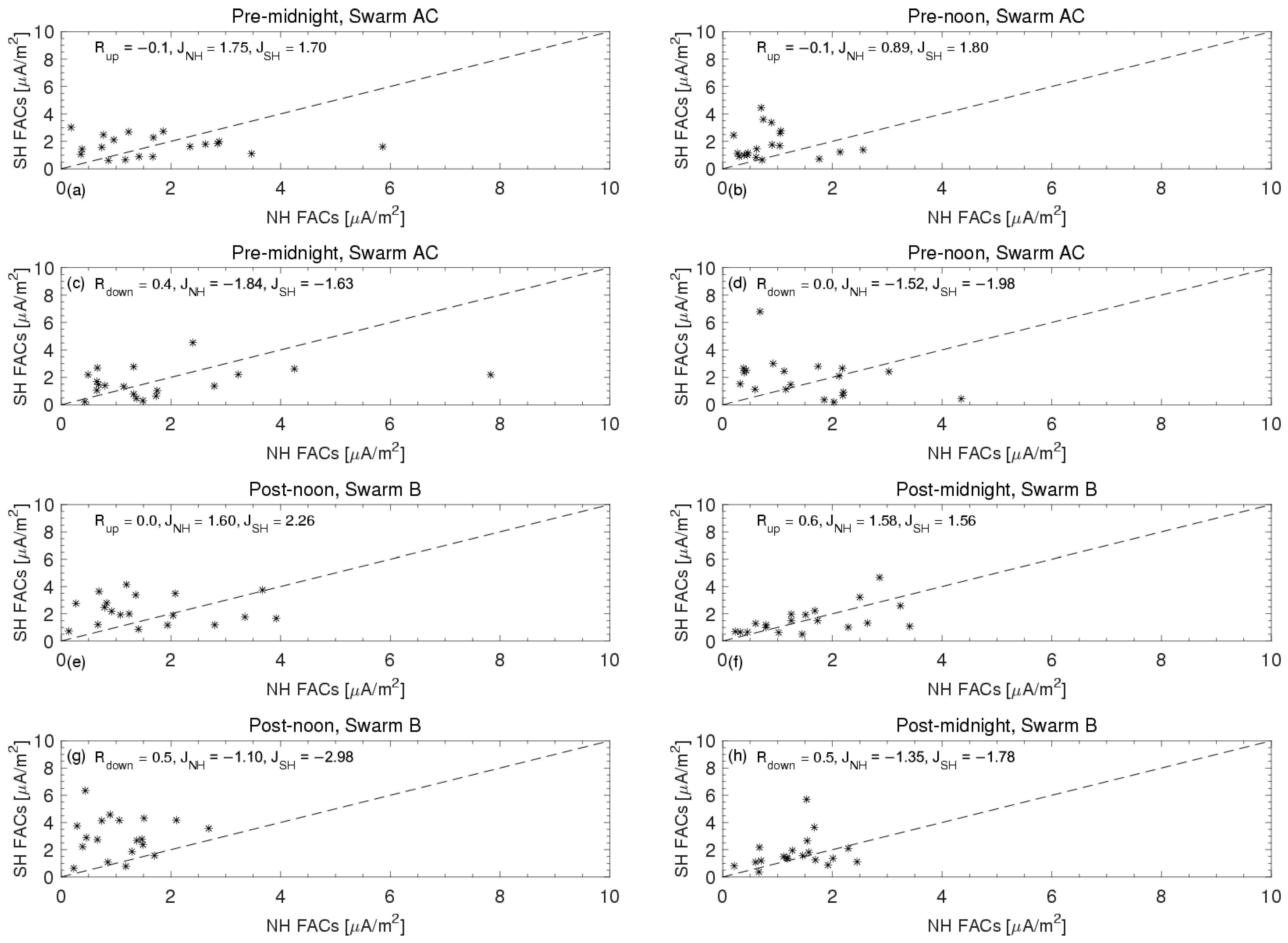
Figure 4 displays the correlation analyses of the peak FACs in both hemispheres, distinguishing between upward and downward currents. The left panels depict pre-midnight and post-noon sectors, while the right panels show pre-noon and post-midnight sectors. Asterisks below the black dashed line indicate stronger FACs in the NH, whereas those above signify stronger currents in the SH. Mean current densities for each hemisphere are detailed within each subfigure. Generally, except for specific instances, such as the pre-midnight and upward FACs in the post-midnight sector, the FACs in the SH exhibit stronger current densities compared to the NH. For instance, as shown in
Figure 4b,d, the peak upward (downward) FACs in the SH are, on average, 1.8 µA/m
2 (−1.98 µA/m
2), while in the NH they are, on average, 0.89 µA/m
2 (−1.52 µA/m
2).
