Disasters and Archaeology: A Remote Sensing Approach for Determination of Archaeology At-Risk to Desertification in Sistan
Abstract
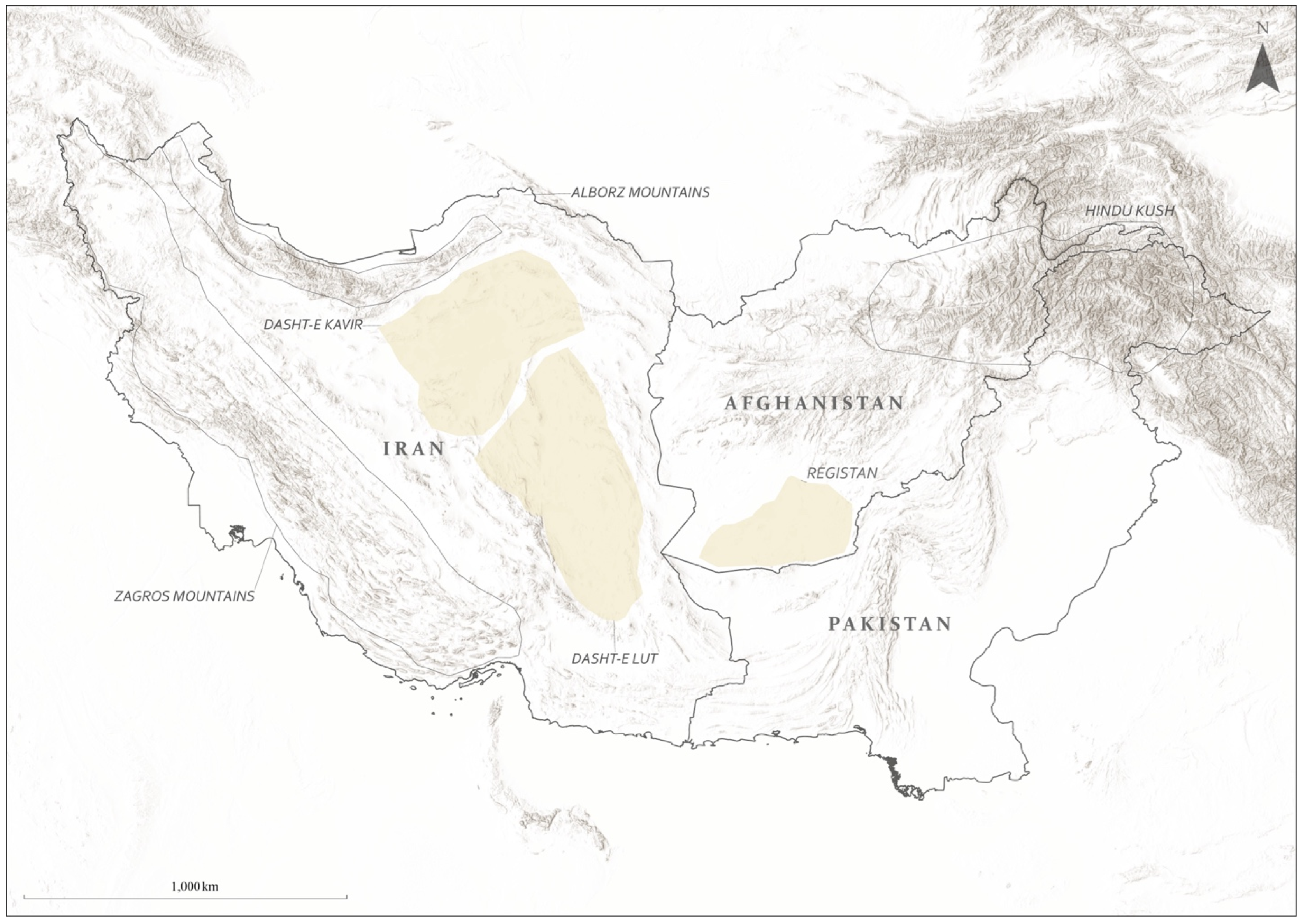
1. Introduction
The Archaeology
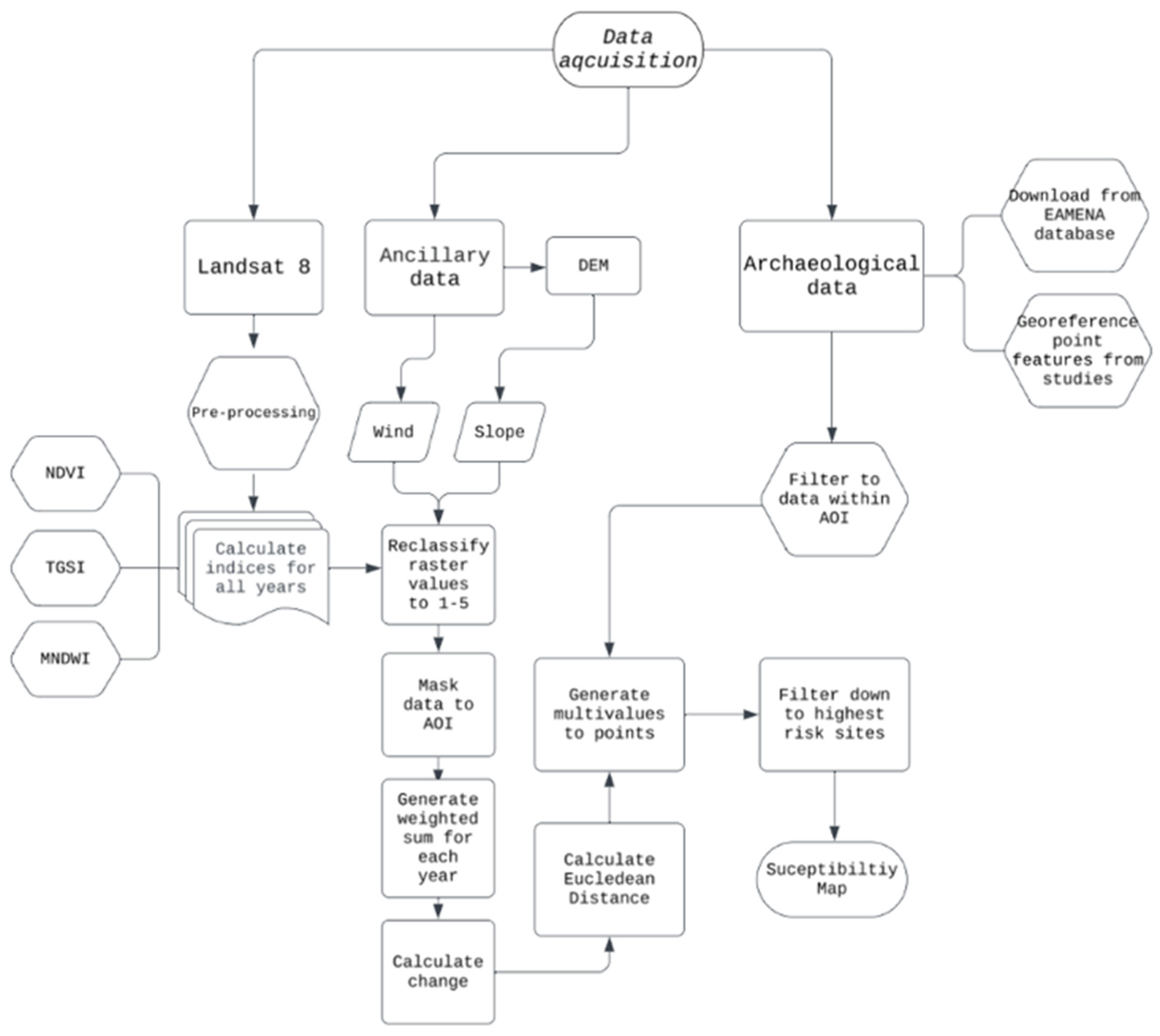
2. Method
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Processing
2.2.1. Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
