Laser Observations of GALILEO Satellites at the CBK PAN Astrogeodynamic Observatory in Borowiec
Abstract
1. Introduction
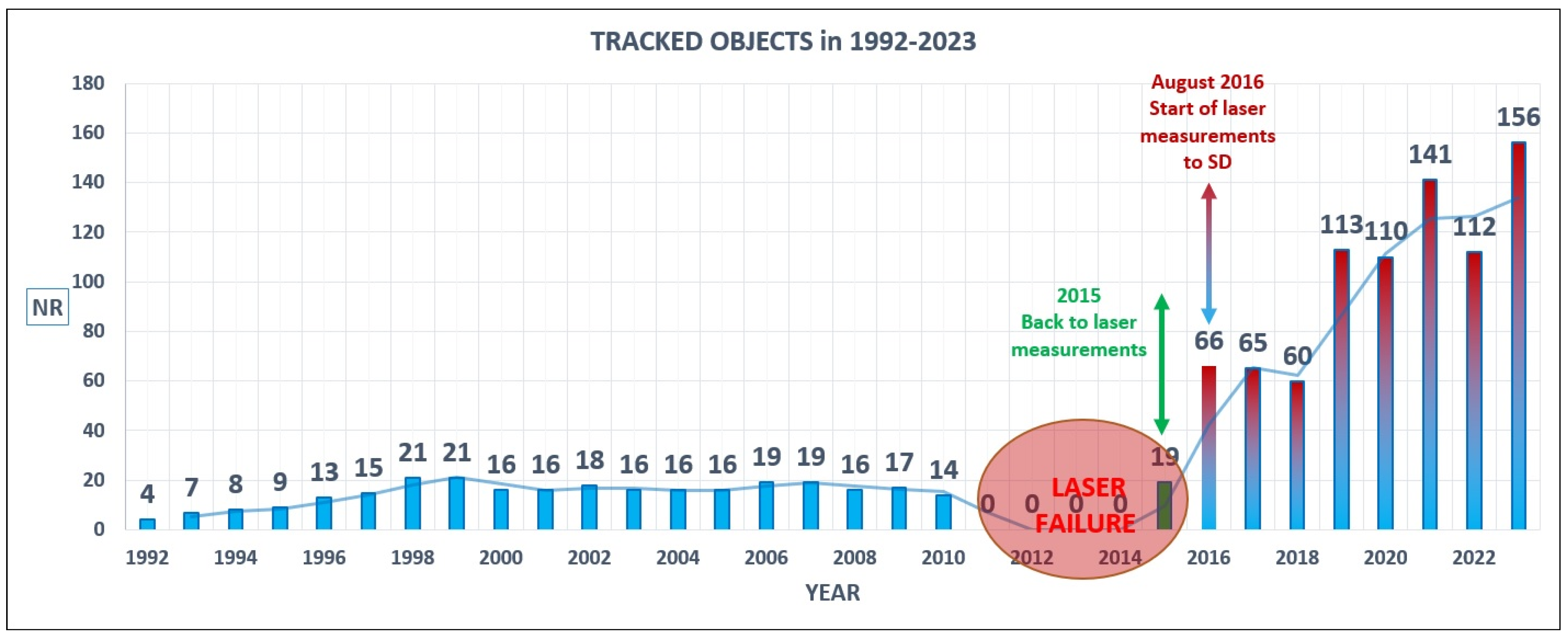
2. Laser Sensor at CBK PAN Borowiec (BORL)
- Station code: BORL;
- Station number: 7811;
- Country: Poland;
- CDDIS SOD database number: 78113802;
- IERS DOMES database number: 12205S001.
- Performing continuous observations of laser satellites covered by the ILRS.
- Supporting missions such as LAGEOS-1, LAGEOS-2, LARES, LARES-2, GRACE, and others for the needs of modern geodesy and geodynamics.
- Providing support for altimetry missions with laser measurements, including missions such as CRYOSAT-2 or JASON-3.
- Calibrating GNSS satellite orbits.
- Providing support with laser measurements for Special Mission Support (SMS) for remote sensing missions such as SENTINEL-3A, SENTINEL-3B, and SENTINEL-6A/JASON-CS-A, and contributing to the European COPERNICUS program.
- Performing continuous observations of space debris under the Space Safety program of the ESA and the Space Surveillance and Tracking program of the European Commission.