It should be noted that satellite transitioning from the southern to the northern polar region takes more than 30 min, inherently resulting, on average, in a time difference of 47 min between hemispheric comparisons.
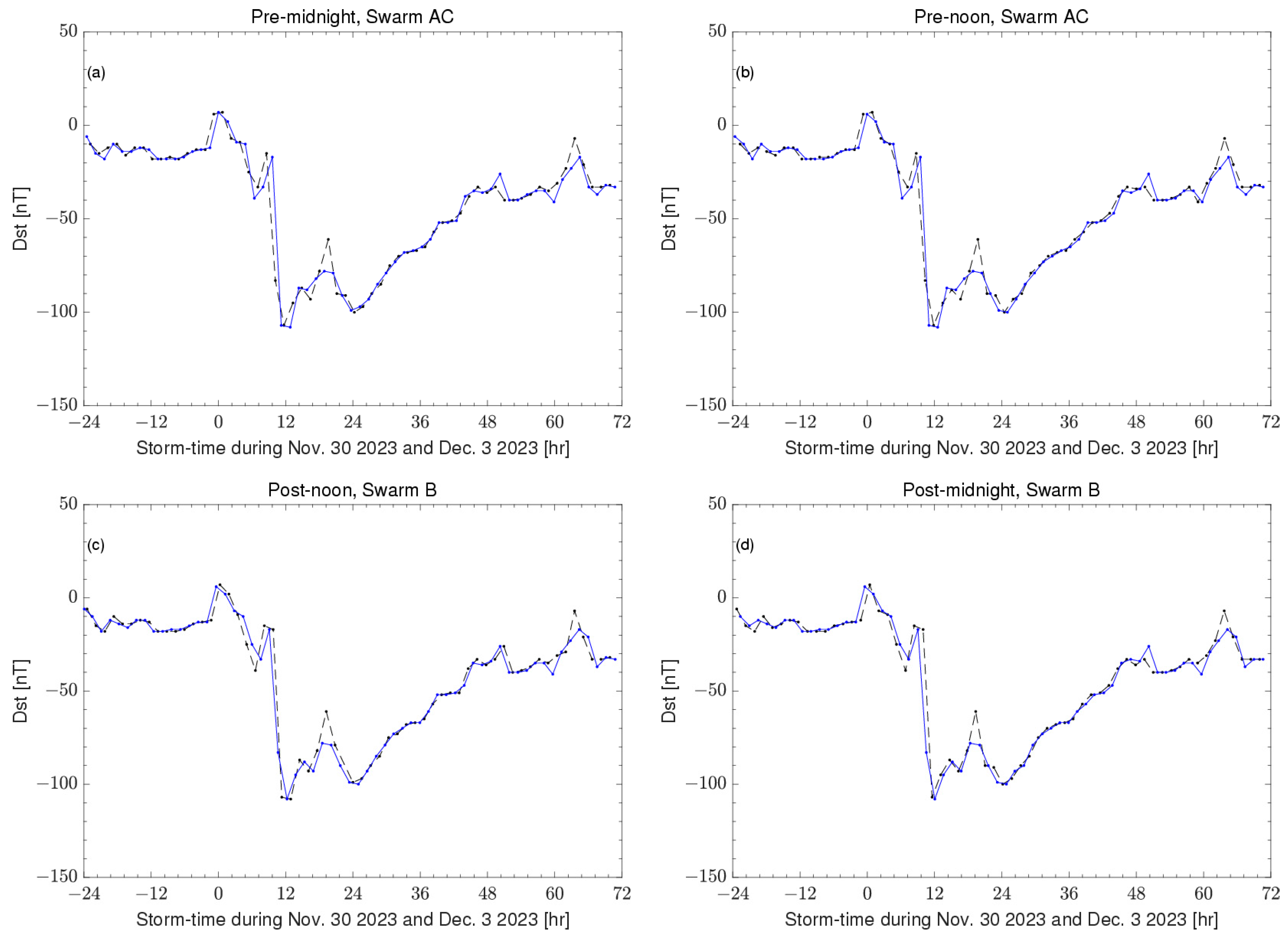
Figure 5 presents the time series of the Dst along the orbit segments observed by the Swarm in the four local time sectors for both hemispheres. It demonstrates the minimal variation in the Dst of the satellite that passed over the northern and southern polar regions, ensuring the reliability of hemispheric comparisons.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated FACs during the strong magnetic storms in December 2023, examining conditions across pre-noon, pre-midnight, post-noon, and post-midnight and in the NH and SH. The peak intensities of the FACs during the storm were observed to be approximately 7.8 times higher than nominal values of ~1 µA/m2, with the most equatorward FACs reaching −52° MLat. Significant local time and hemispheric variations in FACs characteristics were identified. A linear correlation analysis between peak current density, corresponding latitude, solar wind parameters (Em, Pd, and IMF By and Bz), and magnetic indices (Dst, AsyH, SMU, and SML) was performed. The main findings are summarized as follows:
- (1)
In the summer hemisphere (i.e., SH), the average pre-noon FACs are larger than those observed in the pre-midnight sector, and the FACs during post-noon are stronger compared to those during post-midnight. The summer daytime westward PEJ exceeds the nighttime westward PEJ.
