Accelerated Atmospheric to Hydrological Spread of Drought in the Yangtze River Basin under Climate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. GRACE Data
2.2.2. GLDAS Data
2.2.3. Precipitation and Potential Evapotranspiration Data
2.2.4. Auxiliary Datasets
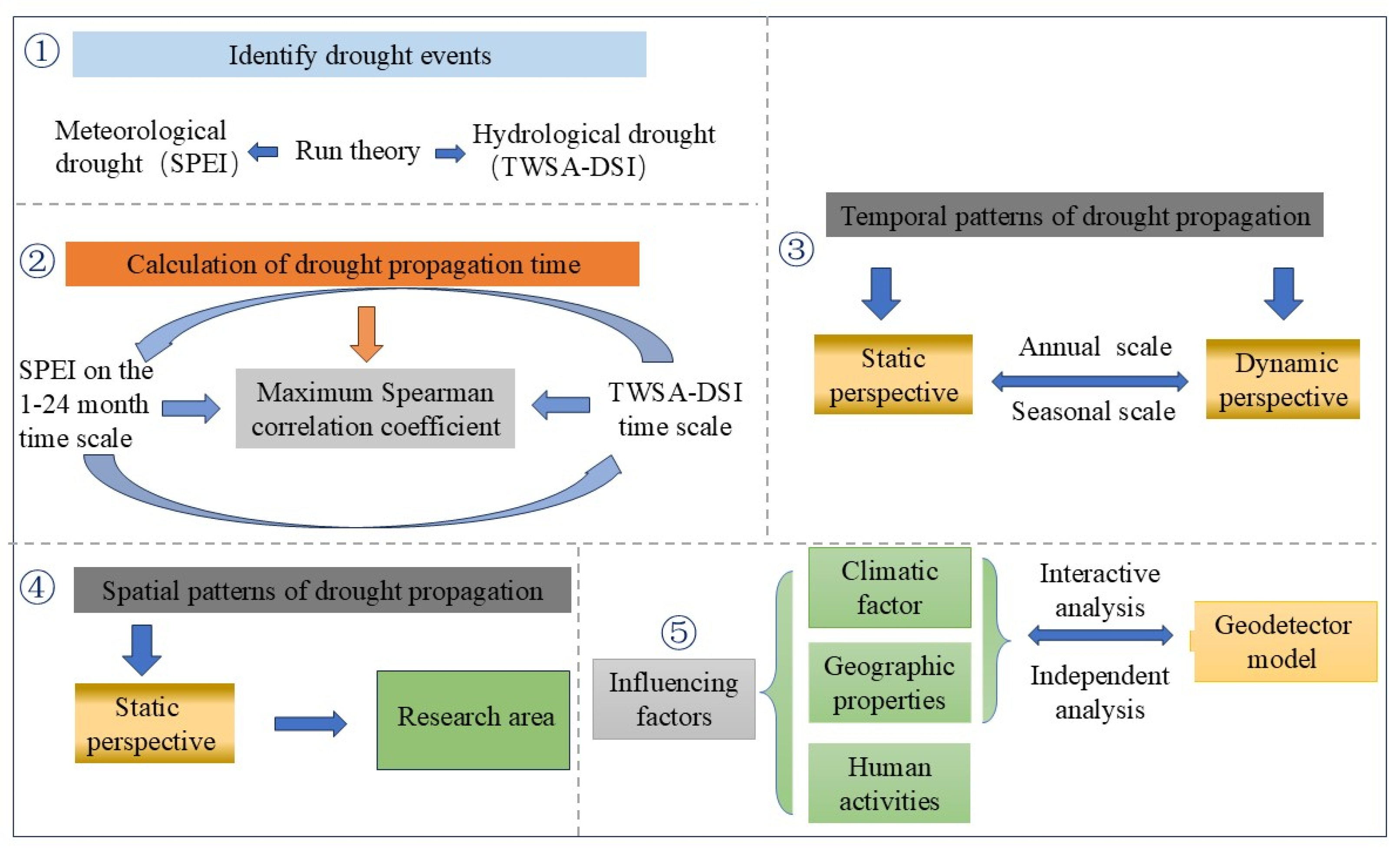
3. Methodology
3.1. SPEI
3.2. TWSA-DSI
3.3. Correlation Analysis
3.4. Geodetector Model
- (1)
- Factor detector
- (2)
- Interaction detector
4. Results
4.1. Static Drought Propagation Time
4.1.1. Annual Drought Propagation Times
4.1.2. Seasonal Drought Propagation Times
4.2. Drought Dynamic Propagation Time
4.2.1. Annual Dynamic Propagation Time
4.2.2. Seasonal Dynamic Propagation
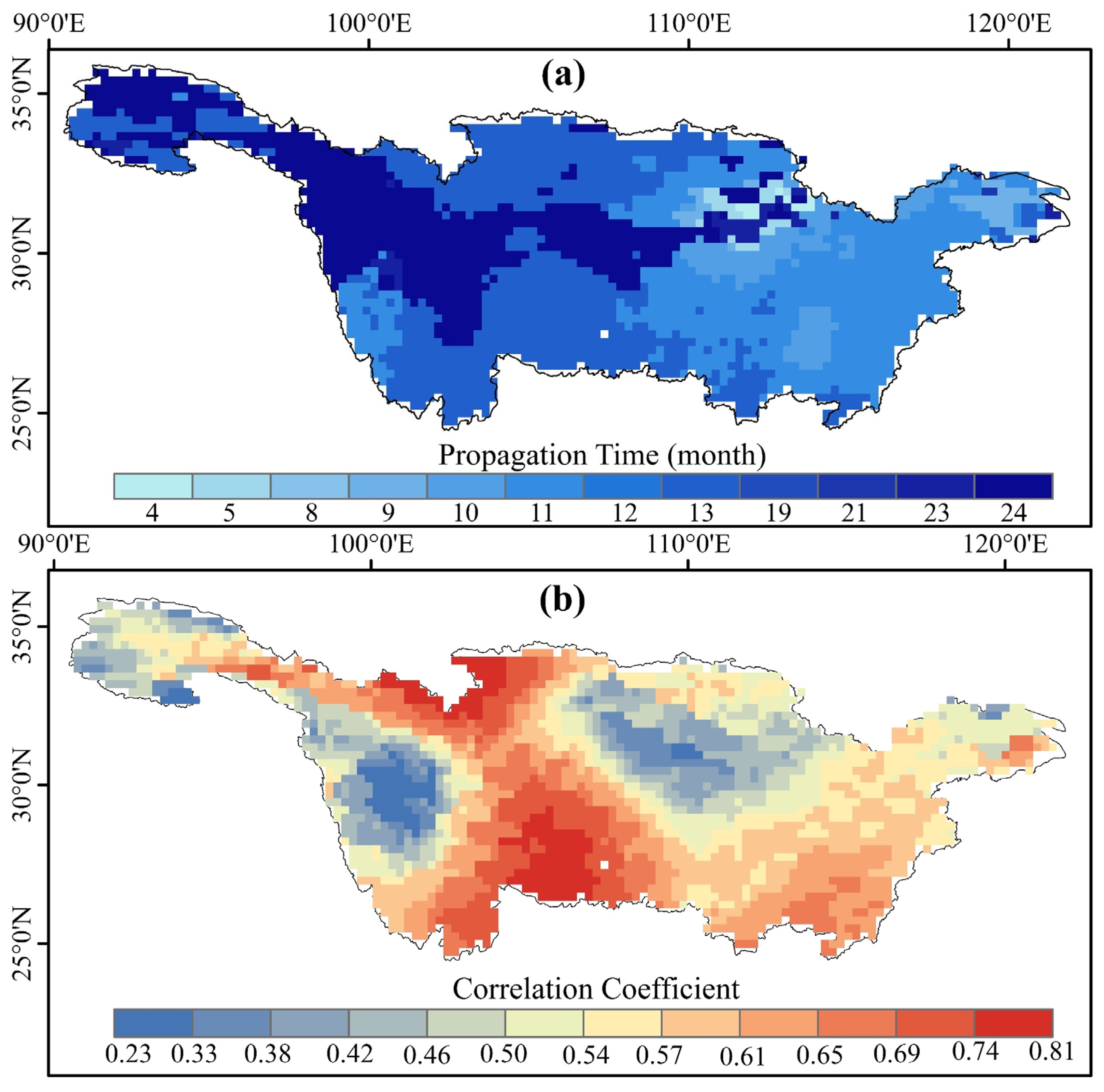
4.3. Spatial Propagation Time
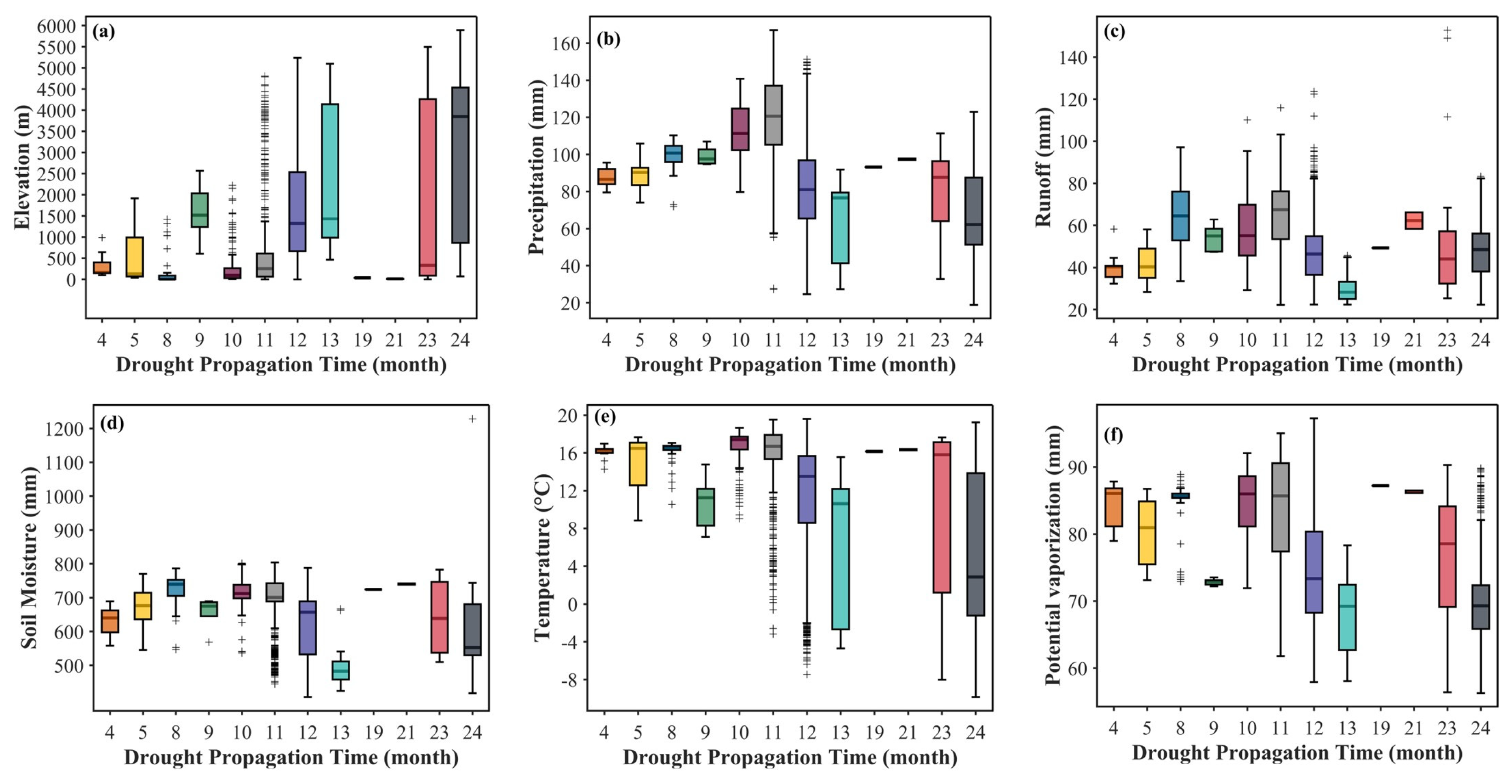
4.4. Influence of Climatic and Geographic Characteristics on the Spatial Propagation of Drought
5. Discussion
5.1. Impact of Climatic and Geographic Characteristics on the Spread of Drought
5.2. Limitation and Prospect
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Fang, W. Copulas-based bivariate socioeconomic drought dynamic risk assessment in a changing environment. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A.F.; Van Lanen, H.A.J. A process-based typology of hydrological drought. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1915–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, P.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Hou, B.; Ma, L. The propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought and its potential influence factors. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Leng, G.; Wang, H.; Bai, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Du, M. Propagation dynamics from meteorological to groundwater drought and their possible influence factors. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hao, Z.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S.; Xu, Y.; Hao, F. Drought propagation under global warming: Characteristics, approaches, processes, and controlling factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Iizumi, T.; Nishimori, M. Global Patterns of Crop Production Losses Associated with Droughts from 1983 to 2009. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A.F. Hydrological drought explained. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.-Water 2015, 2, 359–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, G.; He, B. Temporal and spatial propagation characteristics of meteorological drought to hydrological drought and influencing factors. Atmos. Res. 2024, 299, 107212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhao, J.; Leng, G.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Long-chain propagation pathways from meteorological to hydrological, agricultural and groundwater drought and their dynamics in China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; She, D.; Zheng, H.; Lin, P.; Yang, Z.-L. Elucidating Diverse Drought Characteristics from Two Meteorological Drought Indices (SPI and SPEI) in China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, N.