Spatially Interpolated CYGNSS Data Improve Downscaled 3 km SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture
Abstract
1. Introduction
CYGNSS Background
2. Materials and Methods
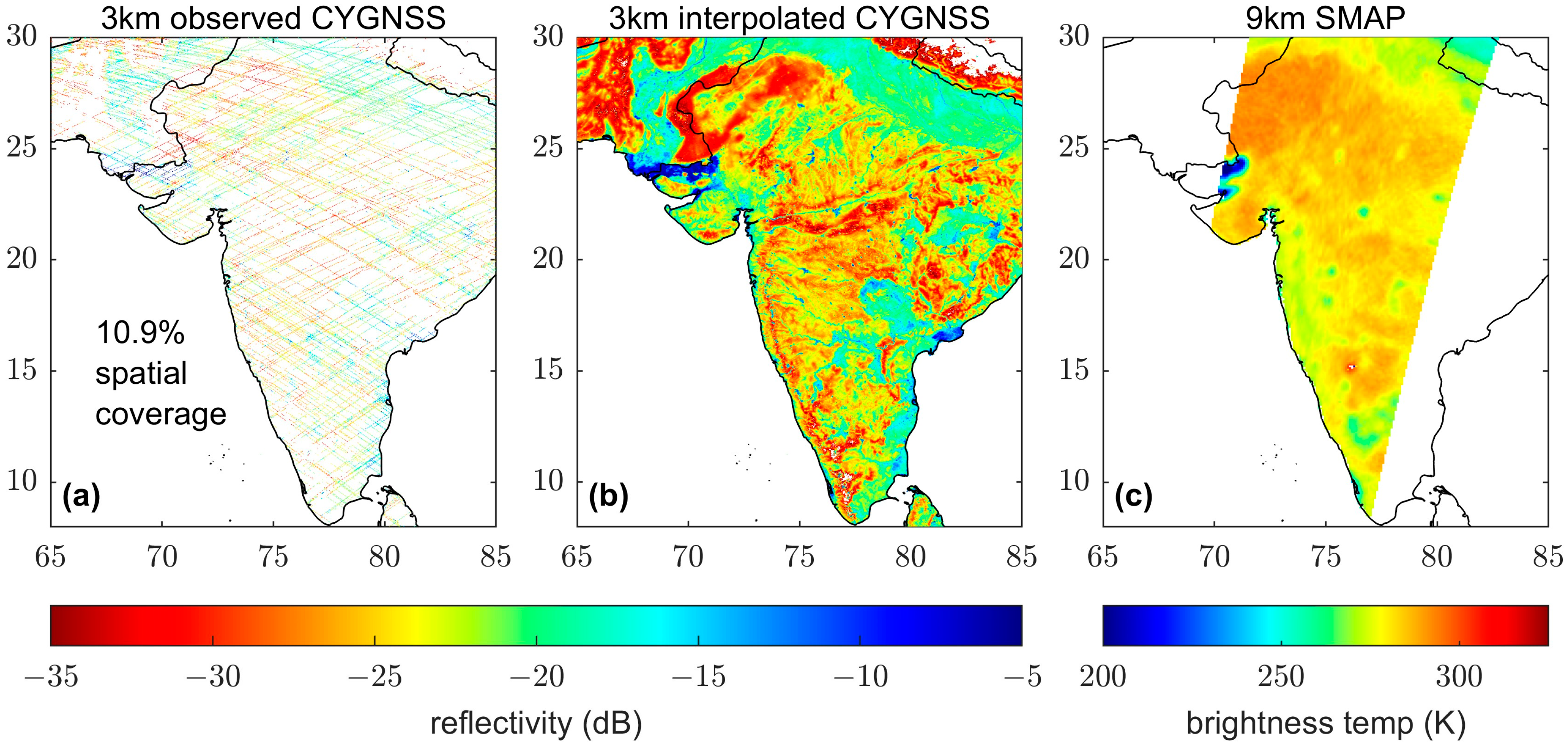
2.1. Deriving CYGNSS Reflectivity
Interpolated CYGNSS Reflectivity
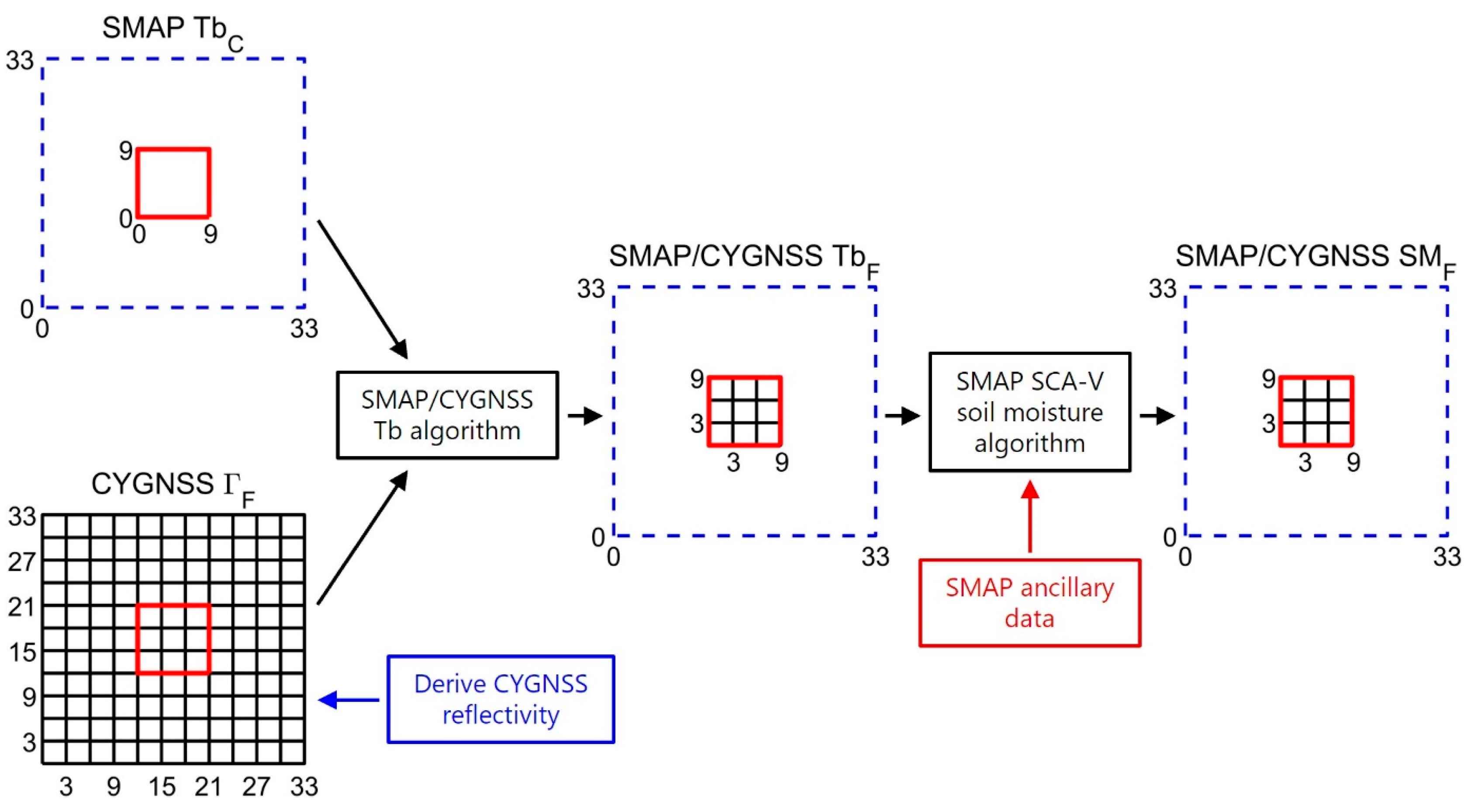
2.2. The SMAP/CYGNSS Brightness Temperature Algorithm
Interpolated Versus Observed SMAP/CYGNSS Brightness Temperatures
2.3. Calculating SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture
3. Results
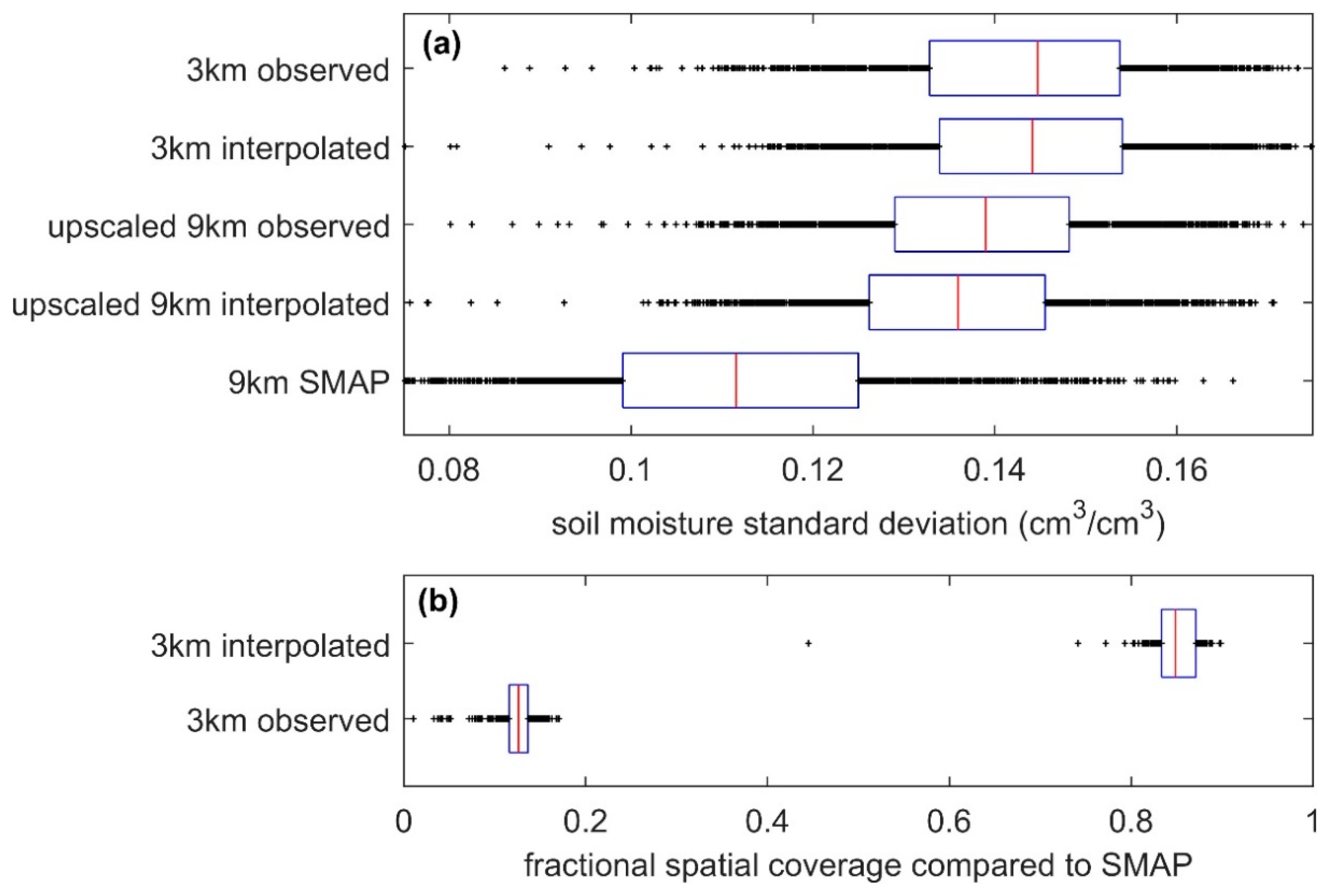
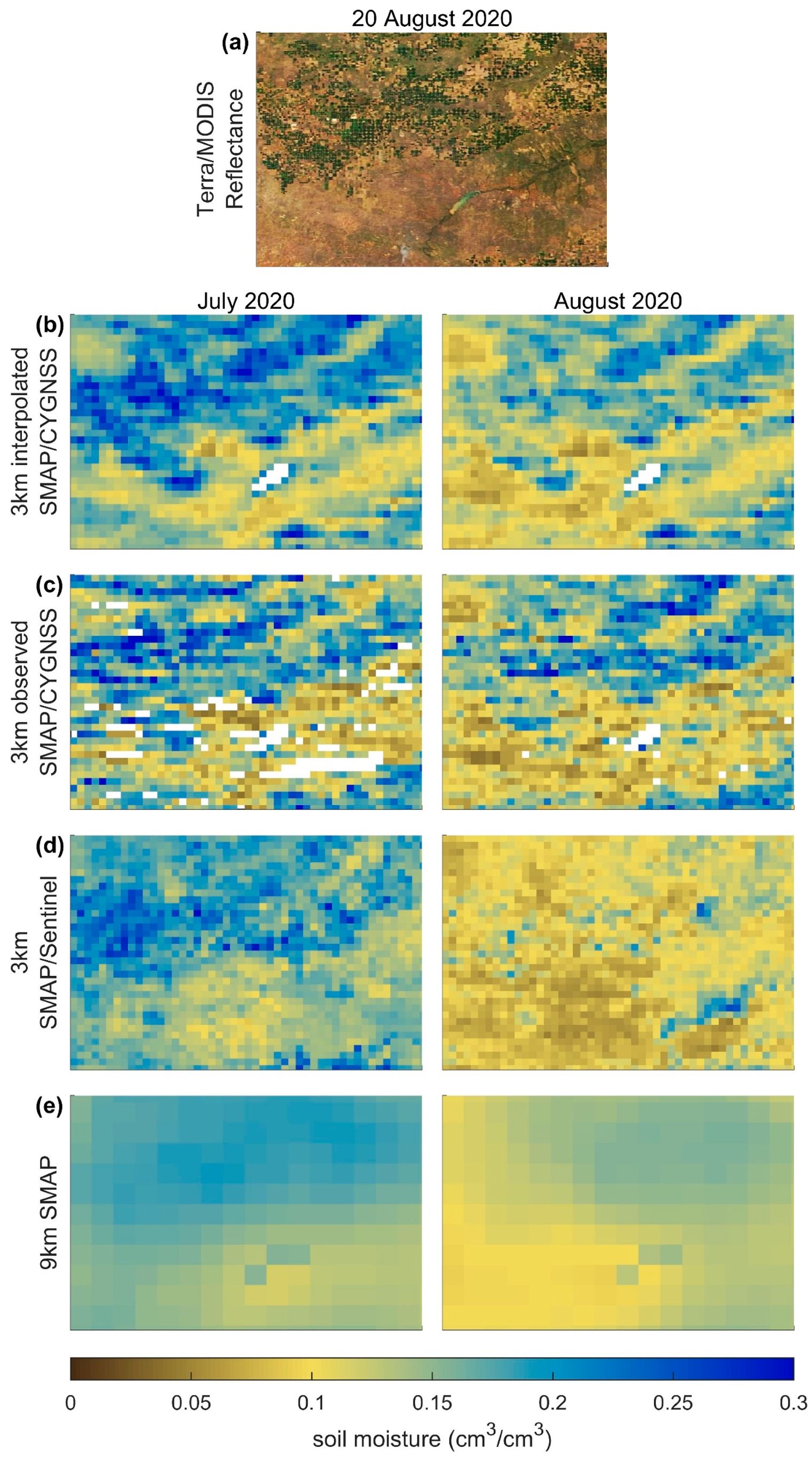
3.1. Spatial Heterogeneity and Spatial Detail
3.2. Spatial Coverage and Repeat Period
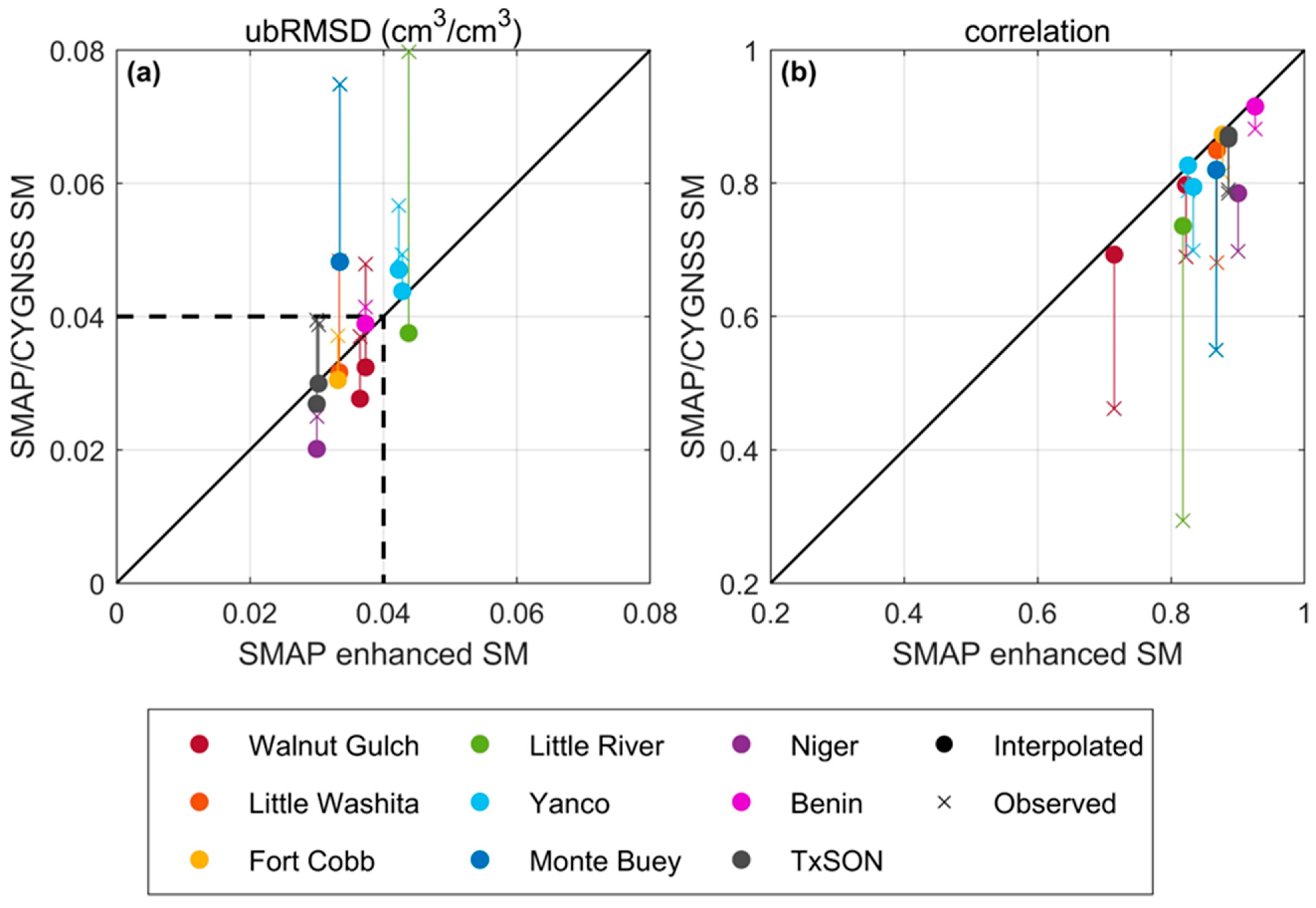
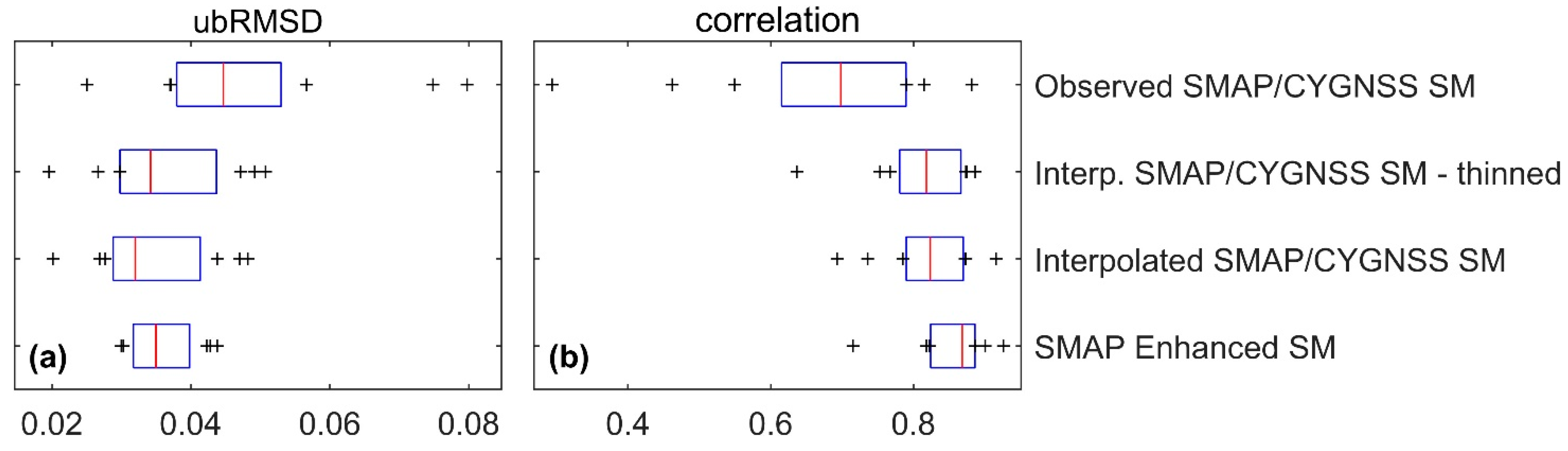
3.3. Validating SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture with SMAP Core Validation Sites
3.4. Validating SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture with Sparse Networks
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Other Fine-Resolution Soil Moistures
4.2. Uncertainties and Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, J.; Albergel, C.; Balenzano, A.; Brocca, L.; Cartus, O.; Cosh, M.H.; Crow, W.T.; Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Dadson, S.; Davidson, M.W.J.; et al. A Roadmap for High-Resolution Satellite Soil Moisture Applications—Confronting Product Characteristics with User Requirements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS Mission: New Tool for Monitoring Key Elements of the Global Water Cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Chan, T.K.; Nghiem, S.V. Soil