Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR)-Based Absence Sampling for Machine-Learning-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: The Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
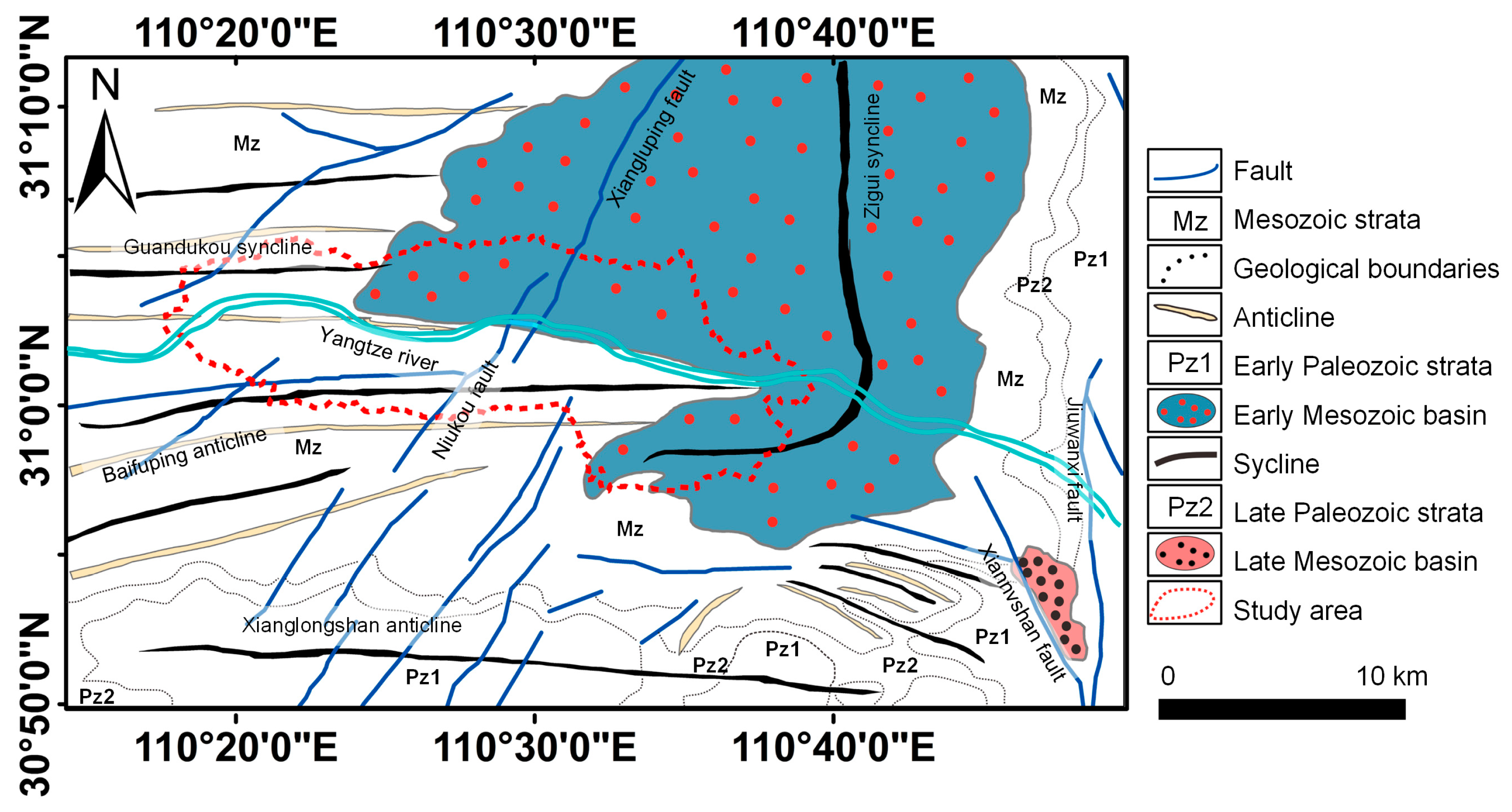
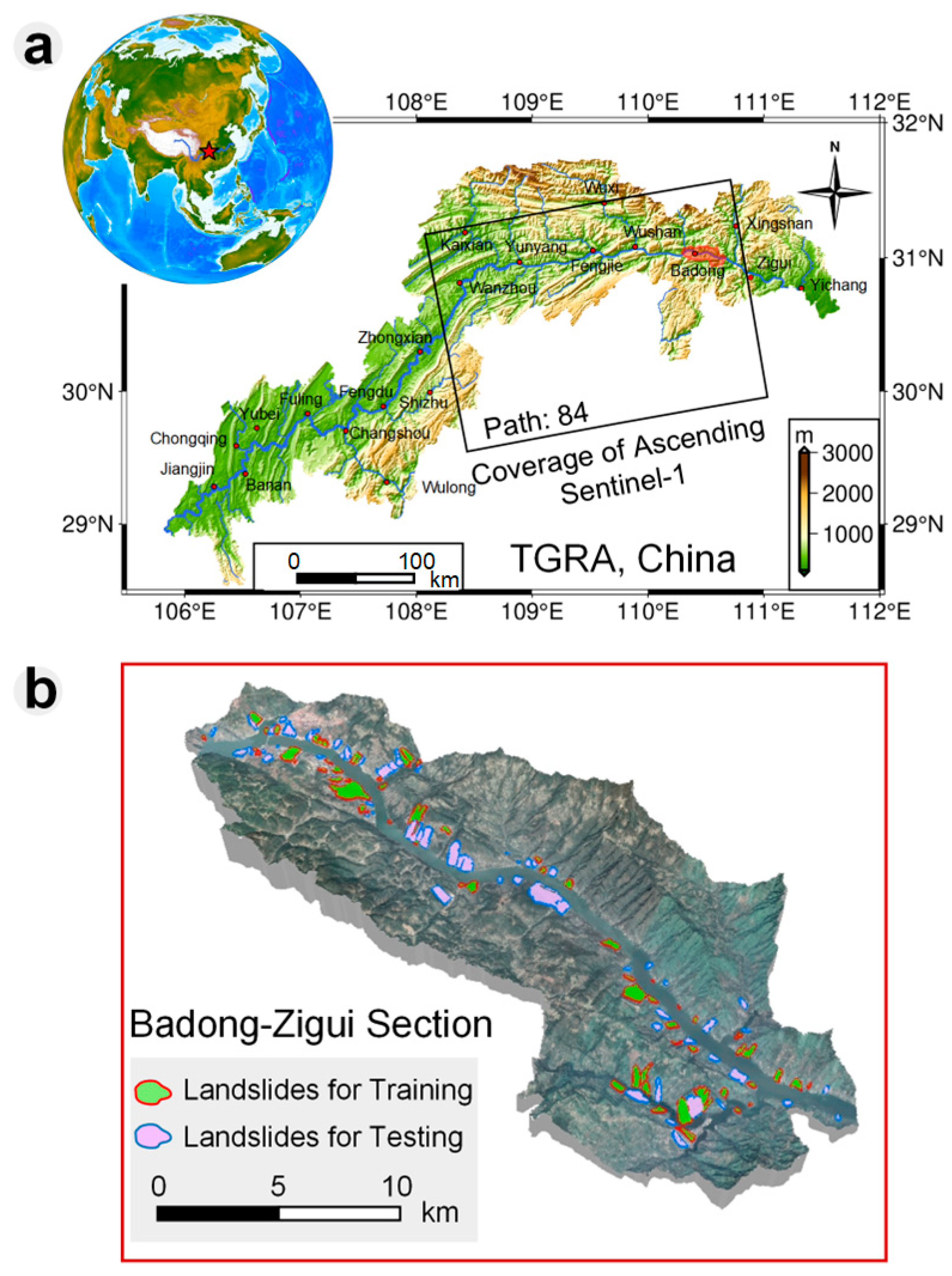
2.1. Study Area and Landslide Inventory
2.2. Methodology
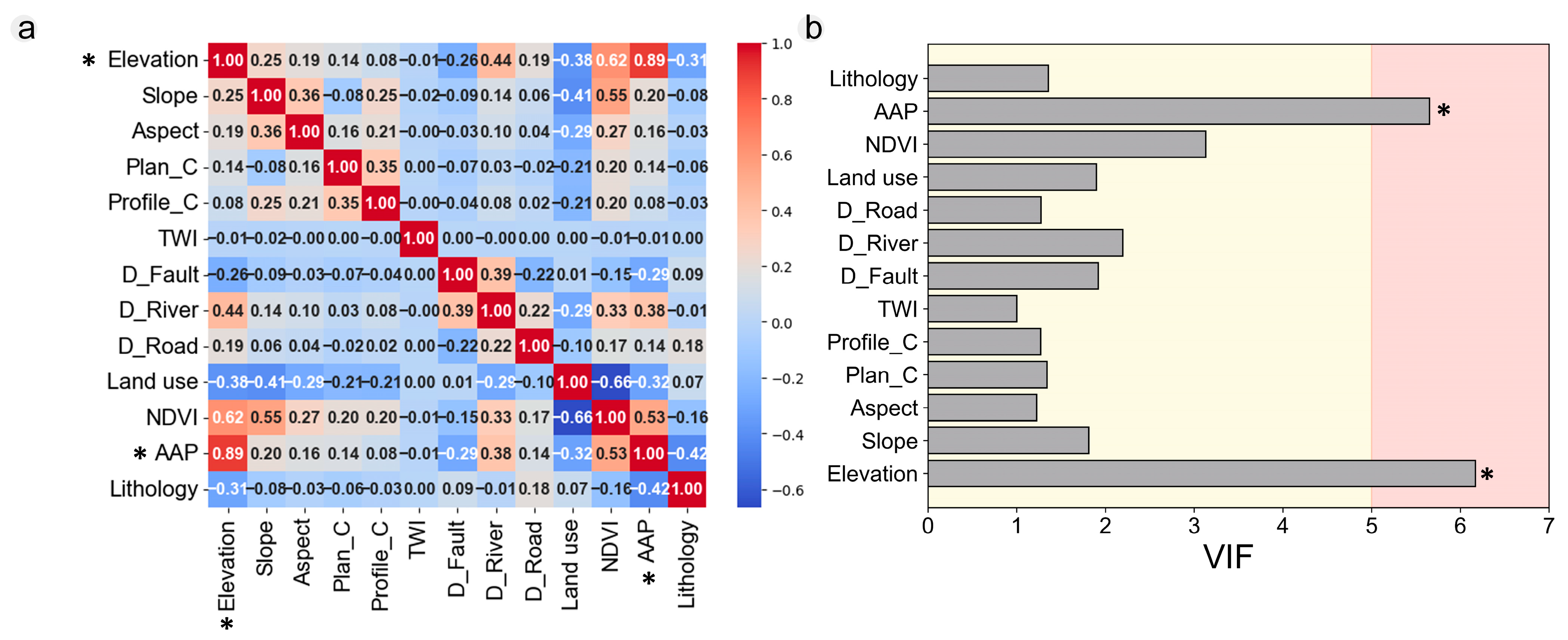
2.2.1. Landslide Conditioning Factors
2.2.2. InSAR-Based Sampling Strategy
2.2.3. Construction of Datasets for LS Modeling
2.2.4. Landslide Susceptibility Prediction Modeling
2.2.5. Model Performance Evaluation
3. Results
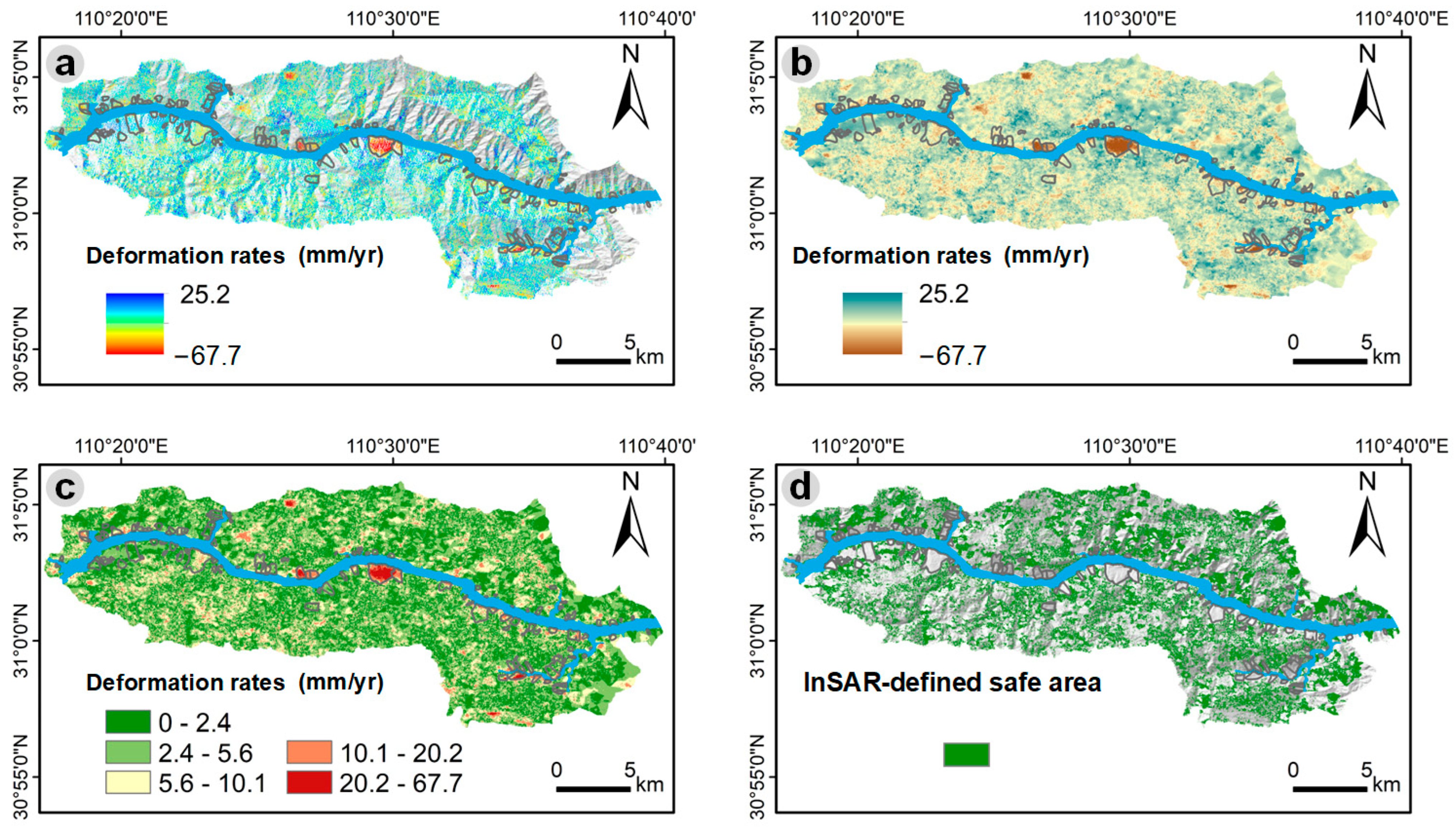
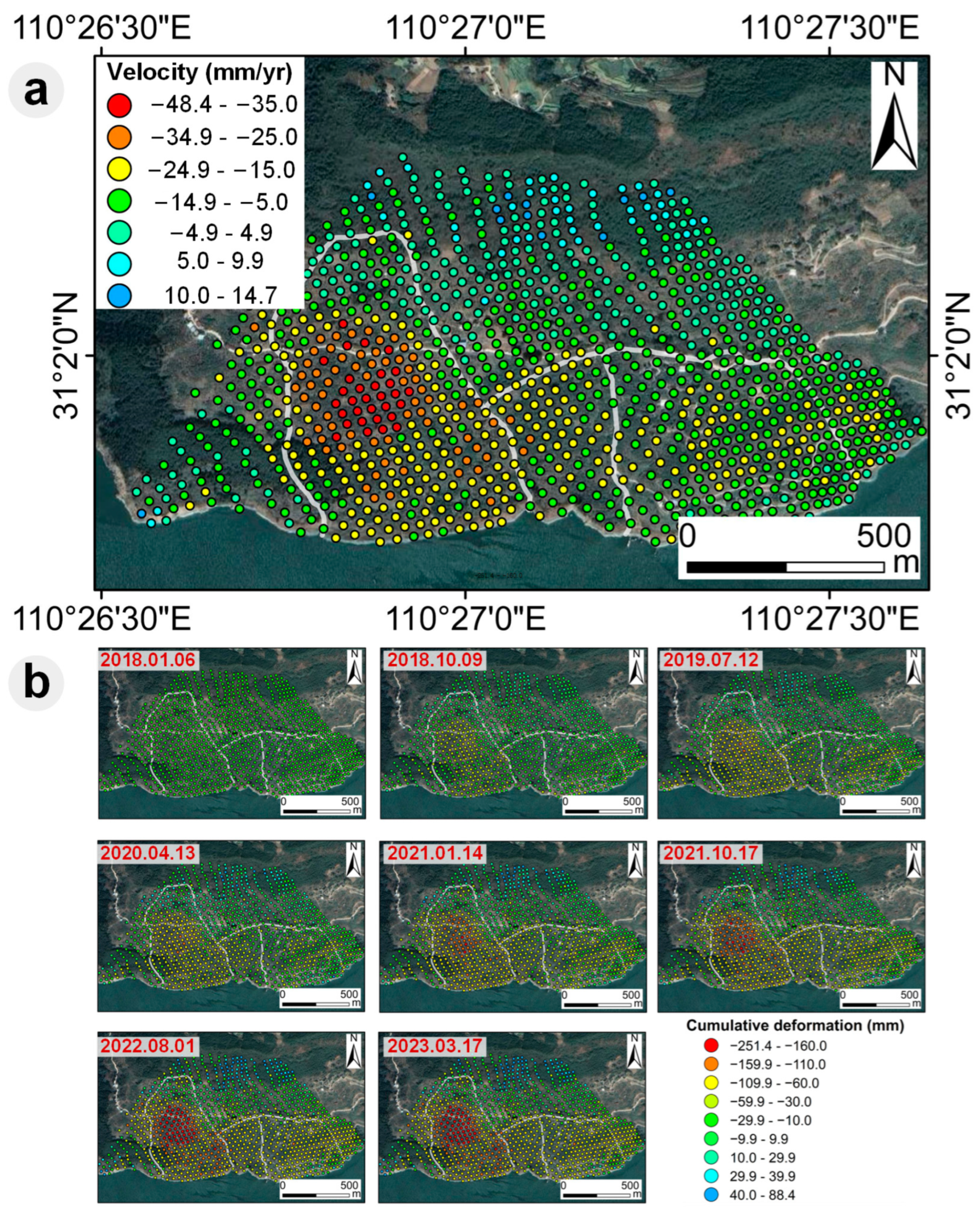
3.1. InSAR-Defined Safe Areas
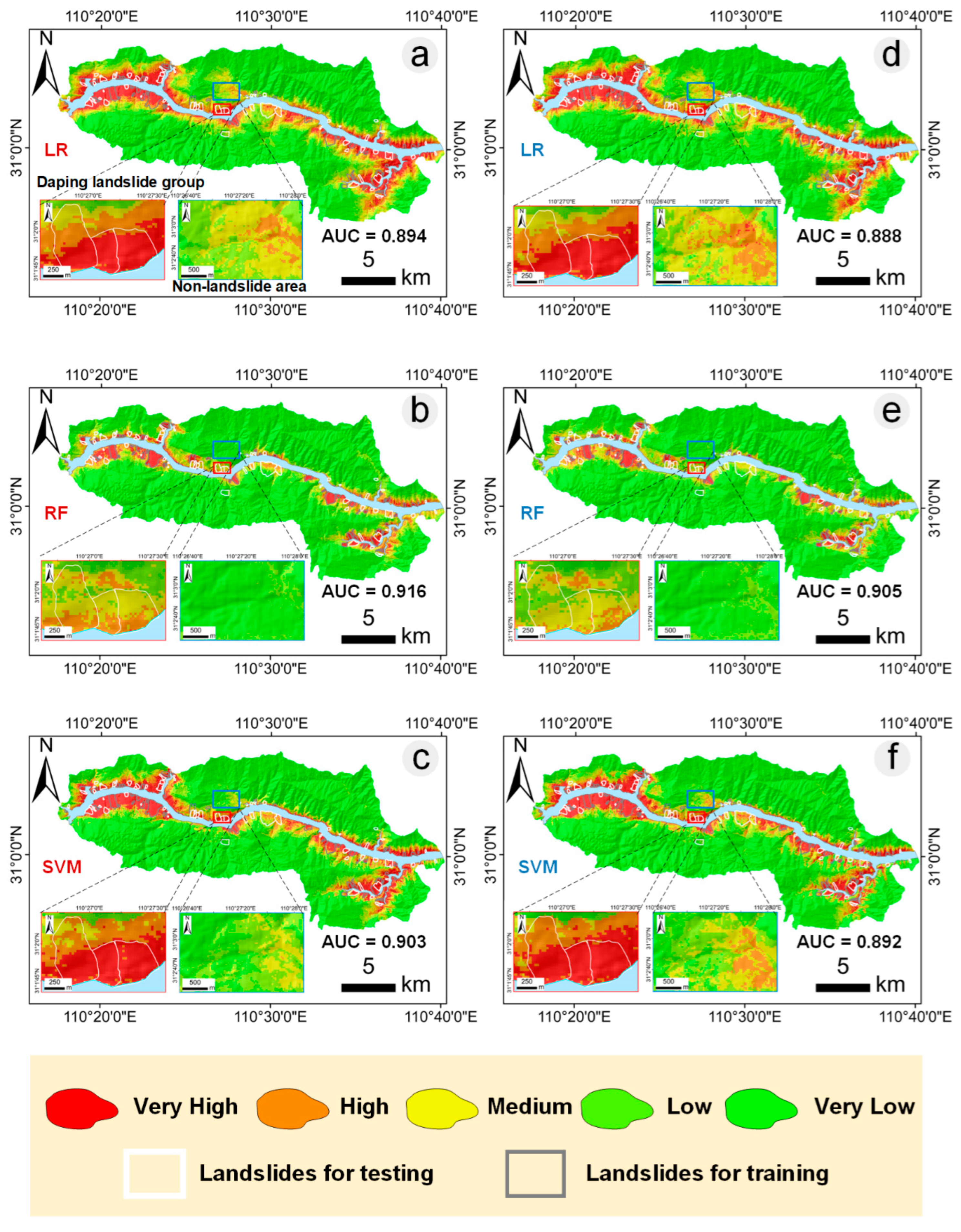
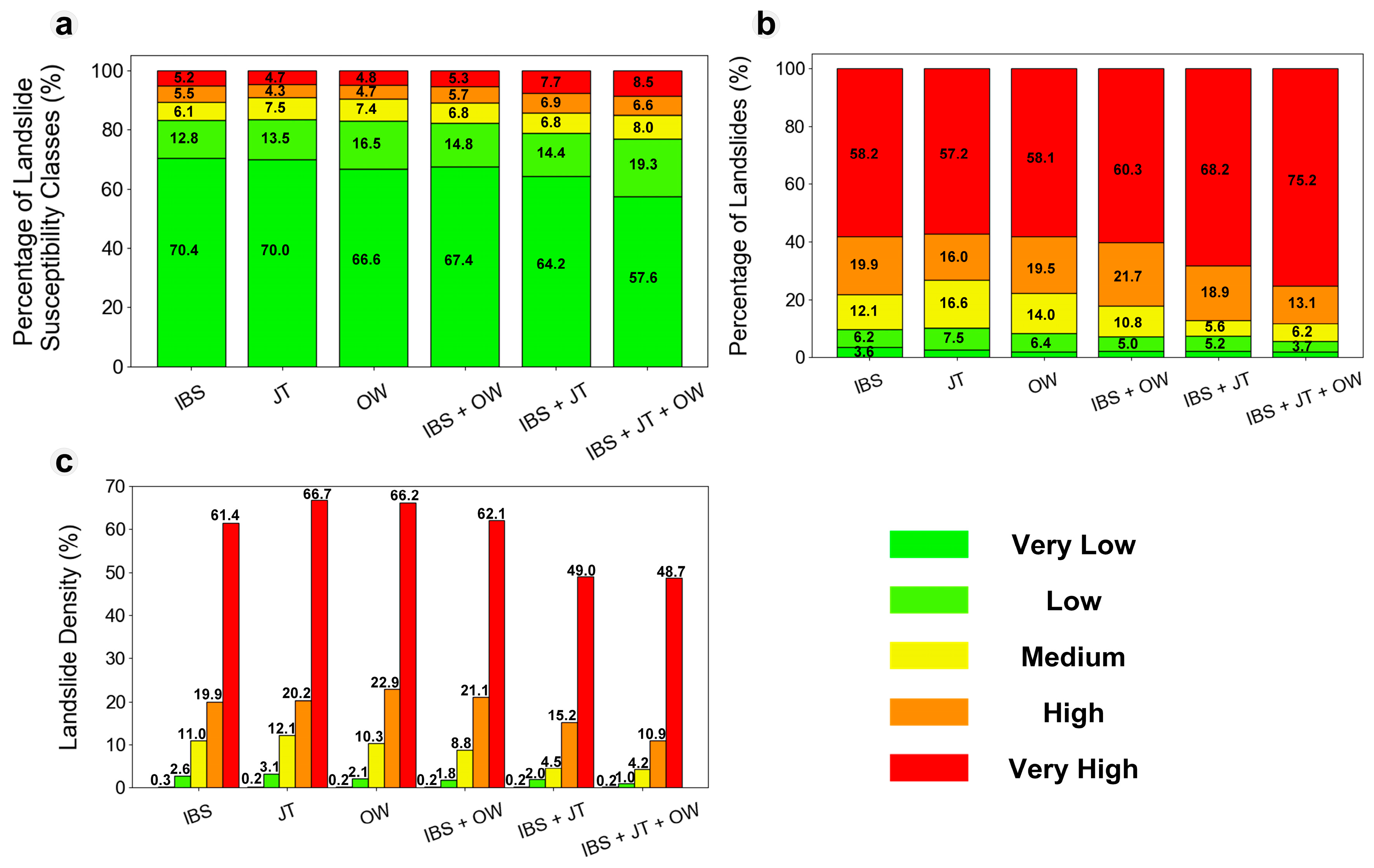
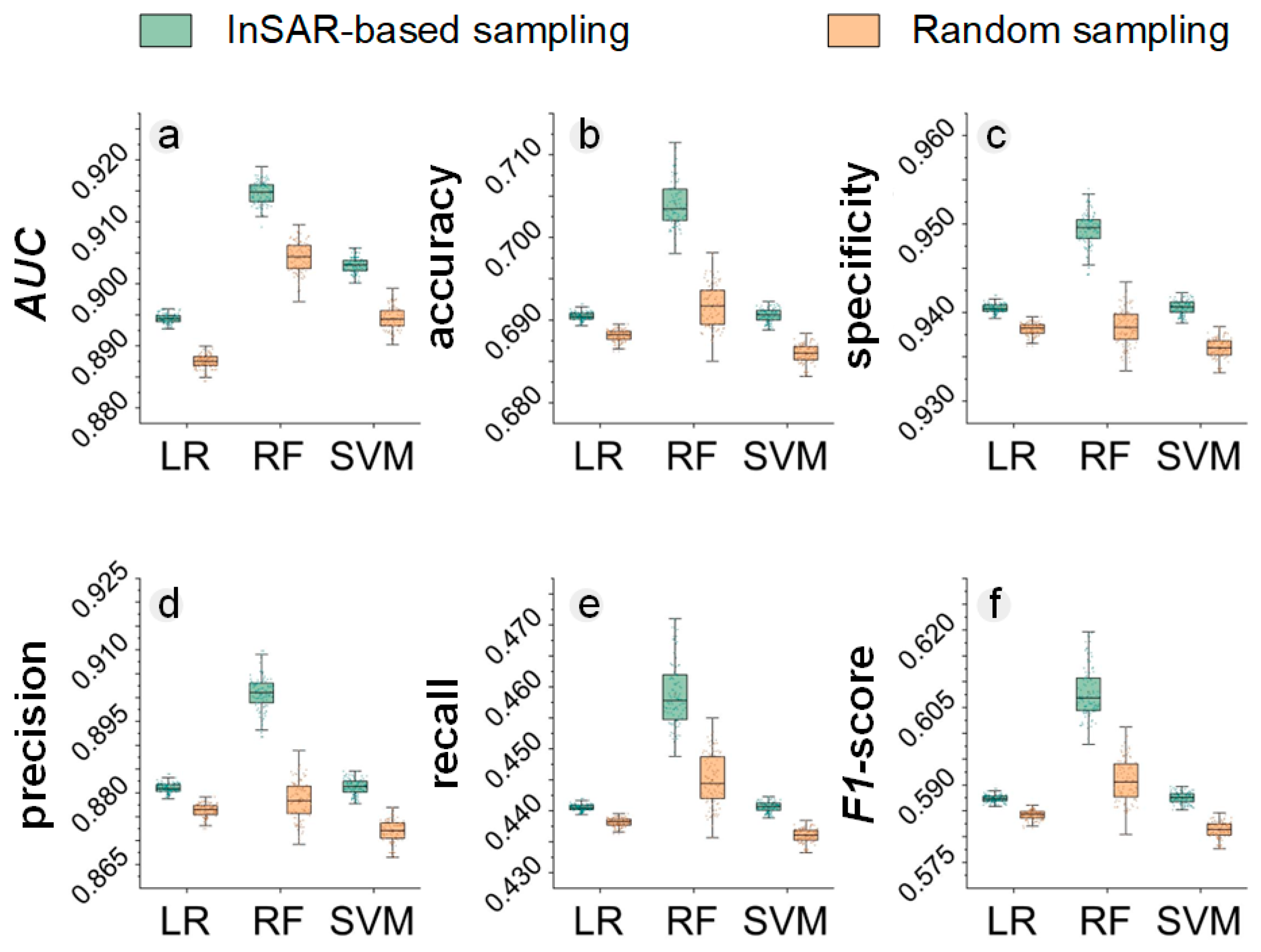
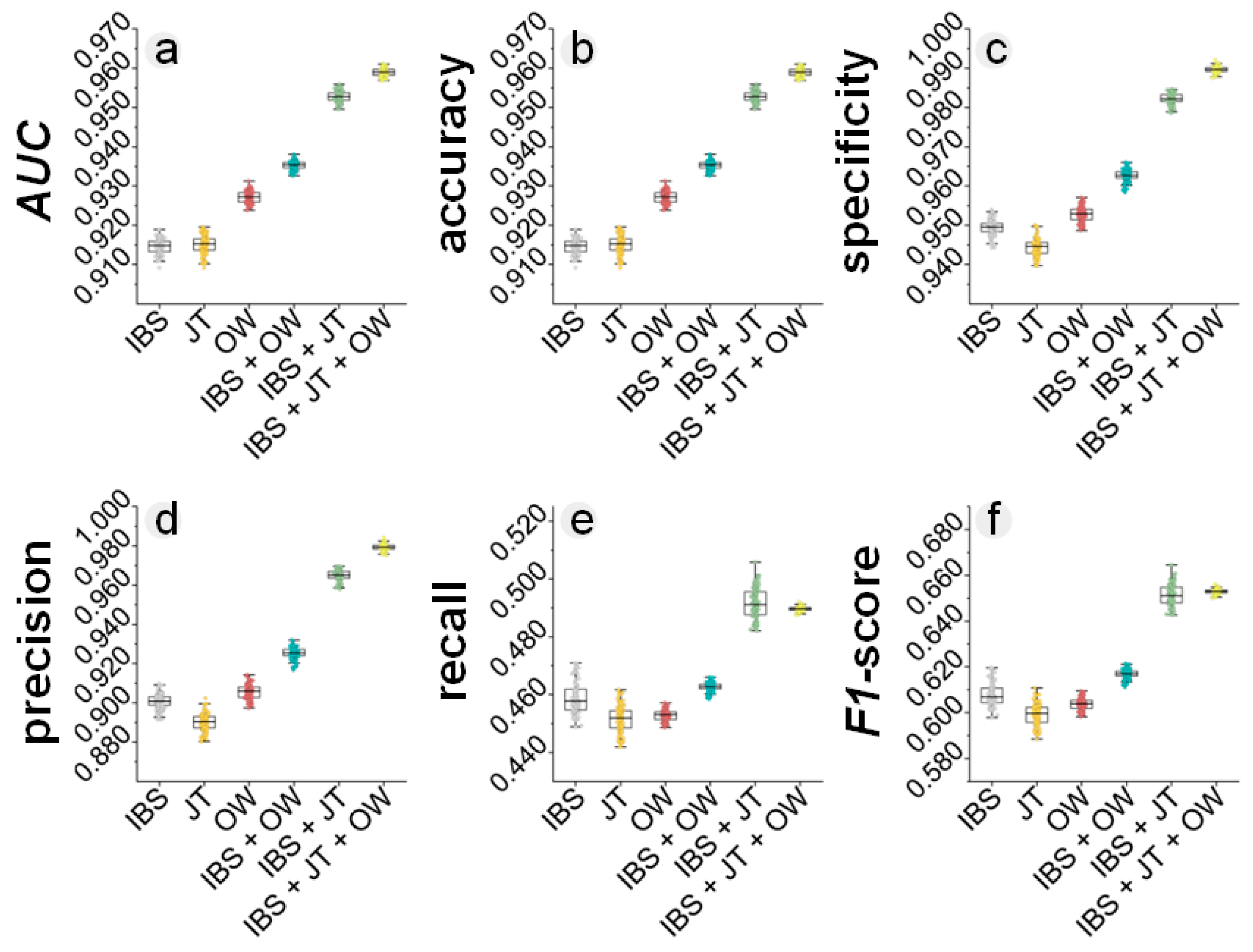
3.2. Enhanced Landslide Susceptibility Maps with InSAR-Based Absence Sampling
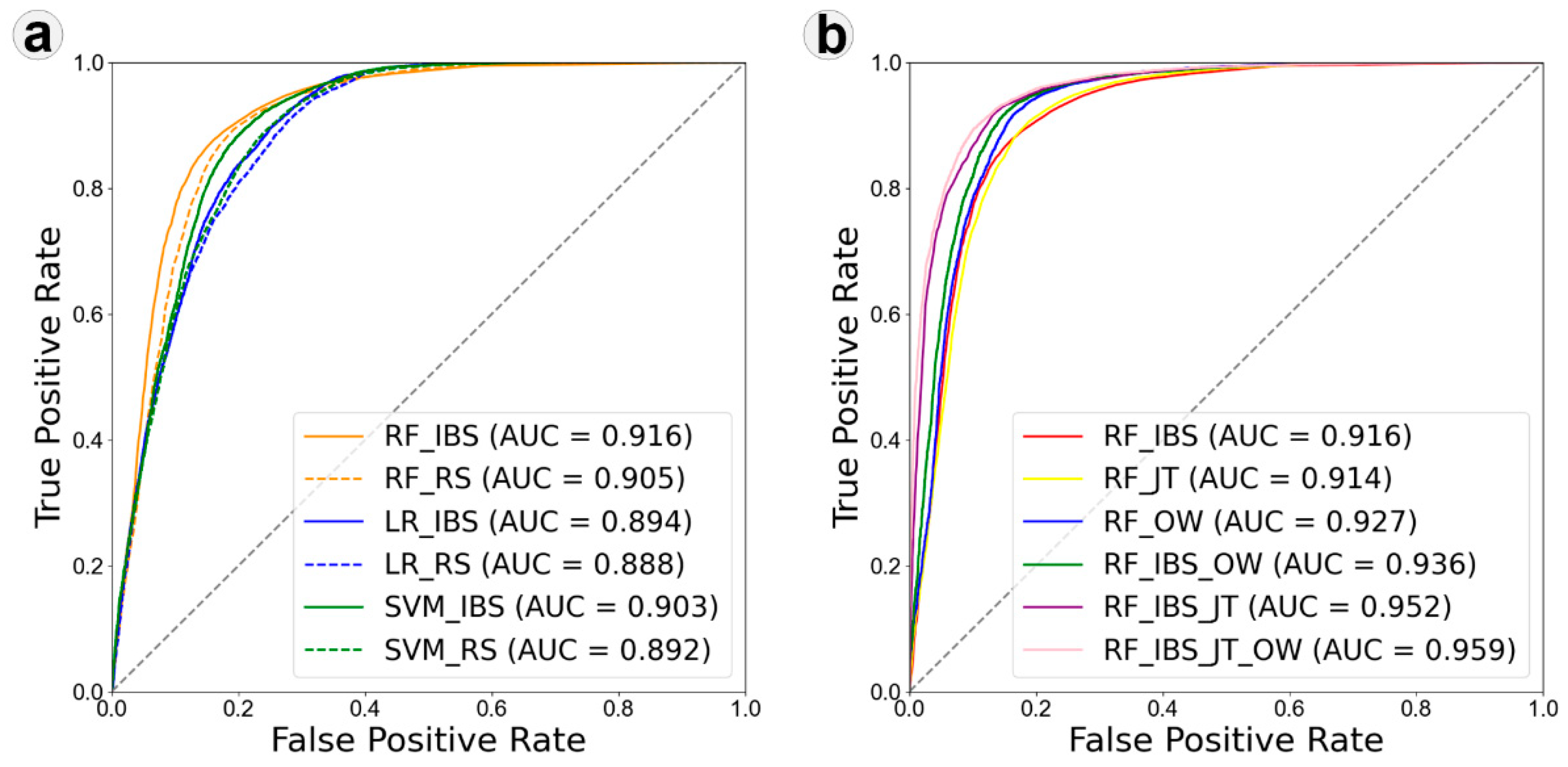
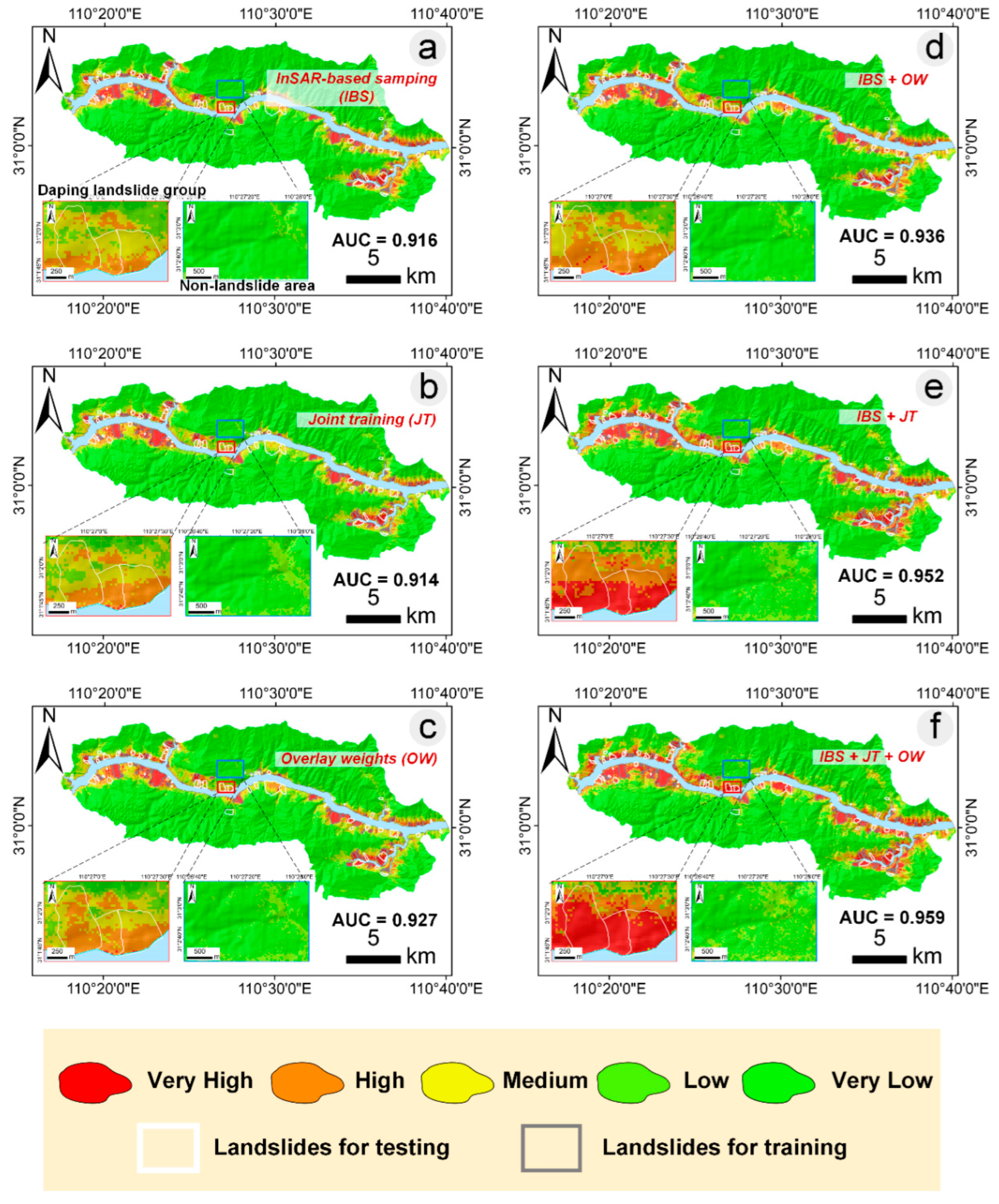
3.3. Comparison of Different InSAR Integration Methods and Their Combined Use
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainty Analysis of InSAR-Enhanced LSM
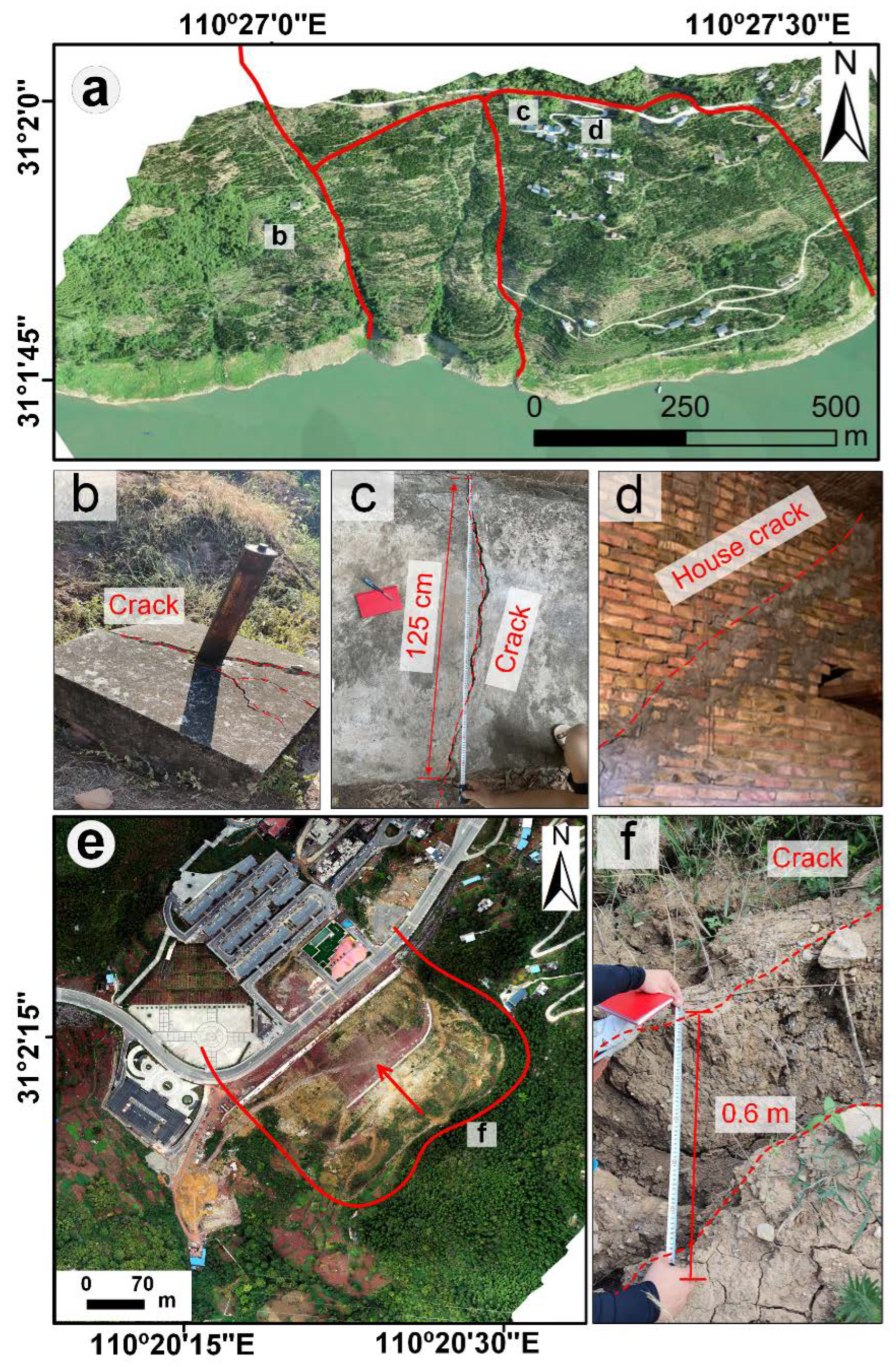
4.2. Empirical Cross-Checking via InSAR Dynamics at the Daping Landslide Group
4.3. Advantages and Future Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Q.; Guo, C.; Dong, X.; Li, W.; Lu, H.; Fu, H.; Liu, X. Mapping and Characterizing Displacements of Landslides with InSAR and Airborne LiDAR Technologies: A Case Study of Danba County, Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhao, B.; Dai, K.; Dong, X.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; et al. Remote sensing for landslide investigations: A progress report from China. Eng. Geol. 2023, 321, 107156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Zhu, K.; Xu, P.; Shan, B.; Yang, G.; Song, S. Refined landslide susceptibility analysis based on InSAR technology and UAV multi-source data. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Sun, P.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Wang, A.; Meng, X. Landslide Risk Assessment Using a Combined Approach Based on InSAR and Random Forest. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Dou, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xing, K. Unraveling the evolution of landslide susceptibility: A systematic review of 30-years of strategic themes and trends. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2256308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, A.; Huang, D. Exploring the uncertainty of landslide susceptibility assessment caused by the number of non–landslides. Catena 2023, 227, 107109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiyong, F.; Changdong, L.; Wenmin, Y. Landslide susceptibility assessment through TrAdaBoost transfer learning models using two landslide inventories. Catena 2023, 222, 106799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; Bai, S.; Zeng, C.; Ma, T.; Hong, H. A similarity-based approach to sampling absence data for landslide susceptibility mapping using data-driven methods. Catena 2019, 183, 104188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, W.; Fu, J.; Xiao, T.; Dai, Z. A physics-informed data-driven model for landslide susceptibility assessment in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, A. Exploring the effects of the design and quantity of absence data on the performance of random forest-based landslide susceptibility mapping. Catena 2019, 176, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabby, Y.W.; Li, Y.; Hilafu, H. An objective absence data sampling method for landslide susceptibility mapping. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, F.; Dou, J.; Nam, K.; Ma, H. Enhanced Absence Sampling Technique for Data-Driven Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: A Case Study in Songyang County, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Liu, D. A hybrid framework integrating physical model and convolutional neural network for regional landslide susceptibility mapping. Nat. Hazards 2021, 109, 471–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zuo, X.; Zhu, D.; Wu, W.; Yang, X.; Guo, S.; Shi, C.; Huang, C.; Li, F.; Liu, X. Identification and Analysis of Landslides in the Ahai Reservoir Area of the Jinsha River Basin Using a Combination of DS-InSAR, Optical Images, and Field Surveys. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Ruan, Q.; Wu, Y.; Qian, Z.; Kong, Z.; Qin, Z. Landslide Dynamic Susceptibility Mapping Base on Machine Learning and the PS-InSAR Coupling Model. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, G.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Tan, L. A comparative study of landslide susceptibility mapping using weight of evidence, logistic regression and support vector machine and evaluated by SBAS-InSAR monitoring: Zhouqu to Wudu segment in Bailong River Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; He, X.; Zhao, Z. An identification method of potential landslide zones using InSAR data and landslide susceptibility. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2185120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ming, D.; Zhu, Y.; Ling, X.; Zhang, X.; Lian, X. Landslide hazard analysis based on SBAS-InSAR and MCE-CNN model: A case study of Kongtong, Pingliang. Geocarto Int. 2022, 38, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cao, Y.; Hu, X.; Yin, K.; Wang, Y.; Catani, F. Enhanced dynamic landslide hazard mapping using MT-InSAR method in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Landslides 2022, 19, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Lagomarsino, D.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Landslide susceptibility map refinement using PSInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Merghadi, A.; Shirzadi, A.; Nguyen, H.; Hussain, Y.; Avtar, R.; Chen, Y.; Pham, B.T.; Yamagishi, H. Different sampling strategies for predicting landslide susceptibilities are deemed less consequential with deep learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Pei, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H. Analysis on the Characteristics of Crustal Structure and Seismotectonic Environment in Zigui Basin, Three Gorges. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 780209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Niu, R.; Huang, B.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, R. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on rough set theory and support vector machines: A case of the Three Gorges area, China. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Gao, H. A landslide susceptibility map based on spatial scale segmentation: A case study at Zigui-Badong in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e229818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Niu, R.; Peng, L. Integration of Information Theory, K-Means Cluster Analysis and the Logistic Regression Model for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping in the Three Gorges Area, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, P.; Xia, W. Dynamic development of landslide susceptibility based on slope unit and deep neural networks. Landslides 2021, 18, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, J.; Feng, W.; Yi, X.