Characteristics of Yellow Sea Fog under the Influence of Eastern China Aerosol Plumes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. Surface Station Data
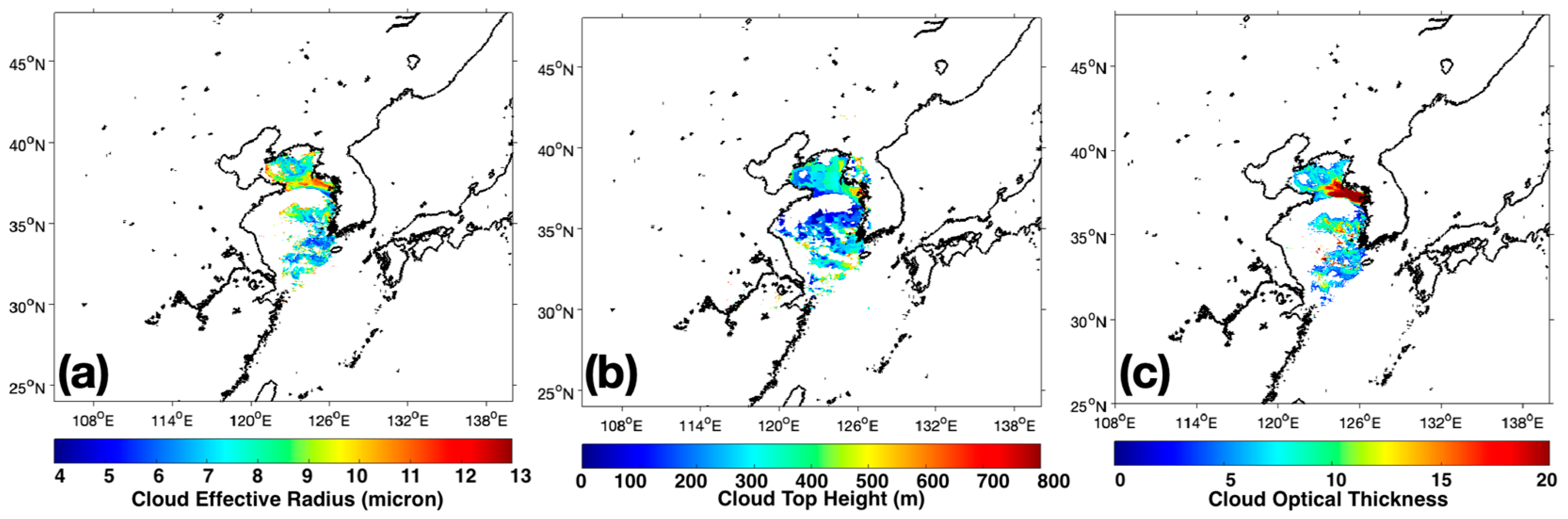
2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Soundings
2.4. Reanalysis Data
3. Methods
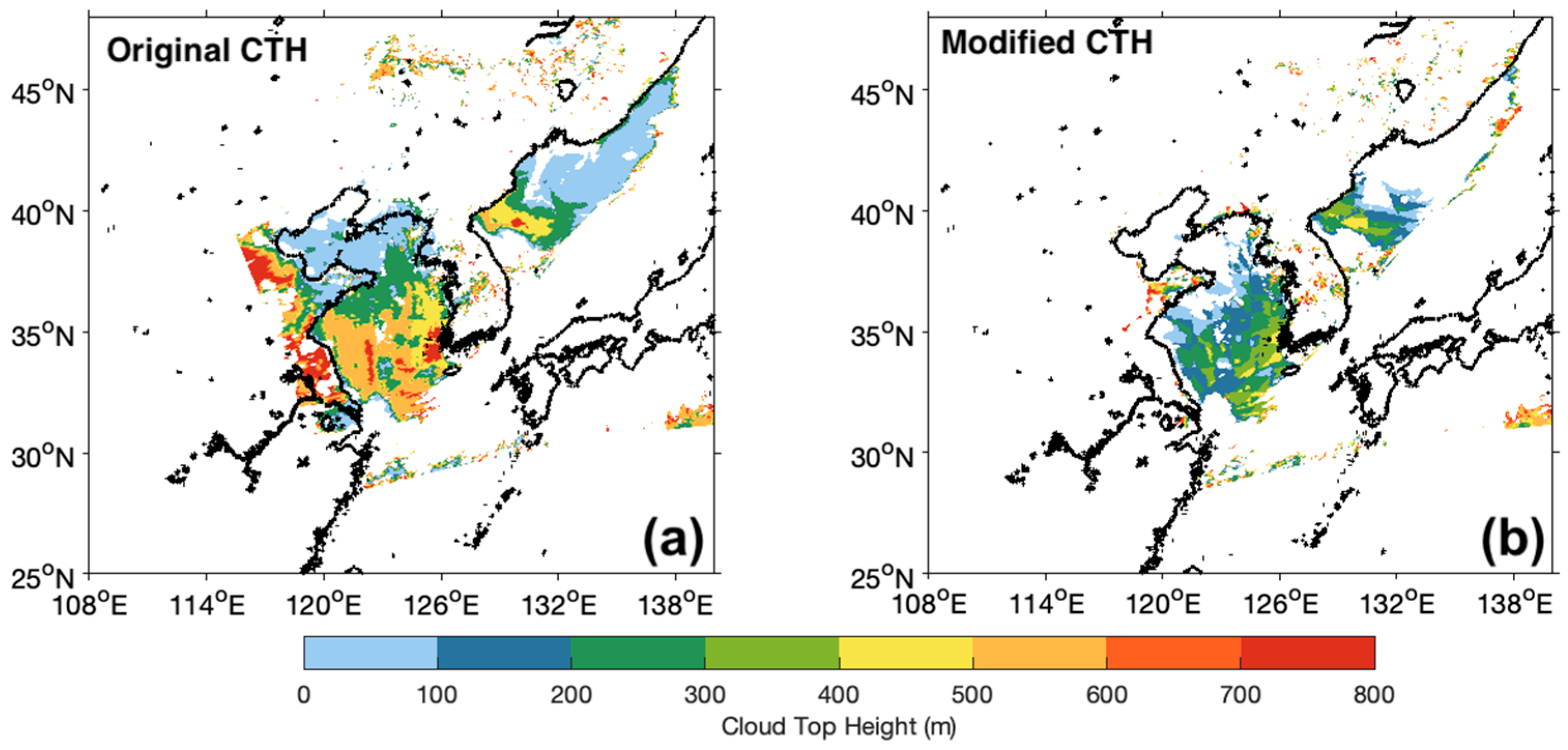
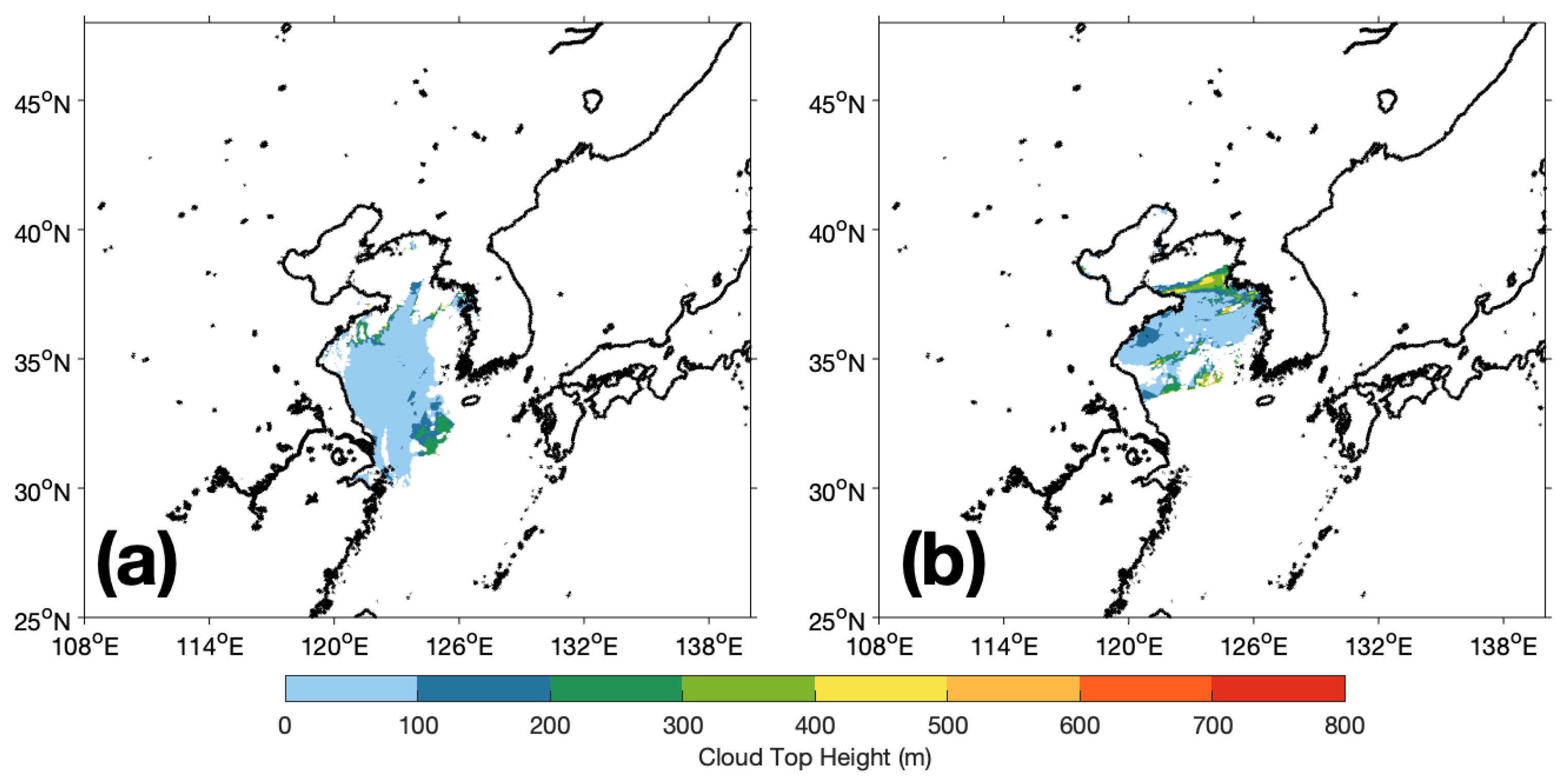
3.1. CTH Modification
3.2. CTH Interpolation
3.3. CTH Filtering
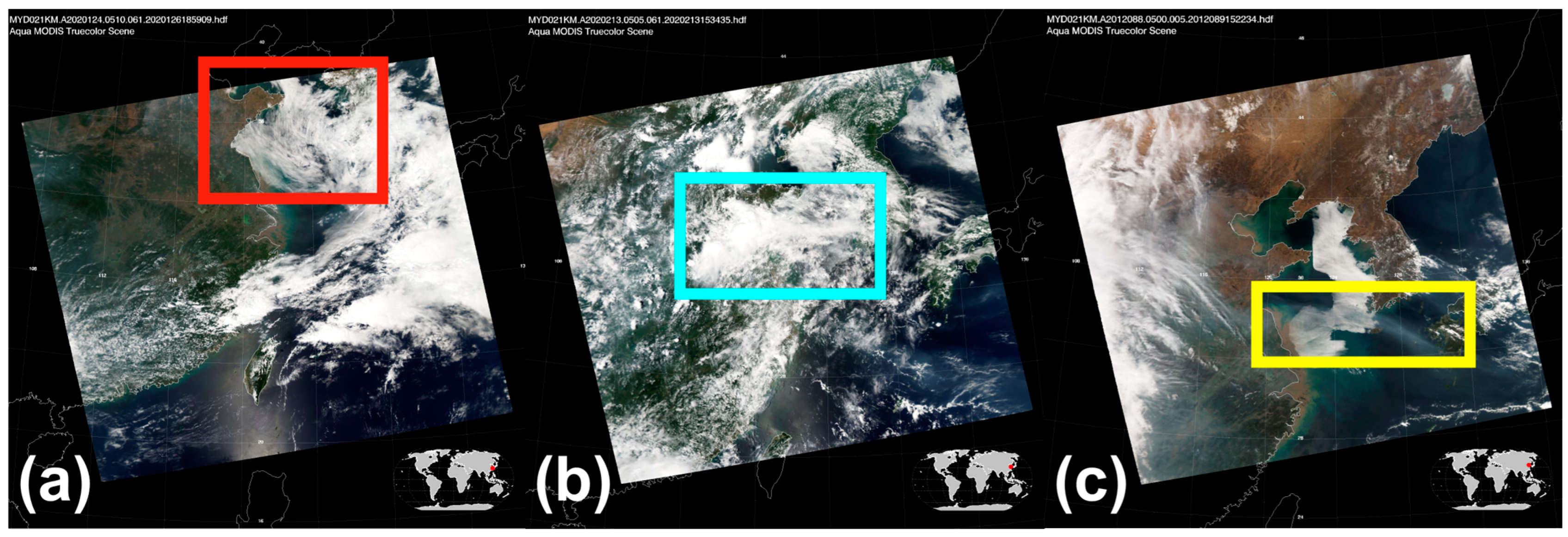
3.4. Fog Area Selection
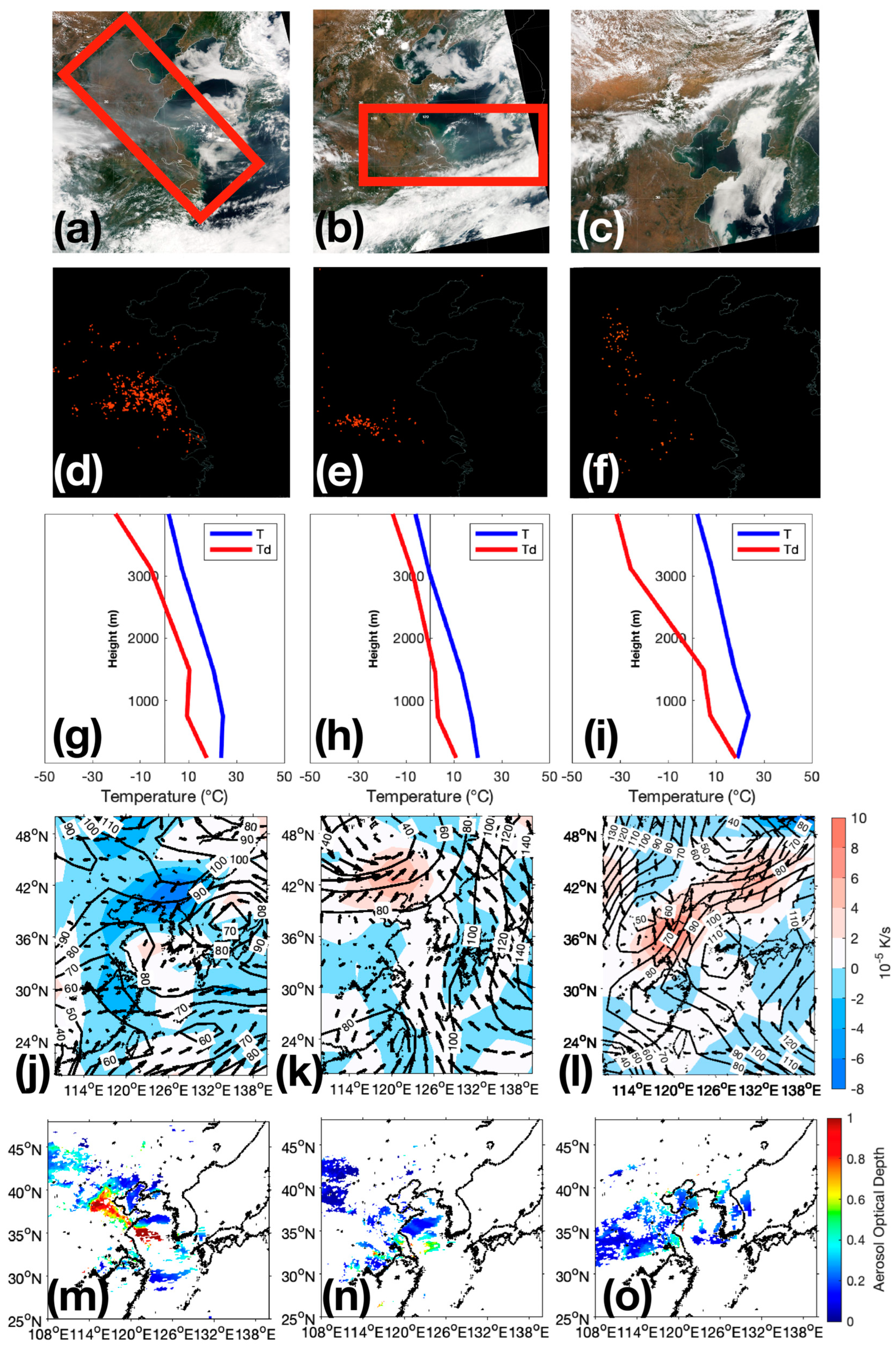
4. Results
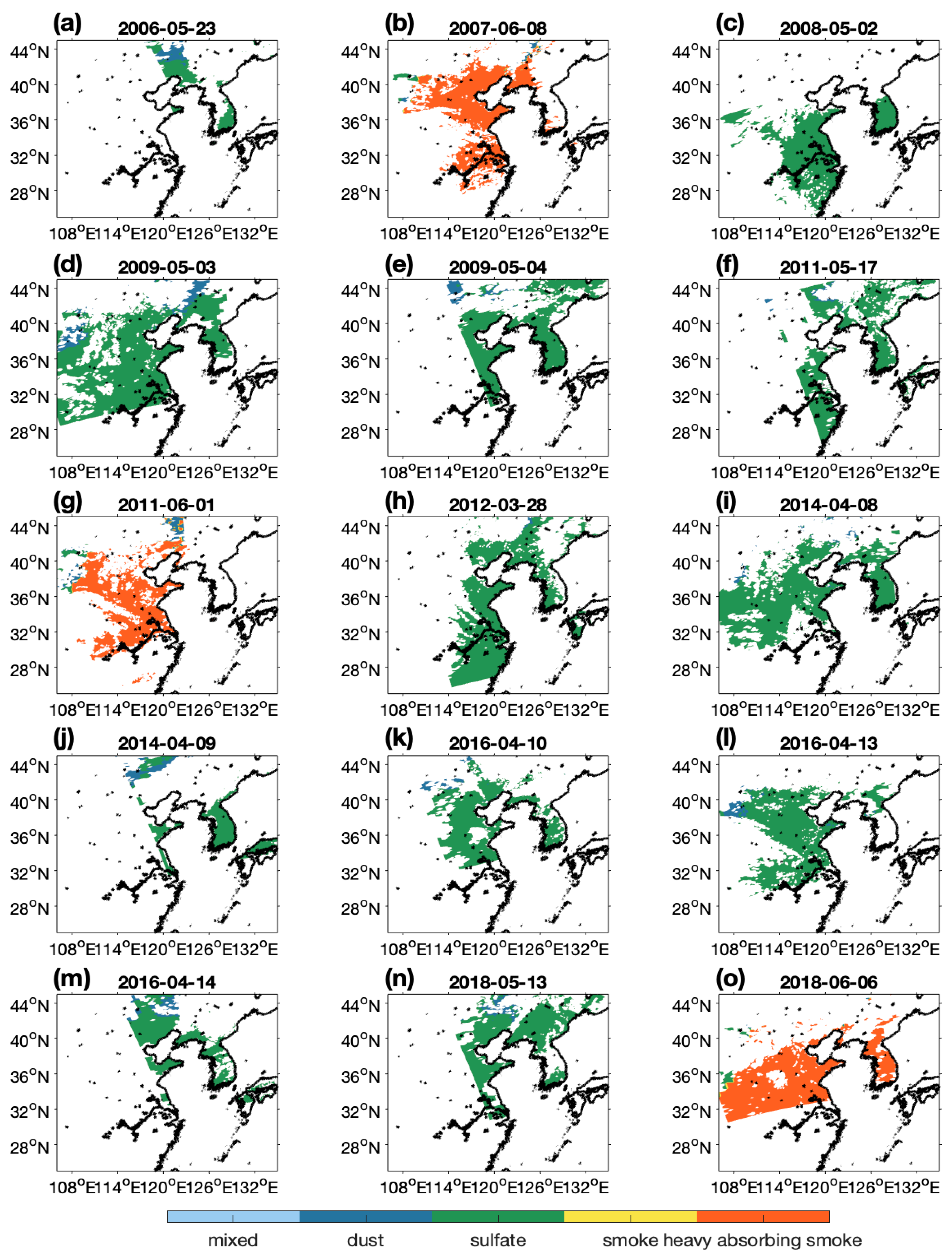
4.1. Terrestrial Aerosol Type
4.2. Fire Cases
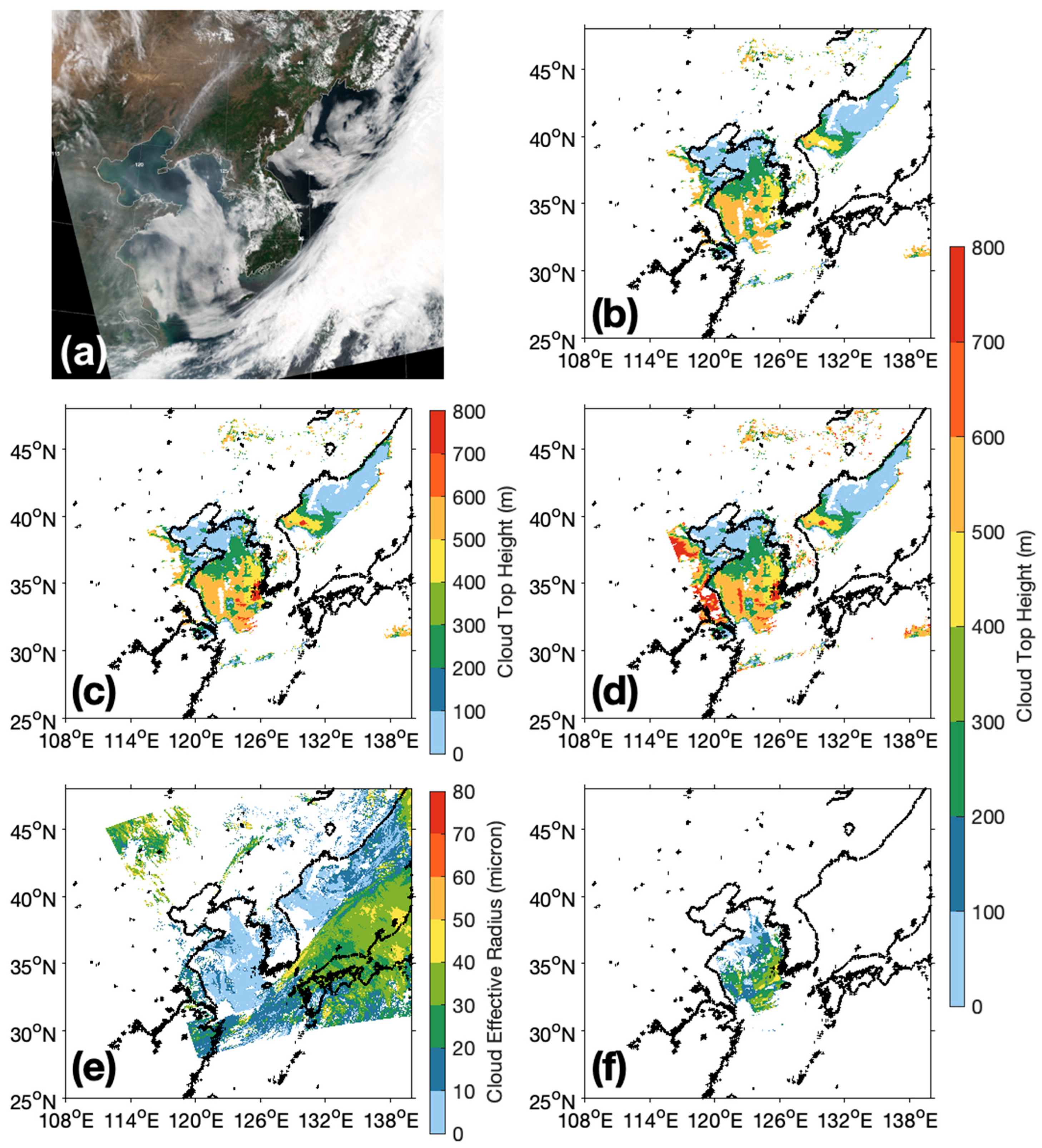
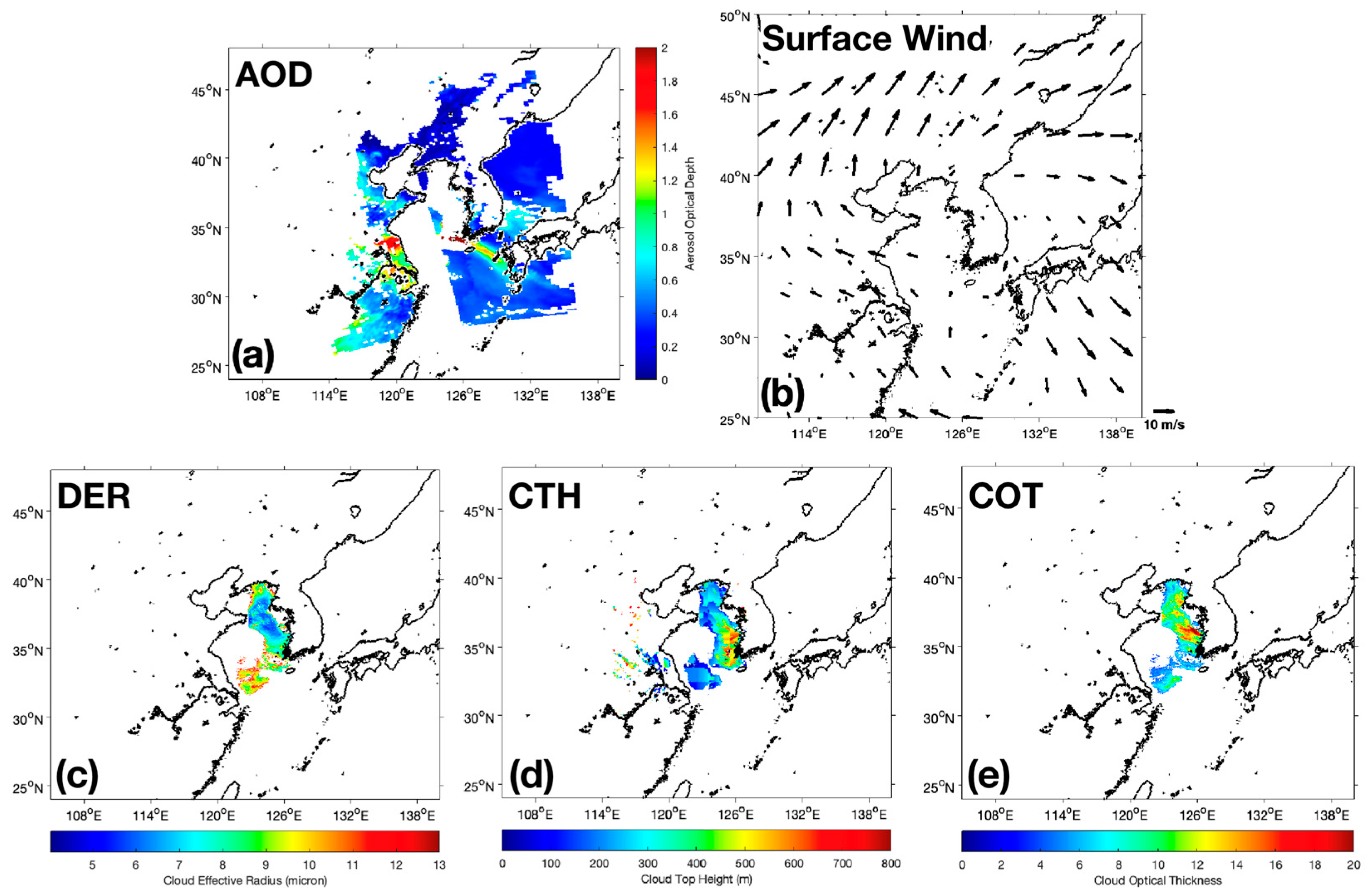
4.3. Relationship between Cloud Properties, Aerosols, and SST
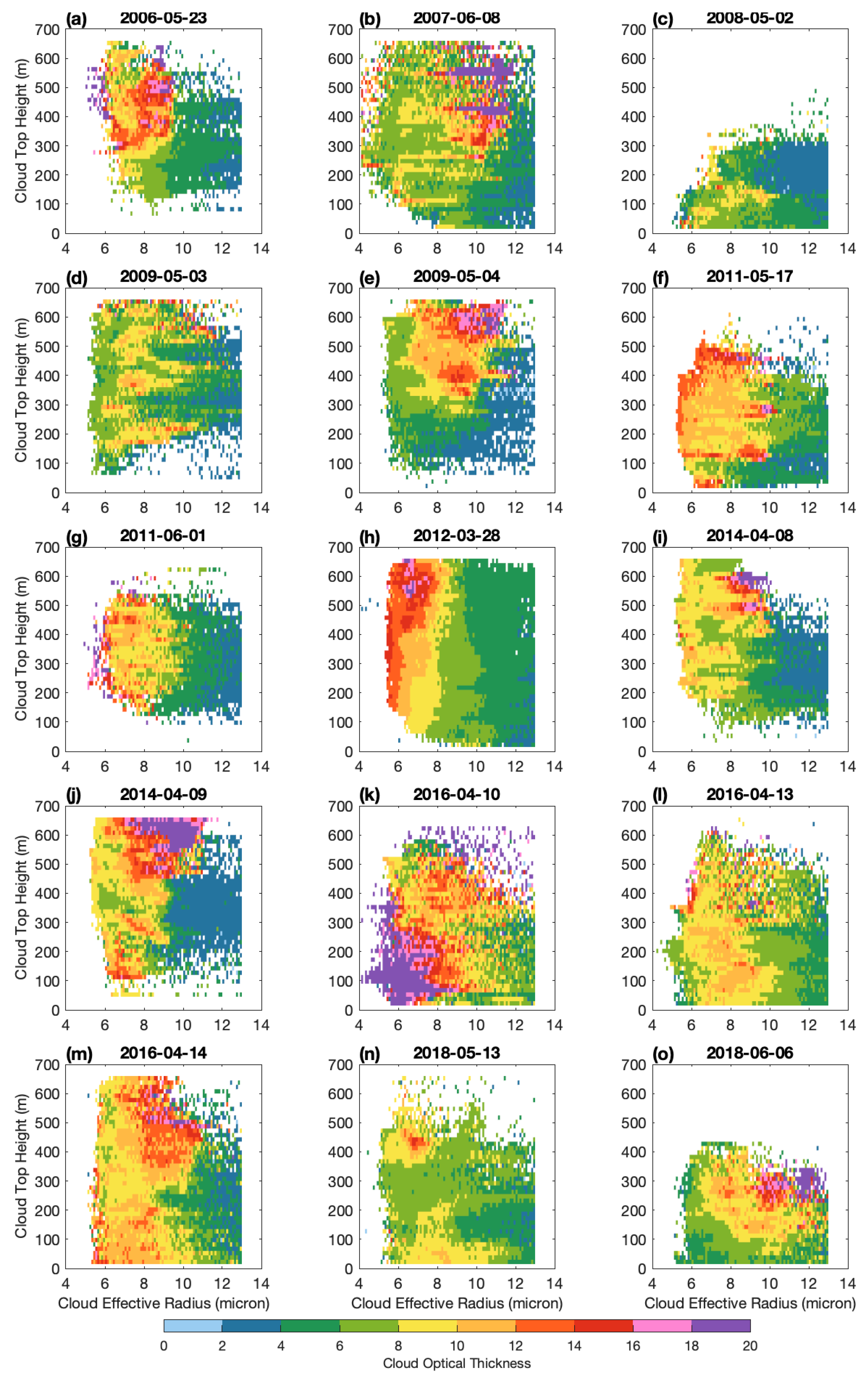
4.4. Bi-Variate Comparison
4.4.1. Diagonal Pattern Cases
4.4.2. Left-Right Pattern
4.4.3. Inverse Diagonal Pattern
4.4.4. Sum Bi-Variate Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baines, P.G. Sea fog. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 1987, 11, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koračin, D.; Dorman, C.E.; Lewis, J.M.; Hudson, J.G.; Wilcox, E.M.; Torregrosa, A. Marine fog: A review. Atmos. Res. 2014, 143, 142–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koračin, D.; Dorman, C.E. (Eds.) Marine Fog: Challenges and Advancements in Observations, Modeling, and Forecasting; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Tardif, R.; Michaelides, S.C.; Cermak, J.; Bott, A.; Bendix, J.; Müller, M.D.; Pagowski, M.; Hansen, B.; Ellrod, G.; et al. Fog Research: A Review of Past Achievements and Future Perspectives. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2007, 164, 1121–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, K.-Y.; Ha, K.-J.; Mahrt, L.; Shim, J.-S. Comparison of advection and steam fogs: From direct observation over the sea. Atmos. Res. 2010, 98, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-P.; Xie, S.-P.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Wang, X.-G.; Ren, Z.-P. Seasonal Variations of Yellow Sea Fog: Observations and Mechanisms. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 6758–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y. Sensitivity of WRF simulations with the YSU PBL scheme to the lowest model level height for a sea fog event over the Yellow Sea. Atmos. Res. 2019, 215, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M. Synoptic and climatic characteristics of Yellow Sea fog and causation analysis. J. Trop. Meteorol./Redai Qixiang Xuebao 2011, 27, 920–929. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.-K.; Kim, M.-O.; Kim, B.-C. Sea Fog around the Korean Peninsula. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.; Fangli, Q.; Changshui, X.; Yongzeng, Y. Tidal effects on temperature front in the Yellow Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2004, 22, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Meng, X.; Fu, G.; Ren, Z.; Gao, S. A Comparison Study Between Spring and Summer Fogs in the Yellow Sea-Observations and Mechanisms. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2012, 169, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Long, J.; Han, G. Interannual variability of sea fog frequency in the Northwestern Pacific in July. Atmos. Res. 2015, 151, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, Clouds, and Climate. Science 2006, 312, 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twomey, S. The Influence of Pollution on the Shortwave Albedo of Clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, Cloud Microphysics, and Fractional Cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, J.T.; John, T. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis: Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J. Global indirect aerosol effects: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Myhre, C.E.L.; Samset, B.H.; Storelvmo, T. Aerosols and their Relation to Global Climate and Climate Sensitivity. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2013, 4, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R. Radiative forcing and climate response. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 6831–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, A.S.; Toon, O.B.; Stevens, D.E.; Heymsfield, A.J.; Ramanathan, V.; Welton, E.J. Reduction of Tropical Cloudiness by Soot. Science 2000, 288, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Quan, J.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; He, H.; Liu, Y. Impacts of Anthropogenic Aerosols on Fog in North China Plain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasakawa, M.; Uematsu, M. Chemical composition of aerosol, sea fog, and rainwater in the marine boundary layer of the northwestern North Pacific and its marginal seas. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, ACH 17-1–ACH 17-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiderwieden, E.; Wrzesinsky, T.; Klemm, O. Chemical characterization of fog and rain water collected at the eastern Andes cordillera. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, V.; Deshpande, C.G.; Kamra, A.K. Changes in concentration and size distribution of aerosols during fog over the south Indian Ocean. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 119, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazoyer, M.; Burnet, F.; Denjean, C.; Roberts, G.C.; Haeffelin, M.; Dupont, J.-C.; Elias, T. Experimental study of the aerosol impact on fog microphysics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4323–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Jin, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, L. Land–atmosphere–aerosol coupling in North China during 2000–2013. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Wen, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Collett, J.L.; Shi, Y.; et al. Severe haze episodes and seriously polluted fog water in Ji’nan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J. Reversal of Aerosol Properties in Eastern China with Rapid Decline of Anthropogenic Emissions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Guo, X. Impacts of Secondary Aerosols on a Persistent Fog Event in Northern China. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2012, 5, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemistry of secondary organic aerosol: Formation and evolution of low-volatility organics in the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3593–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, D.S.; Gupta, T.; Tripathi, S.N.; Tare, V.; Collett, J.L. Secondary Organic Aerosol: A Comparison between Foggy and Nonfoggy Days. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7307–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidema, P.; Redemann, J.; Haywood, J.; Wood, R.; Piketh, S.; Hipondoka, M.; Formenti, P. Smoke and Clouds above the Southeast Atlantic: Upcoming Field Campaigns Probe Absorbing Aerosol’s Impact on Climate. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomonson, V.V.; Barnes, W.; Masuoka, E.J. Introduction to MODIS and an Overview of Associated Activities. In Earth Science Satellite Remote Sensing; Qu, J.J., Gao, W., Kafatos, M., Murphy, R.E., Salomonson, V.V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, D.; Bergot, T.; El Khlifi, M. Local Meteorological and Large-Scale Weather Characteristics of Fog over the Grand Casablanca Region, Morocco. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 1731–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Fu, G.; Lu, C. Large-Scale Environmental Influences on the Onset, Maintenance, and Dissipation of Six Sea Fog Cases over the Yellow Sea. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2012, 169, 983–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lu, B.; Zhang, T.; Yan, F. A method of detecting sea fogs using CALIOP data and its application to improve MODIS-based sea fog detection. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 153, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Yue, X. Daytime sea fog retrieval based on GOCI data: A case study over the Yellow Sea. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MODIS Atmosphere Science Team. MOD04_L2 MODIS/Terra Aerosol 5-Min L2 Swath 10 km [Dataset]; NASA Level 1 and Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System Distributed Active Archive Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Ackerman, S.A.; King, M.D.; Meyer, K.; Menzel, W.P.; Holz, R.E.; Baum, B.A.; Yang, P. MODIS Atmosphere L2 Cloud Product (06_L2), NASA MODIS Adaptive Processing System; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015.
