SPTrack: Spectral Similarity Prompt Learning for Hyperspectral Object Tracking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a spectral similarity prompt learning method that only trains the FCP to generate complementary features that are similar in format to the pre-trained data, achieving better alignment with the pre-trained model while consuming fewer computational resources;
- We design a spectral matching map as the prompt template. Through converting data from different bands into a unified prompt template form, our tracker can adapt to hyperspectral data with different spectral ranges and numbers of bands without the need for re-training or additional network structures;
- The experimental results show that SPTrack achieves SOTA performance with low computational costs on hyperspectral video data sets captured using three different camera types.
2. Related Work
2.1. Hyperspectral Object Tracking
2.1.1. Object Tracking Based on Generative Models
2.1.2. Object Tracking Based on Discriminative Models
2.2. Transformer-Based Tracking
2.3. Visual Prompt Learning
3. Methods
3.1. Preliminaries
3.2. Network Structure
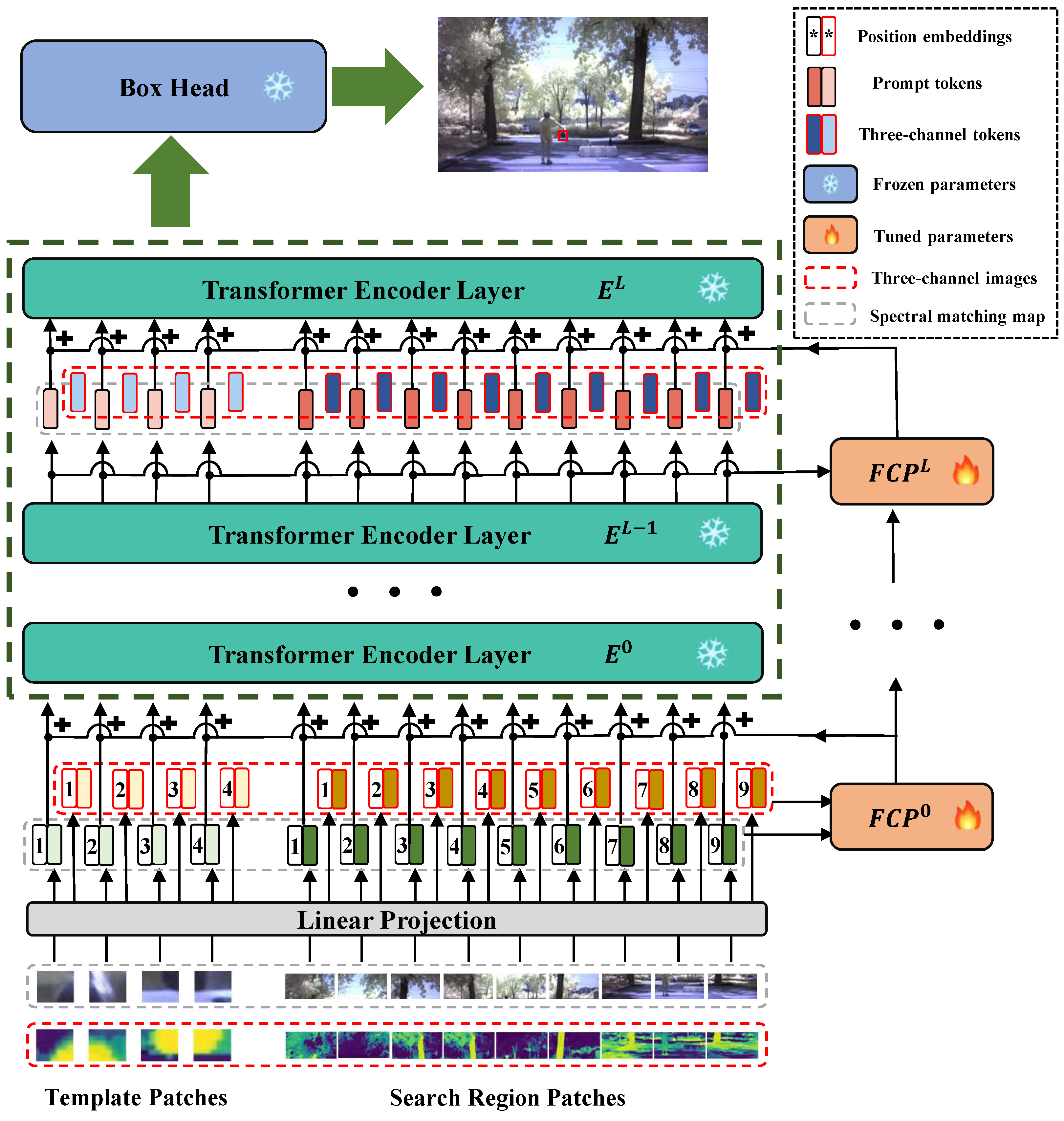
3.2.1. Overall Architecture
3.2.2. Vision Transformer Block
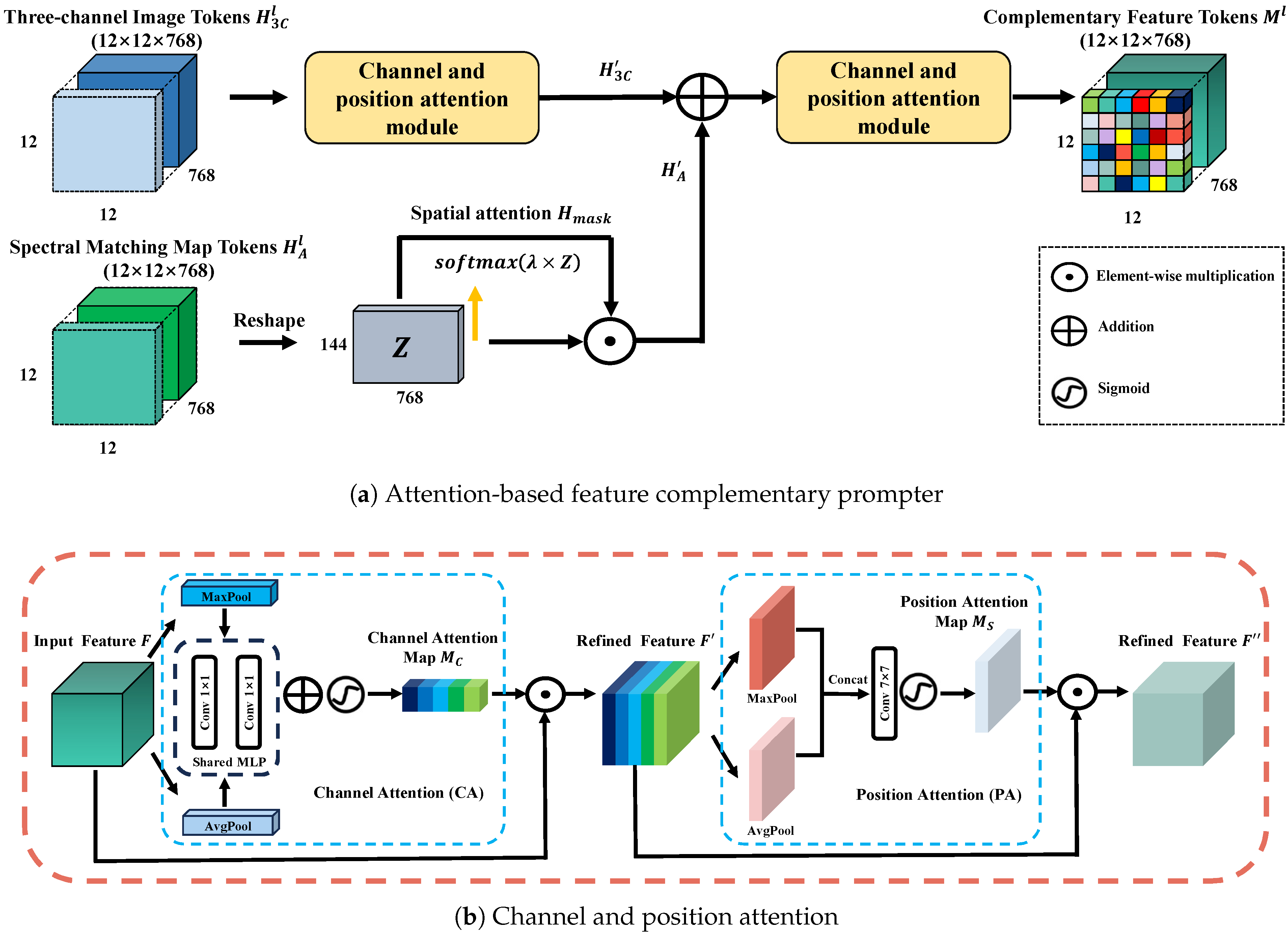
3.2.3. Feature Complementary Prompter
3.2.4. Head and Loss Function
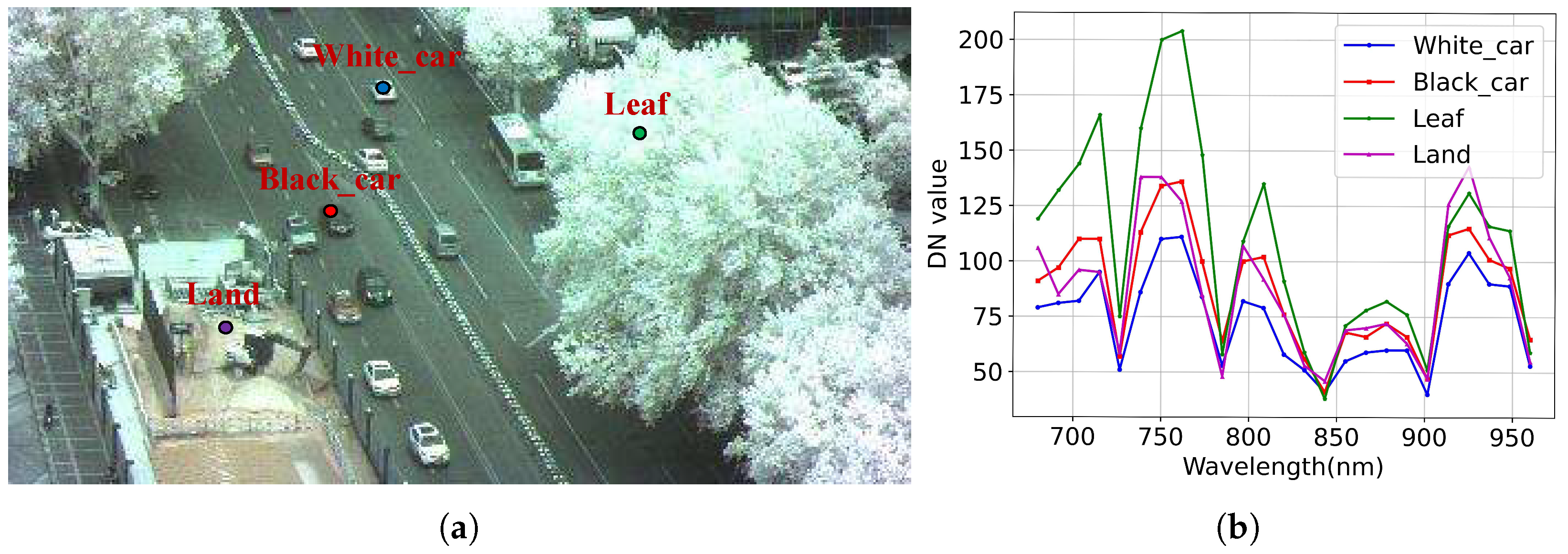
3.3. Spectral Matching Map Generation
| Algorithm 1 Spectral matching map generation algorithm. |
|
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.1.1. Data Sets
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.1.3. Implementation Details
5. Results and Analysis
5.1. Quantitative Comparison with State-of-the-Art Trackers
5.1.1. Quantitative Comparison on HOT2023
5.1.2. Quantitative Comparison on IMEC25
5.2. Visual Comparison
5.3. Ablation Analysis
5.3.1. With and without Spectral Matching Map
5.3.2. With and without Feature Complementary Prompter
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, L.; Yu, F.R.; Wang, Y.; Ning, B.; Tang, T. Big data analytics in intelligent transportation systems: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, M.; Alam, M.M.; Yafi, E.; Su’ud, M.M. A systematic review of human–computer interaction and explainable artificial intelligence in healthcare with artificial intelligence techniques. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 153316–153348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.T.; Du, J.; Zhu, H.; Peng, X.; Liu, Y.; Goh, R.S.M. Anomalynet: An anomaly detection network for video surveillance. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 2537–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Kurup, U.; Shah, M. Is it safe to drive? An overview of factors, metrics, and datasets for driveability assessment in autonomous driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 3135–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Bai, H.; Lin, L.; Yang, F.; Ling, H. LaSOT: A High-quality Large-scale Single Object Tracking Benchmark. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 129, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, X.; Huang, K. GOT-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 1562–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 850–865. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, G.; Danelljan, M.; Gool, L.V.; Timofte, R. Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6182–6191. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yan, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Lu, H. Transformer tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8126–8135. [Google Scholar]