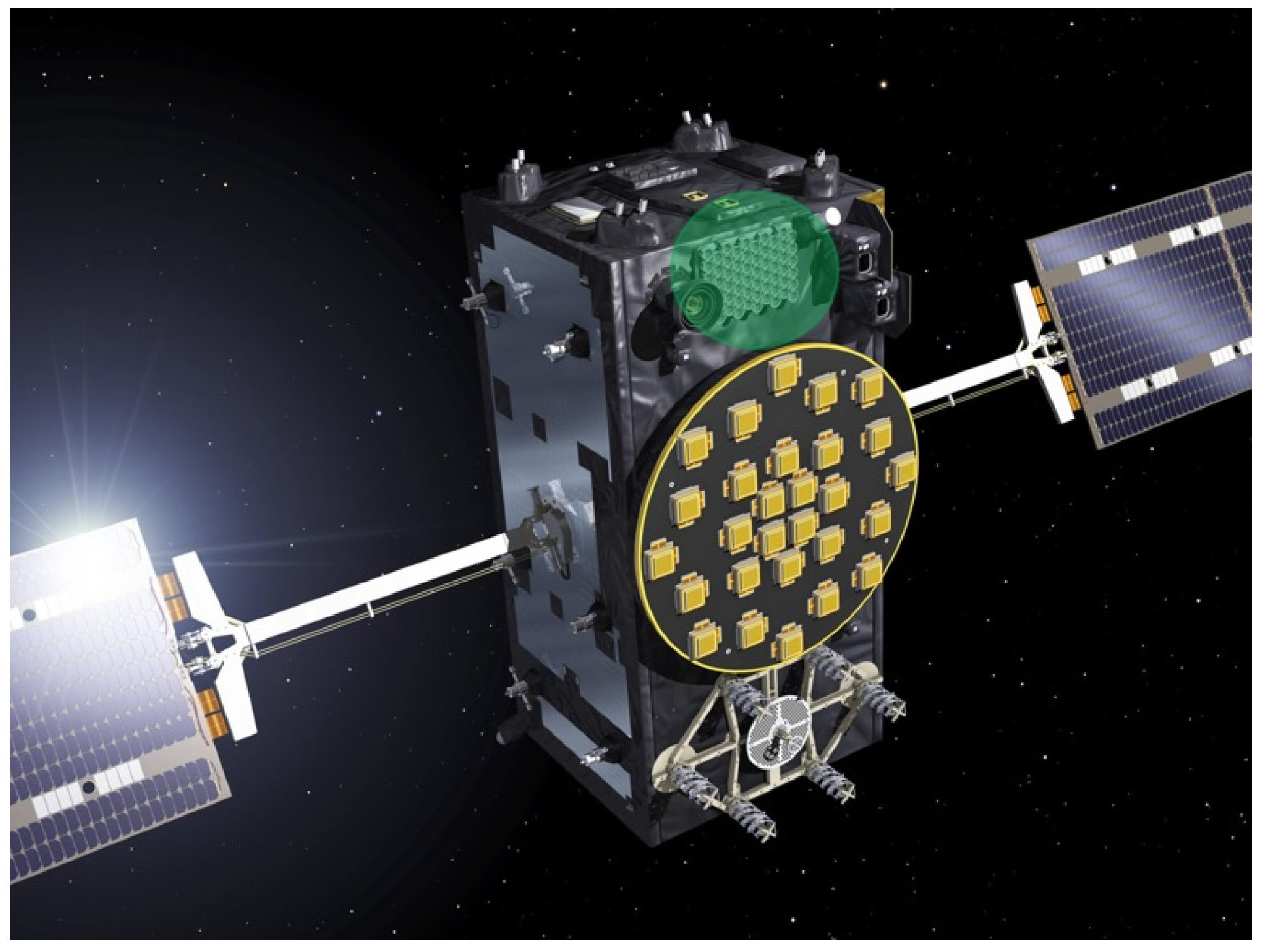
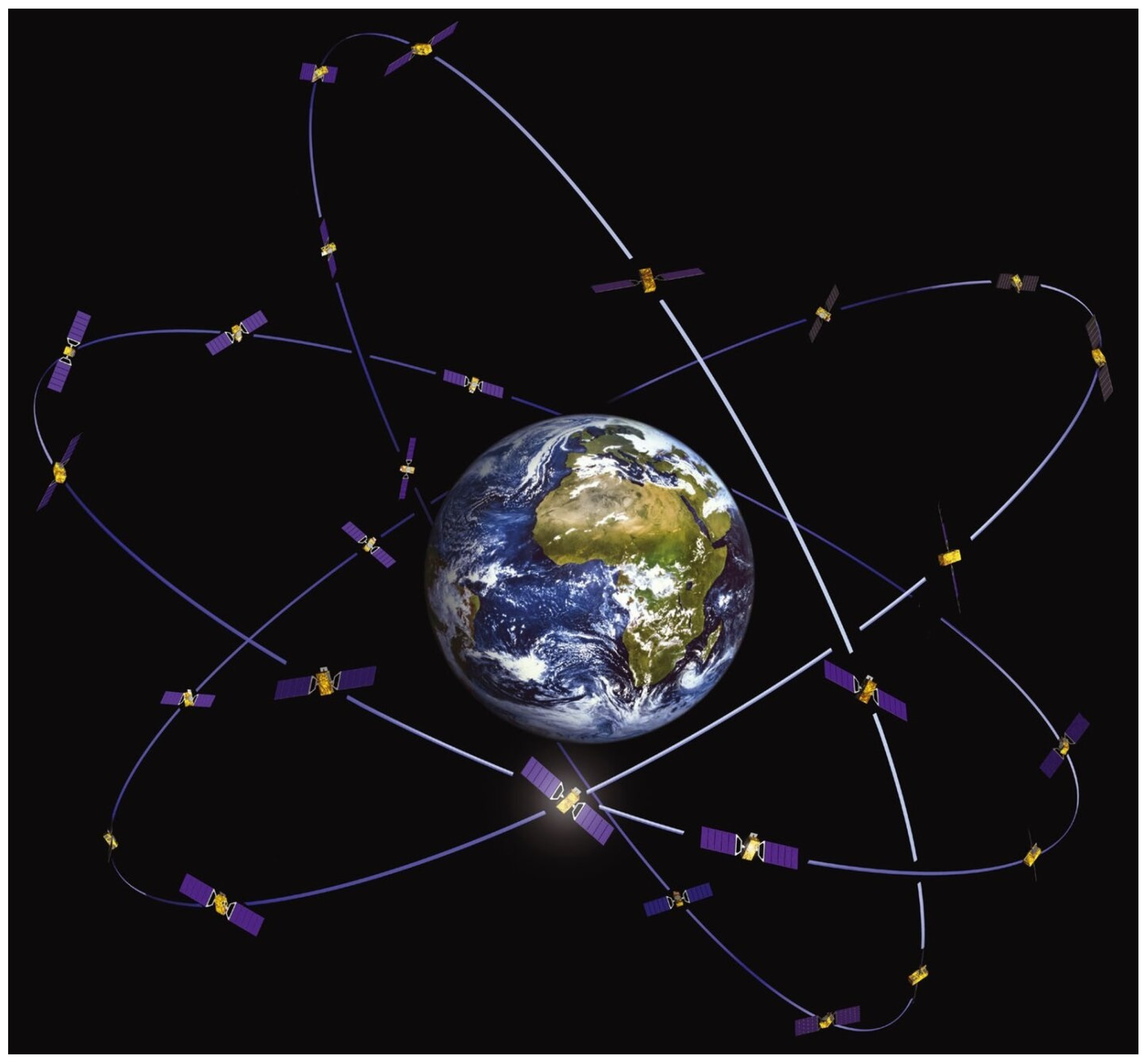
3. GALILEO Constellation
- Open Service (OS);
- High-Accuracy Service (HAS);
- Public Regulated Service (PRS);