- Hao, Y.; Cui, T.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, J.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Z. Validation of MODIS Sea Surface Temperature Product in the Coastal Waters of the Yellow Sea. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmospheric Soundings. Available online: http://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Garay, M.J.; De Szoeke, S.P.; Moroney, C.M. Comparison of marine stratocumulus cloud top heights in the southeastern Pacific retrieved from satellites with coincident ship-based observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 2008JD009975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, R.E.; Ackerman, S.A.; Nagle, F.W.; Frey, R.; Dutcher, S.; Kuehn, R.E.; Vaughan, M.A.; Baum, B. Global Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) cloud detection and height evaluation using CALIOP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 2008JD009837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshvardhan Guangyu Zhao Di Girolamo, L.; Green, R.N. Satellite-Observed Location of Stratocumulus Cloud-Top Heights in the Presence of Strong Inversions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidema, P.; Painemal, D.; De Szoeke, S.; Fairall, C. Stratocumulus Cloud-Top Height Estimates and Their Climatic Implications. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 4652–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painemal, D.; Zuidema, P. Assessment of MODIS cloud effective radius and optical thickness retrievals over the Southeast Pacific with VOCALS-REx in situ measurements: MODIS VALIDATION DURING VOCALS-REx. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, L.; Bréon, F.-M. Aerosol indirect effect on warm clouds over South-East Atlantic, from co-located MODIS and CALIPSO observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Choi, Y.; Wong, D.C.; Nelson, D.; Lee, S. Role of Sea Fog Over the Yellow Sea on Air Quality with the Direct Effect of Aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczodrak, M.; Austin, P.H.; Krummel, P.B. Variability of Optical Depth and Effective Radius in Marine Stratocumulus Clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 2912–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Feingold, G. On the Importance of Sea Surface Temperature for Aerosol-Induced Brightening of Marine Clouds and Implications for Cloud Feedback in a Future Warmer Climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Pearson, G.; Milbrandt, J.A.; Hansen, B.; Platnick, S.; Taylor, P.; Gordon, M.; Oakley, J.P.; Cober, S.G. The Fog Remote Sensing and Modeling Field Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Seto, S.; Oki, T. Relationship between cloud droplet effective radius and cloud top height for deep convective clouds in CloudSat data product. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 2649–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.-J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS Collection 6 “Deep Blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cases | Mean AOD | Mean Optical Thickness | Mean DER (Micron) | Mean SST (°C) | Temperature Inversion Height (m) | CTH Pixels (633 m) | CTH Pixels (700 m) | CTH Pixels (800 m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 May 2009 | 0.4605 | 9.7006 | 7.7972 | 10.6673 | 156 | 8680 | 13,696 | 13,907 |
| 14 April 2016 | 0.5102 | 9.3236 | 8.1057 | 7.9965 | 763 | 21,274 | 25,596 | 26,047 |
| 1 June 2011 | 0.5196 | 8.6431 | 8.4656 | 14.3343 | Nan | 5025 | 5508 | 6525 |
| 17 May 2011 | 0.5296 | 10.1061 | 7.7874 | 13.0364 | 754 | 19,072 | 21,151 | 22,377 |
| 6 June 2018 | 0.5488 | 8.0181 | 8.1329 | 15.8386 | 762 | 8281 | 8302 | 9554 |
| 3 May 2009 | 0.5596 | 7.569 | 8.464 | 10.137 | 166 | 4738 | 7491 | 7840 |
| 28 March 2012 | 0.5626 | 8.5409 | 8.4318 | 8.1441 | 211 | 20,746 | 24,841 | 25,140 |
| 9 April 2014 | 0.6189 | 10.4064 | 7.4462 | 8.0927 | 798 | 17,067 | 22,770 | 22,878 |
| 13 May 2018 | 0.7091 | 7.7615 | 7.6294 | 11.5593 | 732 | 24,247 | 25,345 | 27,705 |
| 2 May 2008 | 0.7559 | 7.3513 | 9.5294 | 13.2741 | 749 | 19,563 | 19,676 | 23,398 |
| 10 April 2016 | 0.7614 | 13.8427 | 8.2615 | 8.3672 | 759 | 16,448 | 20,348 | 20,525 |
| 8 April 2014 | 0.7639 | 8.4725 | 7.4141 | 9.2278 | 795 | 14,661 | 17,442 | 18,237 |
| 8 June 2007 | 0.907 | 8.4842 | 8.1693 | 16.8071 | 751 | 14,194 | 14,225 | 18,849 |
| 23 May 2006 | 0.9853 | 9.5122 | 8.4959 | 11.2939 | 756 | 15,834 | 20,376 | 21,435 |
| 13 April 2016 | 0.9905 | 9.1233 | 8.8142 | 8.9151 | 711 | 16,104 | 16,766 | 17,080 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, J.; Griswold, J.D.S. Characteristics of Yellow Sea Fog under the Influence of Eastern China Aerosol Plumes. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132262
Liang J, Griswold JDS. Characteristics of Yellow Sea Fog under the Influence of Eastern China Aerosol Plumes. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(13):2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132262
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Jiakun, and Jennifer D. Small Griswold. 2024. "Characteristics of Yellow Sea Fog under the Influence of Eastern China Aerosol Plumes" Remote Sensing 16, no. 13: 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132262
APA StyleLiang, J., & Griswold, J. D. S. (2024). Characteristics of Yellow Sea Fog under the Influence of Eastern China Aerosol Plumes. Remote Sensing, 16(13), 2262. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16132262