- (2)
In the winter hemisphere (i.e., NH), both the upward and downward averaged FACs exhibit greater strength in the pre-midnight sector compared to the pre-noon sector, and the mean downward FACs during post-noon are weaker than those during post-midnight. The winter nighttime westward PEJ is greater than during daytime.
- (3)
In most local time sectors, the FACs are generally stronger in the SH compared to the NH. Similarly, the southern westward PEJs are larger than the northern PEJs. Such hemispheric differences are due to the summer vs. winter variations in the ionospheric conductivity.
- (4)
The FACs and westward PEJ in the northern winter pre-midnight sector are significantly stronger than in the southern summer pre-midnight sector, indicating that the nighttime stronger substorm DP-1 westward currents in the winter hemisphere compared to the summer hemisphere.
- (5)
The nighttime FACs are located at a lower MLat than the daytime. The pre-noon FACs are at a higher latitude than the post-noon. The winter hemispheric FACs are positioned more euqatorward than the summer hemispheric FACs.
- (6)
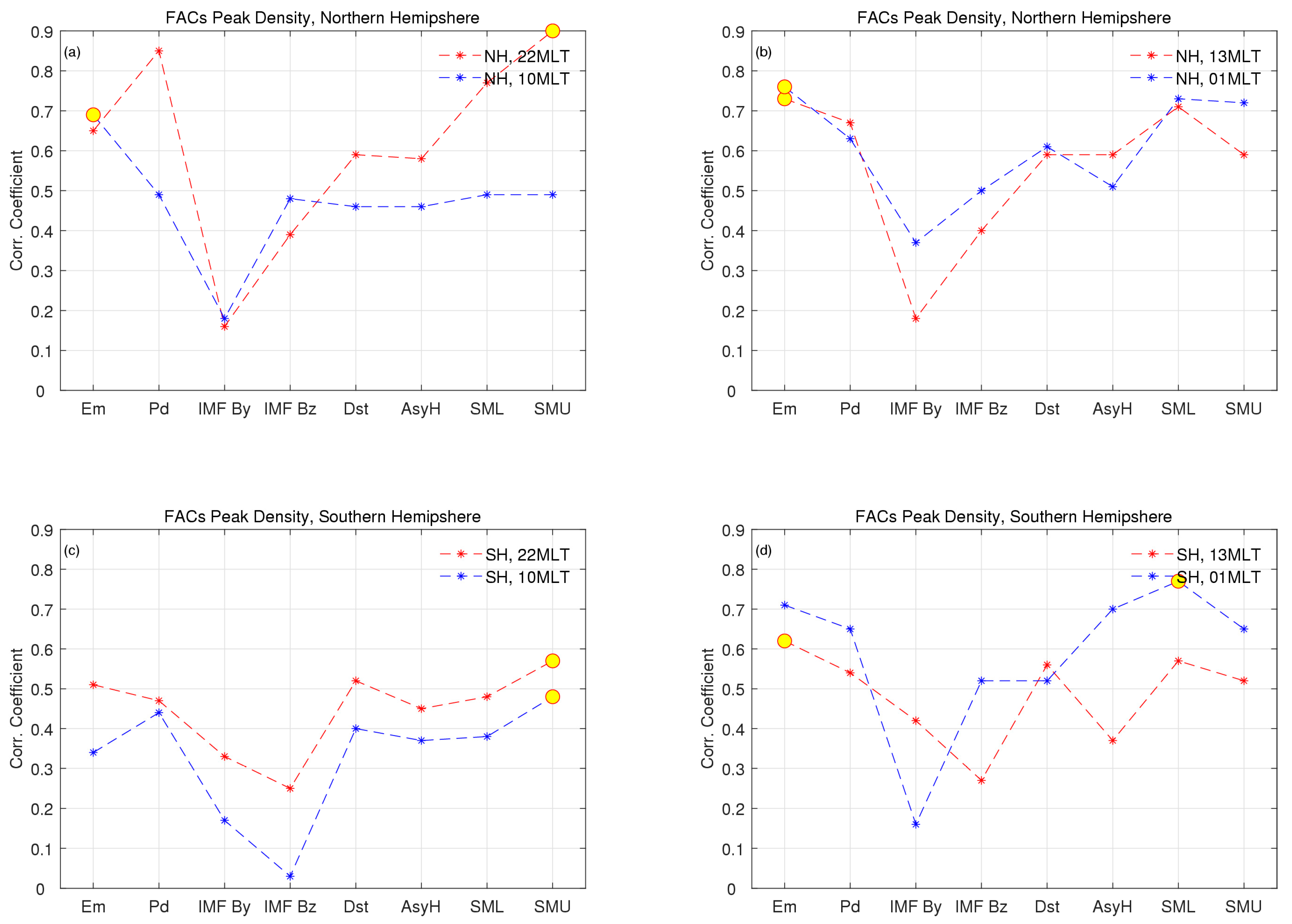
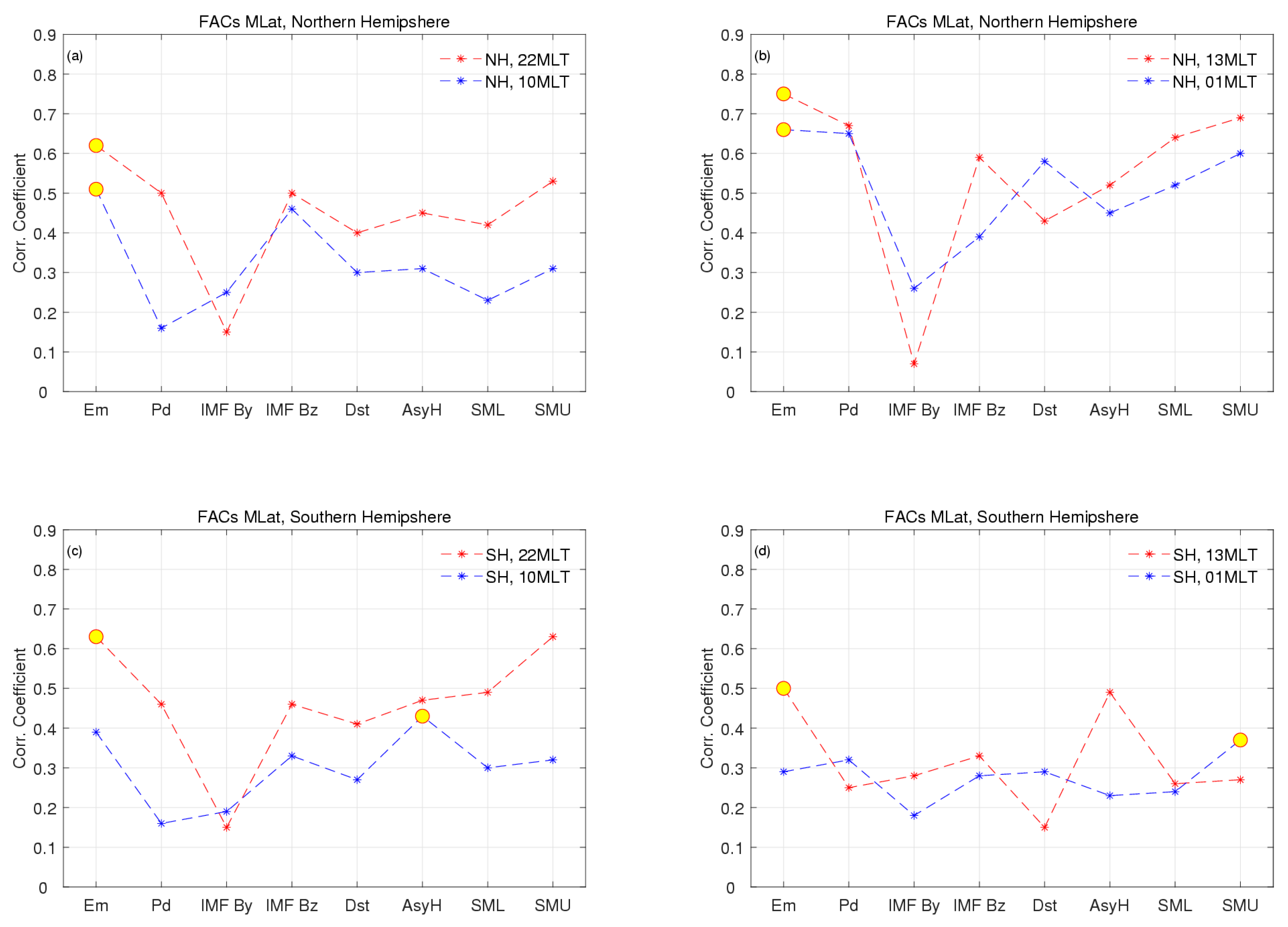
The FACs in the NH correlate best with the Em in the pre-noon, post-noon, and post-midnight sector, while they correlate best with the SMU in the pre-midnight sector. In the Southern Hemisphere, the FACs correlate best with the SMU in the pre-midnight and pre-noon sectors and with the SML in the post-midnight sector and Em post-noon.
- (7)
The latitude of peak FACs shows the strongest correlation with Em in most four local times and two hemispheres, except for the SH pre-noon and post-midnight.