- Search and Rescue Service (SAR);
- Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA);
- Commercial Authentication Service (CAS);
- GALILEO Emergency Warning Satellite Service (EWSS).
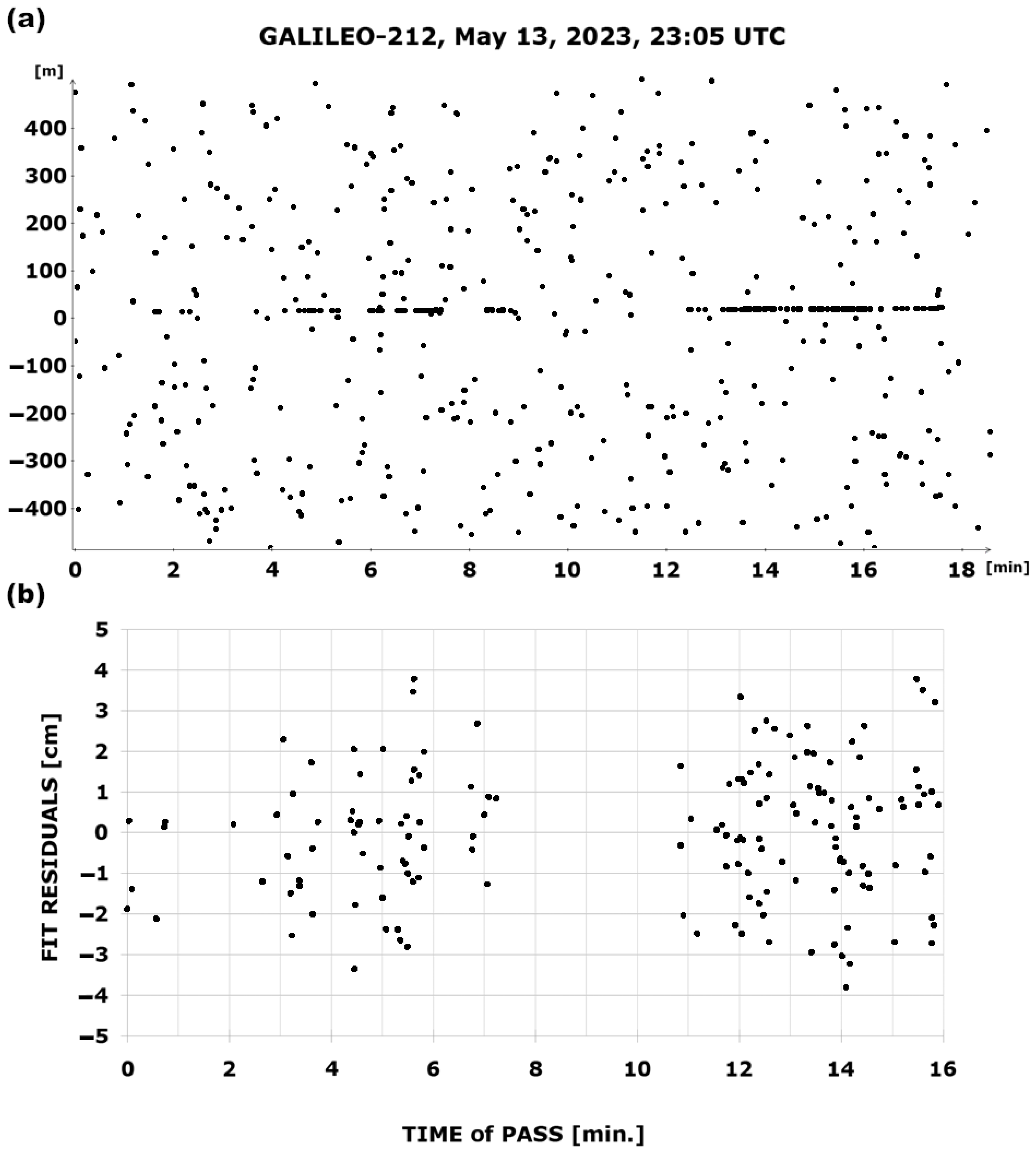
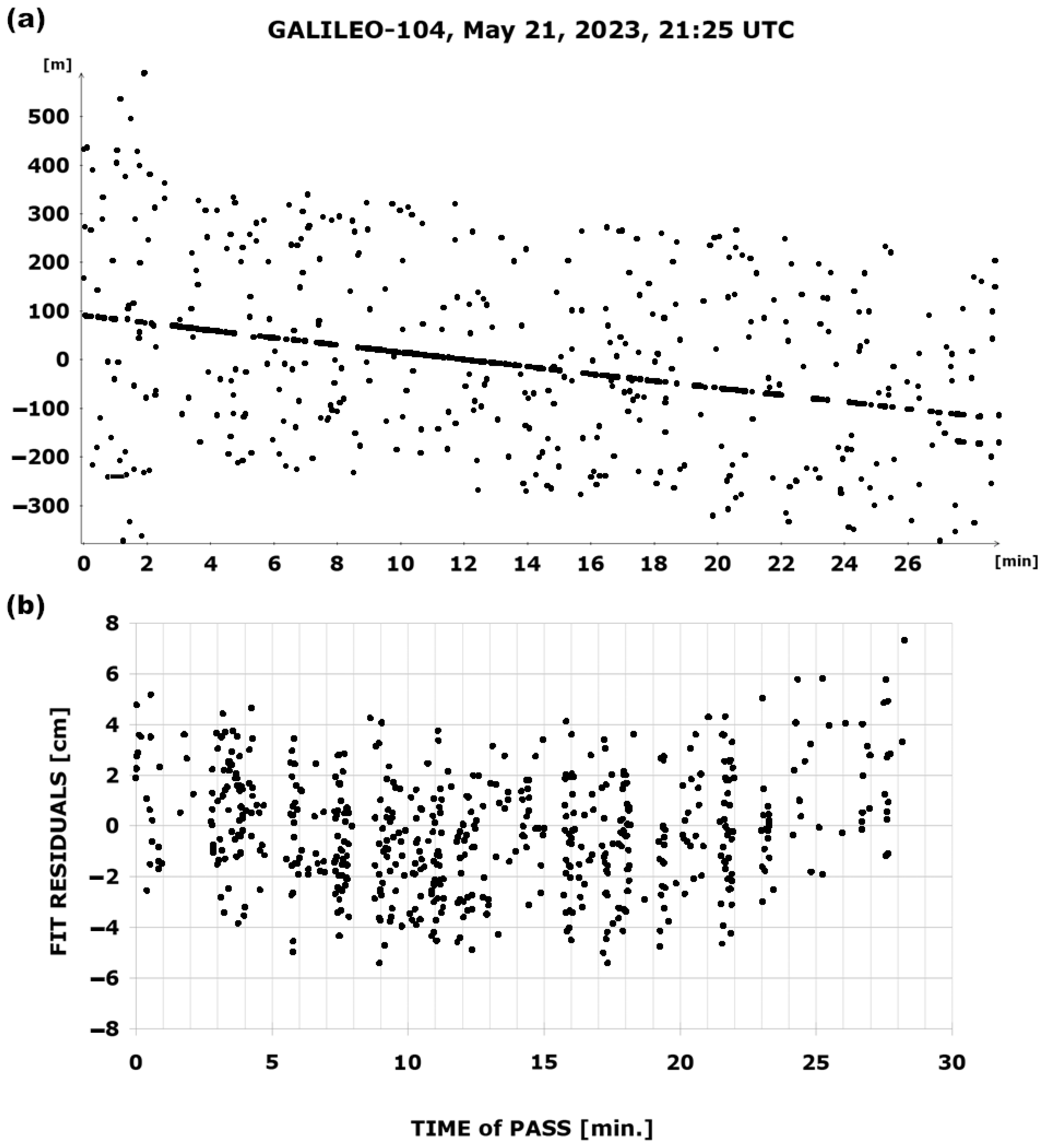
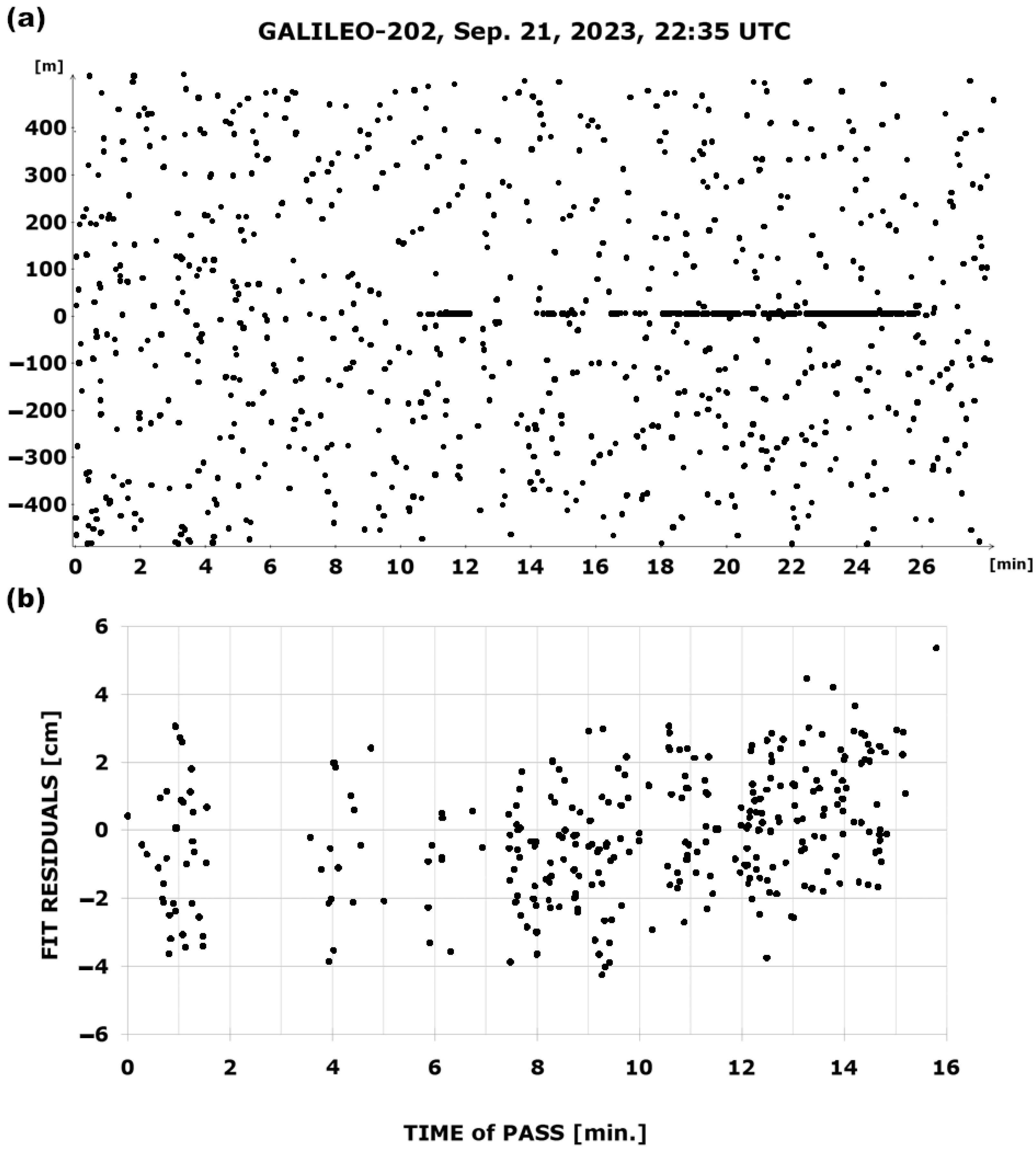
4. The Results of Laser Ranging to the GALILEO Satellites
5. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Annual Report 2022; Centrum B adań Kosmicznych Polska Akademia Nauk; Space Research Centre Polish Academy of Sciences: Warsaw, Poland, 2022; ISBN 978-83-89439-09-3.