- Marvasti-Zadeh, S.M.; Cheng, L.; Ghanei-Yakhdan, H.; Kasaei, S. Deep learning for visual tracking: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 3943–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Lu, H. Deep visual tracking: Review and experimental comparison. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 76, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Mondal, S. Recent developments on target tracking problems: A review. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 236, 109558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Zhou, J.; Tong, L.; Bai, X.; Wang, B. Material based salient object detection from hyperspectral images. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 76, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chanussot, J.; Jia, X.; Benediktsson, J.A. Multiple kernel learning for hyperspectral image classification: A review. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6547–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Song, W.; Fang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ghamisi, P.; Benediktsson, J.A. Deep learning for hyperspectral image classification: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6690–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Ling, Q.; Lin, Z.; An, W. You only train once: Learning a general anomaly enhancement network with random masks for hyperspectral anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5506718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, J.; Ling, Q.; Li, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, S. Anomaly detection for hyperspectral imagery via tensor low-rank approximation with multiple subspace learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5509917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; An, W.; Guo, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z. SpecDETR: A Transformer-based Hyperspectral Point Object Detection Network. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.10148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Cheng, C.; Jiao, L.; Zhou, H. Hybrid unmixing based on adaptive region segmentation for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3861–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Realistic mixing miniature scene hyperspectral unmixing: From benchmark datasets to autonomous unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5502515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Chanussot, J.; Yokoya, N.; Heiden, U.; Heldens, W.; Zhu, X.X. WU-Net: A weakly-supervised unmixing network for remotely sensed hyperspectral imagery. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tao, R.; Zhang, B. Graph-feature-enhanced selective assignment network for hyperspectral and multispectral data classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5526914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mei, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Self-supervised feature learning with CRF embedding for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 2628–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Wu, X.; Yao, J.; Zhang, B. Revisiting Graph Convolutional Networks with Mini-Batch Sampling for Hyperspectral Image Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, L. SPIRIT: Spectral Awareness Interaction Network with Dynamic Template for Hyperspectral Object Tracking. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 5503116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hou, Z.; Zhou, J.; Tao, R. SiamBAG: Band Attention Grouping-based Siamese Object Tracking Network for Hyperspectral Videos. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5514712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzair, M.; Mahmood, A.; Mian, A. Hyperspectral face recognition with spatiospectral information fusion and PLS regression. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ye, X.; Xiong, F.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Qian, Y. Spectral-Spatial-Temporal attention network for hyperspectral tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, L.; Huang, H. Robust hyperspectral object tracking by exploiting background-aware spectral information with band selection network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6013405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qian, K.; Shen, J.; Ma, H.; Chen, P. AD-SiamRPN: Anti-Deformation Object Tracking via an Improved Siamese Region Proposal Network on Hyperspectral Videos. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Shu, M.; Sun, C. SiamHYPER: Learning a hyperspectral object tracker from an RGB-based tracker. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 7116–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodge, J.; Ilharco, G.; Schwartz, R.; Farhadi, A.; Hajishirzi, H.; Smith, N. Fine-Tuning Pretrained Language Models: Weight Initializations, data orders, and early stopping. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.06305. [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey, M.; Cohen, N.J. Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: The sequential learning problem. Psychol. Learn. Motiv. 1989, 24, 109–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, H.; Su, N.; Xu, C.; Yan, Y.; Feng, S. TMTNet: A Transformer-Based Multimodality Information Transfer Network for Hyperspectral Object Tracking. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, J.; Wang, J.; Su, N.; Zhao, C.; Yan, Y.; Feng, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z. Multi-Band Hyperspectral Object Tracking: Leveraging Spectral Information Prompts and Spectral Scale-Aware Representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Hu, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J.; Li, X. VP-HOT: Visual Prompt for Hyperspectral Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiong, F.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J.; Qian, Y. Learning a deep ensemble network with band importance for hyperspectral object tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 2901–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Burlina, P.; Broadwater, J. Hyperspectral video for illumination-invariant tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Banerjee, A.; Burlina, P.; Broadwater, J.; Chellappa, R. Tracking and identification via object reflectance using a hyperspectral video camera. Mach. Vis. Beyond Visible Spectr. 2011, 1, 201–219. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Zhou, J.; Xiong, F.; Zhou, H.; Du, J. Object tracking in hyperspectral videos with convolutional features and kernelized correlation filter. In Proceedings of the Smart Multimedia: First International Conference, Toulon, France, 24–26 August 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 308–319. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, F.; Zhou, J.; Qian, Y. Material based object tracking in hyperspectral videos. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 3719–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H. Target-aware and spatial-spectral discriminant feature joint correlation filters for hyperspectral video object tracking. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 223, 103535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzkent, B.; Rangnekar, A.; Hoffman, M.J. Tracking in aerial hyperspectral videos using deep kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xiong, F.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Qian, Y. BAE-Net: A band attention aware ensemble network for hyperspectral object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 25–28 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 2106–2110. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xiong, F.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Qian, Y. Material-guided siamese fusion network for hyperspectral object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 4–10 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 2809–2813. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. A Siamese network-based tracking framework for hyperspectral video. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 2381–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, B.; Chang, H.; Ma, B.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Joint feature learning and relation modeling for tracking: A one-stream framework. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 341–357. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Wu, G. Mixformer: End-to-end tracking with iterative mixed attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 13608–13618. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Song, T.; Wu, G.; Wang, L. Mixformerv2: Efficient fully transformer tracking. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 58736–58751. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Yuan, W.; Fu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Hayashi, H.; Neubig, G. Pre-train, prompt, and predict: A systematic survey of prompting methods in natural language processing. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ji, K.; Fu, Y.; Tam, W.L.; Du, Z.; Yang, Z.; Tang, J. P-tuning v2: Prompt tuning can be comparable to fine-tuning universally across scales and tasks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.07602. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Liang, P. Prefix-tuning: Optimizing continuous prompts for generation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.00190. [Google Scholar]
- Bahng, H.; Jahanian, A.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Isola, P. Exploring visual prompts for adapting large-scale models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.17274. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Tang, L.; Chen, B.C.; Cardie, C.; Belongie, S.; Hariharan, B.; Lim, S.N. Visual prompt tuning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 709–727. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Ge, C.; Tong, Z.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, P. AdaptFormer: Adapting vision transformers for scalable visual recognition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 16664–16678. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, F.; Leonardis, A.; Song, J. Prompting for multi-modal tracking. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 3492–3500. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Lai, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Lu, H. Visual prompt multi-modal tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 9516–9526. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Peng, H.; Fu, J.; Wang, D.; Lu, H. Learning spatio-temporal transformer for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10448–10457. [Google Scholar]