2.2.2. Top Grain Soil Index (TGSI)
2.2.3. Modified Normalised Difference Water Index (MNDWI)
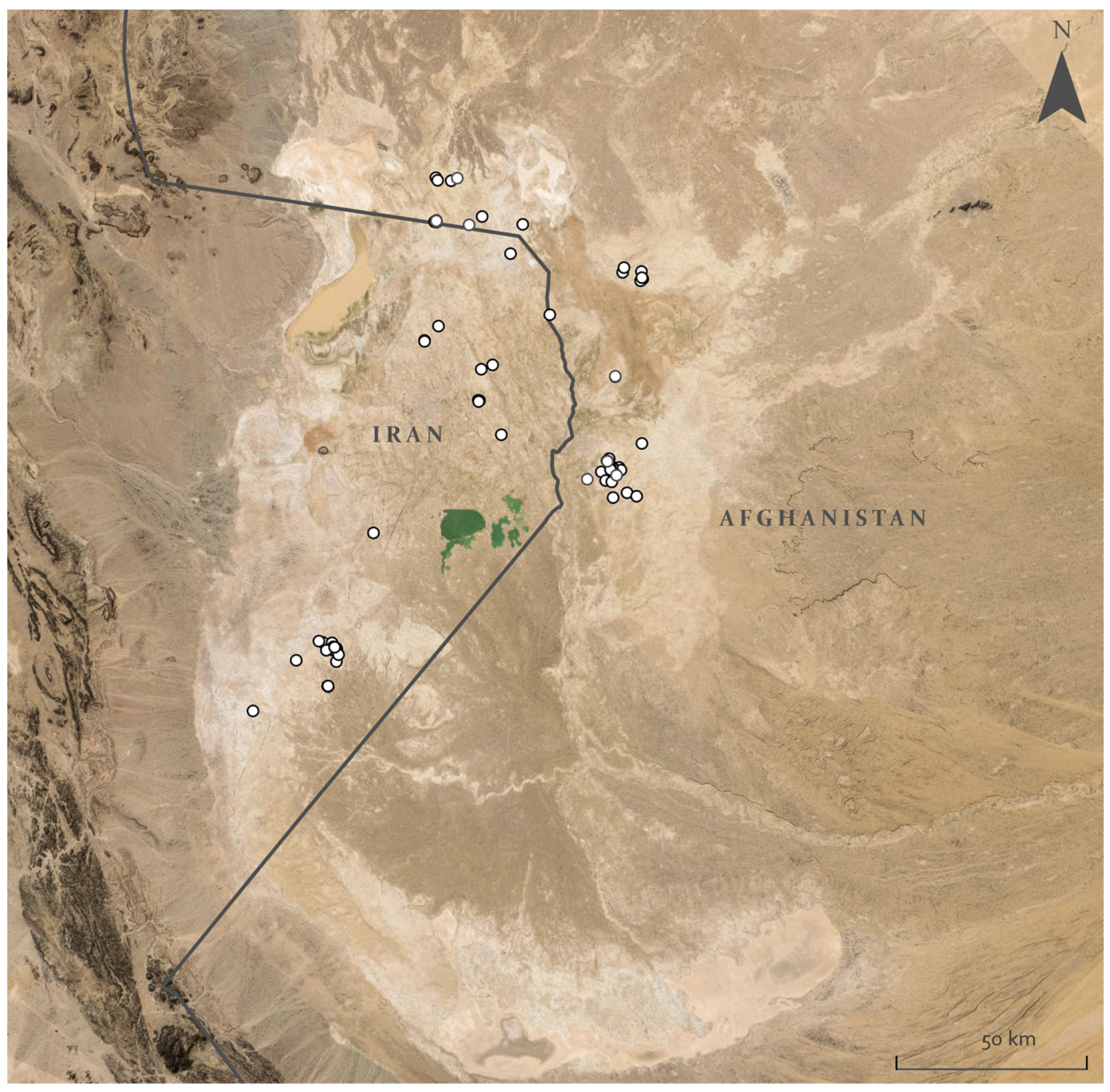
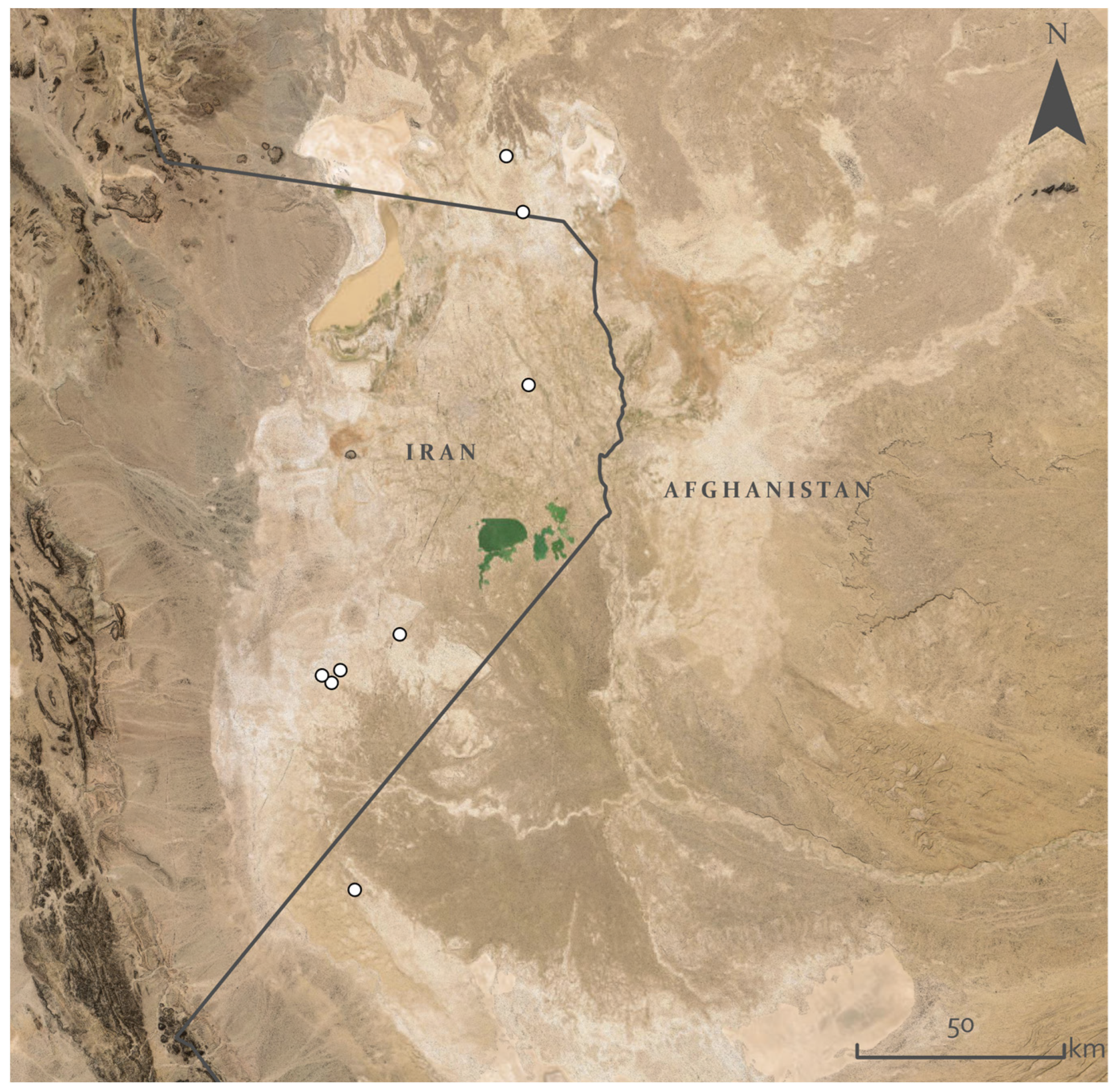
2.3. Archaeological Data
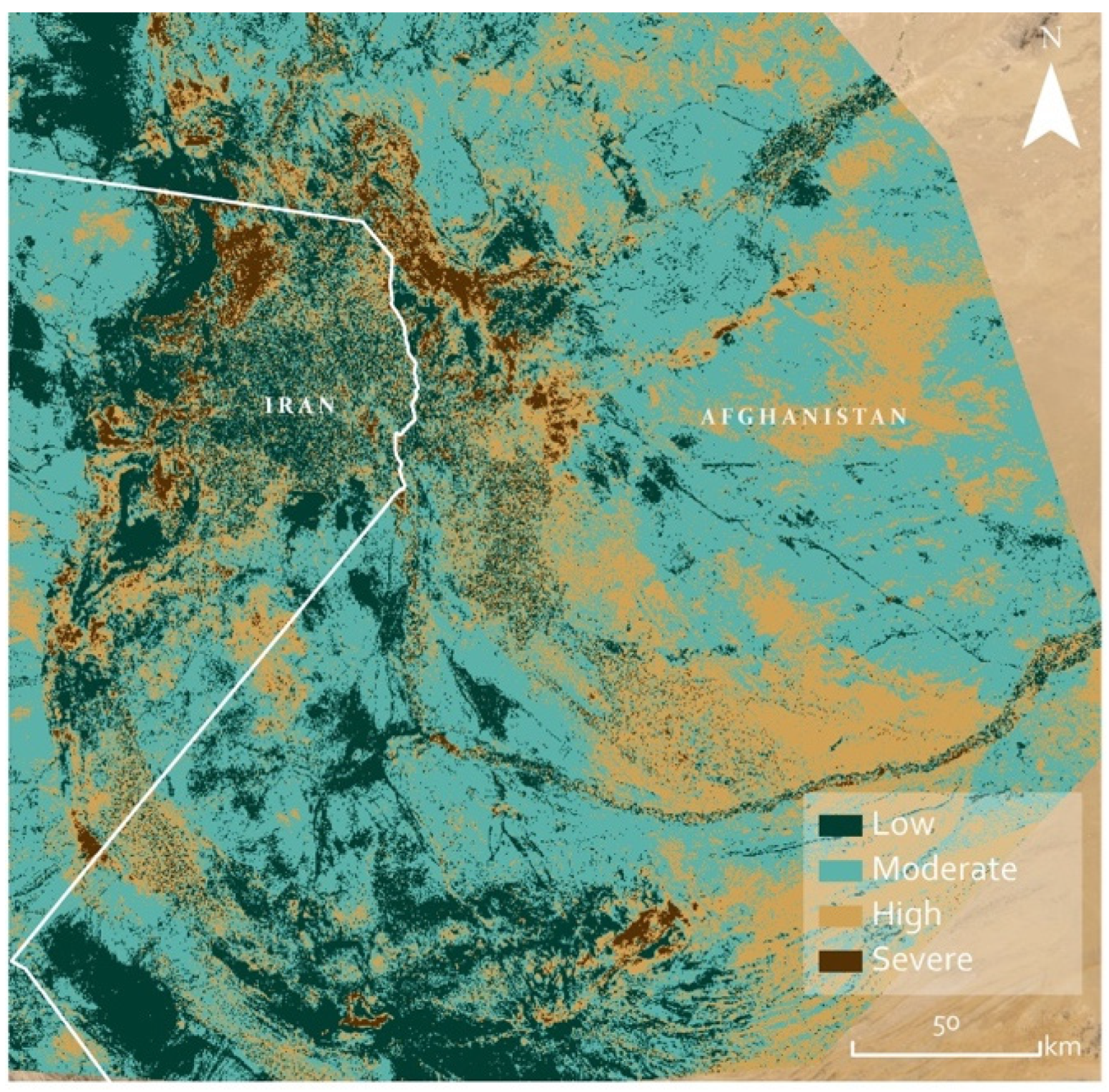
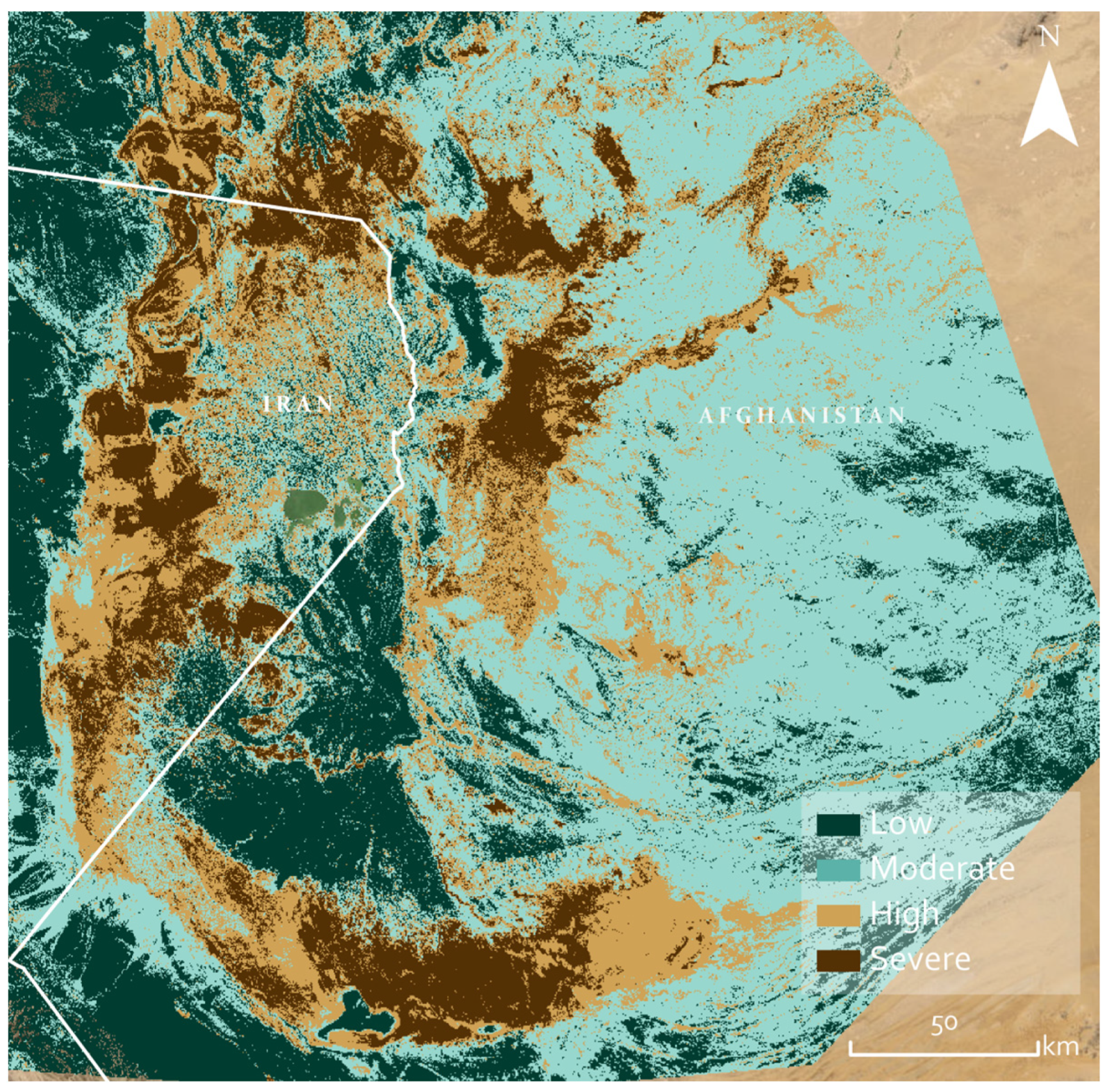
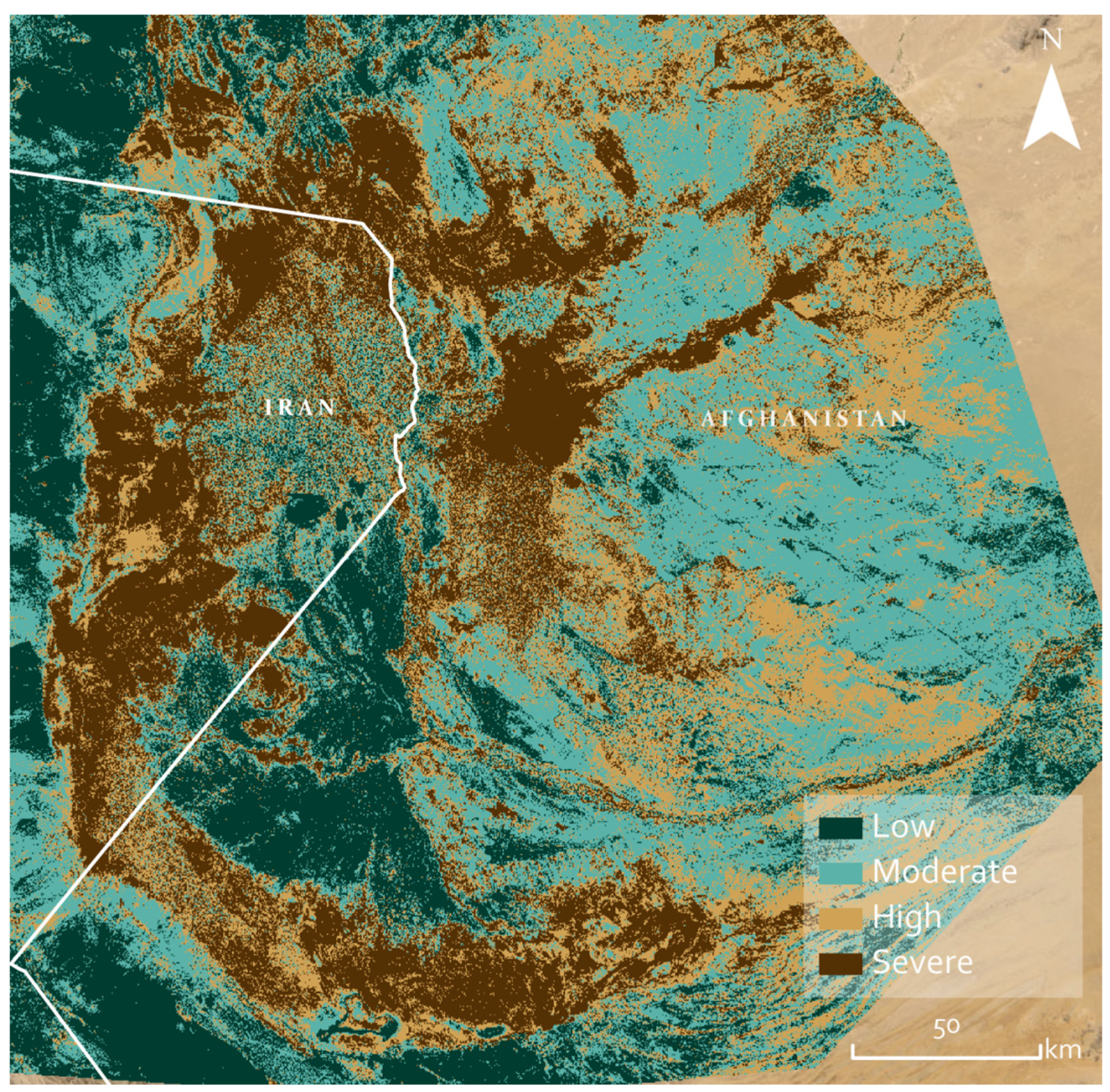
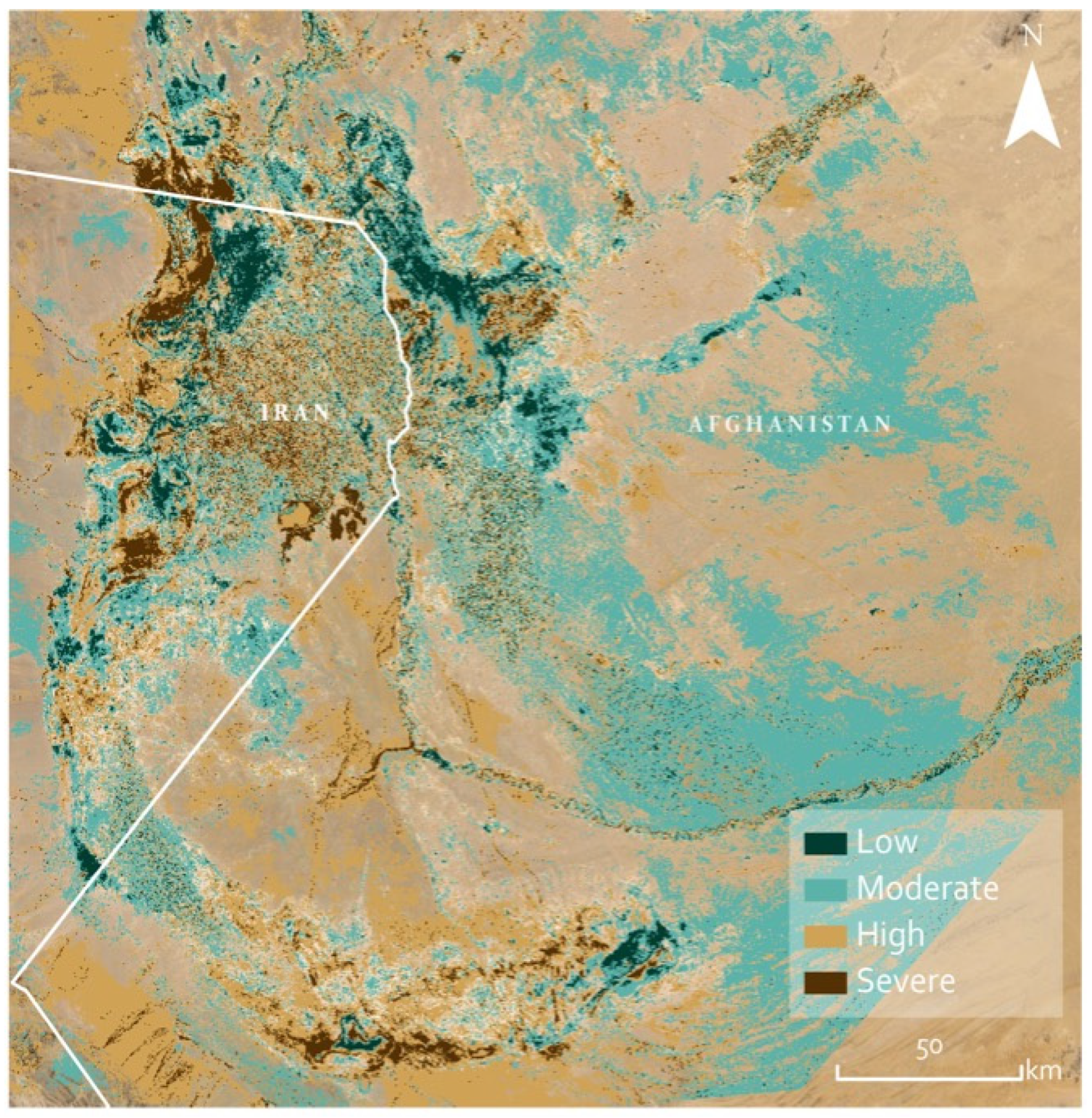
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Application to Archaeology