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jin, T. Retrieving Groundwater Depletion and Drought in the Tigris-Euphrates Basin Between 2003 and 2015. Groundwater 2018, 56, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Ferreira, V.G.; Chen, J. Monitoring groundwater changes in the Yangtze River basin using satellite and model data. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Yuan, L.; Cheng, S.; Feng, W.; Tang, M.; Yang, X. Insights into hydrological drought characteristics using GNSS-inferred large-scale terrestrial water storage deficits. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 578, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feng, X.; Ciais, P.; Fu, B.; Hu, B.; Sun, Z. GRACE satellite-based drought index indicating increased impact of drought over major basins in China during 2002–2017. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Geruo, A.; Velicogna, I.; Kimball, J.S. Satellite Observations of Regional Drought Severity in the Continental United States Using GRACE-Based Terrestrial Water Storage Changes. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6297–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, A.F.; Laaha, G. Hydrological drought severity explained by climate and catchment characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konapala, G.; Mishra, A. Quantifying Climate and Catchment Control on Hydrological Drought in the Continental United States. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2018WR024620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Yao, H.; Zhang, D. Multi-timescale assessment of propagation thresholds from meteorological to hydrological drought. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y. The Three Gorges Dam has weakened the drought propagation process in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Xu, C.-Y.; Menzel, L.; Yuan, F.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Separating the effects of climate change and human activities on drought propagation via a natural and human-impacted catchment comparison method. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Characterizing drought events occurred in the Yangtze River Basin from 1979 to 2017 by reconstructing water storage anomalies based on GRACE and meteorological data. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhu, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Drought evaluation using the GRACE terrestrial water storage deficit over the Yangtze River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.Q.; Liu, B.; Hartmann, H.; Su, B.D.; Jiang, T.; Fraedrich, K. Dryness/wetness variations in ten large river basins of China during the first 50 years of the 21st century. Quat. Int. 2010, 226, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Chen, J. Global evaluation of new GRACE mascon products for hydrologic applications. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 9412–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Biswas, A.; Bennett, E.M. Socio-ecological determinants on spatio-temporal changes of groundwater in the Yellow River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 138725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagib, N.A.; Ali, M.M.A.; Schneider, K. Evaluation and bias correction of CRU TS4.05 potential evapotranspiration across vast environments with limited data. Atmos. Res. 2024, 299, 107194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Huang, J.; Mondal, S.K.