- Law, H.; Deng, J. Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 734–750. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Krähenbühl, P. Objects as points. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07850. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Schlamm, A.; Messinger, D. Improved detection and clustering of hyperspectral image data by preprocessing with a euclidean distance transformation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kruse, F.A.; Lefkoff, A.; Boardman, J.; Heidebrecht, K.; Shapiro, A.; Barloon, P.; Goetz, A. The spectral image processing system (SIPS)-interactive visualization and analysis of imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 44, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, J.N. The spectral similarity scale and its application to the classification of hyperspectral remote sensing data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Advances in Techniques for Analysis of Remotely Sensed Data, Greenbelt, MD, USA, 27–28 October 2003; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, N.; Chan, J.C.W.; Kong, S.G. Object tracking in hyperspectral-oriented video with fast spatial-spectral features. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Guo, G.; He, X.; Xu, Q.; Wang, W.; Ling, Q.; Lin, Z.; An, W. RawTrack: Toward Single Object Tracking on Mosaic Hyperspectral Raw Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Hyperspectral Image and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–26 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Ji, R. Siamese box adaptive network for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 6668–6677. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S. SiamCAR: Siamese fully convolutional classification and regression for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 6269–6277. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Shao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Shen, C. Graph attention tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 9543–9552. [Google Scholar]
- Lukezic, A.; Vojir, T.; Cehovin Zajc, L.; Matas, J.; Kristan, M. Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6309–6318. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; pp. 702–715. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chan, J.C.W.; Kong, S.G. Histograms of oriented mosaic gradients for snapshot spectral image description. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 183, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani Galoogahi, H.; Fagg, A.; Lucey, S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, W.; Tian, Q.; Hong, R.; Wang, M.; Li, H. Multi-cue correlation filters for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4844–4853. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gonzalez-Garcia, A.; Weijer, J.V.D.; Danelljan, M.; Khan, F.S. Learning the model update for siamese trackers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4010–4019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, M.; Mei, S. A spectral–spatial transformer fusion method for hyperspectral video tracking. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| VIS | NIR | RedNIR | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | 55 | 40 | 15 | 110 |