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M. Detection and Mapping of Active Landslides before Impoundment in the Baihetan Reservoir Area (China) Based on the Time-Series InSAR Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dai, K.; Deng, J.; Ge, D.; Liang, R.; Li, W.; Xu, Q. Identifying Potential Landslides by Stacking-InSAR in Southwestern China and Its Performance Comparison with SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Chen, C.; Shi, X.; Wu, M.; Feng, W.; Xu, Q.; Liang, R.; Zhuo, G.; Li, Z. Dynamic landslides susceptibility evaluation in Baihetan Dam area during extensive impoundment by integrating geological model and InSAR observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Yao, X.; Liu, X. Landslide Detection and Mapping Based on SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR: A Case Study in Gongjue County, Tibet, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruden, D.M.; Varnes, D.J. Landslide Types and Processes. In Landslides, Investigation and Mitigation; Transportation Research Board Special Report; Turner, A.K., Schuster, R.L., Eds.; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; Volume 247, pp. 36–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Liang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Yan, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Li, W. Integration of Sentinel-1A, ALOS-2 and GF-1 Datasets for Identifying Landslides in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cao, Y.; Yin, K.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Catani, F.; Ahmed, B. Landslide Characterization Applying Sentinel-1 Images and InSAR Technique: The Muyubao Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhu, W.; Liu-Zeng, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, C. Integration of Sentinel-1 and ALOS/PALSAR-2 SAR datasets for mapping active landslides along the Jinsha River corridor, China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 284, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, A.; Liang, Y.; Su, X.; Zeng, R.; Chen, X. Automatic Mapping of Potential Landslides Using Satellite Multitemporal Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, D.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R. InSAR Study of Landslides: Early Detection, Three-Dimensional, and Long-Term Surface Displacement Estimation—A Case of Xiaojiang River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, L.; Gardoni, P.; Chen, Y.; Tan, L.; Liu, D.; Du, C.; Li, H. Comparison of hybrid data-driven and physical models for landslide susceptibility mapping at regional scales. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 4453–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, J.; Yunus, A.P.; Bui, D.T.; Merghadi, A.; Sahana, M.