- Pearlman, M.; Arnold, D.; Davis, M.; Barlier, F.; Biancale, R.; Vasiliev, V.; Ciufolini, I.; Paolozzi, A.; Pavlis, E.C.; Sośnica, K. Laser geodetic satellites: A high-accuracy scientific tool. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, M.R.; Noll, C.E.; Pavlis, E.C.; Lemoine, F.G.; Combrink, L.; Degnan, J.J.; Kirchner, G.; Schreiber, U. The ILRS: Approaching 20 years and planning for the future. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2161–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejba, P.; Schillak, S. Determination of station positions and velocities fromlaser ranging observations to Ajisai, Starlette and Stella satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Yu, X.; Li, J. Earth rotation parameter and variation during 2005–2010 solved with LAGEOS SLR data. Geod. Geodyn. 2015, 6, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnica, K.; Jäggi, A.; Meyer, U.; Thaller, D.; Beutler, G.; Arnold, D.; Dach, R. Time variable Earth’s gravity field from SLR satellites. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoda, M.; Rutkowska, M.; Kraszewska, K. The evaluation of time variability of tidal parameters h and l using SLR technique. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2016, 14, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloßfeld, M.; Rudenko, S.; Kehm, A.; Panafidina, N.; Müller, H.; Angermann, D.; Hugentobler, U.; Seitz, M. Consistent estimation of geodetic parameters from SLR satellite constellation measurements. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1003–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillak, S.; Lejba, P.; Michałek, P. Analysis of the quality of SLR station coordinates determined fromLaser Ranging to the LARES satellite. Sensors 2021, 21, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajdel, R.; Masoumi, S.; Sośnica, K.; Gałdyn, F.; Strugarek, D.; Bury, G. Combination and SLR validation of IGS Repro3 orbits for ITRF2020. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILRS Operational Station Identification Table, Active Stations. Available online: https://ilrs.cddis.eosdis.nasa.gov/network/stations/active/index.html (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- ILRS Current Missions. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/missions/satellite_missions/current_missions/index.html (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- First 2018 ILRS LARGE (Laser Ranging to GNSS s/c Experiment) Campaign, Summary Report. May 2018. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2018/LARGE1_20180215_20180515_final.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Second 2018 ILRS LARGE (Laser Ranging to GNSS s/c Experiment) Campaign, Summary Report. February 2019. Available online: https://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/2018/LARGE2_20180801_20181031_final.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- ILRS BORL Site Log. Available online: https://ilrs.cddis.eosdis.nasa.gov/network/stations/active/BORL_sitelog.html (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Smagło, A.; Lejba, P.; Schillak, S.; Suchodolski, T.; Michałek, P.; Zapaśnik, S.; Bartoszak, J. Measurements to space debris in 2016-2020 by laser sensor at Borowiec Poland. Artif. Satell. J. Planet. Geod. 2022, 56, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Constellation of GALILEO Satellites CREDIT European Space Agency—J. Huart. Available online: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2007/05/GALILEO_constellation (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Artist’s View of a GALILEO Full Operational Capability (FOC) CREDIT European Space Agency—Pierre Carril. Available online: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2014/07/GALILEO_satellite2 (accessed on 8 May 2024).
- Steindorfer, M.A.; Kirchner, G.; Koidl, F.; Wang, P.; Wirnsberger, H.; Schoenemann, E.; Gonzalez, F. Attitude determination of Galileo satellites using high-resolution kHz SLR. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindorfer, M.A.; Koidl, F.; Kirchner, G.; Wang, P.; Dilssner, F.; Schoenemann, E.; Strangfeld, A.; Gonzalez, F. Satellite laser ranging to Galileo satellites: Symmetry conditions and improved normal point formation strategies. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUSPA EO and GNSS Market Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2024; ISBN 978-92-9206-079-4.