Moisture Retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. Remote Sensing of Environment GMES Sentinel-1 Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, K.; Rosen, P.; Barela, P.; Hoffman, P.; Edelstein, W.; Standley, S.; Dunn, C.; Guerrero, A.M.; Harinath, N.; Shaffer, S.; et al. NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) Mission. In Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, Montana, USA, 7–14 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Entekhabi, D.; Yueh, S.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Allen, A.; Bindlish, R.; Brown, M.; Chan, S.; Colliander, A.; Crow, W.T.; et al. SMAP Handbook: Soil Moisture Active Passive: Mapping Soil Moisture and Freeze/Thaw from Space; Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Das, N.; Entekhabi, D.; Dunbar, R.S.; Chaubell, M.J.; Colliander, A.; Yueh, S.; Jagdhuber, T.; Chen, F.; Crow, W.; O’Neill, P.E.; et al. The SMAP and Copernicus Sentinel 1A/B Microwave Active-Passive High Resolution Surface Soil Moisture Product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.K.; Bindlish, R.; Neill, P.O.; Jackson, T.; Njoku, E.; Dunbar, S.; Chaubell, J.; Piepmeier, J.; Yueh, S.; Entekhabi, D.; et al. Development and Assessment of the SMAP Enhanced Passive Soil Moisture Product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Merlin, O.; Verhoest, N.E.C. A Review of Spatial Downscaling of Satellite Remotely Sensed Soil Moisture. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Entekhabi, D.; Dunbar, R.S.; Colliander, A.; Chen, F.; Crow, W.; Jackson, T.J.; Berg, A.; Bosch, D.D.; Caldwell, T.; et al. The SMAP Mission Combined Active-Passive Soil Moisture Product at 9 km and 3 km Spatial Resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Peng, J.; Meng, L. Downscaling SMAP Soil Moisture Estimation with Gradient Boosting Decision Tree Regression over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Sánchez, N.; Lu, H.; Li, A. A Spatial Downscaling Approach for the SMAP Passive Surface Soil Moisture Product Using Random Forest Regression. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, P.; Moradkhani, H.; Zhan, X. Downscaling SMAP Radiometer Soil Moisture Over the CONUS Using an Ensemble Learning Method. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 324–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yao, N.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.; Hu, A.; Gustavo Goncalves De Goncalves, L.; Liu, G. Downscaling SMAP Soil Moisture Using a Wide & Deep Learning Method over the Continental United States. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J. Downscaling of SMAP Soil Moisture Using Land Surface Temperature and Vegetation Data. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandridge, C.; Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V. Downscaling of SMAP Soil Moisture in the Lower Mekong River Basin. Water 2019, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Lakshmi, V.; Cosh, M.; Liu, P.-W.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J. A Global 1-km Downscaled SMAP Soil Moisture Product Based on Thermal Inertia Theory. Vadose Zone J. 2022, 21, e20182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Merlin, O.; Molero, B.; Suere, C.; Olivera-Guerra, L.; Ait Hssaine, B.; Amazirh, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Escorihuela, M.; Er-Raki, S. Stepwise Disaggregation of SMAP Soil Moisture at 100 m Resolution Using Landsat-7/8 Data and a Varying Intermediate Resolution. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Fisher, J.B.; Halverson, G.; Merlin, O.; Misra, S.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J.; Yueh, S. Spatial Downscaling of SMAP Soil Moisture Using MODIS Land Surface Temperature and NDVI During SMAPVEX15. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2107–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Ellenburg, W.L.; Griffin, R.E.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Cruise, J.F.; Hain, C.R.; Anderson, M.C. An Initial Assessment of a SMAP Soil Moisture Disaggregation Scheme Using TIR Surface Evaporation Data over the Continental United States. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; He, Y.; Zhang, X. NIR-Red Spectra-Based Disaggregation of SMAP Soil Moisture to 250 m Resolution Based on OzNet in Southeastern Australia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montzka, C.; Rötzer, K.; Bogena, H.; Sanchez, N.; Vereecken, H. A New Soil Moisture Downscaling Approach for SMAP, SMOS, and ASCAT by Predicting Sub-Grid Variability. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, L.J.; Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E.; Das, N.N. Downscaling SMAP Brightness Temperatures to 3 Km Using CYGNSS Reflectivity Observations: Factors That Affect Spatial Heterogeneity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.; Chang, P.; Clarizia, M.P.; Gleason, S.; Jalenak, Z.; Majumdar, S.; Morris, M.; Murray, J.; Musko, S.; Posselt, D.; et