4.1.1. Record Prioritisation
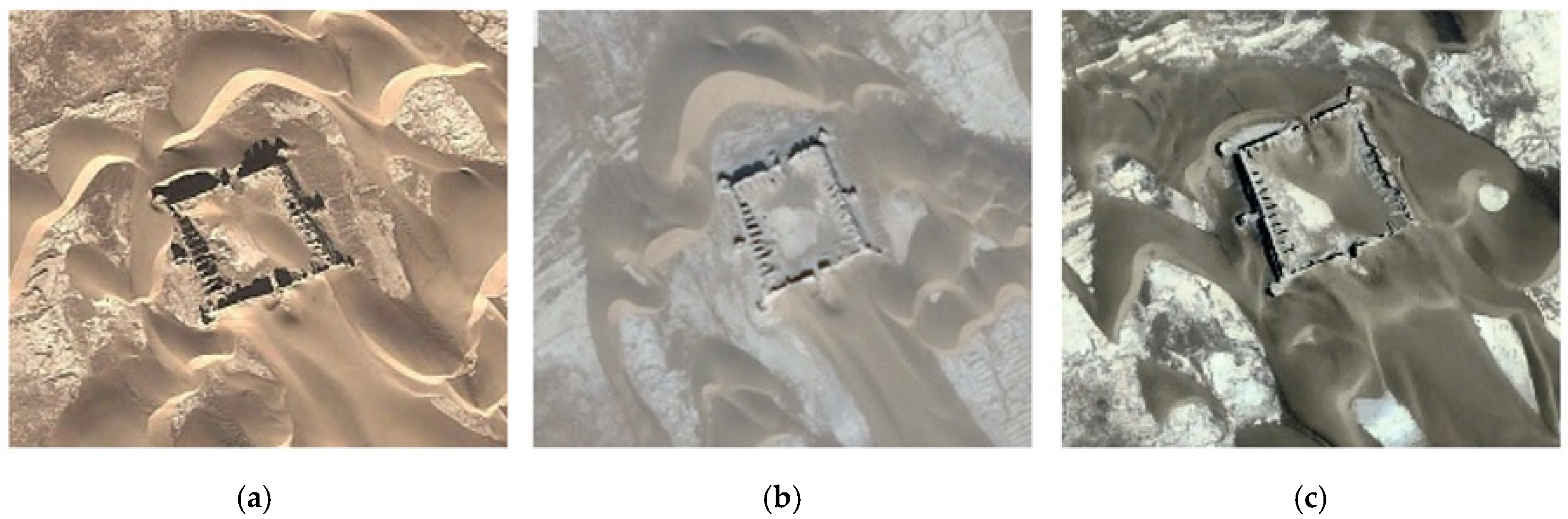
4.1.2. Transitional Sites
4.1.3. Landscape Regional Prioritisation
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification. UNCCD FAQ. Available online: https://www.unccd.int/unccd-faq#:~:text=What%20is%20Desertification%3F,and%20dry%20sub%2Dhumid%20areas (accessed on 22 December 2023).