- Altamimi, Z.; Rebischung, P.; Collilieux, X.; Metivier, L.; Chanard, K. ITRF2020: Main results and key performance indicators. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2022, Vienna, Austria, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sośnica, K.; Bury, G.; Zajdel, R.; Strugarek, D.; Drożdżewski, M.; Kazmierski, K. Estimating global geodetic parameters using SLR observations to GALILEO, GLONASS, BeiDou, GPS, and QZSS. Earth Planets Space 2019, 71, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajdel, R.; Sośnica, K.; Bury, G.; Dach, R.; Prange, L. System-specific systematic errors in earth rotation parameters derived from GPS, GLONASS, and GALILEO. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wei, E.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Earth rotation parameters from BDS, GPS, and GALILEO data: An accuracy analysis. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 3968–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, G.; Sośnica, K.; Zajdel, R.; Strugarek, D.; Hugentobler, U. Determination of precise GALILEO orbits using combined GNSS and SLR observations. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnica, K.; Prange, L.; Kaźmierski, K.; Bury, G.; Drożdżewski, M.; Zajdel, R.; Hadas, T. Validation of GALILEO orbits using SLR with a focus on satellites launched into incorrect orbital planes. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sośnica, K.; Bury, G.; Zajdel, R.; Ventura-Traveset, J.; Mendes, L. GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo orbit geometry variations caused by general relativity focusing on Galileo in eccentric orbits. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciufolini, I.; Matzner, R.; Paolozzi, A.; Pavlis, E.C.; Sindoni, G.; Ries, J.; Gurzadyan, V.; Koenig, R. Satellite Laser-Ranging as a Probe of Fundamental Physics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delva, P.; Puchades, N.; Schönemann, E.; Dilssner, F.; Courde, C.; Bertone, S.; Gonzalez, F.; Hees, A.; Le Poncin-Lafitte, C.; Meynadier, F. Gravitational Redshift Test Using Eccentric Galileo Satellites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 231101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampf, D.; Niebler, F.; Bartels, N.; Riede, W. The miniSLR®: A low-cost, high-performance laser ranging system for the ILRS. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Workshop on Laser Ranging (IWLR), Yebes, Spain, 7–11 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