| Validation set | 46 | 30 | 11 | 87 |
| Methods | MHT | SiamBAN | SiamCAR | STARK | SiamGAT | TranST | OSTrack | SSAMB | SIPHOT | RawTrack | SPTrack (Ours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | 0.453 | 0.532 | 0.554 | 0.557 | 0.561 | 0.569 | 0.597 | 0.623 | 0.635 | 0.638 | 0.640 |
| DP@20 | 0.717 | 0.756 | 0.762 | 0.768 | 0.770 | 0.777 | 0.802 | 0.837 | 0.844 | 0.840 | 0.857 |
| Methods | MHT | SiamBAN | SiamCAR | STARK | SiamGAT | TranST | OSTrack | SSAMB | SIPHOT | RawTrack | SPTrack (Ours) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIS | AUC | 0.507 | 0.534 | 0.565 | 0.561 | 0.552 | 0.576 | 0.601 | 0.612 | 0.625 | 0.622 | 0.616 |
| DP@20 | 0.760 | 0.763 | 0.787 | 0.783 | 0.760 | 0.808 | 0.818 | 0.829 | 0.842 | 0.834 | 0.858 | |
| NIR | AUC | 0.425 | 0.567 | 0.600 | 0.594 | 0.620 | 0.617 | 0.646 | 0.698 | 0.709 | 0.723 | 0.726 |
| DP@20 | 0.756 | 0.808 | 0.834 | 0.805 | 0.858 | 0.816 | 0.852 | 0.932 | 0.928 | 0.938 | 0.929 | |
| RedNIR | AUC | 0.317 | 0.441 | 0.387 | 0.439 | 0.445 | 0.389 | 0.451 | 0.461 | 0.471 | 0.482 | 0.509 |
| DP@20 | 0.427 | 0.573 | 0.504 | 0.550 | 0.566 | 0.522 | 0.599 | 0.611 | 0.623 | 0.598 | 0.657 | |
| Methods | CSK | CSRDCF | BACF | MCCT | UpdateNet | TranST | SiamCAR | SiamFC | SSTFT | HOMG | SPTrack (Ours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | 0.222 | 0.527 | 0.540 | 0.552 | 0.530 | 0.547 | 0.481 | 0.582 | 0.619 | 0.746 | 0.588 |
| DP@20 | 0.429 | 0.775 | 0.797 | 0.797 | 0.859 | 0.871 | 0.777 | 0.832 | 0.888 | 0.823 | 0.927 |
| SMM | Prompter | AUC | ΔAUC | DP@20 | ΔDP@20 | FPS | Params |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w.o. | w.o. | 0.597 | n/a | 0.802 | n/a | 27.4 | 92.83M |
| ED | MCP [60] | 0.612 | 2.513% | 0.826 | 2.993% | 24.2 | 0.84 M |
| FCP | 0.638 | 6.868% | 0.846 | 5.486% | 22.8 | 1.49 M | |
| SAM | MCP [60] | 0.610 | 2.178% | 0.820 | 2.244% | 24.2 | 0.84 M |
| FCP | 0.640 | 7.203% | 0.857 | 6.858% | 22.8 | 1.49 M | |
| SSS | MCP [60] | 0.614 | 2.848% | 0.817 | 1.870% | 24.2 | 0.84 M |
| FCP | 0.630 | 5.528% | 0.834 | 3.990% | 22.8 | 1.49 M |
| Methods | ED | SAM | SSS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIS | AUC | 0.615 | 0.616 | 0.618 |
| DP@20 | 0.845 | 0.858 | 0.844 | |
| NIR | AUC | 0.710 | 0.726 | 0.684 |
| DP@20 | 0.898 | 0.929 | 0.867 | |
| RedNIR | AUC | 0.543 | 0.509 | 0.535 |
| DP@20 | 0.707 | 0.657 | 0.699 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, G.; Li, Z.; An, W.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Luo, Y.; Ling, Q.; Li, M.; Lin, Z. SPTrack: Spectral Similarity Prompt Learning for Hyperspectral Object Tracking. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162975
Guo G, Li Z, An W, Wang Y, He X, Luo Y, Ling Q, Li M, Lin Z. SPTrack: Spectral Similarity Prompt Learning for Hyperspectral Object Tracking. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162975
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Gaowei, Zhaoxu Li, Wei An, Yingqian Wang, Xu He, Yihang Luo, Qiang Ling, Miao Li, and Zaiping Lin. 2024. "SPTrack: Spectral Similarity Prompt Learning for Hyperspectral Object Tracking" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162975
APA StyleGuo, G., Li, Z., An, W., Wang, Y., He, X., Luo, Y., Ling, Q., Li, M., & Lin, Z. (2024). SPTrack: Spectral Similarity Prompt Learning for Hyperspectral Object Tracking. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 2975. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162975