al. CYGNSS Handbook: Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System: Deriving Surface Wind Speeds in Tropical Cyclones; University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-60785-380-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, C. Spatial Interpolation Based on Previously-Observed Behavior: A Framework for Interpolating Spaceborne GNSS-R Data from CYGNSS. J. Spat. Sci. 2021, 2021, 1942253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernicke, L.J.; Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E. 3km SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture, version 1; Zenodo: Boston, MA, USA, 2024. [Dataset]. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/10402590 (accessed on 23 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E. Soil Moisture Sensing Using Spaceborne GNSS Reflections: Comparison of CYGNSS Reflectivity to SMAP Soil Moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4049–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.; Small, E. Description of the UCAR/CU Soil Moisture Product. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lakshmi, V. Use of Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CyGNSS) Observations for Estimation of Soil Moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8272–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, M.P.; Pierdicca, N.; Costantini, F.; Floury, N. Analysis of Cygnss Data for Soil Moisture Retrieval. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W.; Jin, S.; Jia, Y. Pan-Tropical Soil Moisture Mapping Based on a Three-Layer Model from CYGNSS GNSS-R Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khaldi, M.M.; Johnson, J.T.; O’Brien, A.J.; Balenzano, A.; Mattia, F. Time-Series Retrieval of Soil Moisture Using CYGNSS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4322–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khaldi, M.M.; Johnson, J.T. Soil Moisture Retrievals Using CYGNSS Data in a Time-Series Ratio Method: Progress Update and Error Analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 3003505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, O.; Kurum, M.; Boyd, D.; Gurbuz, A.C. High Spatio-Temporal Resolution Cygnss Soil Moisture Estimates Using Artificial Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senyurek, V.; Lei, F.; Boyd, D.; Kurum, M.; Gurbuz, A.C.; Moorhead, R. Machine Learning-Based CYGNSS Soil Moisture Estimates over ISMN Sites in CONUS. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, M.M.; Senyurek, V.; Gurbuz, A.C.; Kurum, M. Deep Learning-Based Soil Moisture Retrieval in CONUS Using CYGNSS Delay–Doppler Maps. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 6867–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Senyurek, V.; Kurum, M.; Gurbuz, A.C.; Boyd, D.; Moorhead, R.; Crow, W.T.; Eroglu, O. Quasi-Global Machine Learning-Based Soil Moisture Estimates at High Spatio-Temporal Scales Using CYGNSS and SMAP Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 276, 113041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzberg, S.J.; Garrison, J.L. Utilizing GPS to Determine Ionospheric Delay over the Ocean; NASA Technical Memorandum 4750; NASA: Hampton, VA, USA, 1996; pp. 1–16.