- Barker, G.W.; Creighton, O.H.; Gilbertson, D.D.; Hunt, C.O.; Mattingly, D.J.; McLaren, S.J.; Thomas, D.C.; Morgan, G.C. The Wadi Faynan Project, Southern Jordan: A Preliminary Report on Geomorphology and Landscape Archaeology. Levant 1997, 29, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barker, G.; Gilbertson, D. Desertification, Land Degradation and Land Abandonment in the Rhône Valley, France. In The Archaeology of Drylands; Routledge: London, UK, 2000; pp. 355–373. [Google Scholar]
- Fairservis, W.A. Archaeological Studies in the Seistan Basin of Southwestern Afghanistan and Eastern Iran. Anthropological Papers of the American Museum of Natural History; American Museum of Natural History: New York, NY, USA, 1961; Volume 48, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Madole, R.F. Stratigraphic Evidence of Desertification in the West-Central Great Plains within the Past 1000 Yr. Geology 1994, 22, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Hajjarpour, A.; Vadez, V. Analysis of chickpea yield gap and water-limited potential yield in Iran. Field Crops Res. 2016, 185, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boloorani, A.D.; Najafi, M.S.; Soleimani, M.; Papi, R.; Torabi, O. Influence of Hamoun Lakes’ Dry Conditions on Dust Emission and Radiative Forcing over Sistan Plain, Iran. Atmos. Res. 2022, 272, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.W. Geology, Water, and Wind in the Lower Helmand Basin, Southern Afghanistan; Scientific Investigations Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2006.