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, C.; Han, Z.; Pham, B.T. Improved landslide assessment using support vector machine with bagging, boosting, and stacking ensemble machine learning framework in a mountainous watershed, Japan. Landslides 2020, 17, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, H.A.H.; Pradhan, B.; Beydoun, G.; Sarkar, R.; Park, H.; Alamri, A. A novel method using explainable artificial intelligence (XAI)-based Shapley Additive Explanations for spatial landslide prediction using Time-Series SAR dataset. Gondwana Res. 2023, 123, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, X.; Niu, R.; Yang, K.; Zhao, L. The assessment of landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest and decision tree methods in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Hong, H.; Chen, W. Regional rainfall-induced landslide hazard warning based on landslide susceptibility mapping and a critical rainfall threshold. Geomorphology 2022, 408, 108236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, T.; Yang, C. A frequency ratio-based sampling strategy for landslide susceptibility assessment. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsyad, A.; Muhiddin, A.B. Landslide Susceptibility Mapping for Road Corridors Using Coupled InSAR and GIS Statistical Analysis. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2023, 24, 05023007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghadi, A.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Whiteley, J.; ThaiPham, B.; Bui, D.T.; Avtar, R.; Abderrahmane, B. Machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility studies: A comparative overview of algorithm performance. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 207, 103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Yan, J.; Fan, X.; Yao, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, W.; Hong, H. Uncertainty pattern in landslide susceptibility prediction modelling: Effects of different landslide boundaries and spatial shape expressions. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graff, J.V.; Romesburg, H.C.; Ahmad, R.; McCalpin, J.P. Producing landslide-susceptibility maps for regional planning in data-scarce regions. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Wu, L.; Hayakawa, Y.S.; Yin, K.; Gui, L.; Jin, B.; Guo, Z.; Peduto, D. Advanced integration of ensemble learning and MT-InSAR for enhanced slow-moving landslide susceptibility zoning. Eng. Geol. 2024, 331, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Lan, H.; Li, L.