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Y.; Wen, S.; Gao, M.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, T.; et al. Insight from CMIP6 SSP-RCP scenarios for future drought characteristics in China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 250, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Shui, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, X.; Cong, J. A multi-scale daily SPEI dataset for drought characterization at observation stations over mainland China from 1961 to 2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Shen, Y. Spatio-temporal variation of drought in China during 1961–2012: A climatic perspective. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X. Changes of terrestrial water storage during 1981–2020 over China based on dynamic-machine learning model. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Geruo, A.; Velicogna, I.; Kimball, J.S. A Global Gridded Dataset of GRACE Drought Severity Index for 2002-14: Comparison with PDSI and SPEI and a Case Study of the Australia Millennium Drought. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 2117–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; Dokuchits, E.Y.; Nkwazema, O.C. How 2022 extreme drought influences the spatiotemporal variations of terrestrial water storage in the Yangtze River Catchment: Insights from GRACE-based drought severity index and in-situ measurements. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Peng, Q.; Wang, M.; Cao, Y.; Gu, X.; Cai, H. Quantitative analysis of vegetation drought propagation process and uncertainty in the Yellow River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 295, 108775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Q.; He, Z.; Zheng, R. Drought propagation characteristics across China: Time, probability, and threshold. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, J.; Cao, Y.; Huang, J.; Guan, H. A downscaling-calibrating framework for generating gridded daily precipitation estimates with a high spatial resolution. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, X.; Bian, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, K. A novel approach for quantifying water resource spatial equilibrium based on the regional evaluation, spatiotemporal heterogeneity and geodetector analysis integrated model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 424, 138791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, X.; Su, X.; Leng, G.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Fang, W.; Liu, Y. Propagation characteristics and mechanism from meteorological to agricultural drought in various seasons. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, Q. Investigation about the correlation and propagation among meteorological, agricultural and groundwater droughts over humid and arid/semi-arid basins in China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Swarnkar, S.; Mujumdar, P. Dam operation affects the evolution and propagation of hydrological extremes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2024, 69, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, B.P.; Bloomfield, J.P. Spatio-temporal modelling of the status of groundwater droughts. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Duan, X.; Guo, Q.; Lu, S.; Hsu, K. The spatiotemporal variations and propagation of droughts in Plateau Mountains of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cong, N.; Wang, N.; Yao, W. Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on riparian vegetation in the Yangtze River Basin under climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Luo, X.; Ji, X.; Ming, W.; Wang, L.; Xiao, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Meteorological and hydrological droughts in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin: Spatiotemporal patterns and propagation. Atmos. Res. 2023, 293, 106913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiya Veettil, A.; Mishra, A.k. Multiscale hydrological drought analysis: Role of climate, catchment and morphological variables and associated thresholds. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wu, J.; Du, E.; Deng, X.; Sun, G.; Wang, G. Deciphering the influence of climate change and human activities on the drought propagation. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Cai, H.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shi, H. Propagation of meteorological to hydrological drought for different climate regions in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 283, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Niu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yao, R.; Gui, X.; Xiang, F.; Ji, Y. Impacts of Drought and Climatic Factors on Vegetation Dynamics in the Yellow River Basin and Yangtze River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuvel, D.; Sivakumar, B. Spatial propagation of different drought types and their concurrent societal risks: A complex networks-based analysis. J. Hydrol. 2024, 636, 131247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Li, B.; Song, J.; Li, Q.; Li, N.; Long, Y.; Feng, J. Evaluating multifaceted effects of watershed properties and human activities on drought propagation in the Wei River Basin with an integrated framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Gu, P.; Feng, H.; Yin, Y.; Chen, W.; Cheng, B. Changes in precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River Basin during 1960–2019 and the association with global warming, ENSO, and local effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, N.; Nam, W.-H.; Niyogi, D. Urbanization-induced drought modification: Example over the Yangtze River Basin, China. Urban Clim. 2022, 44, 101231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, F.; Wang, B. Trends and variability of daily temperature extremes during 1960–2012 in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 124, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, K.; Liu, M. Spatial and Decadal Variations in Potential Evapotranspiration of China Based on Reanalysis Datasets during 1982-2010. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Wang, T.; Gao, C.; Pan, S.; Sun, Z.; Xu, Y.-P. Potential evapotranspiration changes in Lancang River Basin and Yarlung Zangbo River Basin, southwest China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 1653–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhou, S.; Leng, G.; Liu, D.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H.; Han, Z.; Liang, H. Clarifying the Propagation Dynamics from Meteorological to Hydrological Drought Induced by Climate Change and Direct Human Activities. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 2359–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W. Anthropogenic drought in the Yellow River basin: Multifaceted and weakening connections between meteorological and hydrological droughts. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Hao, Z.; Singh, V.P.; Hao, F. Propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought under the impact of human activities: A case study in northern China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, X.; Tang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D. Impacts of climate change and reservoir operation on streamflow and flood characteristics in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Category | Description | SPEI | TWSA-DSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | No Drought | (−0.5, +∞) | (−0.5, +∞) |
| D1 | Mild Drought | (−1.0, −0.5] | (−0.8, −0.5] |
| D2 | Moderate Drought | (−1.5, −1.0] | (−1.3, −0.8] |
| D3 | Severe Drought | (−2.0, −1.5] | (−1.6, −1.3] |
| D4 | Extreme Drought | (−∞, −2.0] | (−2.0, −1.6] |
| D5 | Exceptional Drought | (−∞, −2.0] |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propagation time | 8.7 | 6.7 | 5 | 7.7 |
| Corresponding correlation | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.89 | 0.69 |
| Corresponding significance | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 |
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z value | 2.10 ** | −1.48 | 0 | 0.62 |
| trend | upward | downward | no trend | upward |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Han, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Cui, C.; Liu, J. Accelerated Atmospheric to Hydrological Spread of Drought in the Yangtze River Basin under Climate. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163033
Zhang C, Han Z, Wang S, Wang J, Cui C, Liu J. Accelerated Atmospheric to Hydrological Spread of Drought in the Yangtze River Basin under Climate. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163033
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chengyuan, Zhiming Han, Shuo Wang, Jiankun Wang, Chenfeng Cui, and Junrong Liu. 2024. "Accelerated Atmospheric to Hydrological Spread of Drought in the Yangtze River Basin under Climate" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163033
APA StyleZhang, C., Han, Z., Wang, S., Wang, J., Cui, C., & Liu, J. (2024). Accelerated Atmospheric to Hydrological Spread of Drought in the Yangtze River Basin under Climate. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16163033








