Geometric Factor Correction Algorithm Based on Temperature and Humidity Profile Lidar
Abstract
1. Introduction
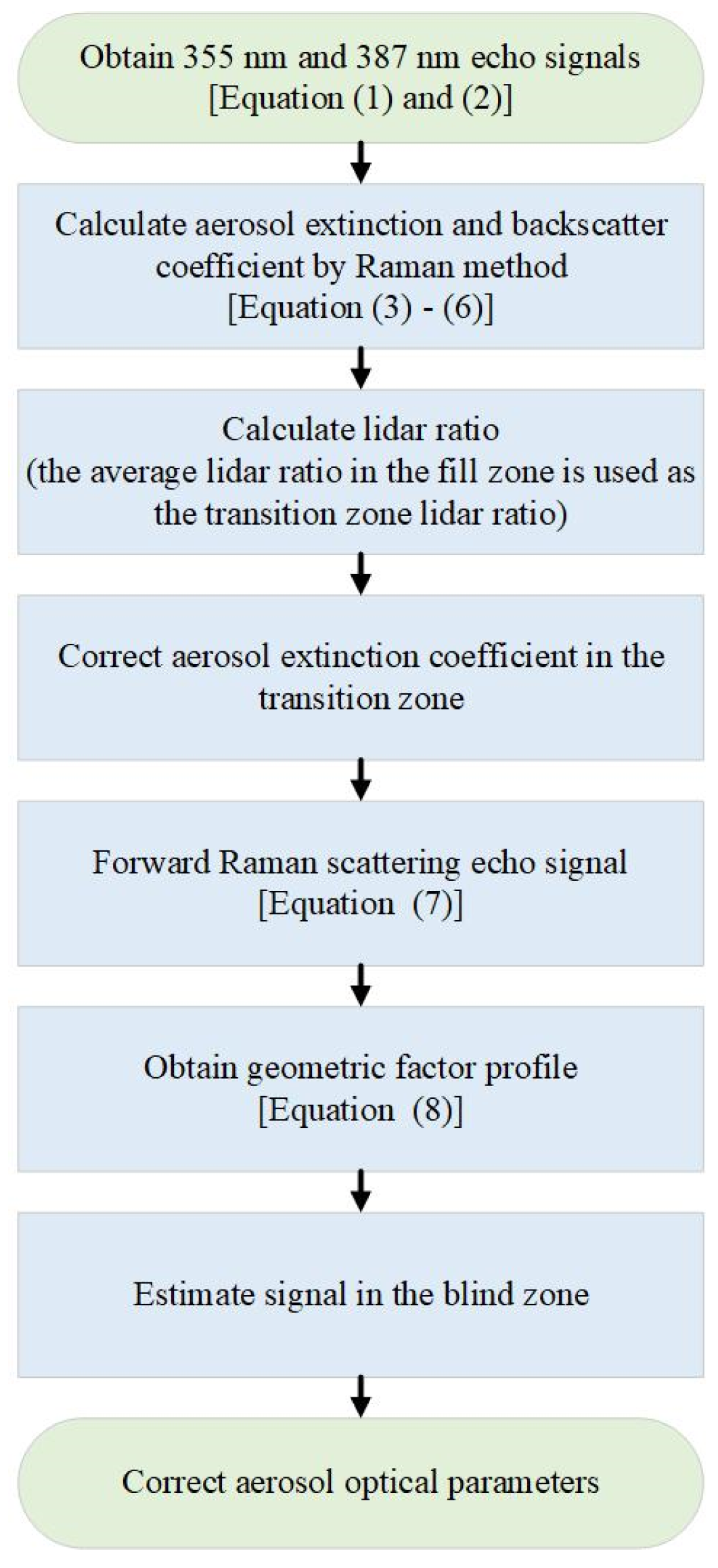
2. Geometric Factor Correction Algorithm
2.1. Mie Scattering Channel Correction Algorithm
2.2. Raman Scattering Channel Correction Algorithm
3. Experimental Analysis and Discussion of Geometric Factor Correction
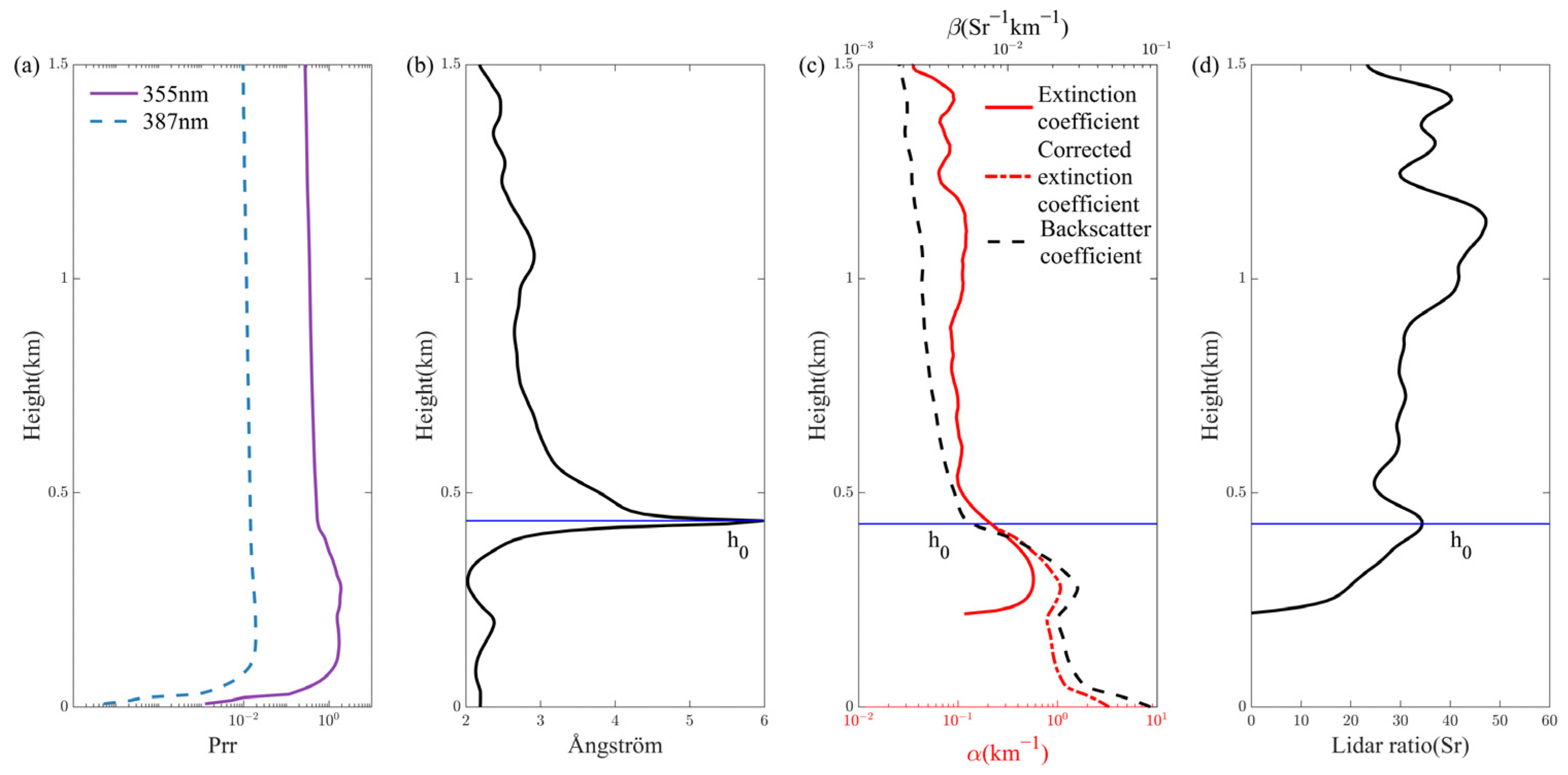
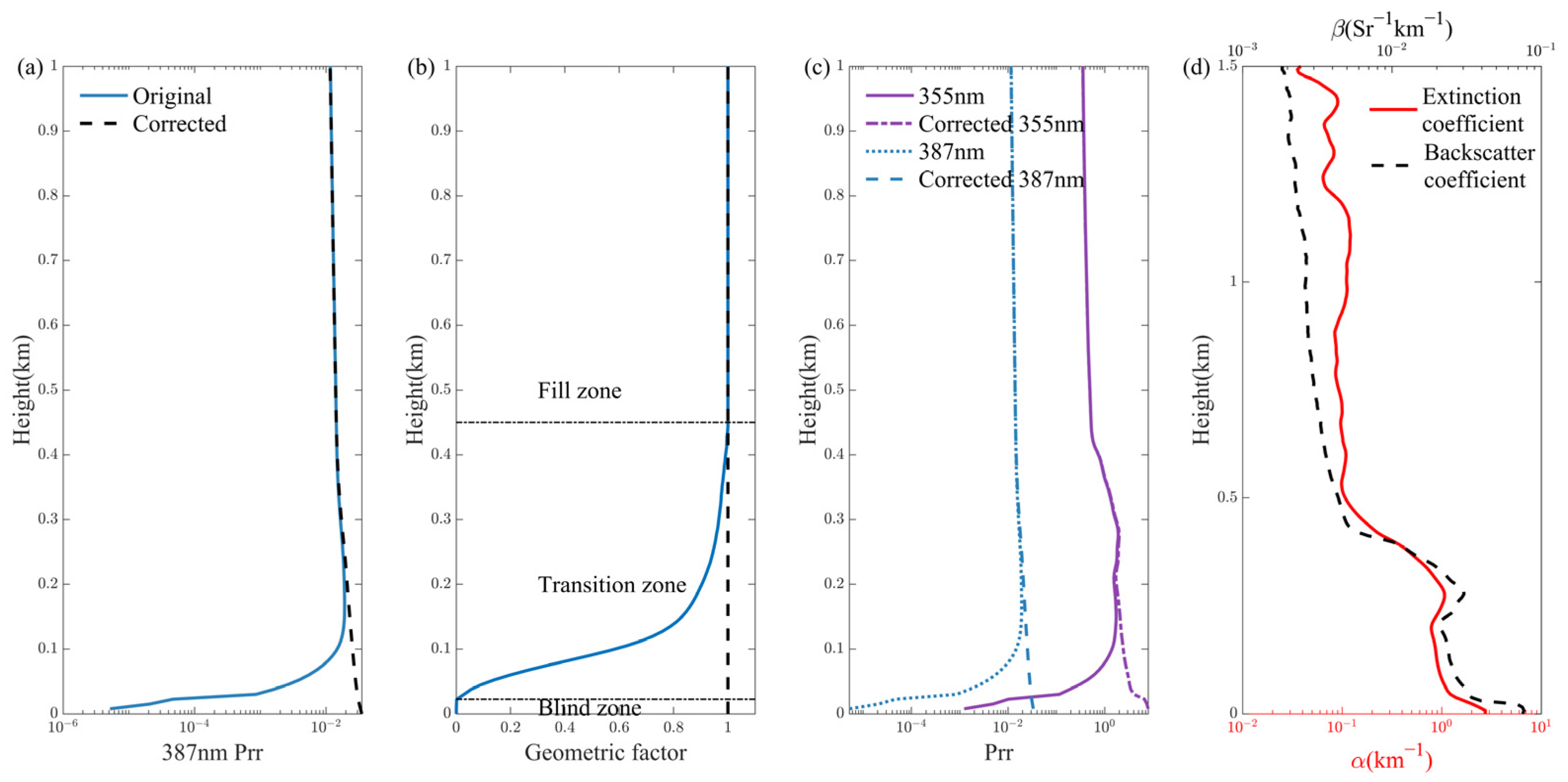
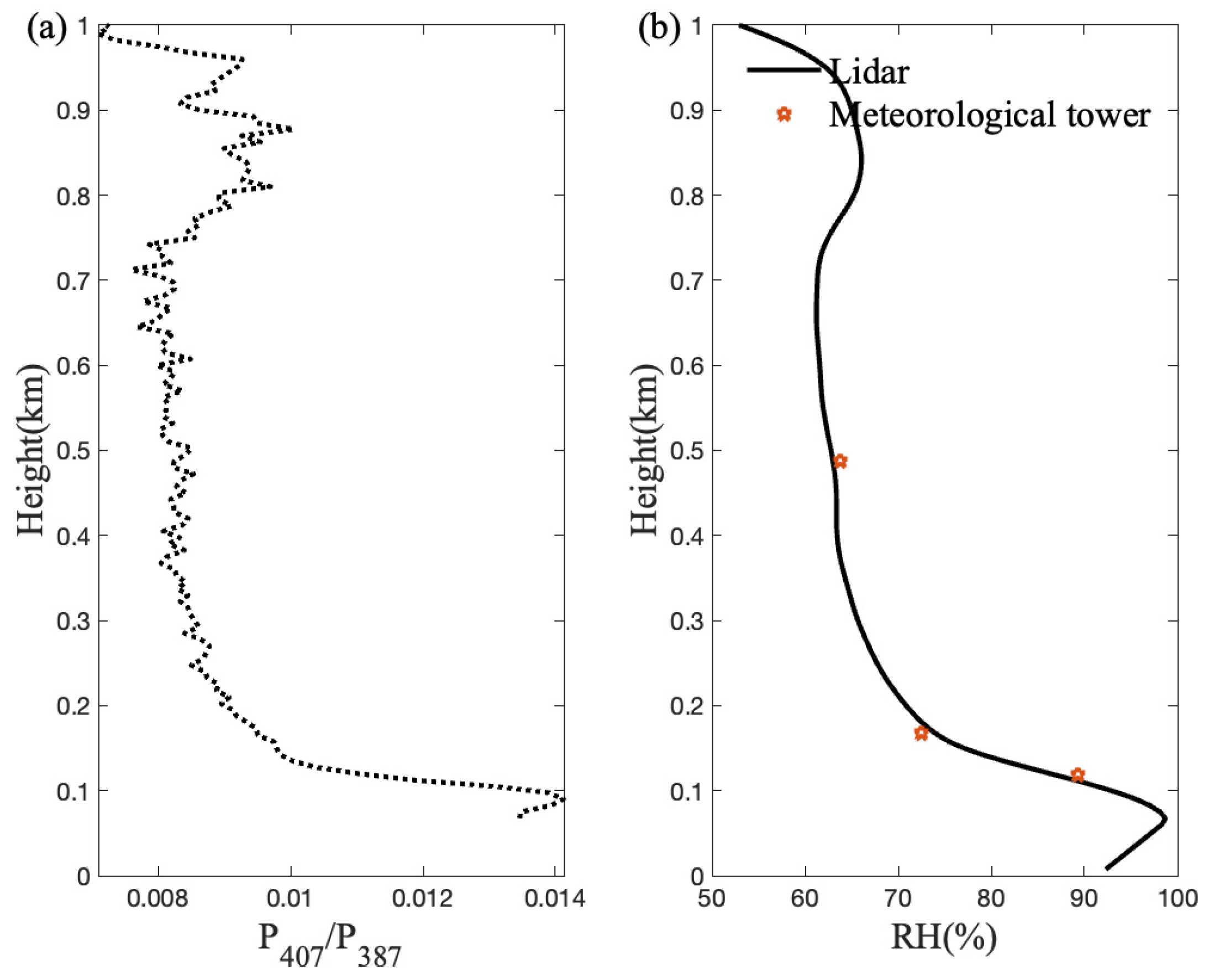
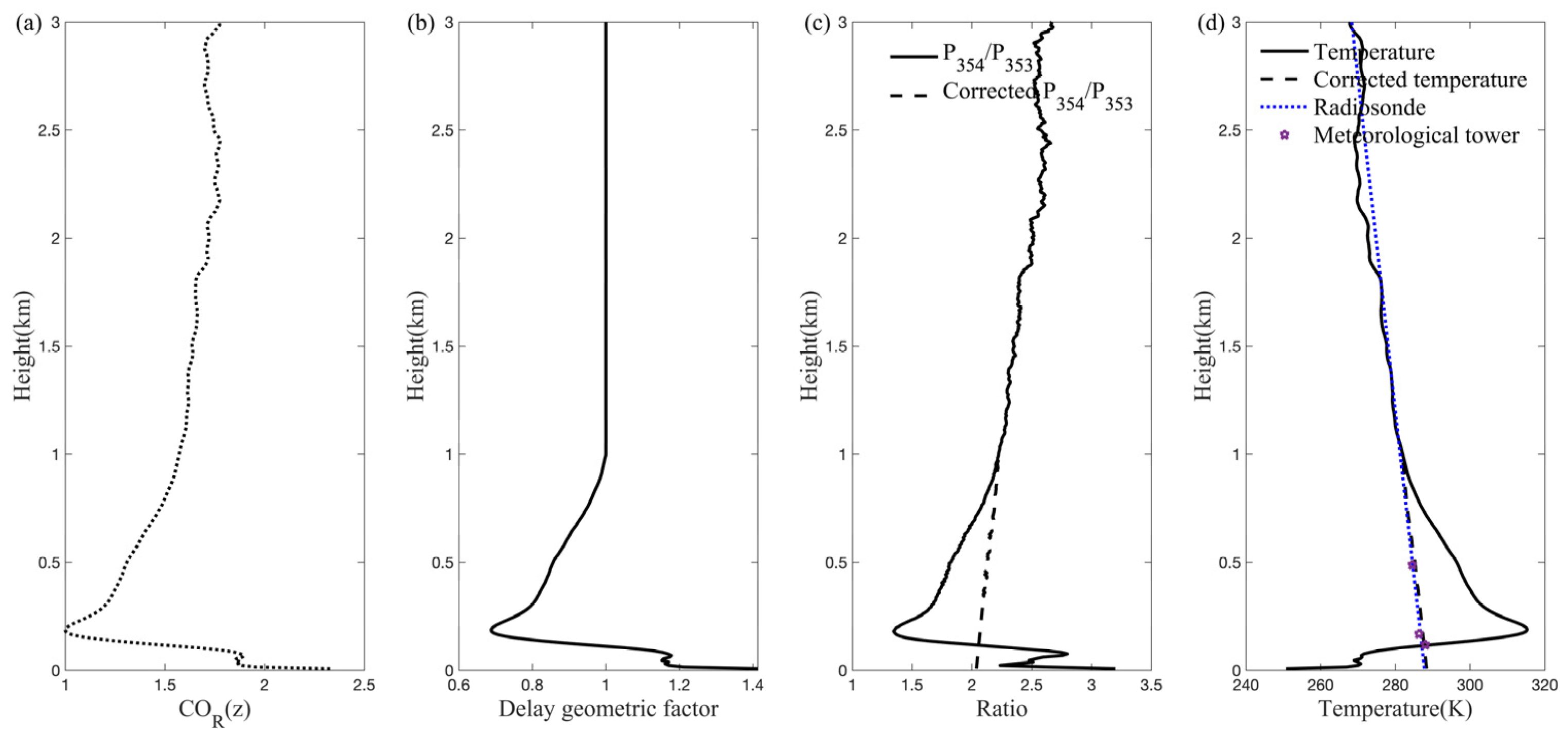
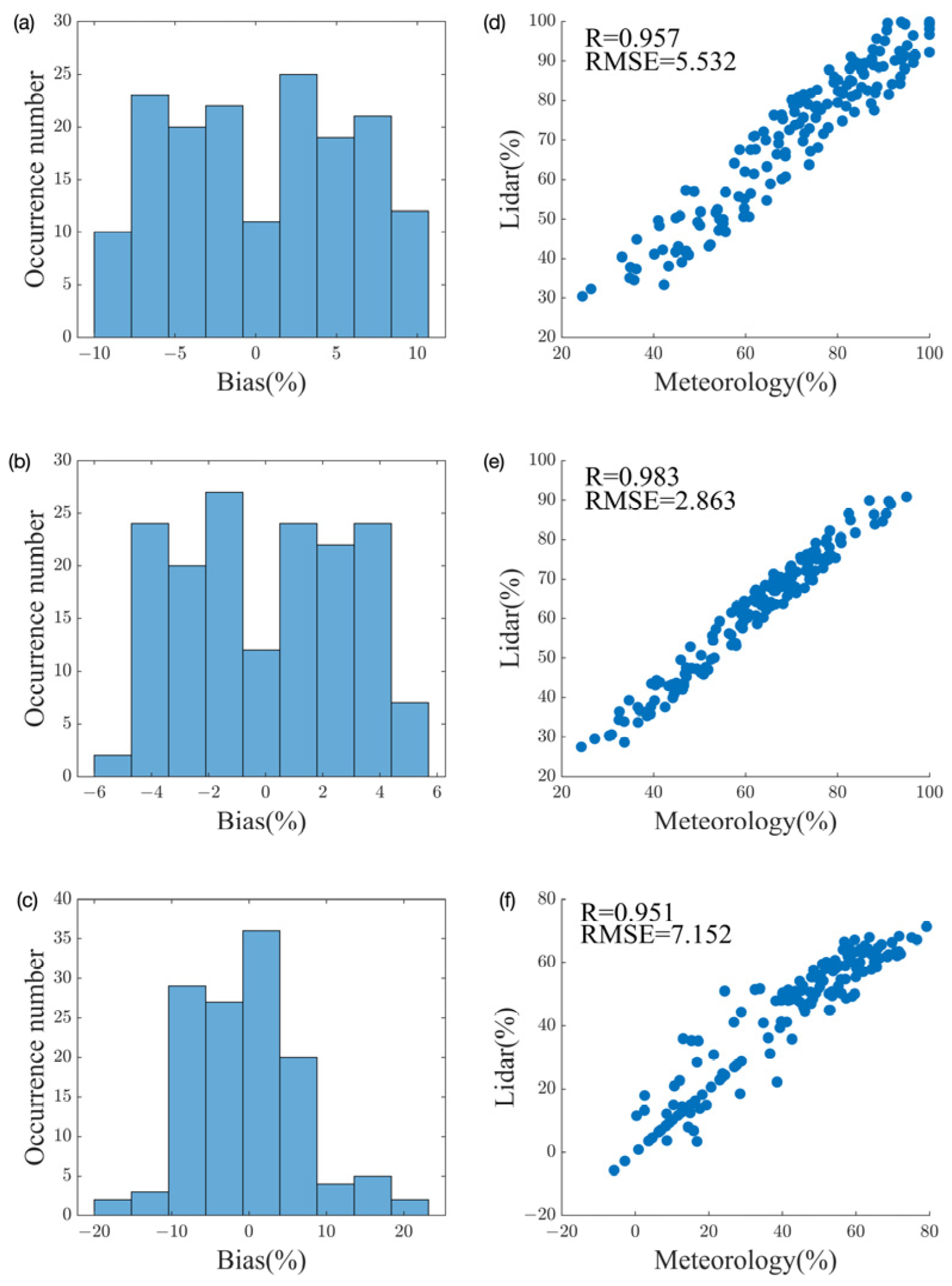
3.1. Analysis of Single-Profile Correction
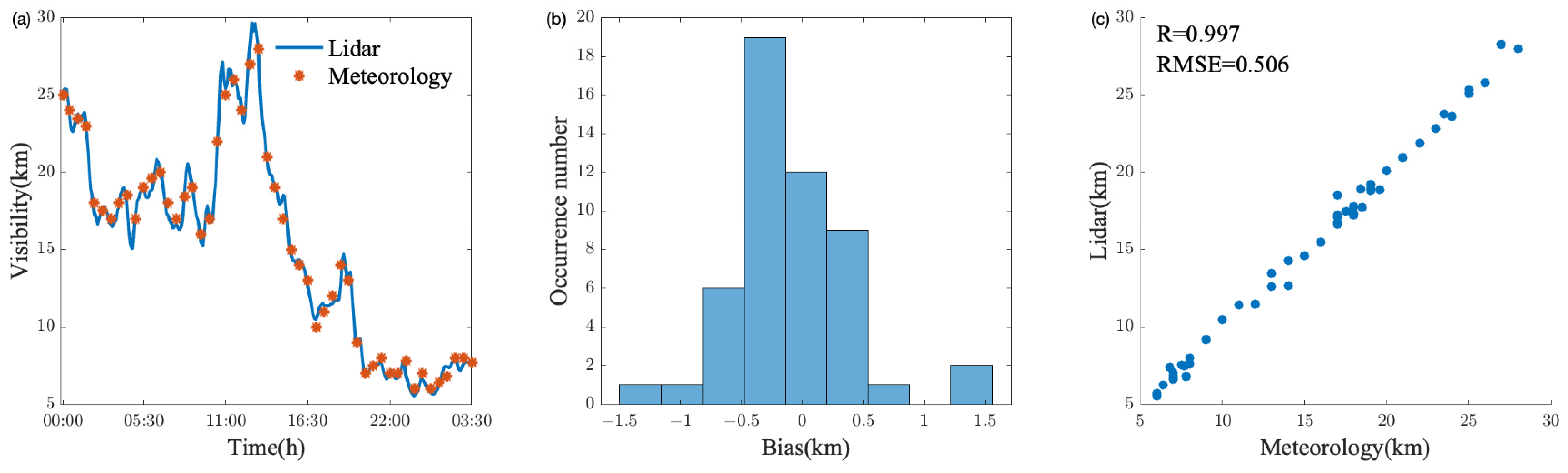
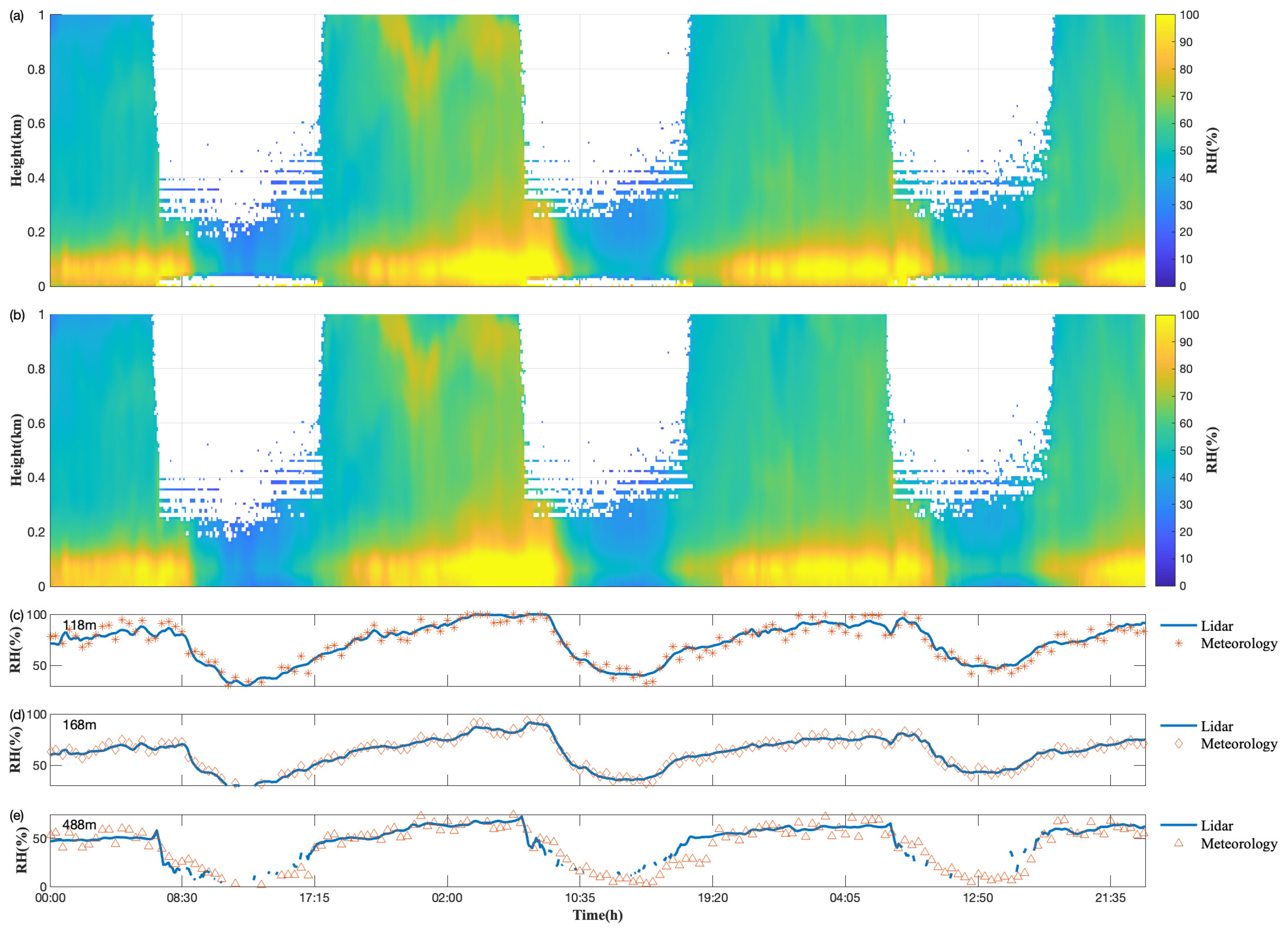
3.2. Analysis of Continuous Profile Correction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veselovskii, I.; Kolgotin, A.; Griaznov, V.; Müller, D.; Franke, K.; Whiteman, D.N. Inversion of multiwavelength Raman lidar data for retrieval of bimodal aerosol size distribution. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 1180–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, D.; Behrendt, A.; Wulfmeyer, V. Compact Operational Tropospheric Water Vapor and Temperature Raman Lidar with Turbulence Resolution. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 14844–14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Guo, P. Aerosol characteristics inversion based on the improved lidar ratio profile with the ground-based rotational Raman–Mie lidar. Opt. Commun. 2018, 416, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Nishizawa, T.; Sugimoto, N. Retrieval of Aerosol Components Using Multi-Wavelength Mie-Raman Lidar and Comparison with Ground Aerosol Sampling. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.; Fallmann, J.; Carvalho, A.; Rocha, A. Surface to boundary layer coupling in the urban area of Lisbon comparing different urban canopy models in WRF. Urban Clim. 2019, 28, 100454–100470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Hu, H. Geometrical form factor determination with Raman backscattering signals. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 1879–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hey, J. Determination of Lidar Overlap; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 81–106. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Mao, F.; Li, J. OFLID: Simple method of overlap factor calculation with laser intensity distribution for biaxial lidar. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 2966–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gong, W.; Mao, F.; Pan, Z. Physical constraint method to determine optimal overlap factor of Raman lidar. J. Opt. 2018, 47, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomine, K.; Hirayama, C.; Michimoto, K.; Takeuchi, N. Experimental determination of the crossover function in the laser radar equation for days with a light mist. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 2194–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuze, H.; Kinjo, H.; Sakurada, Y.; Takeuchi, N. Field-of-view dependence of lidar signals by use of Newtonian and Cassegrainian telescopes. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 3128–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; McCormick, M.; Liu, Z.; Leavor, K.H.; Lee, R.B.; Lewis, J.; Hill, M.T. Obtaining a ground-based lidar geometric form factor using coincident spaceborne lidar measurements. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger, U.; Ansmann, A. Experimental determination of the lidar overlap profile with Raman lidar. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, P.; Chen, H. Calibration method for the reference parameter in Fernald and Klett inversion combining Raman and Elastic return. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 188, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Wandinger, U.; Riebesell, M.; Weitkamp, C.; Michaelis, W. Independent measurement of extinction and backscatter profiles in cirrus clouds by using a combined Raman elastic-backscatter lidar. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 7113–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z. Feasibility study of water vapor and temperature retrieval using a combined vibrational rotational Raman and Mie scattering multi-wavelength lidar. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere, Clouds, and Precipitation V, Beijing, China, 13–16 October 2014; Volume 9259. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteman, D. Examination of the traditional Raman lidar technique. I. Evaluating the temperature-dependent lidar equations. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 2571–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, D. Examination of the traditional Raman lidar technique. II. Evaluating the ratios for water vapor and aerosols. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 2593–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrare, R.; Melfi, S.; Whiteman, D.; Evans, K.D.; Leifer, R. Raman lidar measurements of aerosol extinction and backscattering: 1. Methods and comparisons. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 19663–19672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Kim, Y.; Baik, S.; Park, S.; Cha, H.; Choi, S.; Chung, C.; Kim, D. Measurement of Aerosol Parameters with Altitude by Using Two Wavelength Rotational Raman Signals. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2010, 14, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penney, C.; Peters, R.; Lapp, M. Absolute rotational Raman cross sections for N2, O2, and CO2. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1974, 64, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yi, F. Lidar-measured atmospheric N2 vibrational-rotational Raman spectra and consequent temperature retrieval. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 27833–27844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrendt, A. Temperature Measurements with Lidar. In Lidar. Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere; Weitkamp, C., Ed.; Springer Series in Optical Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 102, pp. 273–305. ISBN 0-387-40075-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zenteno-Hernández, J.A.; Comerón, A.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Muñoz-Porcar, C.; D’Amico, G.; Sicard, M. A Comparative Analysis of Aerosol Optical Coefficients and Their Associated Errors Retrieved from Pure-Rotational and Vibro-Rotational Raman Lidar Signals. Sensors 2021, 21, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Fu, Y.; Pei, C.; Lou, S.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W. Accuracy Evaluation of Differential Absorption Lidar for Ozone Detection and Intercomparisons with Other Instruments. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.; Cho, S.; Yun, C.; Sohn, H. Finite element model updating of Canton Tower using regularization technique. Smart Struct. Syst. 2012, 10, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Multi-dimensional sensor placement optimization for Canton Tower focusing on application demands. Smart Struct. Syst. 2013, 12, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschmieder, H. Theorie der horizontalen Sichtweite. Beitrz Physd Freien Atm. 1924, 12, 33–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, B. Overlap determination for temperature measurements from a pure rotational Raman lidar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2805–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerón, A.; Muñoz-Porcar, C.; Rodríguez-Gómez, A.; Sicard, M.; Dios, F.; Gil-Díaz, C.; Oliveira, D.C.F.d.S.; Rocadenbosch, F. An explicit formulation for the retrieval of the overlap function in an elastic and Raman aerosol lidar. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, P. Determination of Geometric Factor for Ground-Based Raman-Mie Lidar with Bi-Static Configuration. Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2019, 39, 644–649. [Google Scholar]

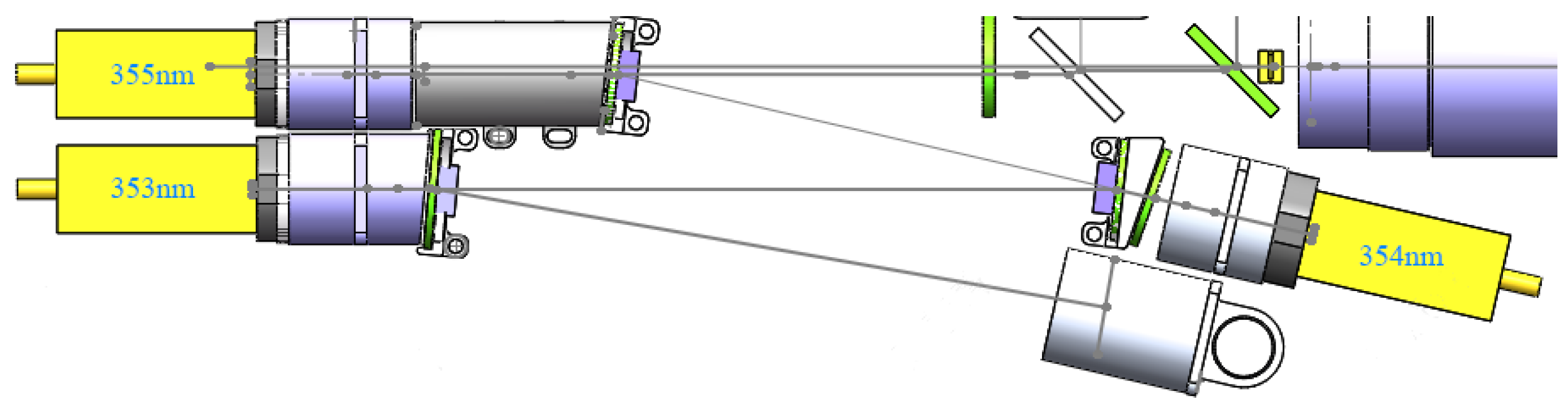





| Laser: Nd: YAG | Receiver: Newton Telescope | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength/(nm) | 355, 532 | Diameter/(mm) | 300 |
| Energy/(mJ) | 3.5, 1.5 | Iris/(mrad) | 1.0 |
| Repetition rate/(Hz) | 2000 | Optical efficiency | 0.3 |
| Divergence/(mrad) | 0.5 | Interference filter bandwidth/(nm) | 0.3–0.5 |
| Temporal resolution/(min) | 5 | Range resolution/(m) | 7.5 |
| Data acquisition | AD + PC | Detector | PMT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Fan, G.; Zhang, T. Geometric Factor Correction Algorithm Based on Temperature and Humidity Profile Lidar. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162977
Zhang B, Fan G, Zhang T. Geometric Factor Correction Algorithm Based on Temperature and Humidity Profile Lidar. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162977
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bowen, Guangqiang Fan, and Tianshu Zhang. 2024. "Geometric Factor Correction Algorithm Based on Temperature and Humidity Profile Lidar" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162977
APA StyleZhang, B., Fan, G., & Zhang, T. (2024). Geometric Factor Correction Algorithm Based on Temperature and Humidity Profile Lidar. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162977