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C. Characteristics of a rapid landsliding area along Jinsha River revealed by multi-temporal remote sensing and its risks to Sichuan-Tibet railway. Landslides 2022, 19, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Xingmin, M.; Allesandro, N.; Tom, D.; Guan, C.; Colm, J.; Yuanxi, L.; Xiaojun, S. Characterization of pre-failure deformation and evolution of a large earthflow using InSAR monitoring and optical image interpretation. Landslides 2022, 19, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, B.; Ding, M.; Zhu, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Peng, J. An integrated framework for wide-area active landslide detection with InSAR observations and SAR pixel offsets. Landslides 2022, 19, 2905–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Dou, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, R.; Xing, K. A Novel Hybrid LMD-ETS-TCN Approach for Predicting Landslide Displacement Based on GPS Time Series Analysis. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Achilli, V.; Fabris, M.; Menin, A.; Monego, M.; Tessari, G.; Floris, M. Combining Sentinel-1 Interferometry and Ground-Based Geomatics Techniques for Monitoring Buildings Affected by Mass Movements. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Deng, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Shi, X.; Hancock, C.; Wen, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhuo, G. Interpretation and sensitivity analysis of the InSAR line of sight displacements in landslide measurements. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1226–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Dai, K.; Wu, M.; Zhuo, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, T.; Xu, Q. Rapid and Automatic Detection of New Potential Landslide Based on Phase-Gradient DInSAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4514205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Handwerger, A.L.; Agram, P.; Kirschbaum, D.B. InSAR-based detection method for mapping and monitoring slow-moving landslides in remote regions with steep and mountainous terrain: An application to Nepal. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 111983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xu, Y.; Kim, J.; Gallegos, A.J. InSAR monitoring of creeping landslides in mountainous regions: A case study in Eldorado National Forest, California. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Coe, J.A.; Lu, Z.; Avdievitch, N.N.; Hults, C.P. Spaceborne InSAR mapping of landslides and subsidence in rapidly deglaciating terrain, Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve and vicinity, Alaska and British Columbia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 281, 113231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yao, X.; Yao, J. Accelerated Movements of Xiaomojiu Landslide Observed with SBAS-InSAR and Three-Dimensional Measurements, Upper Jinsha River, Eastern Tibet. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Rehman, M.U.; Khalid, Z.; Yue, D. Updating Inventory, Deformation, and Development Characteristics of Landslides in Hunza Valley, NW Karakoram, Pakistan by SBAS-InSAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, D.; Xi, W.; Li, Y. Combined SBAS-InSAR and PSO-RF Algorithm for Evaluating the Susceptibility Prediction of Landslide in Complex Mountainous Area: A Case Study of Ludian County, China. Sensors 2022, 22, 8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zou, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Yao, H.; Cui, J.; Zhou, W.; Chen, S. Development of an integrated model for assessing landslide susceptibility on vegetated slopes under random rainfall scenarios. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 199, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, P.; Yu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, Y. Landslide susceptibility assessment in multiple urban slope settings with a landslide inventory augmented by InSAR techniques. Eng. Geol. 2023, 327, 107342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yin, T.; Dai, K.; Pirasteh, S.; Zhuo, G.; Li, Z.; Yu, B.; Xu, Q. Identifying Potential Landslides on Giant Niexia Slope (China) Based on Integrated Multi-Remote Sensing Technologies. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, L.; Defaflia, N.; Merghadi, A.; Fehdi, C.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Pham, Q.B.; Abdo, H.G.; Almohamad, H.; Al-Mutiry, M. Ground Surface Deformation Analysis Integrating InSAR and GPS Data in the Karstic Terrain of Cheria Basin, Algeria. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghadi, A.; Abderrahmane, B.; Tien Bui, D. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment at Mila Basin (Algeria): A Comparative Assessment of Prediction Capability of Advanced Machine Learning Methods. Isprs Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, L.; Defaflia, N.; Fehdi, C.; Merghadi, A. InSAR Investigation on DRAA-Douamis Sinkholes in Cheria Northeastern of Algeria. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1034–1037. [Google Scholar]