- CYGNSS. CYGNSS Level 1 Science Data Record, version 2.1; NASA Physical Oceanography Distributed Active Archive Center: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2018; [Dataset]. Available online: https://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/dataset/CYGNSS_L1_V2.1 (accessed on 23 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Brodzik, M.J.; Billingsley, B.; Haran, T.; Raup, B.; Savoie, M.H. EASE-Grid 2.0: Incremental but Significant Improvements for Earth-Gridded Data Sets. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inform. 2012, 1, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E. UCAR/CU CYGNSS Soil Moisture Product: User Guide; University Corporation for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, P.E.; Chan, S.; Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R.; Chaubell, J.; Colliander, A. SMAP Enhanced L3 Radiometer Global and Polar Grid Daily 9 Km EASE-Grid Soil Moisture, version 5; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2021; [Dataset]. Available online: https://nsidc.org/data/spl3smp_e/versions/5 (accessed on 23 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Entekhabi, D. Passive Microwave Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture. J. Hydrol. 1996, 184, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.E.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Chaubell, J.; Njoku, E.; Jackson, T. Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP): Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Level 2 & 3 Soil Moisture (Passive) Data Products; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mironov, V.L.; Kosolapova, L.G.; Fomin, S.V. Physically and Mineralogically Based Spectroscopic Dielectric Model for Moist Soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Asanuma, J.; Berg, A.; Bongiovanni, T.; Bosch, D.; Caldwell, T.; Holifield-Collins, C.; Jensen, K. SMAP/In Situ Core Validation Site Land Surface Parameters Match-Up Data, version 1; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017; [Dataset]. Available online: https://nsidc.org/data/nsidc-0712/versions/1 (accessed on 23 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; O’Neill, P.E. Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP): Ancillary Data Report: Soil Attributes; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.; Bindlish, R.; Hunt, R.; Jackson, T.; Kimball, J. Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP): Ancillary Data Report: Vegetation Water Content; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schaap, M.G. Rosetta Model; Agricultural Water Efficiency and Salinity Research Unit, USDA: Riverside, CA, USA, 1999.
- Vermote, E.; Wolfe, R. MODIS/Terra Surface Reflectance Daily L2G Global 1 km and 500 m SIN Grid V061; NASA EOSDIS Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2021; [Dataset]. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod09gav061/ (accessed on 23 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Entekhabi, D.; Dunbar, R.S.; Kim, S.; Yueh, S.; Colliander, A.; O’Neill, P.E.; Jackson, T.; Jagdhuber, T.; Chen, F.; et al. SMAP/Sentinel-1 L2 Radiometer/Radar 30-Second Scene 3 Km EASE-Grid Soil Moisture, version 3; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2020; [Dataset]. Available online: https://nsidc.org/data/spl2smap_s/versions/3 (accessed on 23 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Colliander, A.; Jackson, T.J.; Bindlish, R.; Chan, S.; Das, N.; Kim, S.B.; Cosh, M.H.; Dunbar, R.S.; Dang, L.; Pashaian, L.; et al. Validation of SMAP Surface Soil Moisture Products with Core Validation Sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiovanni, T.; Caldwell, T. Texas Soil Observation Network (TxSON), Version 5; Texas Data Repository: Austin, TX, USA, 2019. [Dataset]. Available online: https://dataverse.tdl.org/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.18738/T8/JJ16CF (accessed on 23 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.; Himmelbauer, I.; Aberer, D.; Schremmer, L.; Petrakovic, I.; Zappa, L.; Preimesberger, W.; Xaver, A.; Annor, F.; Ardö, J.; et al. The International Soil Moisture Network: Serving Earth System Science for over a Decade. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 5749–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, G.L.; Cosh, M.H.; Jackson, T.J. The USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Soil Climate Analysis Network (SCAN). J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 2073–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.E.; Palecki, M.A.; Baker, C.B.; Collins, W.G.