Last but not least, our work makes key contributions in the following three main aspects: Firstly, our study offers new observational references for aurora sightings at lower latitudes during this specific geomagnetic storm. Since the position of FACs can represent the location of the auroral oval [
3,
34], our analysis of the FACs’ latitude provides valuable insights for understanding the auroral oval’s behavior during geomagnetic storms. It is well known that during geomagnetic storm periods, the auroral oval could expand equatorward. While this storm’s intensity did not reach the level of a superstorm (with a Dst Index of −108 nT), the auroral oval extended to approximately 50° MLat at around midnight—similar to the lowest latitudes observed during previous superstorms. For instance, during the major storms of 29–31 October 2003, when the Dst Index dropped to −363 nT at around 24 UT on 29 October and −401 nT at around 24 UT on October 30, the lowest latitude reached by the FACs near midnight was also around 50° MLat [
20]. Despite the lower intensity of this storm compared to those previous superstorms, the rare occurrence of auroral current systems at such low latitudes could be attributed to the high solar wind dynamic pressure (~20 nPa) during the storm main phase, which likely compressed the magnetosphere and ring current closer to the Earth. This compression allowed for auroral displays at latitudes (i.e., Beijing) at which such phenomena are typically not visible during storms of similar intensity.
Secondly, our work revealed significant variations in the intensities and latitudes of FACs during the geomagnetic storm, depending on the local time and hemisphere. We found that the dayside currents in the summer hemisphere were stronger than those on the nightside, a difference attributed to the ionospheric conductivity caused by solar illumination in the summer and winter hemispheres. However, in the pre-midnight, the currents were stronger in the winter hemisphere than in the summer hemisphere, likely due to more intense substorms occurring in the winter hemisphere. Additionally, we observed that the currents in the summer hemisphere were located at higher latitudes compared to those in the winter hemisphere. There were marked differences in the position of FACs between pre-noon and post-noon. To the best of our knowledge, no previous studies have conducted a comparative analysis of the storm-time FACs across these local time sectors, including pre-noon, post-noon, pre-midnight, and post-midnight.
Finally, we performed a correlation analysis to identify the key factors controlling the intensities and locations of FACs in different local time sectors and between the two hemispheres. Our results indicate that different factors dominate in these local times and hemispheres, highlighting the unique characteristics of this geomagnetic storm compared to previous storm events.
These findings can contribute to an understanding of FAC dynamics influenced by solar wind conditions and geomagnetic indices across different latitudes and local times. Future work can incorporate advanced modeling techniques and data from upcoming satellite missions, which can enhance our understanding of FACs behavior and mechanism during extreme geomagnetic storms, especially those expected in the coming years.