| LCFs | Resolution | Variable Type | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elevation | 30 m | Continuous | ASTER GDEM (30-m DEM) |
| Slope | 30 m | Continuous | Derived from the DEM |
| Aspect | |||
| Plan_C | |||
| Profile_C | |||
| TWI | |||
| D_Fault | 30 m | Continuous | Adapted and digitized from [23,25] |
| D_River | |||
| D_Road | 30 m | Continuous | OpenStreetMap https://www.91weitu.com/ (accessed on 11 October 2023) |
| Land use | 30 m | Discrete | GlobaLand30 dataset https://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 11 October 2023) |
| NDVI | 30 m | Continuous | Derived from Landsat 8 images |
| AAP | 1 km | Continuous | 1-km annual average precipitation dataset for China http://www.gis5g.com/ (accessed on 11 October 2023) |
| Lithology | 30 m | Discrete | Adapted and digitized from [23,25] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Z.; Oguchi, T.; Merghadi, A.; Fu, Z.; Dong, A.; Dou, J. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR)-Based Absence Sampling for Machine-Learning-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: The Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132394
Zhang R, Zhang L, Fang Z, Oguchi T, Merghadi A, Fu Z, Dong A, Dou J. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR)-Based Absence Sampling for Machine-Learning-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: The Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(13):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132394
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ruiqi, Lele Zhang, Zhice Fang, Takashi Oguchi, Abdelaziz Merghadi, Zijin Fu, Aonan Dong, and Jie Dou. 2024. "Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR)-Based Absence Sampling for Machine-Learning-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: The Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China" Remote Sensing 16, no. 13: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132394
APA StyleZhang, R., Zhang, L., Fang, Z., Oguchi, T., Merghadi, A., Fu, Z., Dong, A., & Dou, J. (2024). Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR)-Based Absence Sampling for Machine-Learning-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: The Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Remote Sensing, 16(13), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132394