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Leeper, R.D.; Hall, M.E.; Kochendorfer, J.; Meyers, T.P.; Wilson, T.; et al. U.S. Climate Reference Network Soil Moisture and Temperature Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B.; Walker, J.P.; Western, A.W.; Young, R.I.; Ellett, K.M.; Pipunic, R.C.; Grayson, R.B.; Siriwardena, L.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Richter, H. The Murrumbidgee Soil Moisture Monitoring Network Data Set. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 2012WR011976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, S. Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS): Level 1B DDM Calibration Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. Rev 3; CYGNSS Project Document. 2020. Available online: http://cygnss.engin.umich.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/534/2021/07/148-0137_ATBD-L1B-DDM-Calibration_R3_release.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Das, N.; Entekhabi, D.; Dunbar, S.; Colliander, A.; Chaubell, M.; Yueh, S.; Jagdhuber, T.; O’Neill, P.E.; Crow, W.; Chen, F. Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP): Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: SMAP-Sentinel L2 Radar/Radiometer Soil Moisture (Active/Passive) Data Products: L2_SM_SP; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- SMAP Algorithm Development Team; SMAP Science Team. Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP): Ancillary Data Report: Surface Temperature; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Unwin, M.J.; Pierdicca, N.; Cardellach, E.; Rautiainen, K.; Foti, G.; Blunt, P.; Guerriero, L.; Santi, E.; Tossaint, M. An Introduction to the HydroGNSS GNSS Reflectometry Remote Sensing Mission. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6987–6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jales, P.; Cartwright, J.; Talpe, M.; Mashburn, J.; Yuasa, T.; Nogues-Correig, O.; Nguyen, V.; Freeman, V. Spire Global’s Operational GNSS-Reflectometry Constellation for Earth Surface Observations. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023–2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16 July 2023; pp. 884–887. [Google Scholar]




| Sparse Network | Location | Sensor Depth (cm) | Number of Sites | Avg. ubRMSD (cm3/cm3) | Avg. Correlation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs. | Interp. | Obs. | Interp. | ||||
| SCAN 1 | United States | 5 | 35 | 0.060 | 0.050 | 0.54 | 0.63 |
| USCRN 2 | United States | 5 | 23 | 0.055 | 0.044 | 0.57 | 0.65 |
| OzNet 3 | Southeast Australia | 0–5 | 9 | 0.073 | 0.063 | 0.61 | 0.69 |
| TAHMO 4 | Central Africa (Ghana and Kenya) | 10 | 17 | 0.059 | 0.058 | 0.74 | 0.75 |
| All: | 84 | 0.060 | 0.051 | 0.60 | 0.67 | ||
| SMAP CVS ubRMSD (cm3/cm3) | SMAP CVS Correlation | Sparse Network ubRMSD (cm3/cm3) | Sparse Network Correlation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed SMAP/CYGNSS | 0.048 | 0.68 | 0.060 | 0.60 |
| Interpolated SMAP/CYGNSS | 0.035 | 0.82 | 0.051 | 0.67 |
| SMAP active–passive | 0.039 | 0.66 | ~0.055 | n/a * |
| SMAP/Sentinel | 0.036 | 0.83 | 0.050 | 0.59 |
| Uncertainty Parameter | Uncertainty Estimate | Interpolated SM RMSE (cm3/cm3) | Observed SM RMSE (cm3/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Veg. Opt. Depth | 5% | 0.0065 | 0.0068 |
| % clay | 5% | 0.0025 | 0.0027 |
| Roughness | 5% | 0.0009 | 0.0009 |
| SSA | 5% | 0.0077 | 0.0072 |
| 9 km Tb | 1.3 K | 0.0136 | 0.0131 |
| Surf. Temp. | 2 K | 0.0184 | 0.0176 |
| SMAP/CYG | 20% | 0.0151 | 0.0174 |
| CYGNSS | 2 dB | 0.0619 | 0.0664 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wernicke, L.J.; Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E. Spatially Interpolated CYGNSS Data Improve Downscaled 3 km SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162924
Wernicke LJ, Chew CC, Small EE. Spatially Interpolated CYGNSS Data Improve Downscaled 3 km SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(16):2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162924
Chicago/Turabian StyleWernicke, Liza J., Clara C. Chew, and Eric E. Small. 2024. "Spatially Interpolated CYGNSS Data Improve Downscaled 3 km SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture" Remote Sensing 16, no. 16: 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162924
APA StyleWernicke, L. J., Chew, C. C., & Small, E. E. (2024). Spatially Interpolated CYGNSS Data Improve Downscaled 3 km SMAP/CYGNSS Soil Moisture. Remote Sensing, 16(16), 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16162924