- Fatemeh, A. Water Dispute Escalating between Iran and Afghanistan; Atlantic Council, Southeast Asia Center: Online, 2016; pp. 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The Wind of 120 Days and Dust Storm Activity over the Sistan Basin. Atmos. Res. 2014, 143, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Moghaddamnia, A.; Pahlavanravi, A.; Panjehkeh, N. Dust Storm Frequency after the 1999 Drought in the Sistan Region, Iran. Clim. Res. 2010, 41, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerrato, U. A Probable Achaemenid Zone in Persian Sistan. East West 1962, 13, 186–197. [Google Scholar]
- Bosworth, C.E. Edmund. Sistan and Its Local Histories. Iran. Stud. 2000, 33, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramiuk, M.A. Correlating Findings from the Central Helmand Archaeological Study (CHAS) with Those from Previous Surveys in the Central Helmand Valley, Afghanistan. Afghanistan 2019, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirshman, R. Recherches Prehistoriques en Afghanistan: Fouilles de Nad-i-Ali dans le Seistan Afghan. Rev. Arts Asiat. 1942, XIII, 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Trousdale, W.B.; Allen, M. The Archaeology of Southwest Afghanistan; Edinburgh University Press: Edinburgh, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dales, G.F. New Excavations at Nad-i-Ali (Sorkh Dagh), Afghanistan. Research Monograph Serie; University of California: Berkley, CA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, A. An Archaeological Tour along the Waziristan Border. Geogr. J. 1928, 71, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.G. Counterinsurgency in Sistan-Baluchistan: Evaluating Iranian Effectiveness in Countering Ethnic Insurgency; Naval Postgraduate School: Monterey, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mirlotfi, M.R.; Jahantigh, H. A Survey of the Sense of Spatial Belonging to a Destination Country among Afghan Transnational Immigrants (Case Study: Border Villages in Sistan). Pizhūhish Barnāmahʹrīzī-I Rūstāyī 2018, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nagheeby, M. The Worst or the Best Treaty? Analysing the Equitable and Reasonable Utilization Principle in the Legal Arrangements of the Helmand River. Asian J. Int. Law 2023, 14, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Marin, D.; Dash, J.; Ogutu, B. The Use of Remote Sensing for Desertification Studies: A Review. J. Arid. Environ. 2022, 206, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.V.; Setia, R.; Sahoo, S.; Prasad, A.; Pateriya, B. Evaluation of NDWI and MNDWI for Assessment of Waterlogging by Integrating Digital Elevation Model and Groundwater Level. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, F.; Azarnivand, H.; Khosravi, H.; Zehtabian, G.; Sigaroudi, S.K. Monitoring the Severity of Degradation and Desertification by Remote Sensing (Case Study: Hamoun International Wetland). Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 902687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Afghanistan Opium Survey. UNODC and Illicit Crop Monitoring. 2020. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/crop-monitoring/index.html?tag=Afghanistan (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Akbari, M.; Mirchi, A.; Roozbahani, A.; Gafurov, A.; Kløve, B.; Haghighi, A.T. Desiccation of the Transboundary Hamun Lakes between Iran and Afghanistan in Response to Hydro-Climatic Droughts and Anthropogenic Activities. J. Great Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Haghighi, A.T. Satellite-Based. Agricultural Water Consumption Assessment in the Ungauged and Transboundary Helmand Basin between Iran and Afghanistan. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 13, 1236–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mianabadi, A.; Davary, K.; Mianabadi, H.; Karimi, P. International Environmental Conflict Management in Transboundary River Basins. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 3445–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, F.; Rahdari, V.; Najafabadi, S.M.; Pradhan, B.; Tabatabaei, T. Erratum to: Multi-Temporal Landsat Images Based on Eco-Environmental Change Analysis in and around Chah Nimeh Reservoir, Sistan and Balochestan (Iran). Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatsaz, M. A Historical Investigation on Water Resources Management in Iran. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 1749–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Nahavandchi, H.; Hoseini, M. Evaluation of CYGNSS Observations for Flood Detection and Mapping during Sistan and Baluchestan Torrential Rain in 2020. Water 2020, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreibich, H.; Van Loon, A.F.; Schröter, K.; Ward, P.J.; Mazzoleni, M.; Sairam, N.; Abeshu, G.W.; Agafonova, S.; AghaKouchak, A.; Aksoy, H.; et al. The Challenge of Unprecedented Floods and Droughts in Risk Management. Nature 2022, 608, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K. The Impact of Increased Flooding Caused by Climate Change on Heritage in England and North Wales, and Possible Preventative Measures: What Could/Should Be Done? Built. Herit. 2023, 7, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, S.; Xing, S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, N. Identification and Frequency Analysis of Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation Events Using a Daily-Scale Standardized Weighted Average of the Precipitation Index. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhao, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Wang, Z. Identification, Physical Mechanisms and Impacts of Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation: A Review. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1203603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-Resolution Mapping of Global Surface Water and Its Long-Term Changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlers, R.; Brandimarte, L.; Kleemans, I.; Sadat, S.H. Ambitious Development on Fragile Foundations: Criticalities of Current Large Dam Construction in Afghanistan. Geoforum 2014, 54, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Oz, G.; Galili, R.; Fuks, D.; Erickson-Gini, T.; Tepper, Y.; Shamir, N.; Avni, G. Caravanserai Middens on Desert Roads: A New Perspective on the Nabataean–Roman Trade Network across the Negev. Antiquity 2022, 96, 592–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanski, K.; Mohan, D.; Horrall, J.; Rountree, B.; Abdulla, G. Deep Learning Predictions of Sand Dune Migration. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.10798. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Review of Desert Mobility Assessment and Desertification Monitoring Based on Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, P. How climate change affects extreme weather events. Science 2016, 352, 1517–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Shoshah, H.; Zeleňáková, M.; Kushwaha, N.L.; El-Dean, O.W. Forecasting of Flash Floods Peak Flow for Environmental Hazards and Water Harvesting in Desert Area of El-Qaa Plain, Sinai. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Platform/Sensor | Processing Level | Dataset Type | Number of Images | Dates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) | Collection 2, Tier 1 | Surface reflectance | 1905 | January 2015–December 2021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, R. Disasters and Archaeology: A Remote Sensing Approach for Determination of Archaeology At-Risk to Desertification in Sistan. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132382
Smith R. Disasters and Archaeology: A Remote Sensing Approach for Determination of Archaeology At-Risk to Desertification in Sistan. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(13):2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132382
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Rachel. 2024. "Disasters and Archaeology: A Remote Sensing Approach for Determination of Archaeology At-Risk to Desertification in Sistan" Remote Sensing 16, no. 13: 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132382
APA StyleSmith, R. (2024). Disasters and Archaeology: A Remote Sensing Approach for Determination of Archaeology At-Risk to Desertification in Sistan. Remote Sensing, 16(13), 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132382