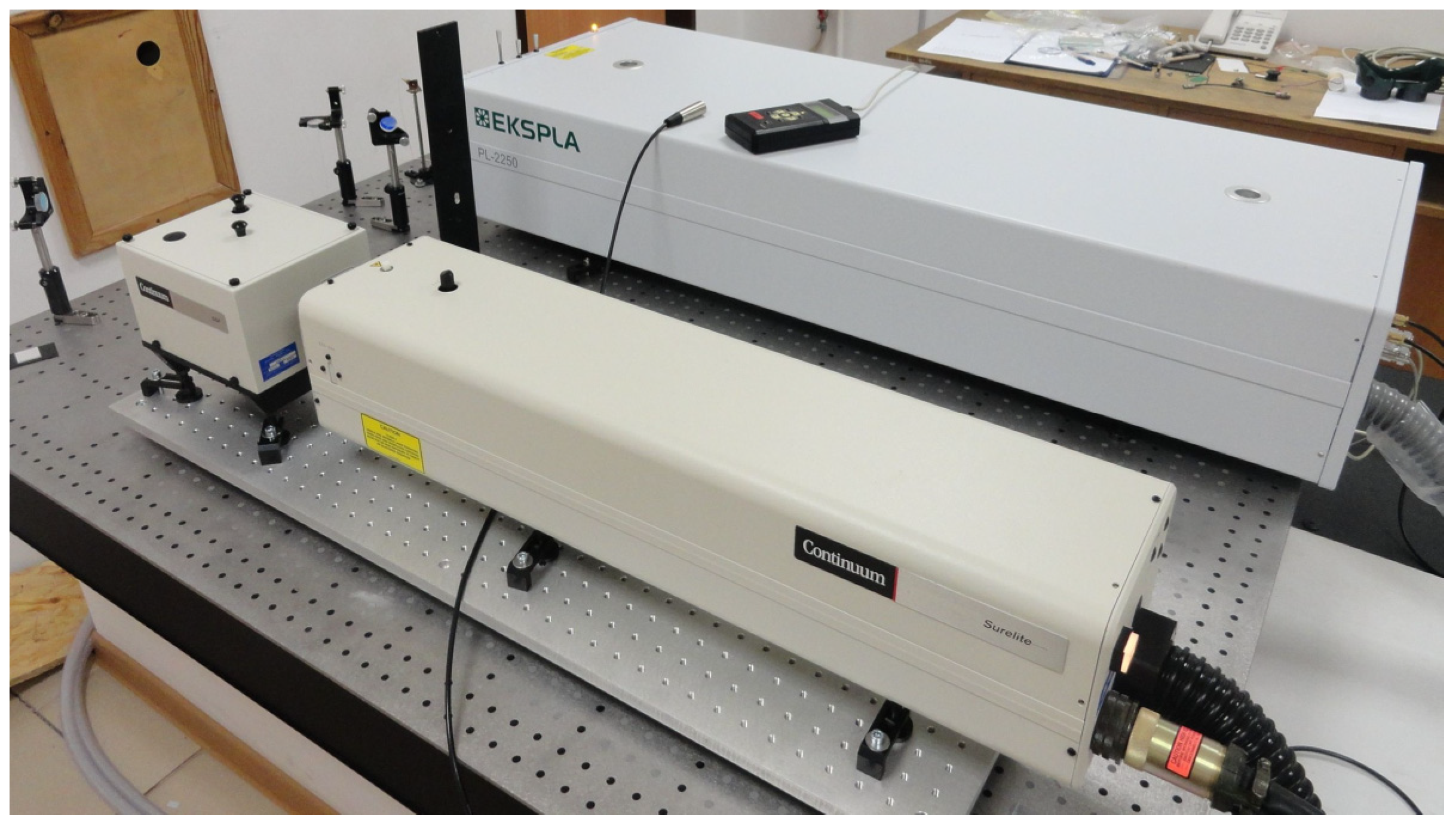



| PARAMETER | EKSPLA PL-2250 | CONTINUUM SURELITE III |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 10 Hz | 10 Hz |
| Pulse energy | 0.05 J | 0.45 J |
| Pulse length | 60 ps | 4 ns |
| Peak power | 833 MW | 112.5 MW |
| Average power | 0.5 W | 4.5 W |
| NR | SATNAME | PASSES | RETURNS | NORMAL POINTS | AVG RMS [cm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GALILEO-103 | 10 | 1118 | 43 | 1.72 |
| 2 | GALILEO-104 | 11 | 2534 | 55 | 1.69 |
| 3 | GALILEO-202 | 2 | 488 | 11 | 1.76 |
| 4 | GALILEO-203 | 1 | 32 | 3 | 1.05 |
| 5 | GALILEO-204 | 1 | 24 | 4 | 1.42 |
| 6 | GALILEO-205 | 2 | 61 | 6 | 1.20 |
| 7 | GALILEO-206 | 2 | 183 | 8 | 1.35 |
| 8 | GALILEO-207 | 2 | 77 | 8 | 1.17 |
| 9 | GALILEO-208 | 6 | 482 | 34 | 1.19 |
| 10 | GALILEO-209 | 4 | 304 | 16 | 1.52 |
| 11 | GALILEO-210 | 4 | 160 | 18 | 1.72 |
| 12 | GALILEO-211 | 3 | 111 | 11 | 1.68 |
| 13 | GALILEO-212 | 7 | 623 | 30 | 1.57 |
| 14 | GALILEO-213 | 7 | 565 | 31 | 1.30 |
| 15 | GALILEO-214 | 4 | 238 | 16 | 1.13 |
| 16 | GALILEO-215 | 1 | 17 | 2 | 1.47 |
| 17 | GALILEO-216 | 1 | 39 | 7 | 0.92 |
| 18 | GALILEO-217 | 3 | 120 | 13 | 1.13 |
| 19 | GALILEO-219 | 1 | 36 | 4 | 1.14 |
| 20 | GALILEO-220 | 2 | 104 | 8 | 1.22 |
| 21 | GALILEO-222 | 3 | 103 | 14 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lejba, P.; Michałek, P.; Suchodolski, T.; Smagło, A.; Matyszewski, M.; Zapaśnik, S. Laser Observations of GALILEO Satellites at the CBK PAN Astrogeodynamic Observatory in Borowiec. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152862
Lejba P, Michałek P, Suchodolski T, Smagło A, Matyszewski M, Zapaśnik S. Laser Observations of GALILEO Satellites at the CBK PAN Astrogeodynamic Observatory in Borowiec. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(15):2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152862
Chicago/Turabian StyleLejba, Paweł, Piotr Michałek, Tomasz Suchodolski, Adrian Smagło, Mateusz Matyszewski, and Stanisław Zapaśnik. 2024. "Laser Observations of GALILEO Satellites at the CBK PAN Astrogeodynamic Observatory in Borowiec" Remote Sensing 16, no. 15: 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152862
APA StyleLejba, P., Michałek, P., Suchodolski, T., Smagło, A., Matyszewski, M., & Zapaśnik, S. (2024). Laser Observations of GALILEO Satellites at the CBK PAN Astrogeodynamic Observatory in Borowiec. Remote Sensing, 16(15), 2862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16152862







